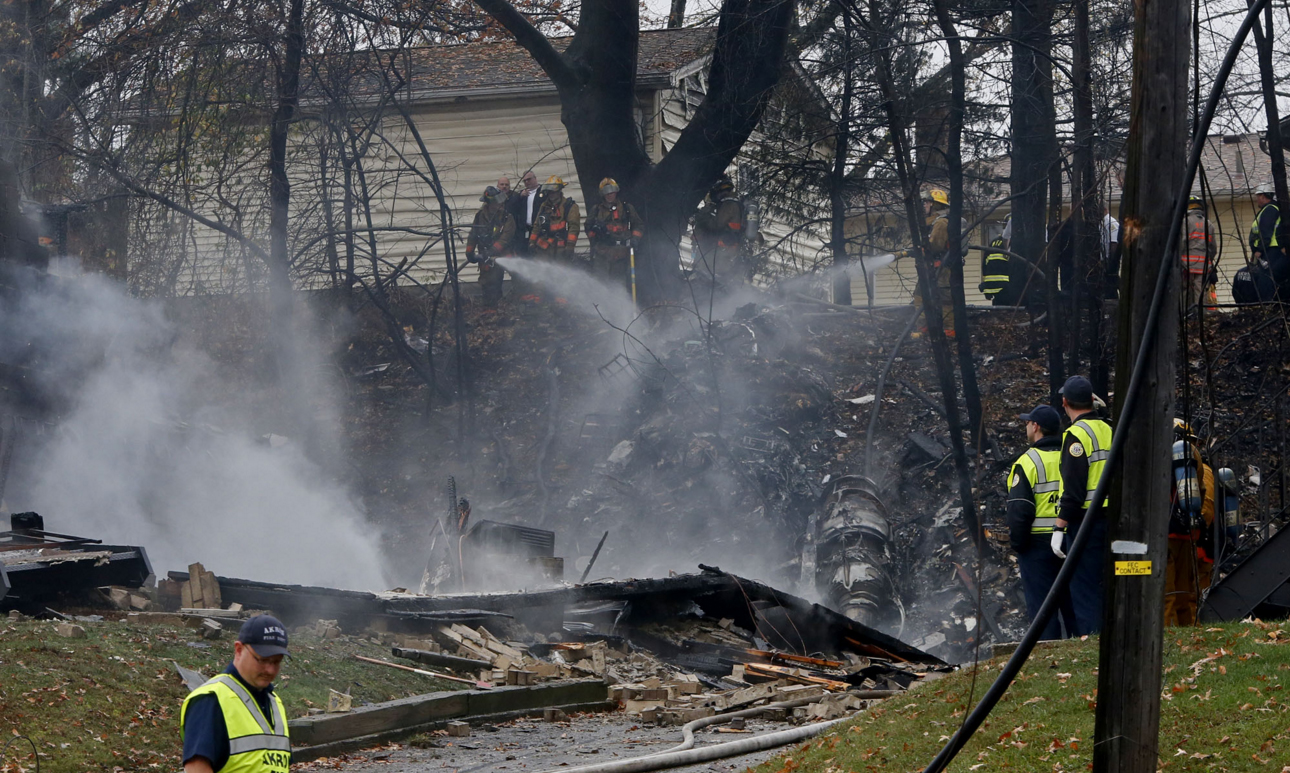Crash of a Beechcraft B200 Super King Air in Melbourne: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 21, 2017 at 0858 LT
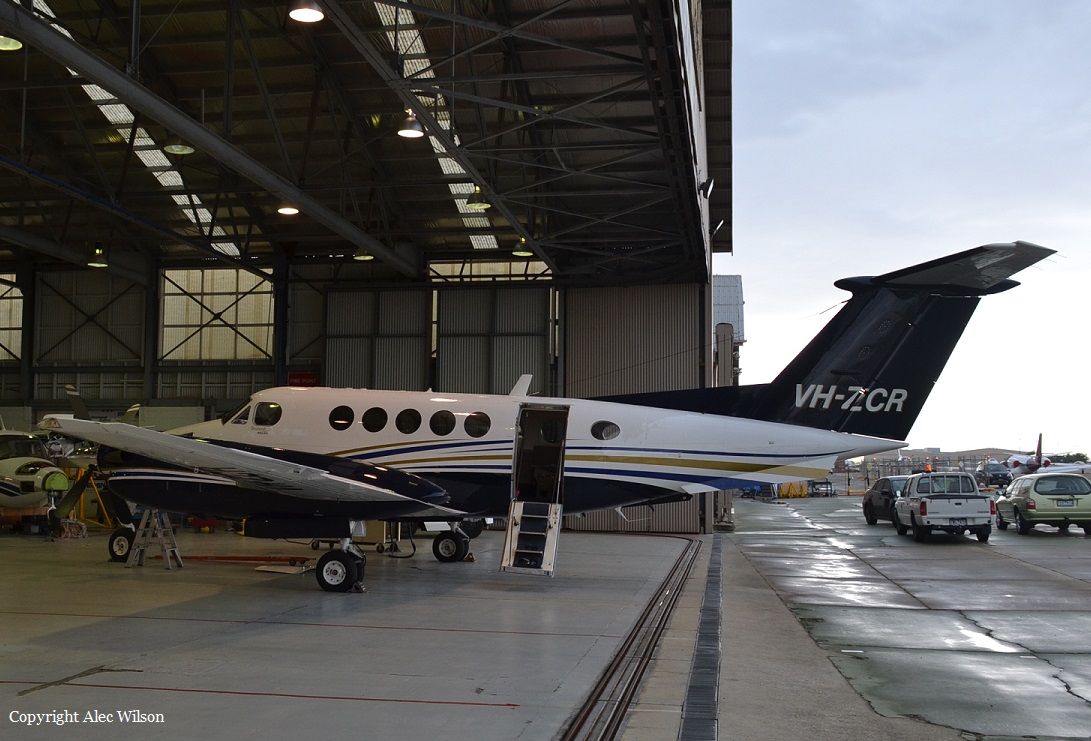
Registration:
VH-ZCR
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Melbourne - King Island
MSN:
BB-1544
YOM:
1996
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Captain / Total hours on type:
2400.00
Aircraft flight hours:
6997
Circumstances:
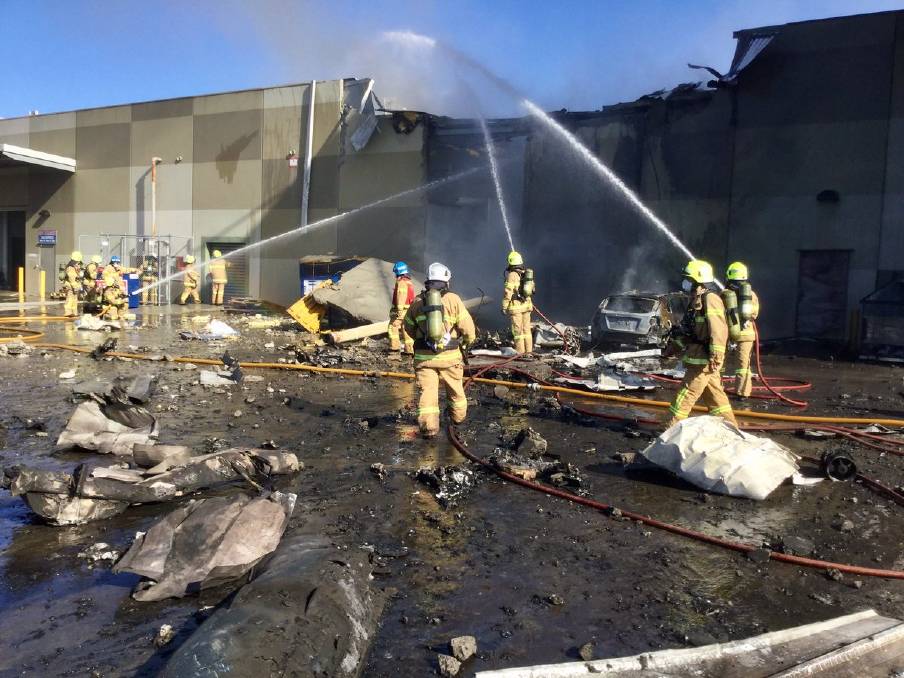
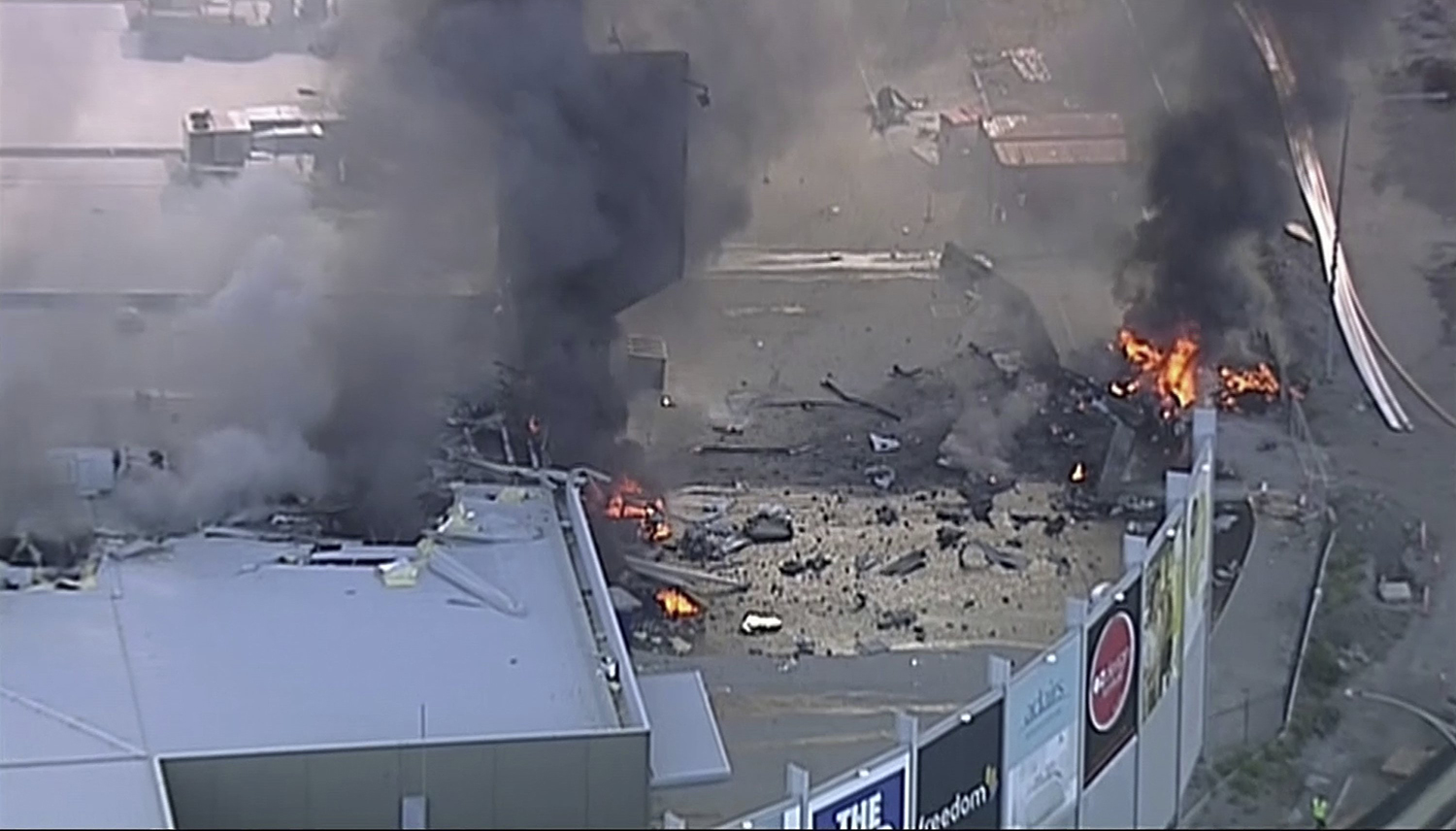
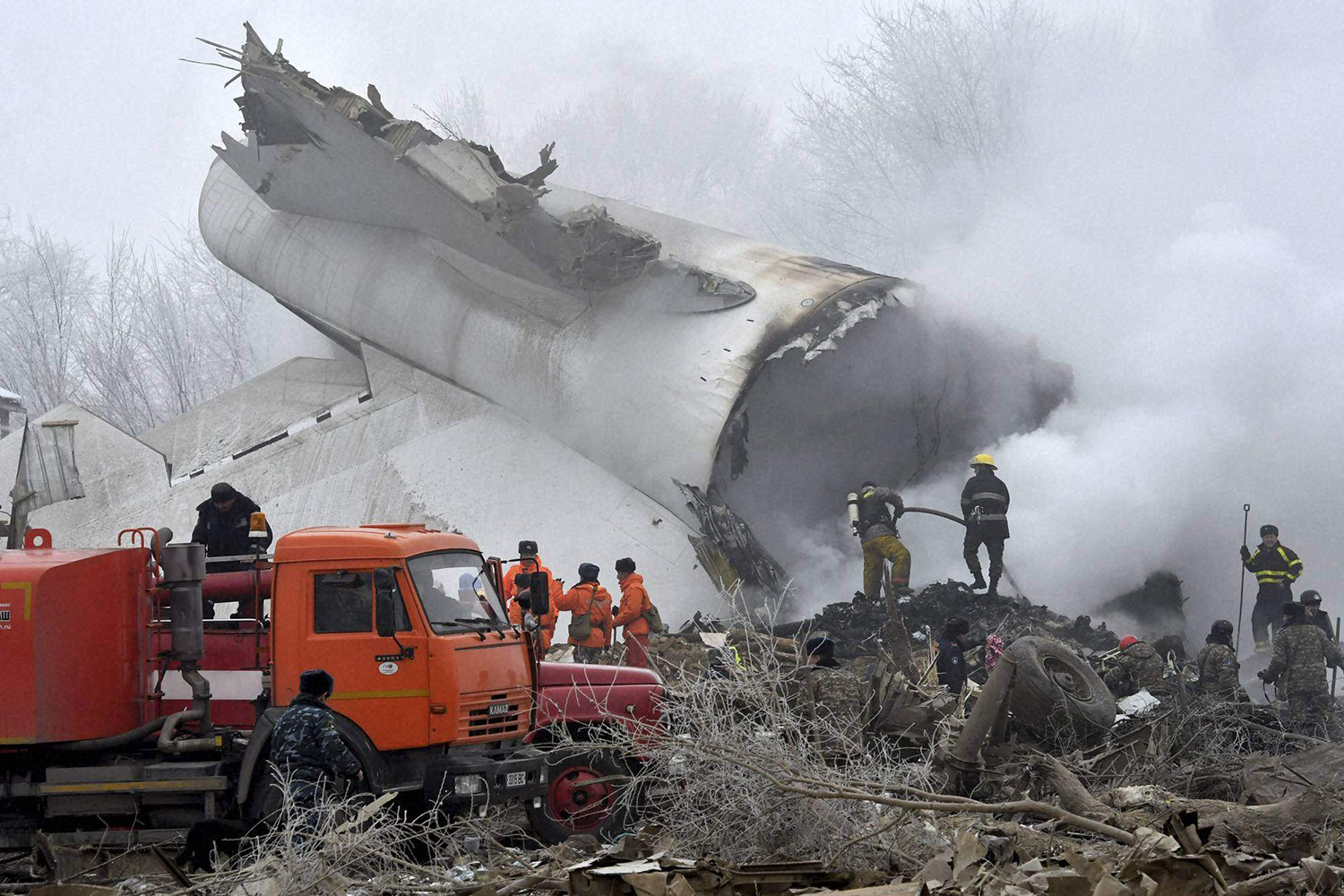
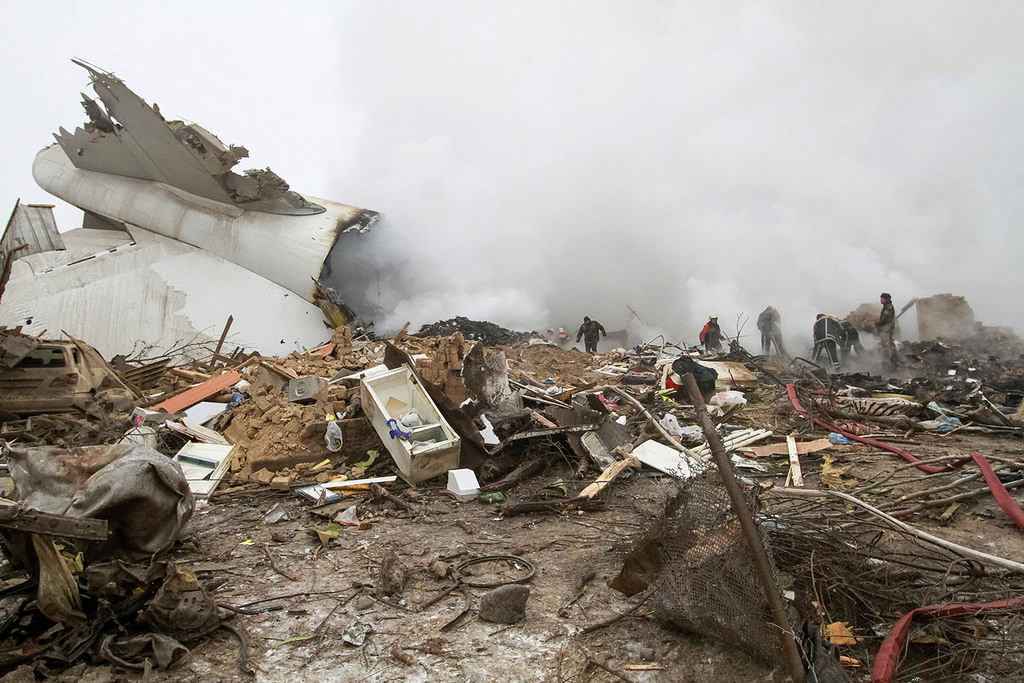
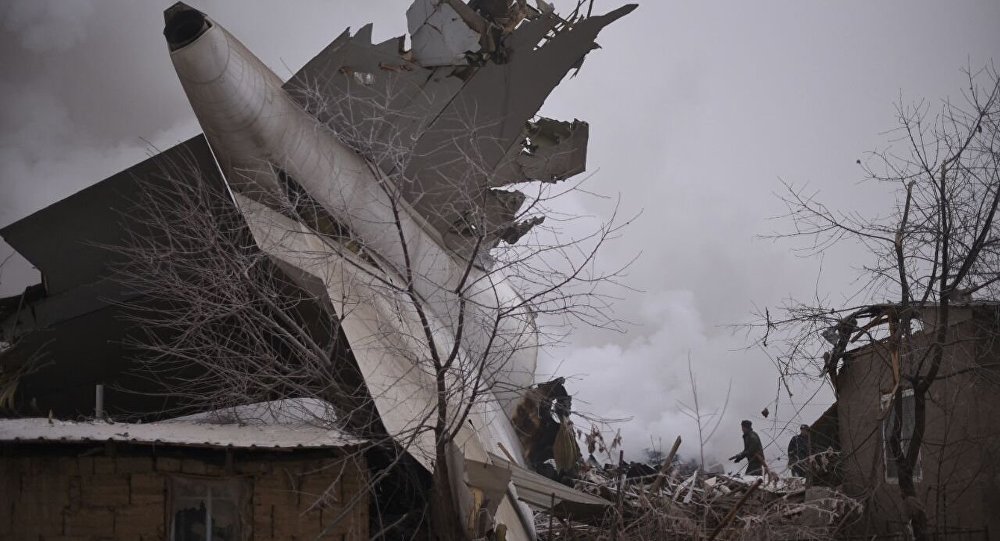
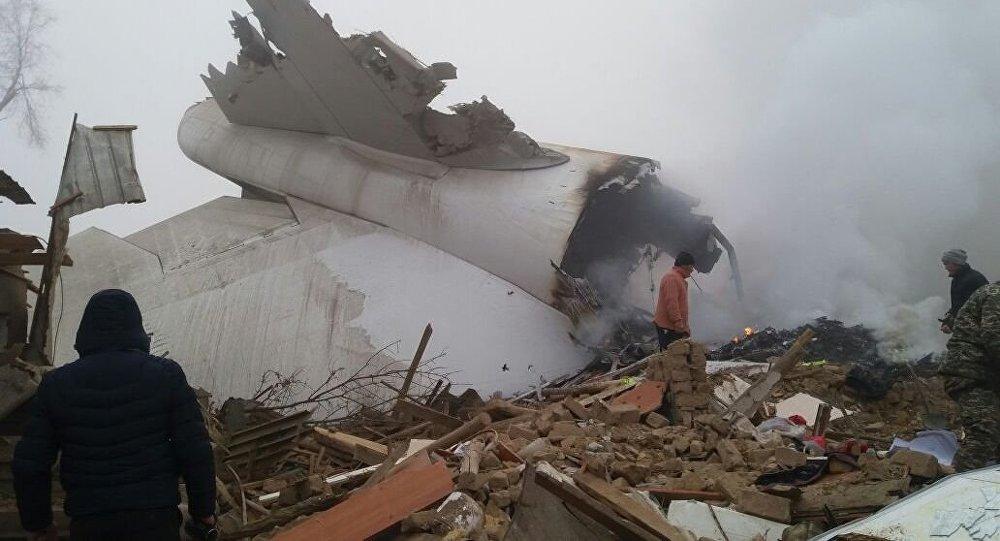
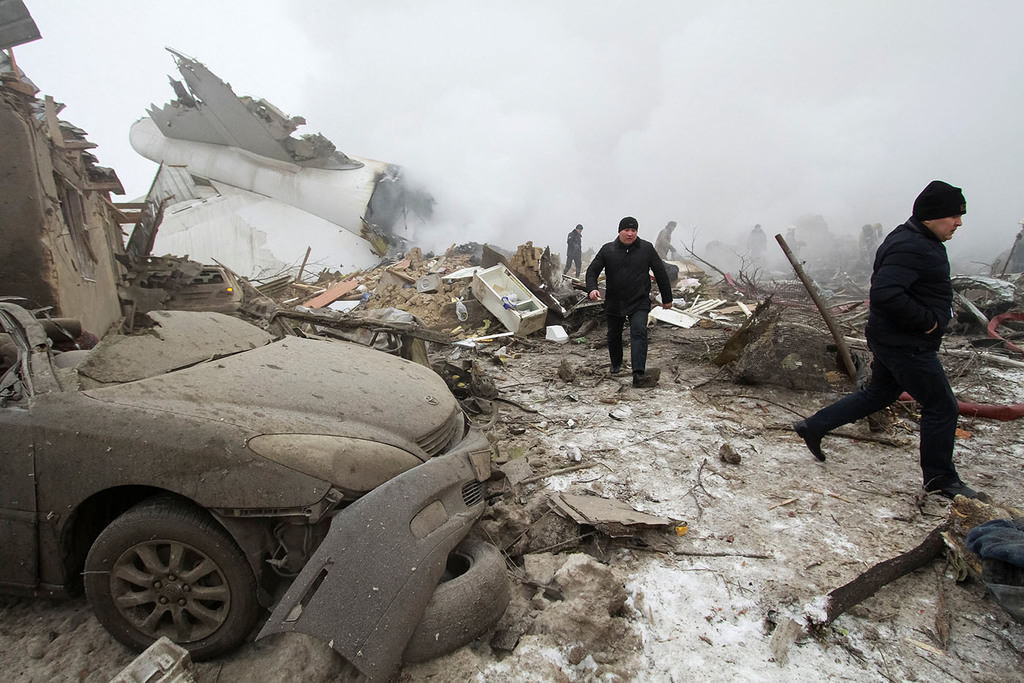
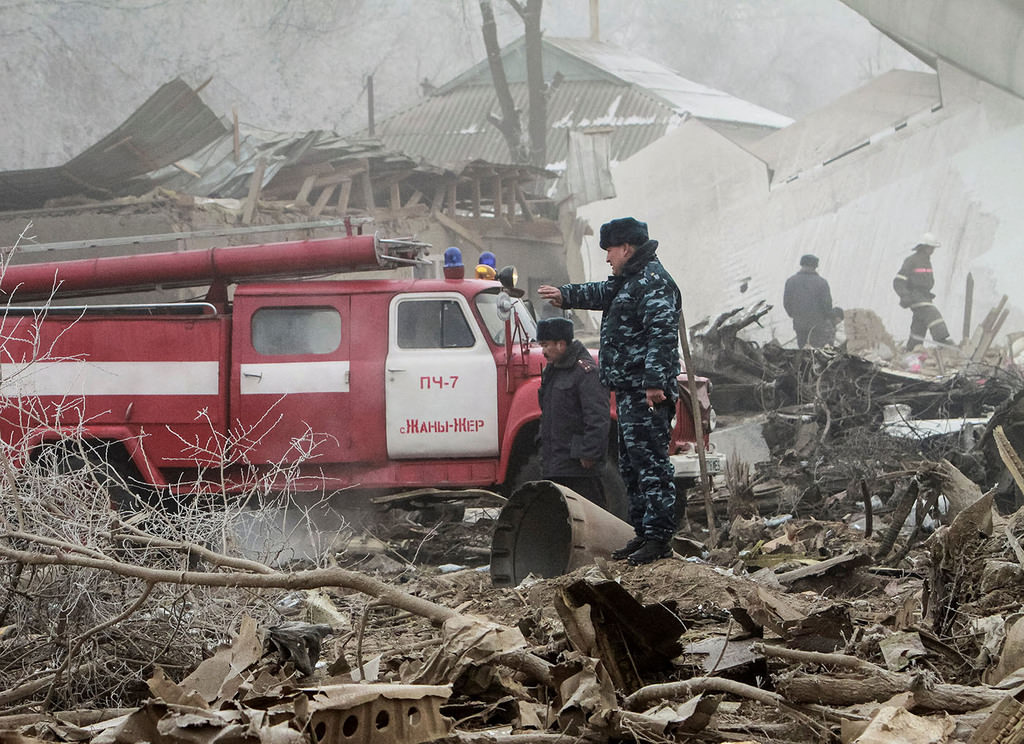
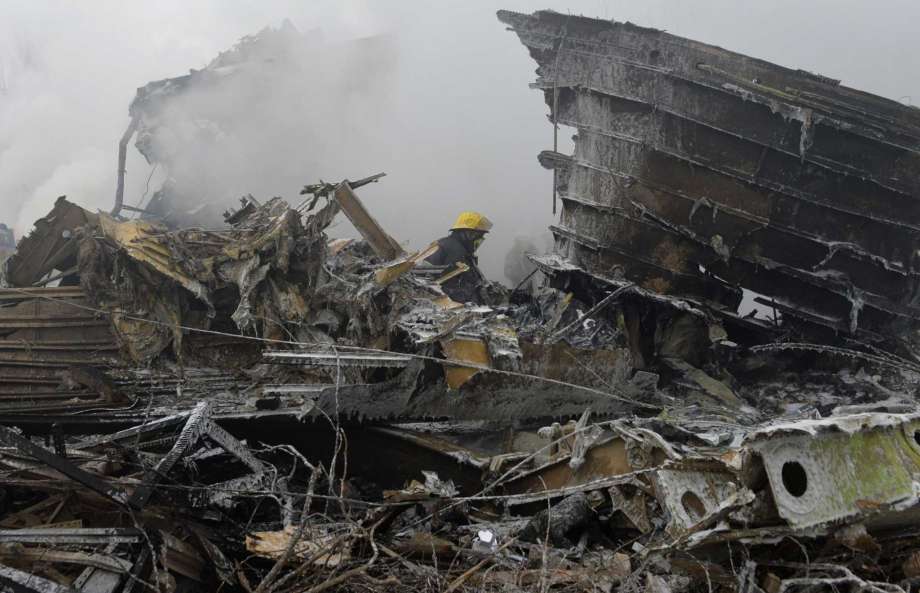
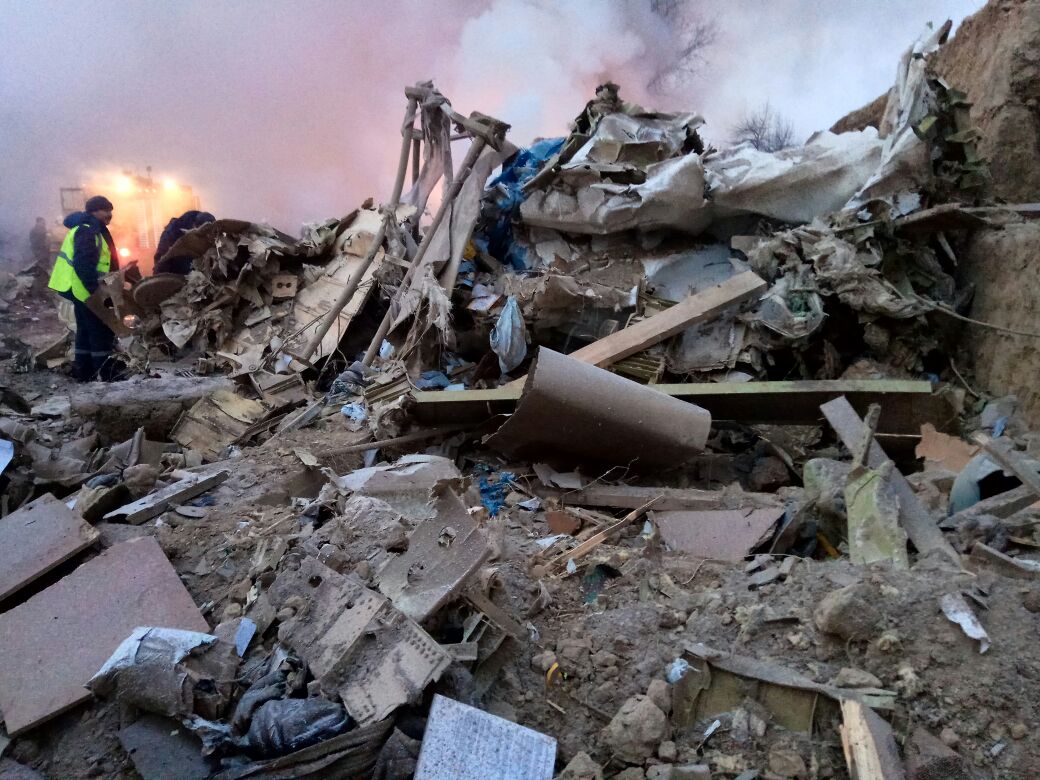
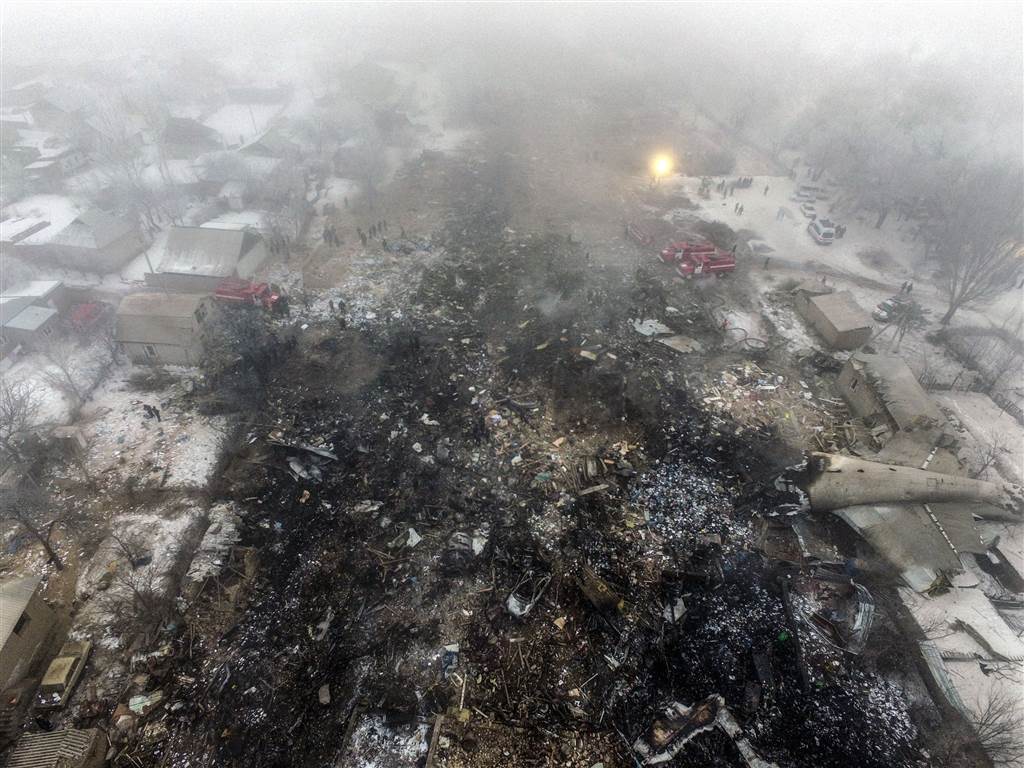
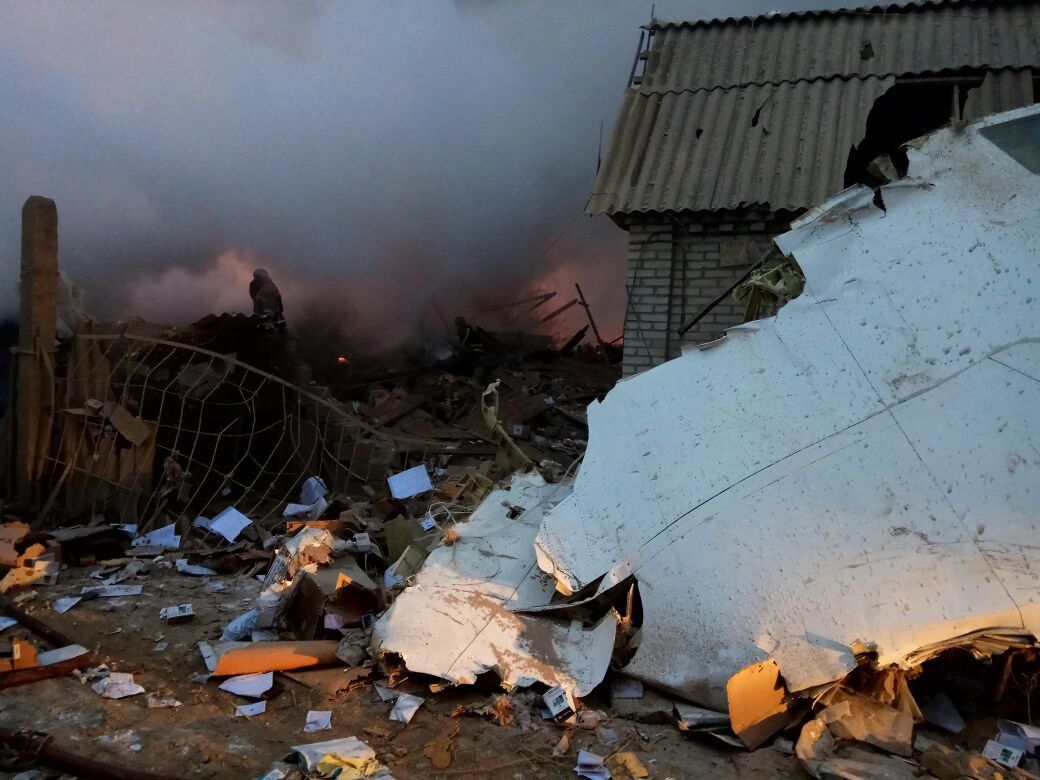
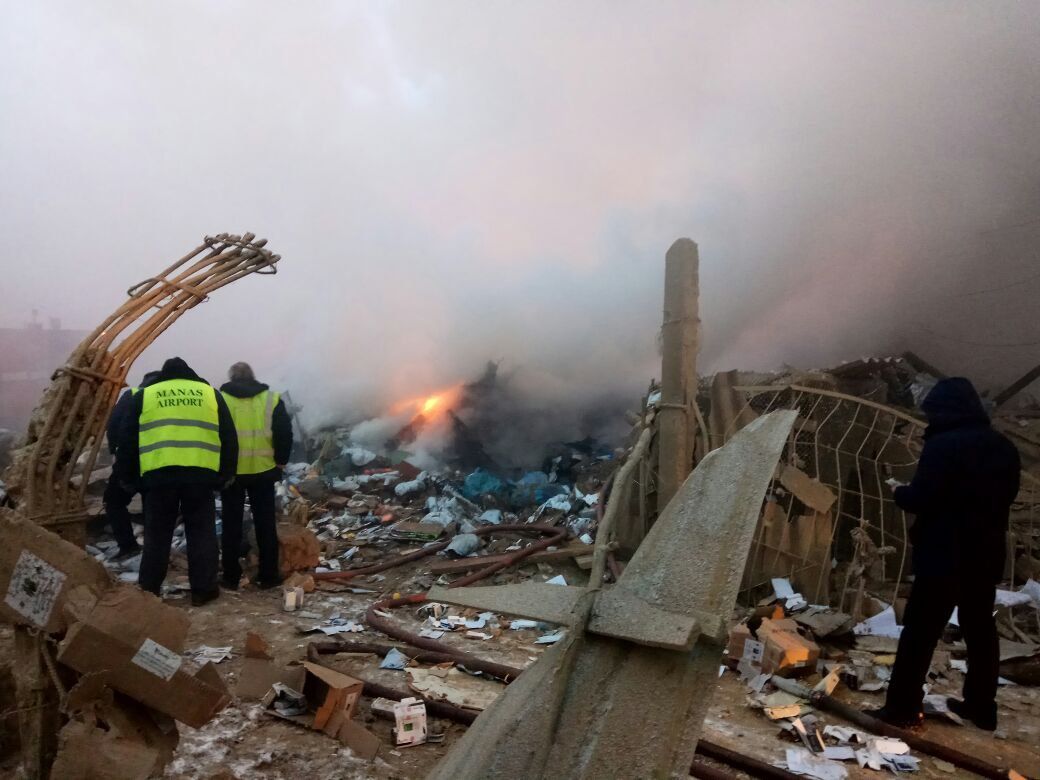
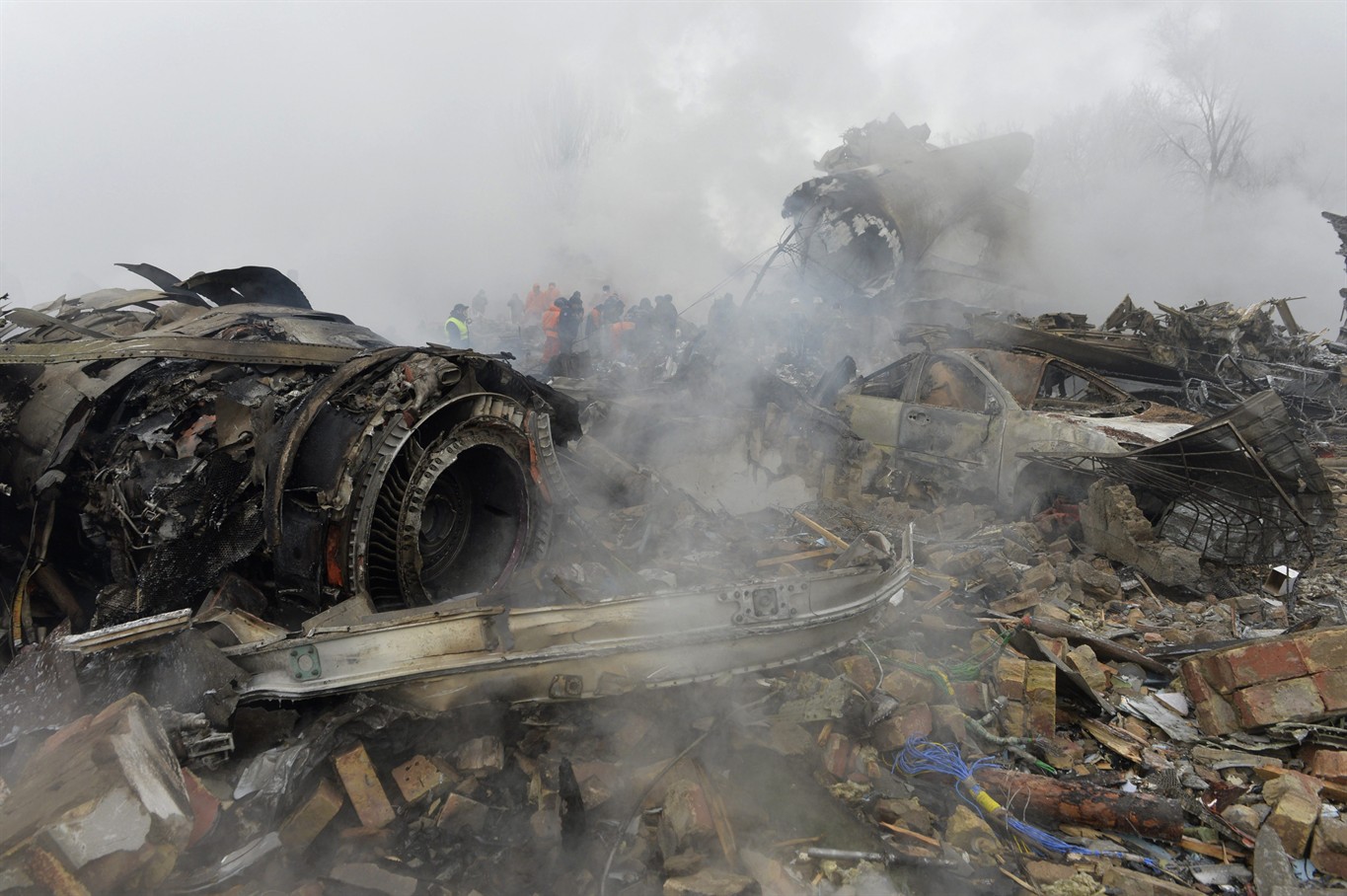
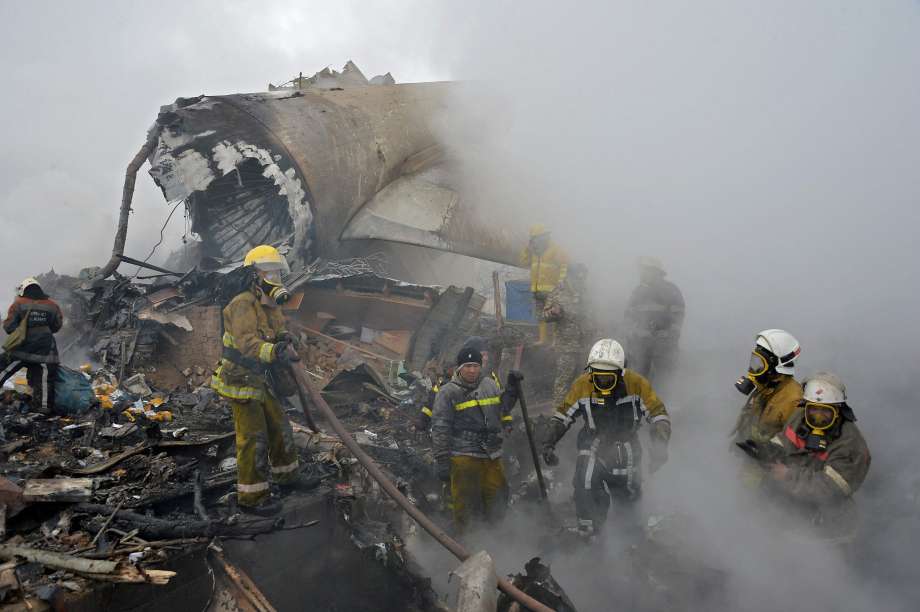
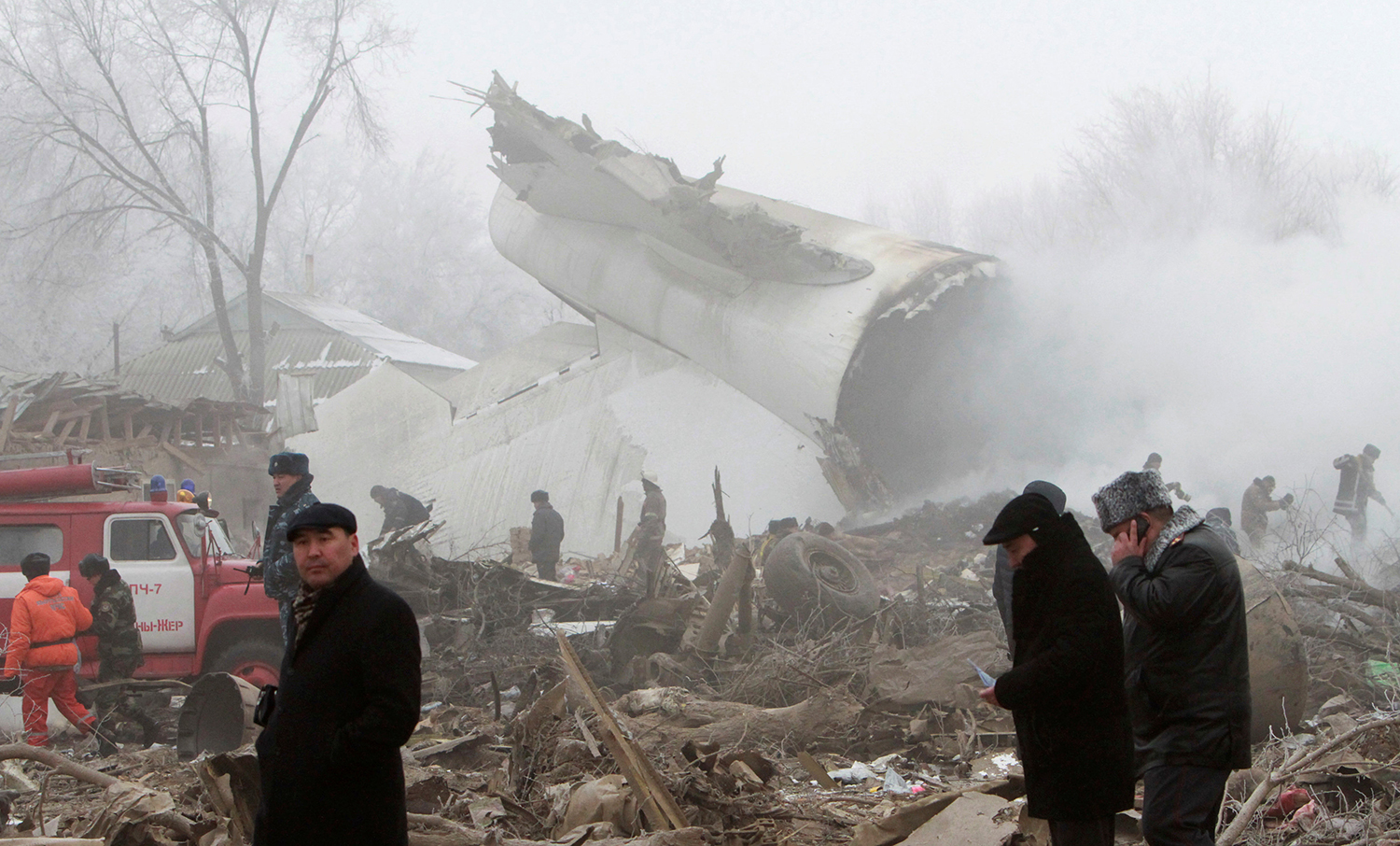
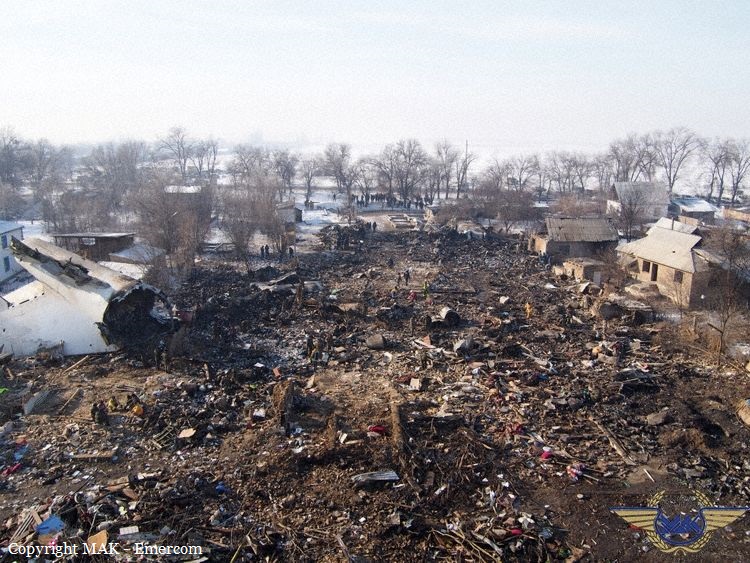
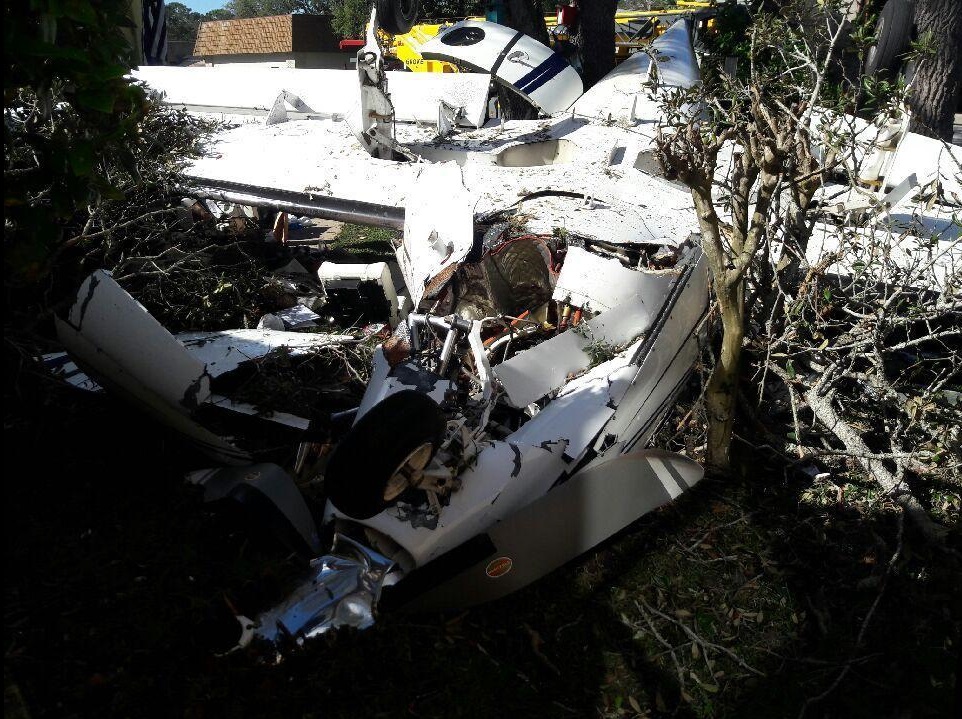
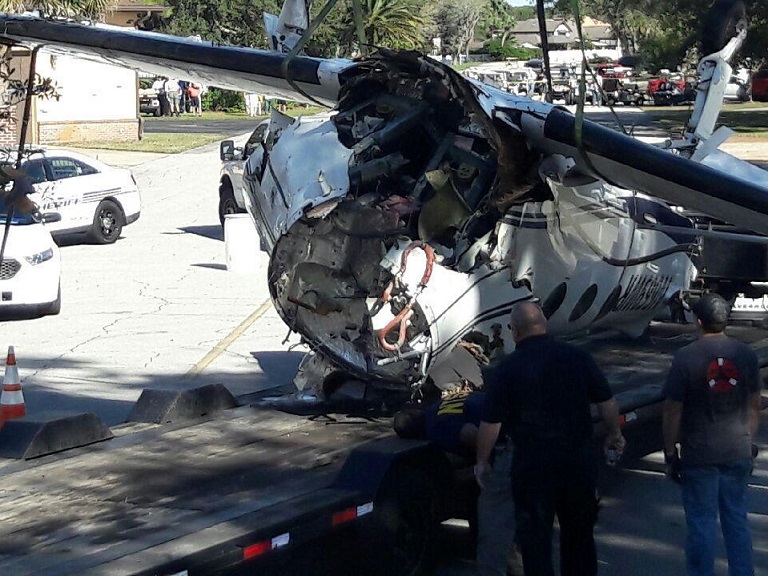
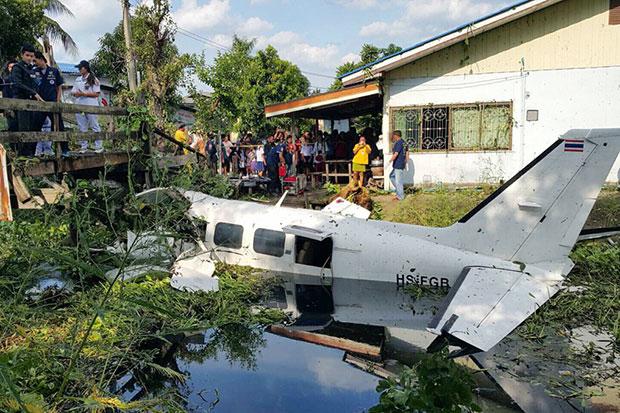
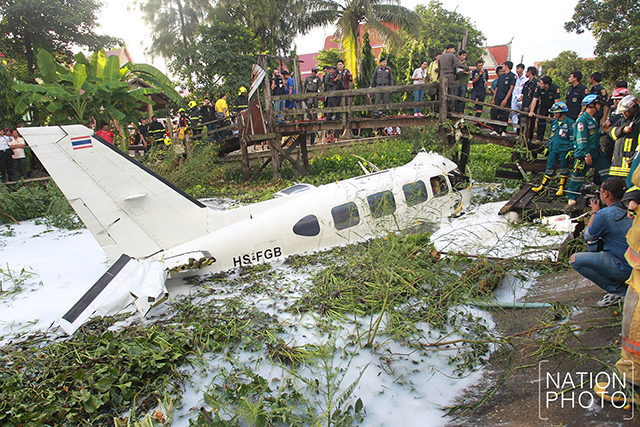
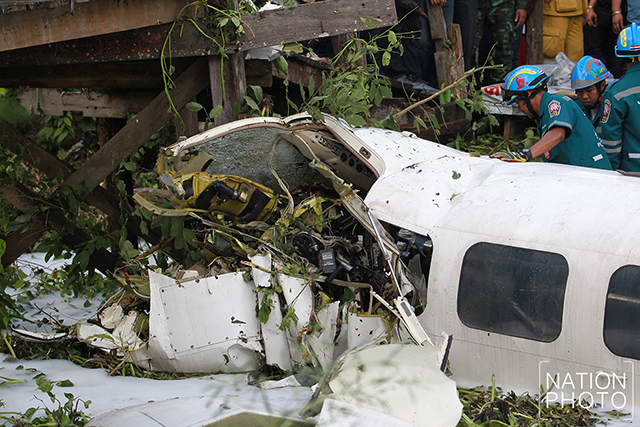
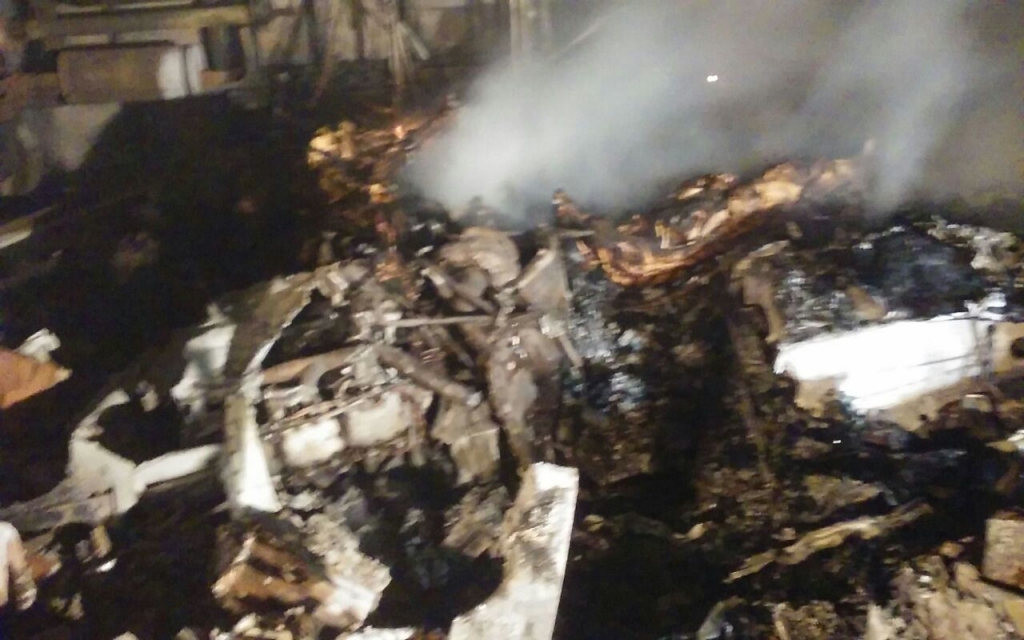
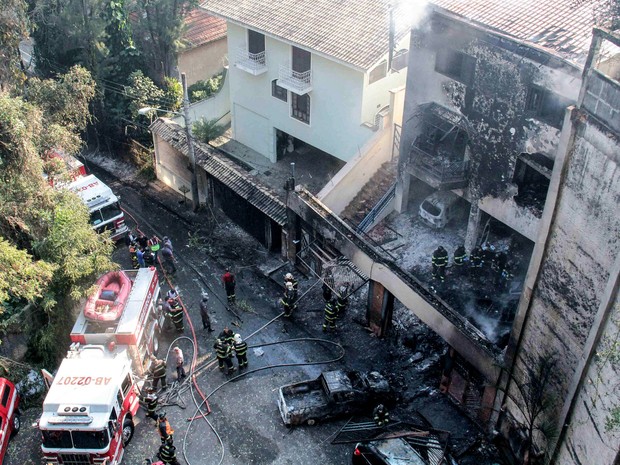
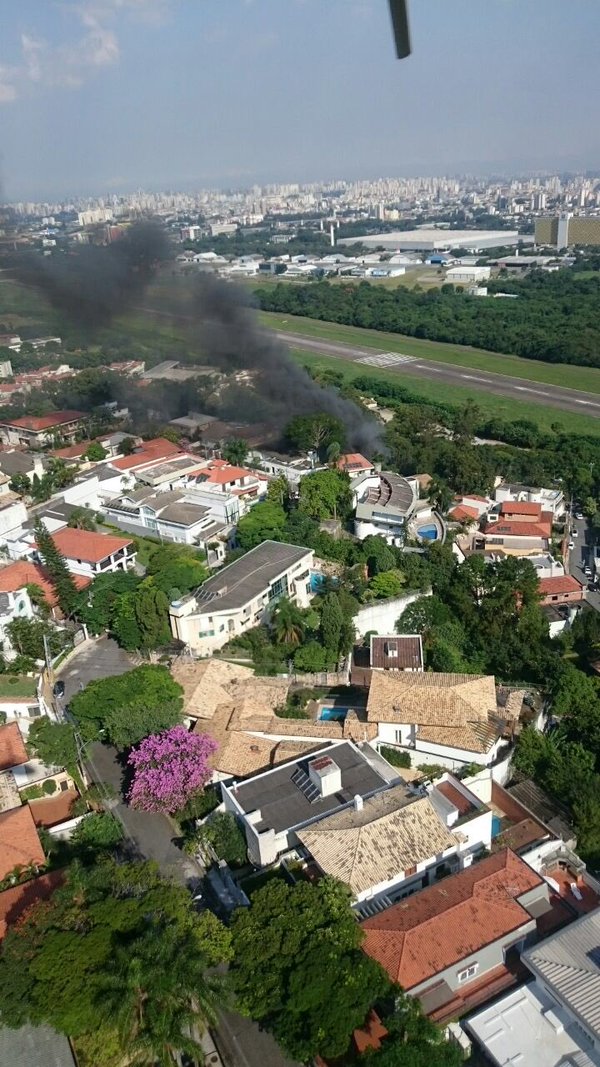
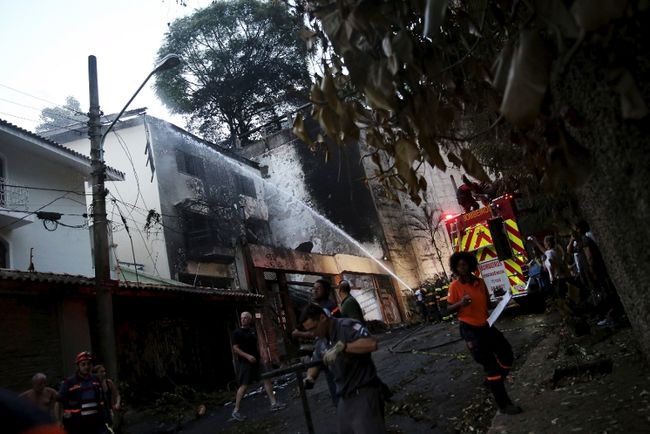
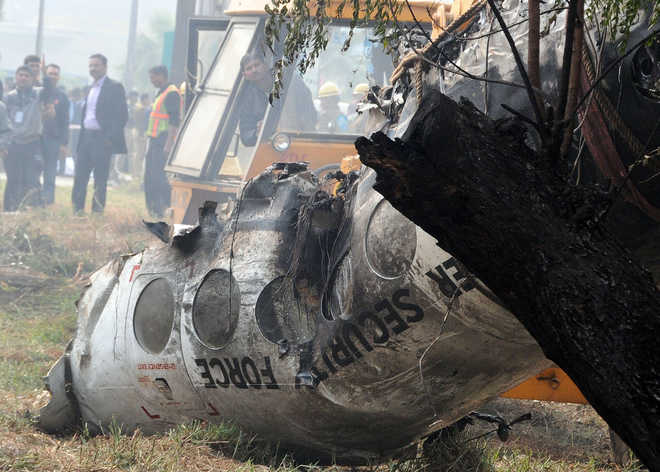
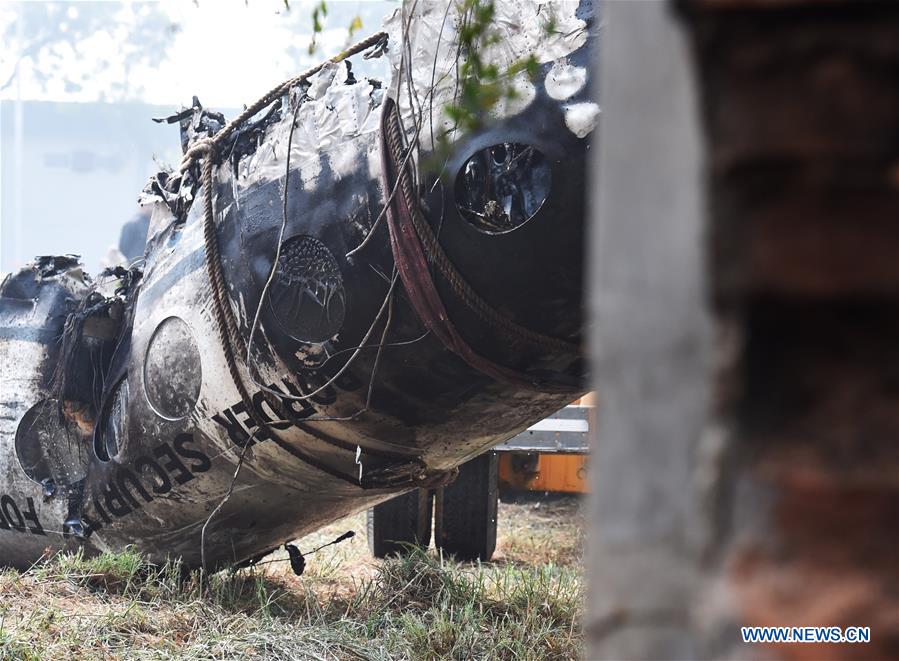
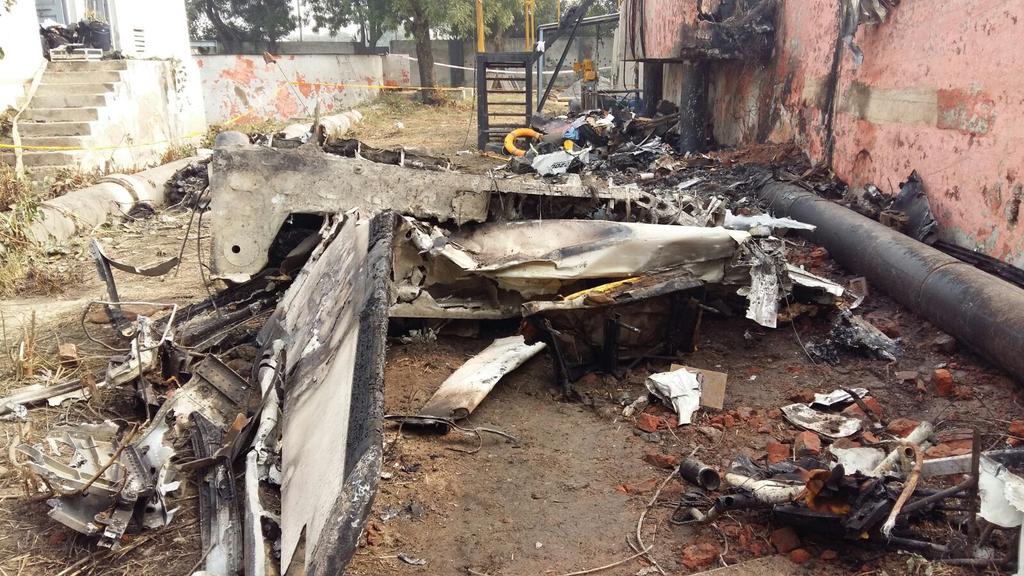
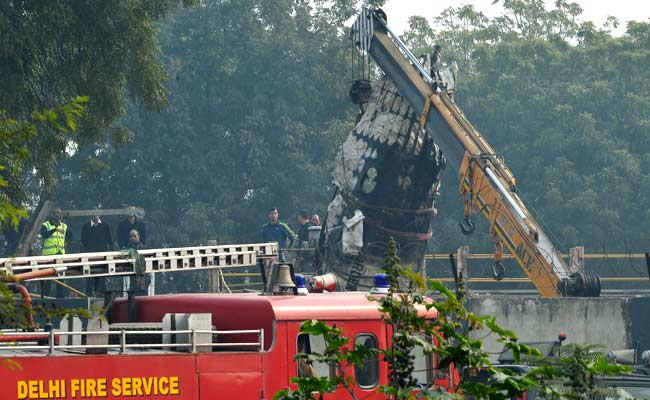
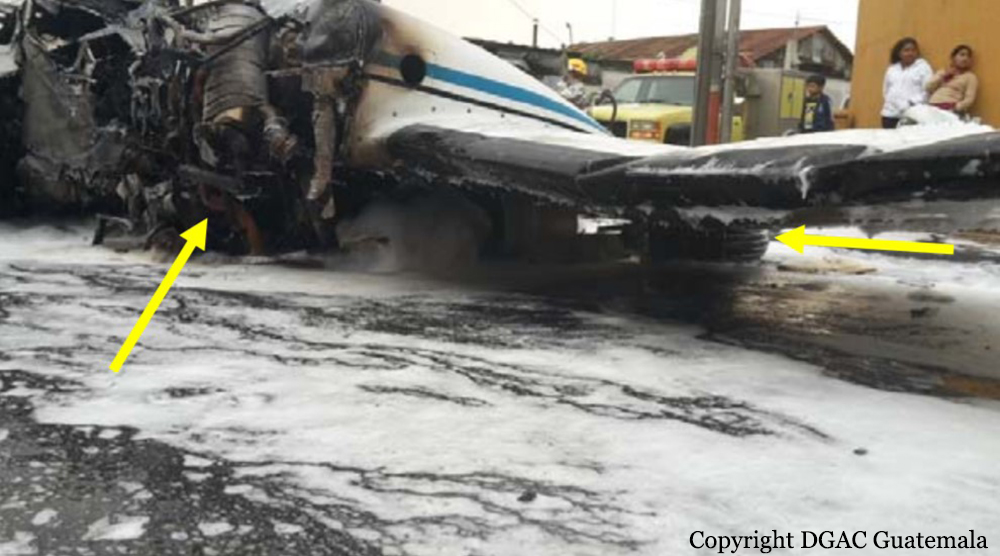
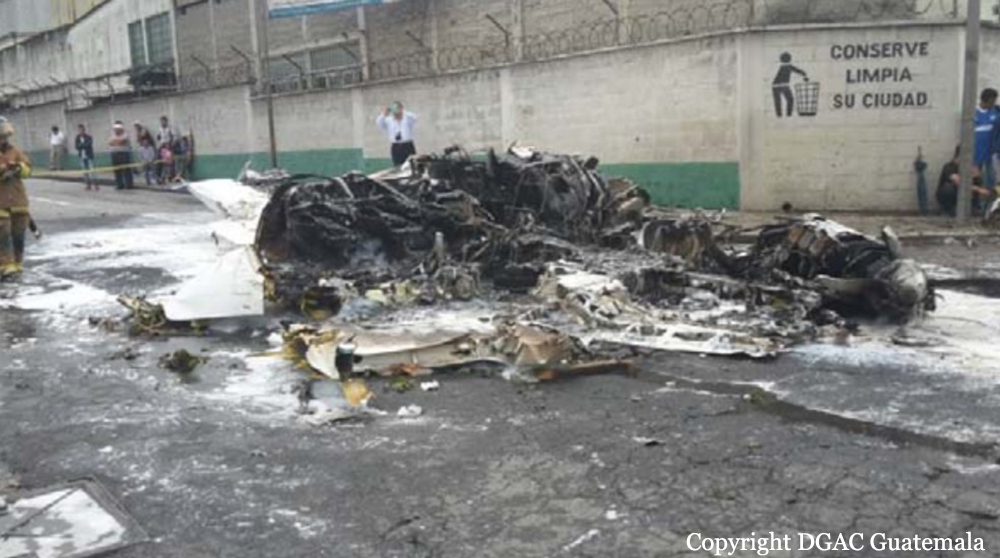
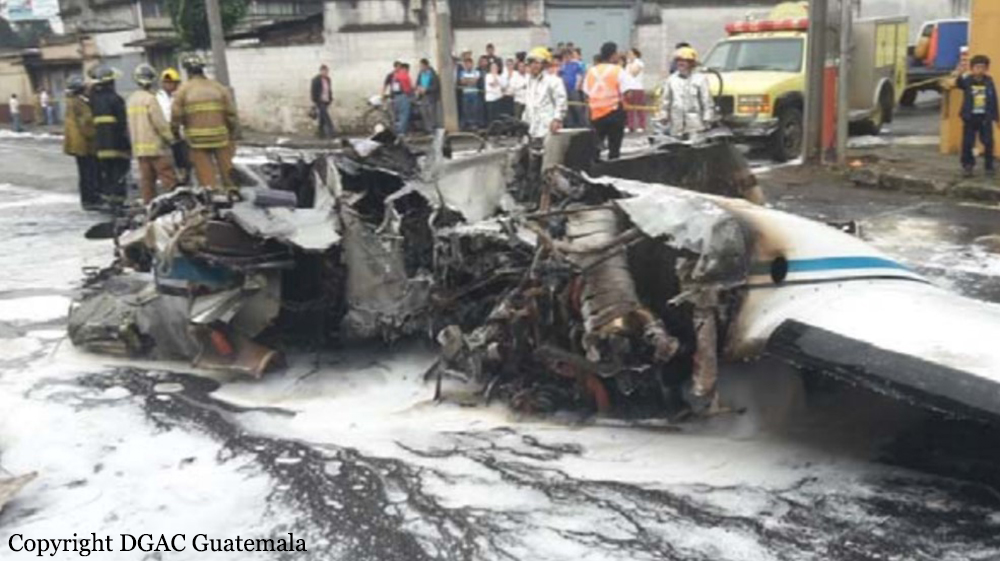
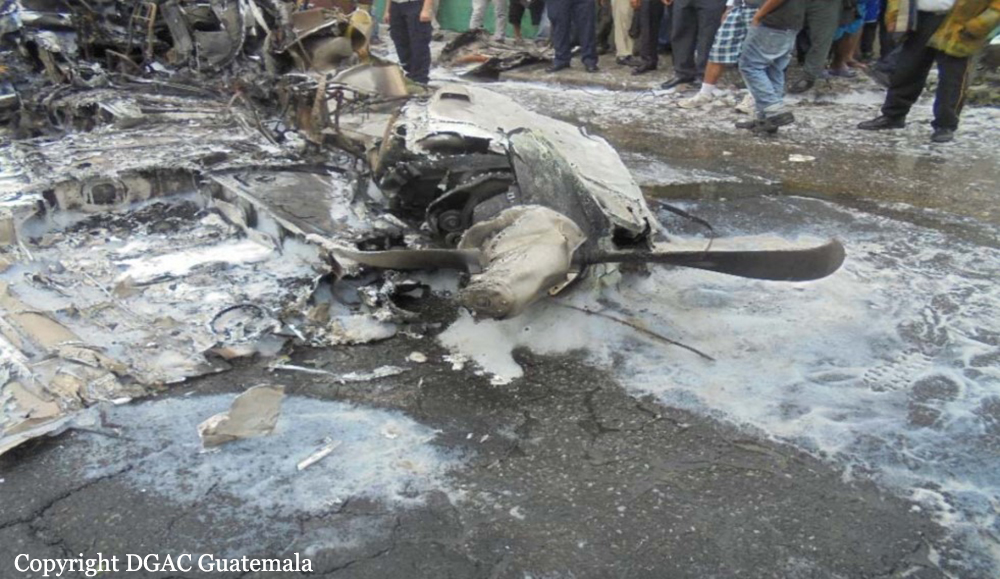
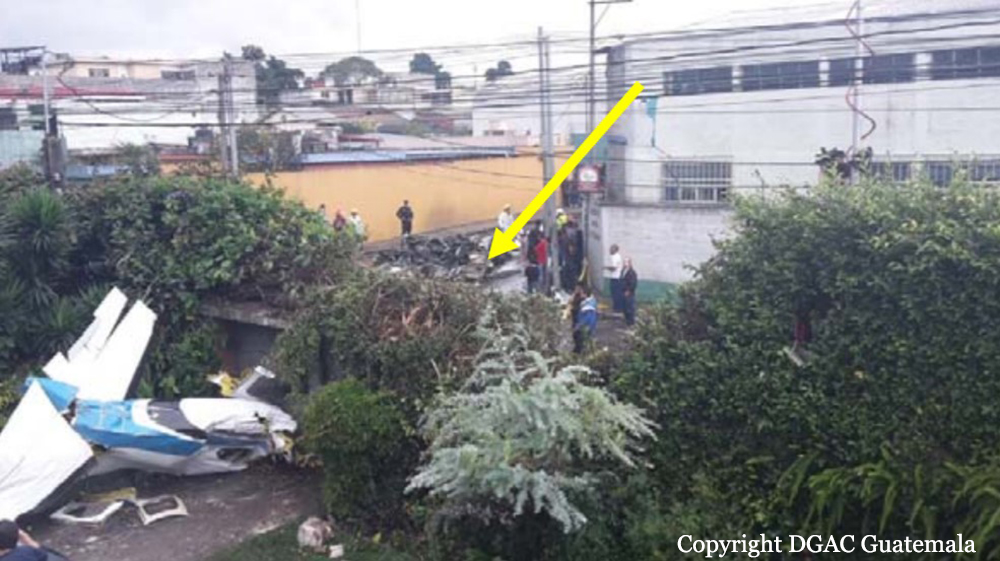
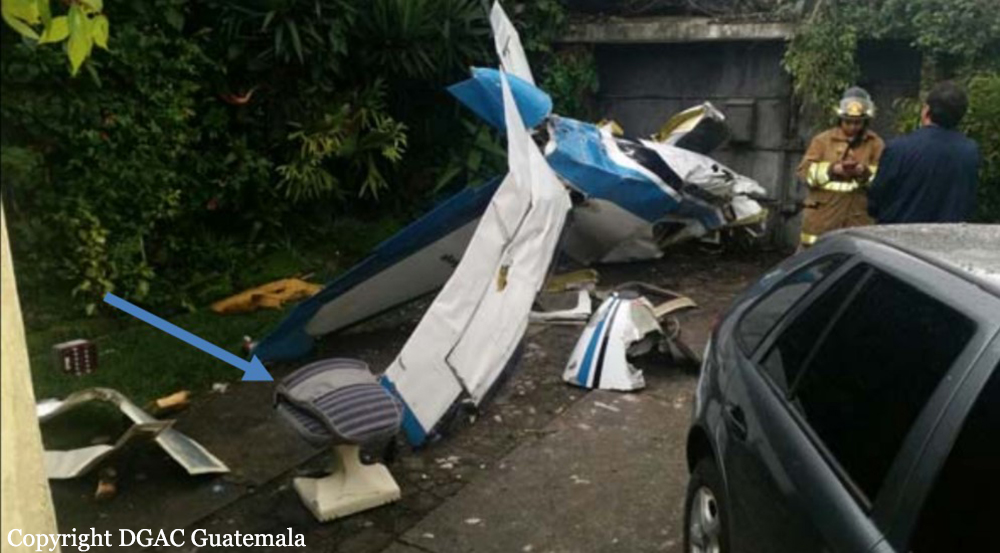
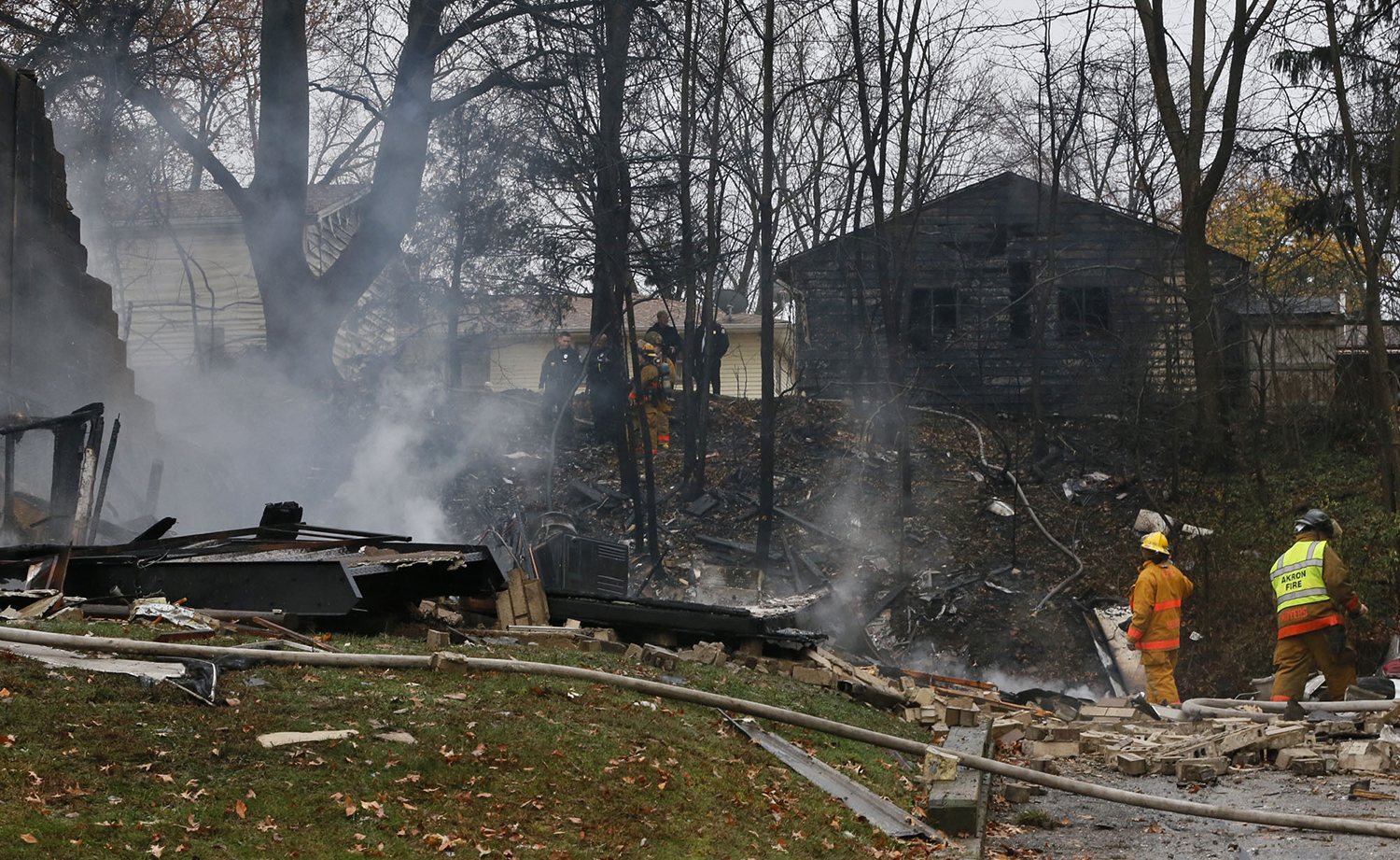
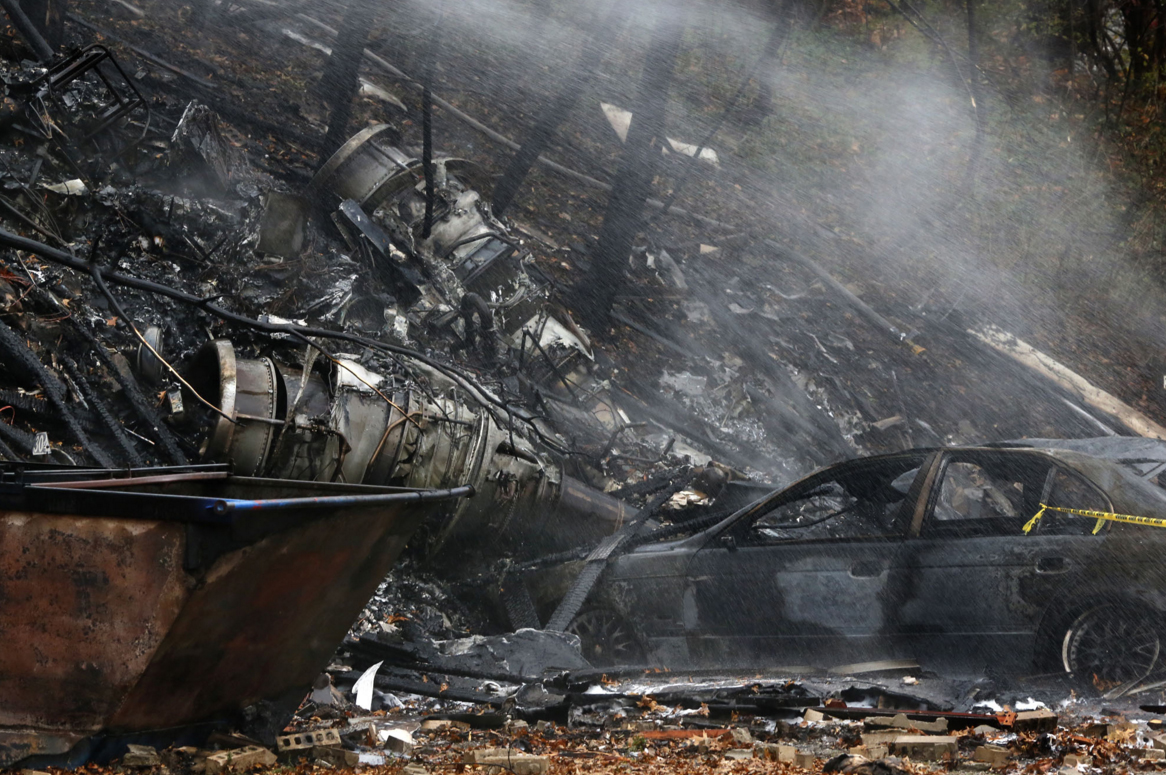
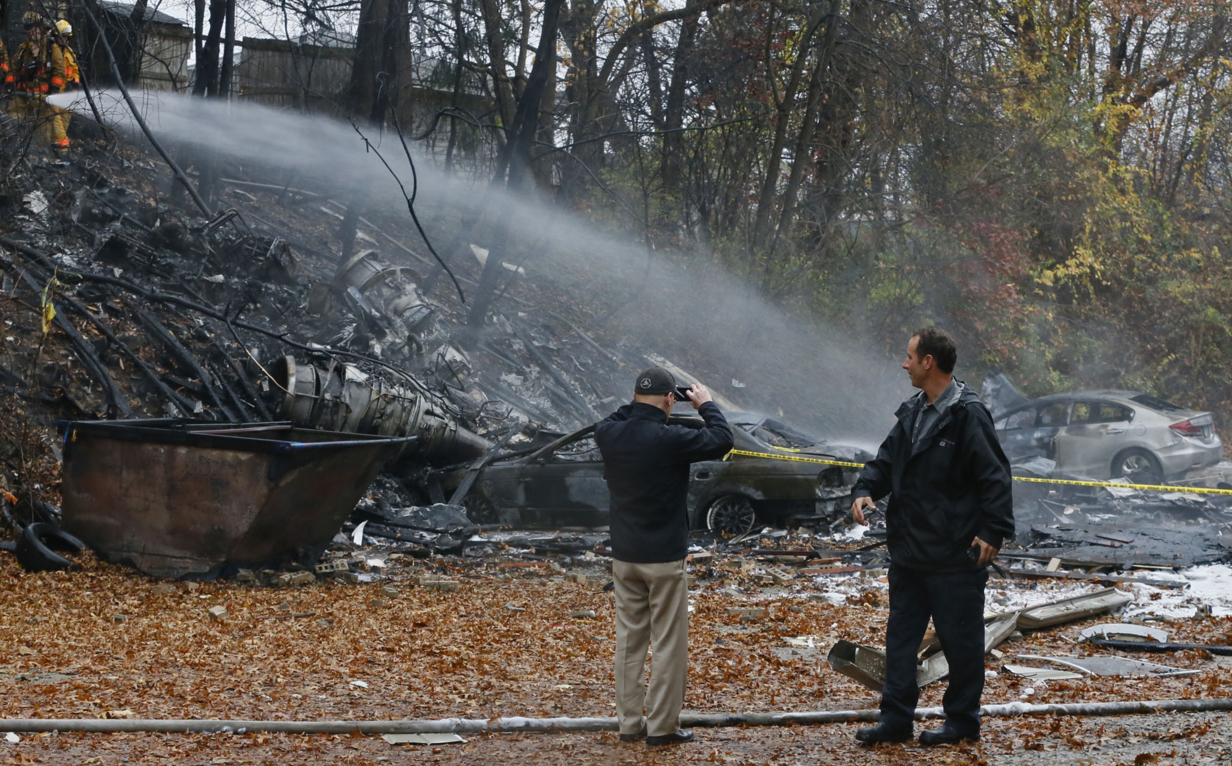
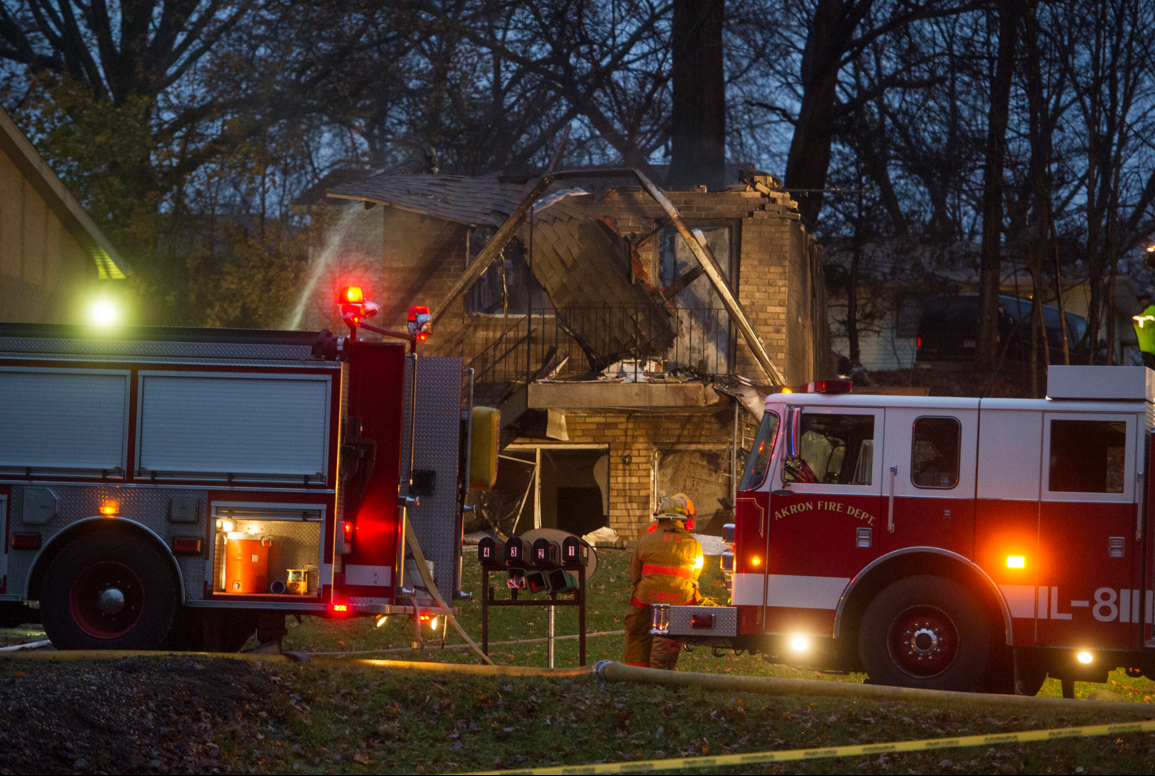
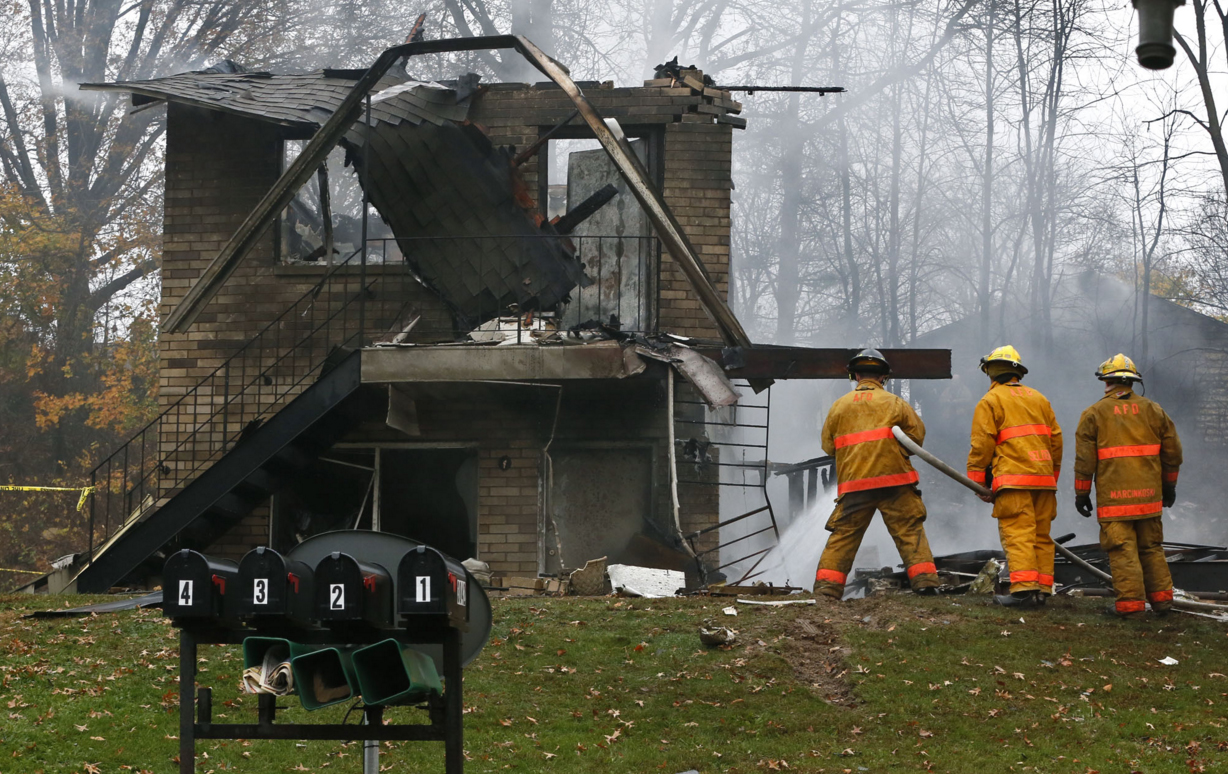
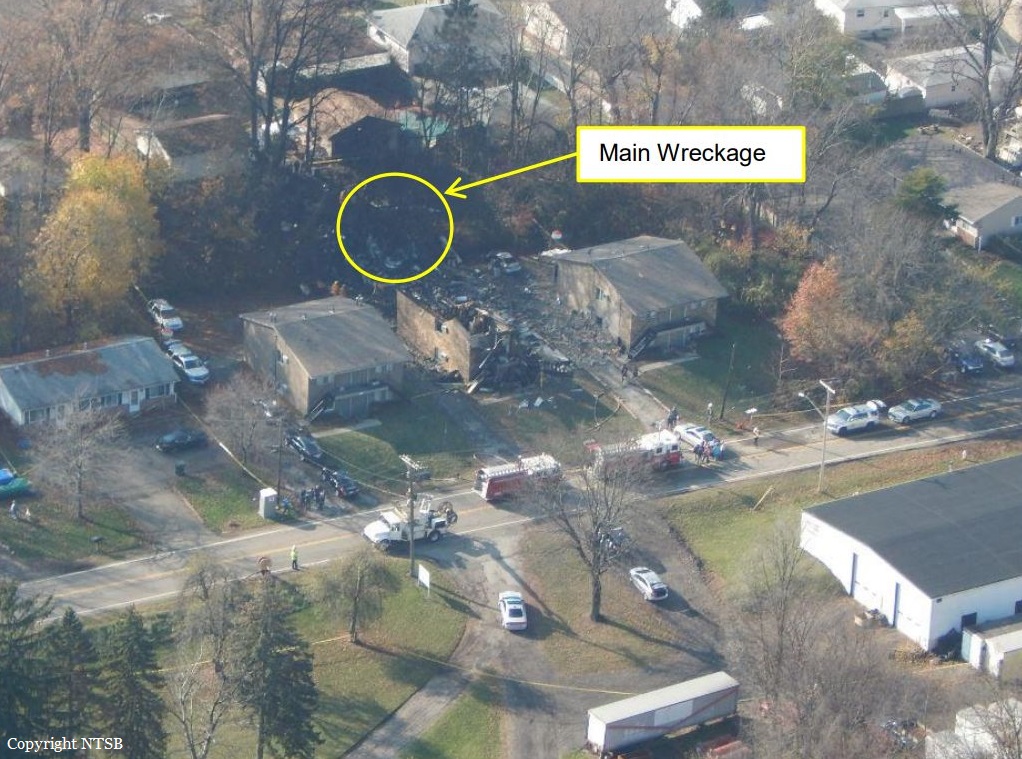
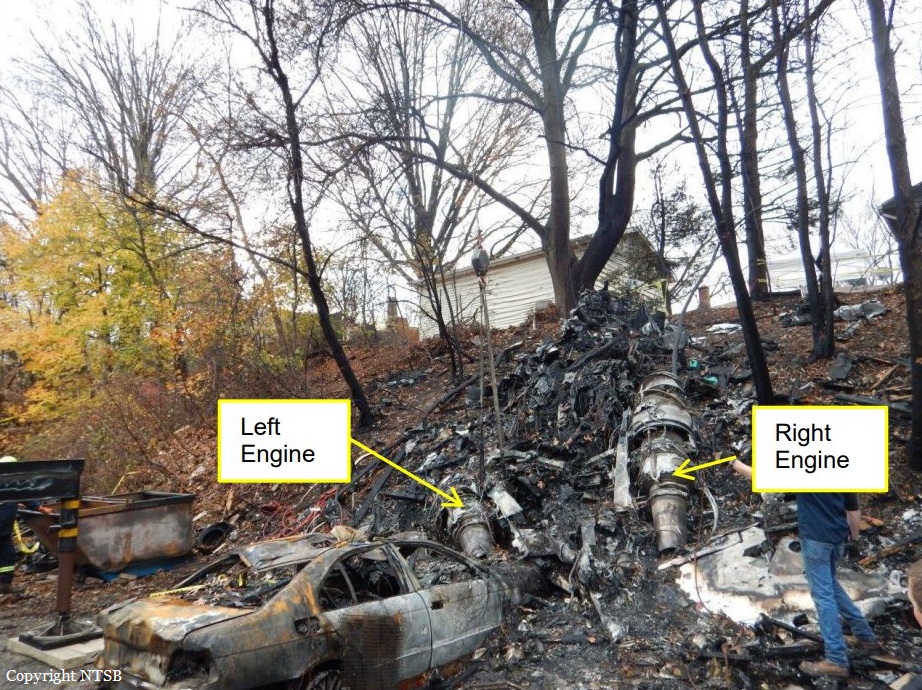
On 21 February 2017, the pilot of a Beechcraft B200 King Air aircraft, registered VH-ZCR (ZCR), and operated by Corporate & Leisure Aviation, was conducting a charter passenger flight from Essendon Airport, Victoria to King Island, Tasmania. There were four passengers on board. ZCR had been removed from a hangar and parked on the apron the previous afternoon in preparation for the flight. The pilot was first seen on the apron at about 0706 Eastern Daylight-saving Time. Closed-circuit television recorded the pilot walking around the aircraft and entering the cabin, consistent with conducting a pre-flight inspection of the aircraft. At about 0712, the pilot entered ZCR’s maintenance provider’s hangar. A member of staff working in the hangar reported that the pilot had a conversation with him that was unrelated to the accident flight. The pilot exited the hangar about 0715 and had a conversation with another member of staff who reported that their conversation was also unrelated to the accident flight. The pilot then returned to ZCR, and over the next 4 minutes he was observed walking around the aircraft. The pilot went into the cabin and re-appeared with an undistinguishable item. The pilot then walked around the aircraft one more time before re-entering the cabin and closing the air stair cabin door. At about 0729, the right engine was started and, shortly after, the left engine was started. Airservices Australia (Airservices) audio recordings indicated that, at 0736, the pilot requested a clearance from Essendon air traffic control (ATC) to reposition ZCR to the southern end of the passenger terminal. ATC provided the clearance and the pilot commenced taxiing to the terminal. At the terminal, ZCR was refueled and the pilot was observed on CCTV to walk around the aircraft, stopping at the left and right engines before entering the cabin. The pilot was then observed to leave the aircraft and wait for the passengers at the terminal. The passengers arrived at the terminal at 0841 and were escorted by the pilot directly to the aircraft. At 0849, the left engine was started and, shortly after, the right engine was started. At 0853, the pilot requested a taxi clearance for King Island, with five persons onboard, under the instrument flight rules. ATC instructed the pilot to taxi to holding point 'TANGO' for runway 17, and provided an airways clearance for the aircraft to King Island with a visual departure. The pilot read back the clearance. Airservices Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast (ADS-B) data (refer to section titled Air traffic services information - Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast data) indicated that, at 0854, ZCR was taxied from the terminal directly to the holding point. The aircraft did not enter the designated engine run-up bay positioned near holding point TANGO. At 0855, while holding at TANGO, the pilot requested a transponder code. The controller replied that he did not have one to issue yet. Two minutes later the pilot contacted ATC and stated that he was ready and waiting for a transponder code. The controller responded with the transponder code and a clearance to lineup on runway 17. At 0858, ATC cleared ZCR for take-off on runway 17 with departure instructions to turn right onto a heading of 200°. The pilot read back the instruction and commenced the takeoff roll. The aircraft’s take-off roll along runway 17 was longer than expected. Witnesses familiar with the aircraft type observed a noticeable yaw to the left after the aircraft became airborne. The aircraft entered a relatively shallow climb and the landing gear remained down. The shallow climb was followed by a substantial left sideslip, while maintaining a roll attitude of less than 10° to the left. Airservices ADS-B data indicated the aircraft reached a maximum height of approximately 160 ft above ground level while tracking in an arc to the left of the runway centreline. The aircraft’s track began diverging to the left of the runway centreline before rotation and the divergence increased as the flight progressed. Following the sustained left sideslip, the aircraft began to descend and at 0858:48 the pilot transmitted on the Essendon Tower frequency repeating the word ‘MAYDAY’ seven times in rapid succession. Approximately 10 seconds after the aircraft became airborne, and 2 seconds after the transmission was completed, the aircraft collided with the roof of a building in the Essendon Airport Bulla Road Precinct - Retail Outlet Centre (outlet centre), coming to rest in a loading area at the rear of the building. CCTV footage from a camera positioned at the rear of the building showed the final part of the accident sequence with post-impact fire evident; about 2 minutes later, first responders arrived onsite. At about 0905 and 0908 respectively, Victoria Police and the Metropolitan Fire Brigade arrived. The pilot and passengers were fatally injured and the aircraft was destroyed. There was significant structural, fire and water damage to the building. Additionally, two people on the ground received minor injuries and a number of parked vehicles were damaged.
Probable cause:
From the evidence available, the following findings are made with respect to the collision with terrain involving Beechcraft B200 King Air, registered VH-ZCR that occurred at Essendon Airport, Victoria on 21 February 2017. These findings should not be read as apportioning blame or liability to any particular organisation or individual.
Contributing factors:
- The aircraft's rudder trim was likely in the full nose-left position at the commencement of the take-off.
- The aircraft's full nose-left rudder trim setting was not detected by the pilot prior to take-off.
- Following a longer than expected ground roll, the pilot took-off with full left rudder trim selected. This configuration adversely affected the aircraft's climb performance and controllability, resulting in a collision with terrain.
Other factors that increased risk:
- The flight check system approval process did not identify that the incorrect checklist was nominated in the operator’s procedures manual and it did not ensure the required checks, related to the use of the cockpit voice recorder, were incorporated.
- The aircraft's cockpit voice recorder did not record the accident flight, resulting in a valuable source of safety related information not being available.
- The aircraft's maximum take-off weight was likely exceeded by about 240 kilograms.
- Two of the four buildings within the Bulla Road Precinct Retail Outlet Centre exceeded the obstacle limitation surface (OLS) for Essendon Airport, however, the OLS for the departure runway was not infringed and VH-ZCR did not collide with those buildings.
Other findings:
- The presence of the building struck by the aircraft was unlikely to have increased the severity of the outcome of this accident.
- Both of the aircraft’s engines were likely to have been producing high power at impact.
Contributing factors:
- The aircraft's rudder trim was likely in the full nose-left position at the commencement of the take-off.
- The aircraft's full nose-left rudder trim setting was not detected by the pilot prior to take-off.
- Following a longer than expected ground roll, the pilot took-off with full left rudder trim selected. This configuration adversely affected the aircraft's climb performance and controllability, resulting in a collision with terrain.
Other factors that increased risk:
- The flight check system approval process did not identify that the incorrect checklist was nominated in the operator’s procedures manual and it did not ensure the required checks, related to the use of the cockpit voice recorder, were incorporated.
- The aircraft's cockpit voice recorder did not record the accident flight, resulting in a valuable source of safety related information not being available.
- The aircraft's maximum take-off weight was likely exceeded by about 240 kilograms.
- Two of the four buildings within the Bulla Road Precinct Retail Outlet Centre exceeded the obstacle limitation surface (OLS) for Essendon Airport, however, the OLS for the departure runway was not infringed and VH-ZCR did not collide with those buildings.
Other findings:
- The presence of the building struck by the aircraft was unlikely to have increased the severity of the outcome of this accident.
- Both of the aircraft’s engines were likely to have been producing high power at impact.
Final Report: