Crash of a Mitsubishi MU-2B-35 Marquise in Den Helder
Date & Time:
Jul 20, 2000
Registration:
N8484T
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Den Helder - Den Helder
MSN:
617
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
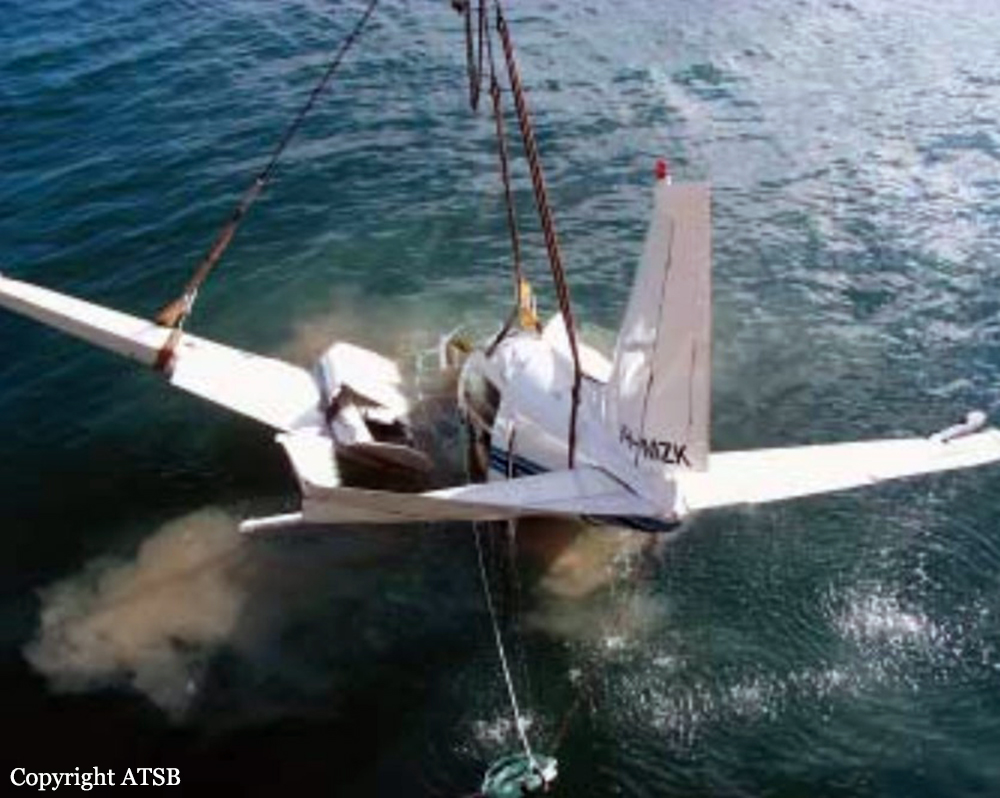
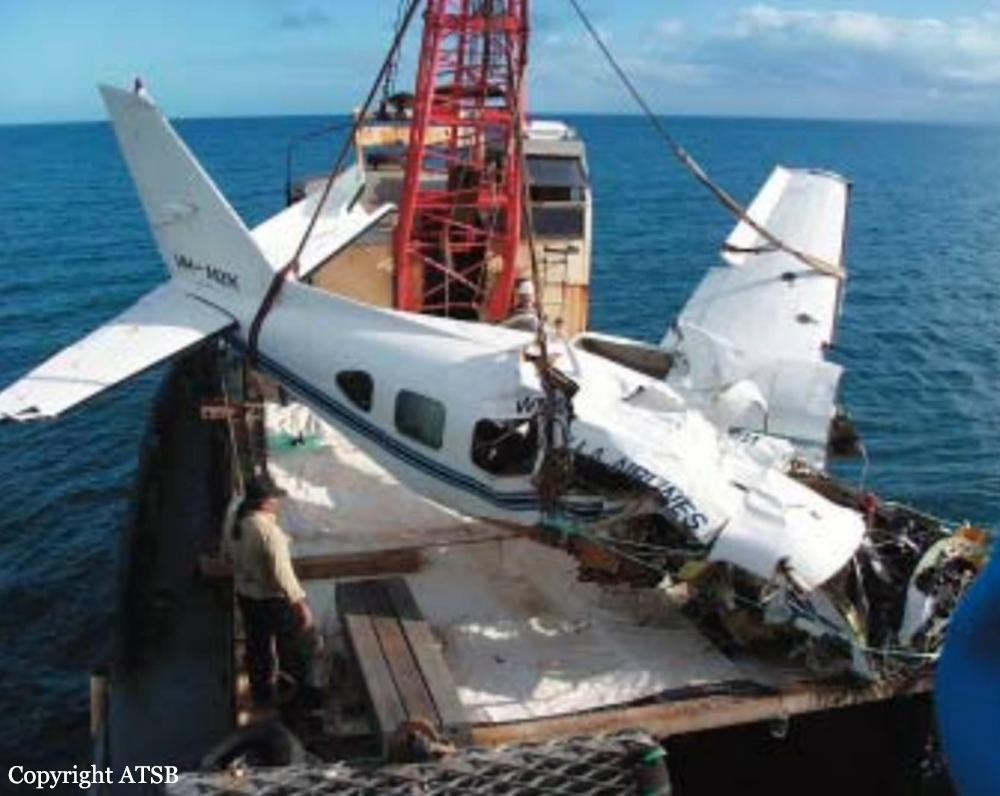
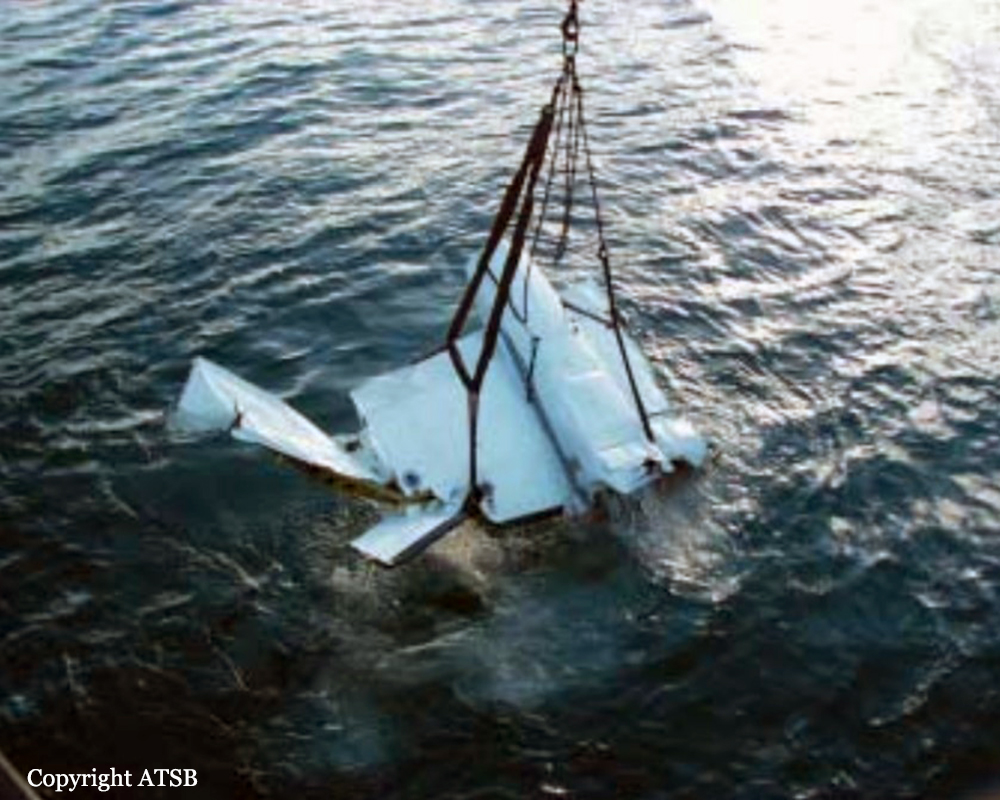
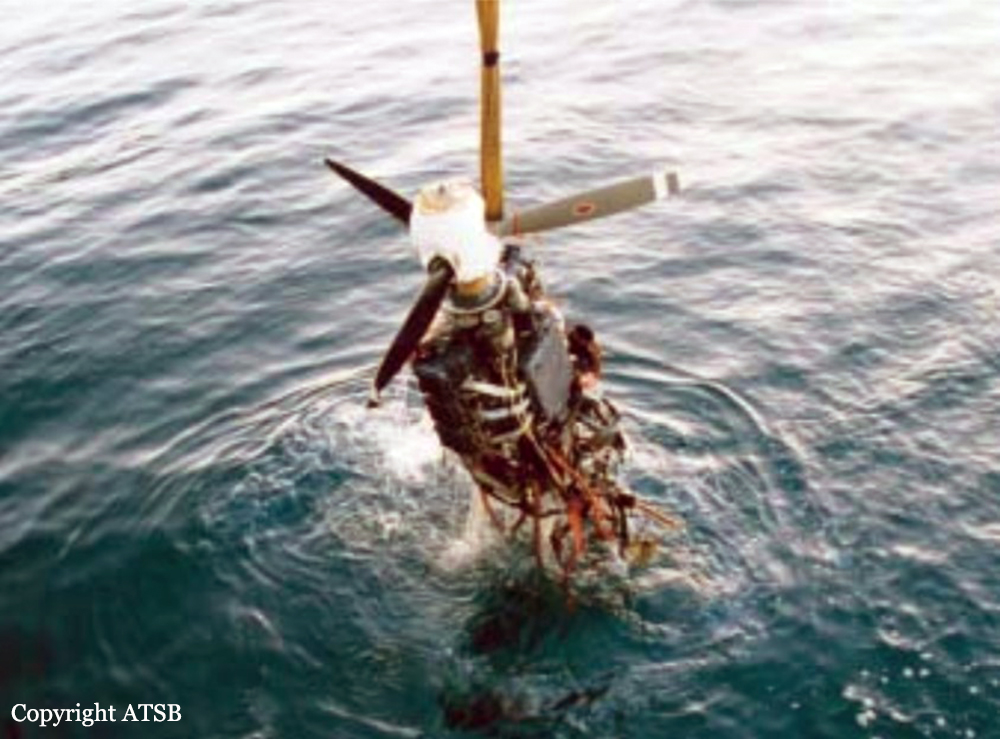
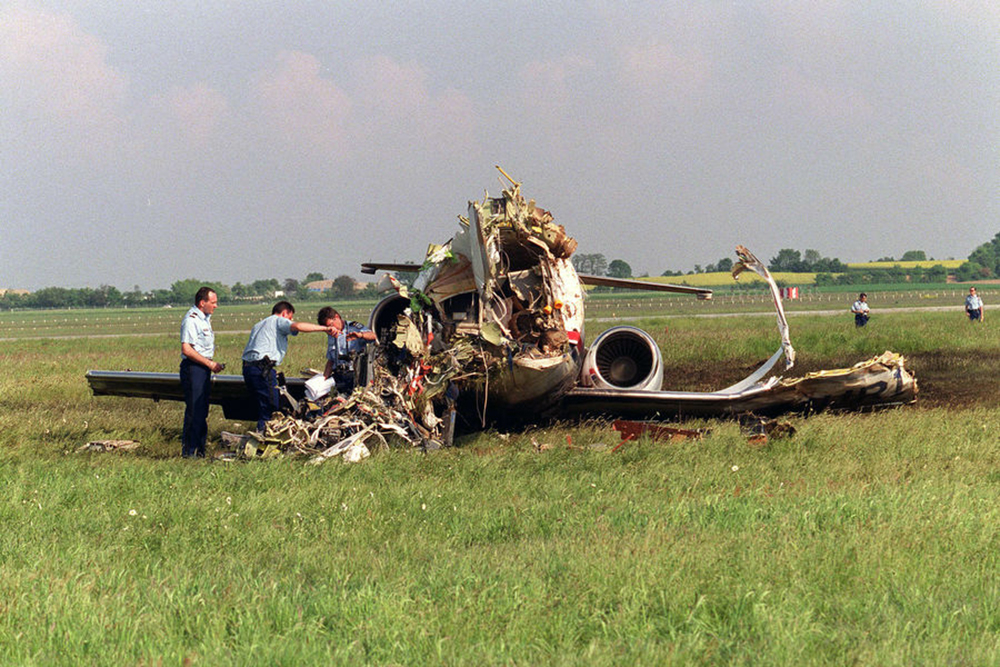
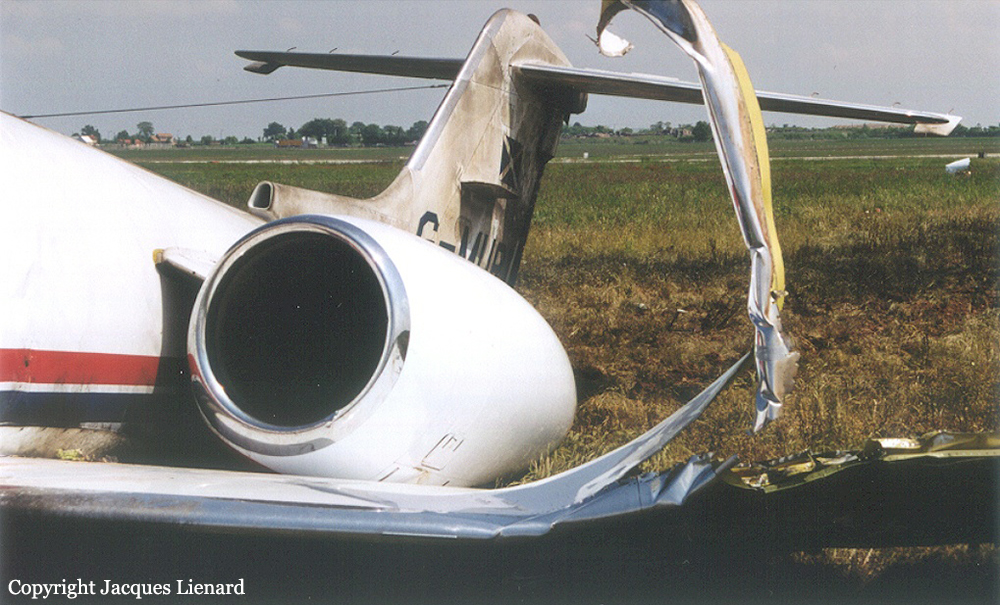
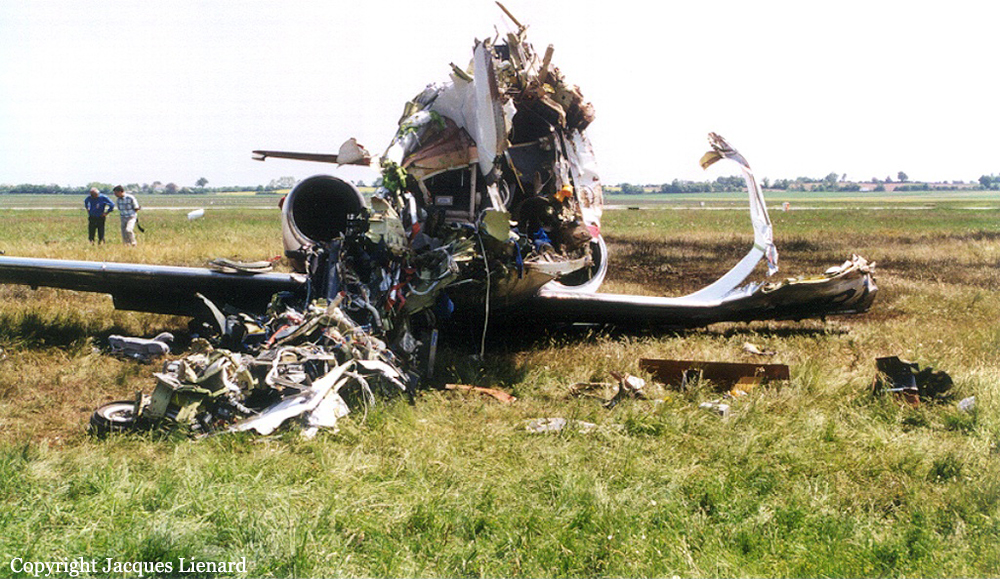
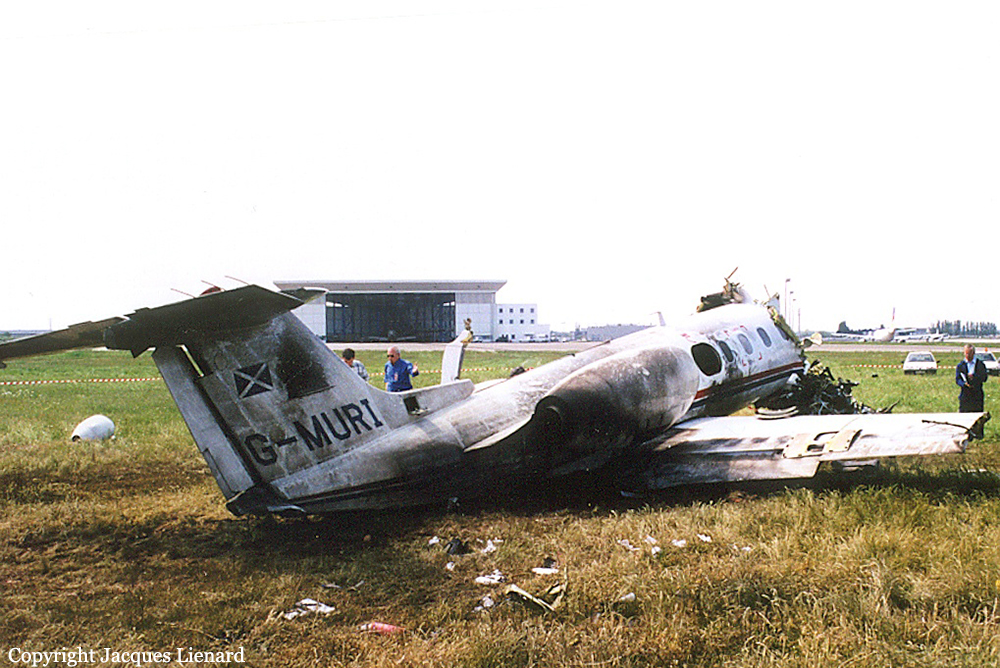
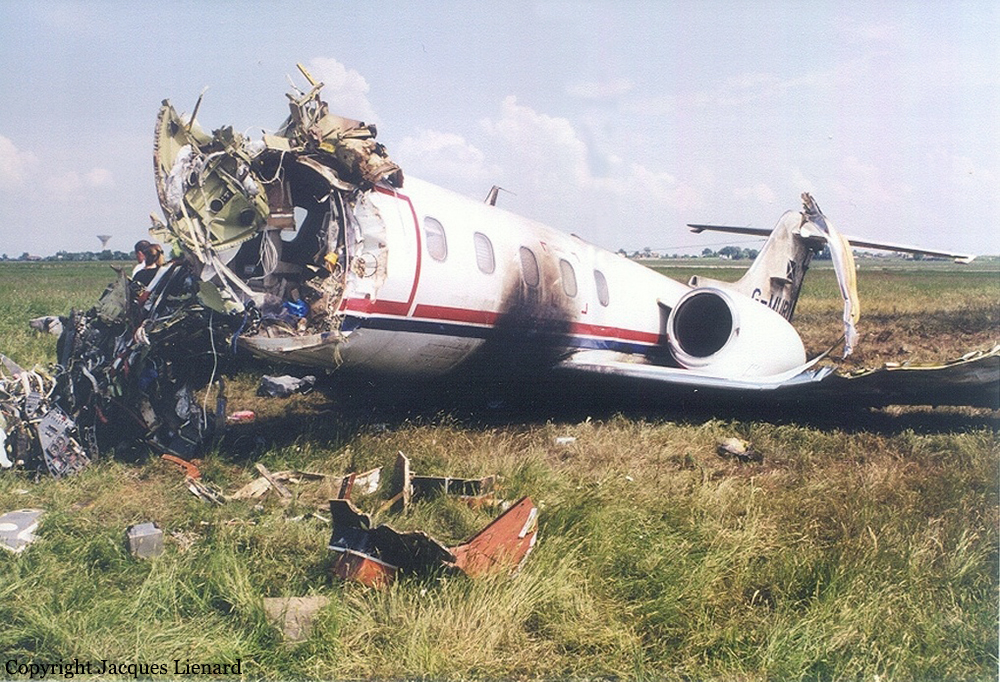
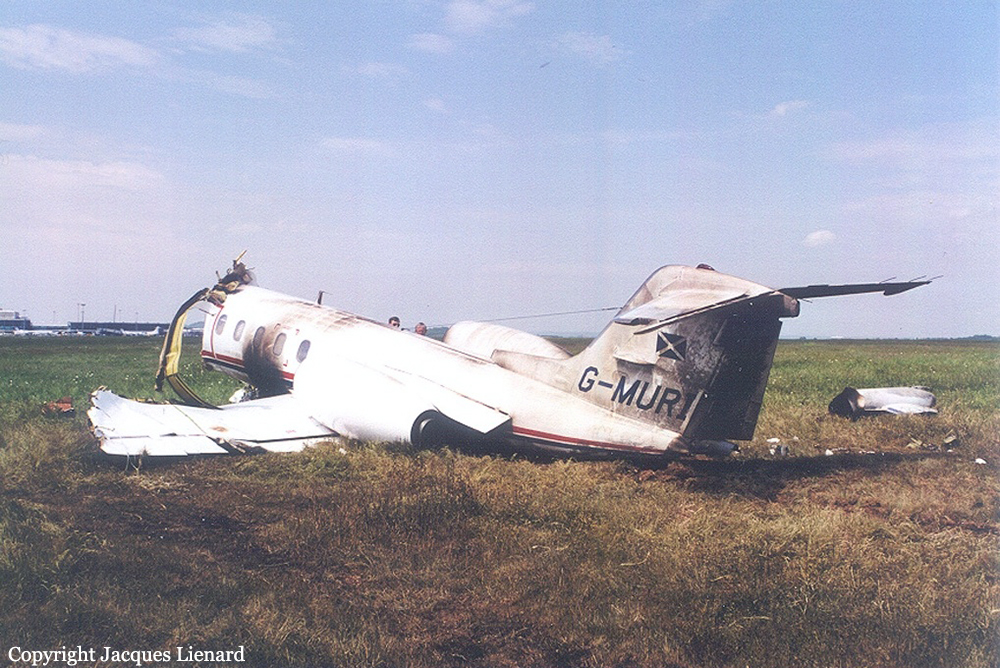
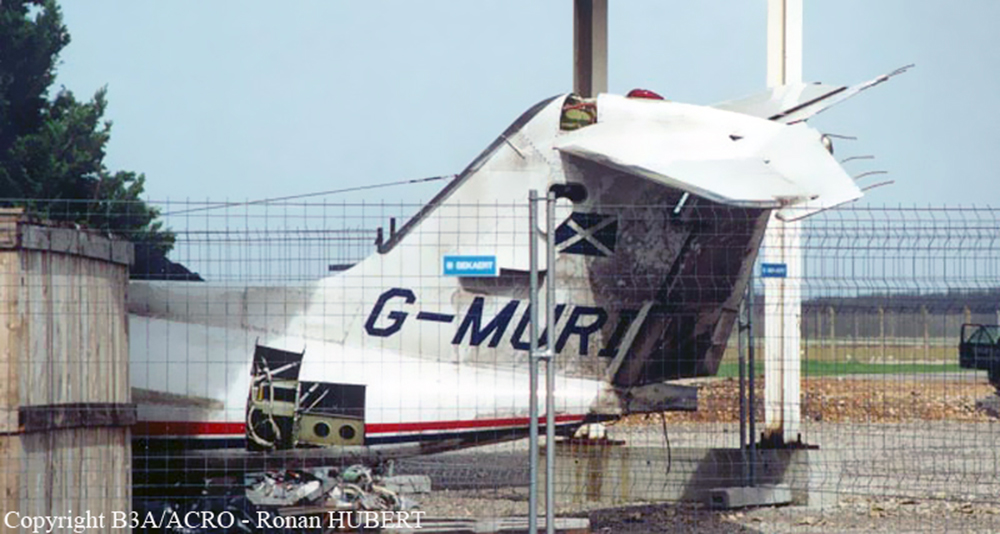
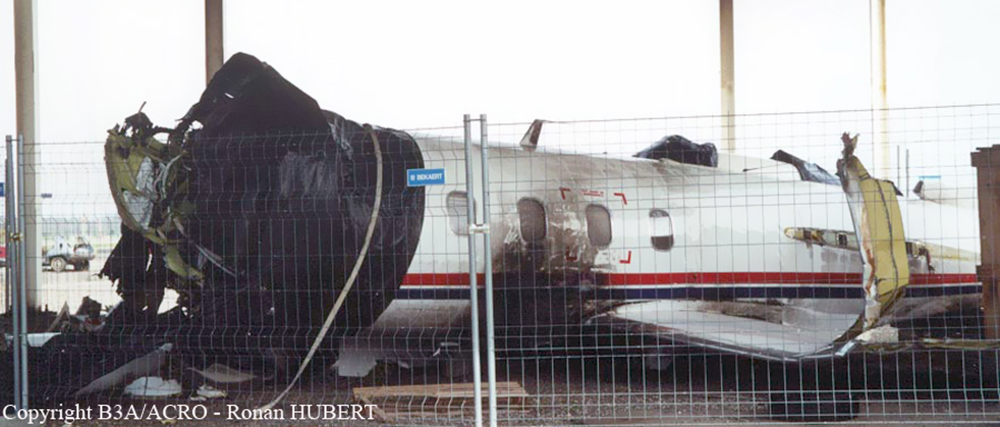
The aircraft departed Den Helder-De Kooy Airport on a radar tracking flight over the North Sea. Following an uneventful mission, the crew was returning to De Kooy Airport. After touchdown on runway 03, the crew activated the thrust reverser systems when the aircraft lost controllability. The pilot attempted to maintain control and selected the left throttle from 'reverse' again to turn to the right. Eventually, he feathered the right propeller and cut off the fuel supply, causing the right engine to stop. The aircraft veered off runway to the left and came to rest in a ditch. Both pilots escaped uninjured and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
The landing speed, the touchdown point, the runway length and runway condition were considered as good. The problem was the consequence of an expired adjustment screw of the speed controller ('prop governor') on the right engine, so that it did not come into 'reverse pitch' but continued to provide forward thrust, causing an asymmetric aerodynamic braking effect. It was also determined that the Beta light indicator burned and could not light on, preventing the pilot from a possible issue on the reverse thrust system.
Final Report: