Circumstances:
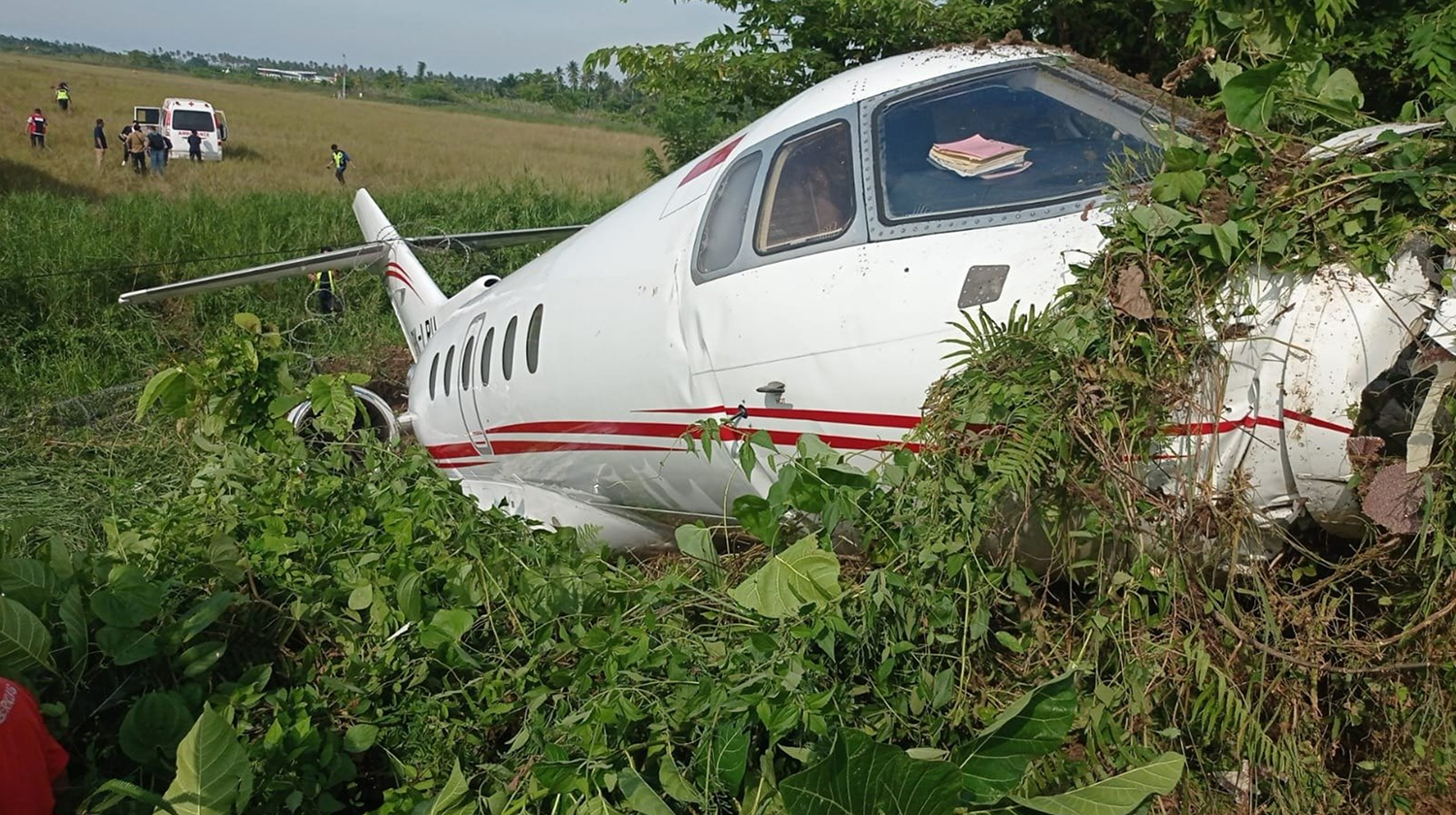
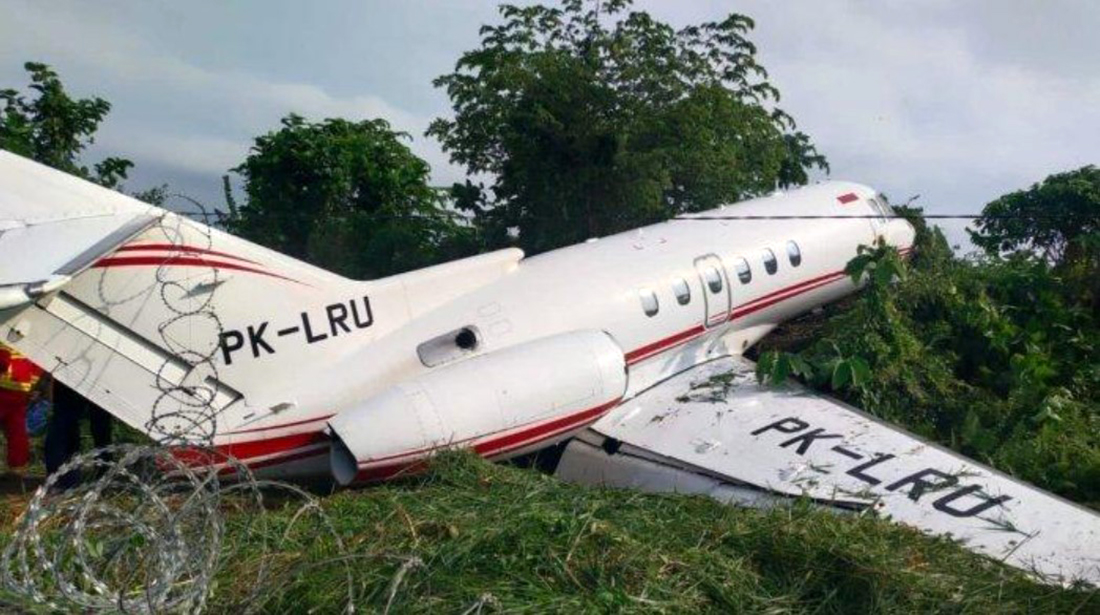
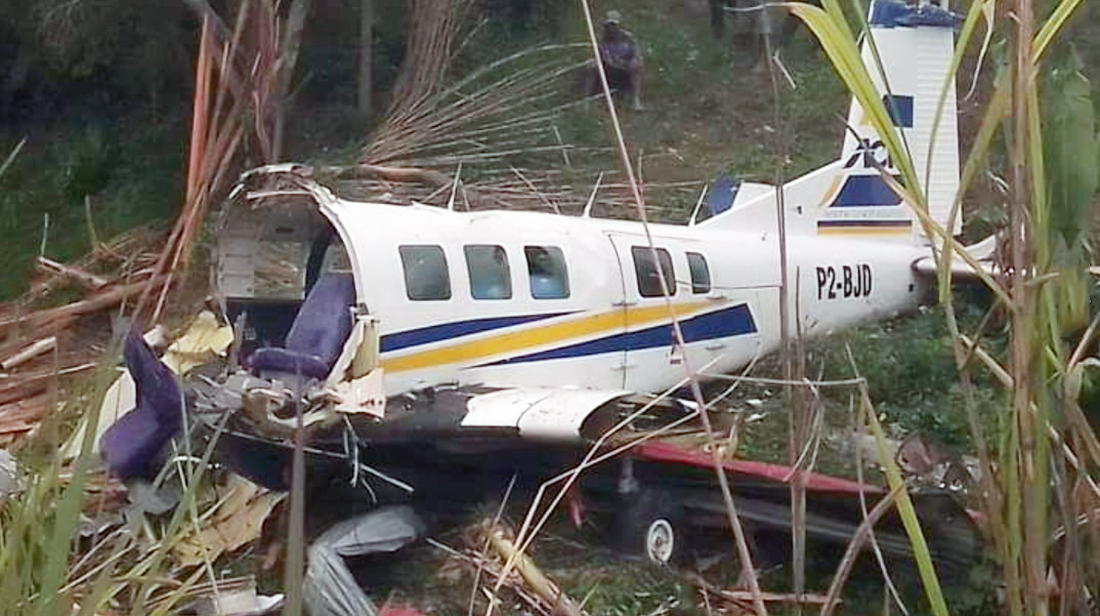
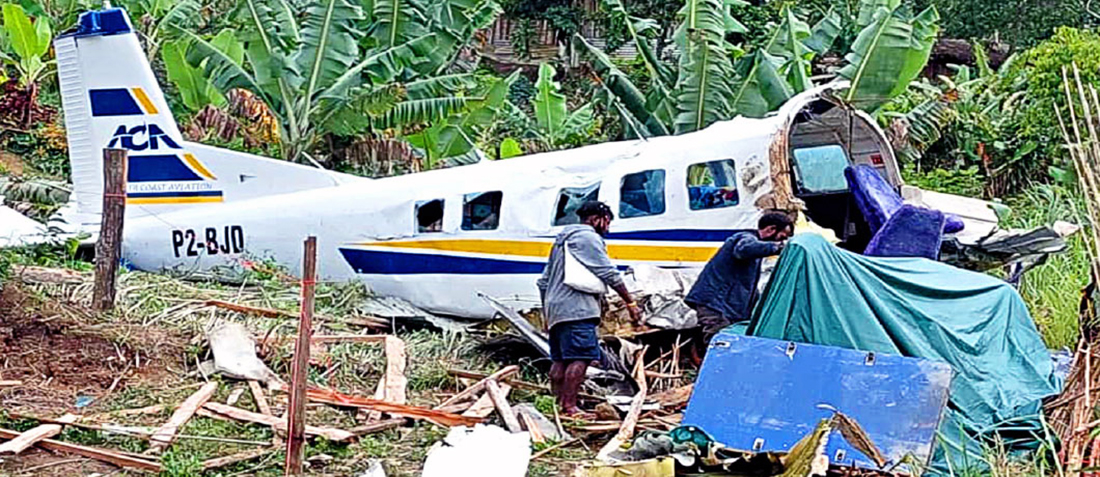
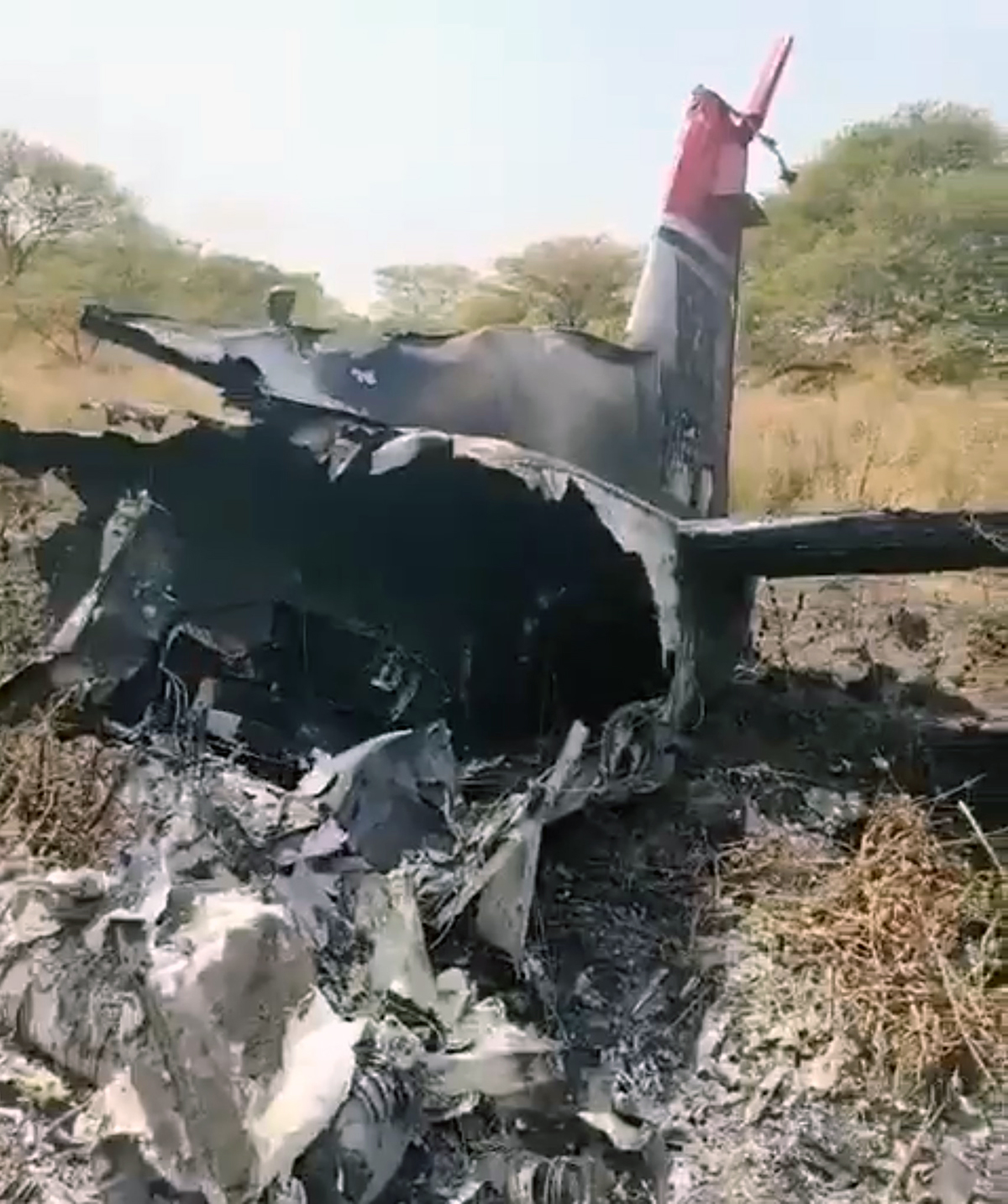
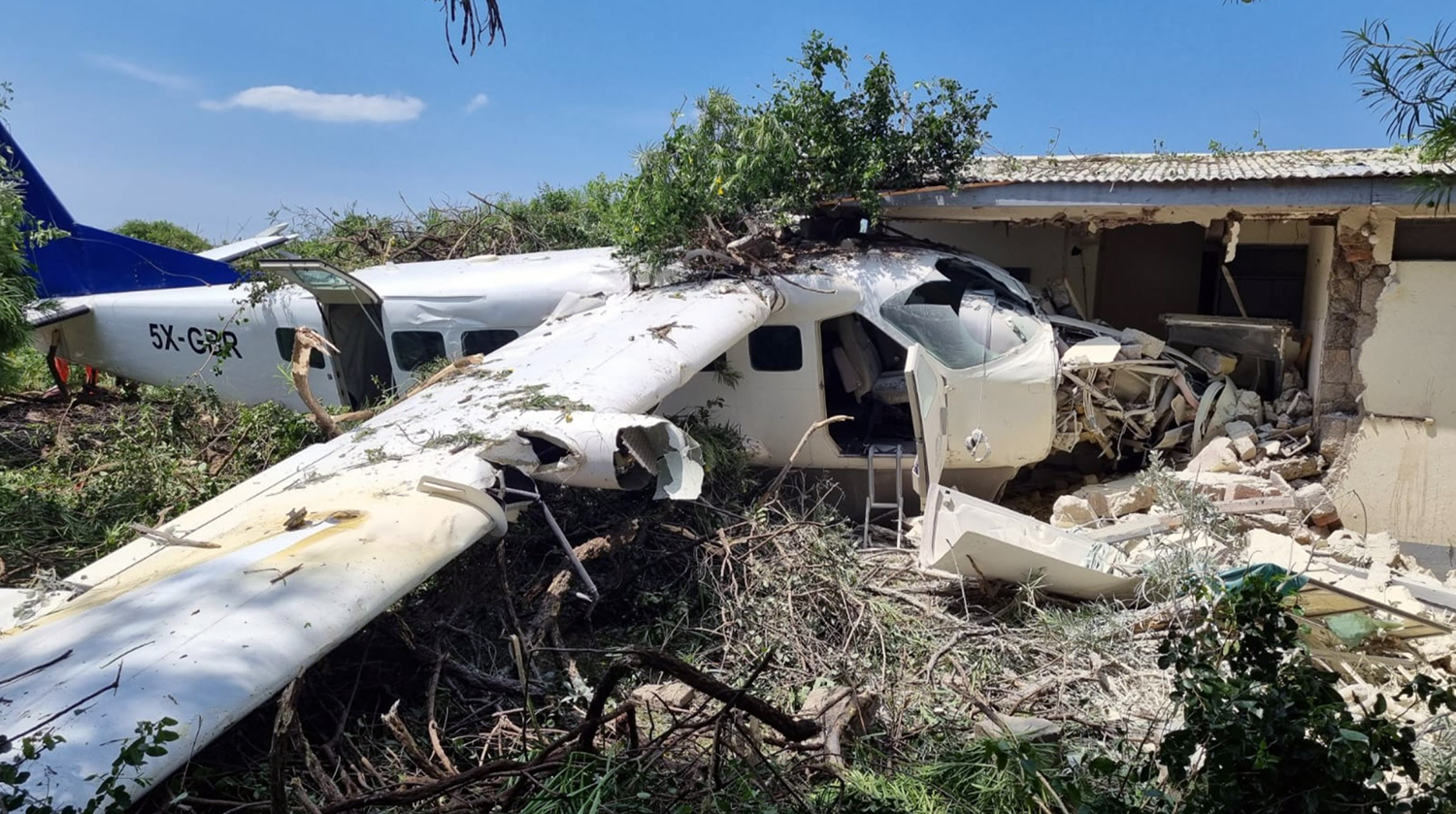
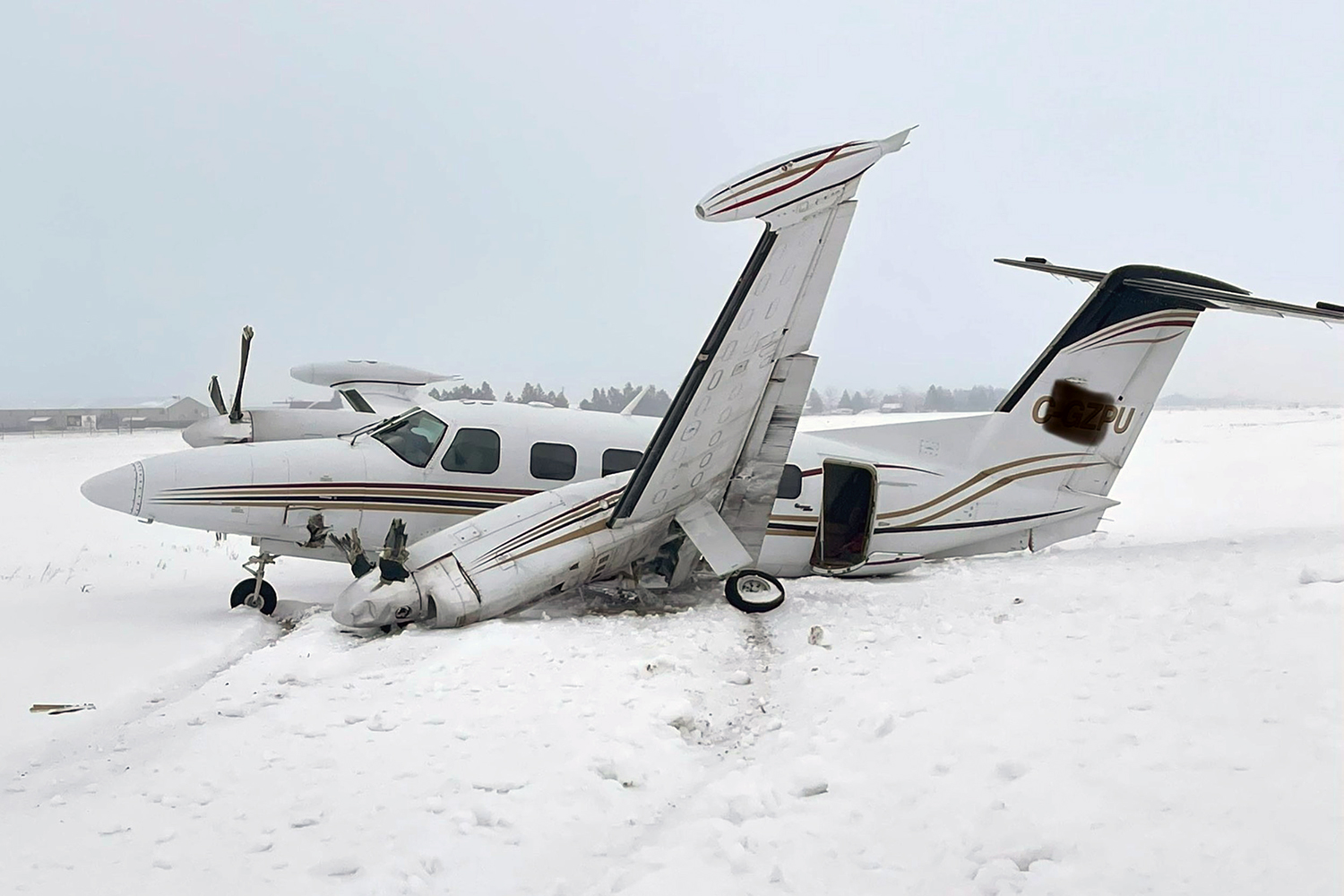
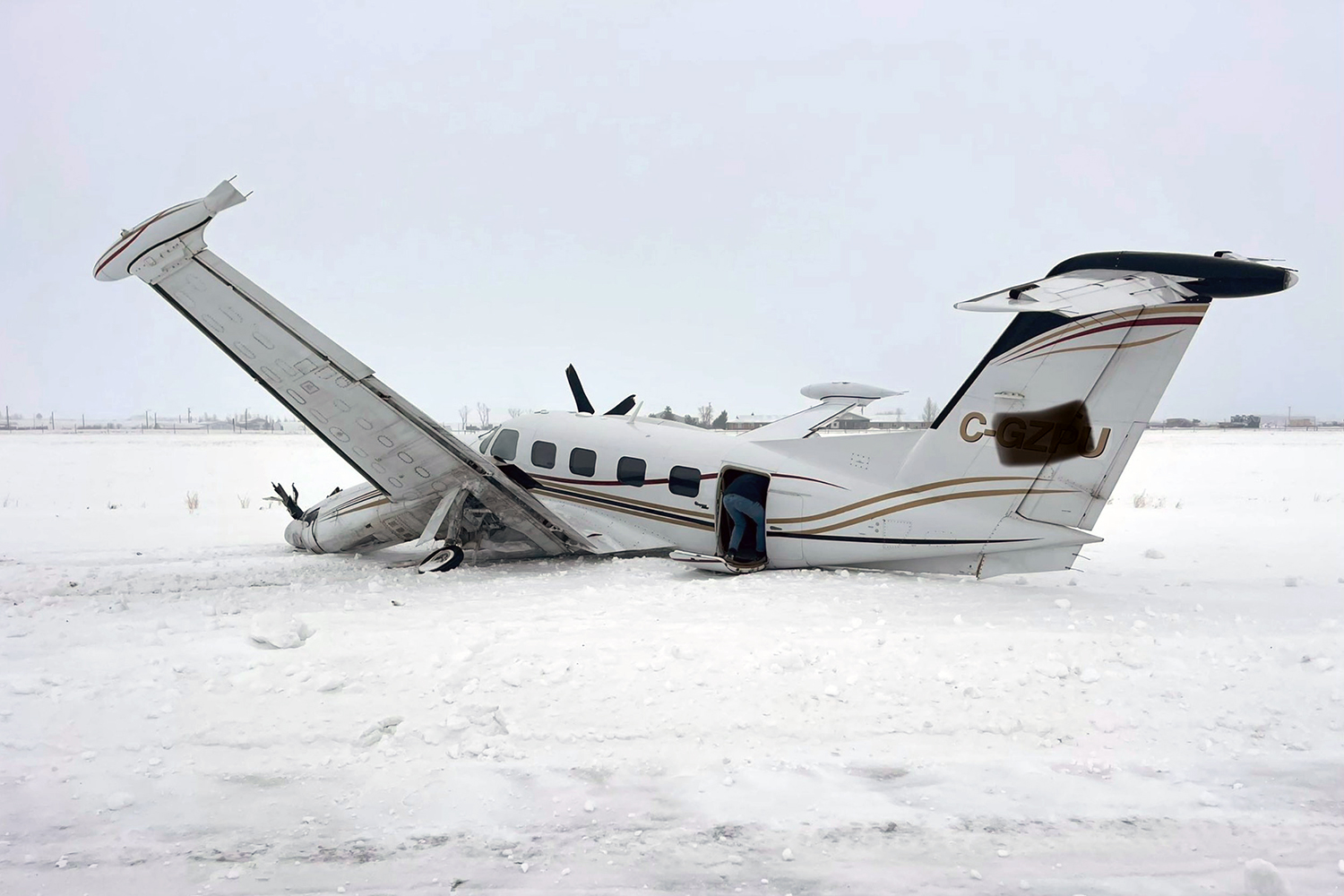
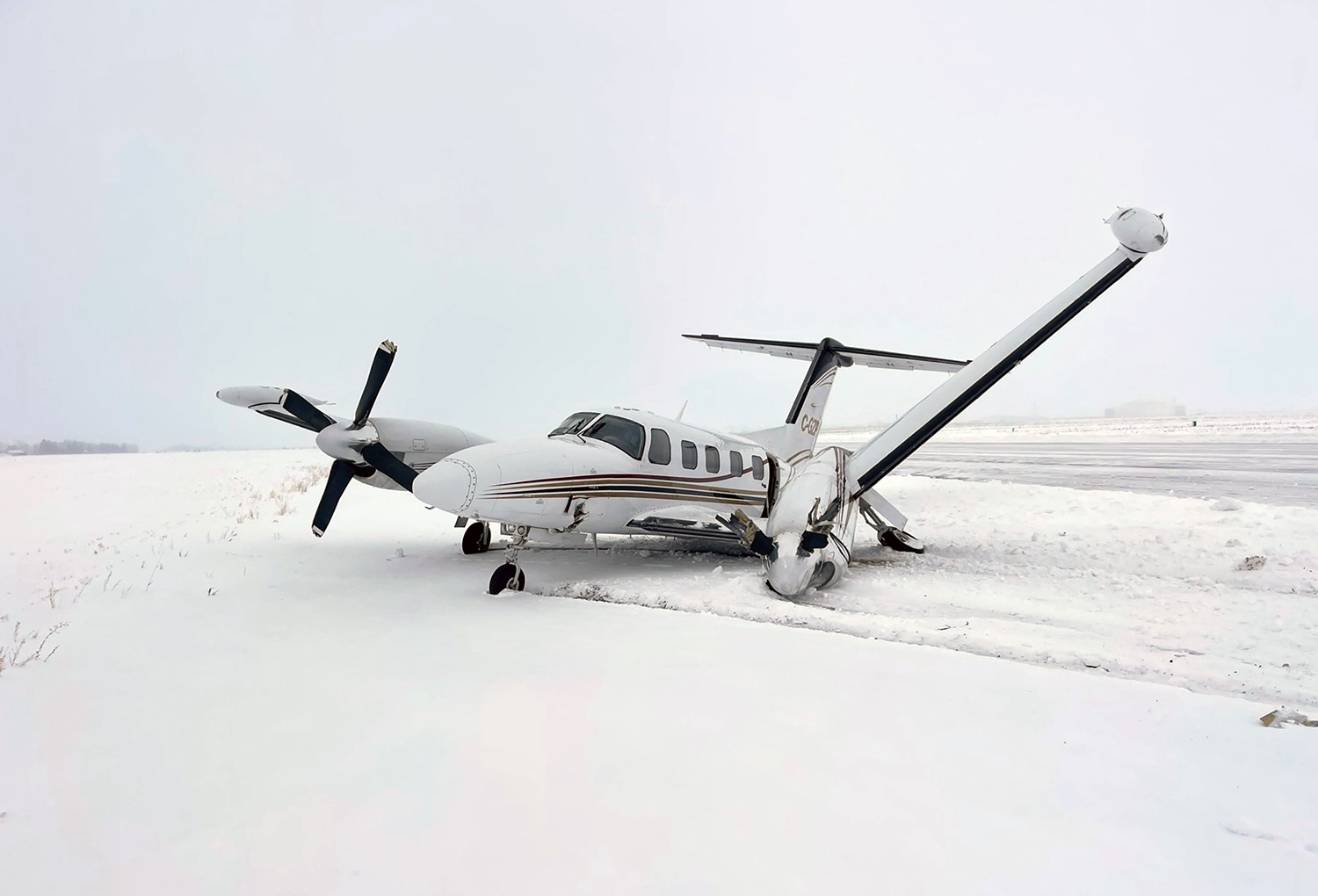
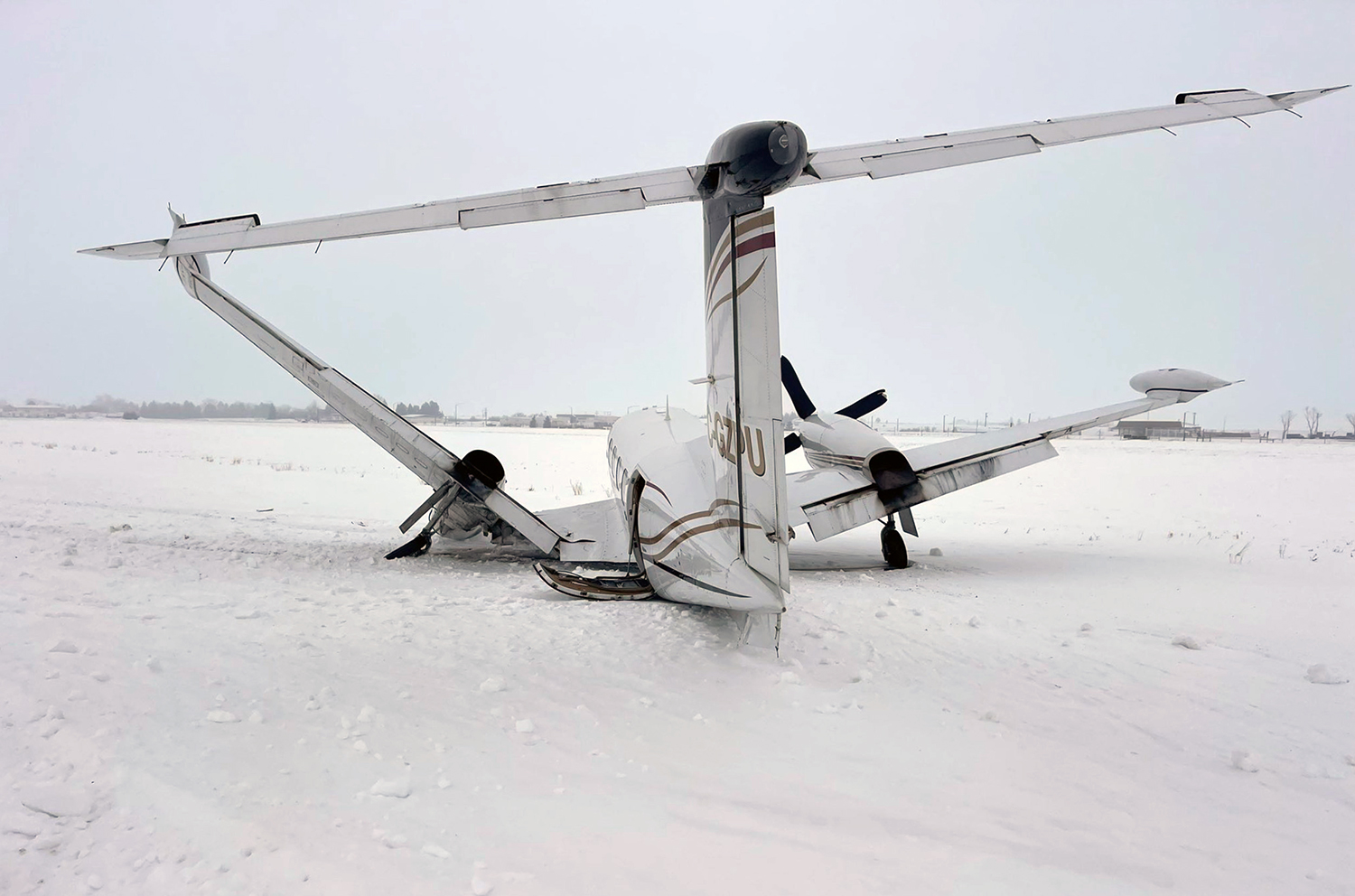
The flight was planned to depart Giramben at 12:40, and track North for Simbai Airstrip, Madang Province at 9,000 ft AMSL. According to the pilot, the aircraft was loaded by NCA ground handlers following his instructions. The manifest was completed by one of the ground handler, who stated that the aircraft was loaded by the other ground handlers while he was completing the manifest in the vehicle, due to no proper shed for him to work from. The pilot also stated that at the time the loading was completed, and the passengers had boarded the aircraft, he observed that the winds were variable, blowing directly from the North and from the East as well. Recorded data showed that the aircraft commenced taxiing at 12:44. During the take-off roll, at the expected airborne point, about 500 m down the runway, as the aircraft accelerated with the airspeed approaching 60 knots, the right wheel hit a soft spot on the strip which dramatically reduced the momentum and speed of the aircraft, as described by the pilot. Eyewitnesses reported seeing the aircraft getting airborne briefly and got back on the ground again. The pilot recalled that by the time the aircraft got back on the ground he realized that he had passed the nominated committal point, which was identified during onsite activities to be about 540 m from the threshold of runway 16. The pilot opted to continue with the take-off roll, with full power hoping that the aircraft would regain speed on the remaining part of the strip to get airborne again. The pilot recalled reaching the end of the runway and getting airborne again with an airspeed of 50 kts airborne again, however, the right wheel got caught on the barbed wire of the perimeter fence that ran across to the runway, and subsequently impacted terrain. The pilot stated that he had lost consciousness at the time of the initial impact and therefore, had no recollection from thereon. The investigation found that the aircraft got airborne about 19 m past the end of runway 16. However, the aircraft’s main landing gears got caught on the perimeter fencing wire, subsequently impacting ground about 100 m from the end of the runway, then continued with the momentum and came to rest, in a local village garden about 160 m from the end of the runway. The aircraft was destroyed by impact forces. The pilot and passengers were rescued by the locals and taken to Nazarene General Hospital, Jiwaka Province, for treatment. The pilot, male adult and infant passengers sustained serious injuries, and the female passenger sustained minor injuries.
Probable cause:
The following factors were identified:
- The pilot did not complete a trim sheet for the flight.
- The manifest was completed by a ground handler who was not present at the time the cargo was being loaded by other ground handlers. The manifest was not signed by the ground handler who completed it, nor was it authorized by the pilot before departure.
- Pilot’s lack of supervision of the aircraft’s loading process to ensure cargo is loaded correctly and in accordance with the prescribed limitations and to prevent calculation errors. As a result, it was likely that the aircraft was overweight when it departed.
- Wet strip surface conditions that caused significant resistance during the take-off roll and impeded the aircraft’s ability to reach its required lift off airspeed.
- Pilot’s decision to continue the take-off roll after passing the committal.
- Training deficiencies of ground handlers and the pilot.
- The lack of adequate Quality Assurance systems oversight on the operator’s operating standard procedures.