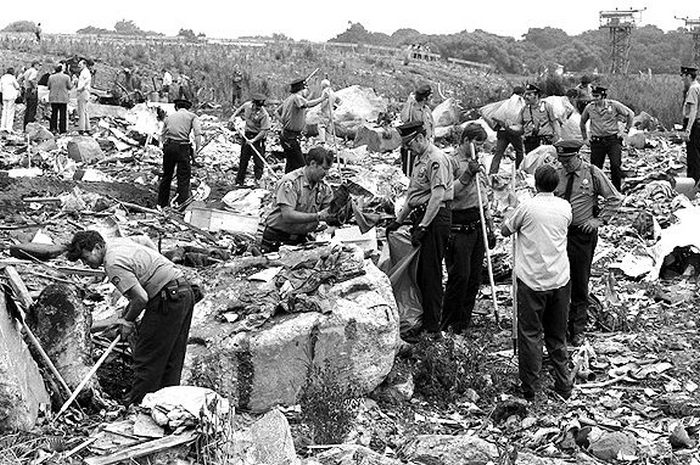
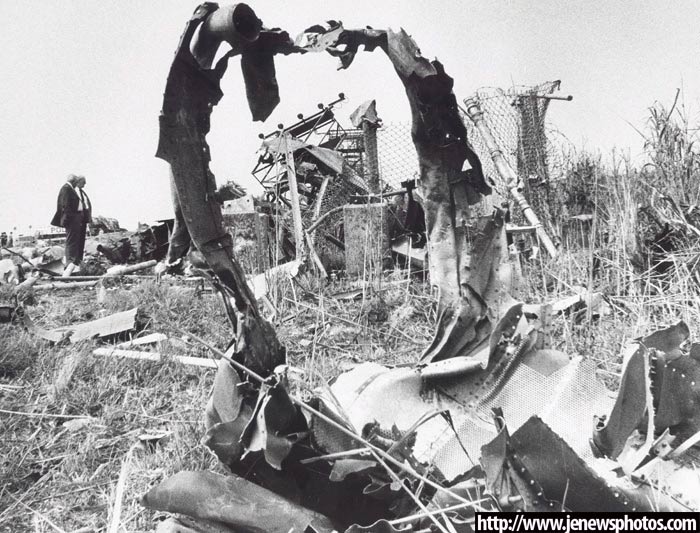
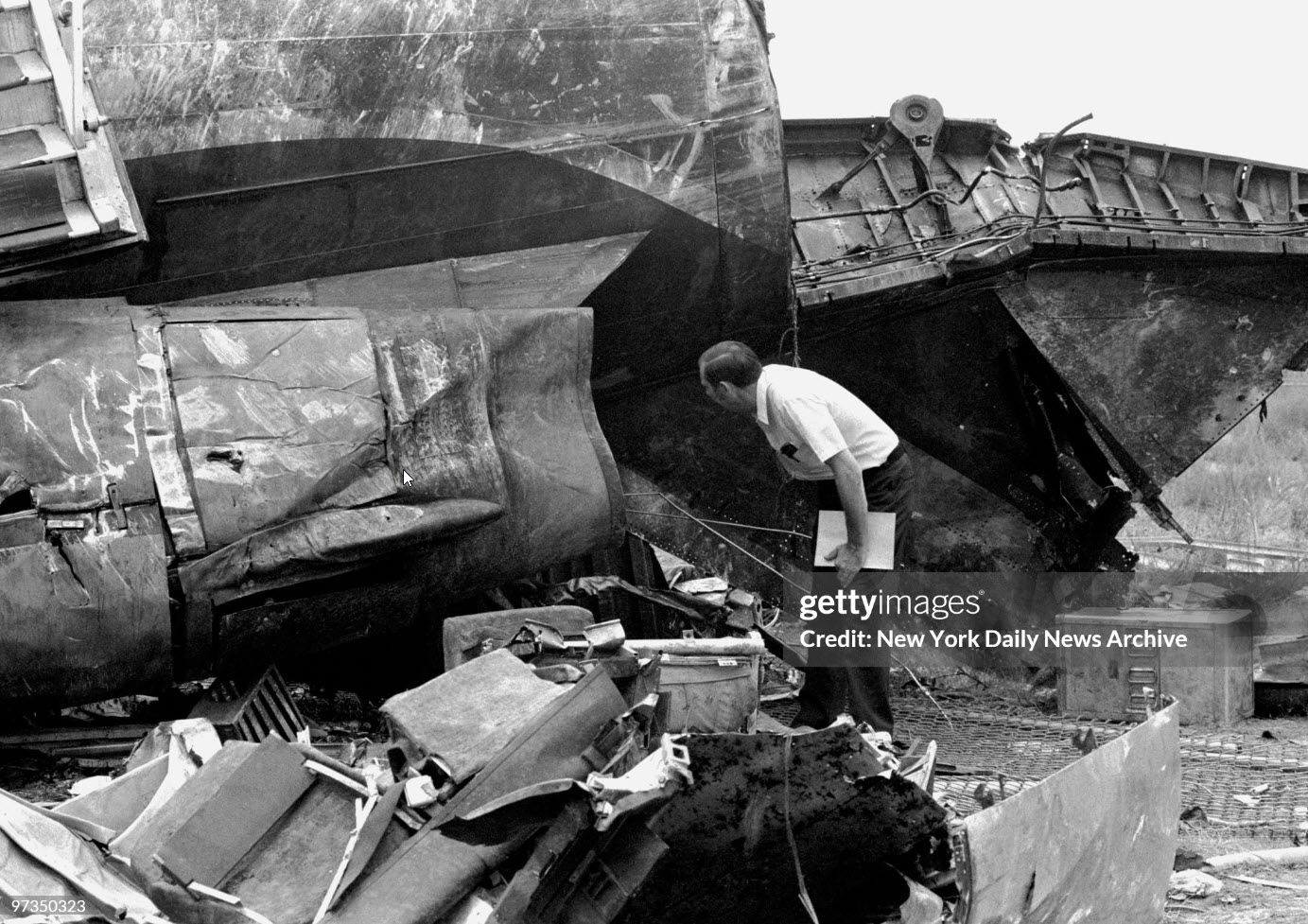
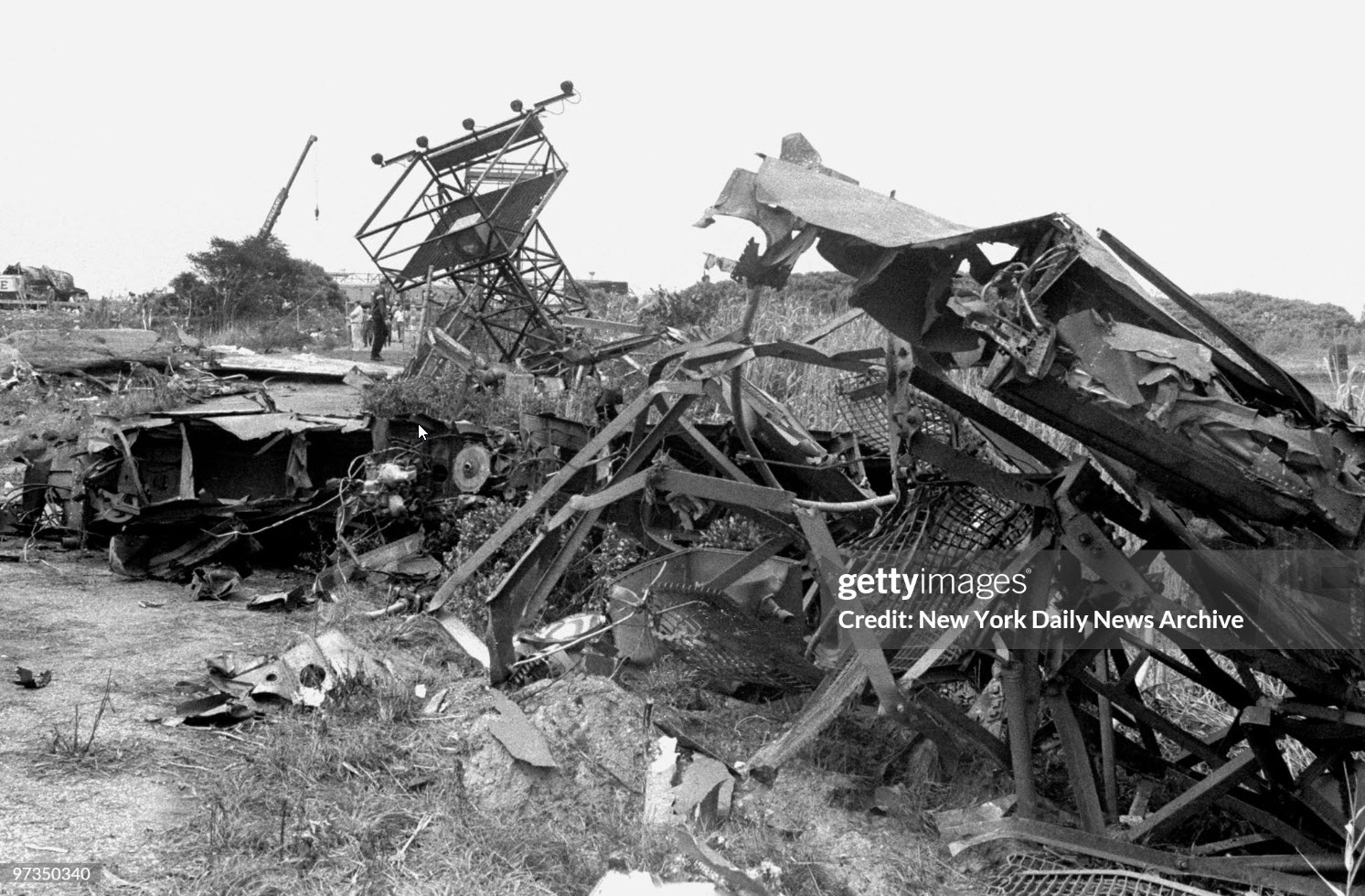
Circumstances:
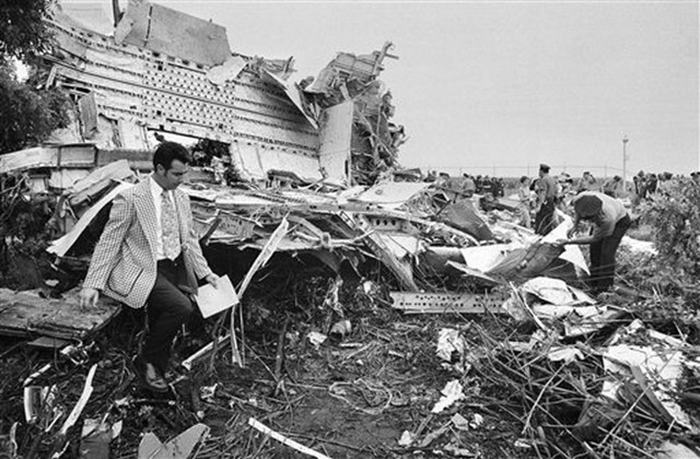
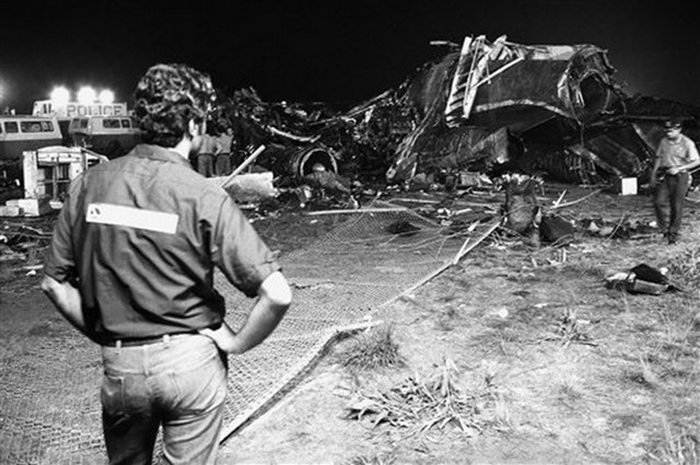
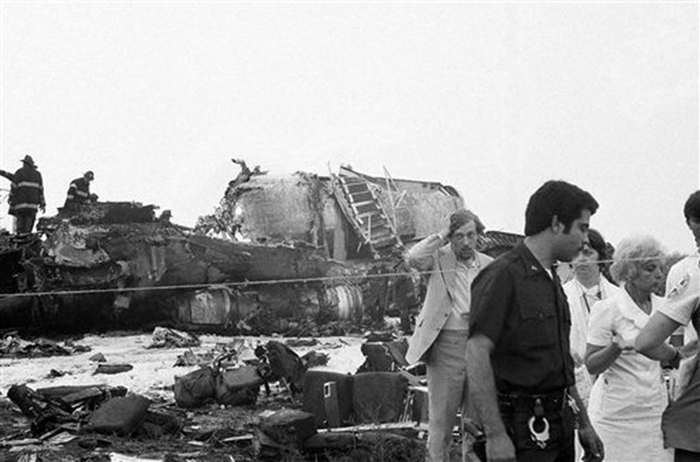
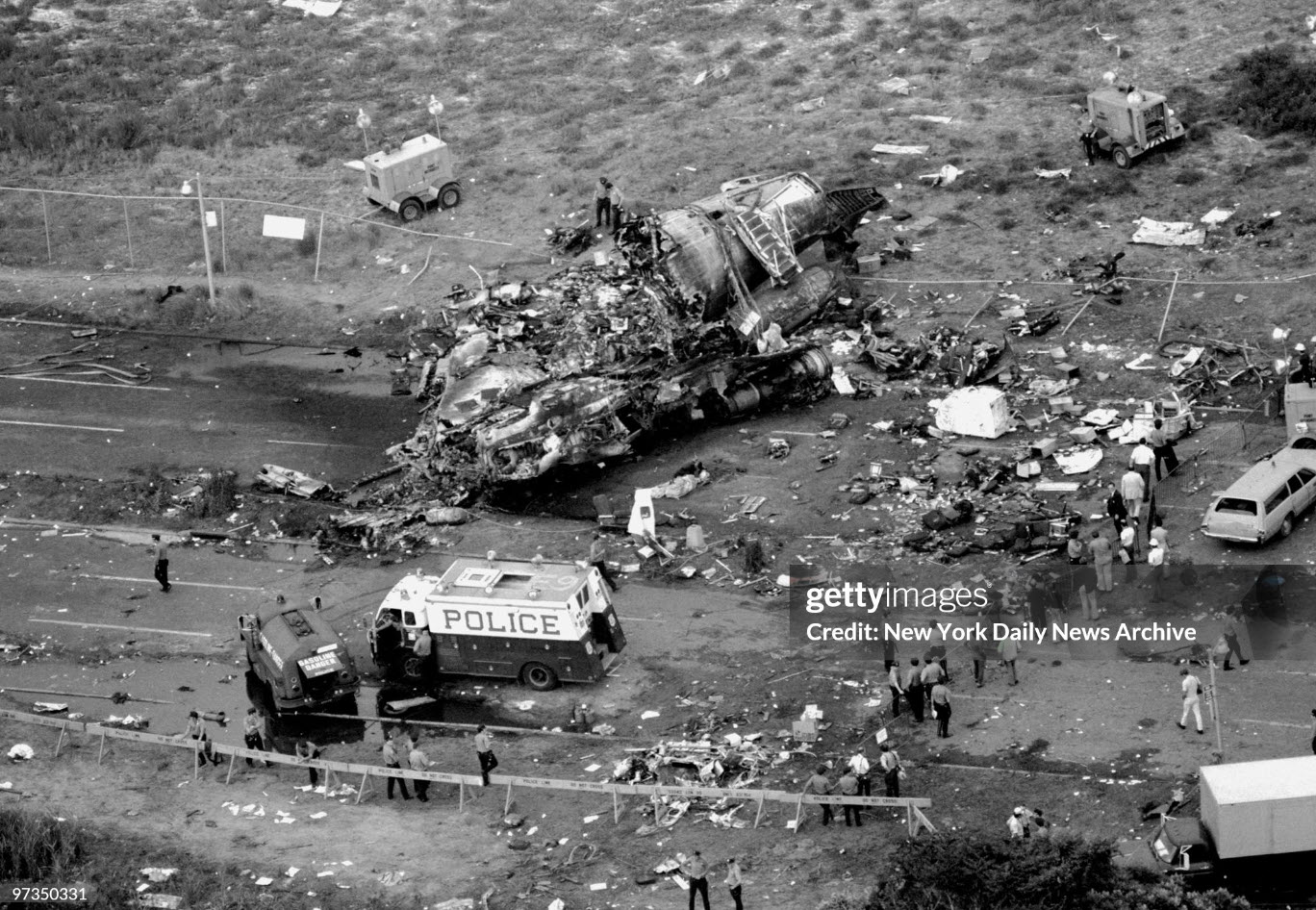
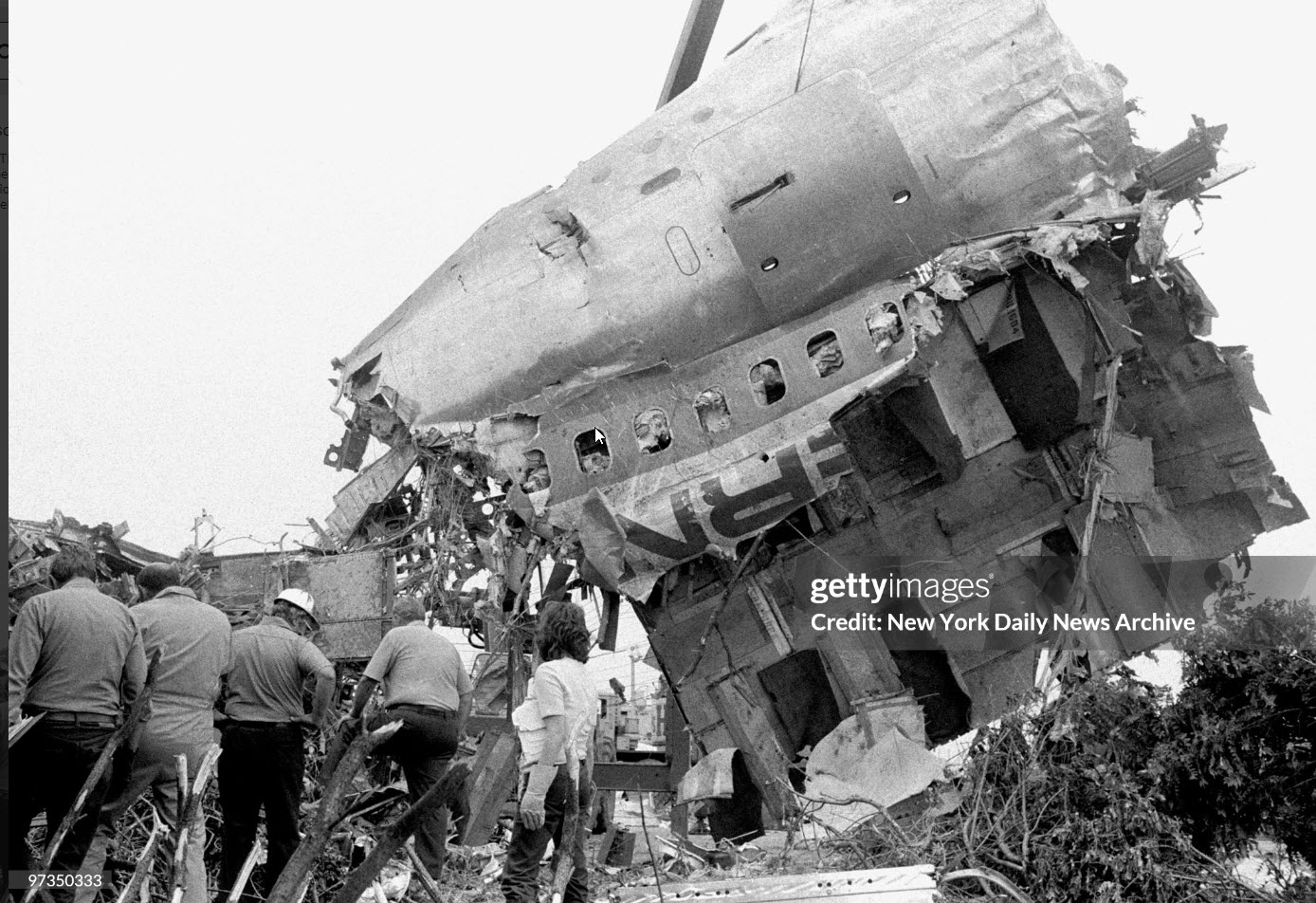
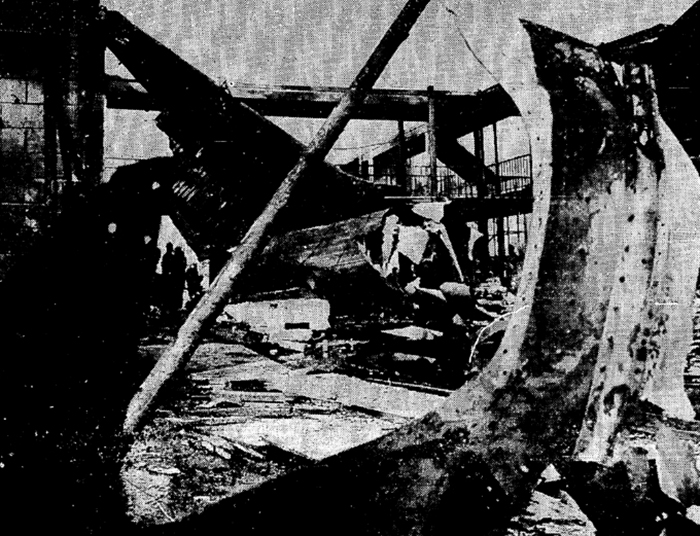
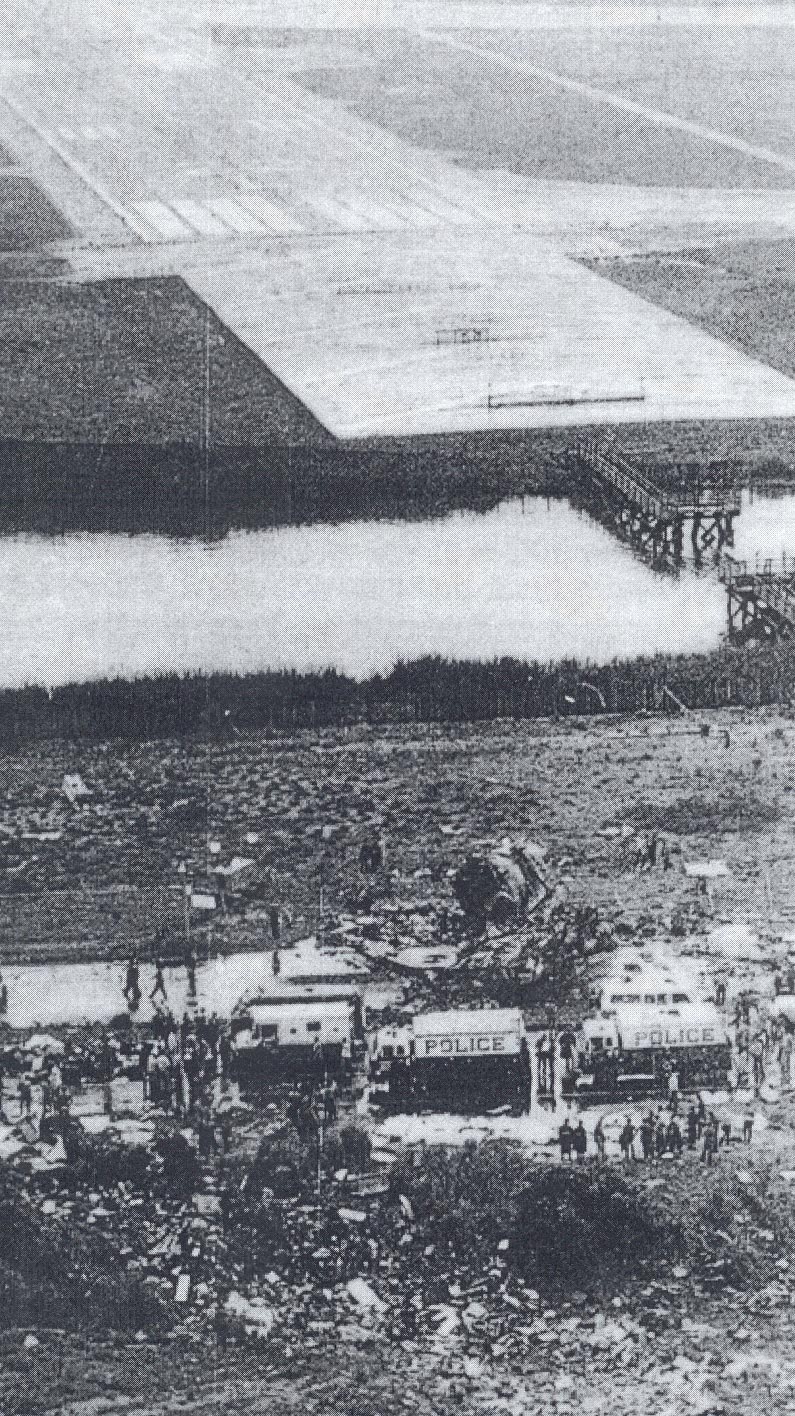
Eastern Air Lines Flight 66, a Boeing 727-225 operated as a scheduled passenger flight from New Orleans to New York-JFK. The flight departed New Orleans about 13:19. It proceeded on an IFR flight plan. Eastern 66 arrived in the New York City terminal area without reported difficulty, and, beginning at 15:35:11, Kennedy approach control provided radar vectors to sequence the flight with other traffic and to position it for an ILS approach to runway 22L at the Kennedy airport. The automatic terminal information service (ATIS) reported: "Kennedy weather, VFR, sky partially obscured, estimated ceiling 4,000 broken, 5 miles with haze... wind 210° at 10, altimeter 30.15, Expect vectors to an ILS runway 22L, landing runway 22L, departures are off 22R... " At 15:52:43, the controller transmitted, "All aircraft this frequency, we just went IFR with 2 miles very light rain showers and haze. The runway visual range is---not available, and Eastern 66 descend and maintain four thousand, Kennedy radar one three two four." Eastern 66 acknowledged the transmission. At 15:53:22, the flight contacted the Kennedy final vector controller, who continued to provide radar vectors around thunderstorms in the area, to sequence the flight with other traffic, and to position the flight on the localizer course. The flight crew then discussed the problems associated with carrying minimum fuel loads when confronted with delays in terminal areas. One of the crewmembers stated that he was going to check the weather at the alternate airport, which was LaGuardia Airport (LGA). Less than a minute later, one of the crewmembers remarked, "... one more hour and we'd come down whether we wanted to or not." At 15:59:19, the final vector controller transmitted a message to all aircraft on his frequency that "a severe wind shift" had been reported on the final approach and that he would report more information shortly. Eastern Air Lines Flight 902, a Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, had abandoned its approach to runway 22L earlier. At 15:59:40, Eastern 902 re-established radio communications with the Kennedy final vector controller, and the flight crew reported, "... we had... a pretty good shear pulling us to the right and... down and visibility was nil, nil out over the marker... correction... at 200 feet it was... nothing." The final vector controller responded, "Okay, the shear you say pulled you right and down?" Eastern 902 replied, "Yeah, we were on course and down to about 250 feet. The airspeed dropped to about 10 knots below the bug and our rate of descent was up to 1,500 feet a minute, so we put takeoff power on and we went around at a hundred feet." While Eastern 902 was making this report, the captain of Eastern 66, said, "You know this is asinine." An unidentified crewmember responded, "I wonder if they're covering for themselves." The final vector controller asked Eastern 66 if they had heard Eastern 902's report. Eastern 66 replied, "...affirmative." The controller then established the flight's position as being 5 miles from the outer marker (OM) and cleared the flight for an ILS approach to runway 22L. Eastern 66 acknowledged the clearance at 16:00:54, "Okay, we'll let you know about the conditions." One minute later, the first officer, who was flying the aircraft, called for completion of the final checklist. While the final checklist items were being completed, the captain stated that the radar was, "Up and off... standby." At 16:02:20, the captain said, "...I have the radar on standby in case I need it, I can get it off later." At 16:02:42, the final vector controller asked Eastern 902, "..would you classify that as severe wind shift, correction, shear?" The flight responded, "Affirmative." The first officer of Eastern 66 then said, "Gonna keep a pretty healthy margin on this one. An unidentified crewmember said, "I...would suggest that you do" the first officer responded, "In case he's right." At 16:02:58, Eastern 66 reported over the OM, and the final vector controller cleared the flight to contact the Kennedy tower. The first officer requested 30° of flaps and the aircraft continued to bracket the glideslope with the airspeed oscillating between 140 and 145 knots. At 1603:12, the flight established communications with Kennedy tower local controller and reported that they were, "outer marker, inbound." The Kennedy tower local controller cleared Eastern 66 to land. The captain acknowledged the clearance and asked, "Got any reports on braking action...?" The local controller did not respond until the query was repeated. The local controller replied, "No,none, approach end of runway is wet... but I'd say about the first half is wet--we've had no adverse reports." At 1603:57.7, the flight engineer called, "1000 feet" and at 1604:25, the sound of rain was recorded. The flight was nearly centered on the glideslope when the flight engineer called, "500 feet." The airspeed was oscillating between 140 and 148 knots and the sound of heavy rain could be heard as the aircraft descended below 500 feet. The windshield wipers were switched to high speed. At 16:04:40, the captain said, "Stay on the gauges." The first officer responded, "Oh, yes. I'm right with it." The flight engineer reported, "Three greens, 30 degrees, final checklist," and the captain responded, "Right." At 16:04:52, the captain said, "I have approach lights," and the first officer said, "Okay." The captain then again said, "Stay on the gauges," and the first officer replied, "I'm with it." N8845E then was passing through 400 feet, and its rate of descent increased from an average of about 675 fpm to 1,500 fpm. The aircraft rapidly began to deviate below the glideslope, and 4 seconds later, the airspeed decreased from 138 kts to 123 kts in 2.5 seconds. The Boeing 727 continued to deviate further below the glideslope, and at 16:05:06.2, when the aircraft was at 150 feet, the captain said, "runway in sight." Less than a second later, the first officer said, "I got it." The captain replied, "got it?" and a second later, at 16:05:10, an unintelligible exclamation was recorded, and the first officer commanded, "Takeoff thrust." The airplane contacted the top of the No. 7 approach light tower at an elevation of 27 feet above the mean low-water level and 2,400 feet from the threshold of runway 22L. The aircraft continued and struck towers 8 and 9. The aircraft’s left wing was damaged severely by impact with these towers--the outboard section was severed. The aircraft then rolled into a steep left bank, well in excess of 90°. It contacted the ground and the fuselage struck five other towers. The aircraft then continued to Rockaway Boulevard, where it came to rest. The approach light towers and large boulders along the latter portion of the path caused the fuselage to collapse and disintegrate. A fire had erupted after the left wing failed.