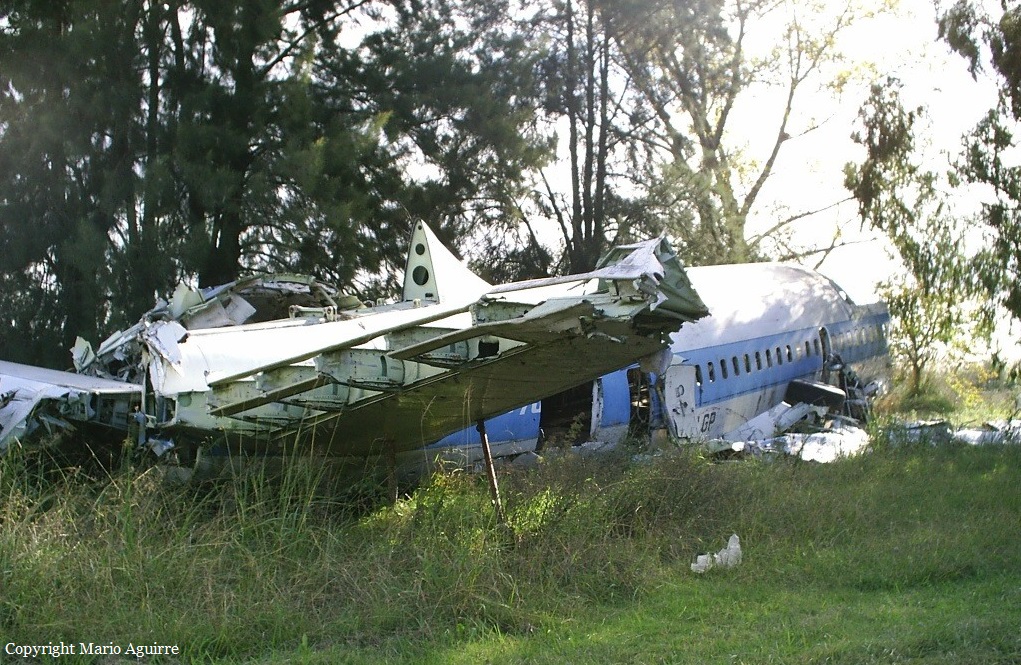
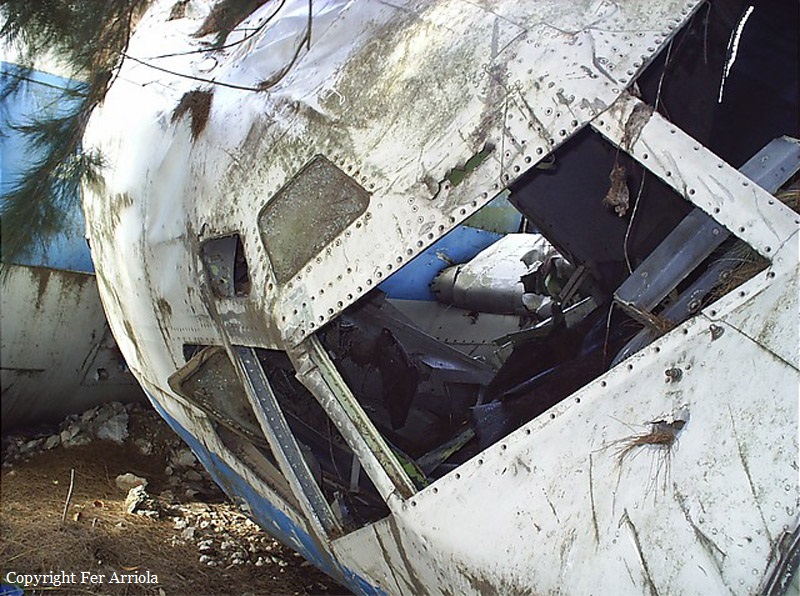
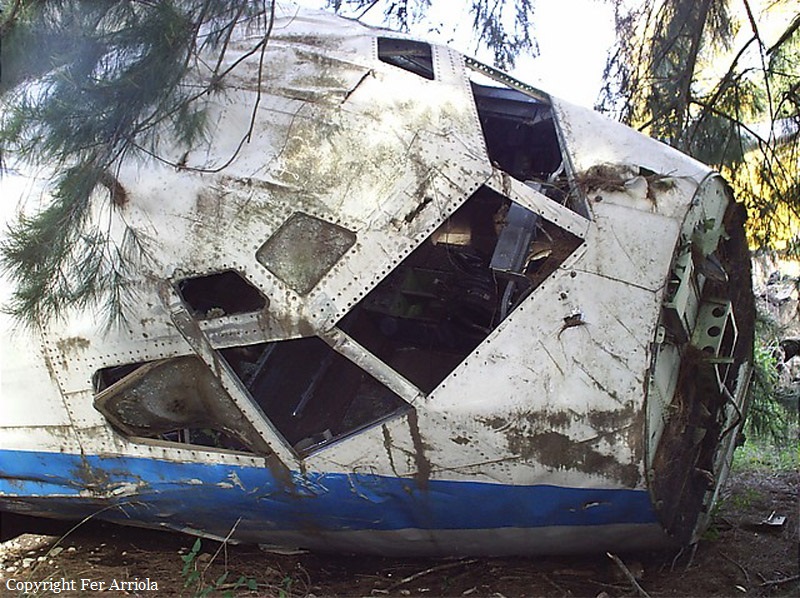
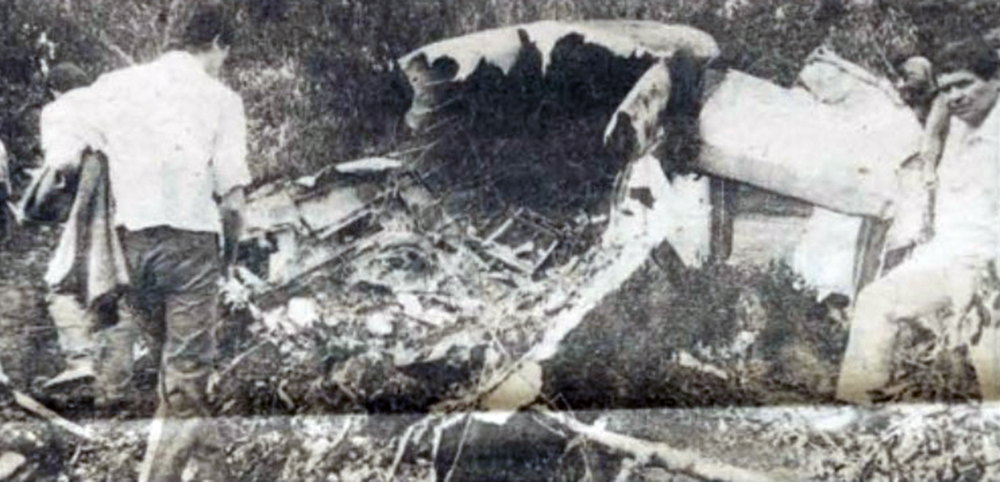
Crash of a Beechcraft C90 King Air in Olivar
Date & Time:
Sep 13, 2025
Registration:
CC-AHN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Puerto Montt – Santiago
MSN:
LJ-517
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
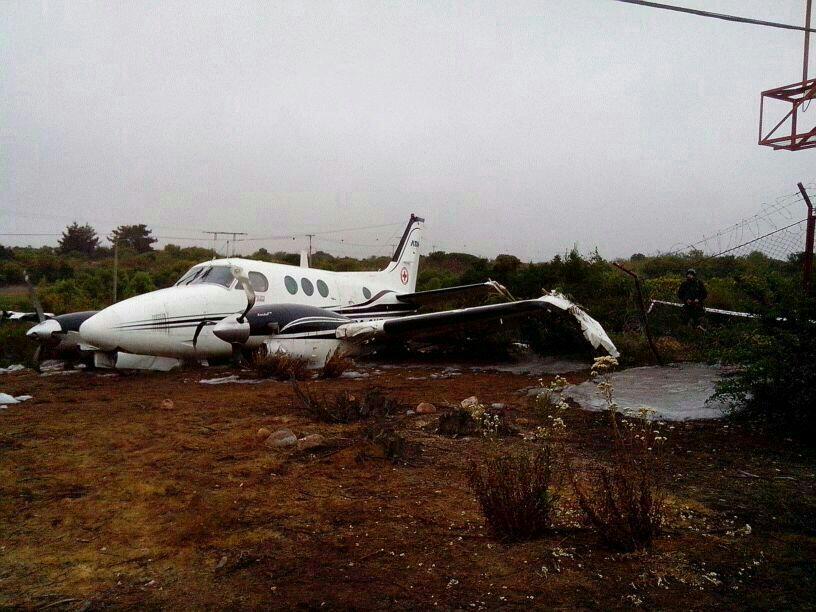
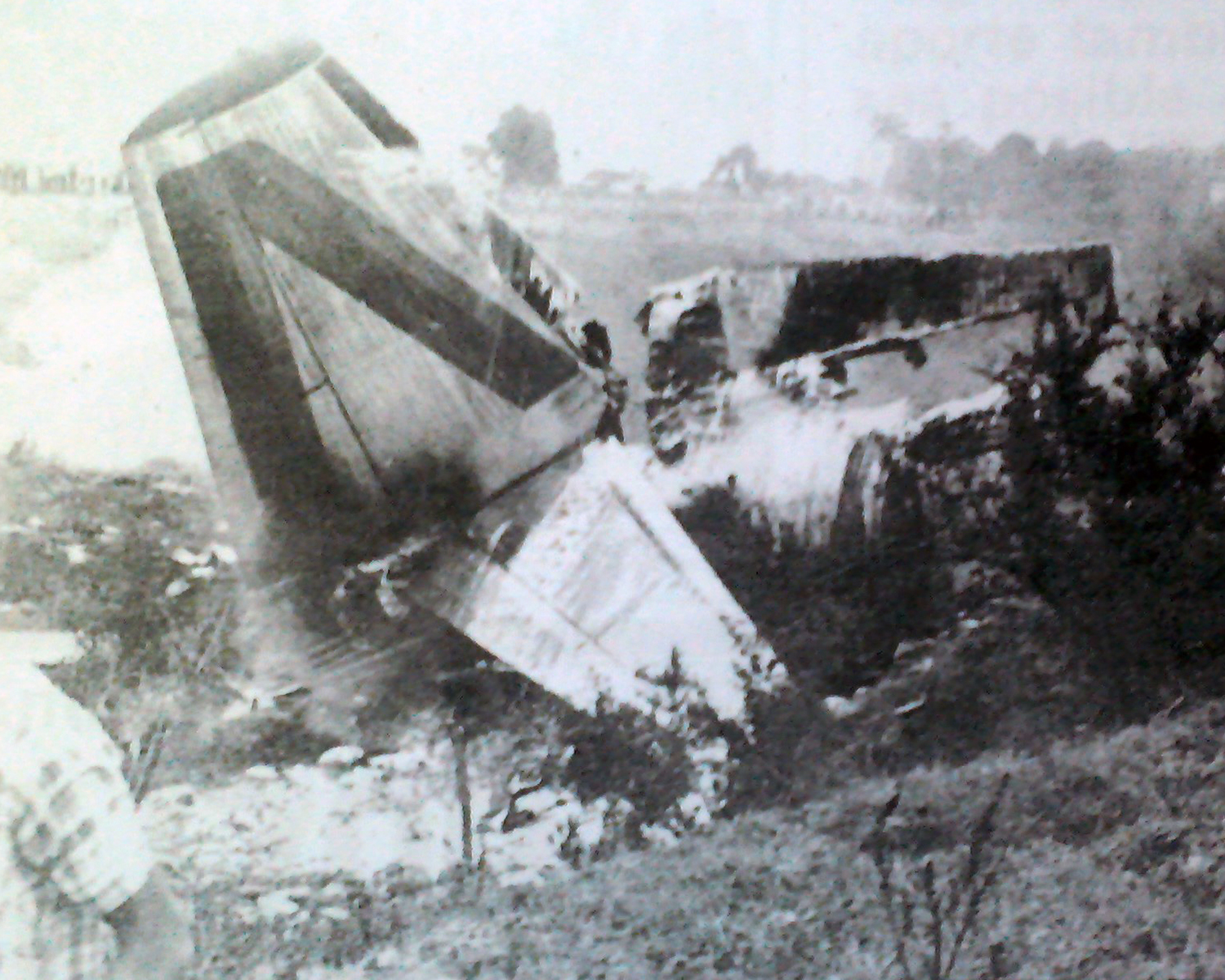
Circumstances:
While on an ambulance flight from Puerto Montt to Santiago, the crew encountered an unexpected situation and was forced to attempt an emergency landing. In the early morning, the twin engine airplane collided with a fence and crashed in a private garden located in Olivar, some 93 km south of Santiago-Arturo Merino Benitez Airport. All four occupants were evacuated with various injuries and the airplane was damaged beyond repair.