Crash of a Piper PA-46-350P Malibu Mirage in the Gulf of Mexico
Date & Time:
Dec 4, 2010 at 1430 LT
Registration:
N350MM
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Cozumel – New Orleans
MSN:
46-22105
YOM:
1990
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
516.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
750
Aircraft flight hours:
2936
Circumstances:
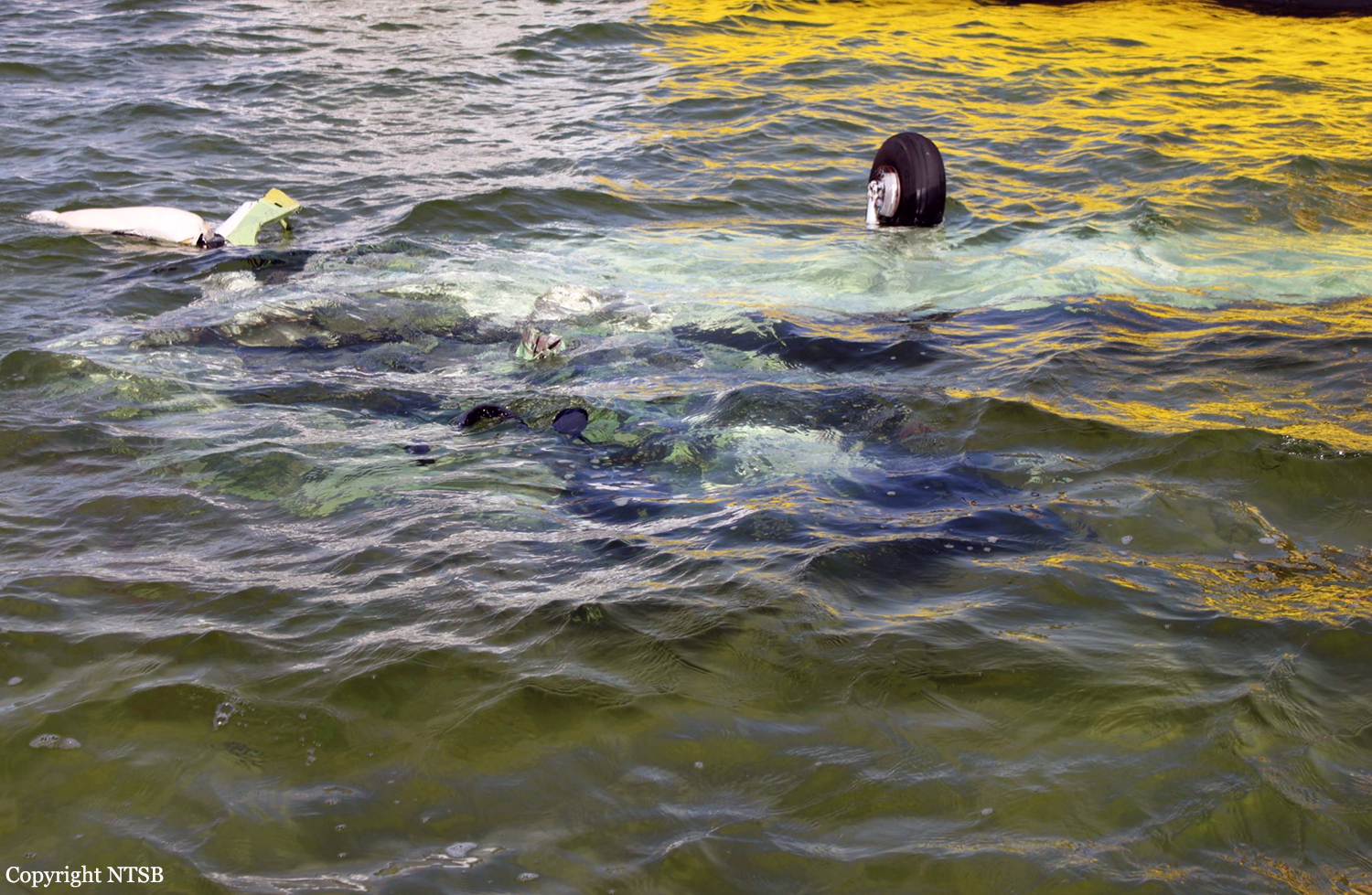
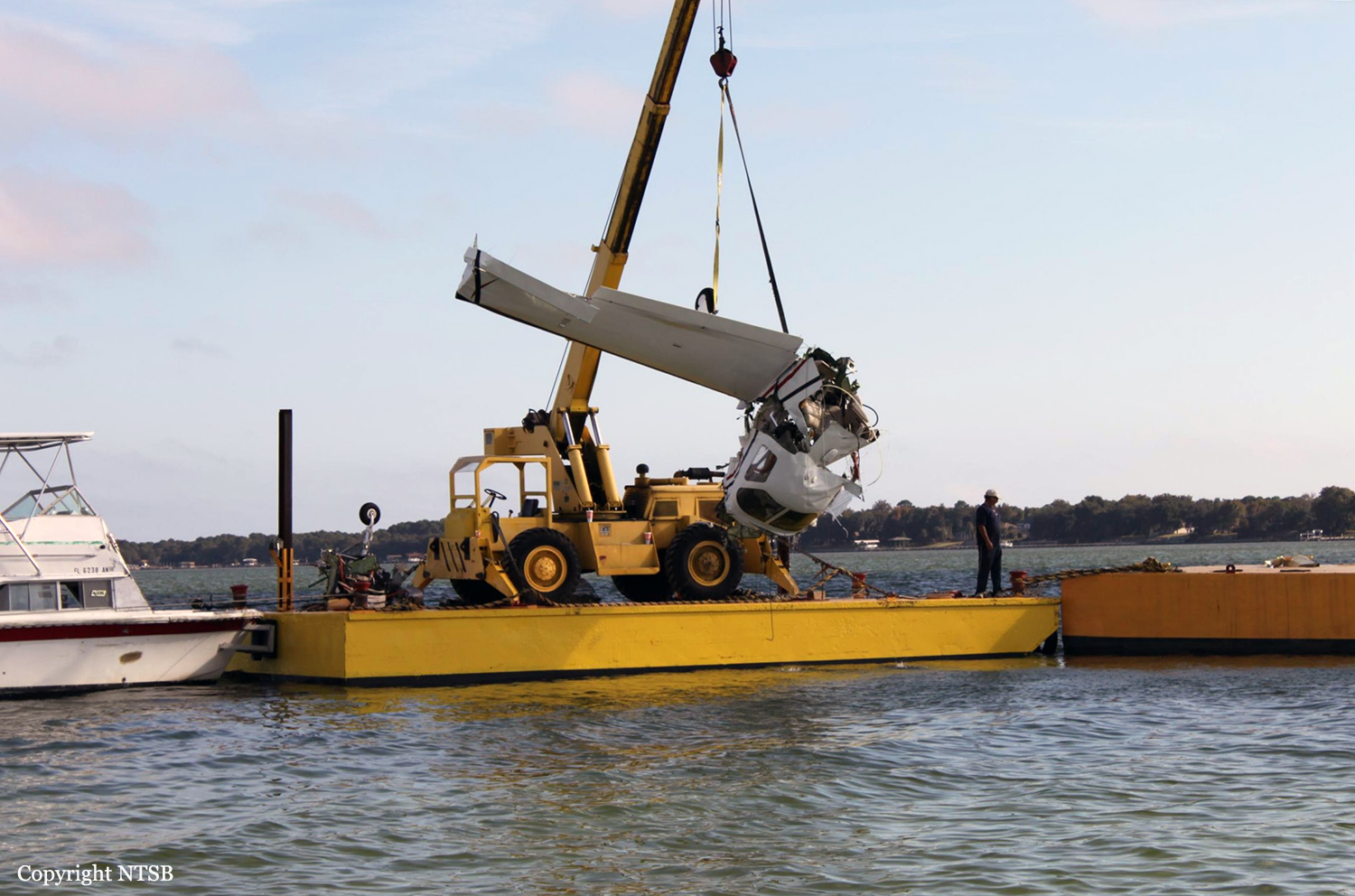
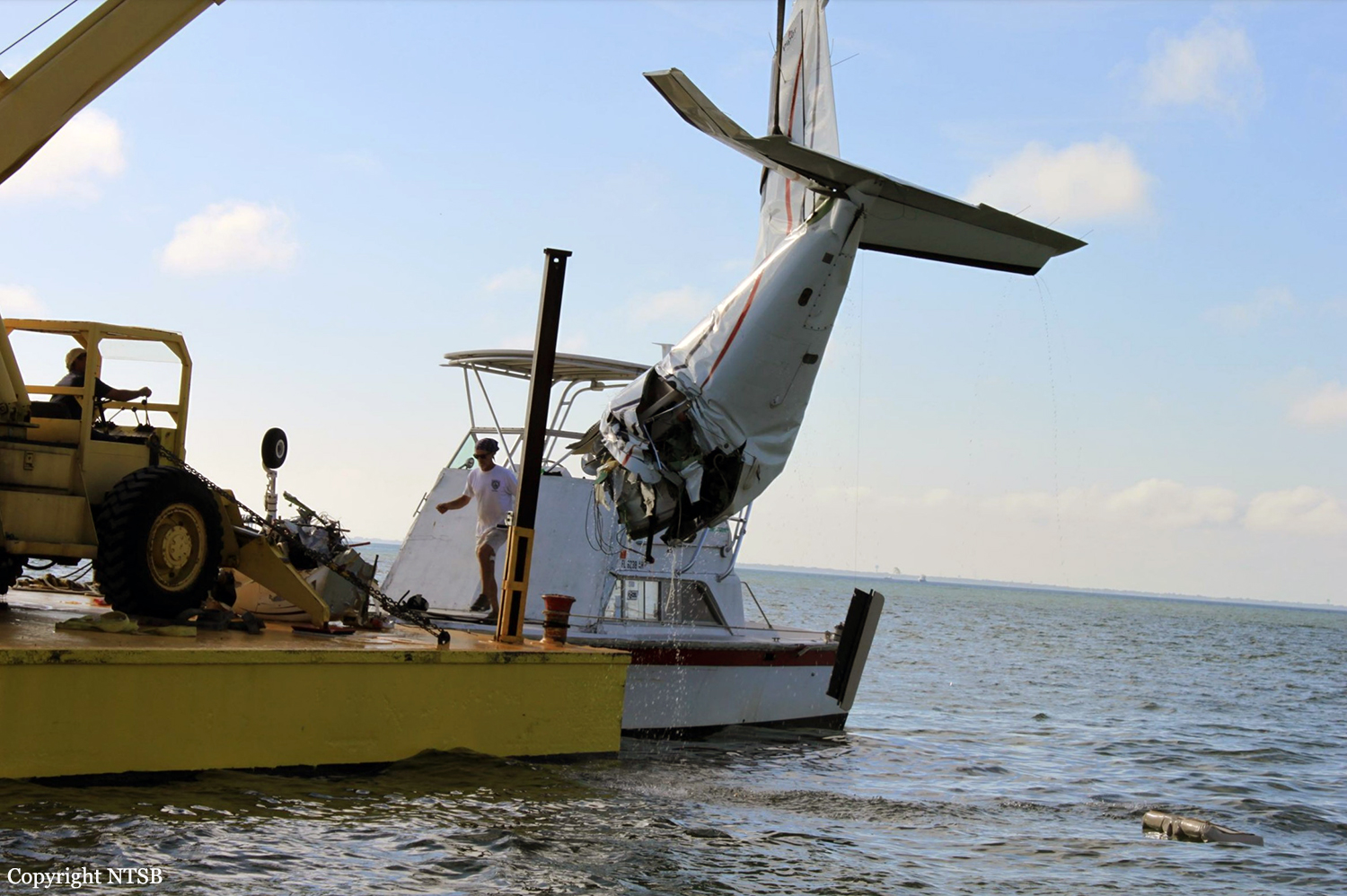
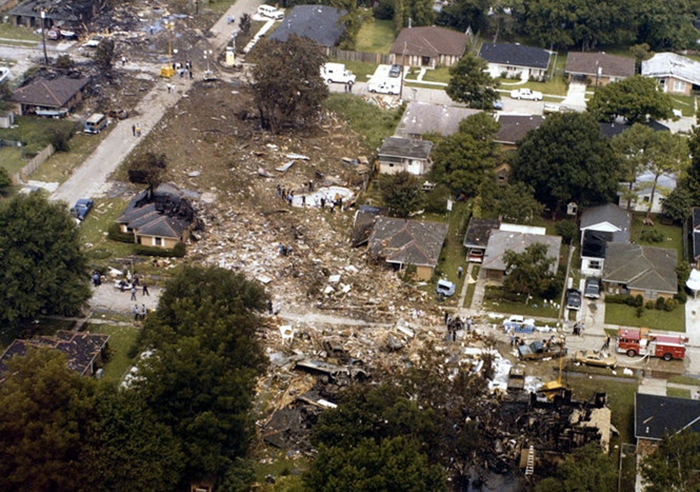
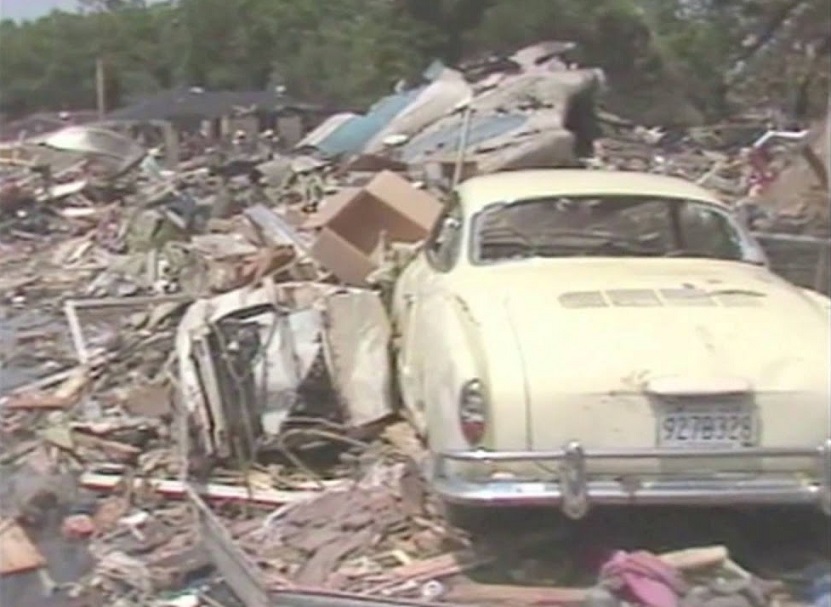
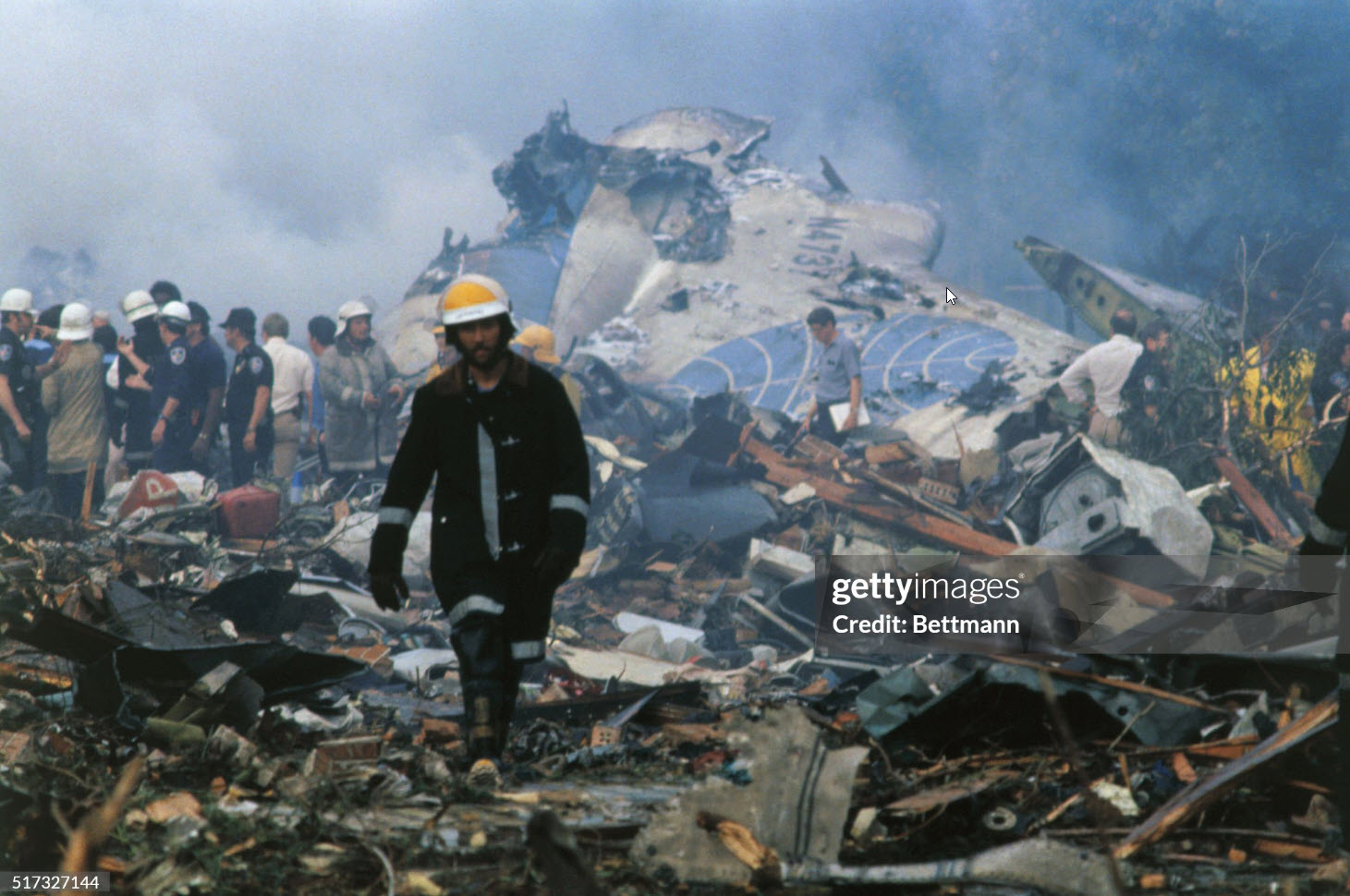
About 2 hours into a cross-country flight over water, the pilot heard a noticeable change in engine noise and observed erratic engine torque readings. Moments later the airplane experienced a complete loss of engine power. After declaring an emergency, the pilot attempted to diagnose the problem and restart the engine to no avail. The airplane ditched 175 miles from land, in water over 5,000 feet deep. The airplane was not recovered and the reason for the loss of engine power could not be determined.
Probable cause:
A total loss of engine power for undetermined reasons.
Final Report: