Crash of a Cessna 207 Skywagon near Bethel: 1 killed
Date & Time:
May 30, 2015 at 1130 LT
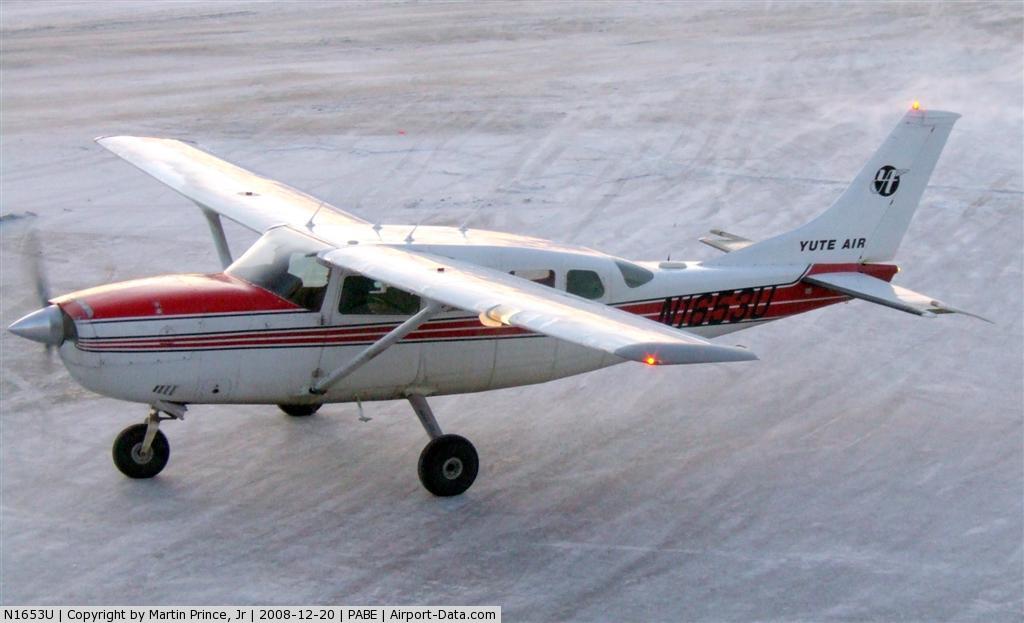
Registration:
N1653U
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bethel - Bethel
MSN:
207-0253
YOM:
1974
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
6600.00
Aircraft flight hours:
28211
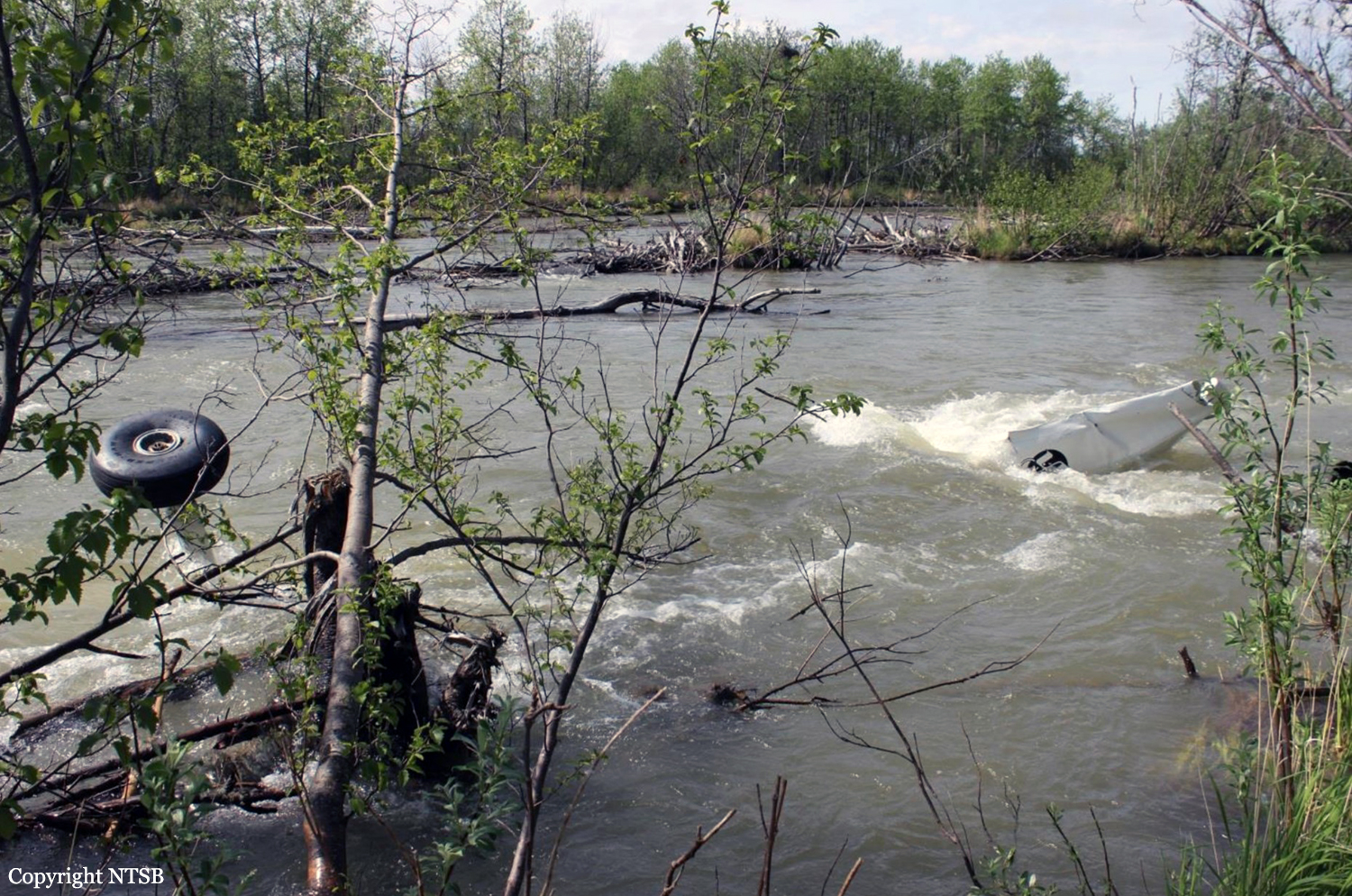
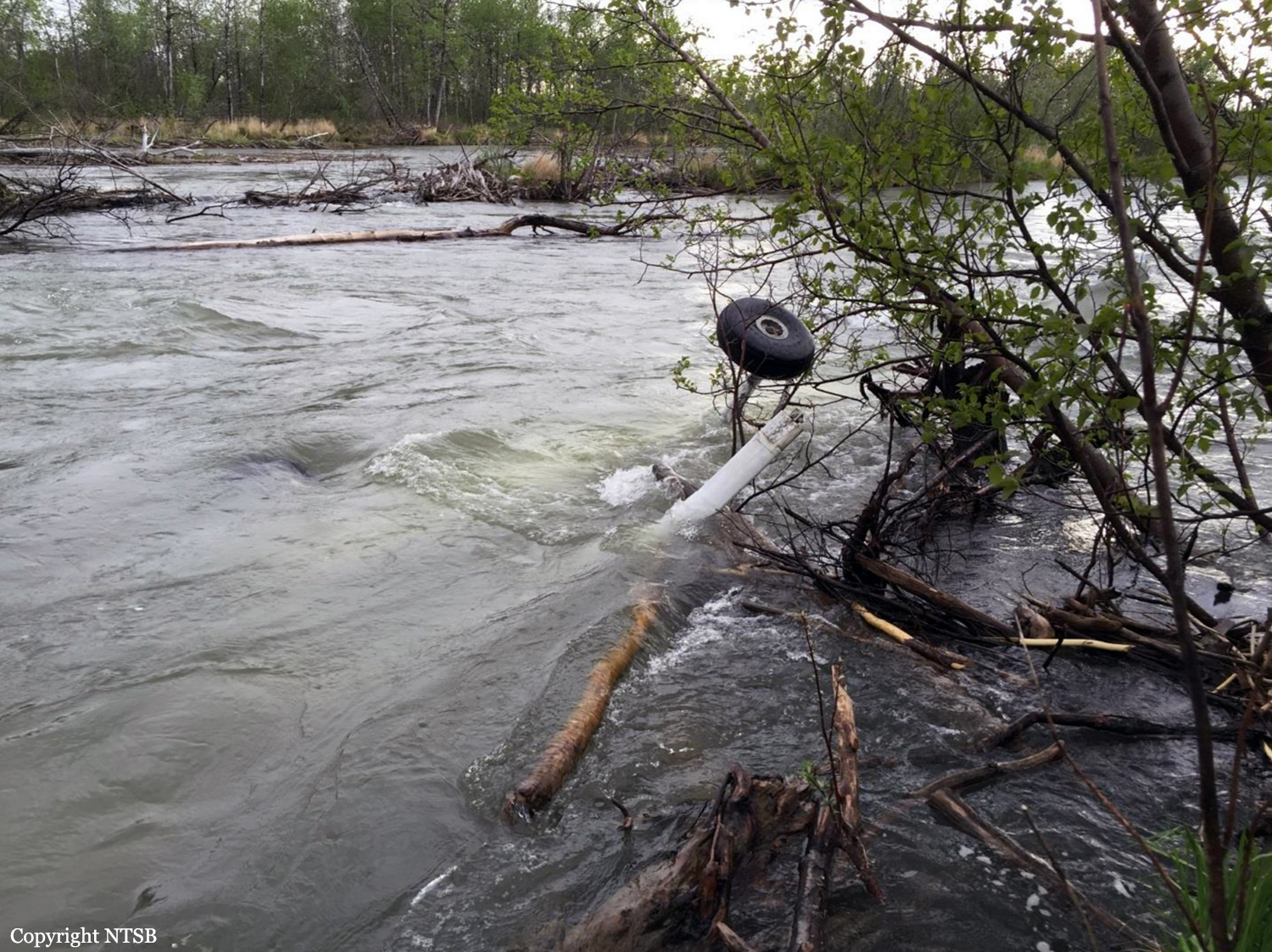
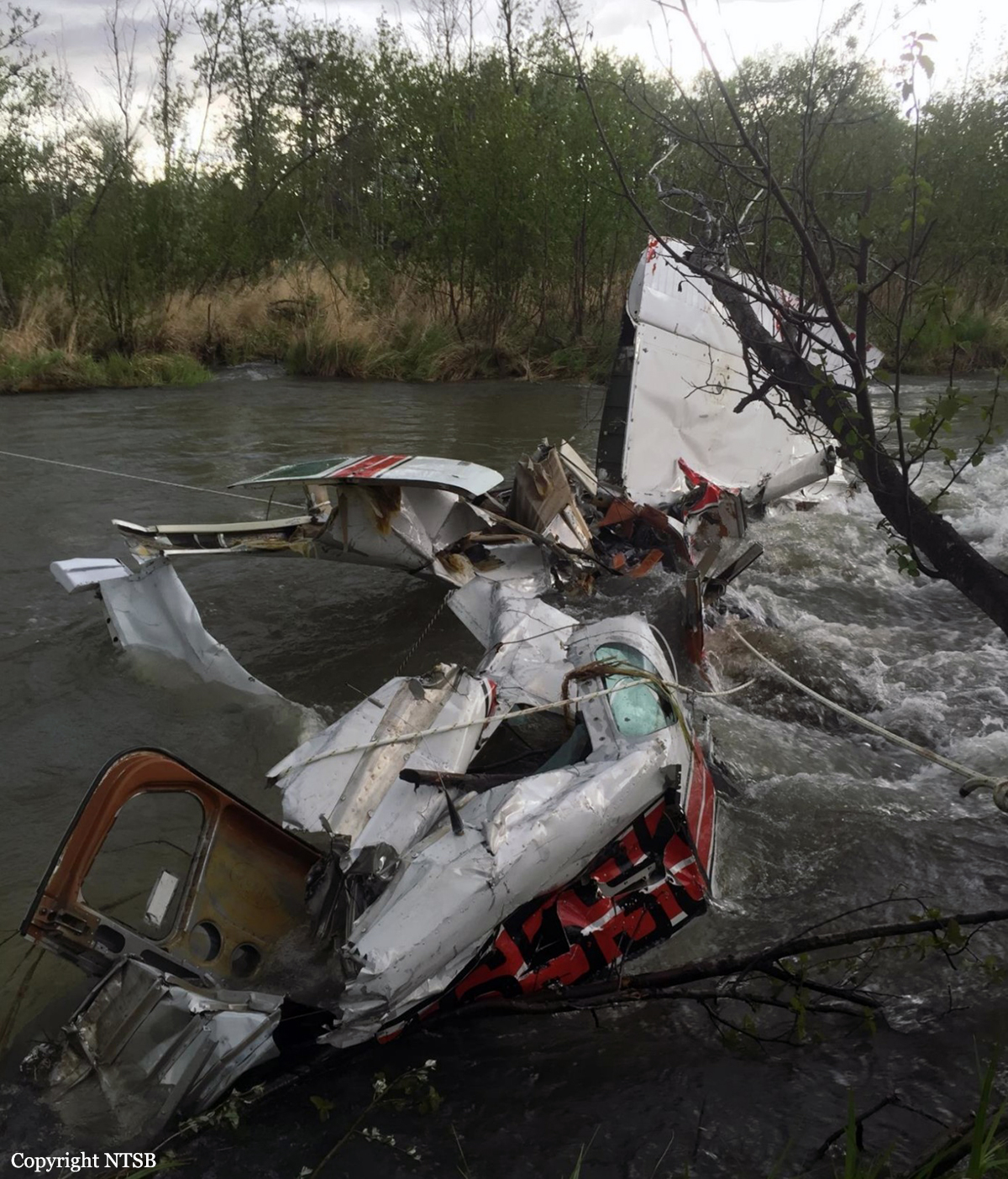
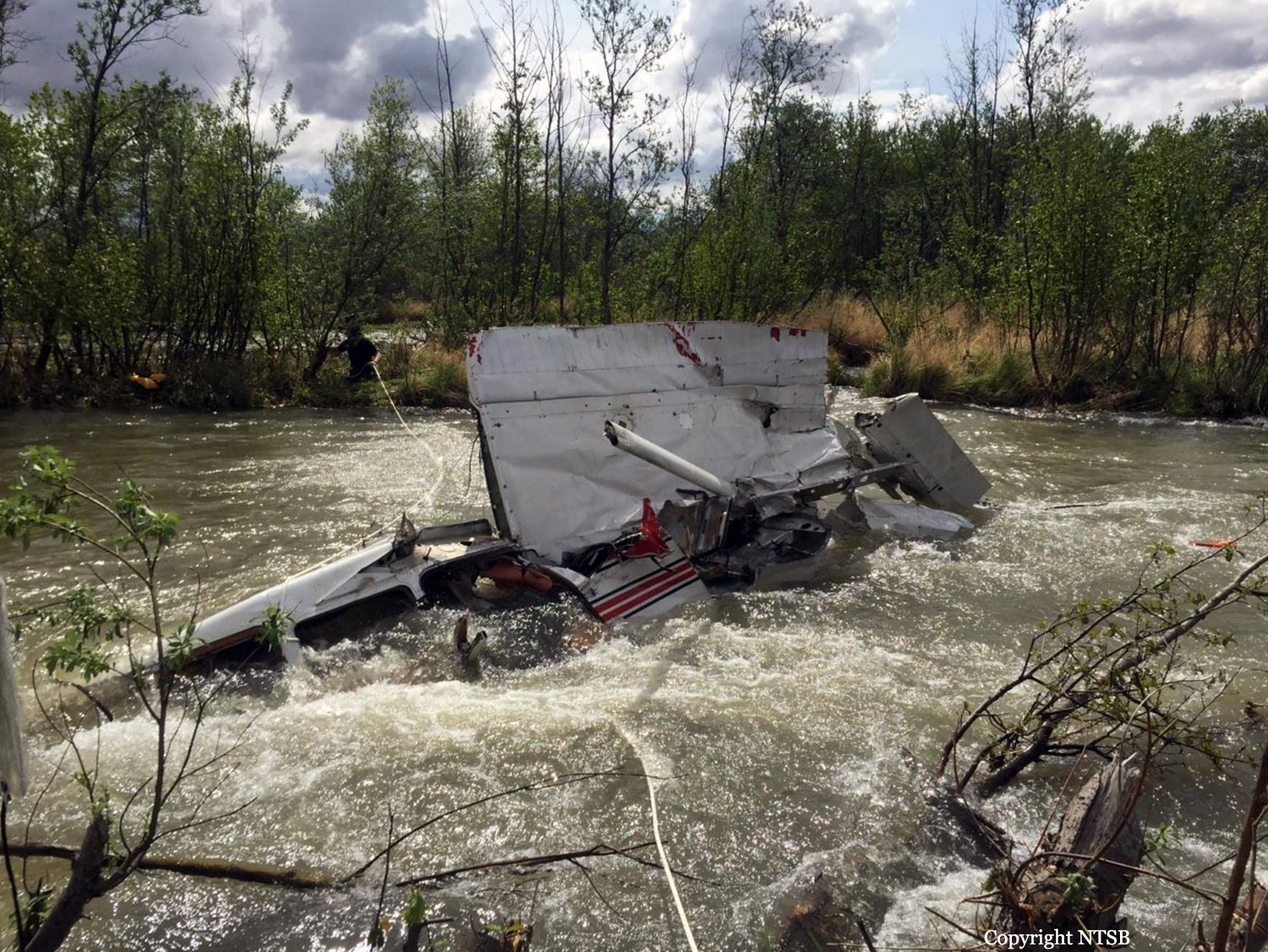
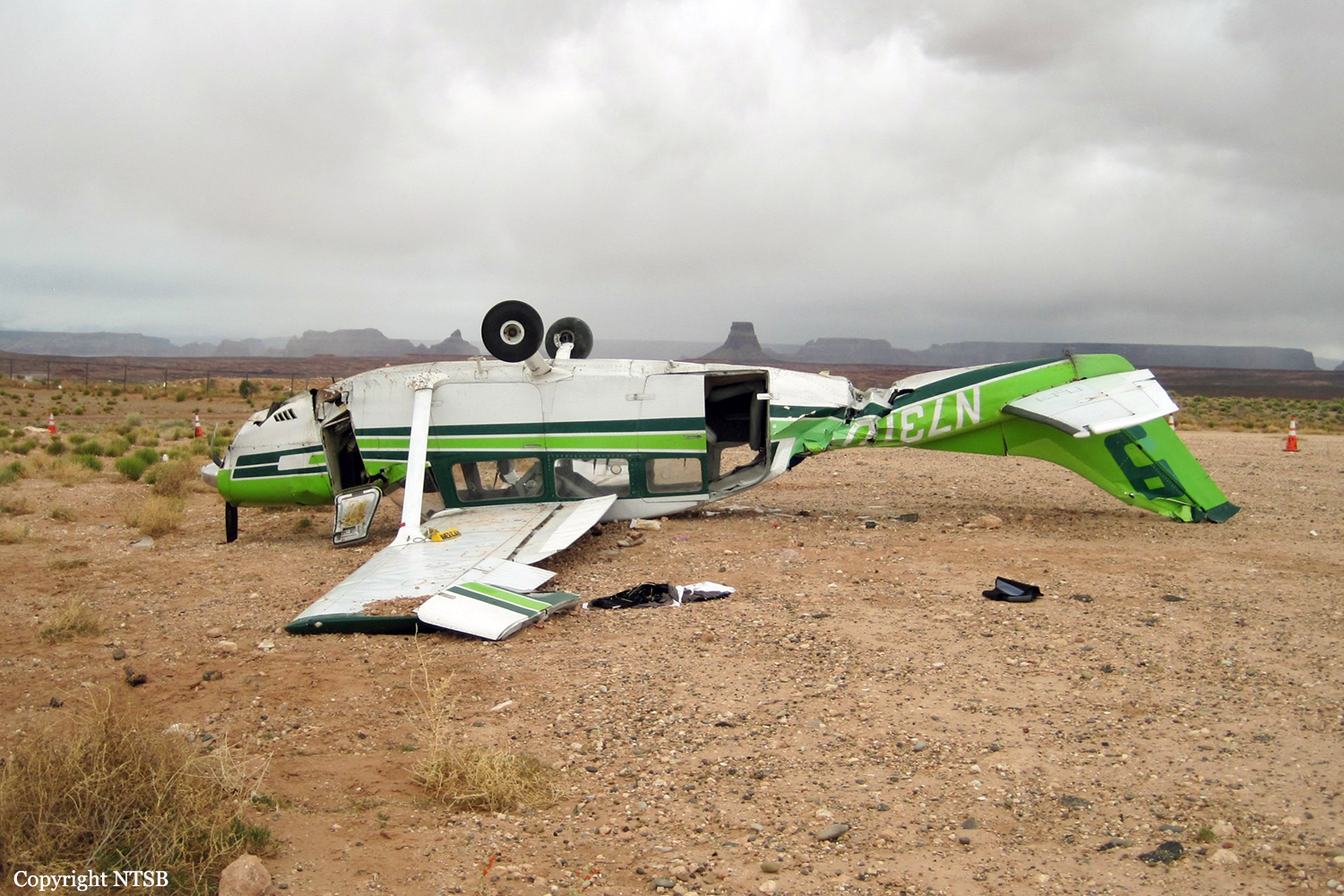
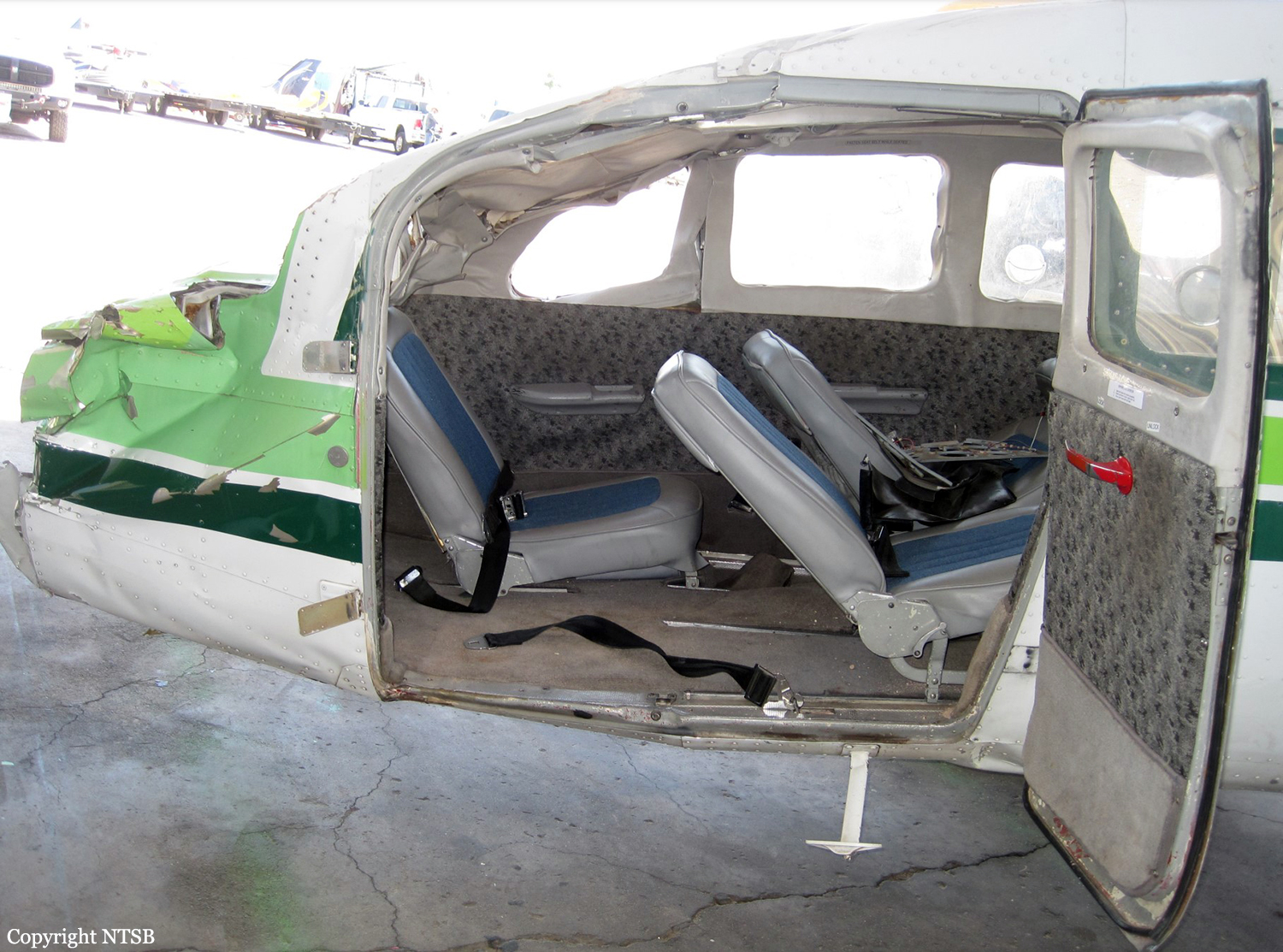
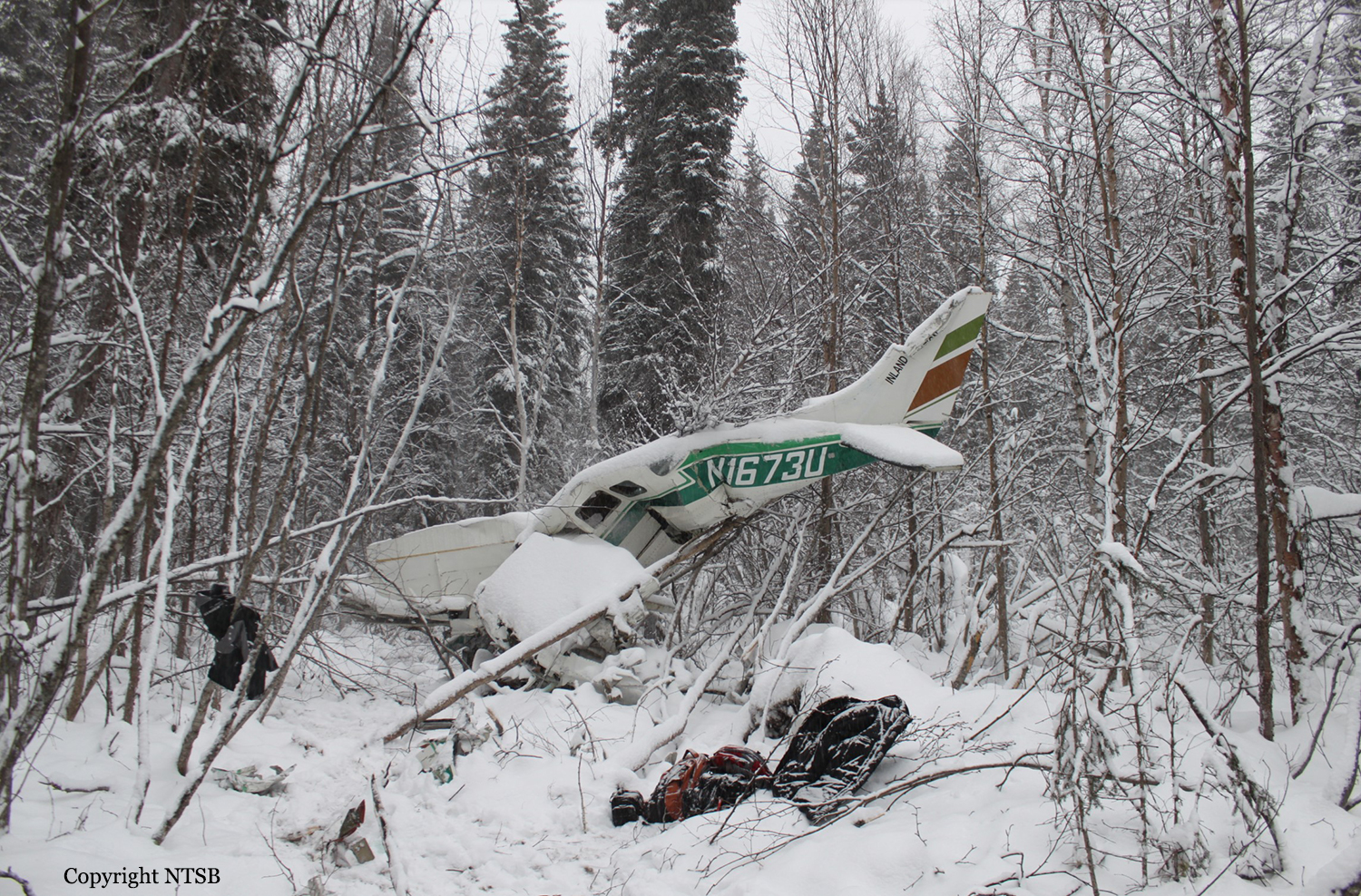
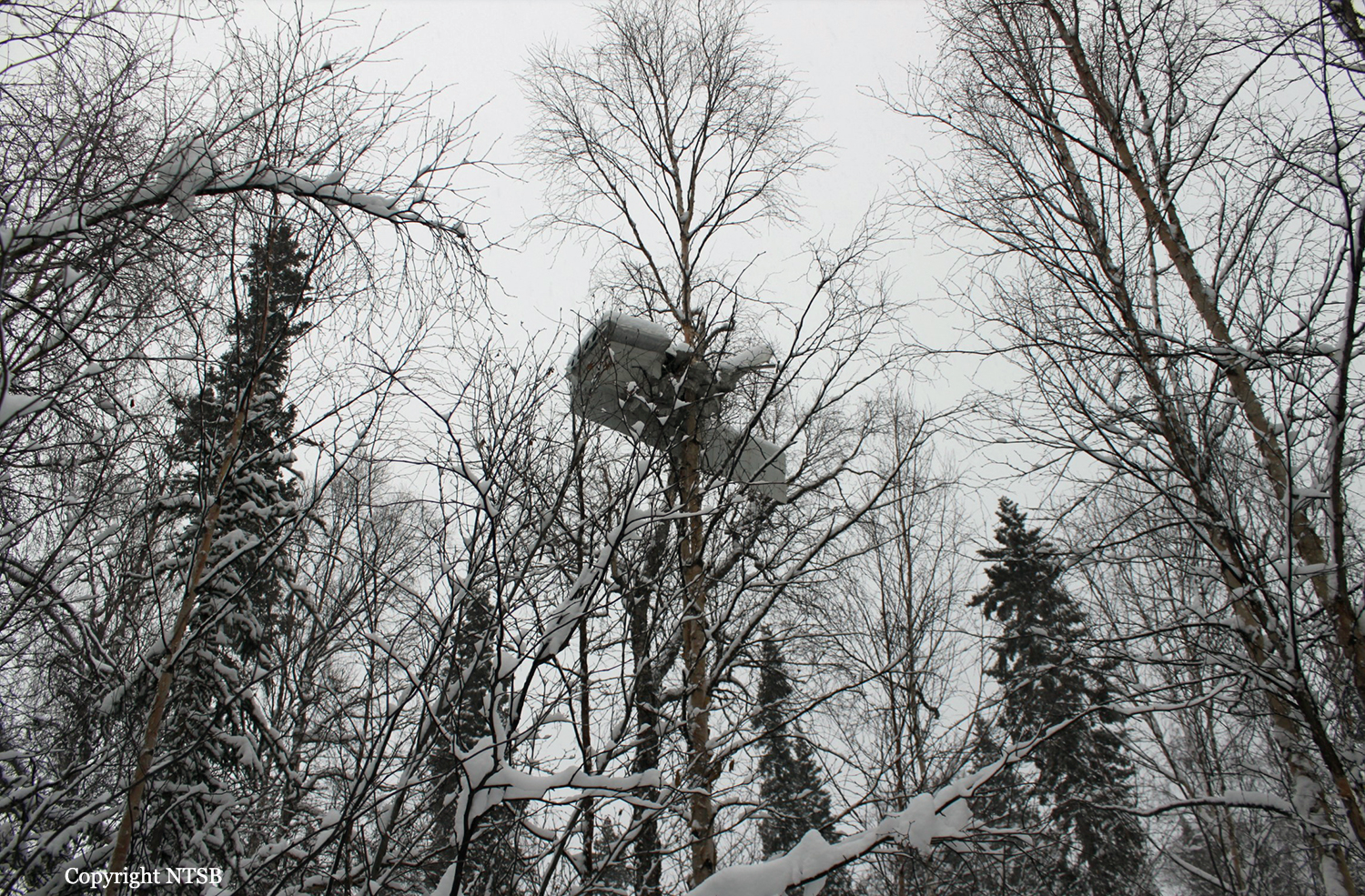
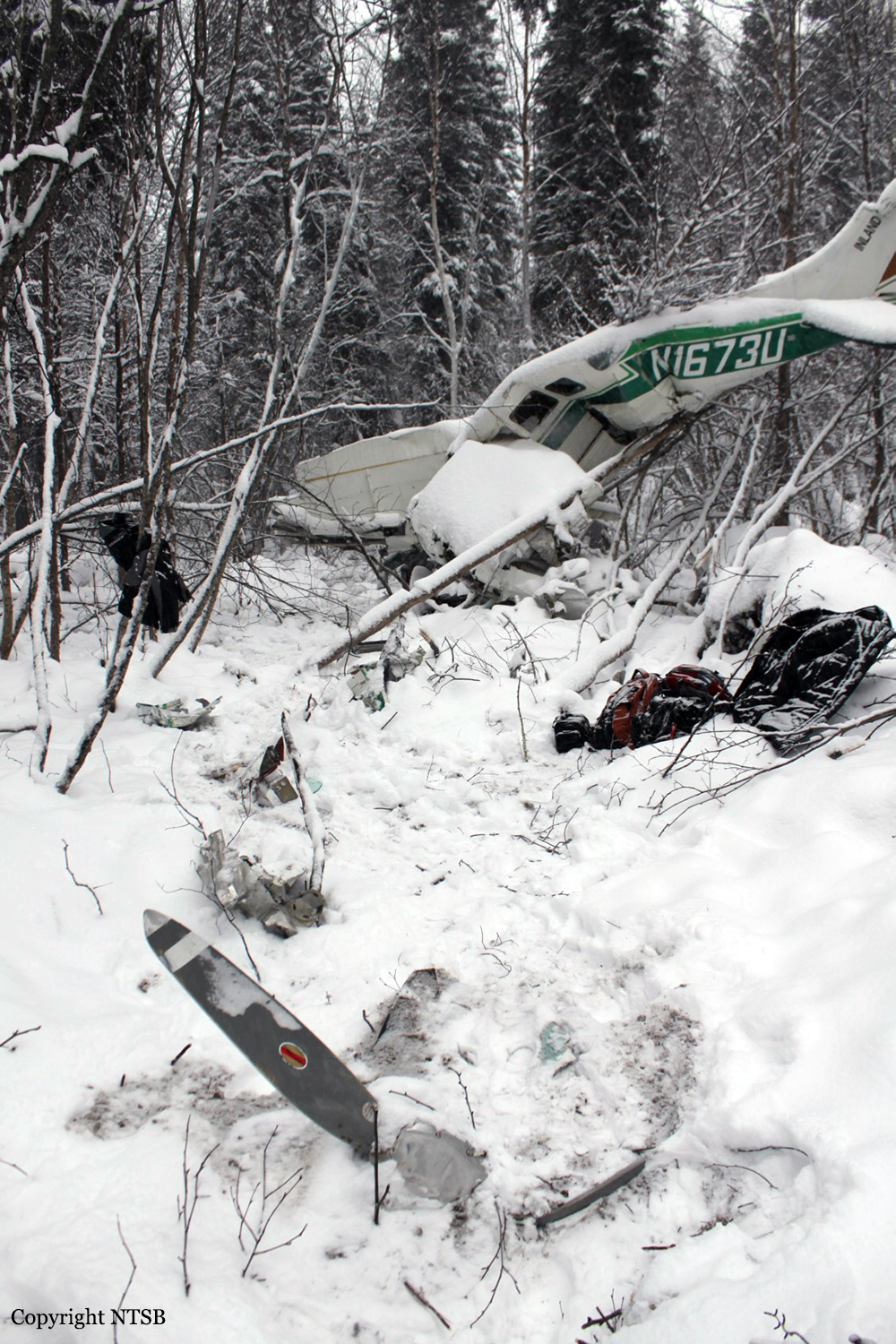
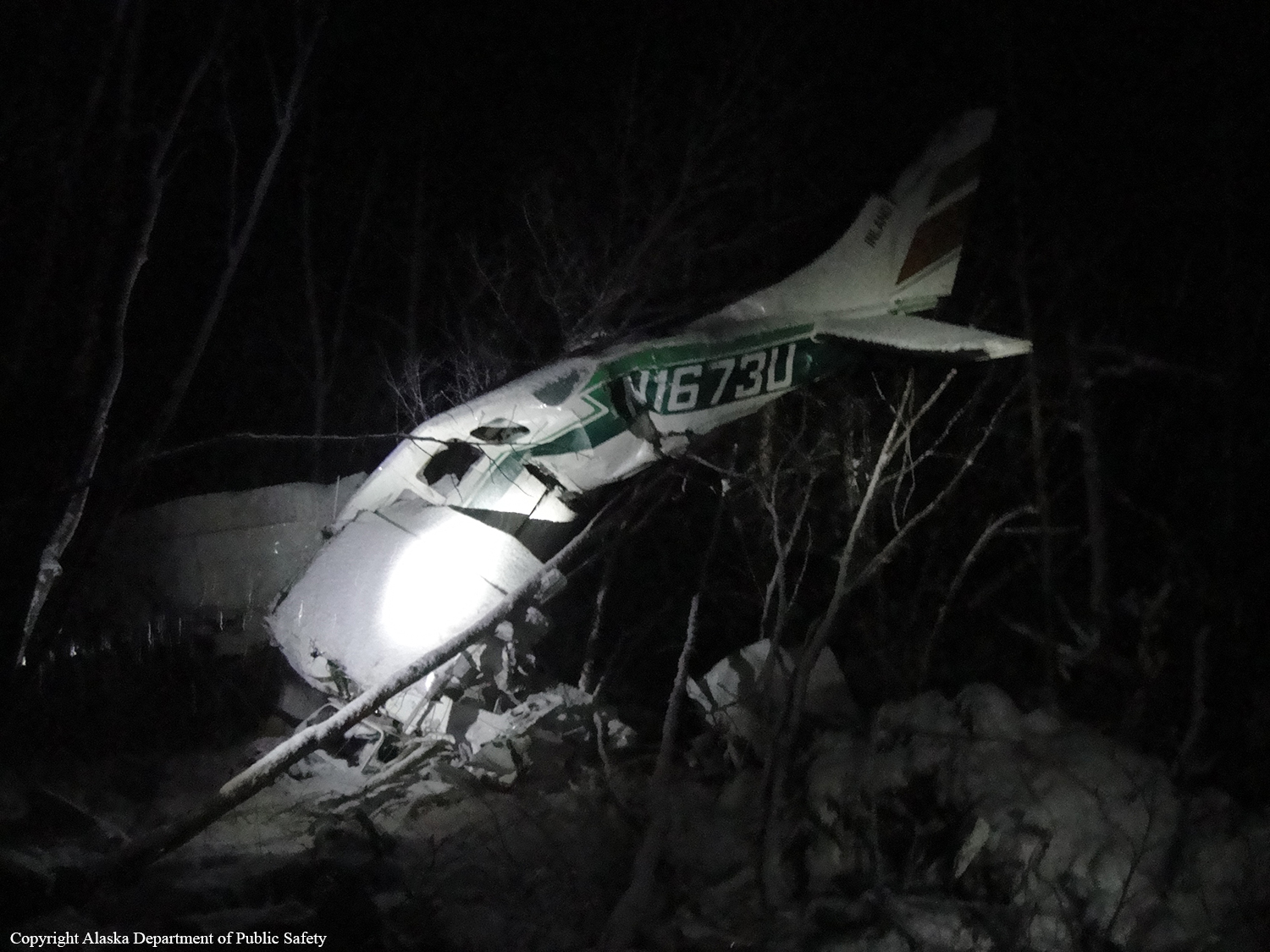
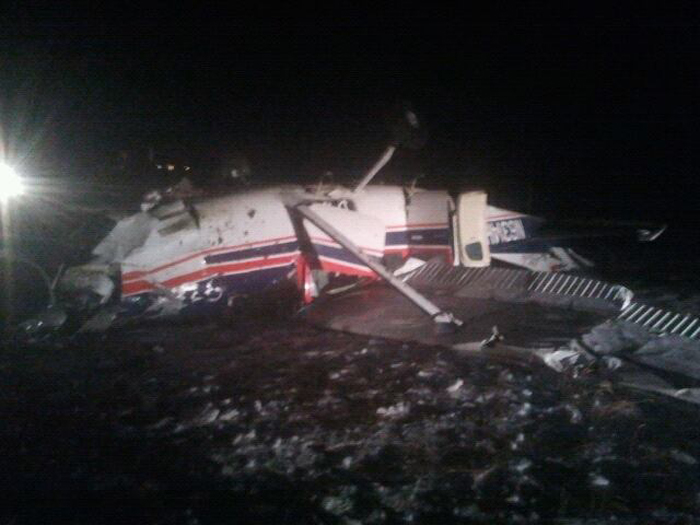
Circumstances:
The pilot departed on a postmaintenance test flight during day visual meteorological conditions. According to the operator, the purpose of the flight was to break in six recently installed engine cylinders, and the flight was expected to last 3.5 hours. Recorded automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast data showed that the airplane was operating at altitudes of less than 500 ft mean sea level for the majority of the flight. The data ended about 3 hours after takeoff with the airplane located about 23 miles from the accident site. There were no witnesses to the accident, which occurred in a remote area. When the airplane did not return, the operator reported to the Federal Aviation Administration that the airplane was overdue. Searchers subsequently discovered the fragmented wreckage submerged in a swift moving river, about 40 miles southeast of the departure/destination airport. Postmortem toxicology tests identified 21% carboxyhemoglobin (carbon monoxide) in the pilot's blood. The pilot was a nonsmoker, and nonsmokers normally have no more than 3% carboxyhemoglobin. There was no evidence of postimpact fire; therefore, it is likely that the pilot's elevated carboxyhemoglobin level was from acute exposure to carbon monoxide during the 3 hours of flight time before the accident. As the pilot did not notify air traffic control or the operator's home base of any problems during the flight, it is unlikely that he was aware that there was carbon monoxide present. Early symptoms of carbon monoxide exposure may include headache, malaise, nausea, and dizziness. Carboxyhemoglobin levels between 10% and 20% can result in confusion, impaired judgment, and difficulty concentrating. While it is not possible to determine the exact symptoms the pilot experienced, it is likely that the pilot had symptoms that may have been distracting as well as some degree of impairment in his judgment and concentration. Given the low altitudes at which he was operating the airplane, he had little margin for error. Thus, it is likely that the carbon monoxide exposure adversely affected the pilot's performance and contributed to his failure to maintain clearance from the terrain. According to the operator, the airplane had a "winter heat kit" installed, which modified the airplane's original cabin heat system. The modification incorporated an additional exhaust/heat shroud system designed to provide increased cabin heat during wintertime operations. Review of maintenance records revealed that the modification had not been installed in accordance with Federal Aviation Administration field approval procedures. Examination of the recovered wreckage did not reveal evidence of any preexisting mechanical anomalies that would have precluded normal operation of the airplane. Examination of the airplane's right side exhaust/heat exchanger did not reveal any leaks or fractures that would have led to carbon monoxide in the cabin. Because the left side exhaust/heat exchanger was
not recovered, it was not possible to determine whether it was the source of the carbon monoxide.
not recovered, it was not possible to determine whether it was the source of the carbon monoxide.
Probable cause:
The pilot's failure to maintain altitude, which resulted in collision with the terrain. Contributing to the accident was the pilot's impairment from carbon monoxide exposure in flight. The source of the carbon monoxide could not be determined because the wreckage could not be completely recovered.
Final Report: