Crash of a Beechcraft E90 King Air in Wiscasset: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 10, 1996 at 0600 LT
Registration:
N916PA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Wiscasset - Philadelphia
MSN:
LW-313
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
1138.00
Aircraft flight hours:
6230
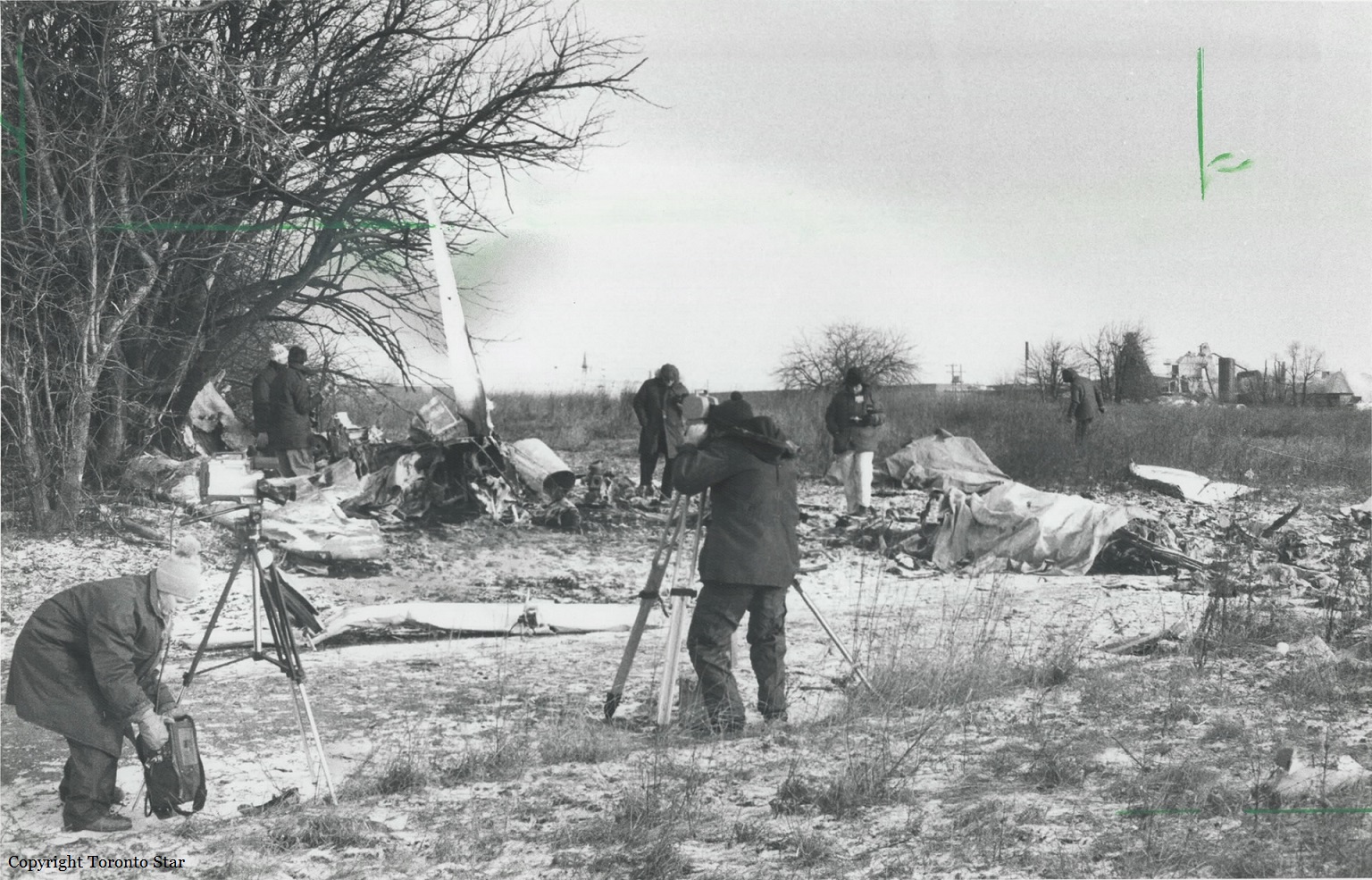
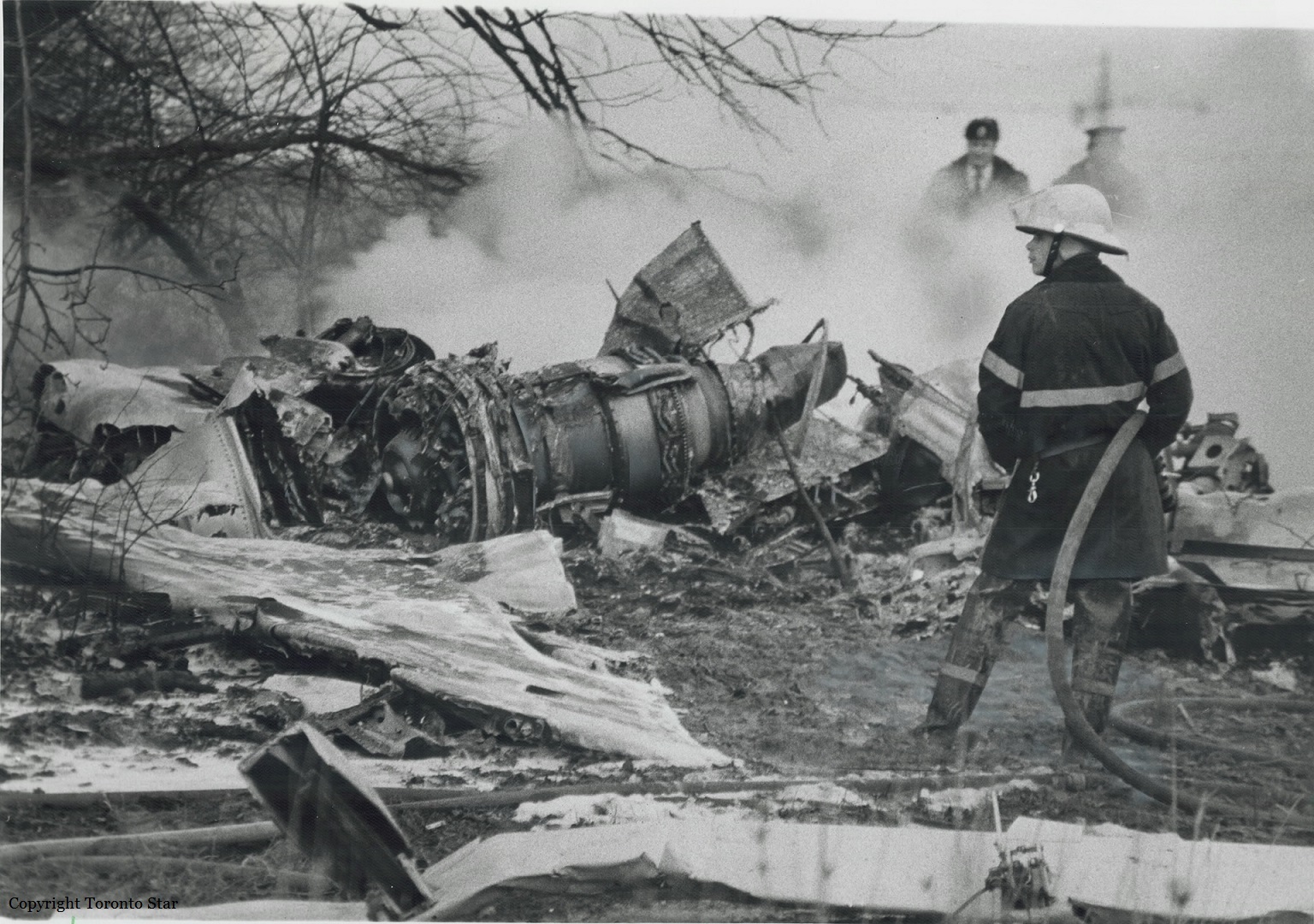
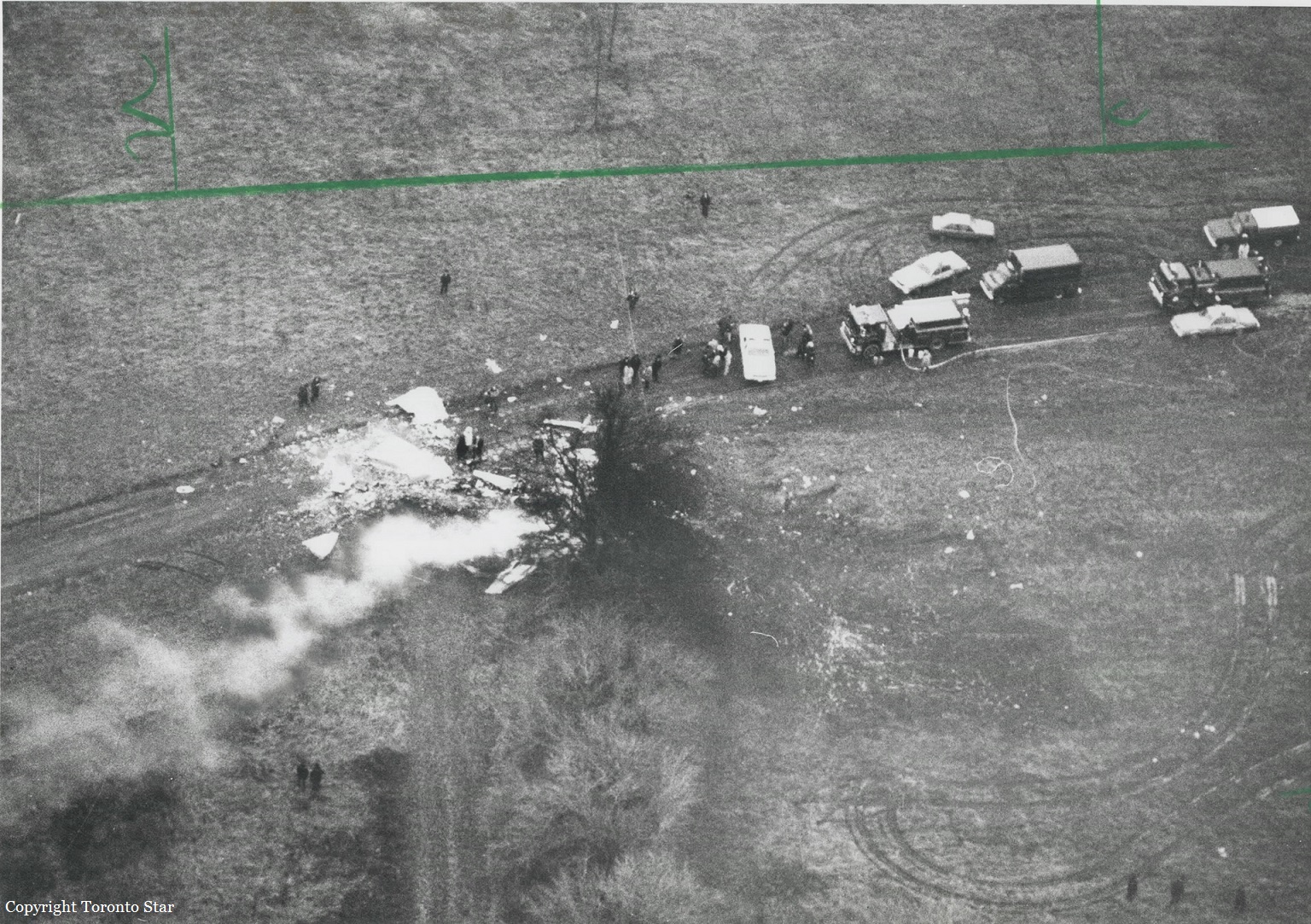
Circumstances:
The pilot took off on runway 07 and was cleared direct to the Wiscasset NDB, east of the airport. Shortly after takeoff, the airplane began turning to the left. The pilot then asked the controller, '. . . can you tell if I'm in a turn? I have a problem here.' Soon thereafter, the airplane collided with terrain in an uncontrolled descent, about 1.6 miles north of the airport. Investigation revealed that three days before the accident, a refueler had fueled the airplane's left wing with 840 pounds of fuel, then the fuel farm ran out of fuel. No further fueling was accomplished, and the pilot was not advised of the uneven fuel load. Procedures in the Beech E90 Pilot's Operating Manual (POM) included a check of the fuel tanks during preflight. The Beech C90 POM specified a maximum fuel imbalance of 200 pounds, but the E90 POM did not specify a maximum fuel imbalance. During examination of the wreckage, no preimpact malfunction or failure was found.
Probable cause:
Failure of the pilot to maintain control of the airplane while climbing after takeoff, due to spatial disorientation, which resulted in an uncontrolled descent and subsequent collision with terrain. Factors relating to the accident were: the improper refueling (servicing of the aircraft) by FBO personnel, and failure of the pilot to note the excessive lateral imbalance of the airplane during preflight.
Final Report: