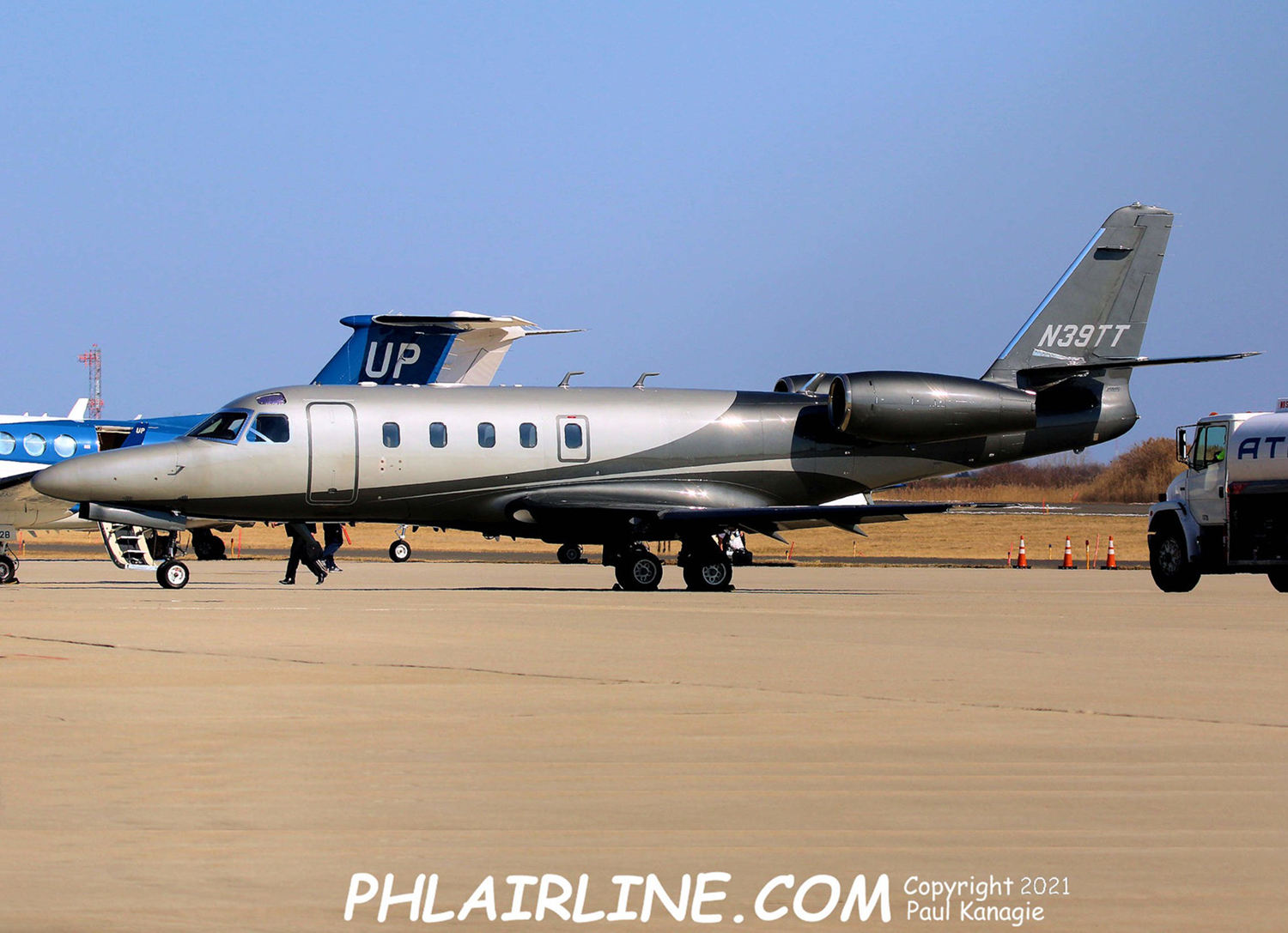
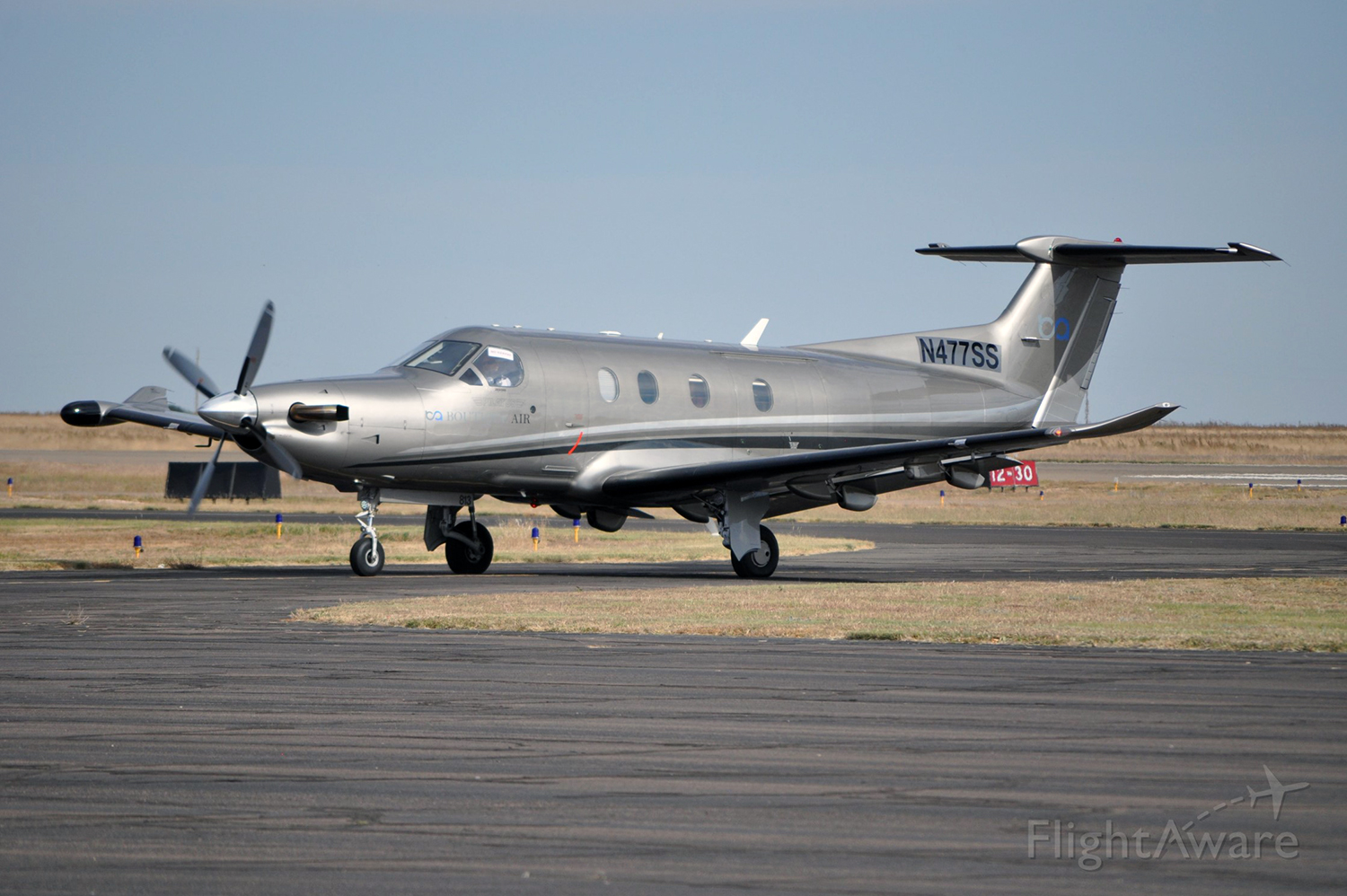
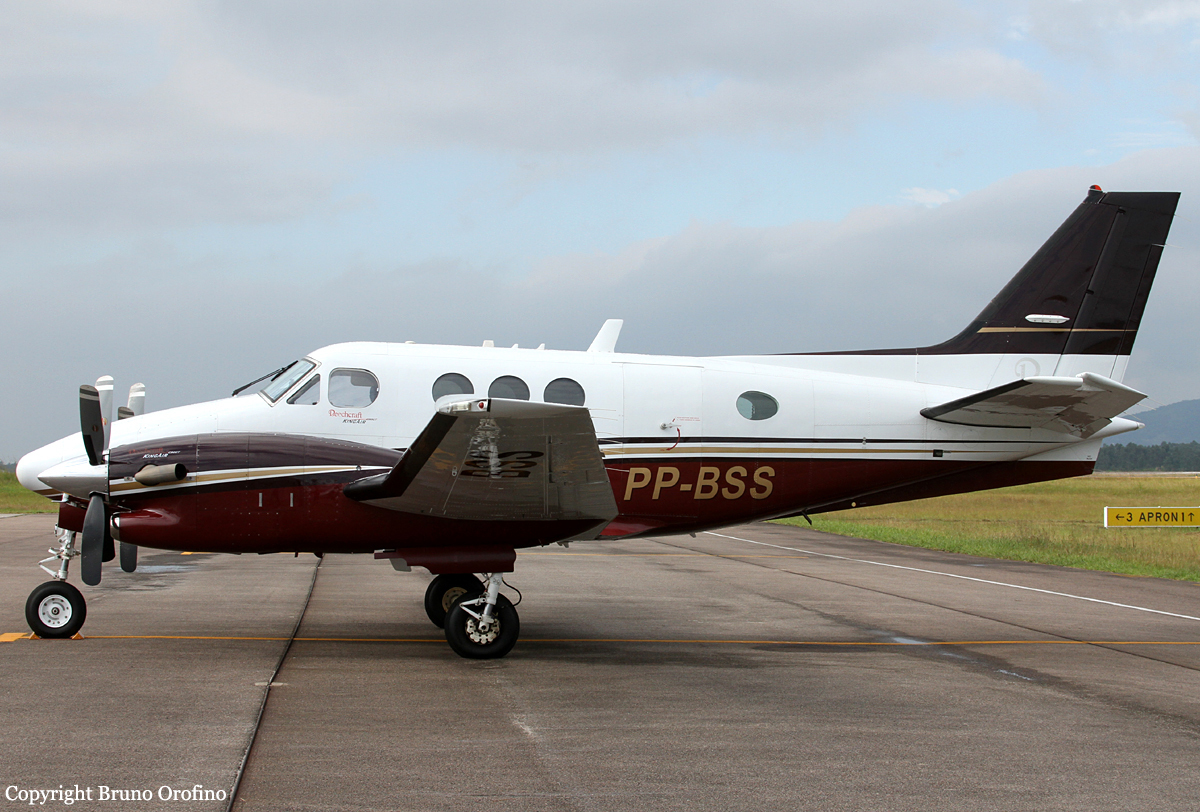
Crash of an IAI 1125 Astra SP in Chicago
Date & Time:
Aug 21, 2023 at 1315 LT
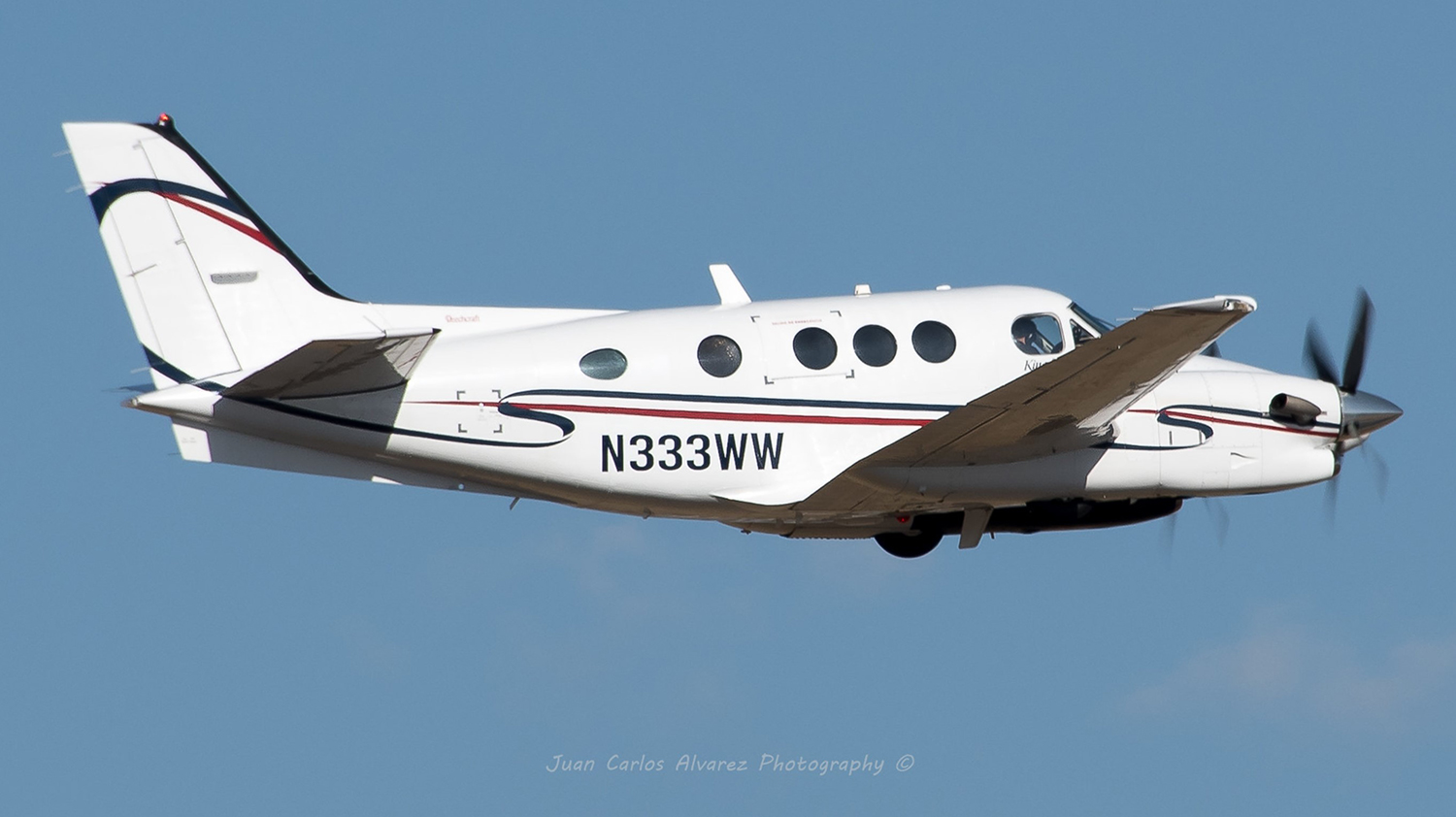
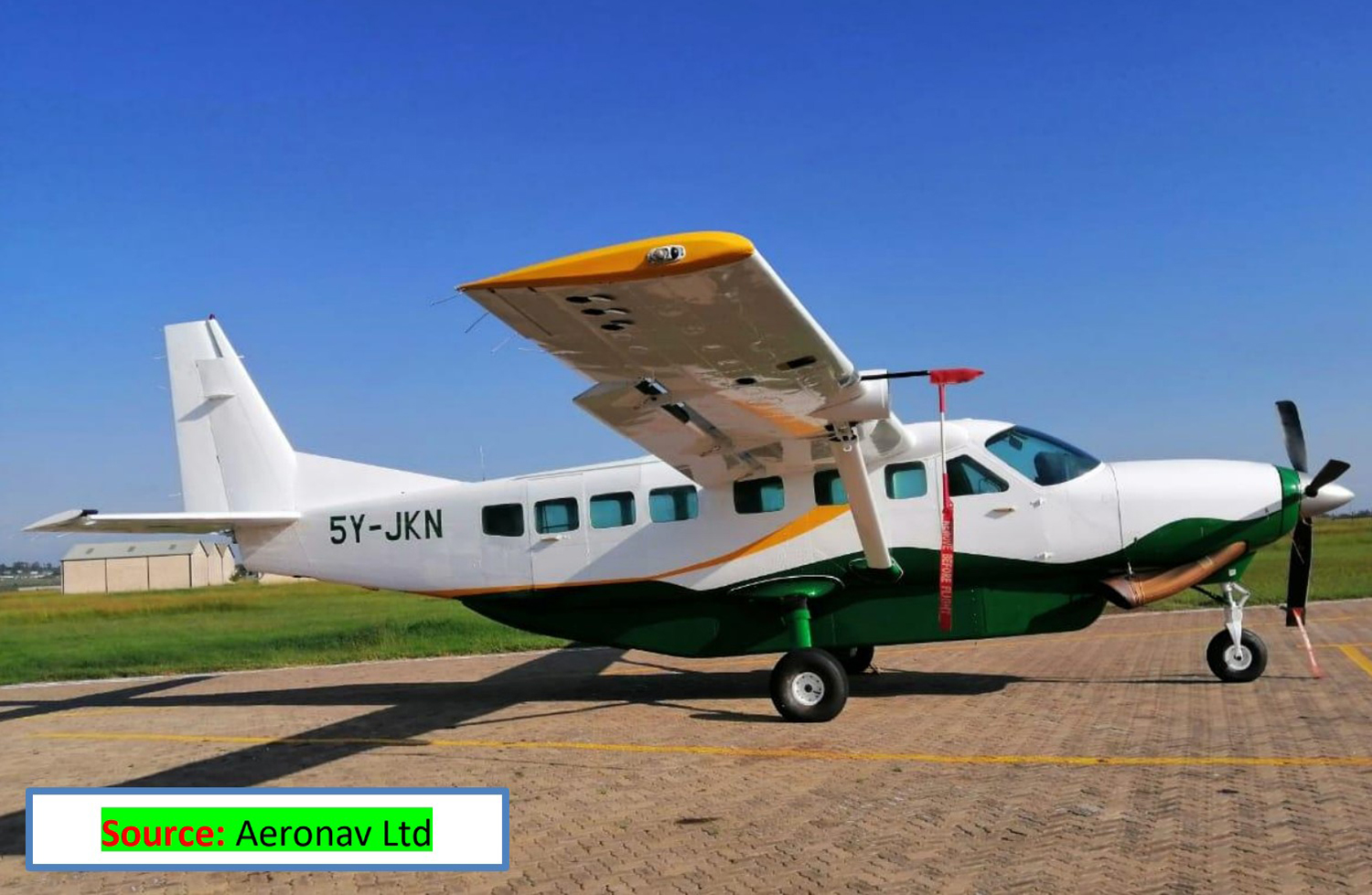
Registration:
N39TT
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Chicago-Midway - Chicago-Palwaukee
MSN:
053
YOM:
1991
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2300
Aircraft flight hours:
8307
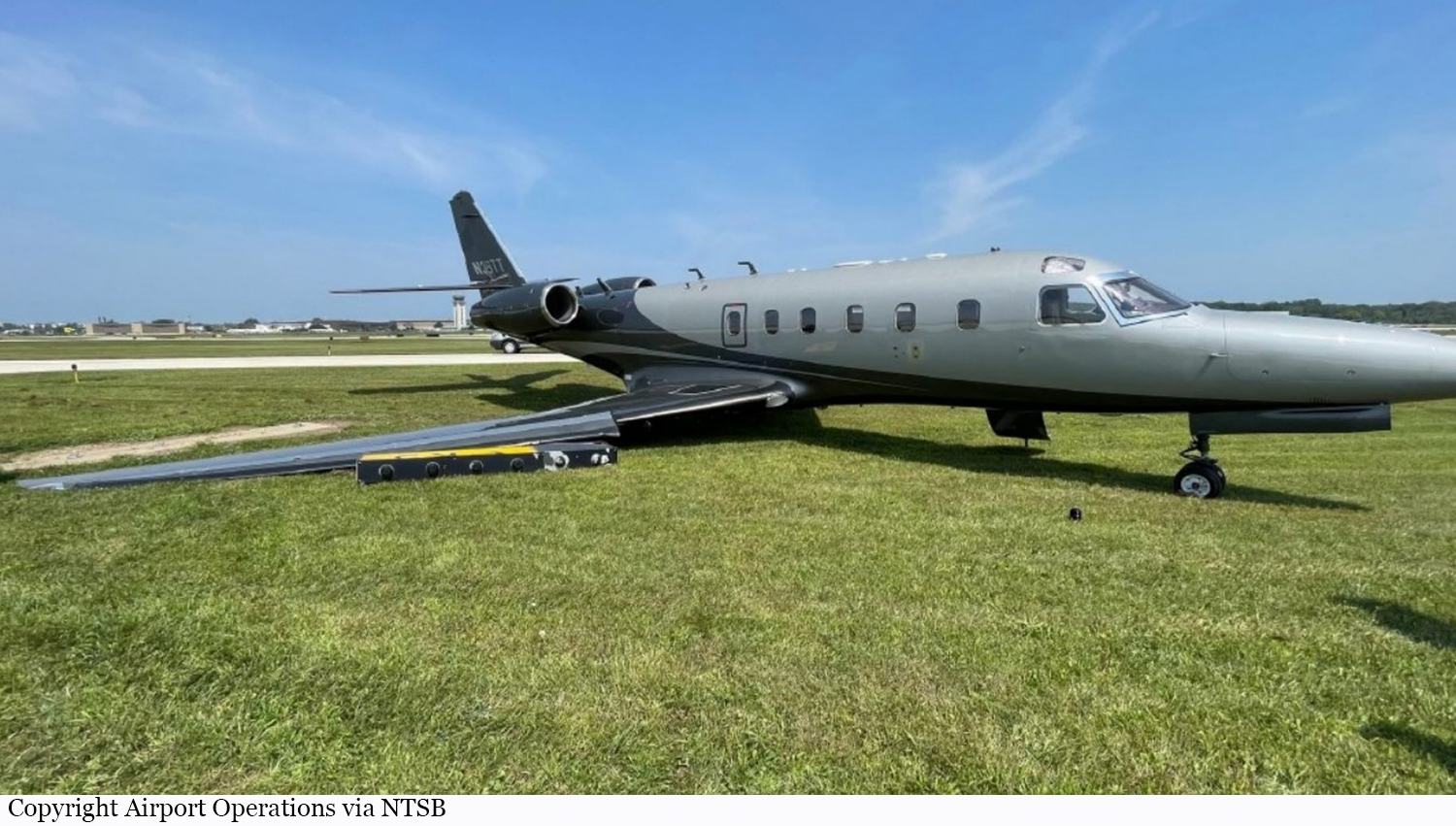
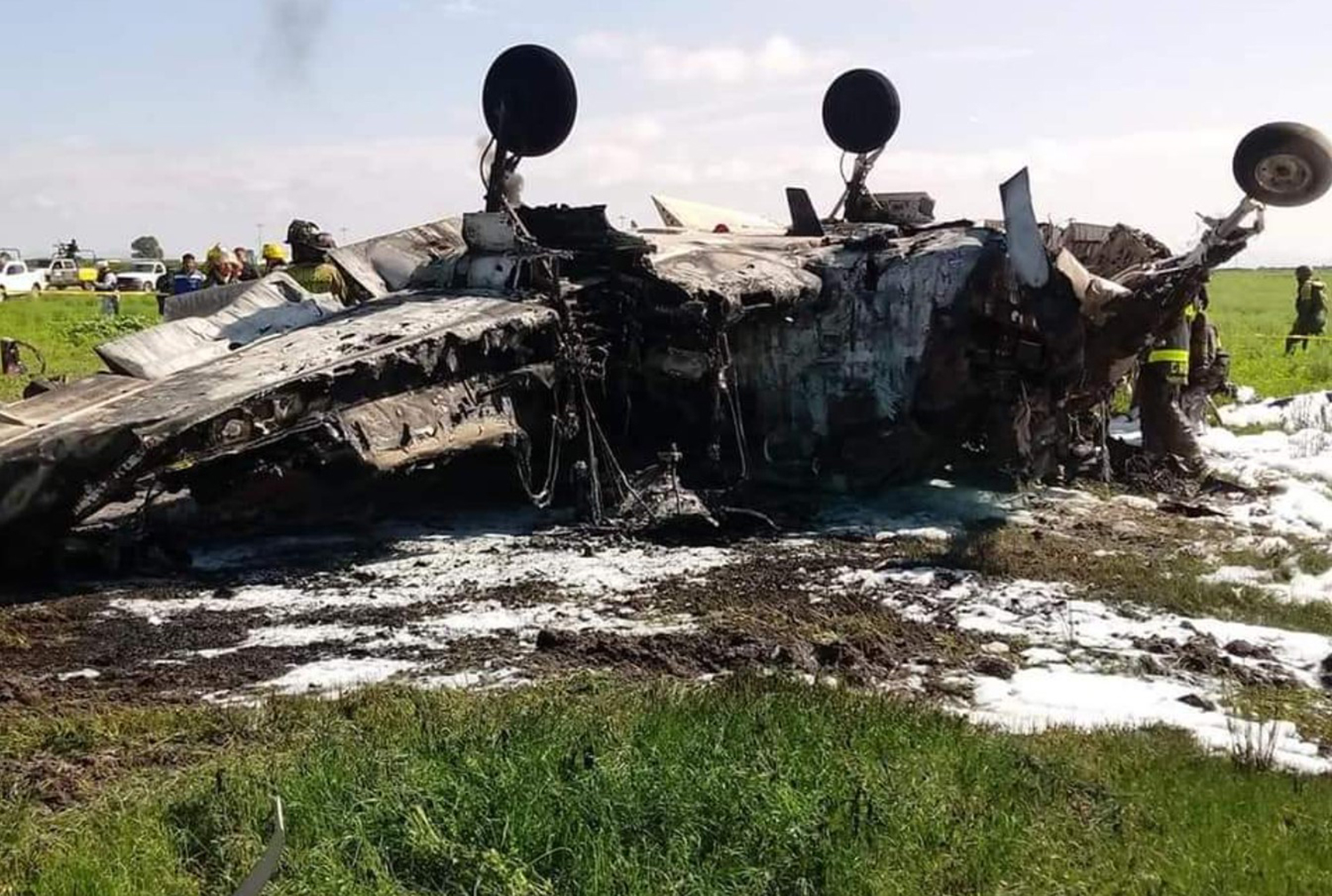
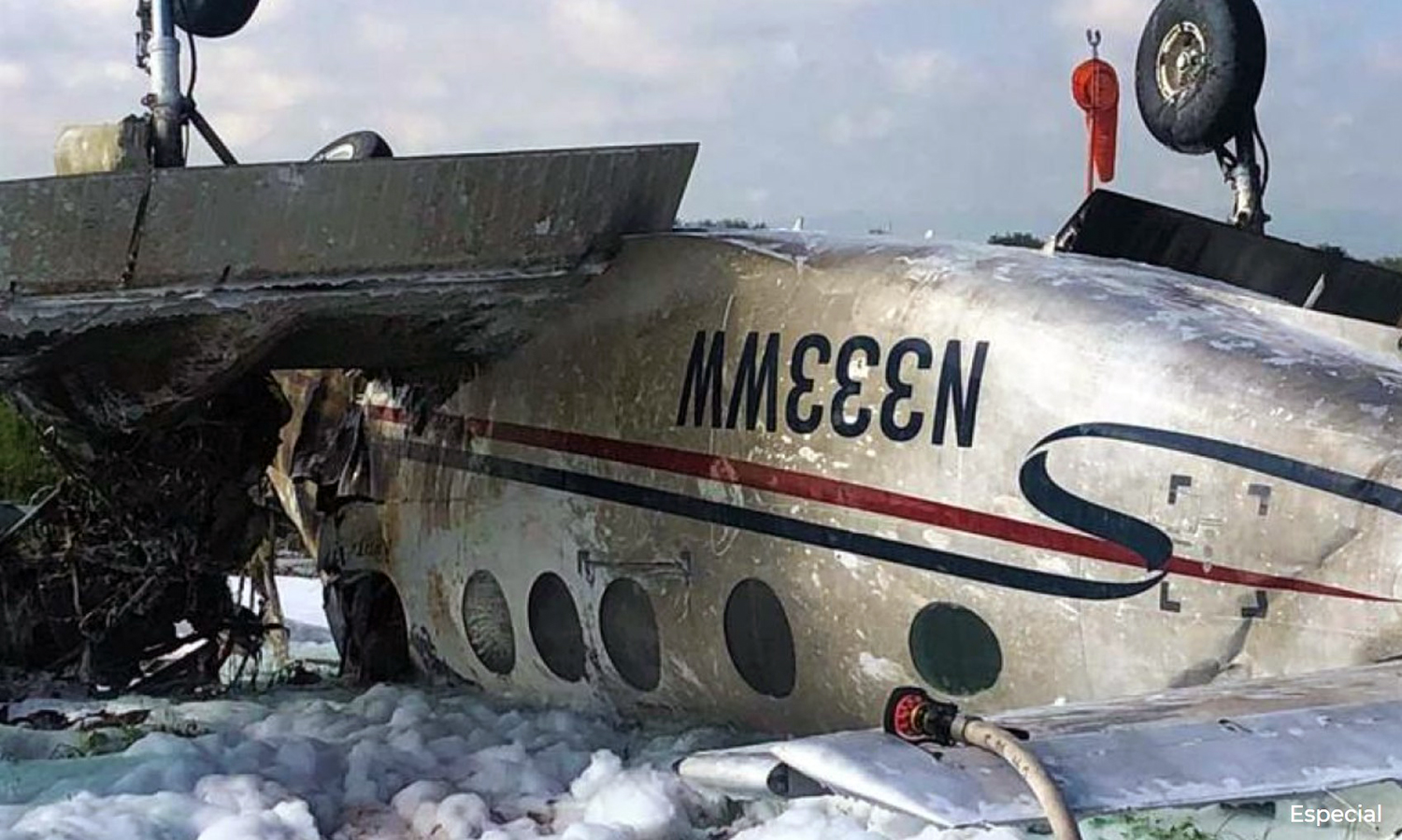
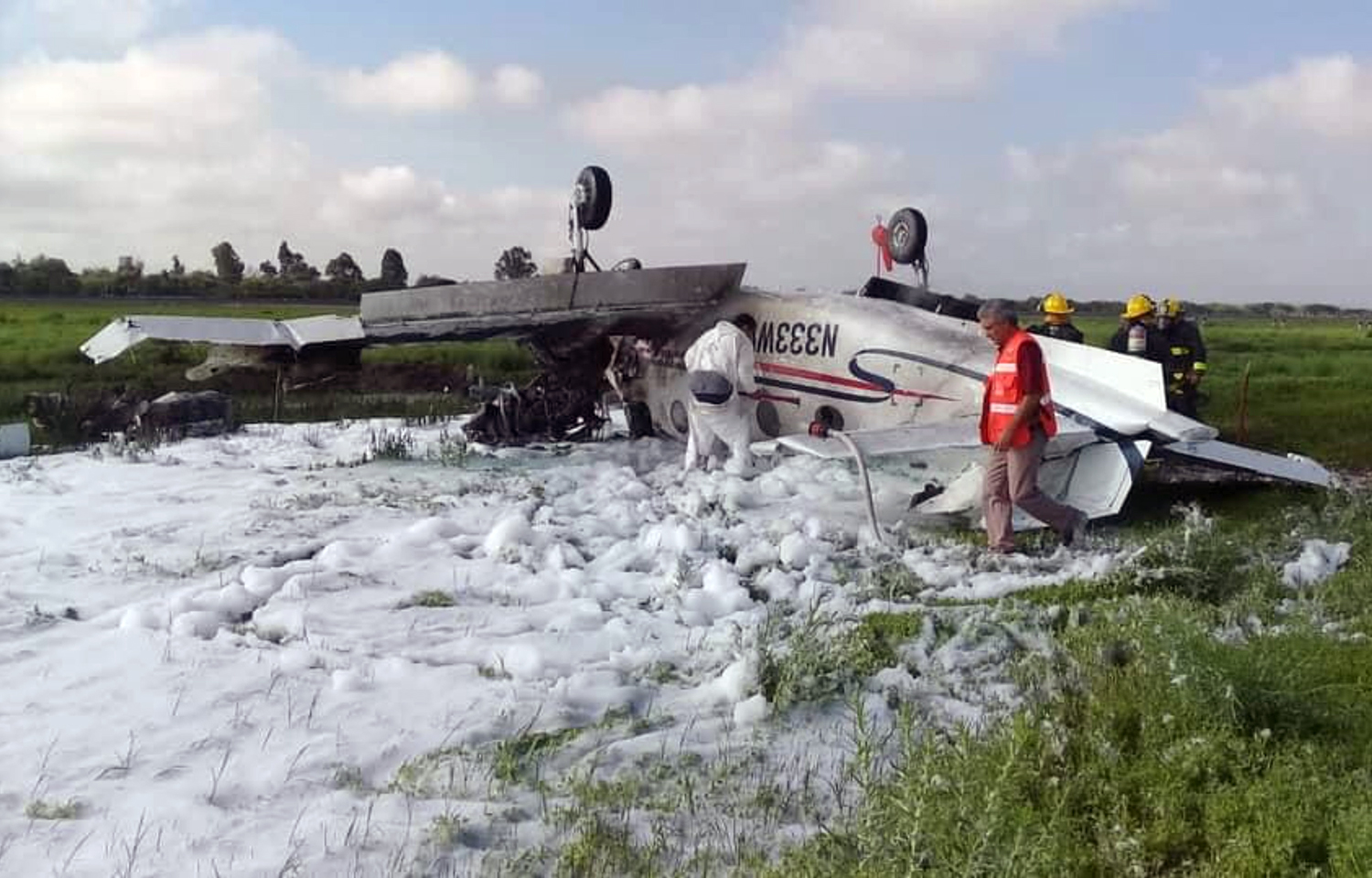
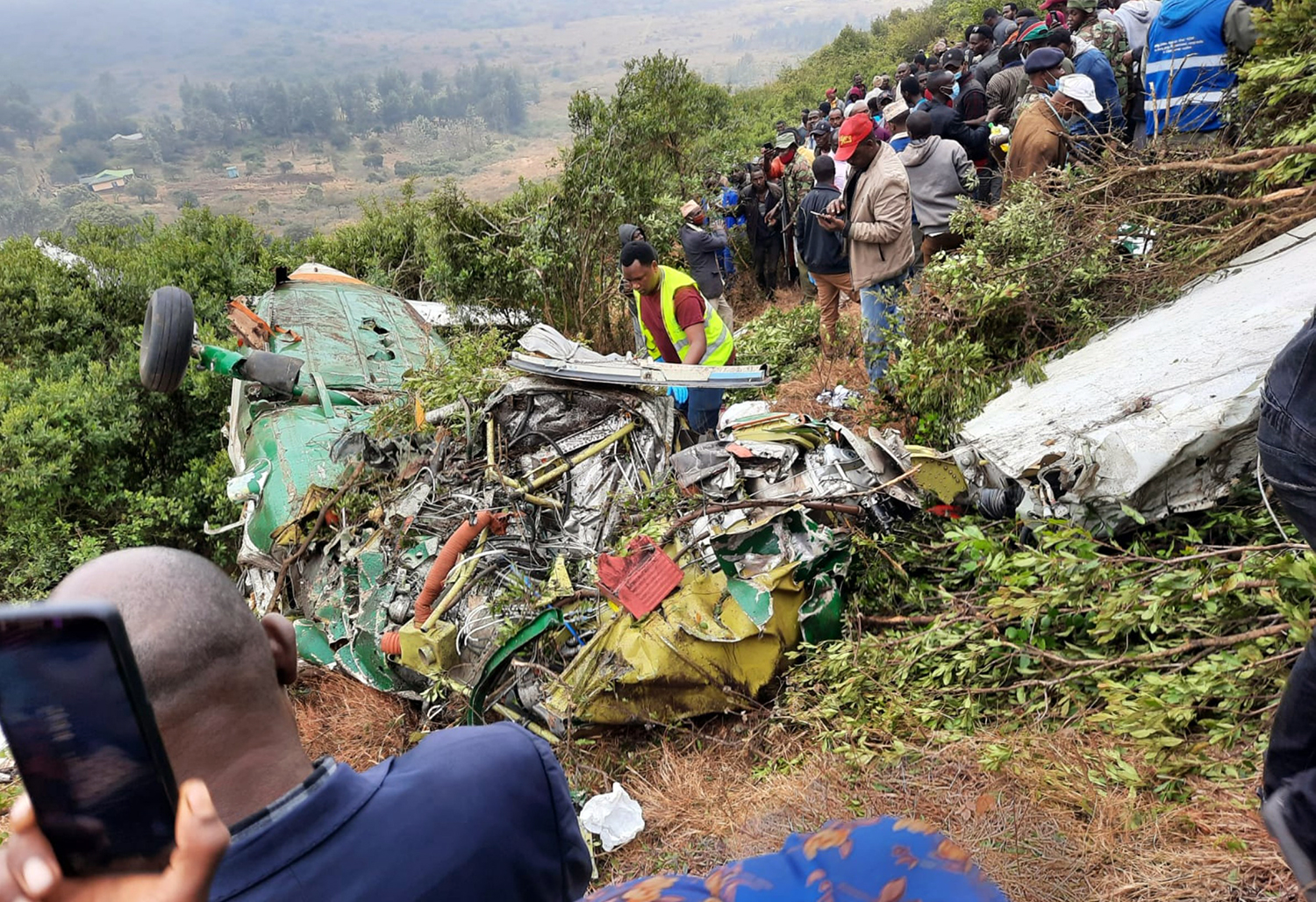
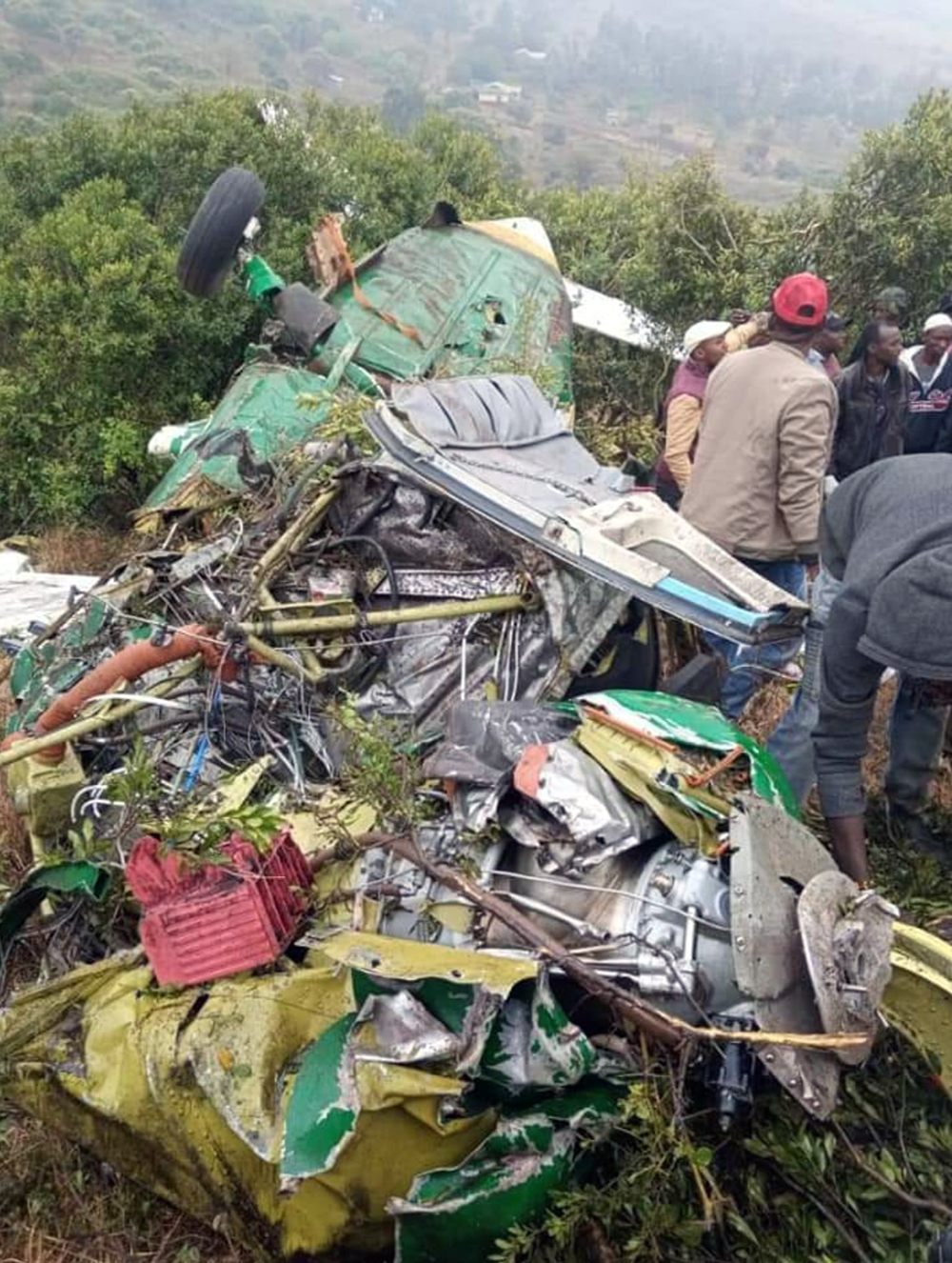
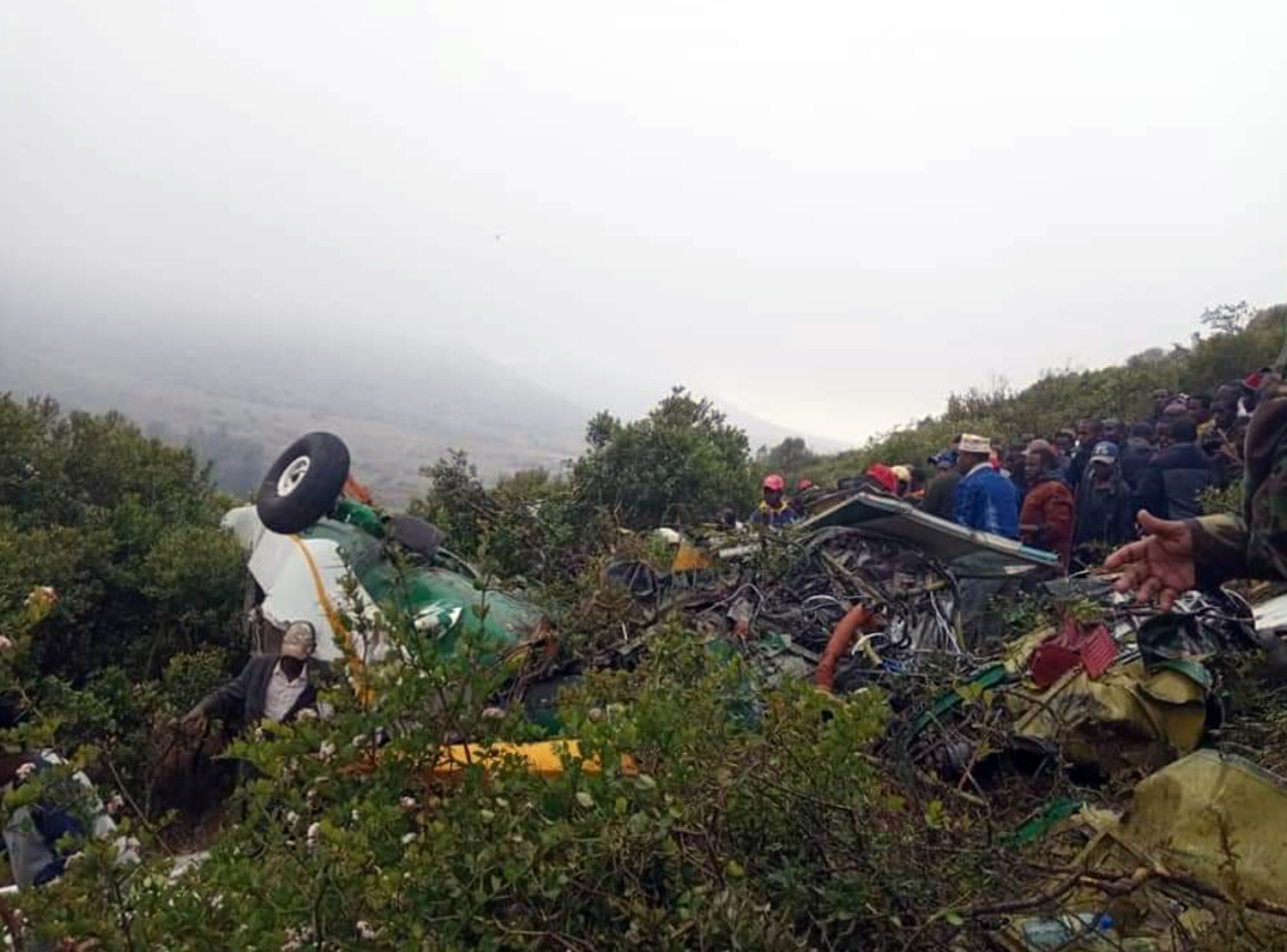
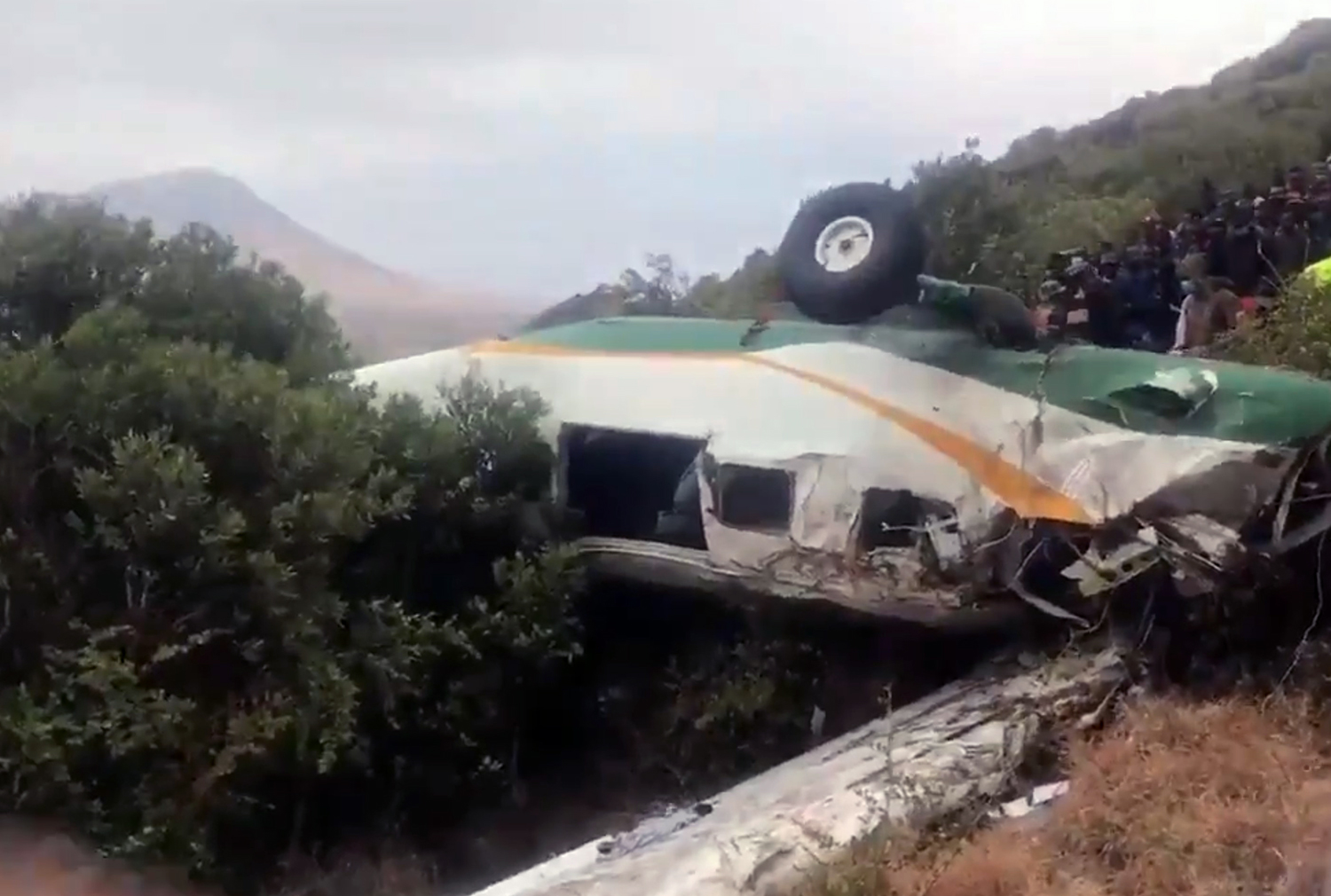
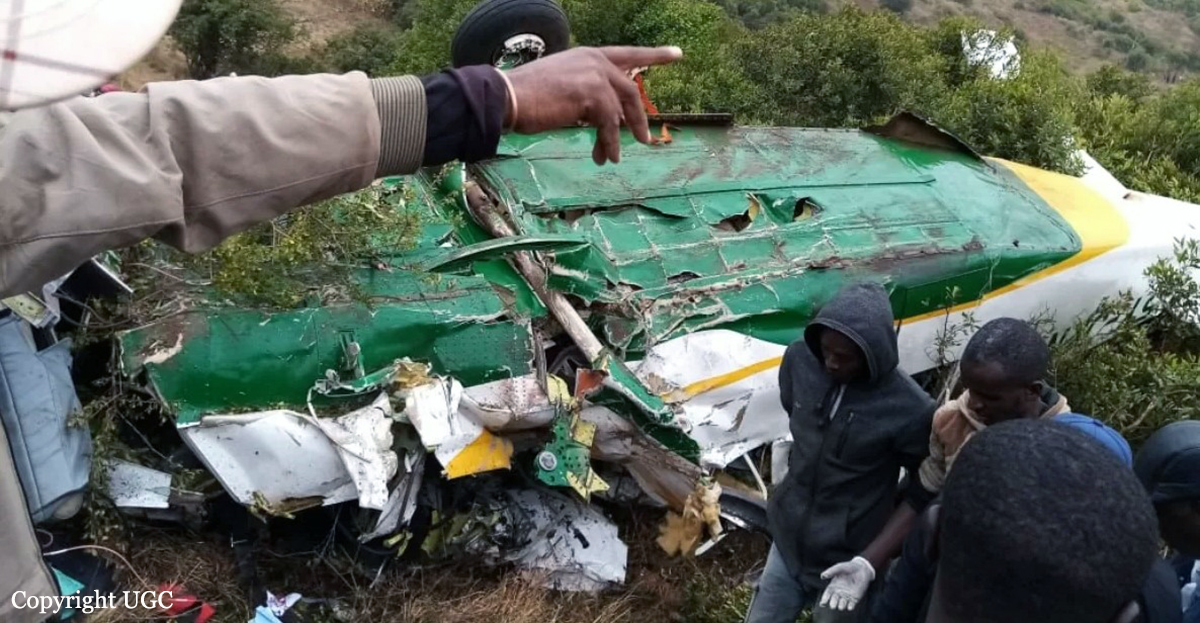
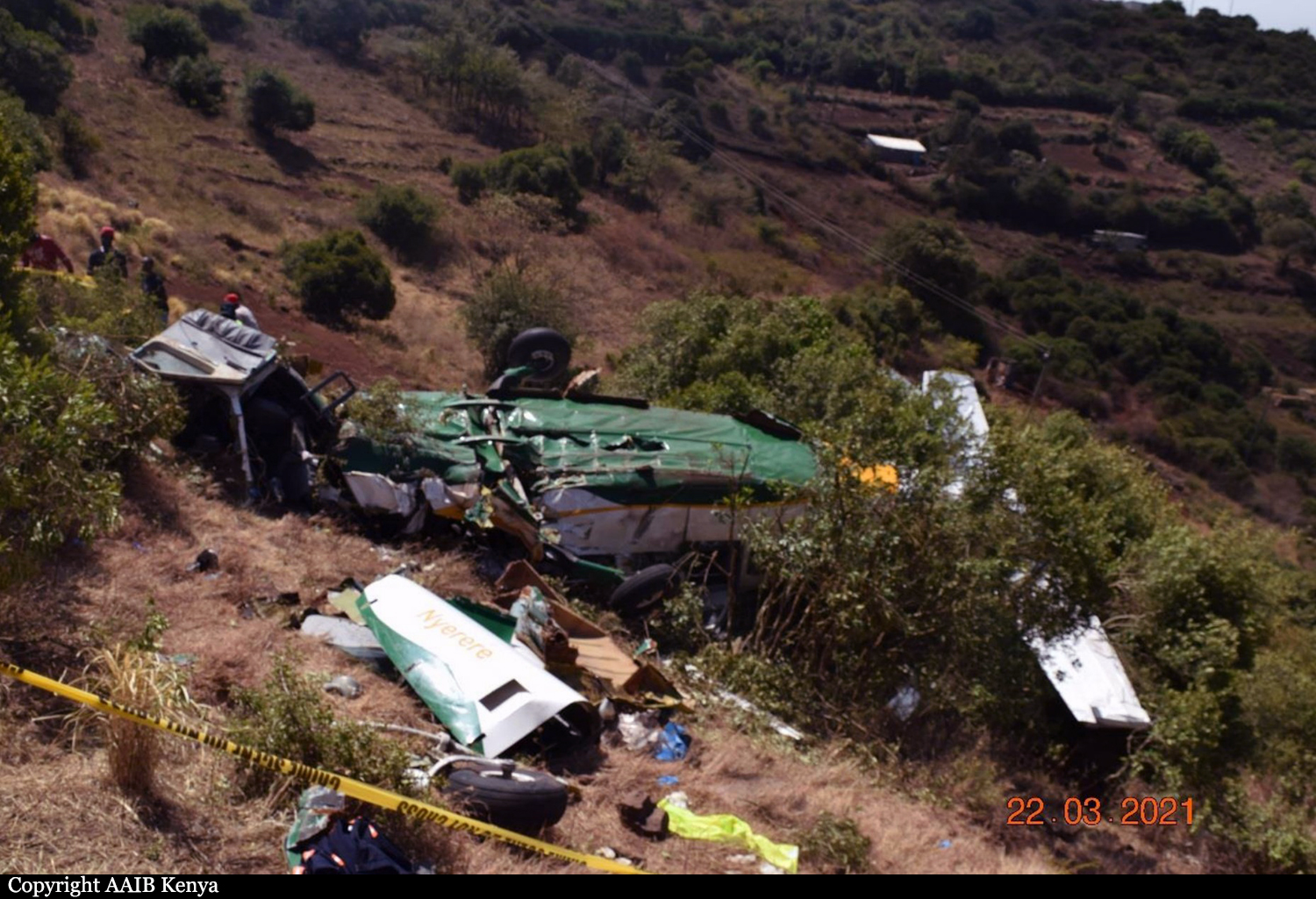
Circumstances:
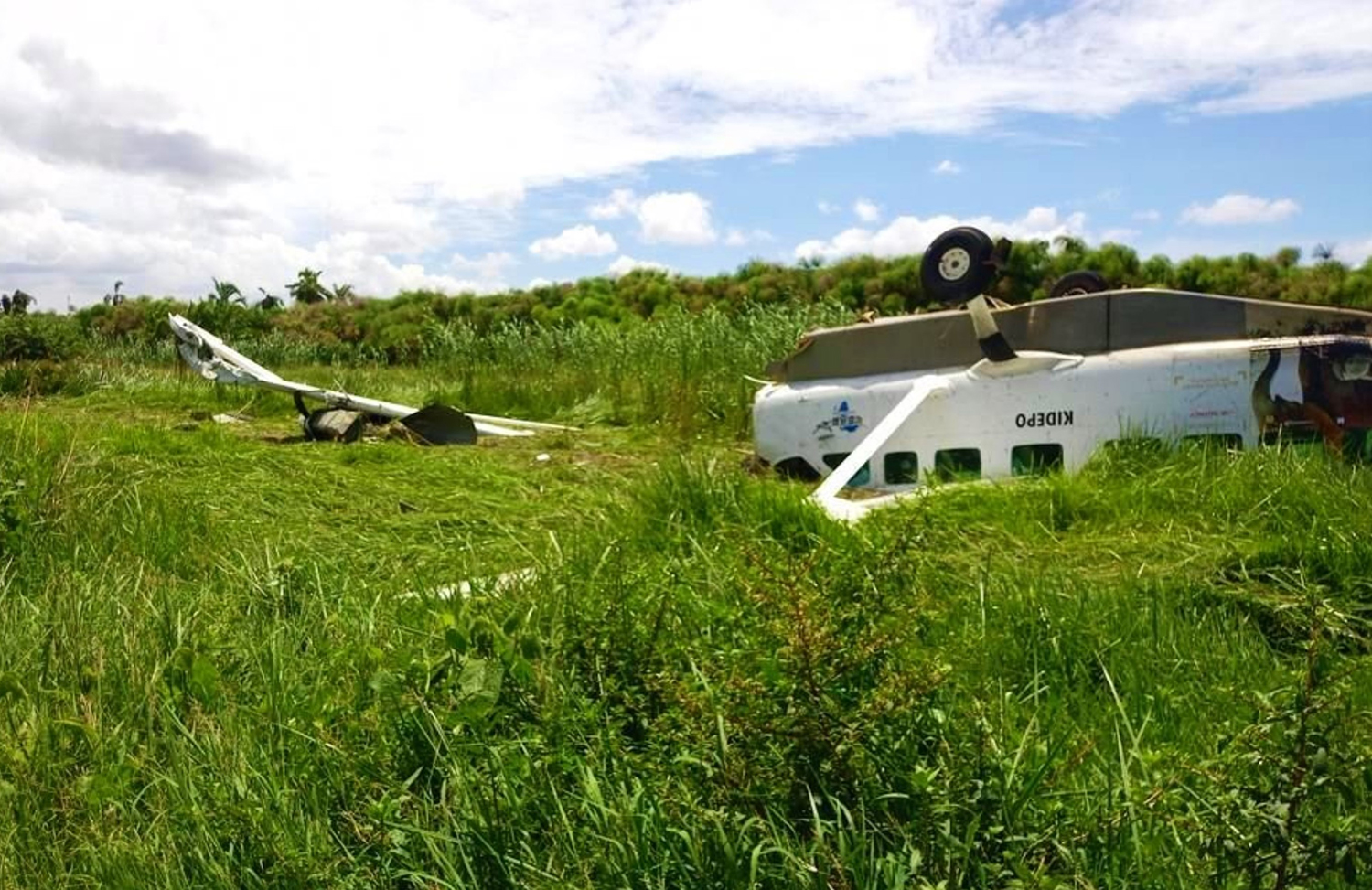
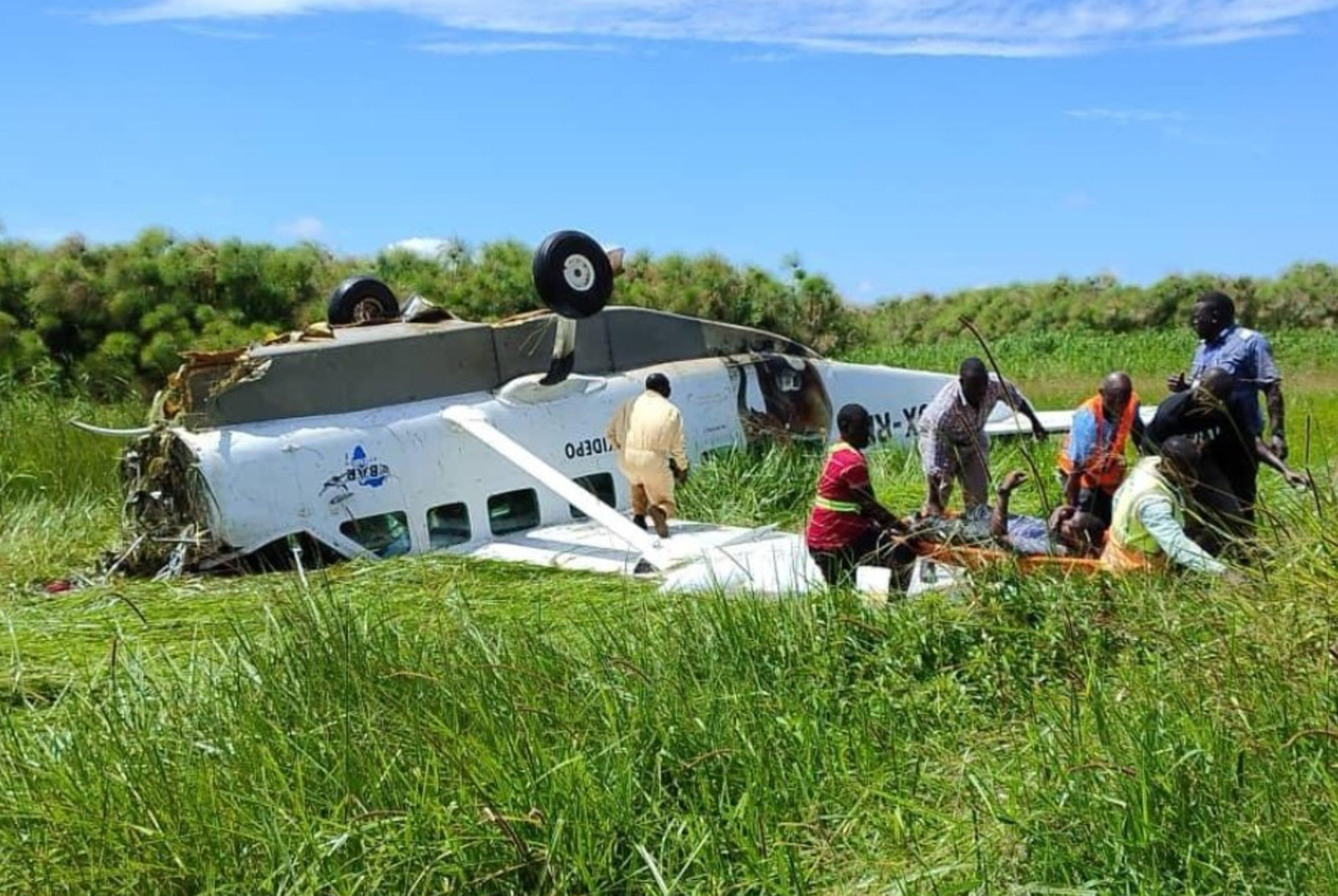
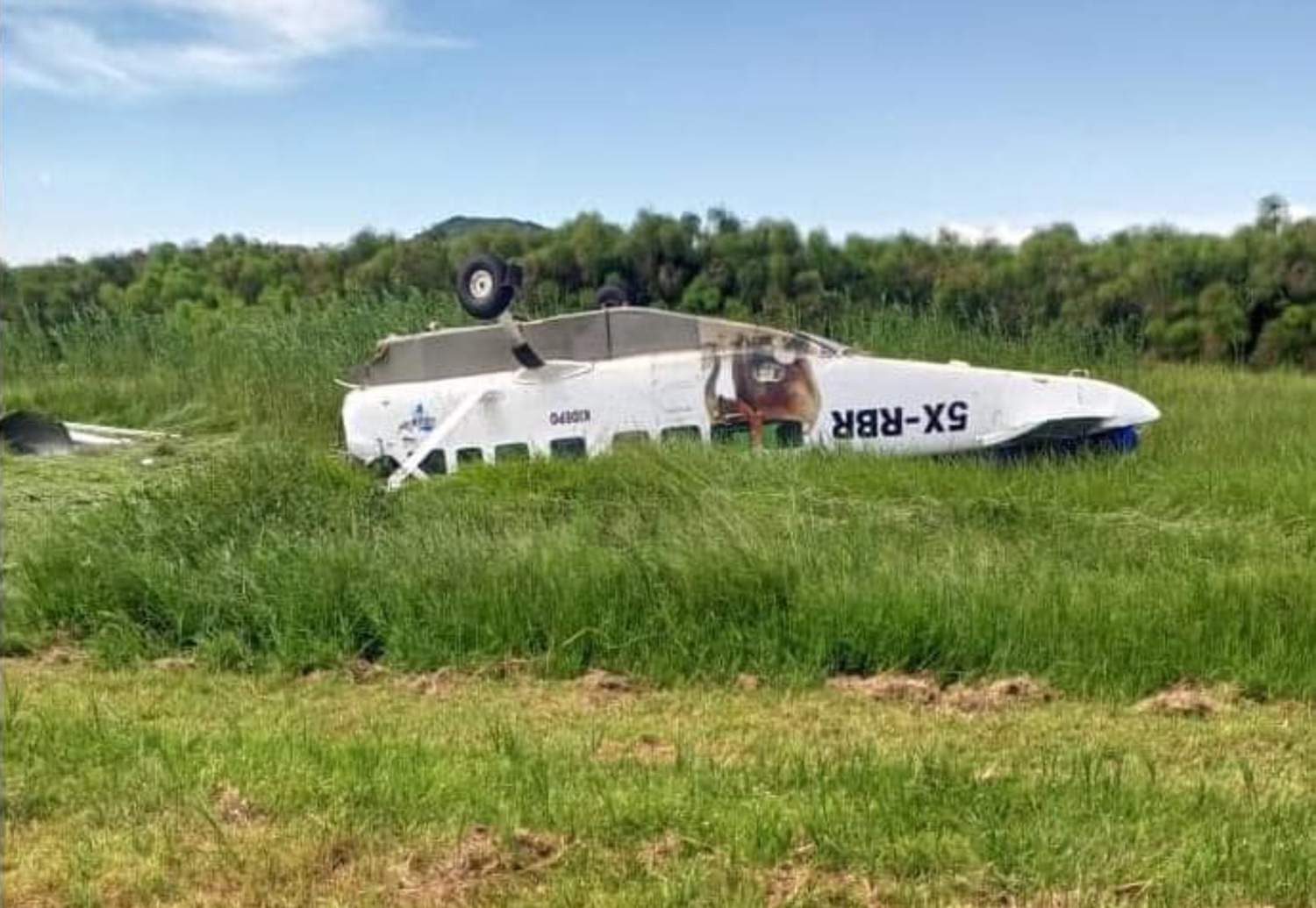
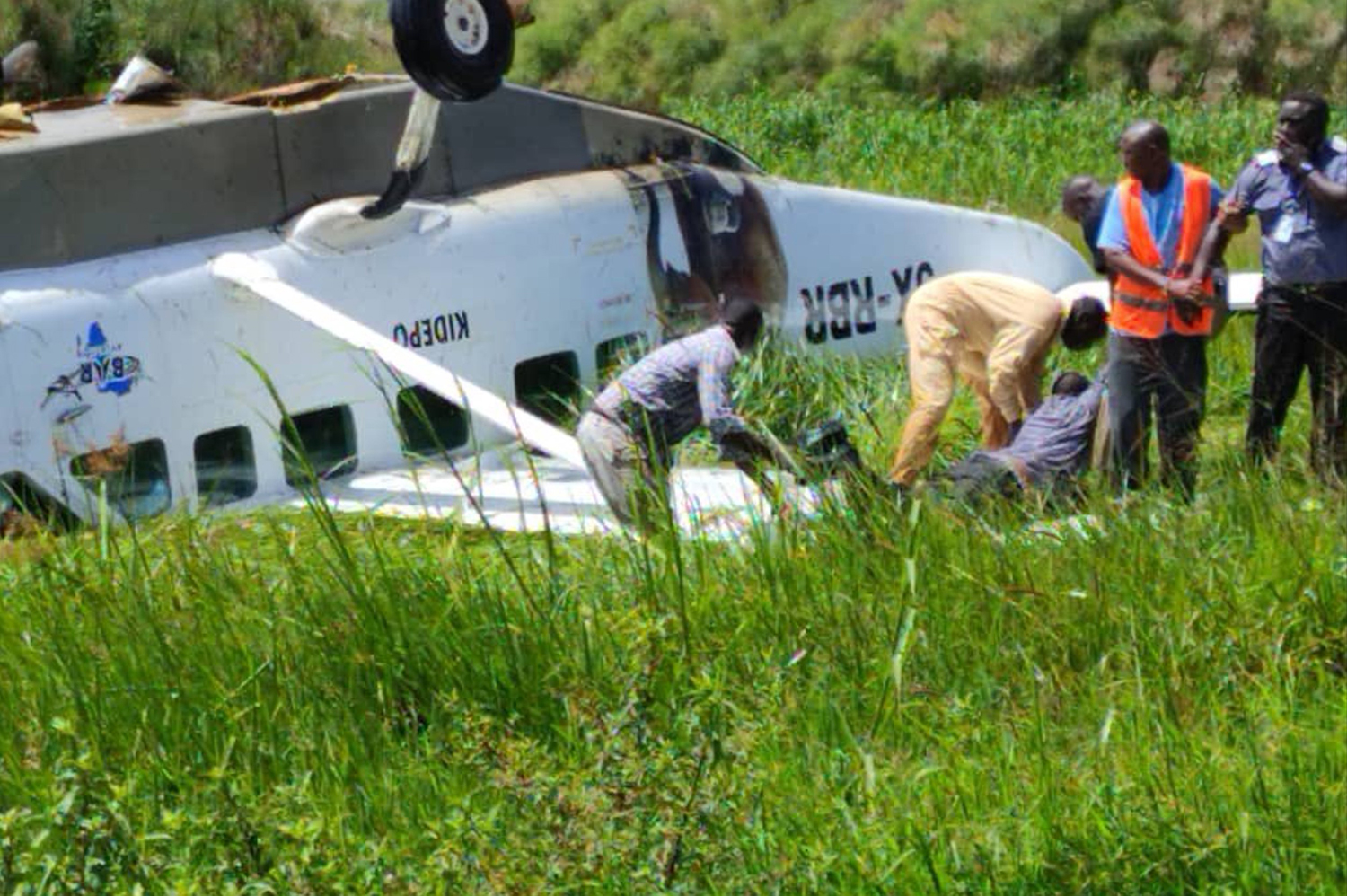
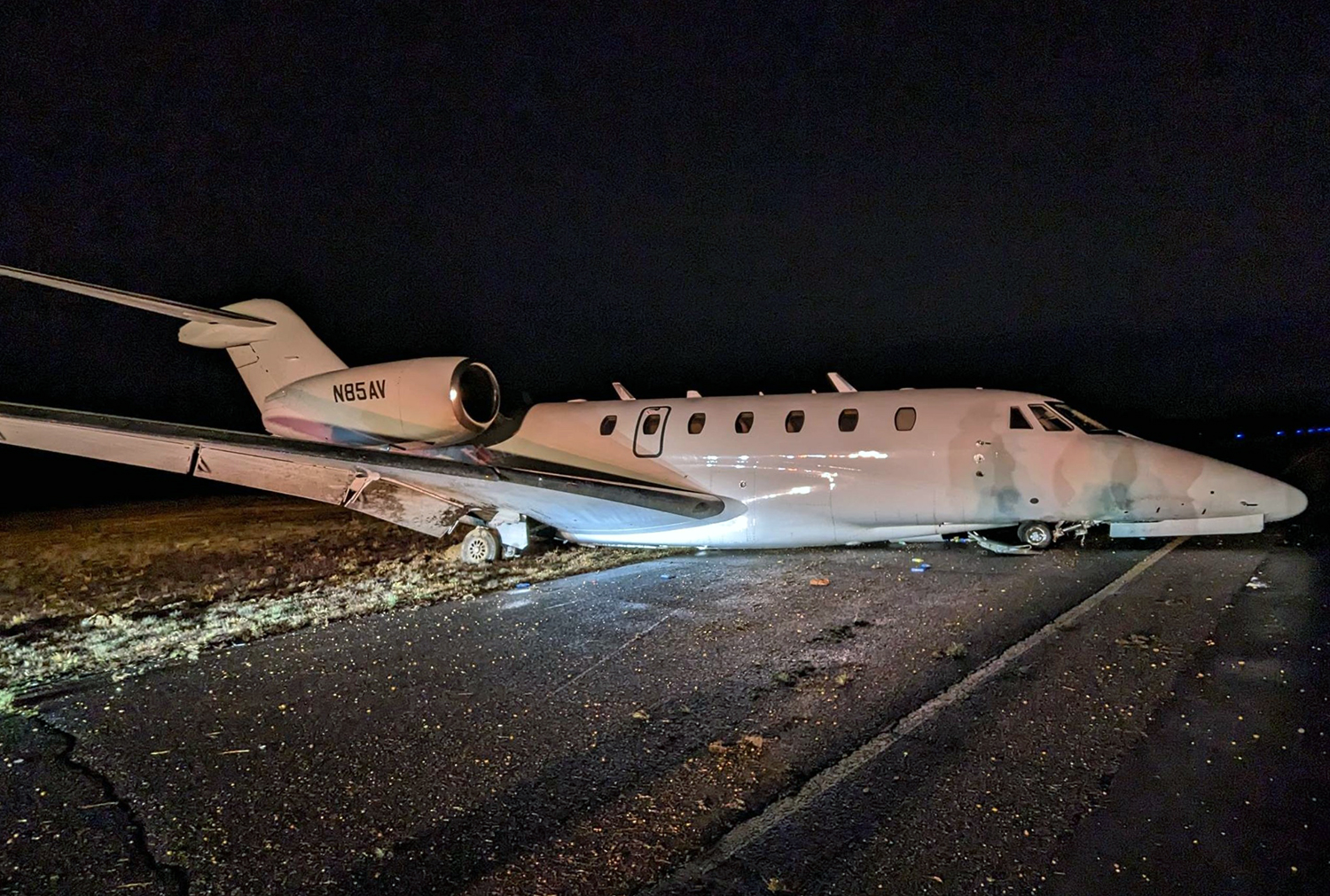
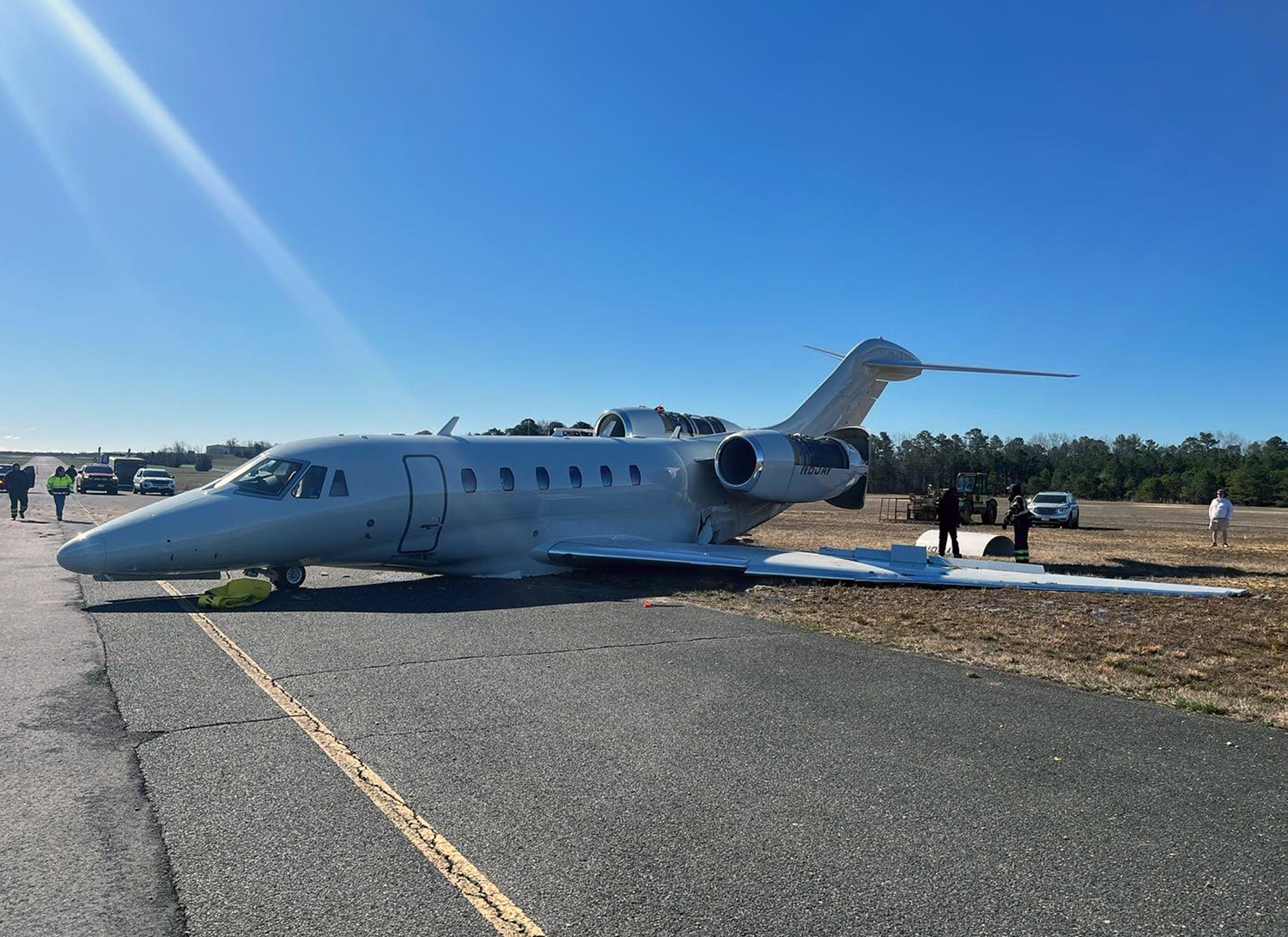
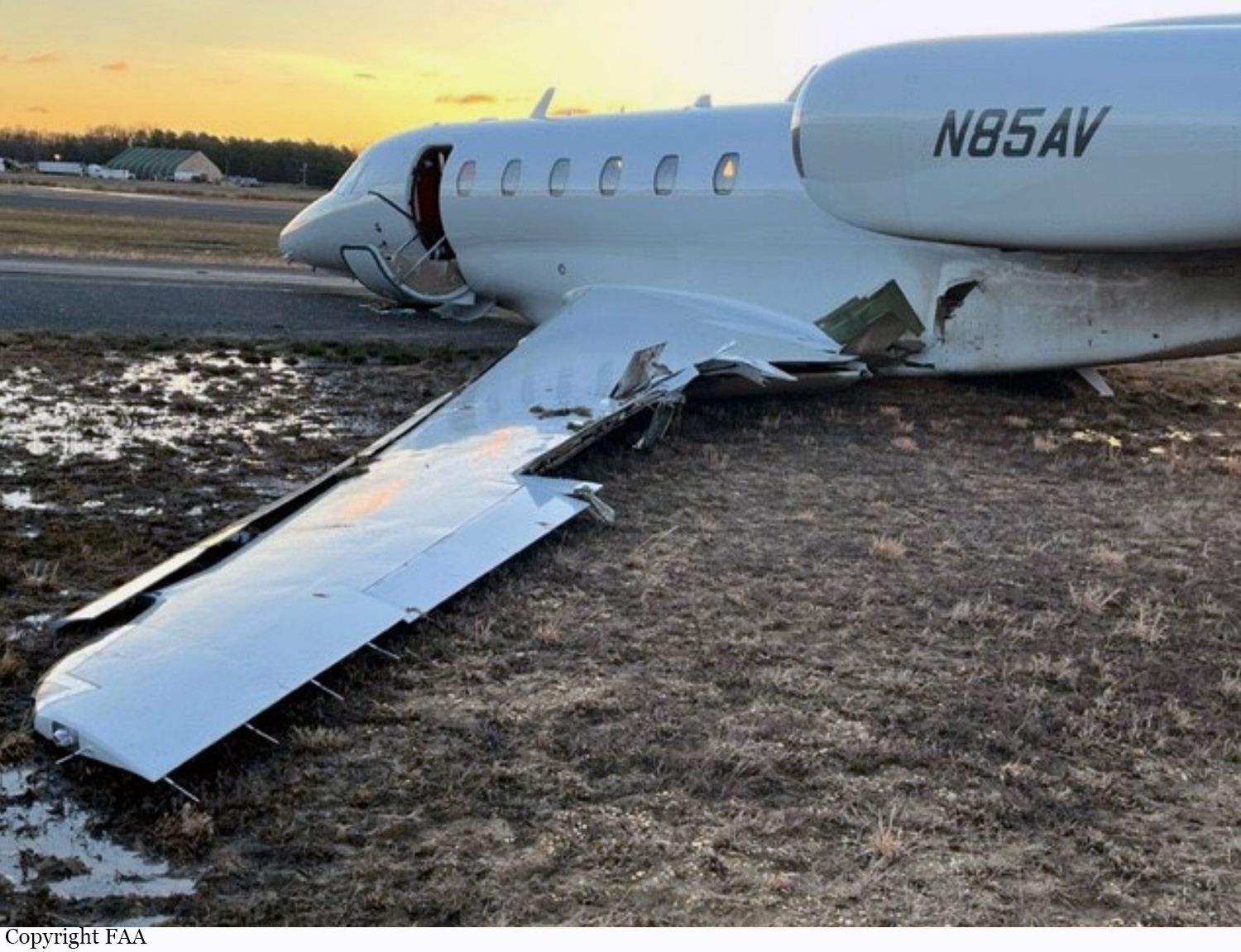
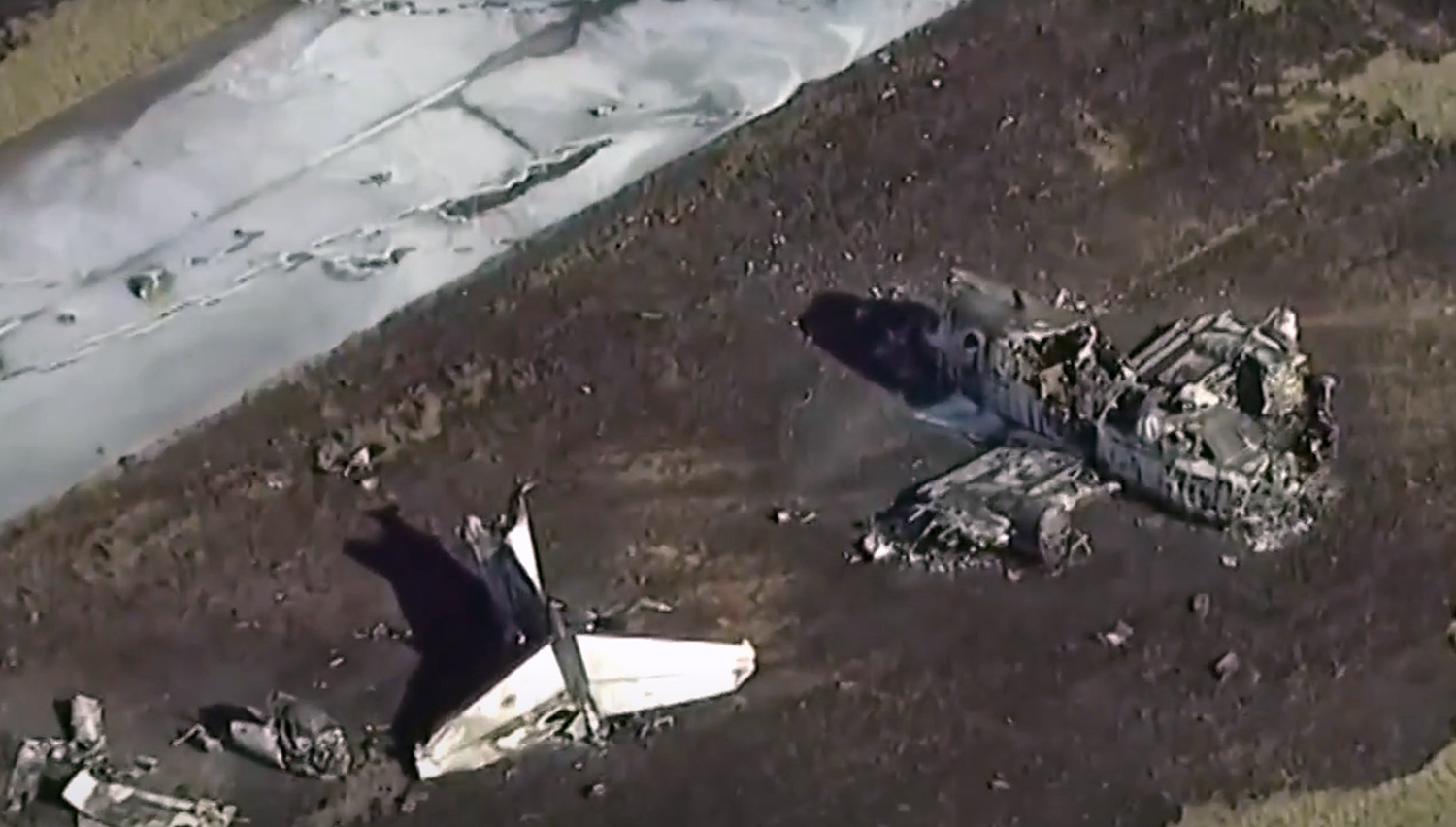
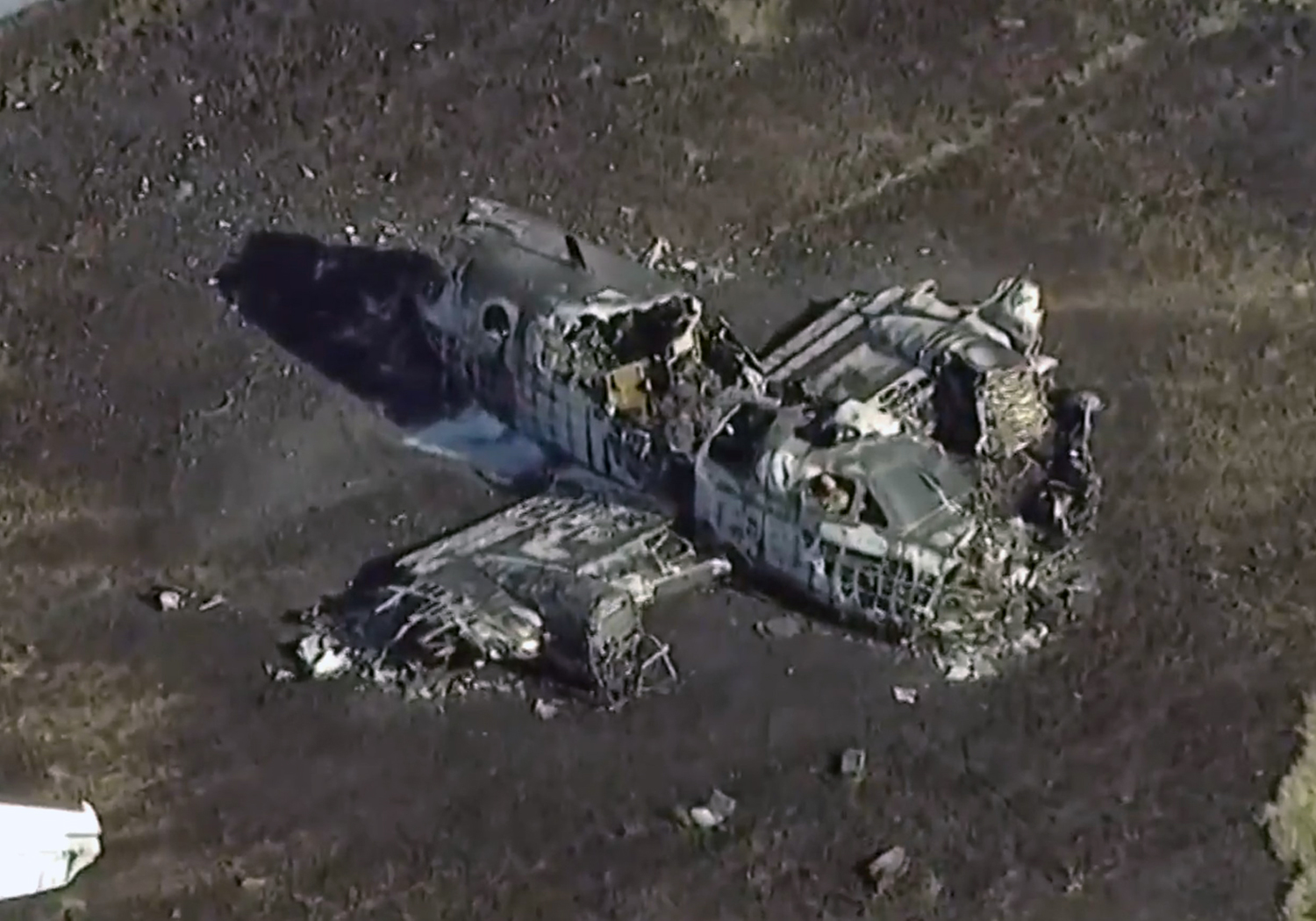
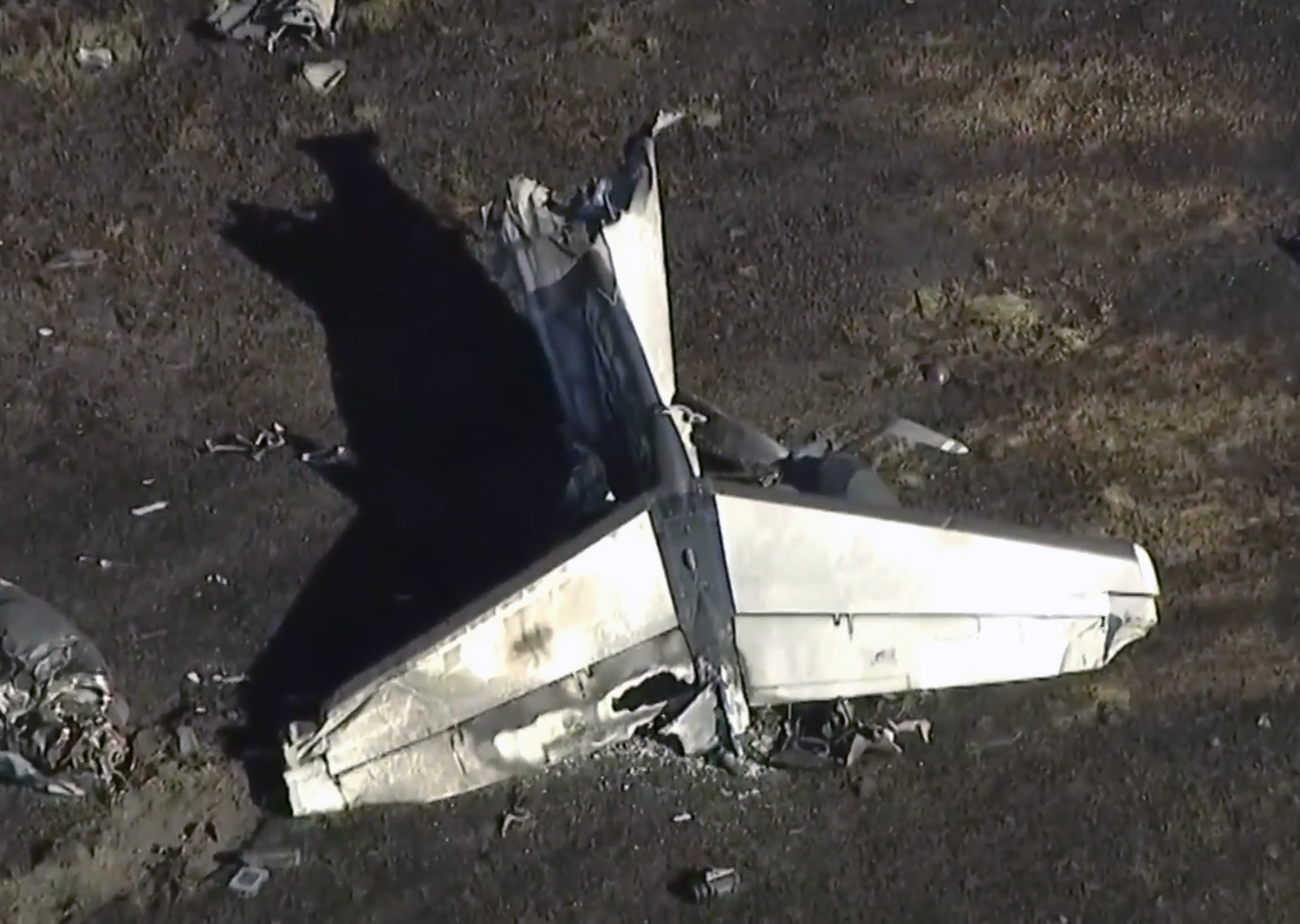
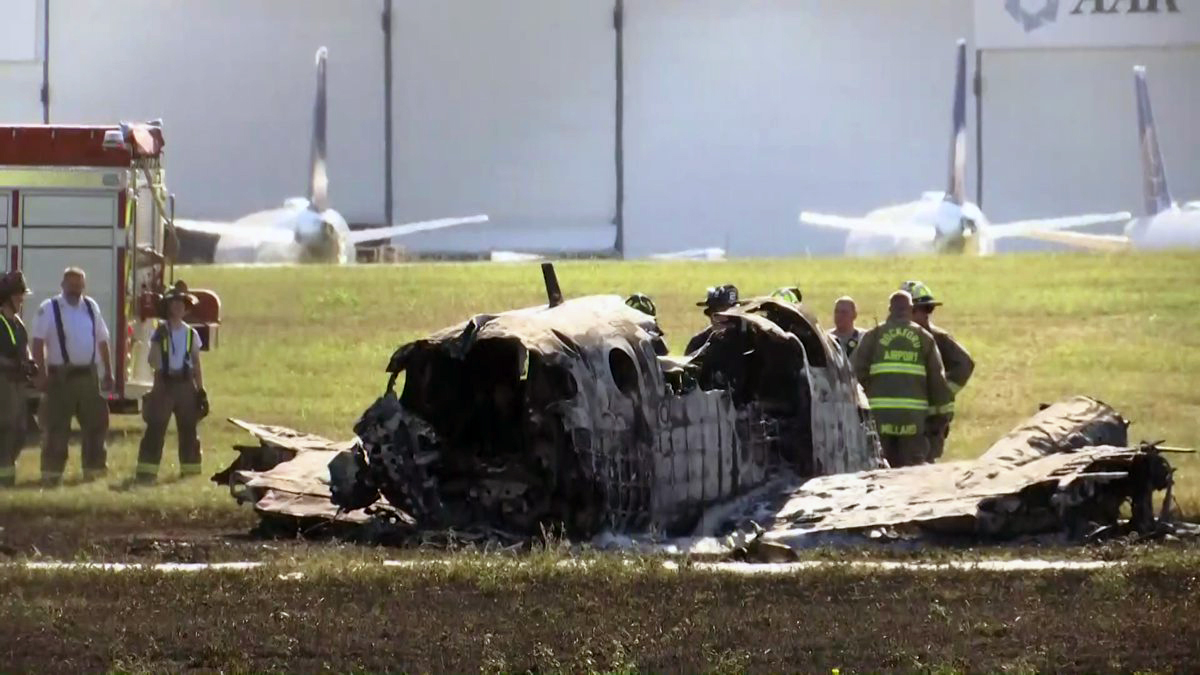
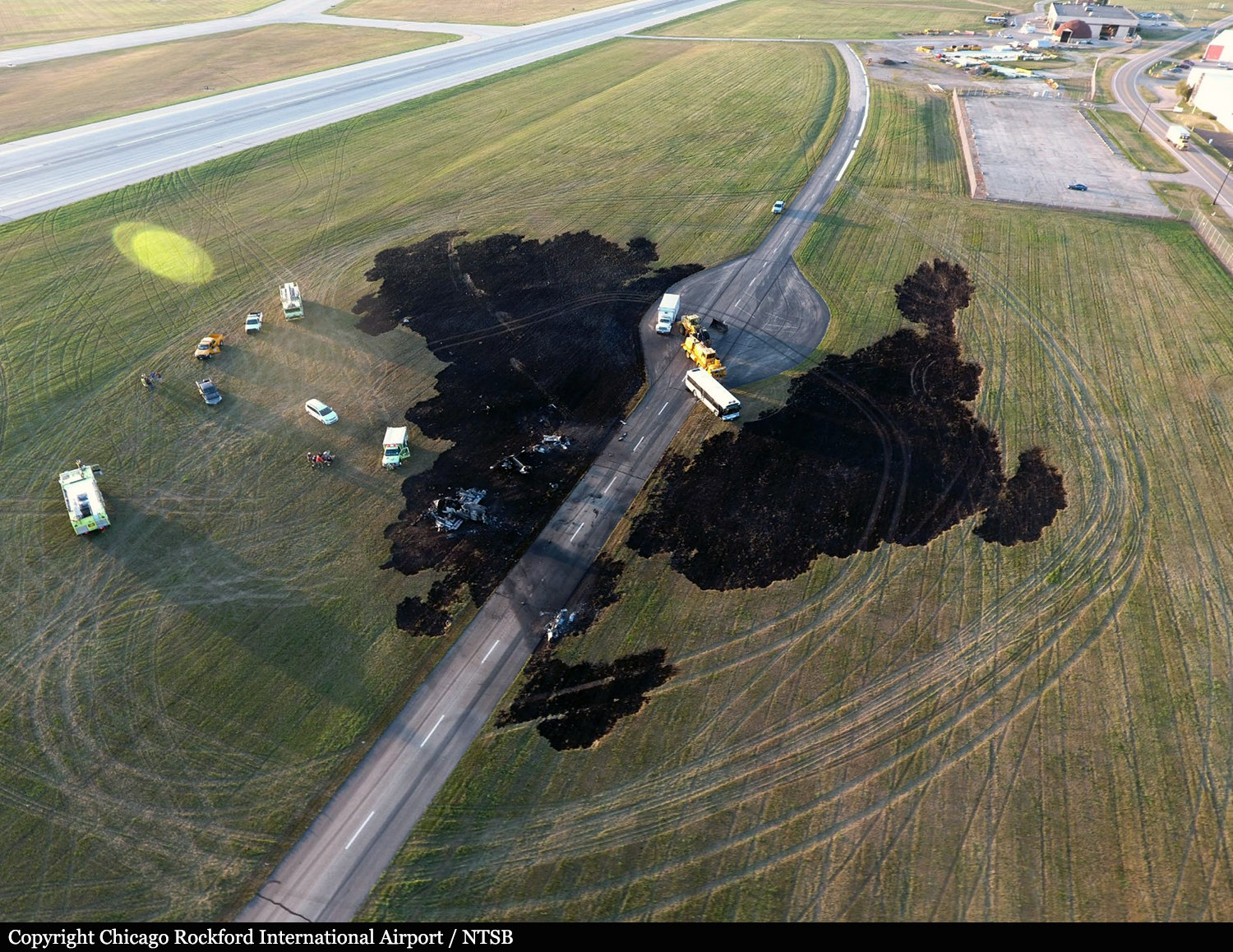
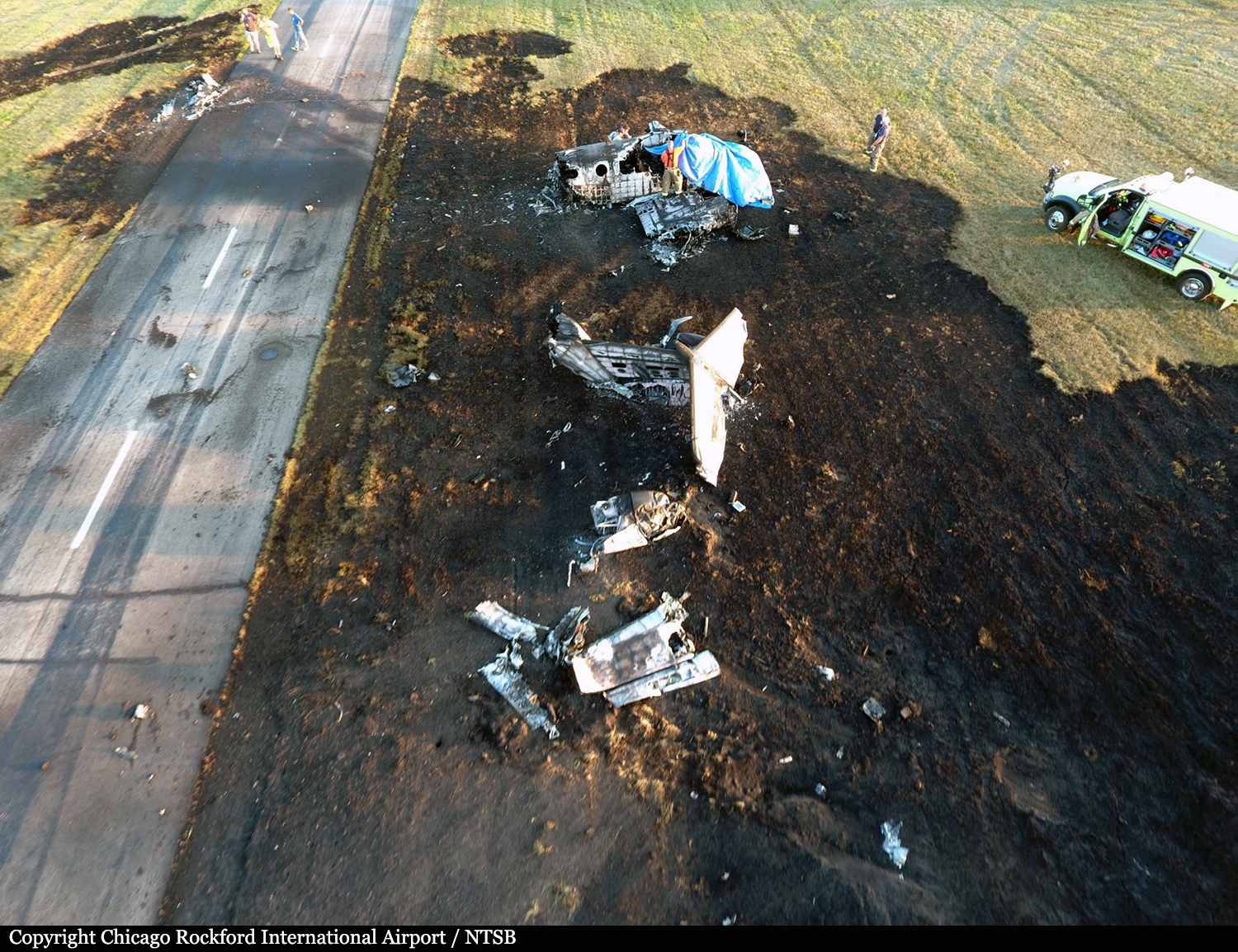
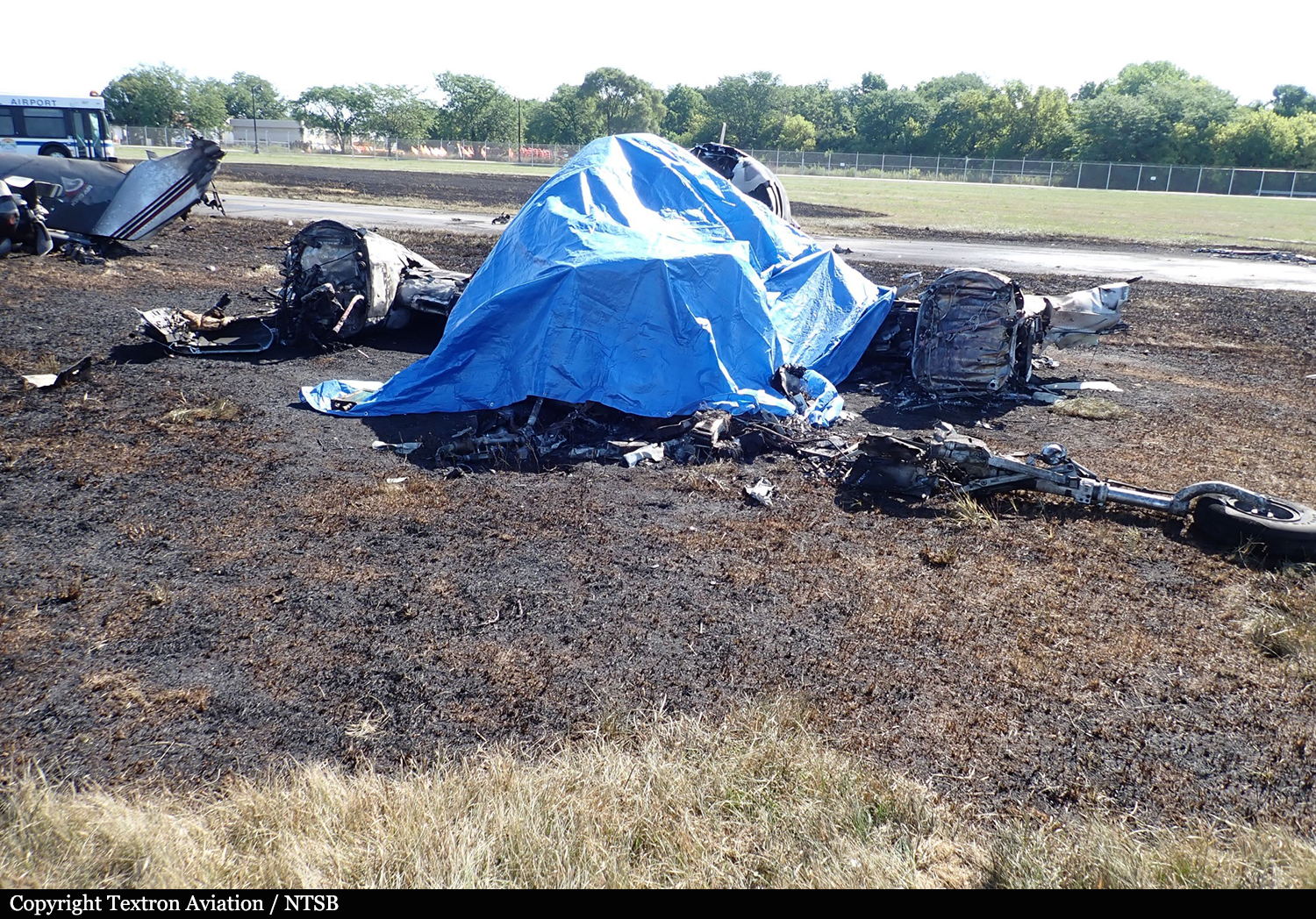
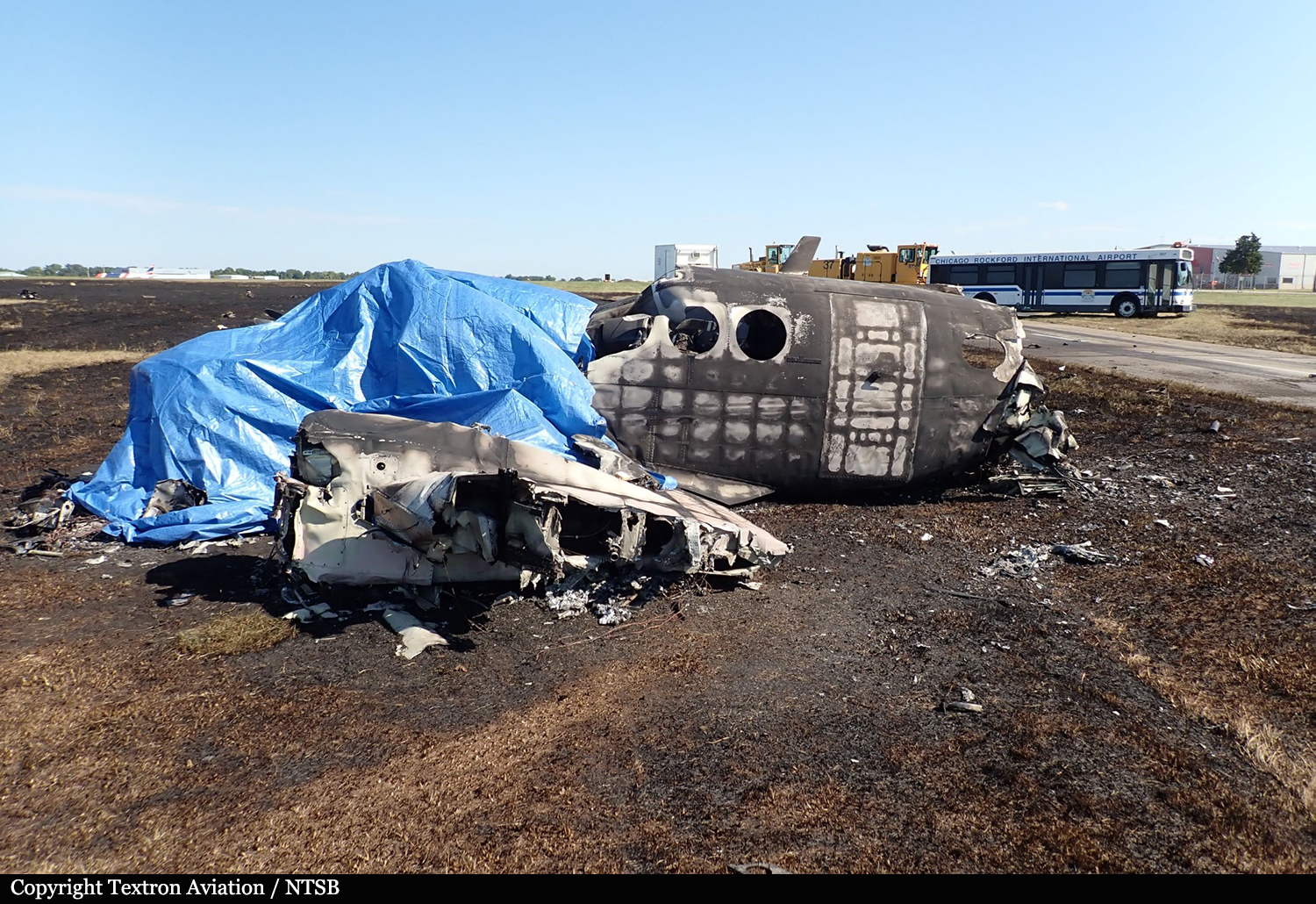
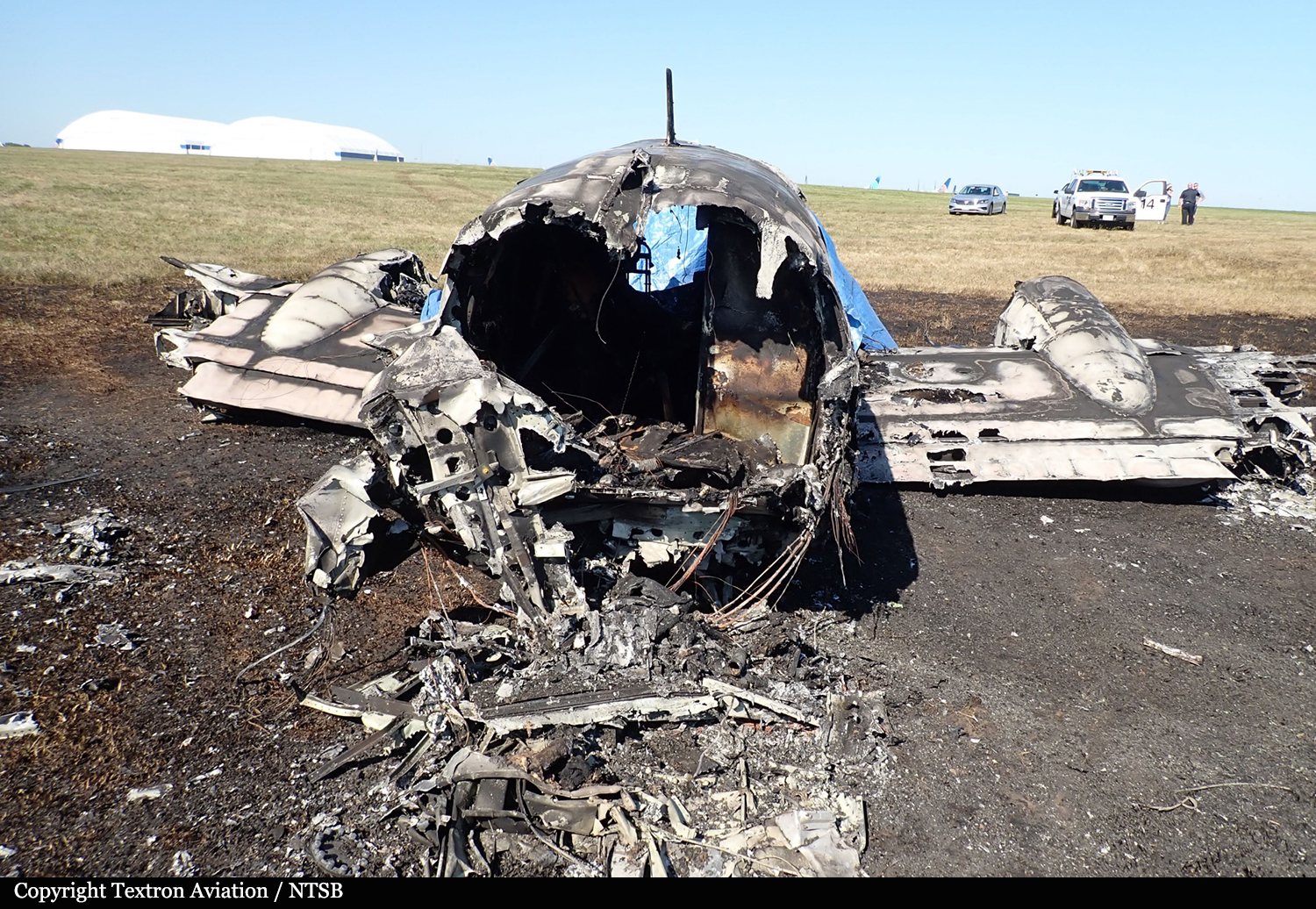
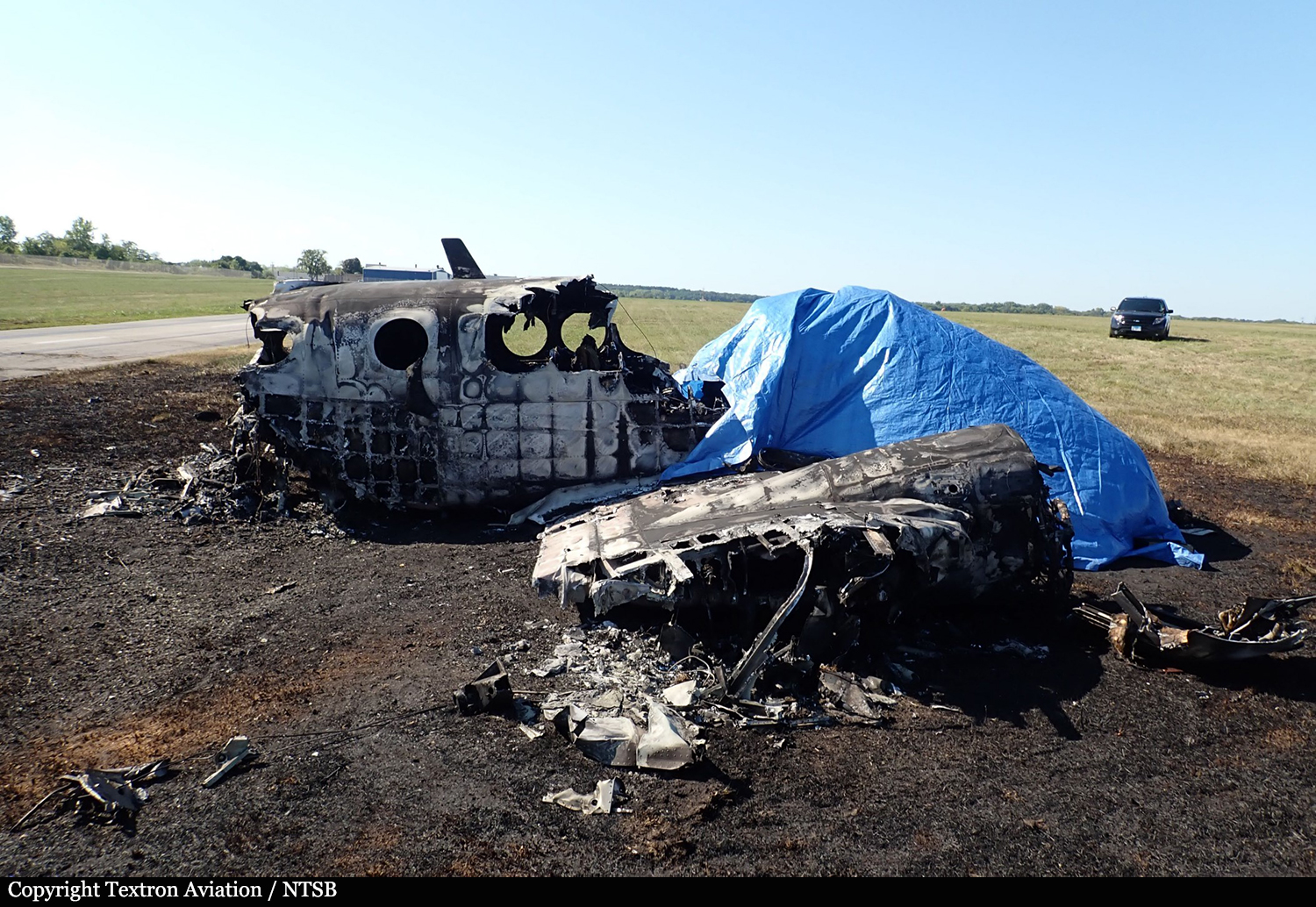
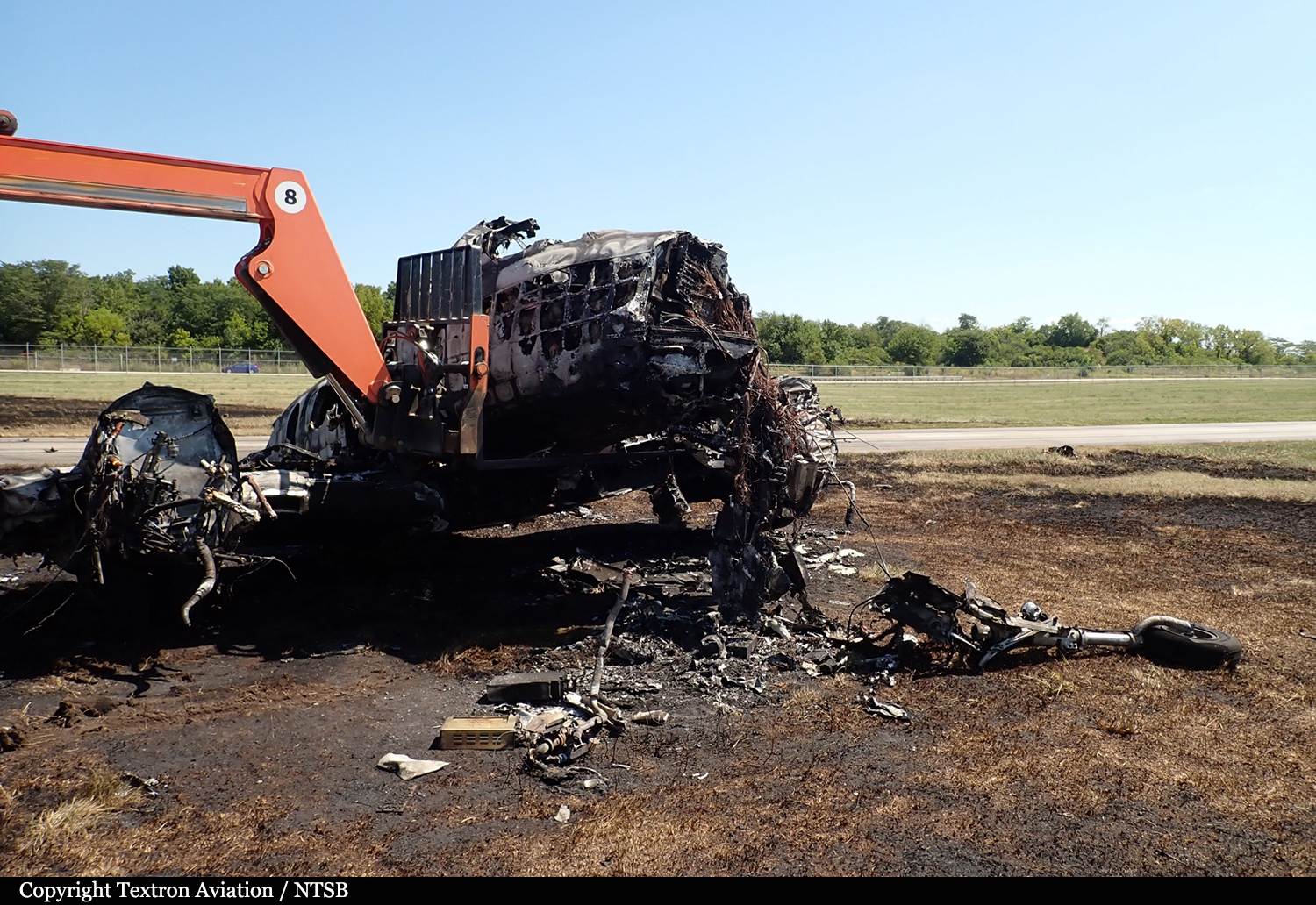
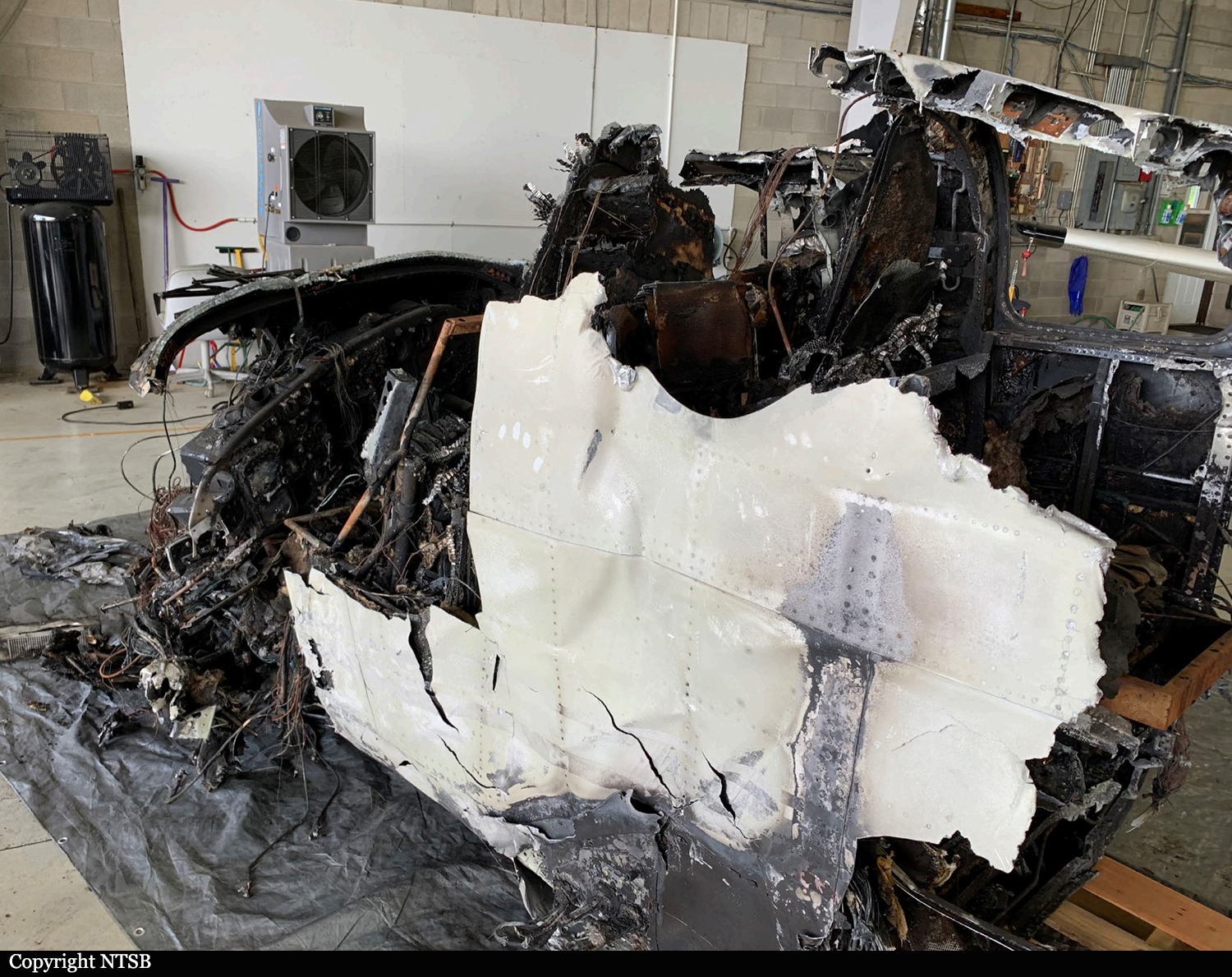
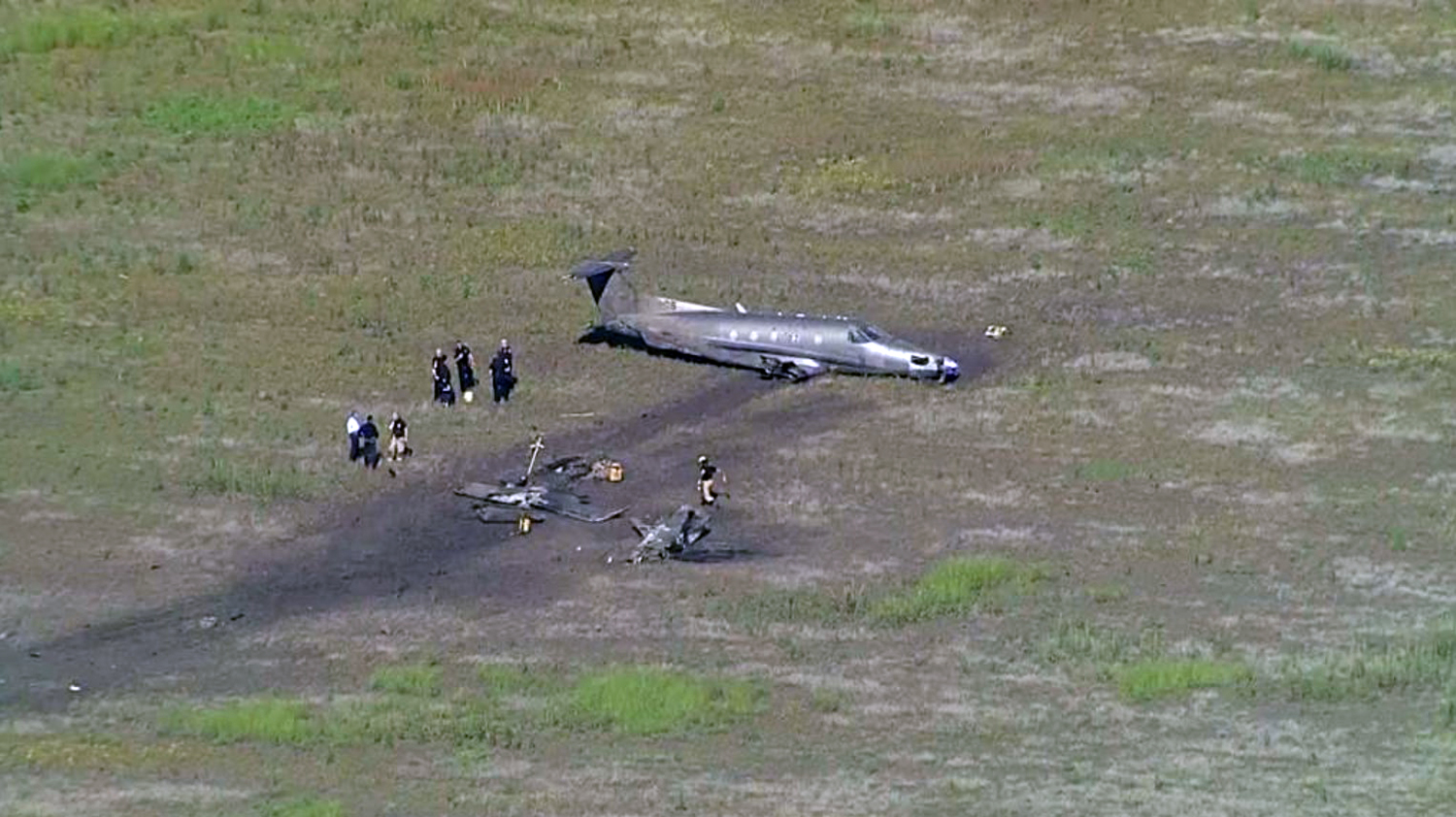
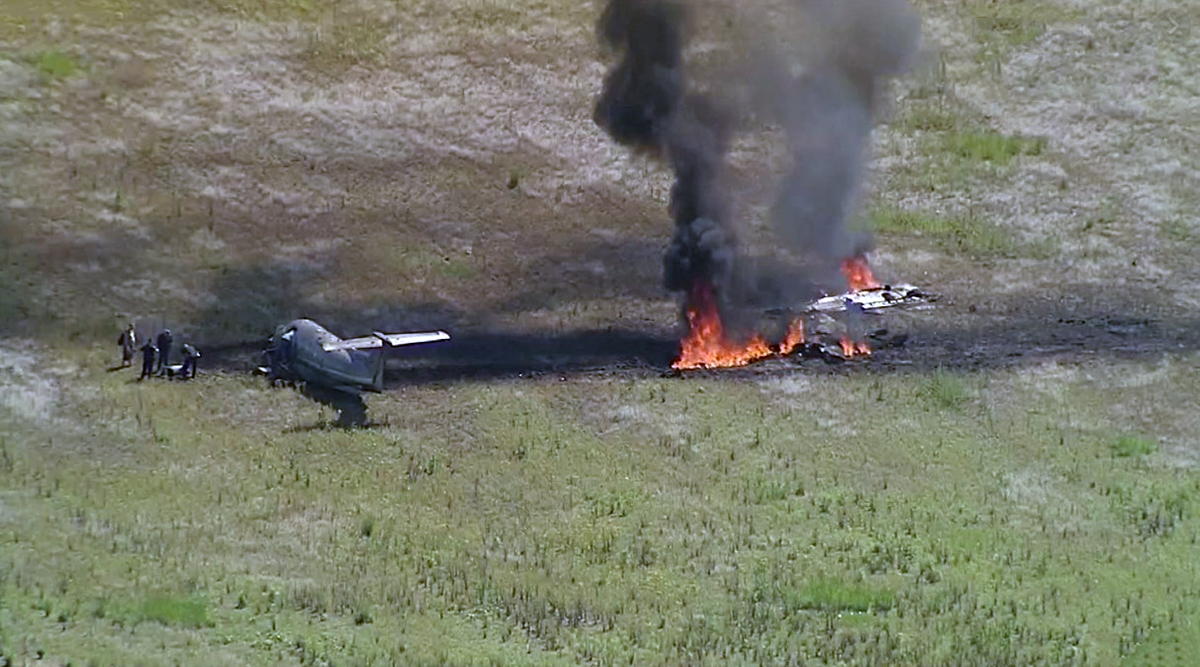
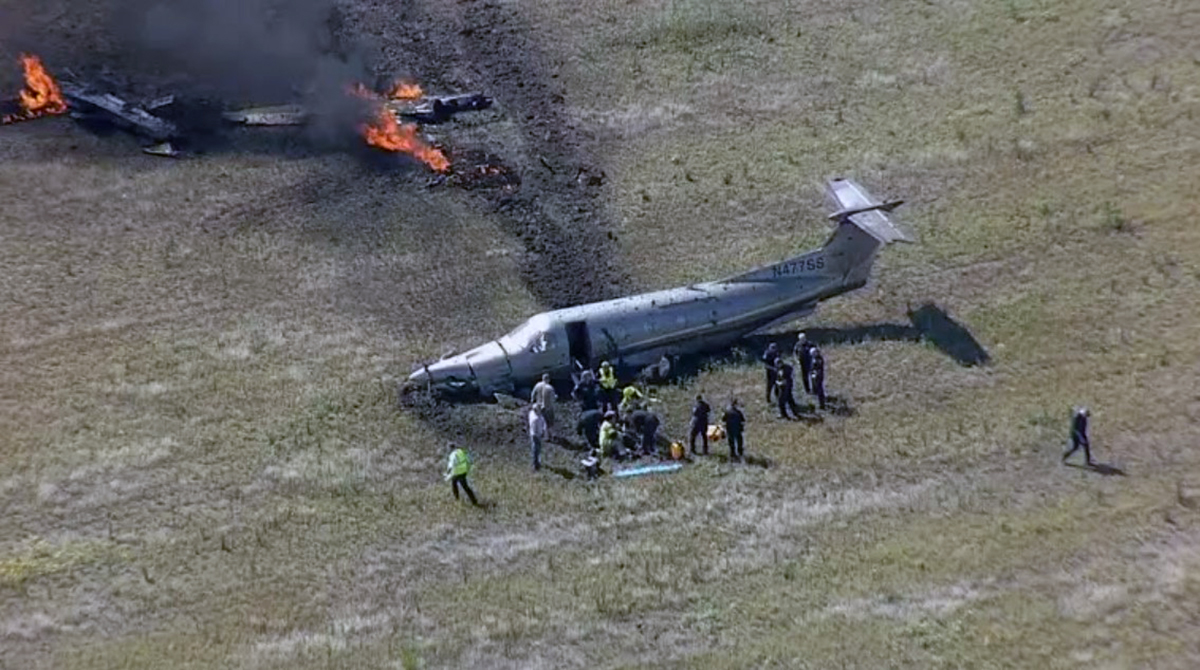
According to the flight crew, the airplane touched down within the touchdown zone. The pilot reported that he applied the brakes and deployed the thrust reversers (TRs), but the brakes “were not grabbing.” The pilot released and reapplied brake pressure with no effect and advised the co-pilot he had no brakes. The co-pilot applied his brakes with no effect. The pilot selected the emergency brake handle and applied emergency braking. The emergency braking produced some slowing, and with the airplane’s nose wheel tiller, the pilot attempted a left turn to exit the runway onto a 45° taxiway, which he thought provided additional stopping distance; however, the airplane slid off the taxiway and into the adjacent grass. The right main landing gear collapsed, and the air plane came to rest upright, resulting in substantial damage to the right wing spar. Examination and testing of the airplane systems did not reveal any evidence of preimpact mechanical malfunctions with the wheel brakes or any other systems. Video evidence and recorded airplane data revealed the TRs were not deployed during the landing sequence. The cockpit voice recorder was overwritten during postaccident maintenance actions, and the accident flight communications were not available. Landing simulations based on available data were consistent with reduced deceleration during the landing roll; however, the simulations could not determine if the airbrakes were stowed or extended during the landing, and the airplane was not equipped with a flight data recorder, which could have captured airbrake deployment and position. Landing performance calculations showed that, without ground airbrakes, the landing ground roll distance exceeded the runway available from the airplane’s touchdown point. Tire skid marks indicated that heavy wheel braking occurred on the runway and taxiway surfaces. Based on the available information, the reason for the flight crew’s reported loss of braking effectiveness during landing could not be determined.
Probable cause:
A loss of braking effectiveness during landing for reasons that could not be determined, which resulted in a runway excursion.
Final Report: