Circumstances:
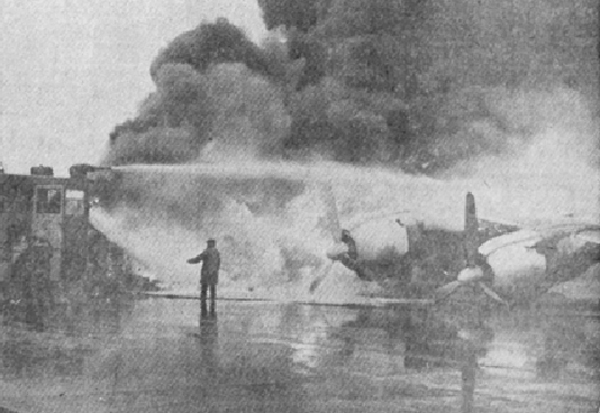
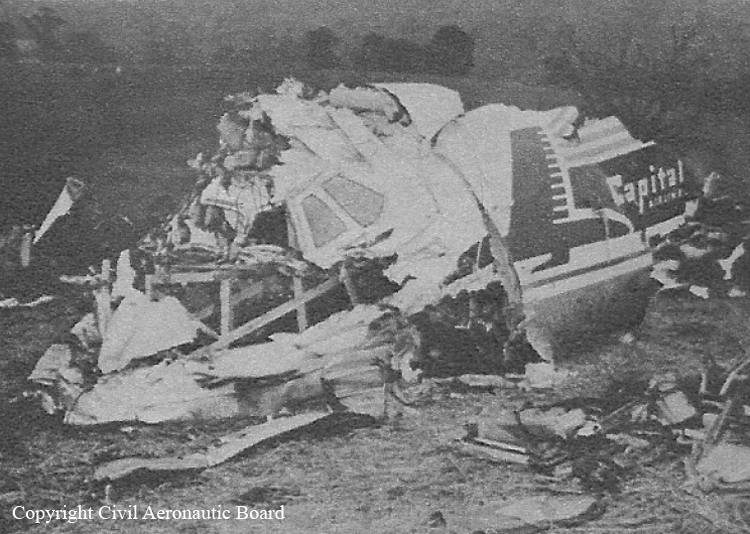
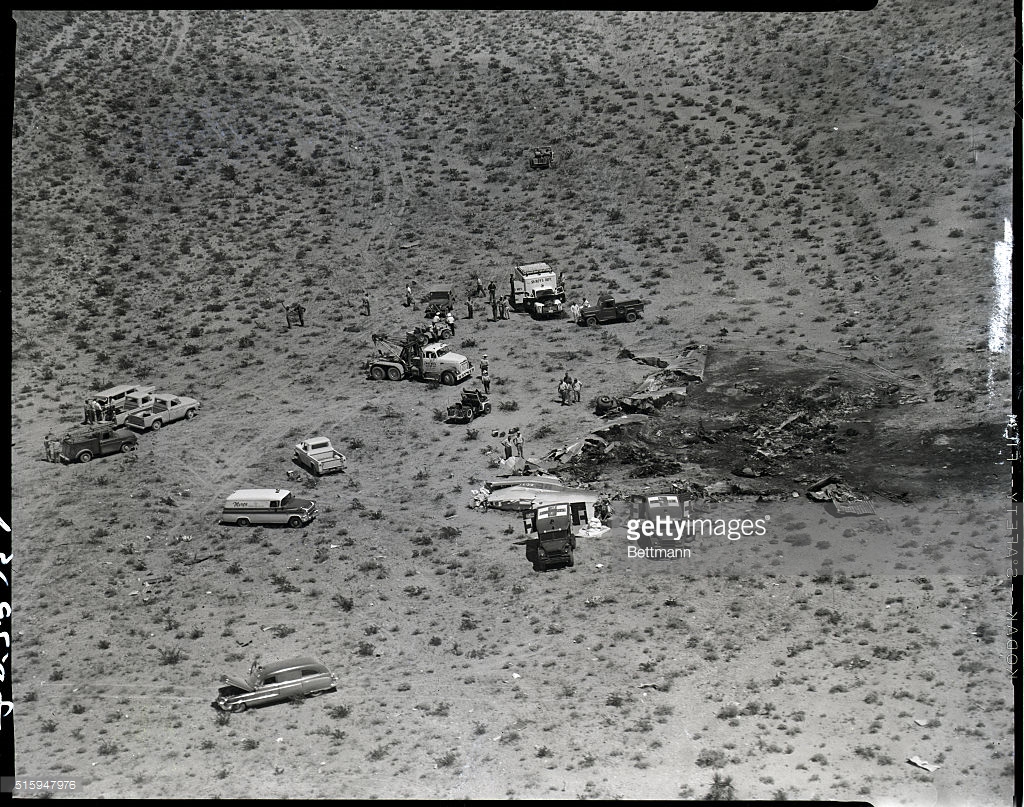
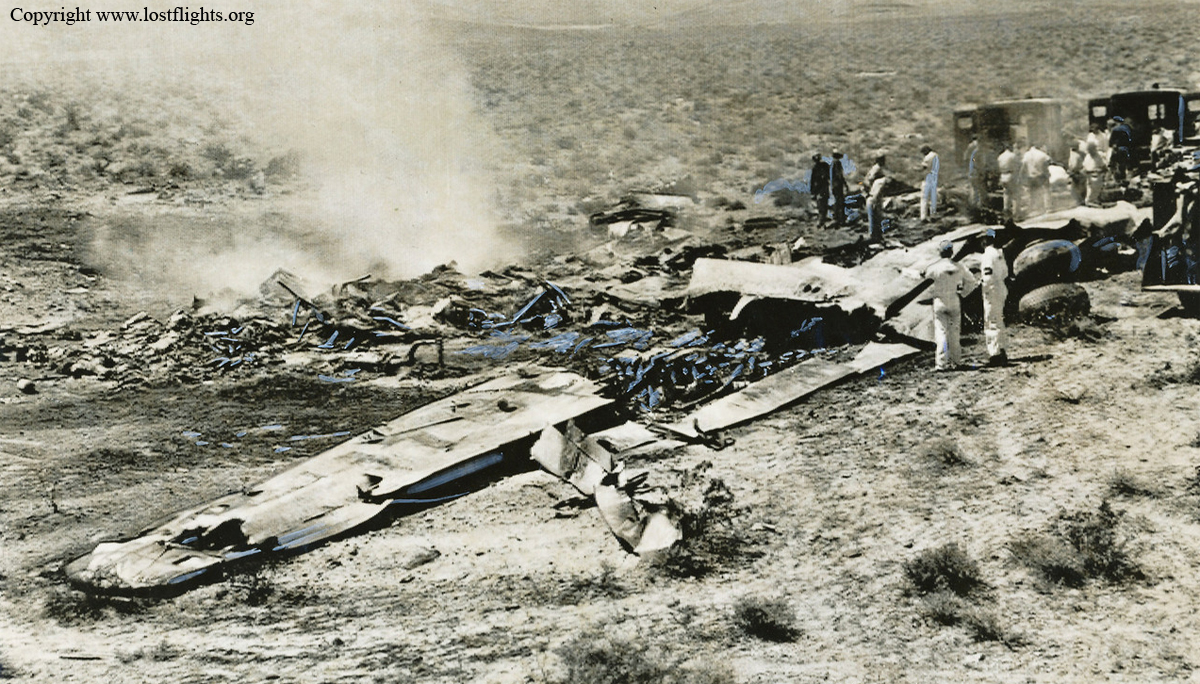
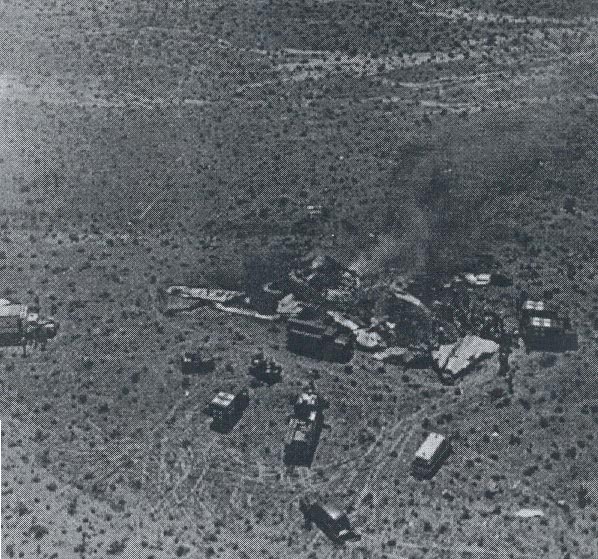
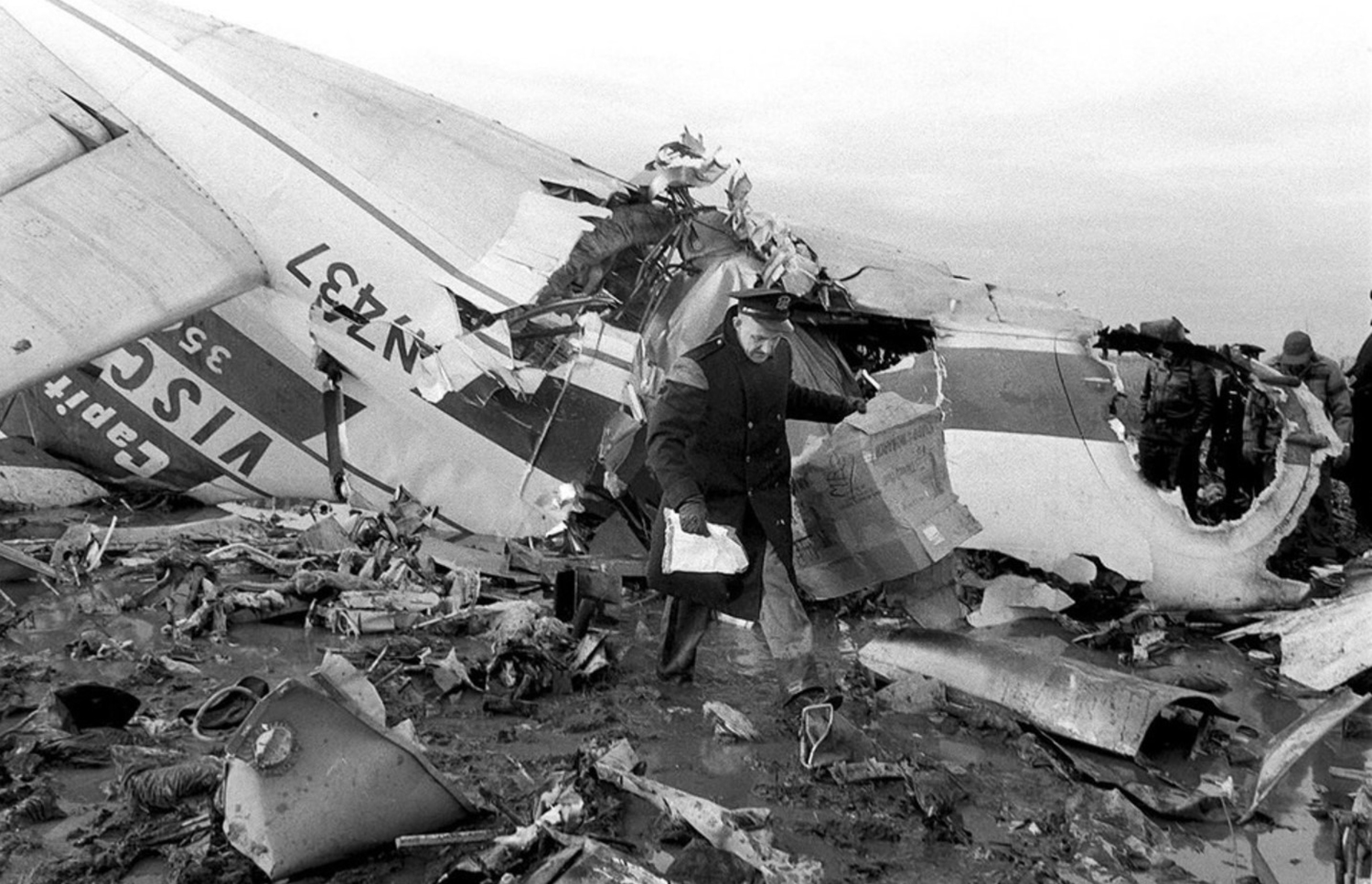
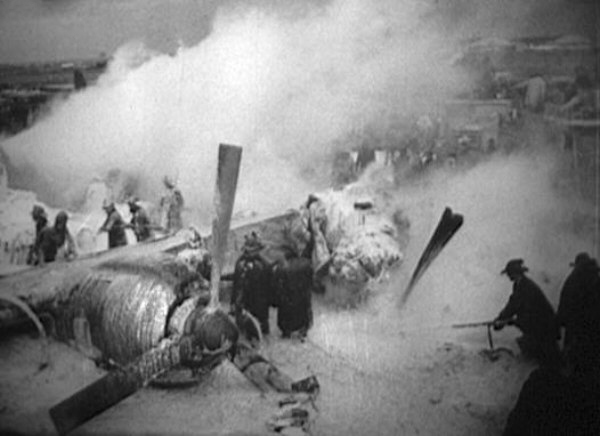
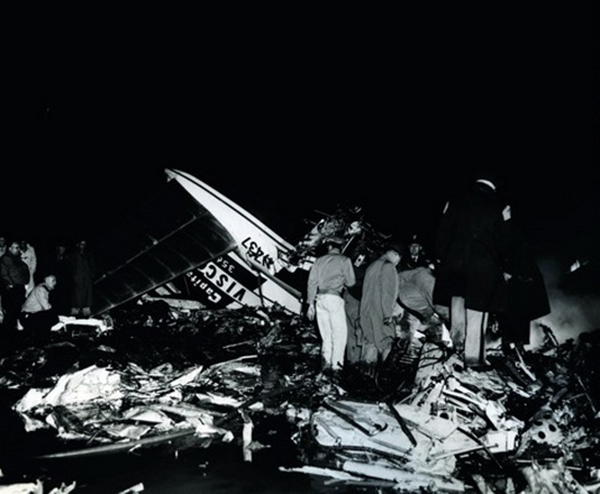
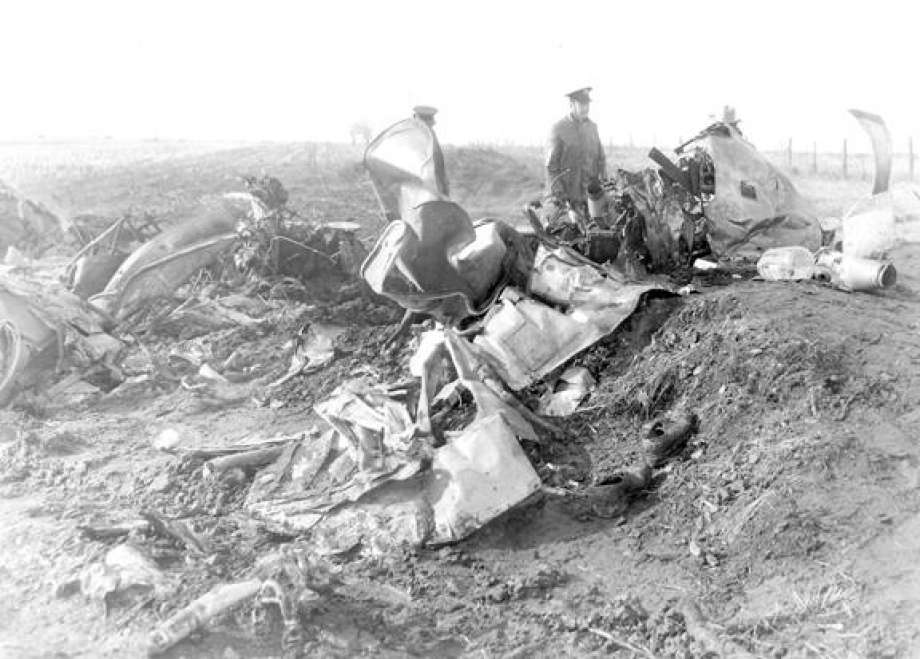
At 2306, four minutes after takeoff, the flight, pursuant to clearance instructions, reported to Flight tower that it was at 3,600 feet and was departing the Flint outer marker. At this time the tower requested the estimated time of arrive at Tri-City and was advised that it was 2315. Flight 67 was then given the following clearance: "ARTC (Air Route Traffic Control) clears Capital 67 to hold north of the Saginaw omni range, one minute pattern, right turn, maintain 3,600 feet. Expect further clearance 2320, change to company frequency for this clearance." This clearance was acknowledged and, as per instructions, the frequency was changed to that of the company at Detroit. At 2310, Capital at Detroit relayed the following clearance to the flight: "ARTC clears Flight 67 for approach at Saginaw (Tri-City) Airport. Report time on the ground to Saginaw radio." These instructions were verified. The flight then called Saginaw ATCS (Air Traffic Communication Station) and was given the local 2300 weather observation and the runway in use, No. 5. The Tri-City Airport does not have a traffic control tower. The 2300 Saginaw weather was reported as: Measured ceiling 900 feet, overcast, visibility 3 miles, light snow showers, temperature 34; dewpoint 33; wind north-northeast 18, peak gusts to 27 knots; altimeter 29.48, comments--drizzle ended and snow showers began at 2225. At 2316 Trip 67 advised Saginaw radio that it was over the airport. A short time later, ground witnesses observed the lights of the aircraft when it was on the downwind leg of the traffic pattern. The aircraft was seen to make a left turn onto base leg and at this time the landing lights of the aircraft were observed to come on. During this portion of the approach the aircraft was flying beneath the overcast, estimated to be 900 feet, and appeared to be descending. When turning on final, Trip 67 flew a short distance beyond the extended centerline of the runway and the turf was seen to steepen for realignment with the runway. Soon after this the aircraft was observed to level off and then to descend steeply and strike the ground. A large fire immediately erupted. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all 47 occupants have been killed.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was an undetected accretion of ice on the horizontal stabilizer which, in conjunction with a specific airspeed and aircraft configuration, caused a loss of pitch control.