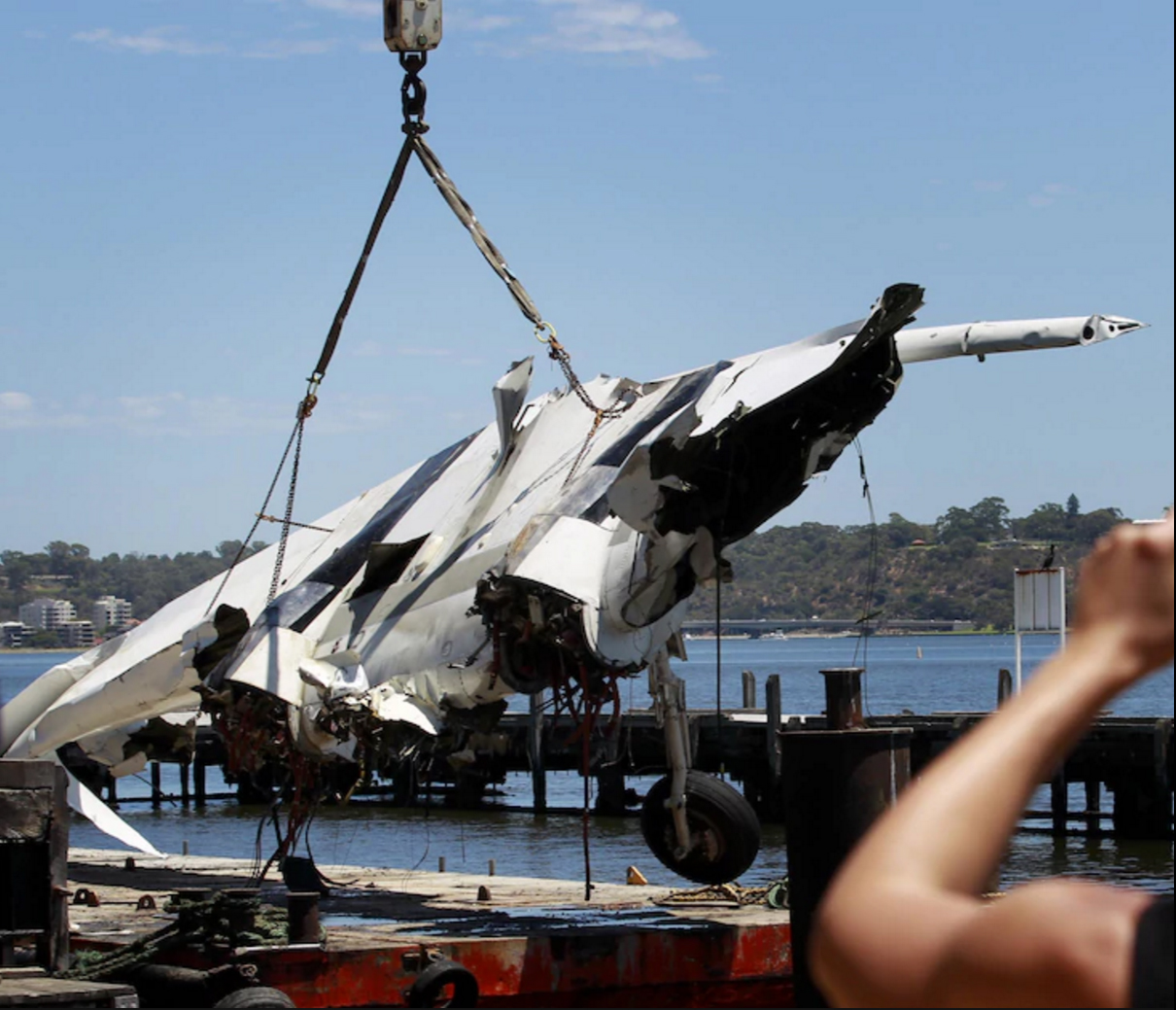
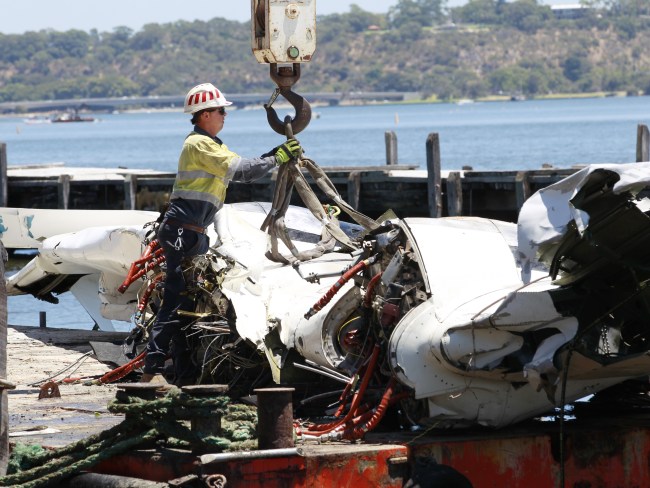
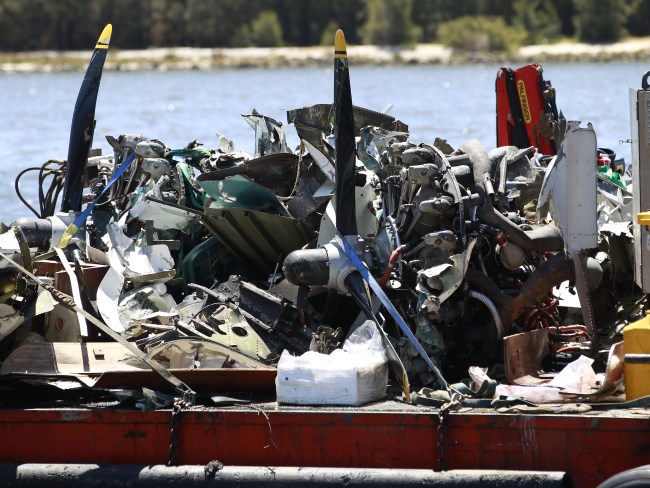
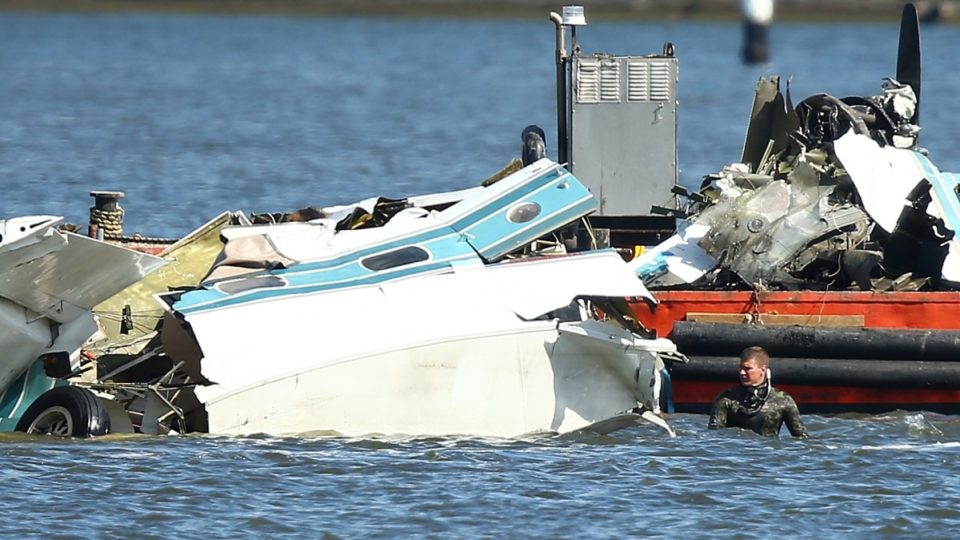
Crash of a Britten-Norman BN-2A-20 Islander in West Portal: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 8, 2018 at 0828 LT
Registration:
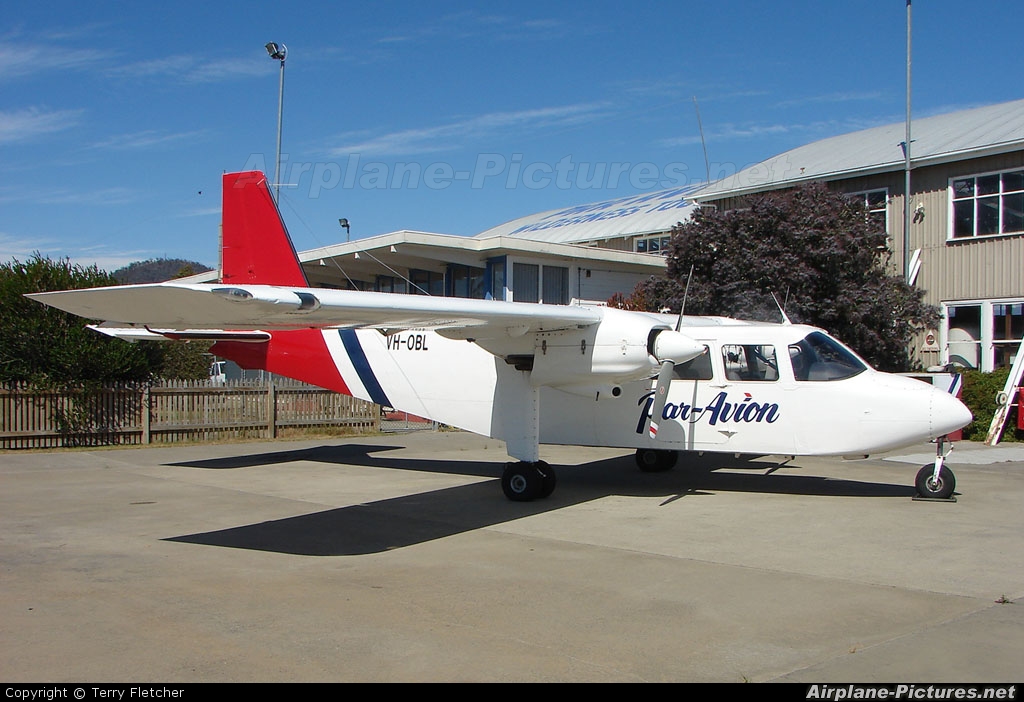
VH-OBL
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Cambridge – Bathurst Harbour
MSN:
2035
YOM:
1986
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
80.00
Aircraft flight hours:
12428
Circumstances:
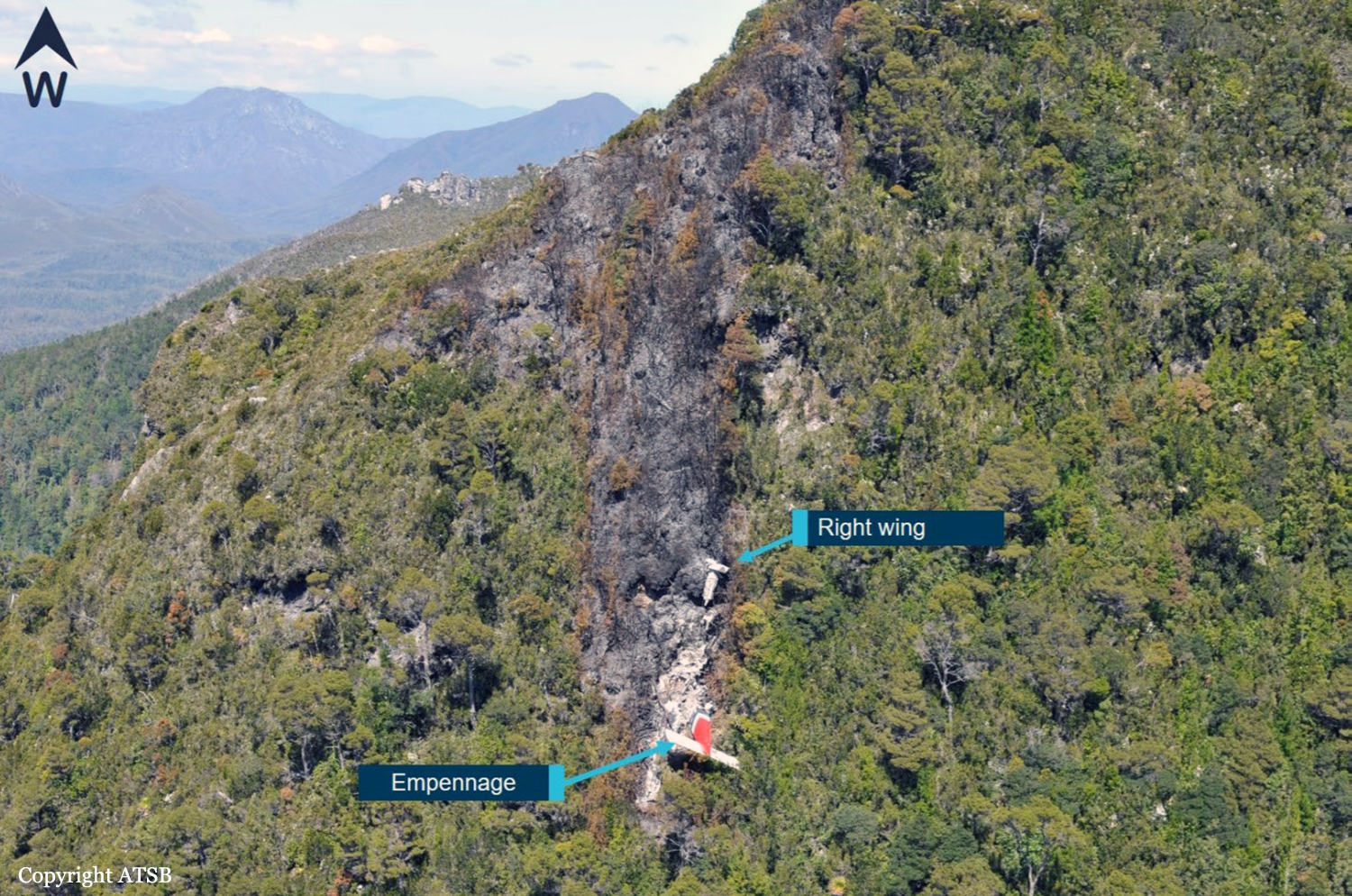
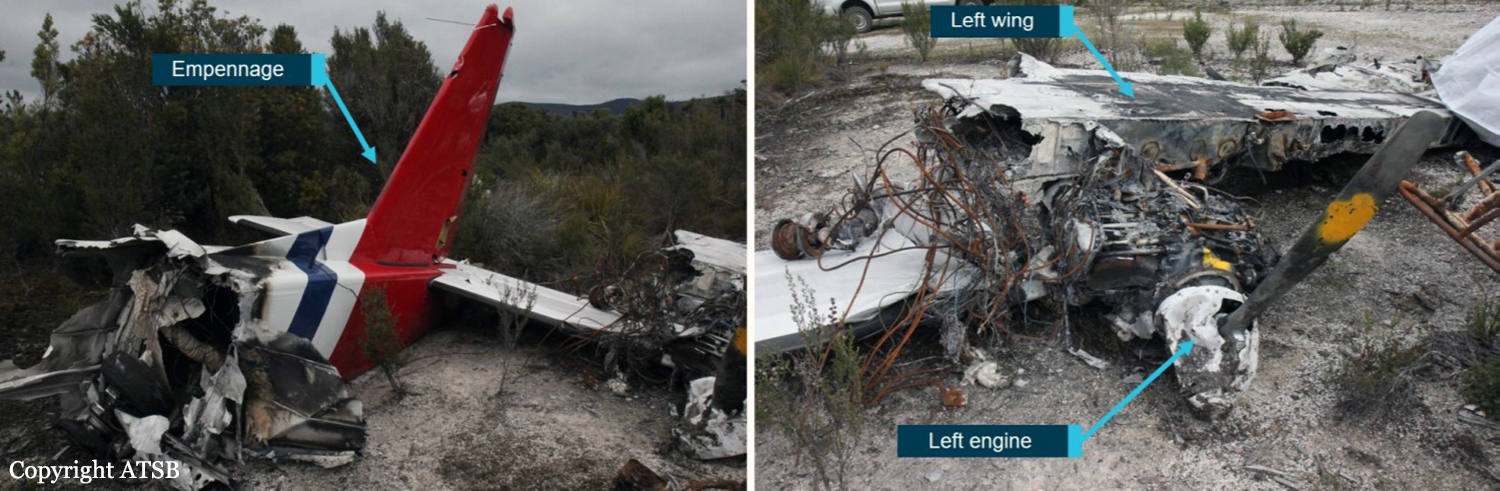
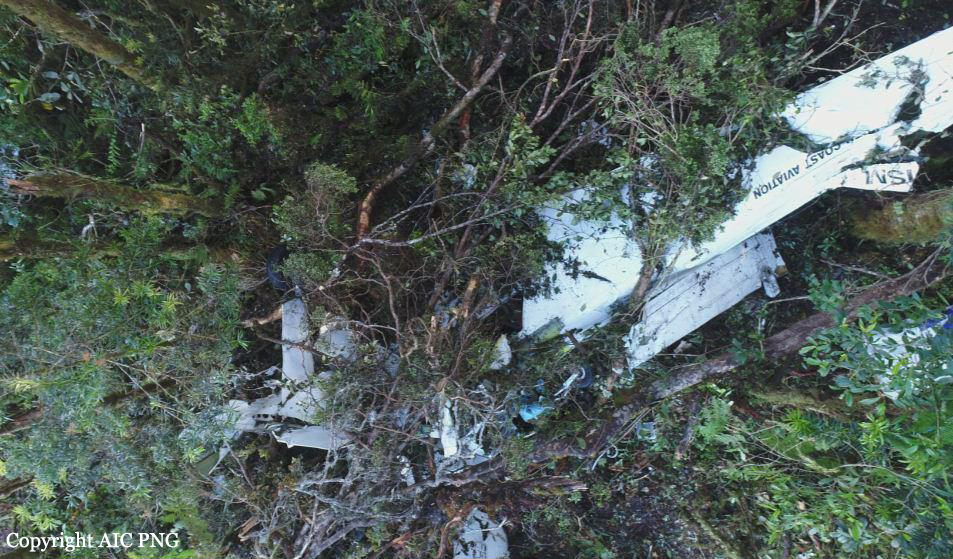
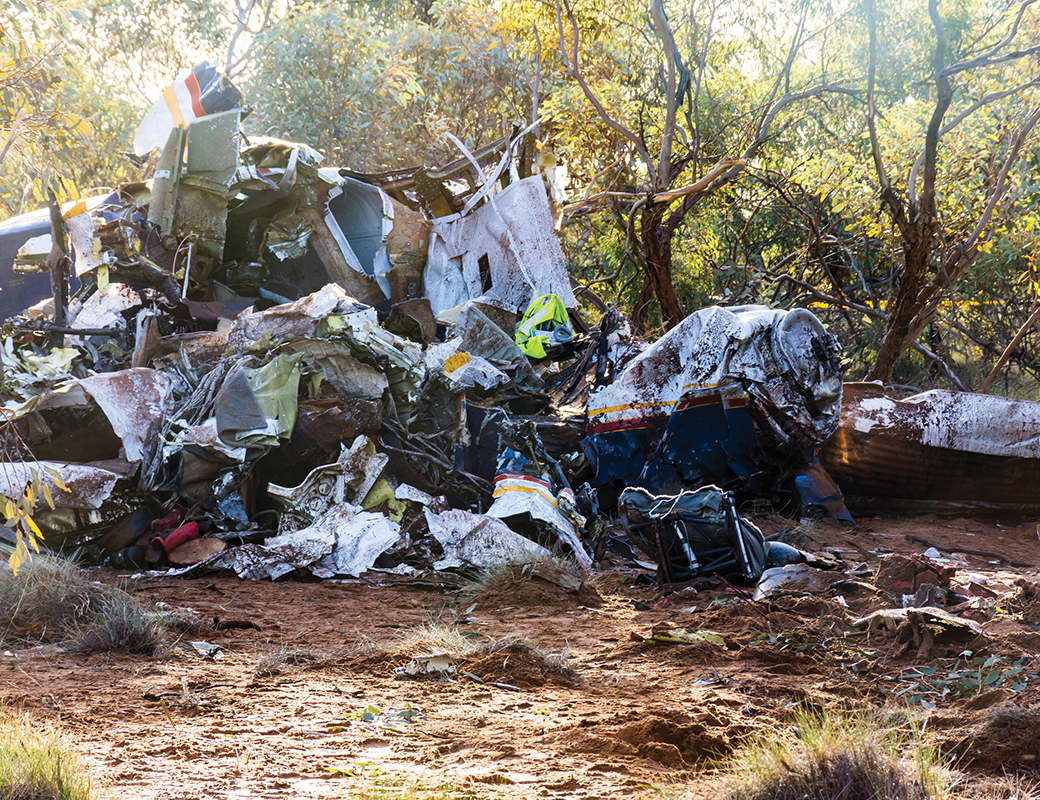
On 8 December 2018, the pilot of a Pilatus Britten-Norman BN2A-20 Islander, registered VH-OBL and operated by Airlines of Tasmania, was conducting a positioning flight under the visual flight rules from Cambridge Airport to the Bathurst Harbour aeroplane landing area (ALA), Tasmania. The aircraft departed Cambridge at about 0748 Eastern Daylight-saving Time and was scheduled to arrive at Bathurst Harbour about 0830 to pick up five passengers for the return flight. The passengers were part of a conservation project that flew to south-west Tasmania regularly, and it was the pilot’s only flight for that day. Automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B) position and altitude data (refer to the section titled Recorded information) showed the aircraft tracked to the south-west towards Bathurst Harbour (Figure 1). At about 0816, the aircraft approached a gap in the Arthur Range known as ‘the portals’. The portals are a saddle (lowest area) between the Eastern and Western Arthur Range, and was an optional route that Airlines of Tasmania used between Cambridge and Bathurst Harbour when the cloud base prevented flight over the mountain range. After passing through the portals, the aircraft proceeded to conduct a number of turns below the height of the surrounding highest terrain. The final data point recorded was at about At about 0829, the Australian Maritime Safety Authority received advice that an emergency locator transmitter allocated to VH-OBL had activated. They subsequently advised the Tasmanian Police and the aircraft operator of the activation, and initiated search and rescue efforts. The rescue efforts included two helicopters and a Challenger 604 search and rescue jet aircraft. The Challenger arrived over the emergency locator transmitter signal location at around 0925, however, due to cloud cover the crew were unable to visually identify the precise location of VH-OBL. A police rescue helicopter arrived at the search area at about 1030. The pilot of that helicopter reported observing cloud covering the eastern side of the Western Arthur Range, and described a wall of cloud with its base sitting on the bottom of the west portal. Multiple attempts were made throughout the day to locate the accident site, however, due to low-level cloud, and fluctuating weather conditions, the search and rescue operation was unable to confirm visual location of the aircraft until about 1900. The aircraft wreckage was found in mountainous terrain of the Western Arthur Range in the Southwest National Park (Figure 2) . The search and rescue crew assessed that the accident was unlikely to have been survivable. The helicopter crew considered winching personnel to the site, however, due to a number of risks, including potential for cloud reforming, the time of day and lighting, and other hazards associated with the mountainous location, the helicopter departed the area. The aircraft wreckage was accessed the following day, when it was confirmed that the pilot was fatally injured.
Probable cause:
From the evidence available, the following findings are made with respect to the controlled flight into terrain involving Pilatus Britten-Norman BN2A, VH-OBL, 101 km west-south-west of Hobart, Tasmania, on 8 December 2018.
Contributing factors:
• The pilot continued descending over the Arthur Range saddle to a lower altitude than previous flights, likely due to marginal weather. This limited the options for exiting the valley surrounded
by high terrain.
• While using a route through the Arthur Range due to low cloud conditions, the pilot likely encountered reduced visual cues in close proximity to the ground, as per the forecast conditions. This led to controlled flight into terrain while attempting to exit the range.
Contributing factors:
• The pilot continued descending over the Arthur Range saddle to a lower altitude than previous flights, likely due to marginal weather. This limited the options for exiting the valley surrounded
by high terrain.
• While using a route through the Arthur Range due to low cloud conditions, the pilot likely encountered reduced visual cues in close proximity to the ground, as per the forecast conditions. This led to controlled flight into terrain while attempting to exit the range.
Final Report: