Crash of a Piper PA-42-720 Cheyenne III off Grand Case: 4 killed
Date & Time:
May 5, 2012 at 0240 LT
Registration:
F-GXES
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Grand Case - Fort-de-France
MSN:
42-8001043
YOM:
1980
Flight number:
TIF520
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
513.00
Aircraft flight hours:
7593
Aircraft flight cycles:
7830
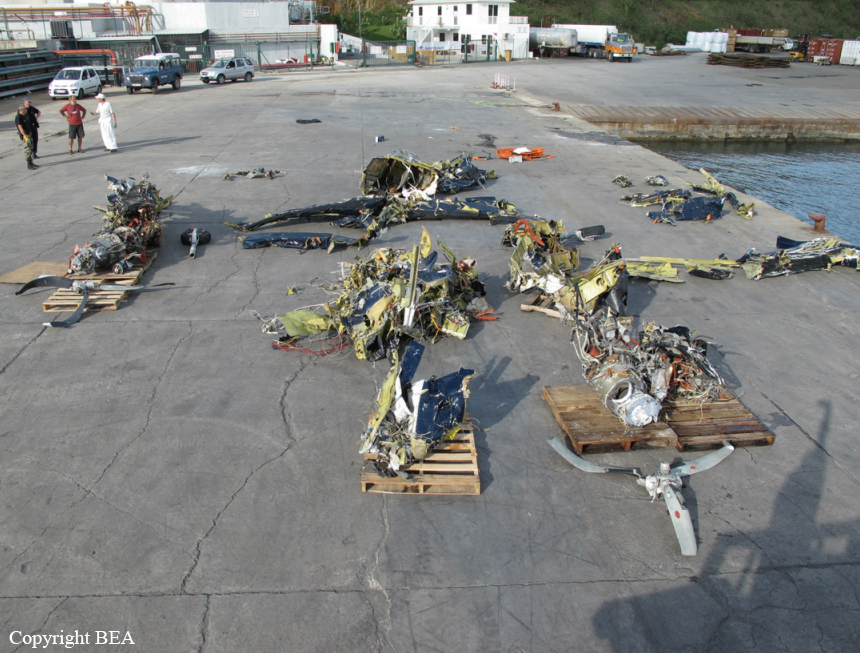
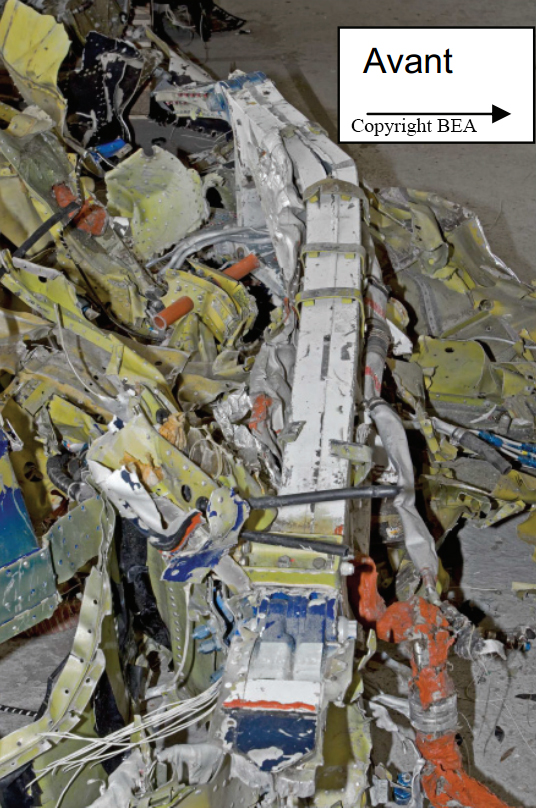
Circumstances:
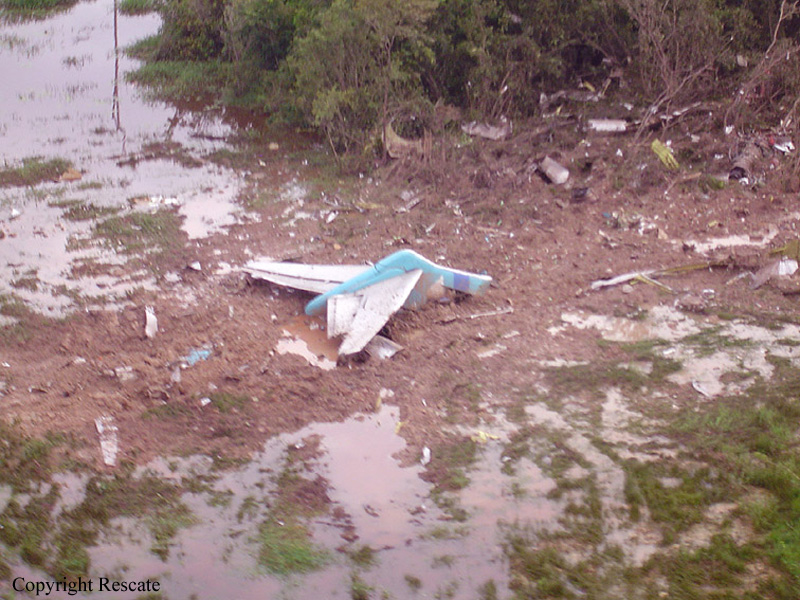
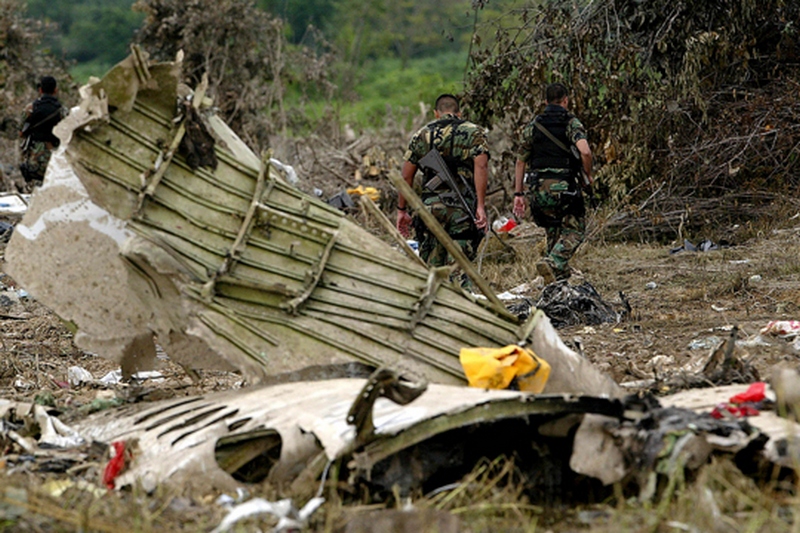
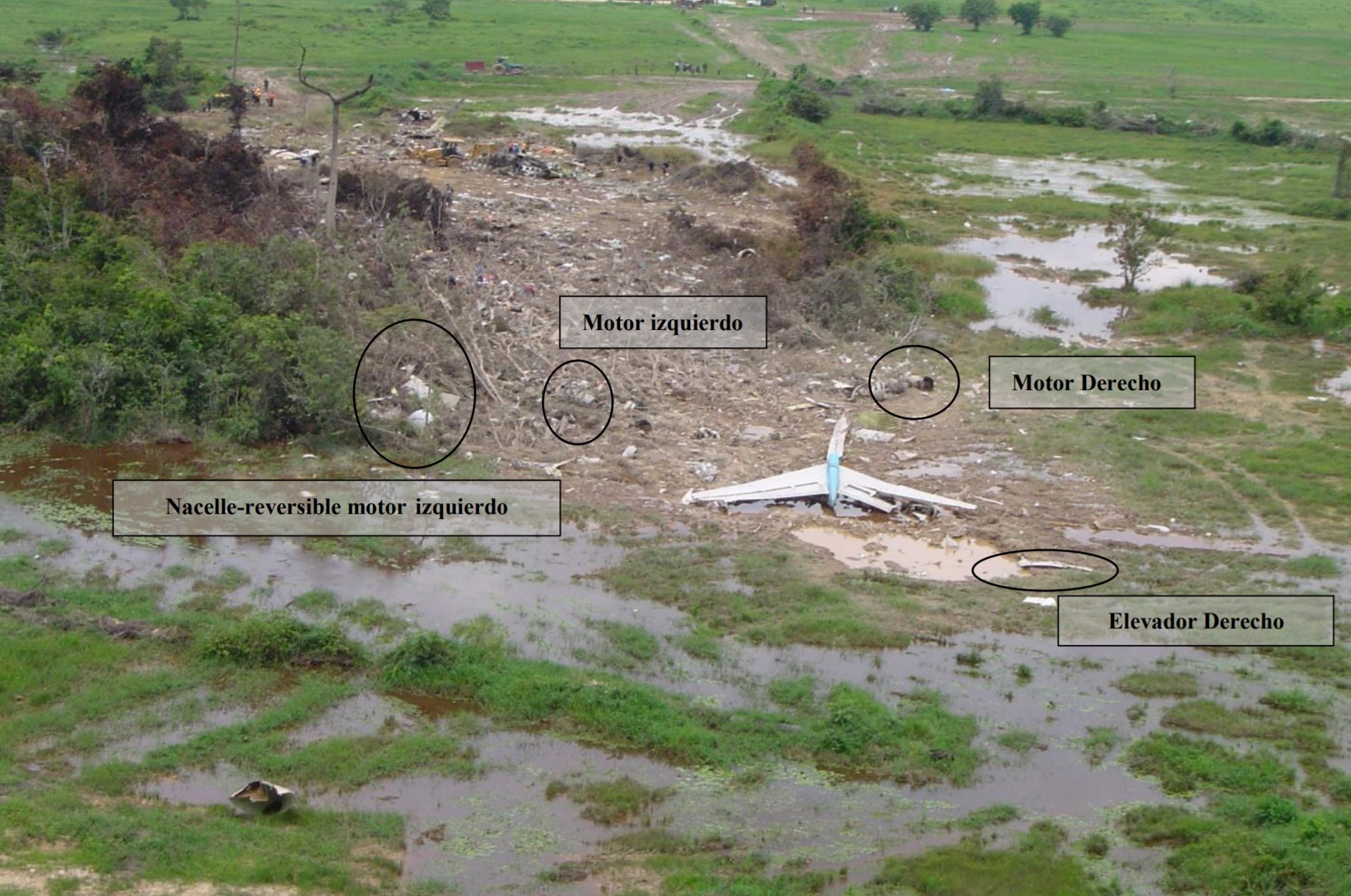
The twin engine aircraft was engaged in an ambulance flight between Grand Case and Fort-de-France and was carrying a pilot, a nurse, a doctor and a patient, a Greek citizen in honeymoon in Saint Martin who suffered a heart attack. He normally should be transferred to Fort-de-France from Saint Martin-Princess Juliana Airport with another Operator but the aircraft suffered technical problem prior to departure and the patient was transferred to Grand Case Airport. Piper PA-42 left Grand Case-L'Espérance runway 12 at 02H39. One minute later, during initial climb, it lost height and crashed into the Caribbean Sea, some three NM off the airport, off Tintamarre Island. Around 1000LT in the morning, a wheel and some others debris were found floating in water and no trace of the four occupants was found. They were later considered as deceased.
Probable cause:
The French BEA said in its final report that no technical anomaly to affect significantly the performance of the airplane or its pitch control could be demonstrated. It appears that the pilot had consumed alcohol before the flight and was awake since 0630LT and did not sleep over 20 hours, which could affect his capabilities. In conclusion, the investigation did not determine the cause of the accident, but the following factors may have contributed:
- aircraft's operation with one pilot only,
- absence of regulation does not allow the Civil Aviation Authority to ensure the adequacy of the operational objectives of an operator and its capacity to maintain its activity. This failure could not ensure that the pilot was able to conduct the flight.
- the presence of a flight recorder would probably help to understand the circumstances of the accident with more precision. Important data failed to the investigation, which was not able to identify all possible measures to avoid a similar accident in the future.
- aircraft's operation with one pilot only,
- absence of regulation does not allow the Civil Aviation Authority to ensure the adequacy of the operational objectives of an operator and its capacity to maintain its activity. This failure could not ensure that the pilot was able to conduct the flight.
- the presence of a flight recorder would probably help to understand the circumstances of the accident with more precision. Important data failed to the investigation, which was not able to identify all possible measures to avoid a similar accident in the future.
Final Report: