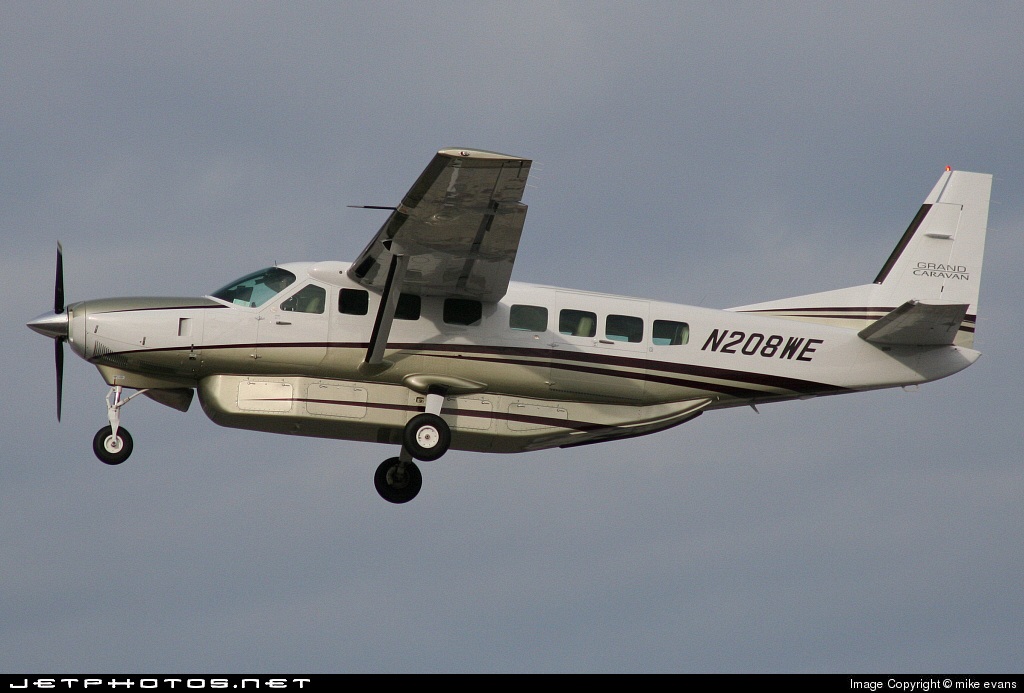
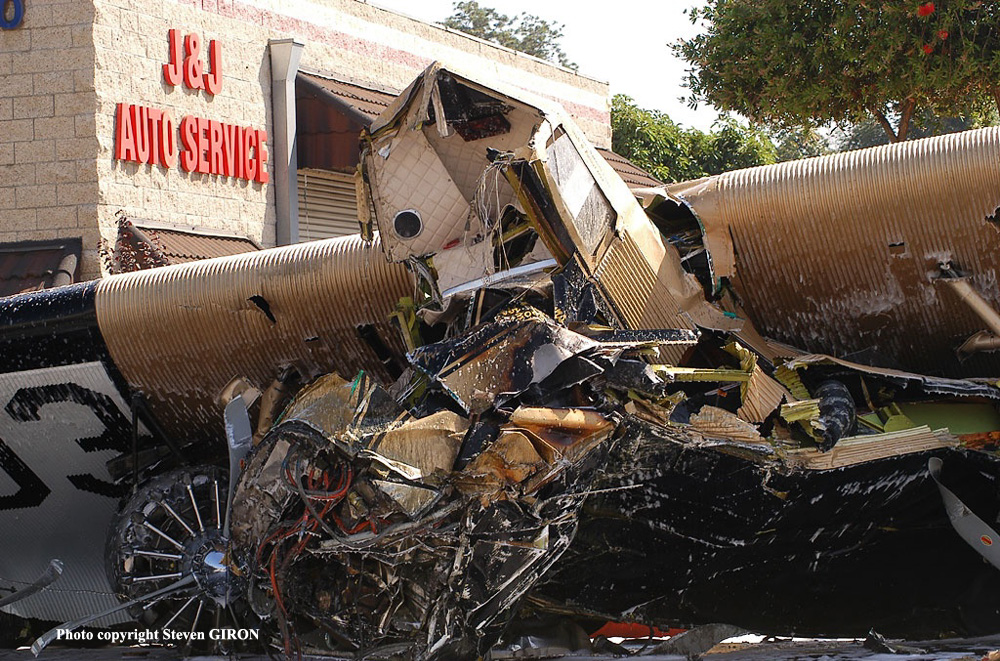
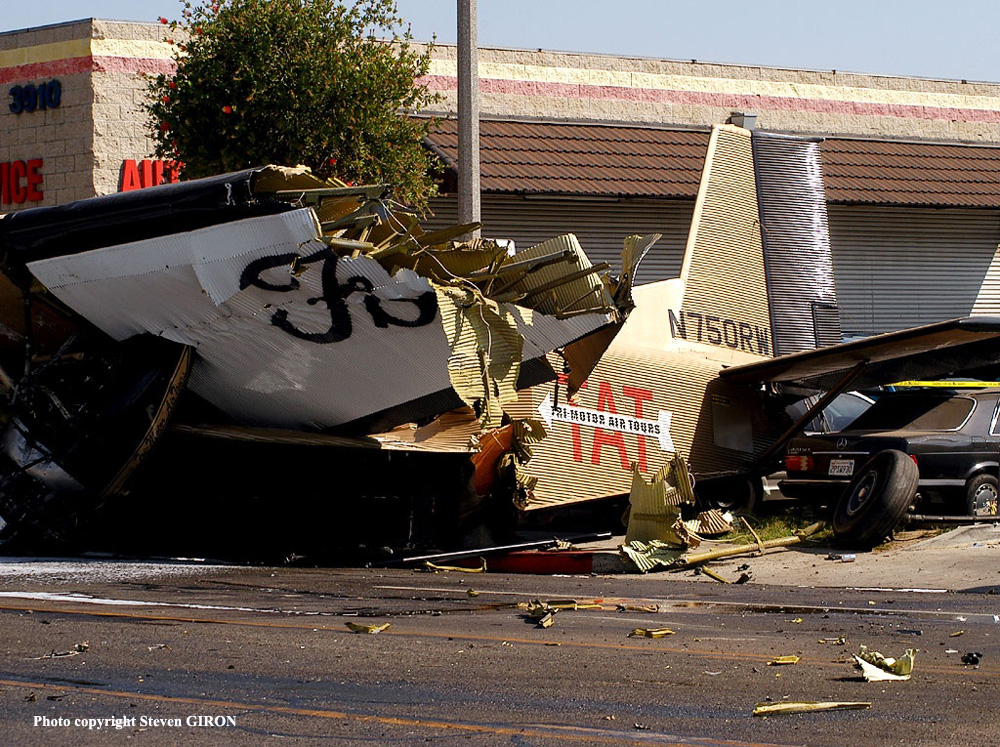
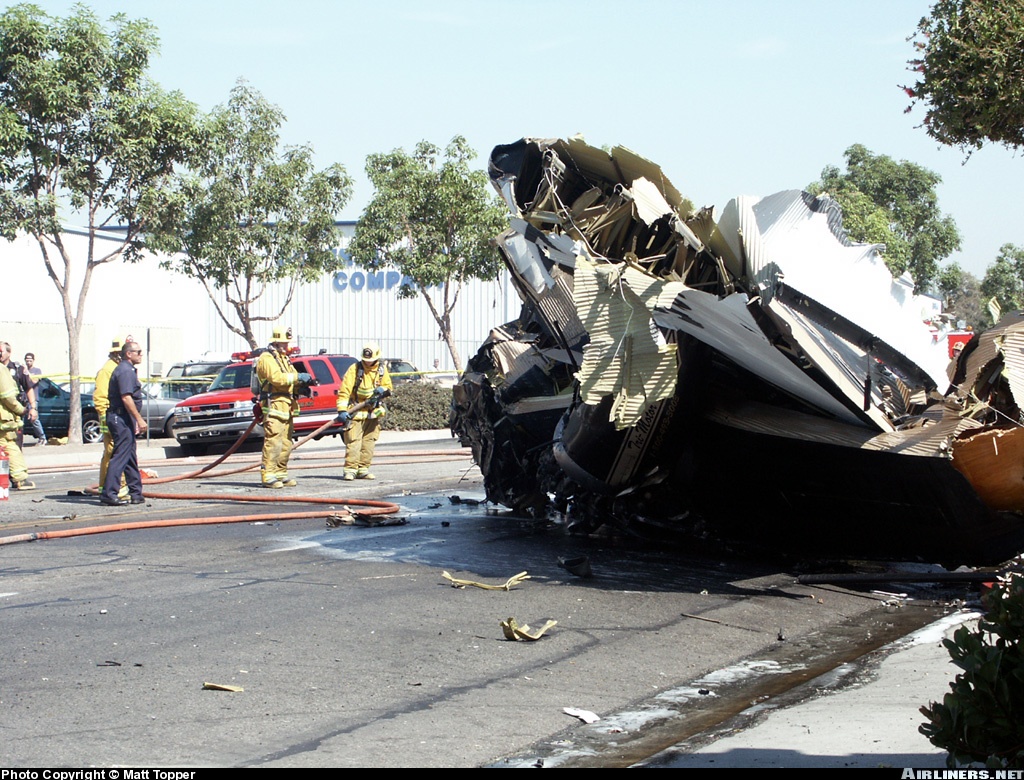
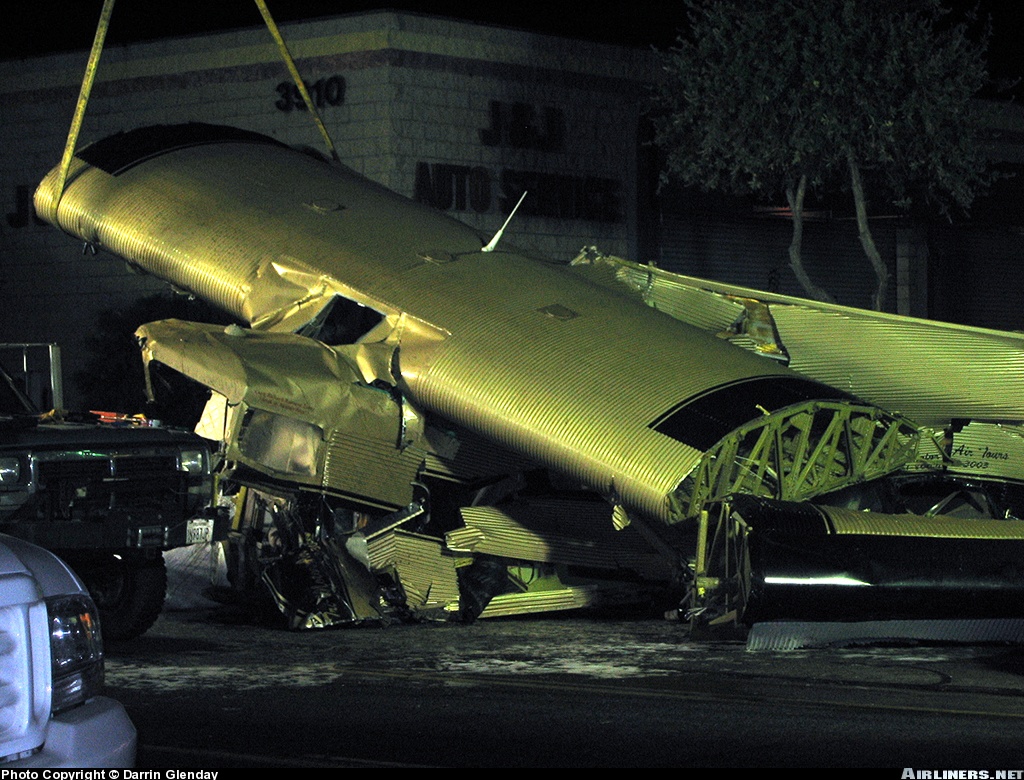
Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Oak Glen: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 28, 2006 at 1655 LT
Registration:
N208WE
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Thermal - Ontario
MSN:
208B-1171
YOM:
2006
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Copilot / Total hours on type:
740
Aircraft flight hours:
52
Circumstances:
The airplane was operated by the manufacturer and was on a sales demonstration itinerary. On the accident flight the airplane was being repositioned following a demonstration and the two pilots included a commercially licensed manufacturer's sales pilot and a private licensed regional sales distributor. One of the two pilots onboard requested, and received, an abbreviated weather briefing prior to departure, the details of which included an airman's meteorological information notice (AIRMET) for occasional moderate rime ice. He then filed an instrument flight rules flight plan for a route passing over mountainous terrain, with a published Minimum En route Altitude (MEA) for the airway that was above the predicted icing level. The flight plan was not activated and the pilots told a TRACON controller who was providing VFR advisories that they intended to continue under visual flight rules through a mountain pass and open their IFR flight plan after reaching the other side of the pass where the MEA was lower. A review of the mode C reported altitudes flown by the pilots and an analysis of the cloud bases and tops revealed that the flight was likely in at least intermittent, if not mostly solid, instrument meteorological conditions as it flew through the pass. As the flight approached the other end of the pass, the controller advised the pilots that the radar showed they were heading into rising terrain. The controller asked, "Do you have the terrain in sight?" One of the pilots responded, "we're maneuvering away from the terrain right now." After that, radar contact was lost. Recorded radar data showed that the airplane made a righthand turn toward rising terrain while continuing to climb to an approximate altitude of 8,800 feet mean sea level (msl). The last minute of radar data showed the airplane at altitudes of 8,000 feet msl, 8,800 feet msl, and 8,600 feet msl. The last radar return was at an altitude of 7,300 feet msl. An aircraft performance study was accomplished using recorded radar data and aerodynamic data provided by Cessna. Based on the radar data and other relevant information, as the aircraft turned toward the rising terrain, the bank angle steadily increased, until a very abrupt change in pitch consistent with a stall occurred, and the airplane departed controlled flight and descended at a very steep nose down attitude into the mountainous terrain. The airplane wreckage was subsequently located at an elevation of 6,073 feet. Nearby ground witnesses first noticed the sound of the airplane, that then suddenly changed to a high pitched increasing rpm. Witnesses then saw the accident airplane coming out of the clouds almost straight nose down. The witnesses described the weather as cold with drizzling rain and reduced visibility due to the clouds. Examination of the wreckage revealed no evidence of mechanical malfunction or failure.
Probable cause:
The pilot's continued flight into instrument meteorological weather conditions and his subsequent failure to maintain an adequate airspeed while maneuvering, that led to a stall/spin.
Final Report: