Crash of a Swearingen SA226TC Metro II in Johannesburg
Date & Time:
Nov 18, 1988
Registration:
ZS-LKG
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
TC-291
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
10
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
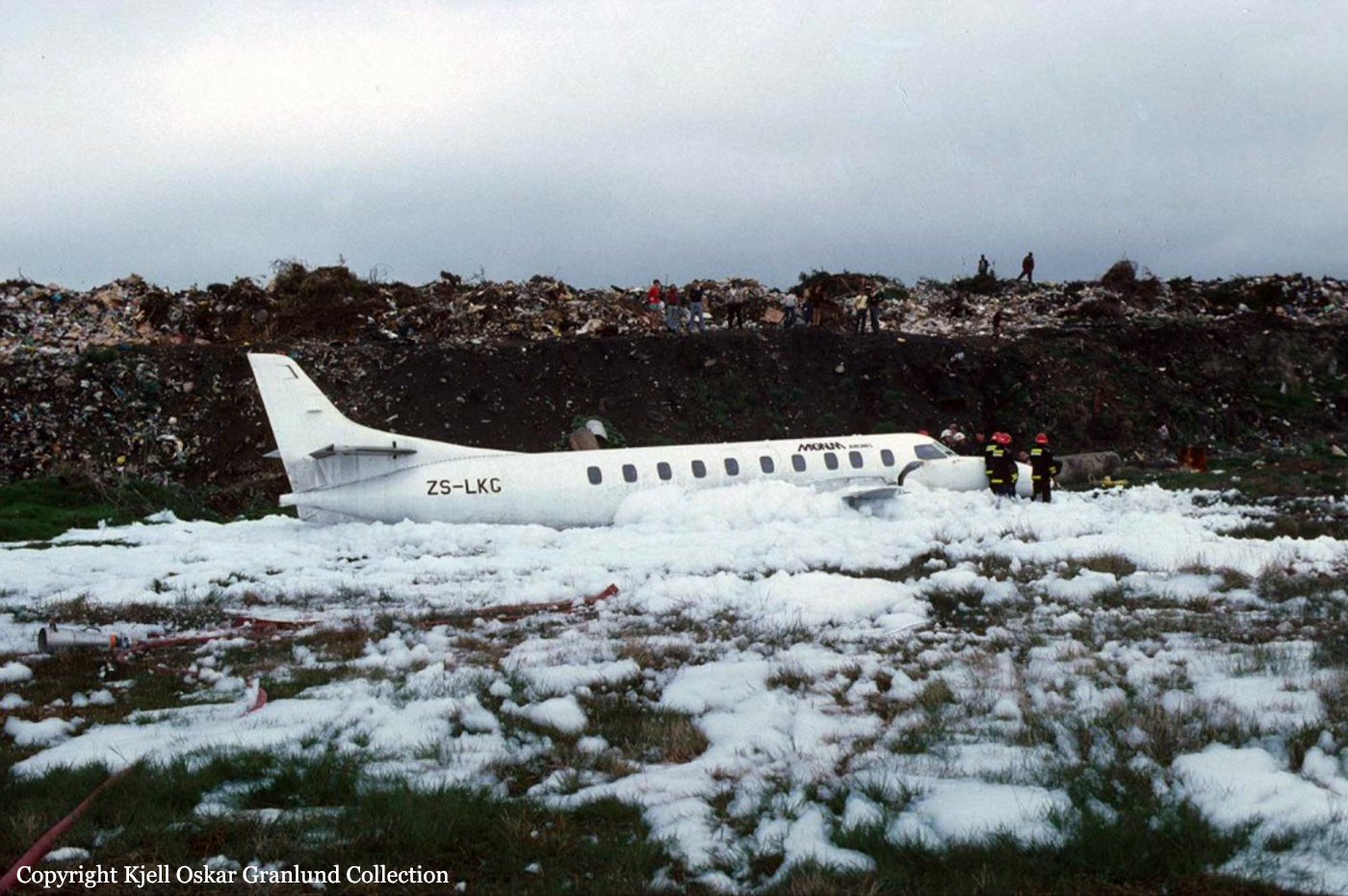
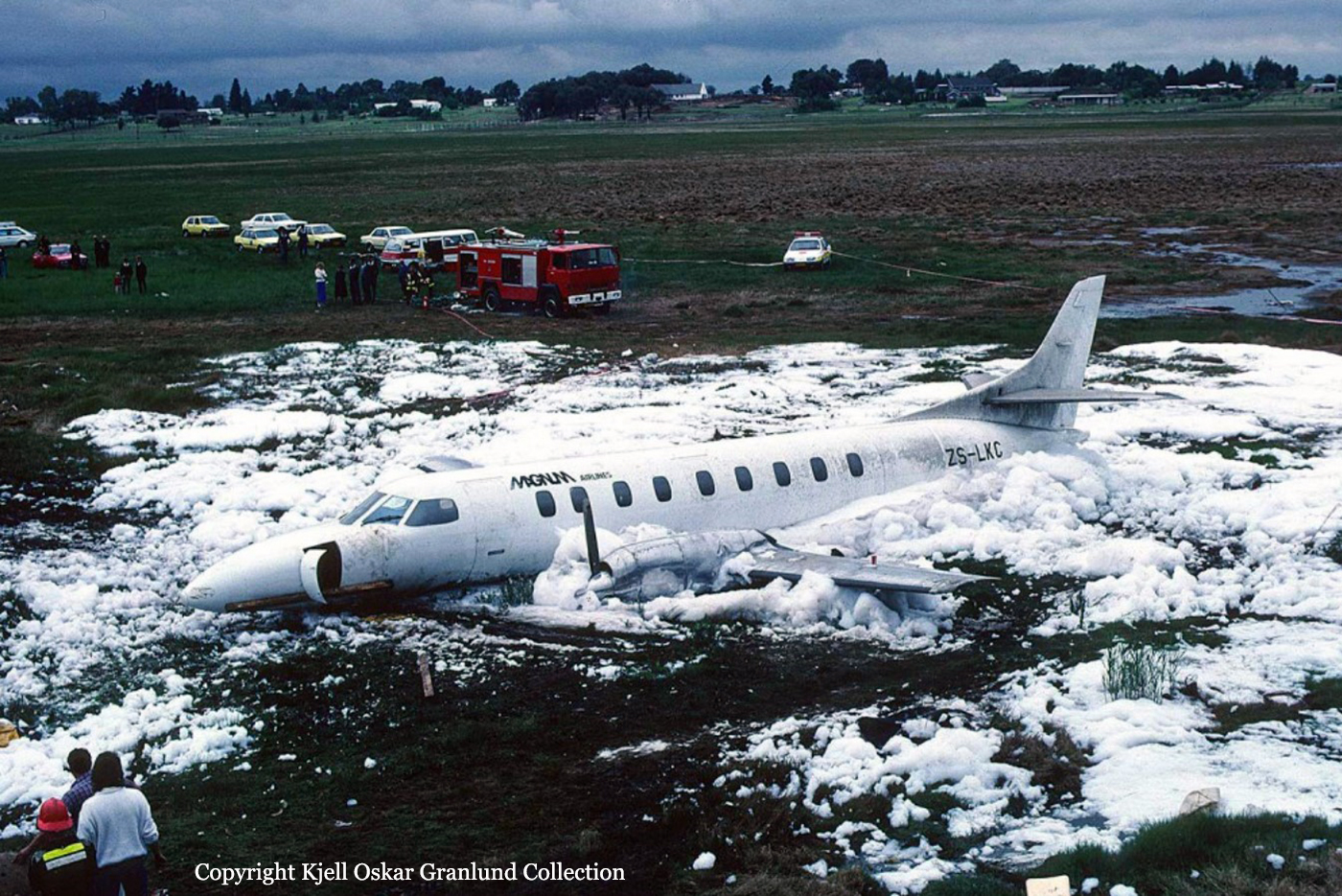
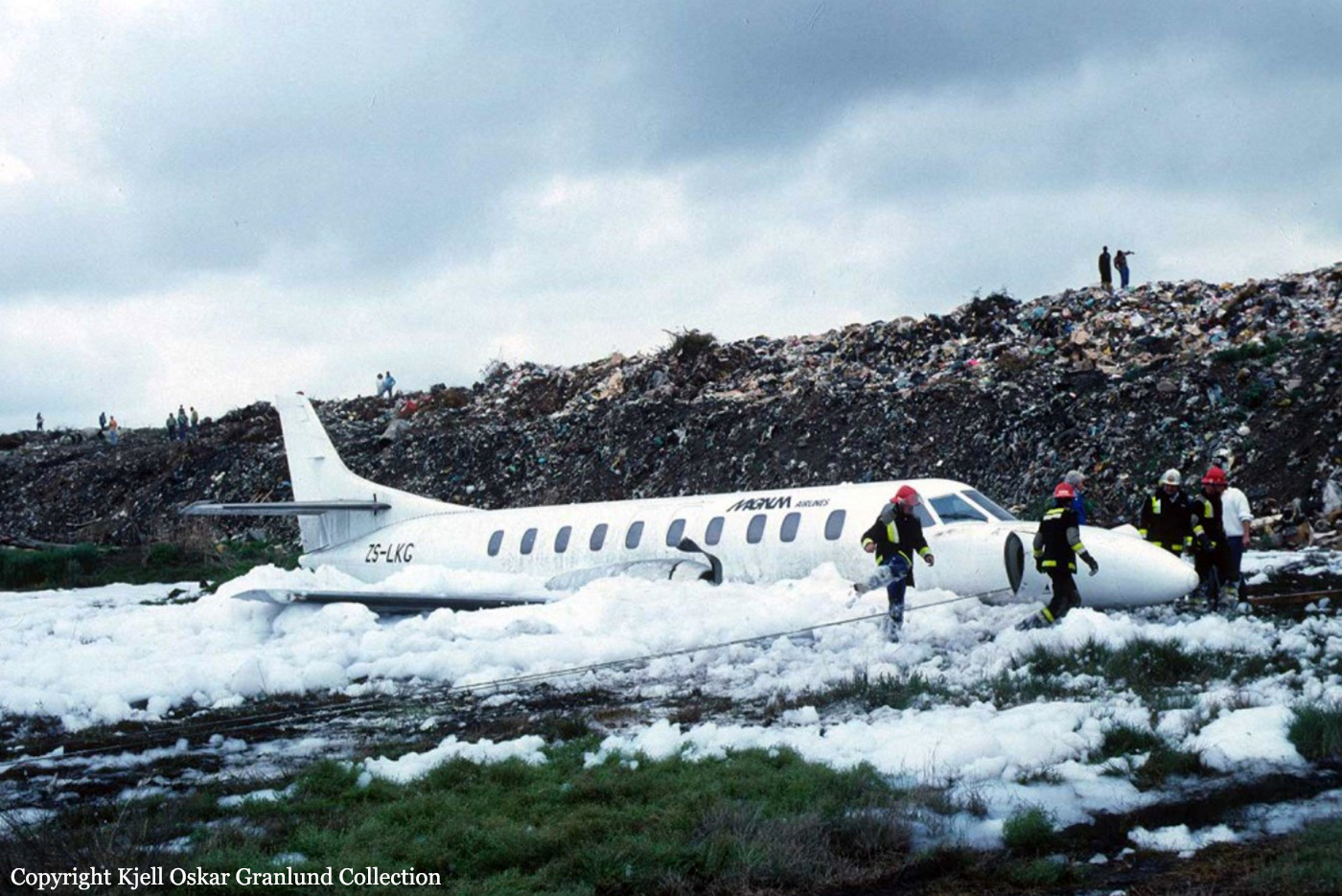
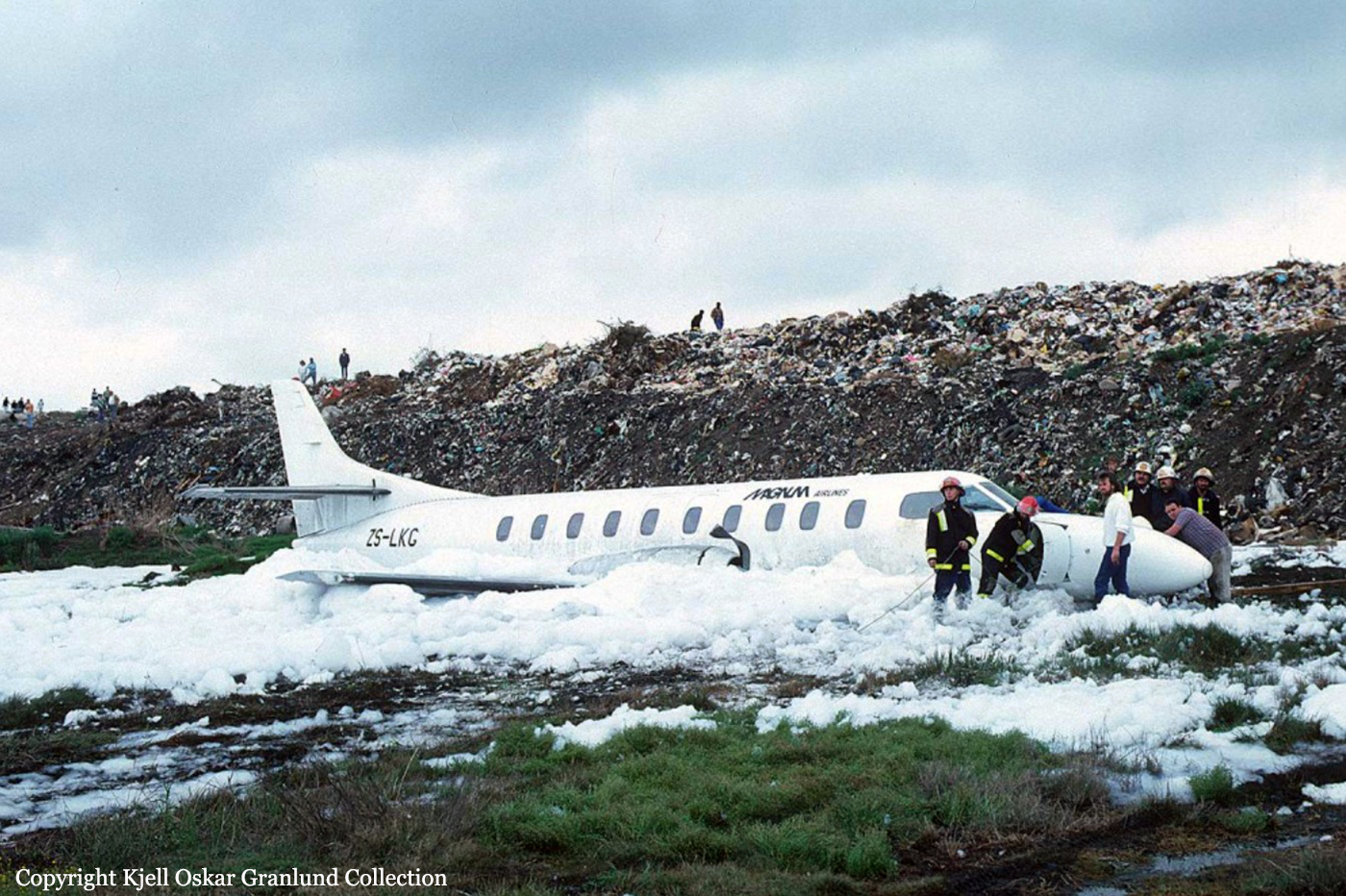
Circumstances:
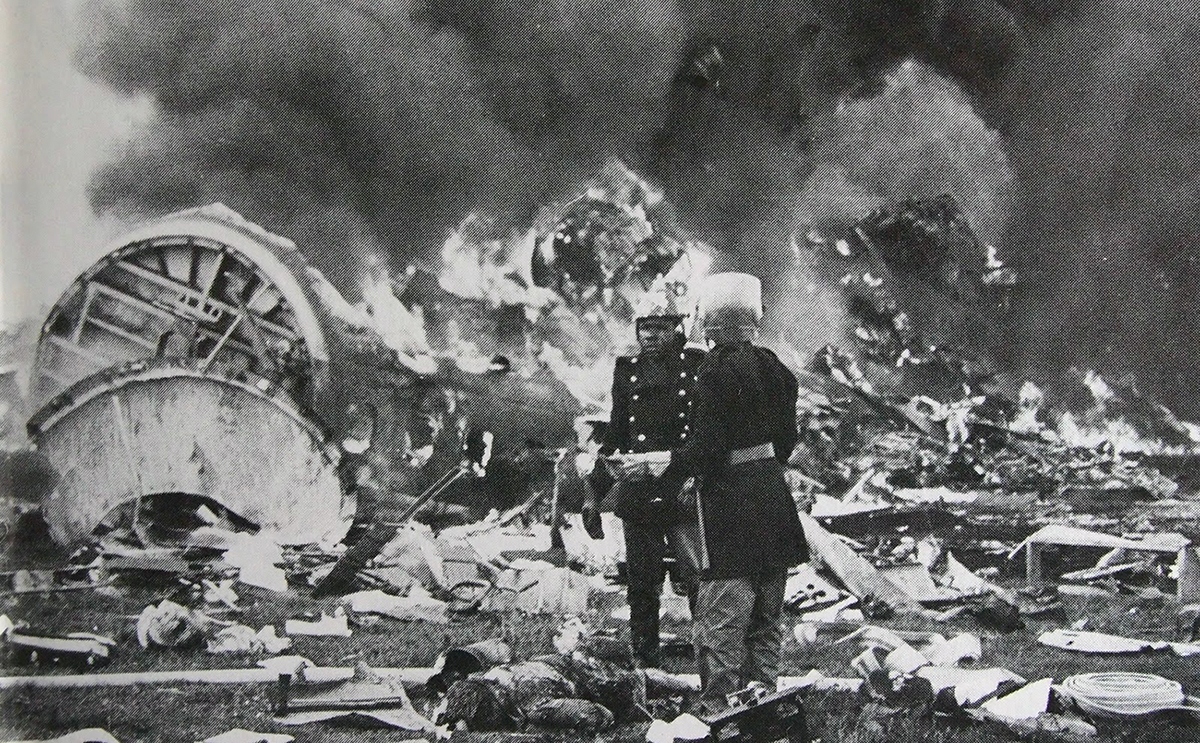
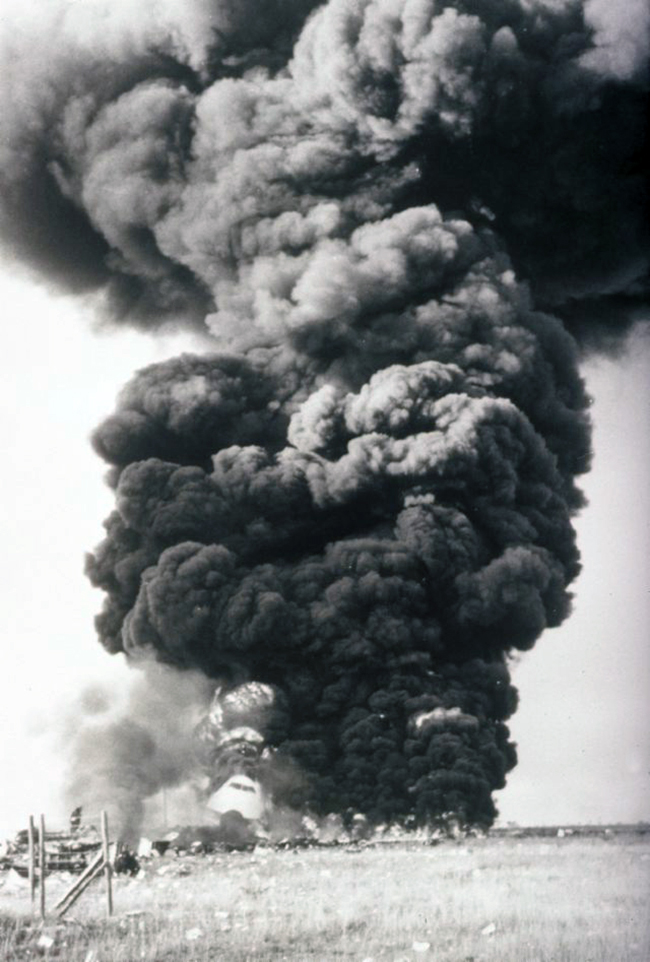
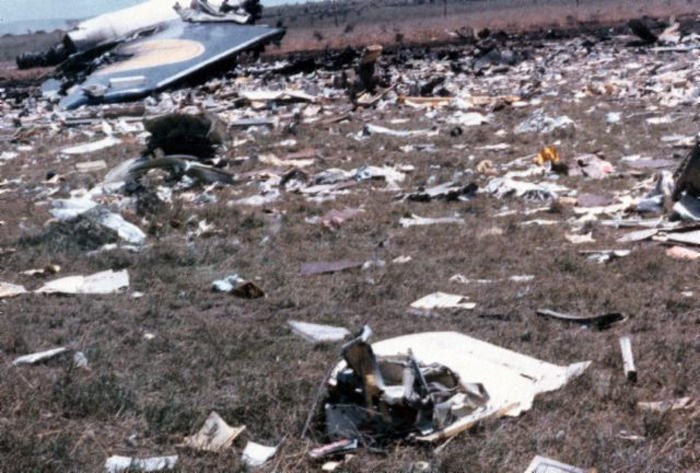
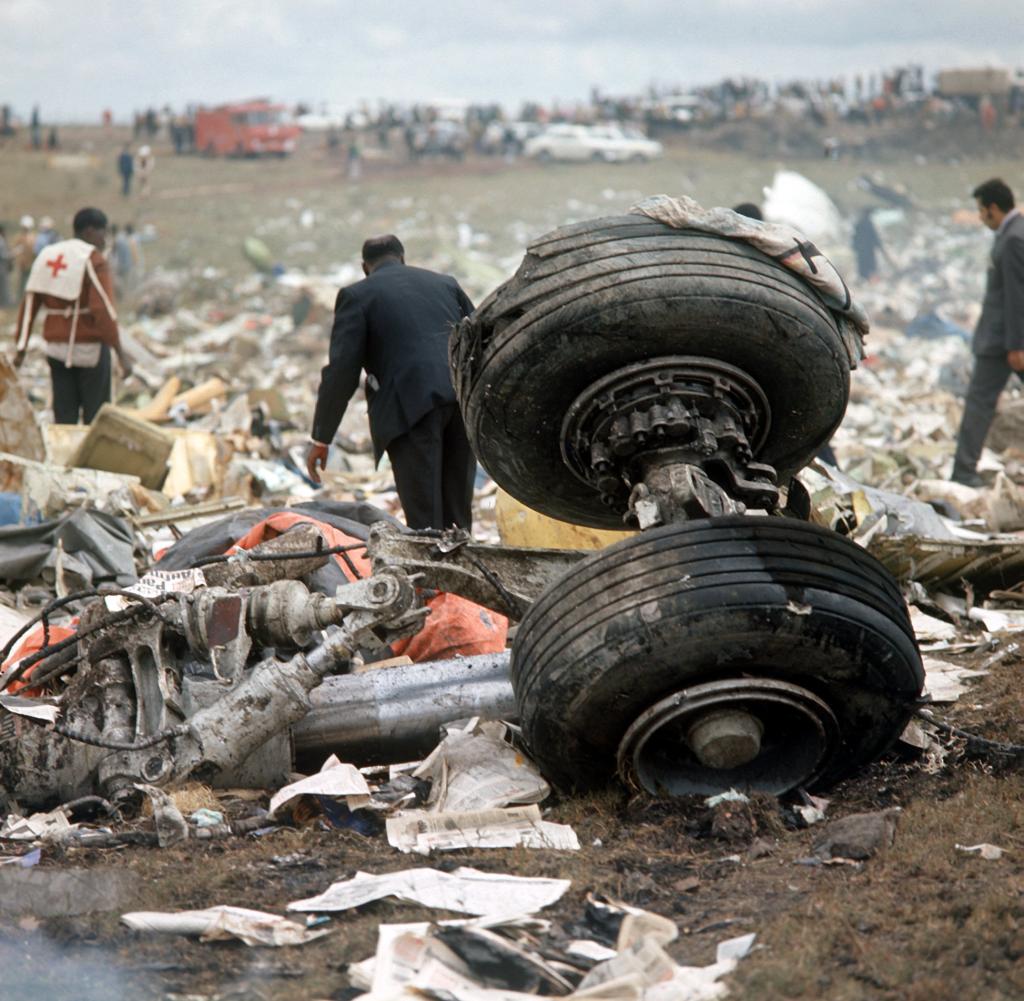
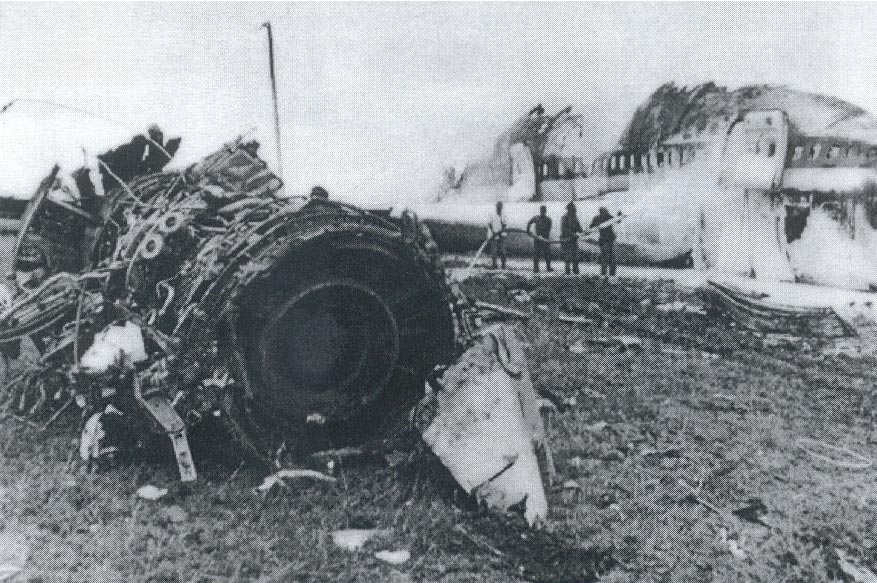
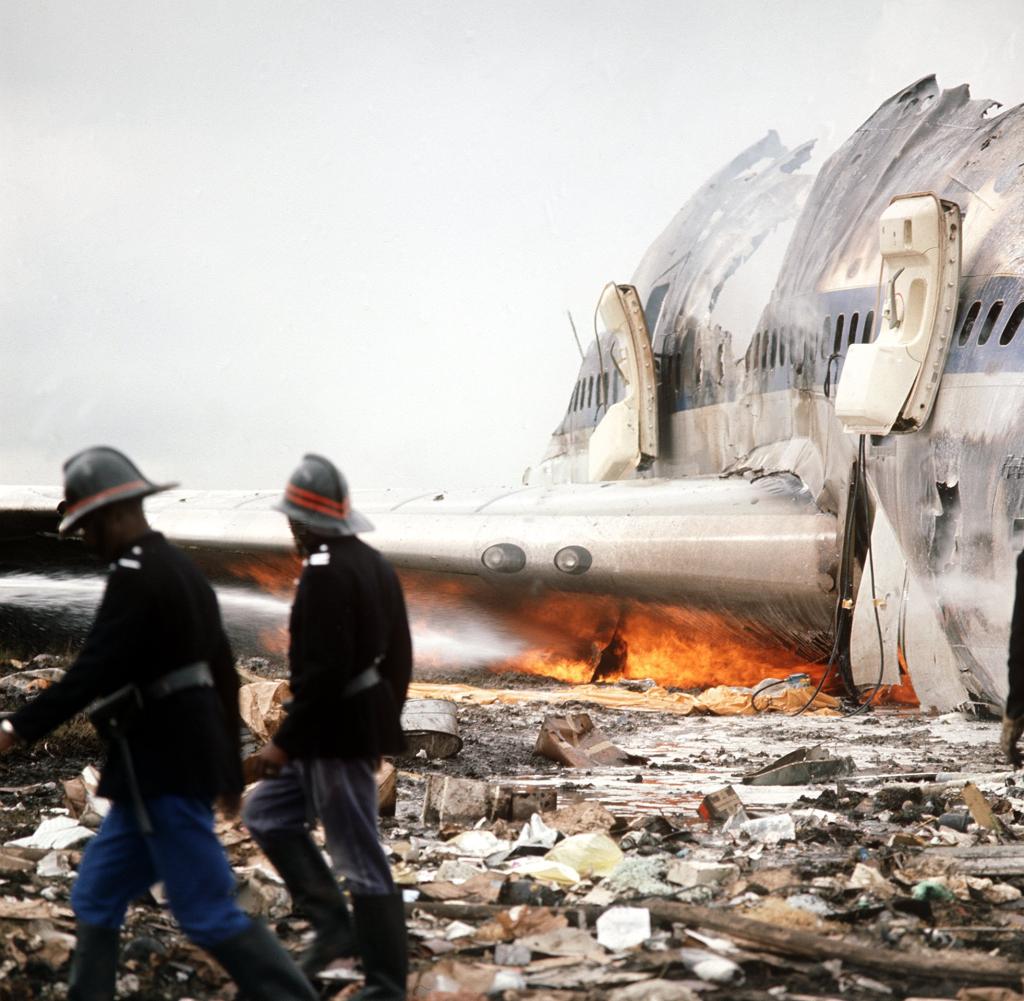
After takeoff from Johannesburg-Jan Smuts Airport, the crew declared an emergency following the failure of the left engine. The crew elected to return but eventually completed a belly landing in a field located near the airport. All 12 occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Failure of the left engine shortly after takeoff for unknown reasons.