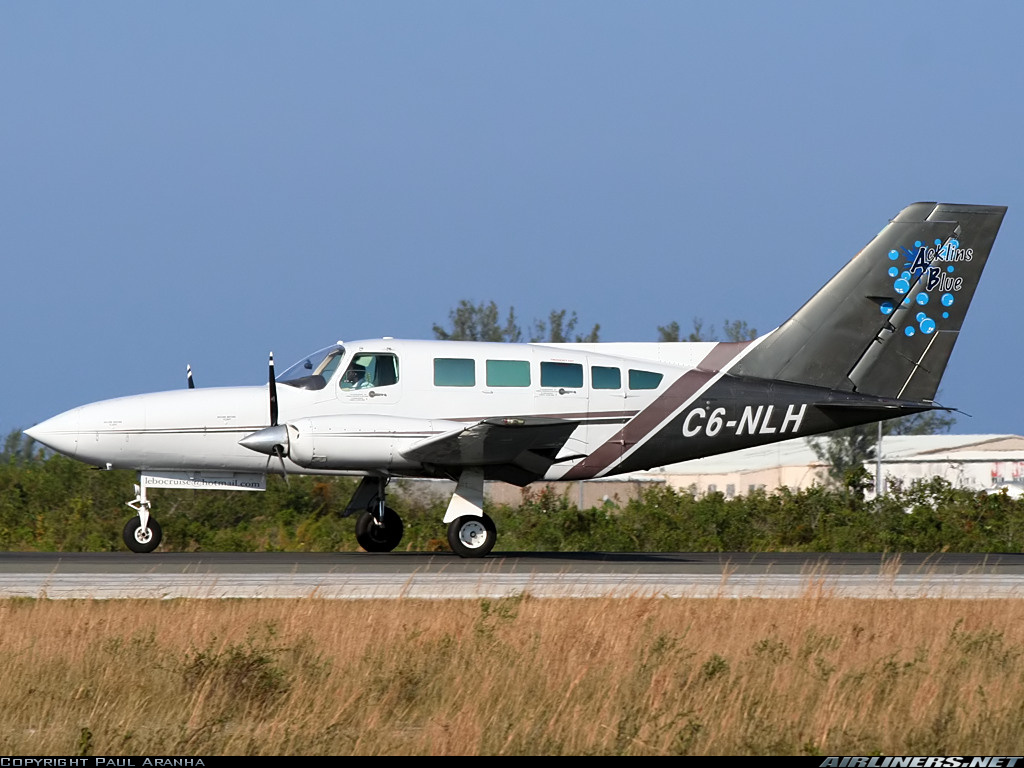
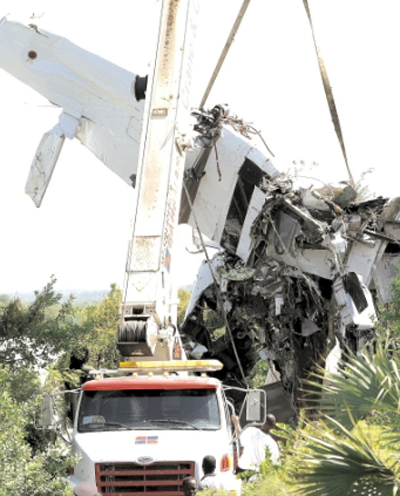
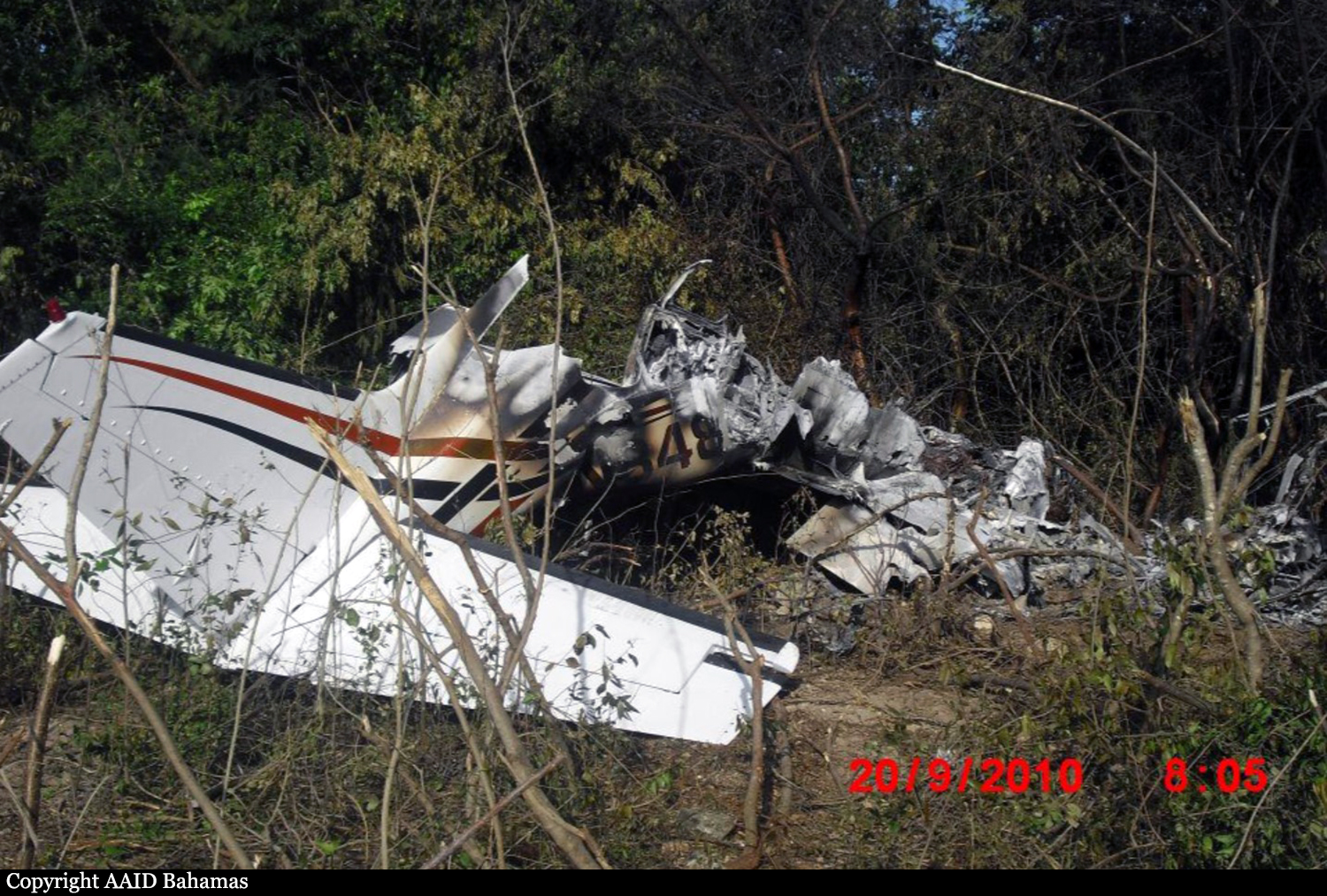
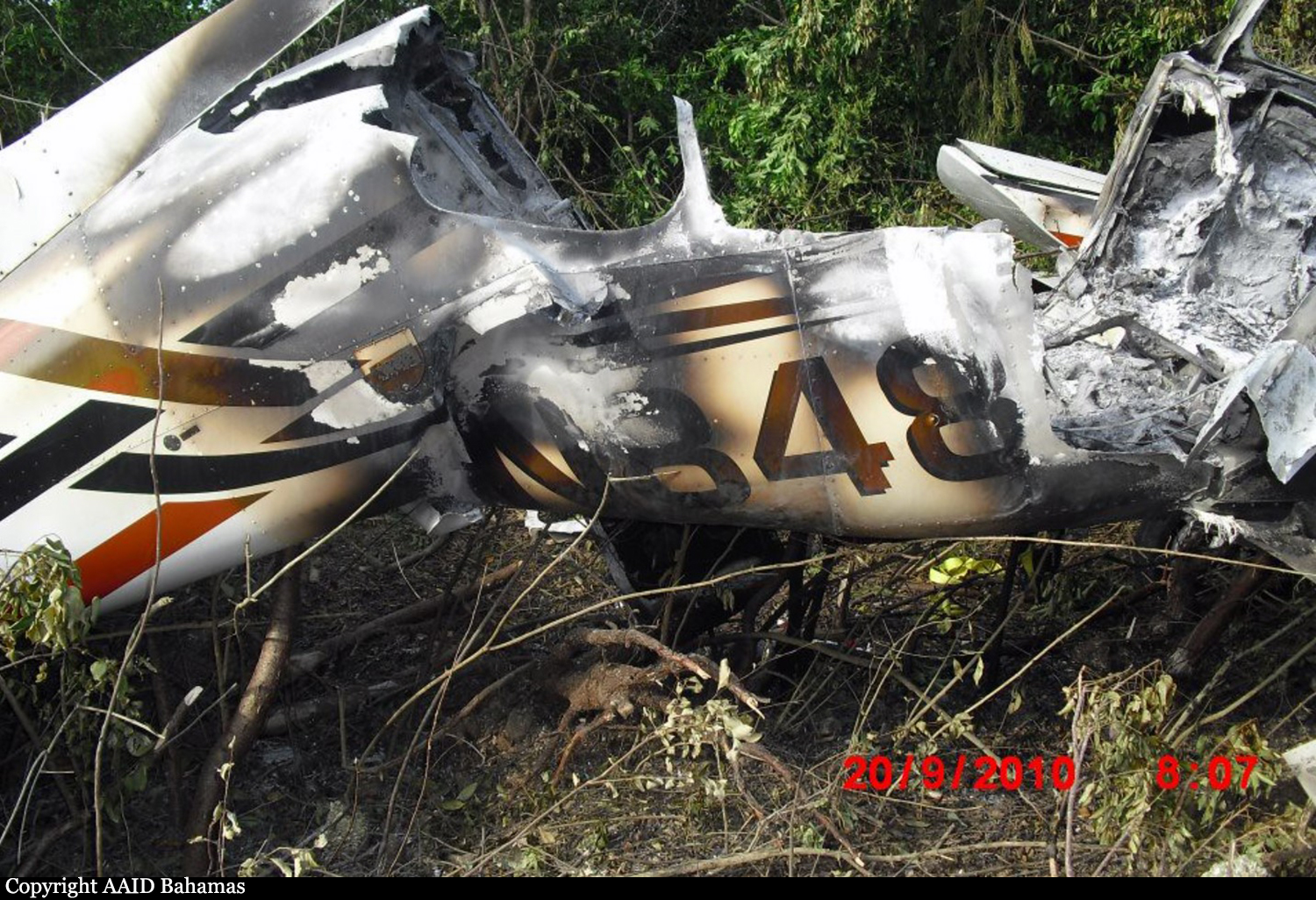
Crash of a Cessna 402C in Nassau: 9 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 5, 2010 at 1236 LT
Registration:
C6-NLH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Nassau – Cockburn Town
MSN:
402C-0458
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
9
Captain / Total hours on type:
10000.00
Circumstances:
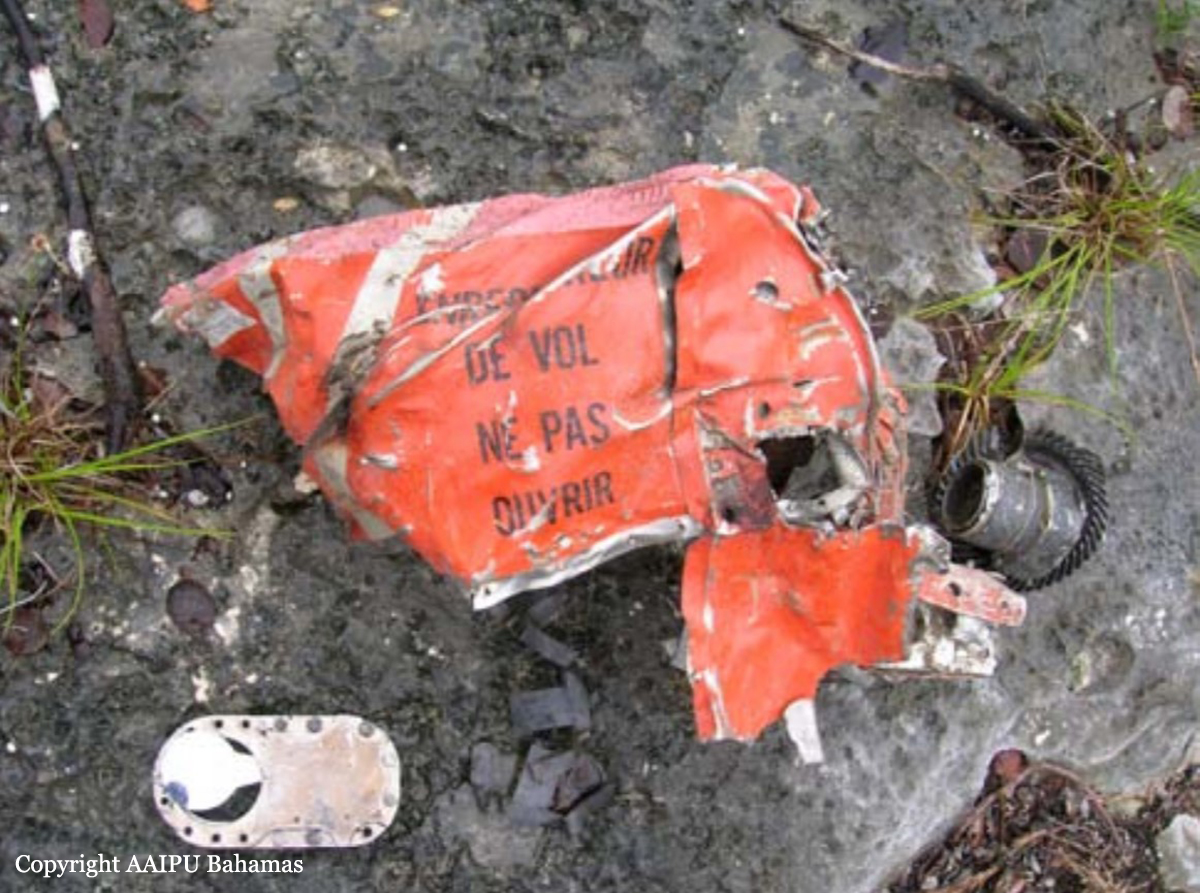
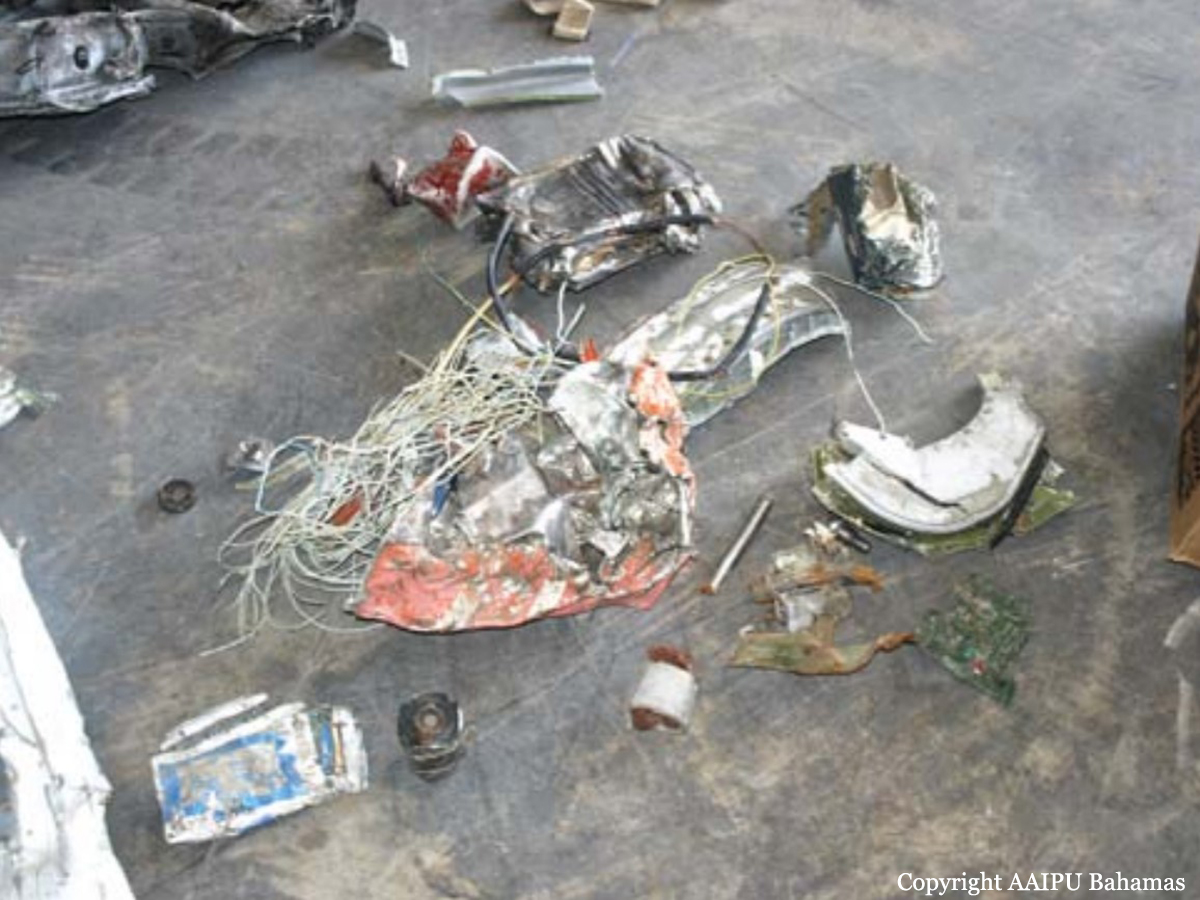
On October 5, 2010 about 1636 UTC / 12:36pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), C6-NLH a Cessna 402C aircraft registered to Lebocruise Air Limited and operated by Acklins Blue Air Charter/Nelson Hanna crashed into lake Killarney shortly after becoming airborne from runway 14 at Lynden Pindling International Airport, Nassau, New Providence, Bahamas. The airplane sustained substantial damages by impact forces. The pilot, copilot and seven (7) passengers aboard the airplane received fatal injuries. The aircraft was on a passenger carrying flight from Lynden Pindling Intl Airport (MYNN) to Cockburn Town, San Salvador, Bahamas (MYSM). The aircraft was on a visual flight rules flight plan. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed at the time of the accident. The official notification of the accident was made to the Manager of the Flight Standards Inspectorate at Lynden Pindling Intl Airport, Nassau, N. P., Bahamas shortly thereafter. The investigation began the same day at approximately 1655 UTC upon notification of the IIC. The investigation was conducted by the Bahamas Civil Aviation Department [BCAD], Inspector Delvin R. Major (Investigator-in-Charge) of the Air Accident Investigation and Prevention Unit (AAIPU), Management of BCAD and Flight Standards Inspectorate (FSI), Airworthiness Inspectors, Operations Inspectors, Human Factors and other administrative staff. Valuable assistance was also received from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and Manufacturers of the aircraft and engine components. Three (3) Air Operator Certificate (AOC) holders at the Domestic Section of Lynden Pindling Intl Airport stated that on the day of the accident flight; one of the victims of the accident aircraft approached each of them individually at different times, requesting a quote and their availability to conduct a charter flight to Cockburn Town, San Salvador, Bahamas. Each AOC holder reported that they declined to conduct the charter because by looking at the amount of luggage and other equipment that accompanied the passengers and the size of the passengers that wanted to travel, in their estimation the combined weight appeared to be in excess of the weight that their respective aircraft (Cessna 402C and Hawker Beechcraft B100) can accommodate. After the AOC holders declined to conduct the charter, sometime thereafter, the same individual that was arranging the flight with the previous AOC holders made contact with Nelson Hanna / Acklins Blue Air Charter where arrangements were made to conduct the charter flight. The aircraft type certificate allowed for the aircraft to be operated by one (1) pilot, but the fatal flight was operated by a crew of two (2) pilots (according to eyewitness reports). The aircraft actual weight and center of gravity was unknown. As far as could be determined, the takeoff weight exceeded the maximum weight allowed of 6,850 pounds by more than 500 pounds. This excess in weight also placed the center of gravity of the aircraft outside of the safe envelope / limits for flight allowed by the manufacturer. The flight crew was given instructions by ATC to taxi from the business aviation apron (Executive Flight Support) for a takeoff on Runway 14 at intersection Foxtrot. (Intersection Foxtrot is 2,000 feet beyond the threshold of Runway 14, with a take-off run available of 9,353 feet. (Runway 14 - 11,353 feet long by 150 feet wide, see Appendix 5.15). According to eyewitness reports, from the initiation of takeoff power up to the point when the aircraft lost control white smoke was observed trailing behind the left engine of the aircraft. Eyewitnesses also reported that the take off appeared normal with gear being retracted shortly after takeoff and the aircraft seemed to be struggling to climb. The aircraft was seen at a low height, turning in a left direction over the lake as if trying to return for a landing at the airport. The bank of the aircraft changed from shallow to very steep to almost perpendicular to the ground, gears were extended and almost immediately the aircraft lost control and nose dived into the lake inverted. It cart wheeled, coming to rest upright, approximately ¼ mile from the approach end of runway 27. The aircraft came to rest on an approximate heading of 210 degrees. Eyewitness also reported hearing the engine run for a few seconds after the aircraft made contact with the water of the lake. There were no reports from the pilot to ATC of an emergency or any abnormalities with the aircraft or its systems after takeoff. The flight plan form filed for this flight listed one (1) soul on board; however, there were 7 additional occupants including a “second pilot” discovered onboard the accident flight the day of the accident. The aircraft's recovery and search for luggage, equipment and additional victims commenced shortly after the accident. This effort however, was hampered by inclement weather, rough lake conditions and darkness. On October 6th, the day after the crash, aircraft recovery continued. Family members of an additional person believed to be on board, advised the authorities that there was a ninth (9th) person on board. Search to recover any additional bodies continued but search and recovery efforts proved fruitless. On October 7th, the second day after the crash, the body of the ninth (9th) victim was found in the marshes and recovered from the southwestern end of the lake in the vicinity of where the fatal crash occurred.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
1. Acklins Blue Air Charter was advertising and operating as a Bahamas air taxi operator without having undergone the certification process in contravention of Bahamas Civil Aviation (Safety) Regulations Schedule 12.
2. The airplane was issued a Certificate of Airworthiness on May 19, 2010, by the Bahamas Flight Standards Inspectorate, and was being operated by Acklins Blue Air Charter.
3. The Cessna 402C aircraft is classified in the performance Group C. This requires rapid feathering of the propeller of a failed engine and the raising of flap and the landing gear in order to achieve maximum climb performance.
4. The airplane maintenance records were not located; therefore, no determination could be made whether the airplane was being maintained in accordance with Bahamas Civil Aviation Regulations.
5. The 12,000 hour pilot and second pilot were not qualified to operate in Bahamas commercial air taxi operations.
6. No determination could be made whether the pilot or second pilot had completed required training and had accomplished a satisfactory recurrent flight check of their flying ability as required by CASR Schedule 12 and 14 for aircraft operating in commercial air transportation as well as the stipulation by the insurance policy.
7. Post-accident weight and balance calculations indicate the airplane was being operated approximately 523 pounds over maximum certificated takeoff weight (6,850 lb)
8. The pilot was advised by an air traffic controller that white smoke was trailing the left engine during takeoff; the pilot did not declare an emergency or advise the controller of any engine failure or mechanical abnormality.
9. The airplane's left engine could not produce rated shaft horsepower during takeoff.
10. Several factors contributing to the degradation of the airplane's performance and its inability to maintain flight include the wind-milling propeller, the pilot's intentional initiation of a steep turn to return to the departure airport, and his intentional lowering of the landing gear during the turn to return.
11. While turning to return, the airplane stalled, pitched nose down, and impacted in a lake.
12. The search and rescue efforts were timely and appropriate; however, the lack of accurate information on the pilot submitted flight plan delayed recovery of all victims.
13. The left propeller was not feathered.
14. The No. 2 cylinder of the left engine failed due to fatigue that originated in the root of the cylinder head thread that was engaged with the first thread on the barrel.
15. Post-accident inspection of the cockpit revealed several switches for the right engine were secured; however, no determination could be made when the switches were placed / moved in those positions.
16. No evidence of failure of the airplane's structures or flight control system contributed to the accident.
17. Existing regulations did not require the aircraft to be fitted with flight recorders. The lack of any recorded data about the aircraft's performance or the flight crew conversations deprived the investigation team of essential factual information.
18. Current Civil Aviation Department personnel and budget resources may not be sufficient to ensure that the quality of surveillance for certified as well as uncertified air carrier operations will improve.
19. Airside access procedures are inadequate at Fixed Base Operators. Access to the secure airside occurring without any check of individuals to challenge whether they have a legitimate reason for accessing the secure airside. FBO door to access airside is not secured or locked continuously; persons observed walking in and out without being challenged.
20. Flight Plan Forms are being accepted and transmitted to ATC with incomplete information. This information is vital for search and rescue purposes.
21. Weather was not a factor in the accident.
22. ATC was not a factor in the accident.
23. Currently flight plans for private flights are only required for international operations.
24. The pilot was aware of discrepancy associated with the manifold pressure reading of the left engine prior to takeoff. This discrepancy was brought to his attention by a client from the flight immediately preceding the accident flight.
25. The exact center of gravity of the accident airplane could not be calculated accurately as no indication of what seat each passenger occupied in the airplane and no indication of where luggage or equipment were placed on the aircraft could be determined. However, due to the exceedance of weight limits the aircraft was already outside the allowable center of gravity envelope developed by the manufacturer.
26. The pilot had insufficient time to prepare for the approach to runway 27 before beginning the approach. The airplane pitched up quickly into a stall, after extension of gear, recovery before ground impact was unlikely once the stall began.
27. Post accident inspection did not reveal any mechanical evidence or problems with the right hand engine.
28. The pilot's decision to return to the airfield was reasonable. Once the aircraft began to lose height a return to the airfield became impractical and a forced landing in the direction of flight should have been attempted.
29. The right propeller was never recovered from the lake.
The following causal factors were identified:
1. The left engine suffered a mechanical failure of the #2 cylinder, and therefore could not produce rated shaft horsepower. No indication of total loss of power with the left engine reported.
2. Right Engine electrical and engine control switches were found in the “OFF” position, therefore the aircraft was incapable of climbing on the power of one engine alone.
3. The excess weight above the maximum weight allowed for takeoff may have been an important factor in the aircraft's inability to gain adequate altitude after takeoff.
4. The pilot secured the right engine which was mechanically capable of producing power resulting in a total loss of thrust. He then sometime thereafter initiated a steep turn with gear down and the left engine already not developing sufficient shaft horsepower to sustain lift.
5. The pilot attempted to return to the departure airfield but lost control of the aircraft during a turn to the left.
1. Acklins Blue Air Charter was advertising and operating as a Bahamas air taxi operator without having undergone the certification process in contravention of Bahamas Civil Aviation (Safety) Regulations Schedule 12.
2. The airplane was issued a Certificate of Airworthiness on May 19, 2010, by the Bahamas Flight Standards Inspectorate, and was being operated by Acklins Blue Air Charter.
3. The Cessna 402C aircraft is classified in the performance Group C. This requires rapid feathering of the propeller of a failed engine and the raising of flap and the landing gear in order to achieve maximum climb performance.
4. The airplane maintenance records were not located; therefore, no determination could be made whether the airplane was being maintained in accordance with Bahamas Civil Aviation Regulations.
5. The 12,000 hour pilot and second pilot were not qualified to operate in Bahamas commercial air taxi operations.
6. No determination could be made whether the pilot or second pilot had completed required training and had accomplished a satisfactory recurrent flight check of their flying ability as required by CASR Schedule 12 and 14 for aircraft operating in commercial air transportation as well as the stipulation by the insurance policy.
7. Post-accident weight and balance calculations indicate the airplane was being operated approximately 523 pounds over maximum certificated takeoff weight (6,850 lb)
8. The pilot was advised by an air traffic controller that white smoke was trailing the left engine during takeoff; the pilot did not declare an emergency or advise the controller of any engine failure or mechanical abnormality.
9. The airplane's left engine could not produce rated shaft horsepower during takeoff.
10. Several factors contributing to the degradation of the airplane's performance and its inability to maintain flight include the wind-milling propeller, the pilot's intentional initiation of a steep turn to return to the departure airport, and his intentional lowering of the landing gear during the turn to return.
11. While turning to return, the airplane stalled, pitched nose down, and impacted in a lake.
12. The search and rescue efforts were timely and appropriate; however, the lack of accurate information on the pilot submitted flight plan delayed recovery of all victims.
13. The left propeller was not feathered.
14. The No. 2 cylinder of the left engine failed due to fatigue that originated in the root of the cylinder head thread that was engaged with the first thread on the barrel.
15. Post-accident inspection of the cockpit revealed several switches for the right engine were secured; however, no determination could be made when the switches were placed / moved in those positions.
16. No evidence of failure of the airplane's structures or flight control system contributed to the accident.
17. Existing regulations did not require the aircraft to be fitted with flight recorders. The lack of any recorded data about the aircraft's performance or the flight crew conversations deprived the investigation team of essential factual information.
18. Current Civil Aviation Department personnel and budget resources may not be sufficient to ensure that the quality of surveillance for certified as well as uncertified air carrier operations will improve.
19. Airside access procedures are inadequate at Fixed Base Operators. Access to the secure airside occurring without any check of individuals to challenge whether they have a legitimate reason for accessing the secure airside. FBO door to access airside is not secured or locked continuously; persons observed walking in and out without being challenged.
20. Flight Plan Forms are being accepted and transmitted to ATC with incomplete information. This information is vital for search and rescue purposes.
21. Weather was not a factor in the accident.
22. ATC was not a factor in the accident.
23. Currently flight plans for private flights are only required for international operations.
24. The pilot was aware of discrepancy associated with the manifold pressure reading of the left engine prior to takeoff. This discrepancy was brought to his attention by a client from the flight immediately preceding the accident flight.
25. The exact center of gravity of the accident airplane could not be calculated accurately as no indication of what seat each passenger occupied in the airplane and no indication of where luggage or equipment were placed on the aircraft could be determined. However, due to the exceedance of weight limits the aircraft was already outside the allowable center of gravity envelope developed by the manufacturer.
26. The pilot had insufficient time to prepare for the approach to runway 27 before beginning the approach. The airplane pitched up quickly into a stall, after extension of gear, recovery before ground impact was unlikely once the stall began.
27. Post accident inspection did not reveal any mechanical evidence or problems with the right hand engine.
28. The pilot's decision to return to the airfield was reasonable. Once the aircraft began to lose height a return to the airfield became impractical and a forced landing in the direction of flight should have been attempted.
29. The right propeller was never recovered from the lake.
The following causal factors were identified:
1. The left engine suffered a mechanical failure of the #2 cylinder, and therefore could not produce rated shaft horsepower. No indication of total loss of power with the left engine reported.
2. Right Engine electrical and engine control switches were found in the “OFF” position, therefore the aircraft was incapable of climbing on the power of one engine alone.
3. The excess weight above the maximum weight allowed for takeoff may have been an important factor in the aircraft's inability to gain adequate altitude after takeoff.
4. The pilot secured the right engine which was mechanically capable of producing power resulting in a total loss of thrust. He then sometime thereafter initiated a steep turn with gear down and the left engine already not developing sufficient shaft horsepower to sustain lift.
5. The pilot attempted to return to the departure airfield but lost control of the aircraft during a turn to the left.
Final Report: