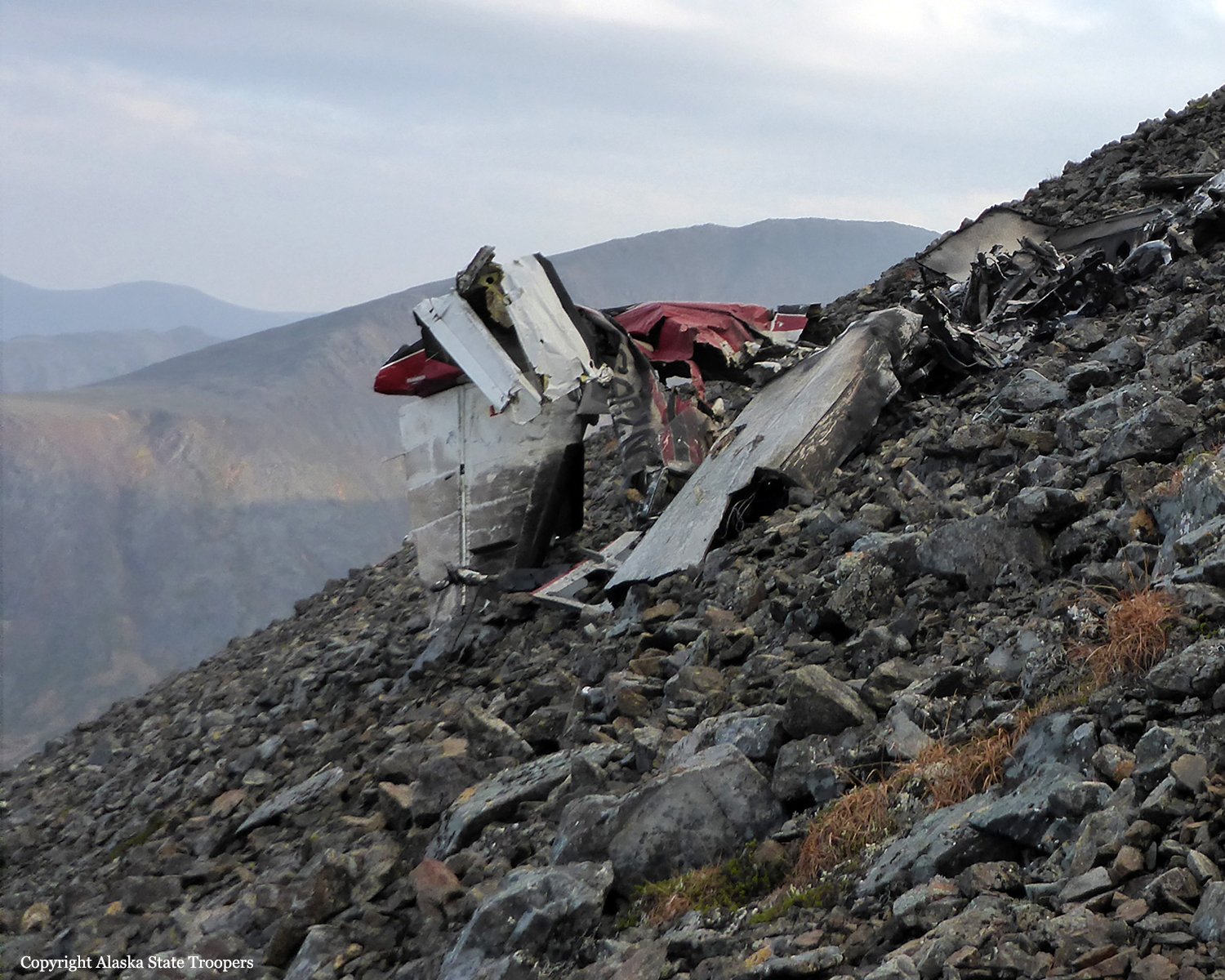
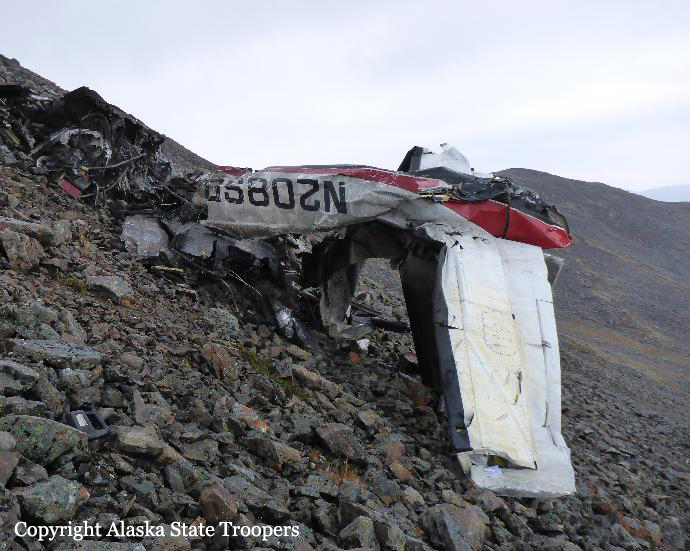
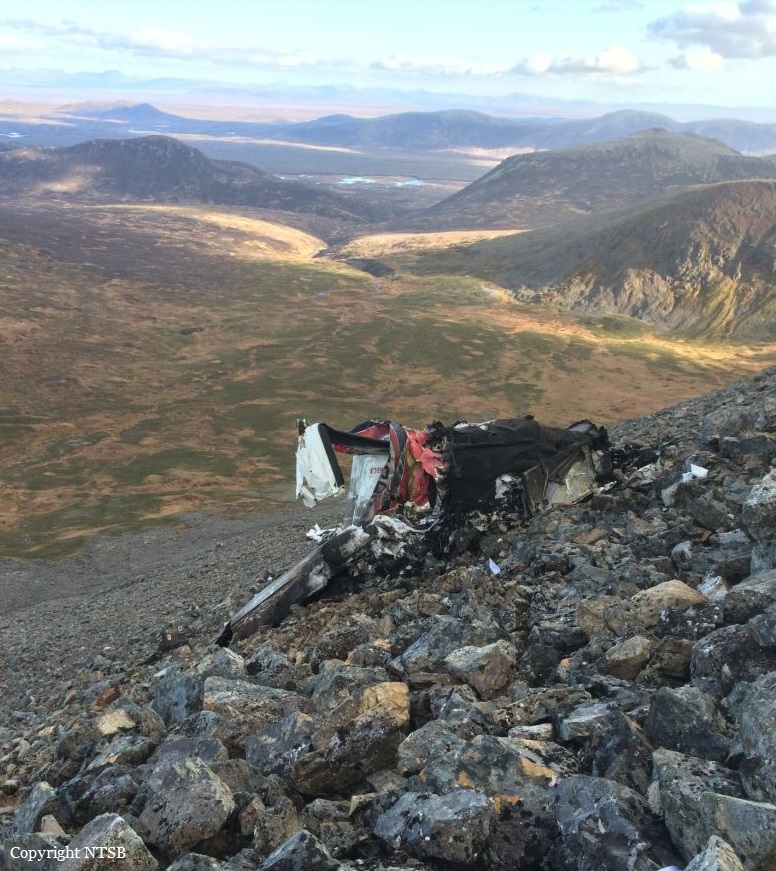
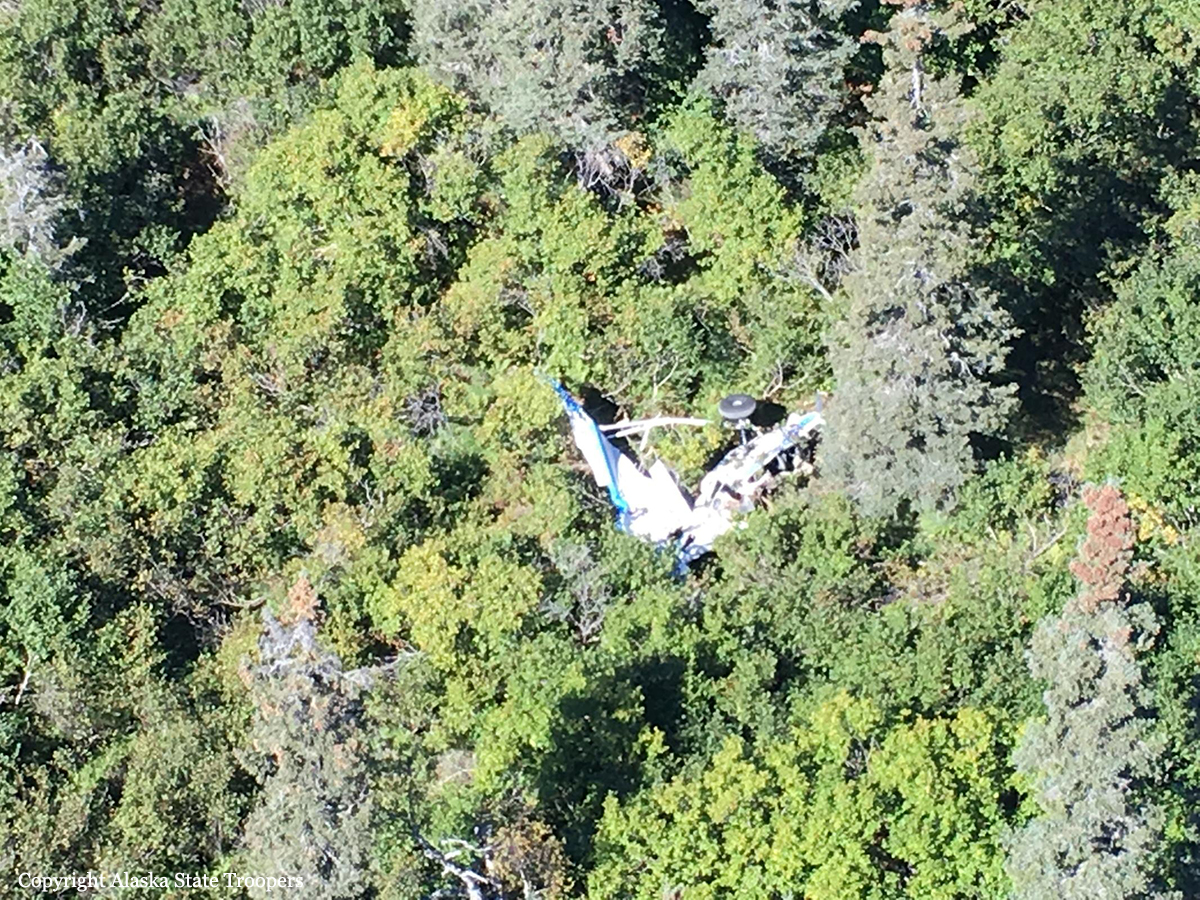
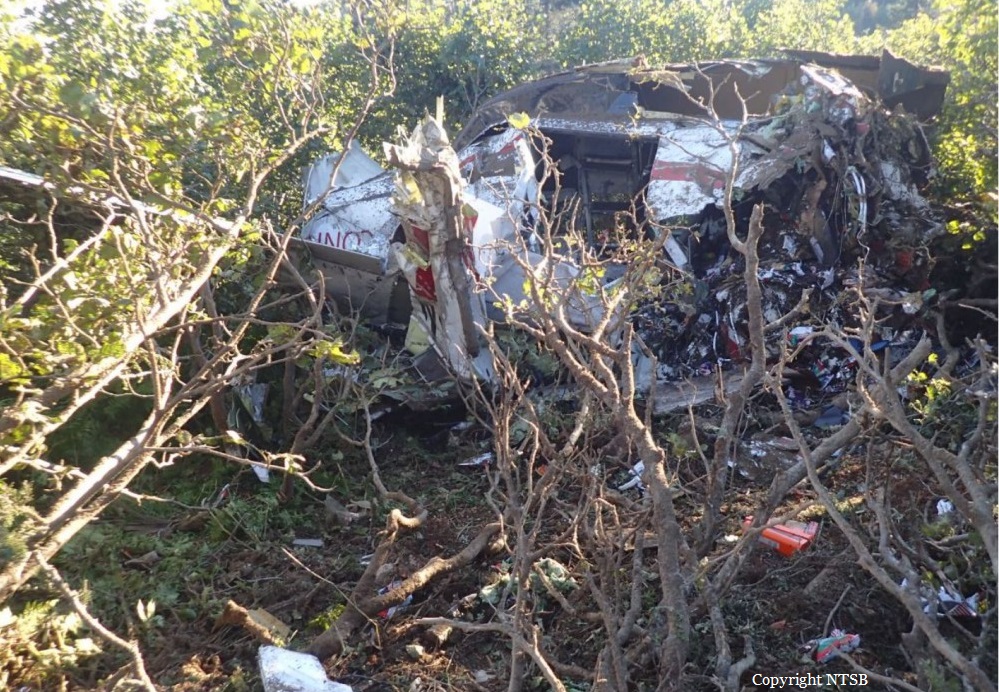
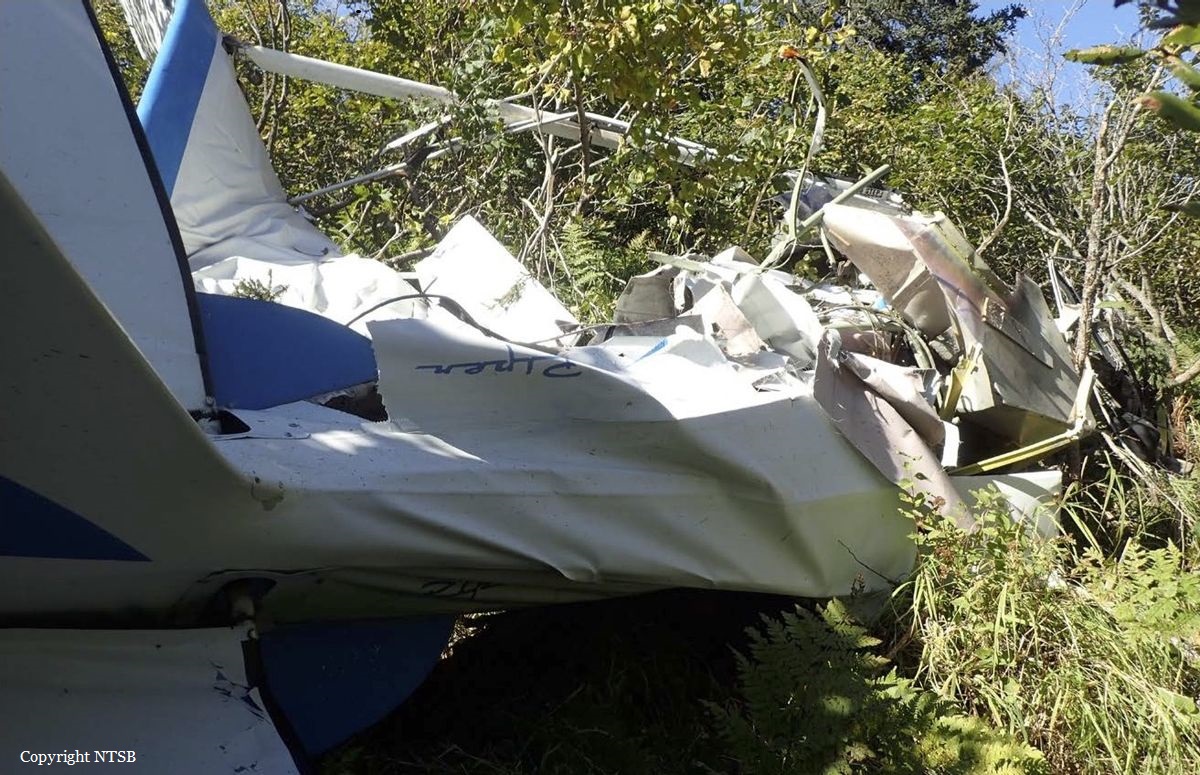
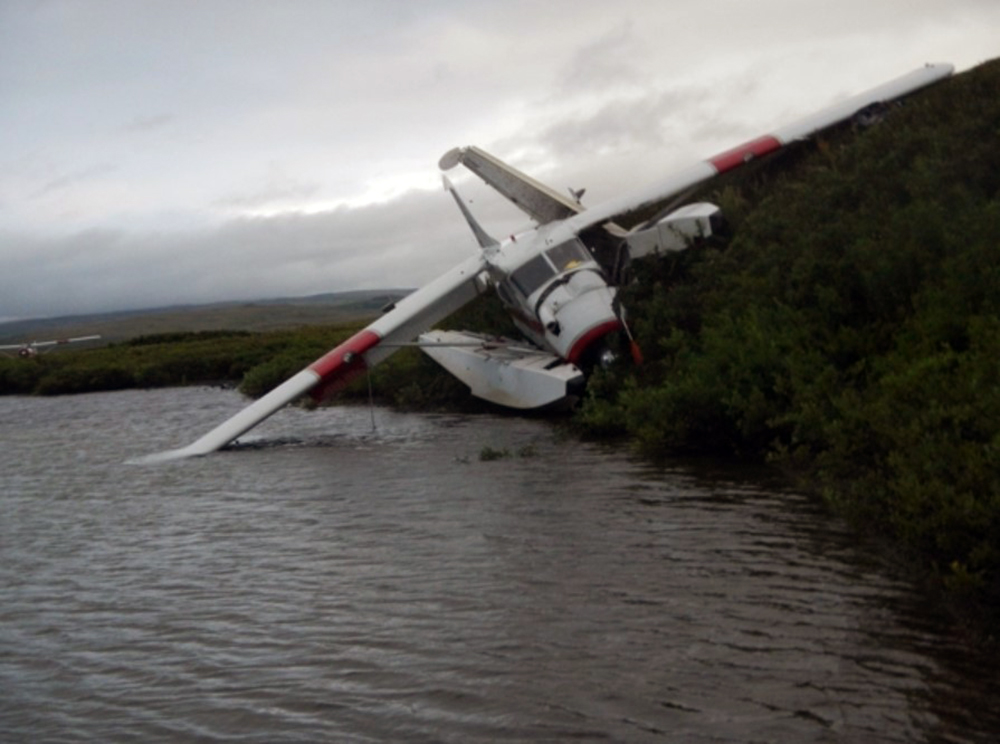
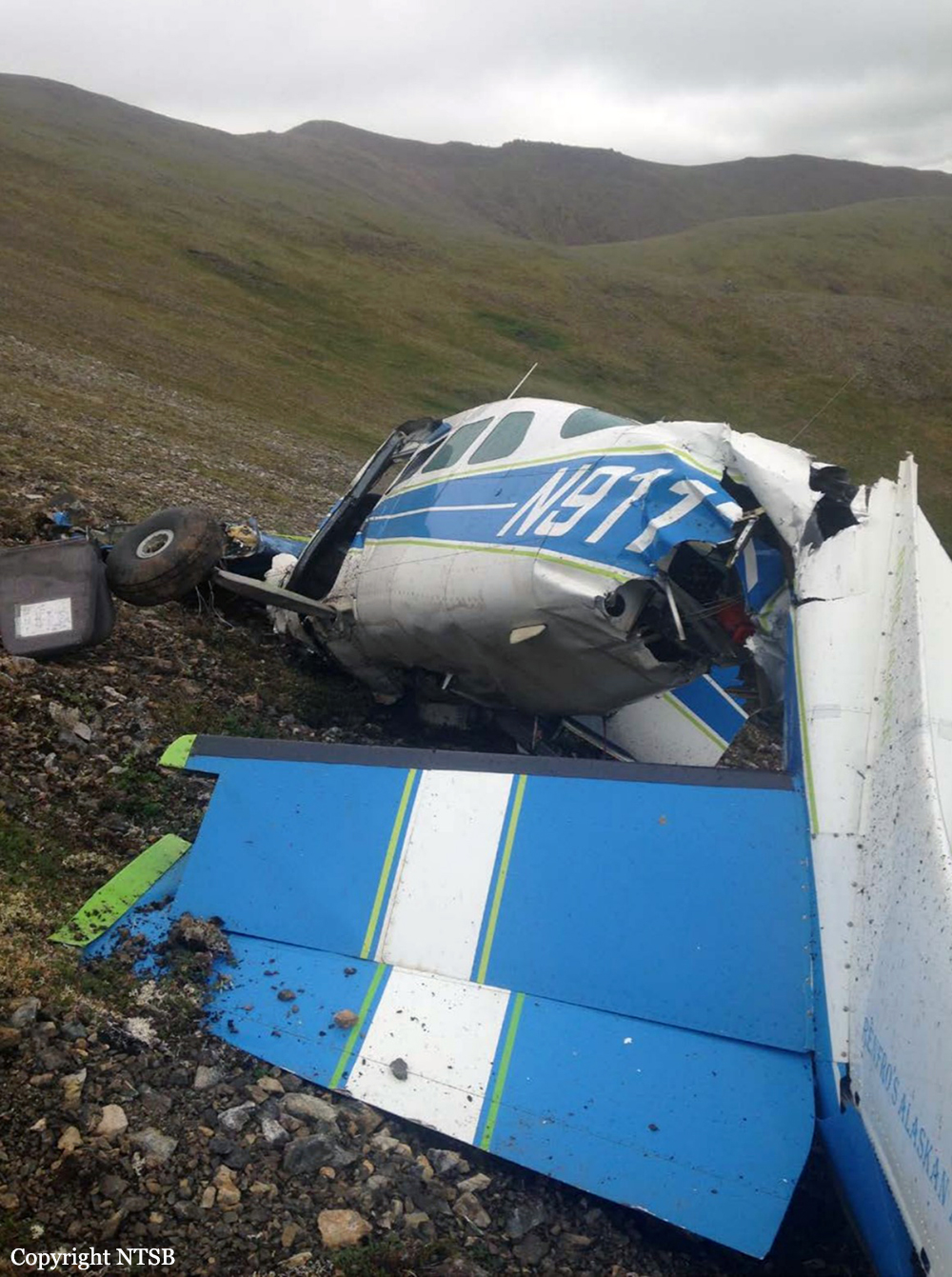
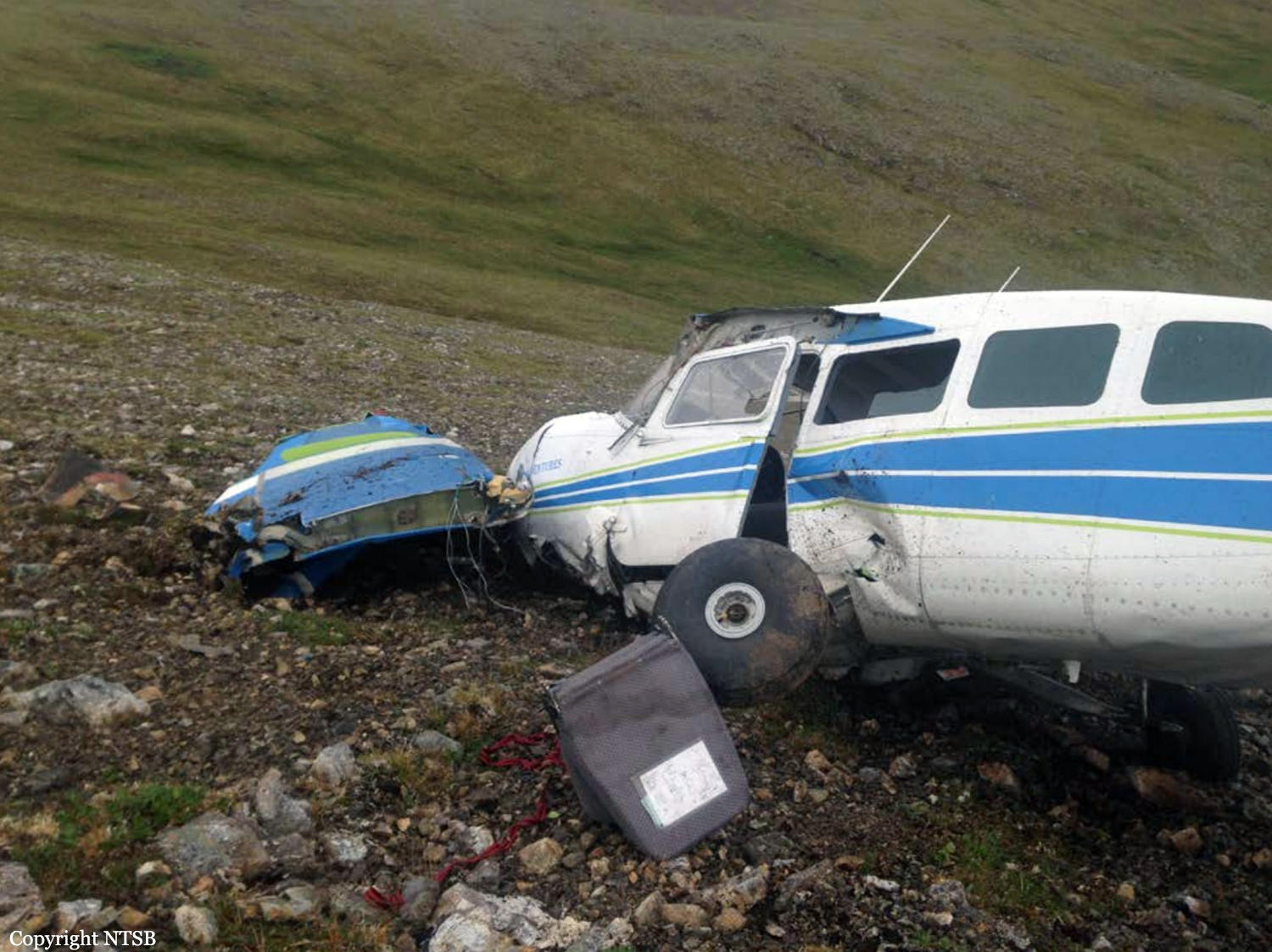
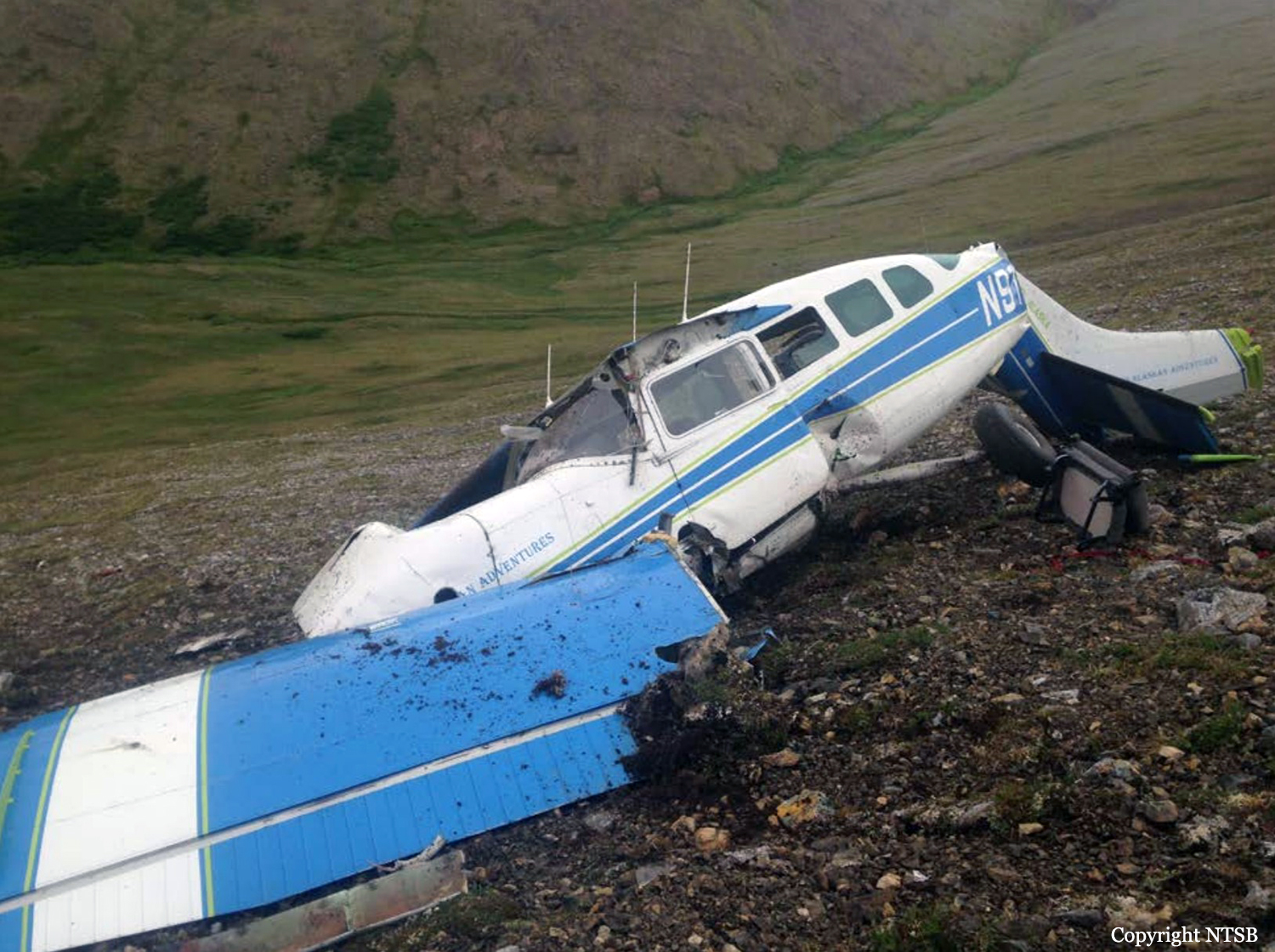
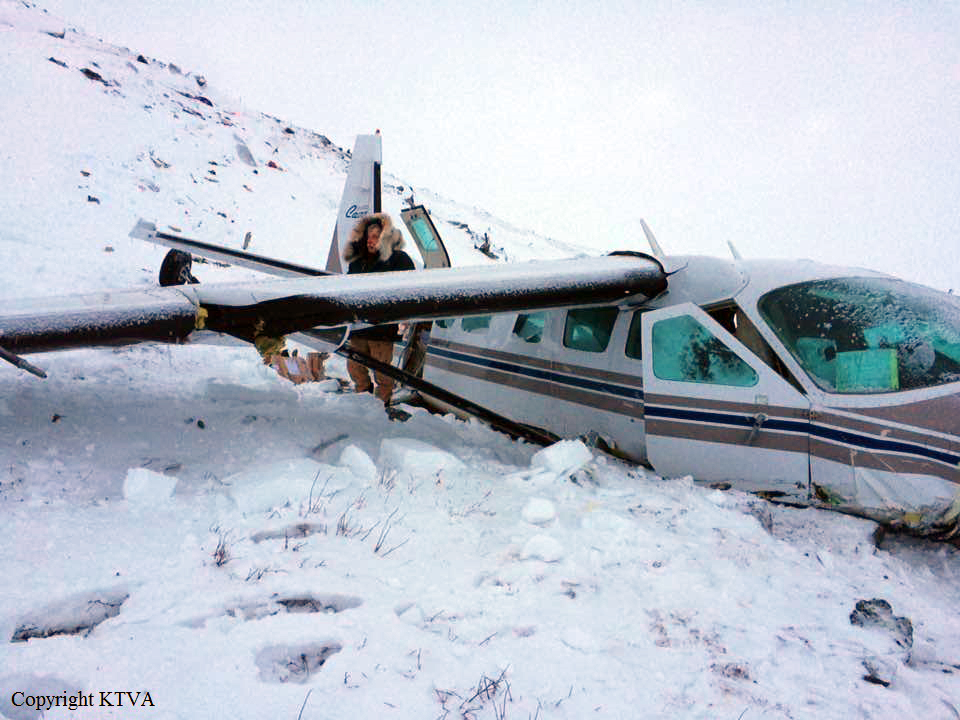
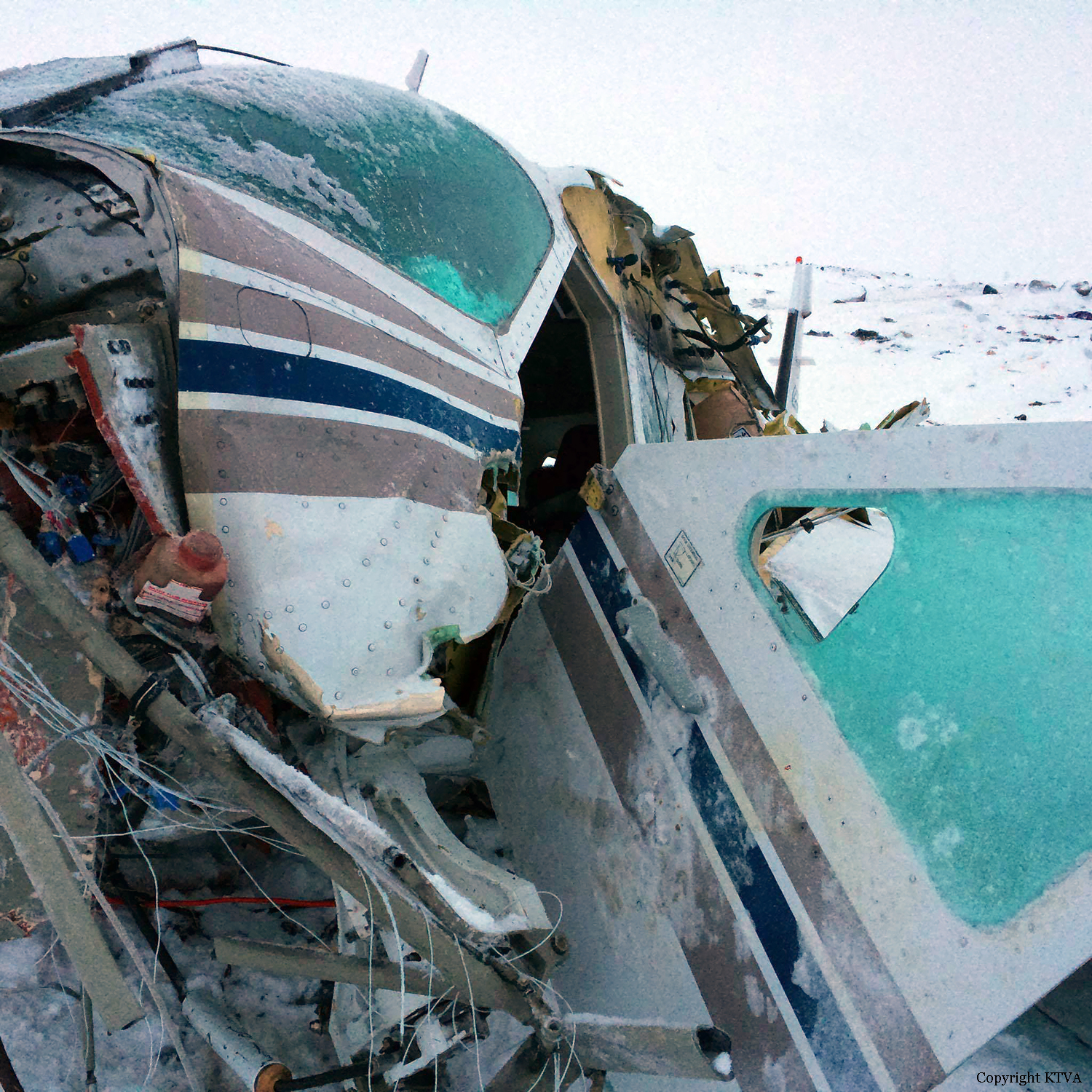
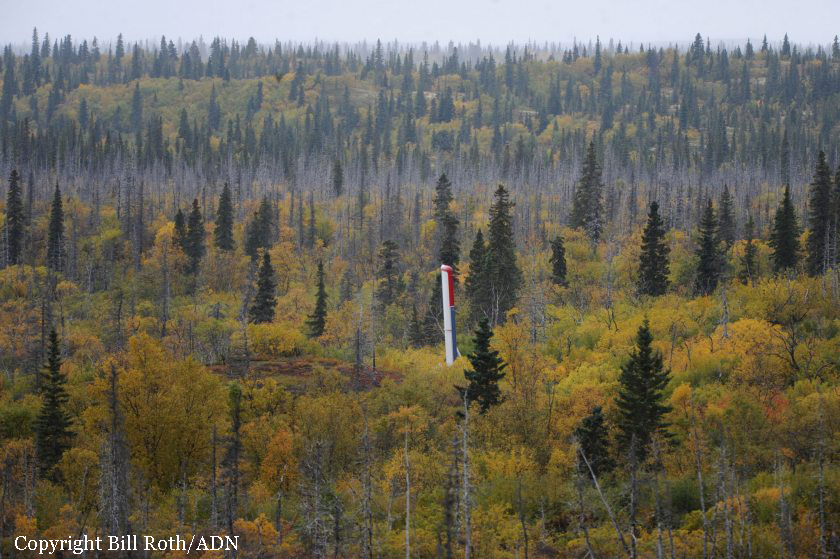
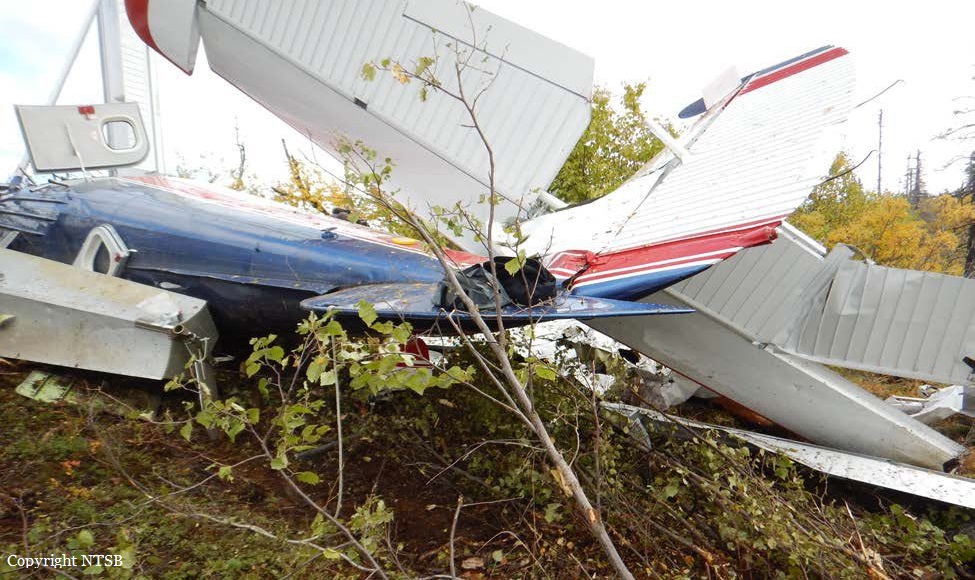
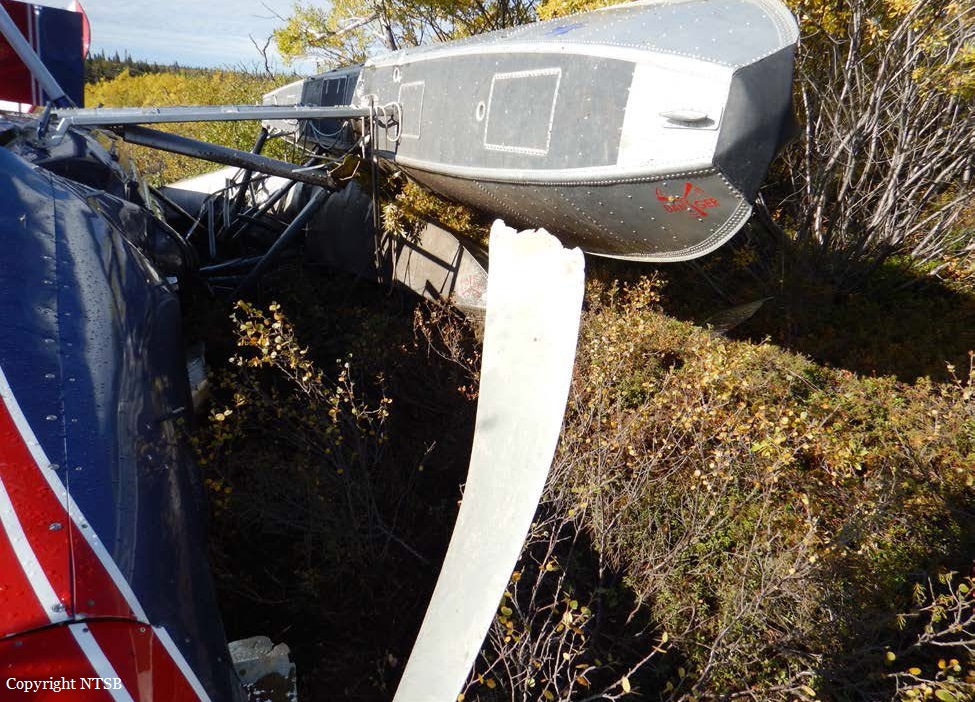
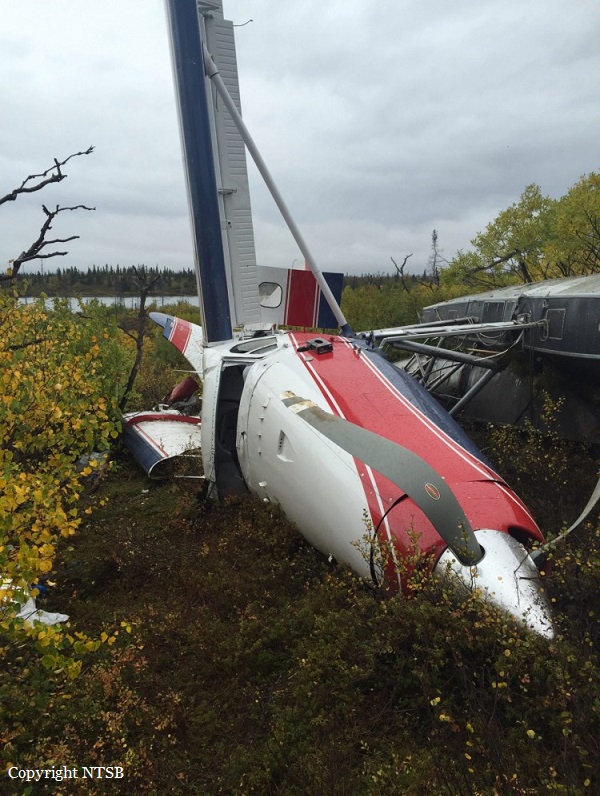
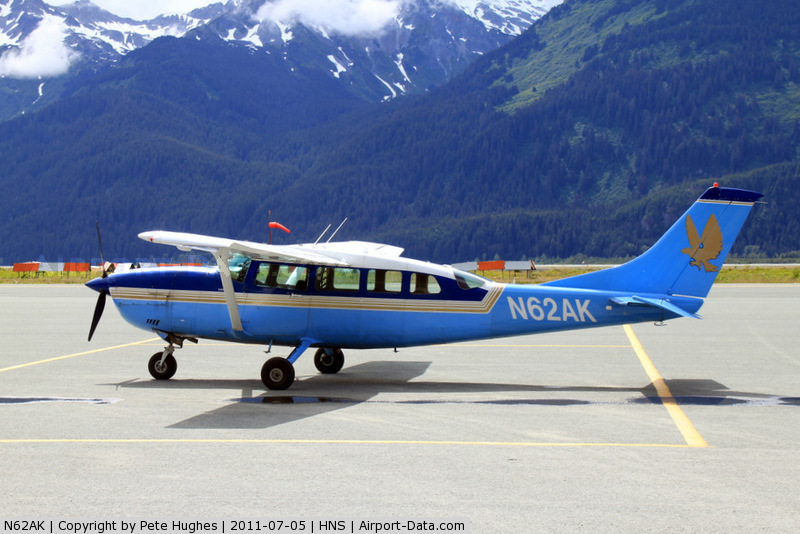
Circumstances:
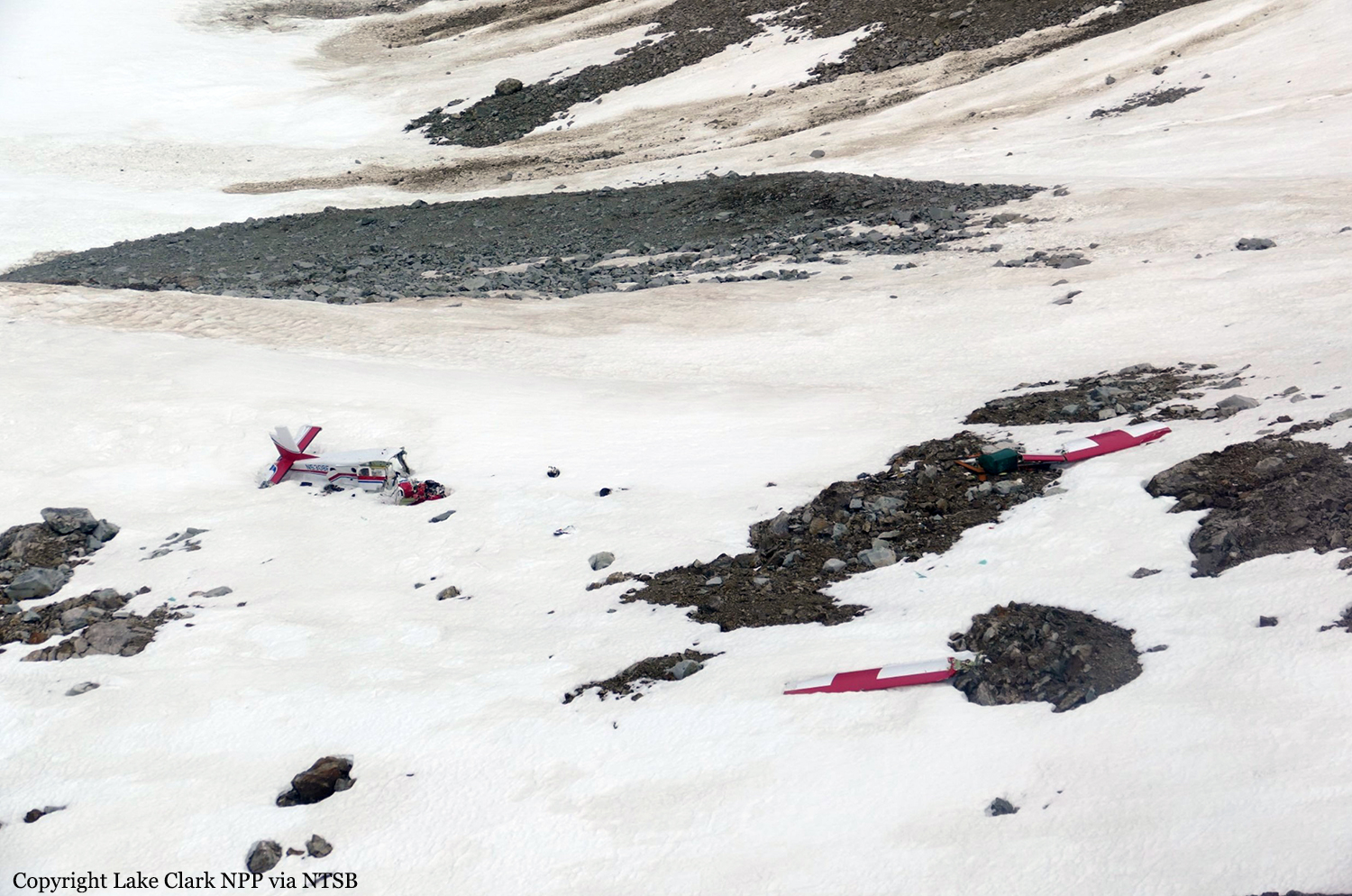
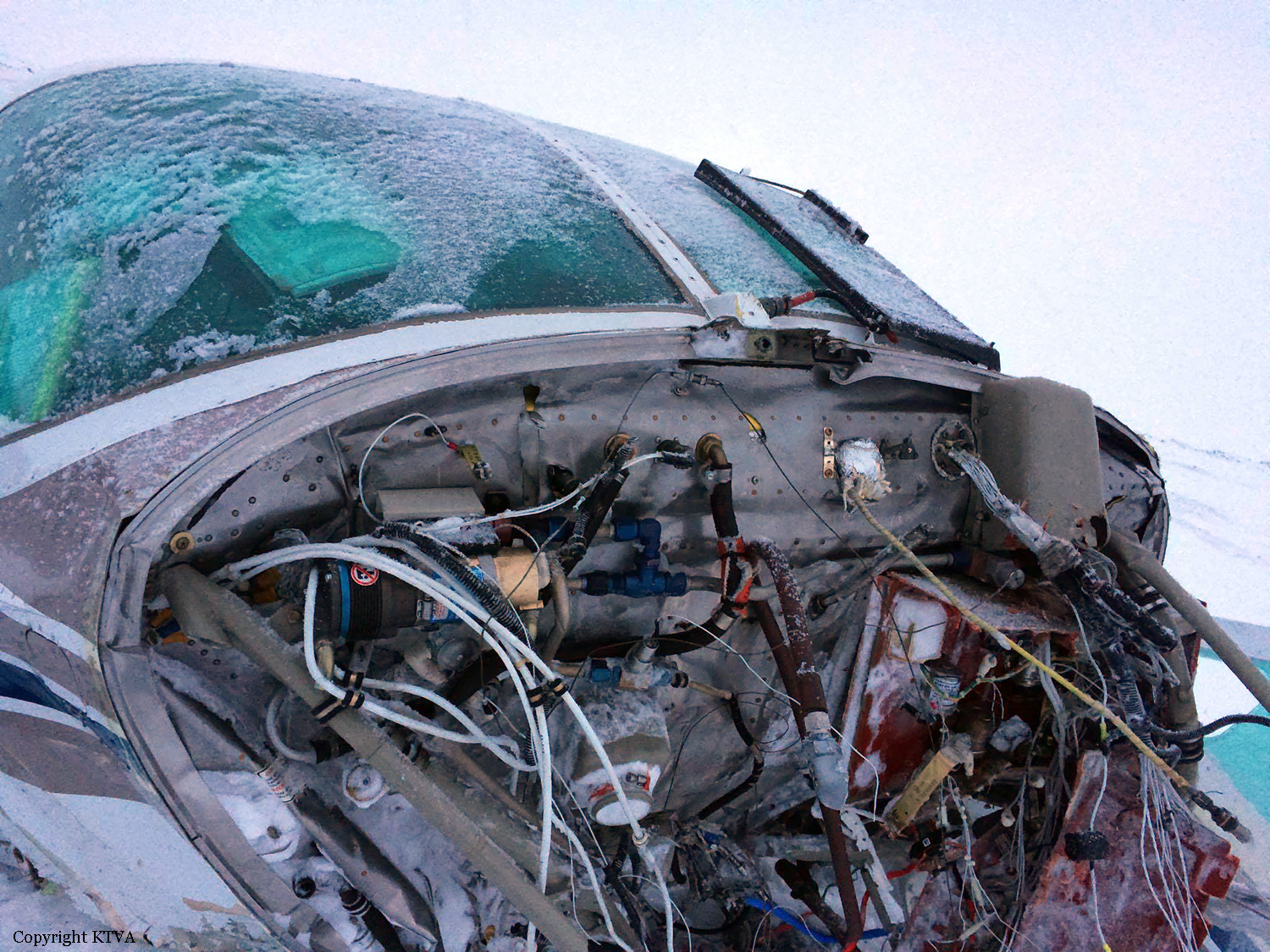
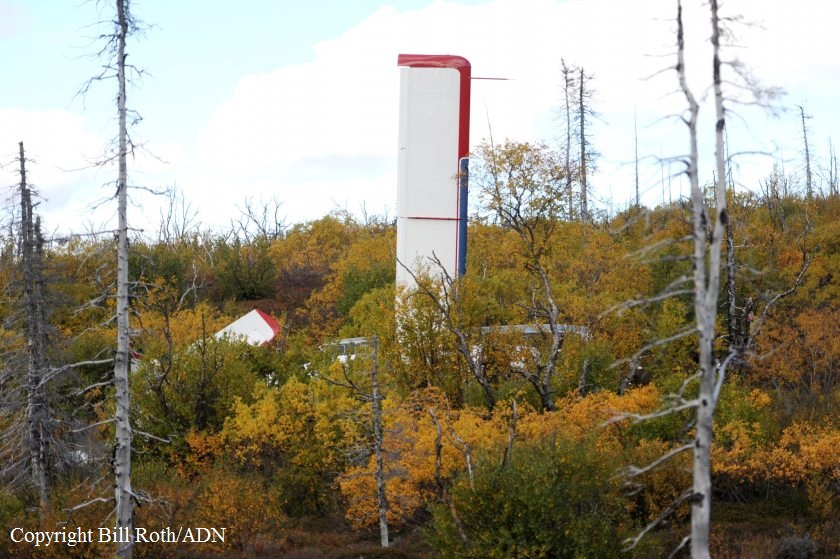
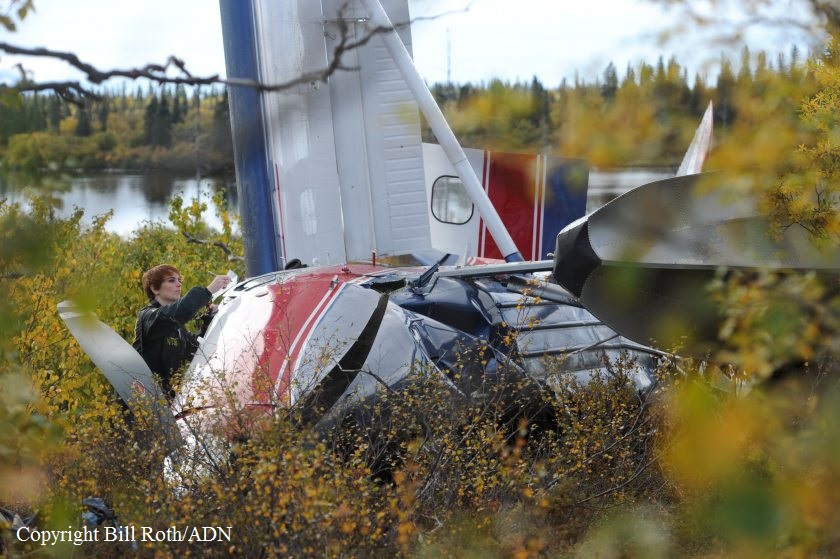
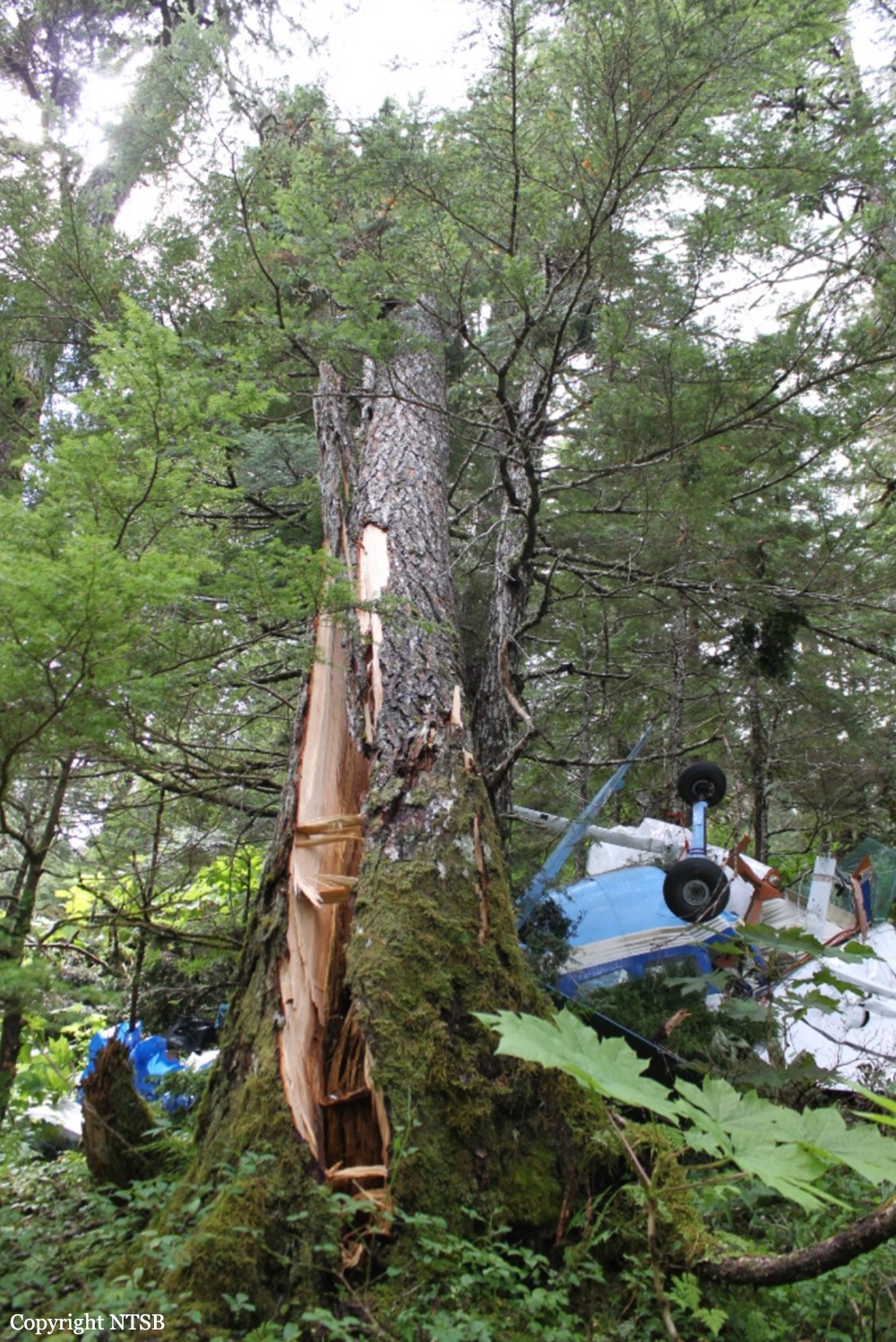
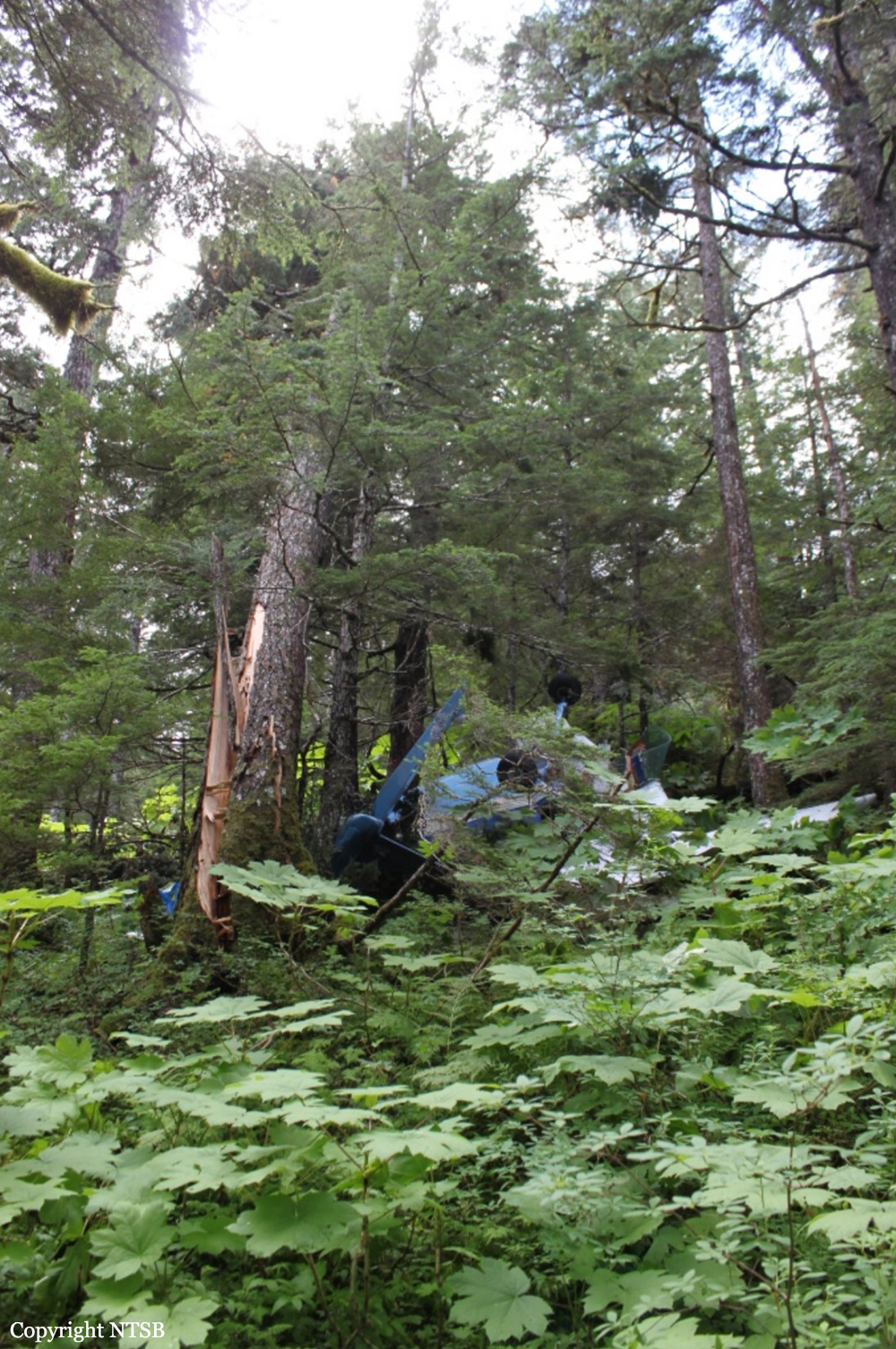
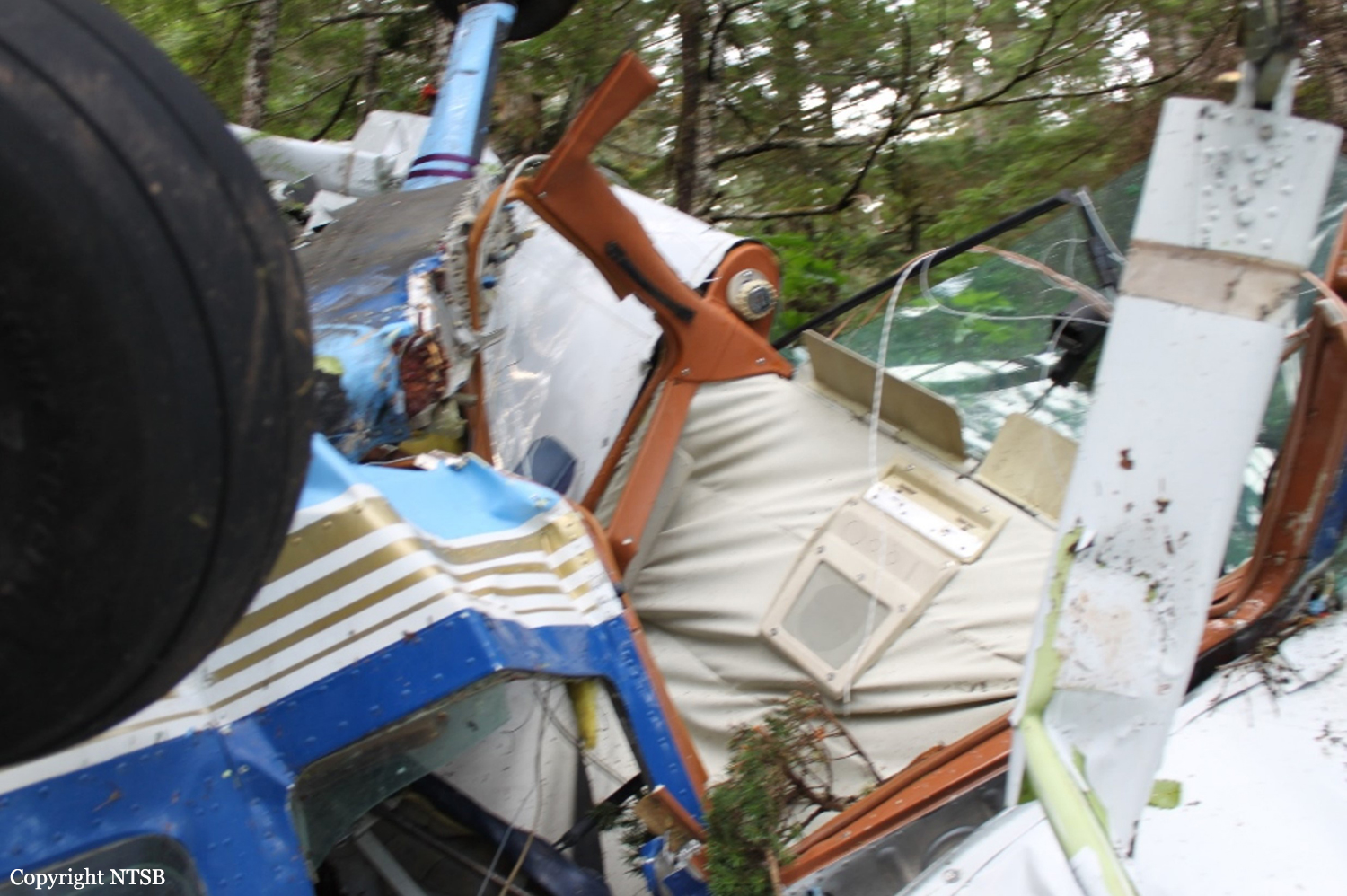
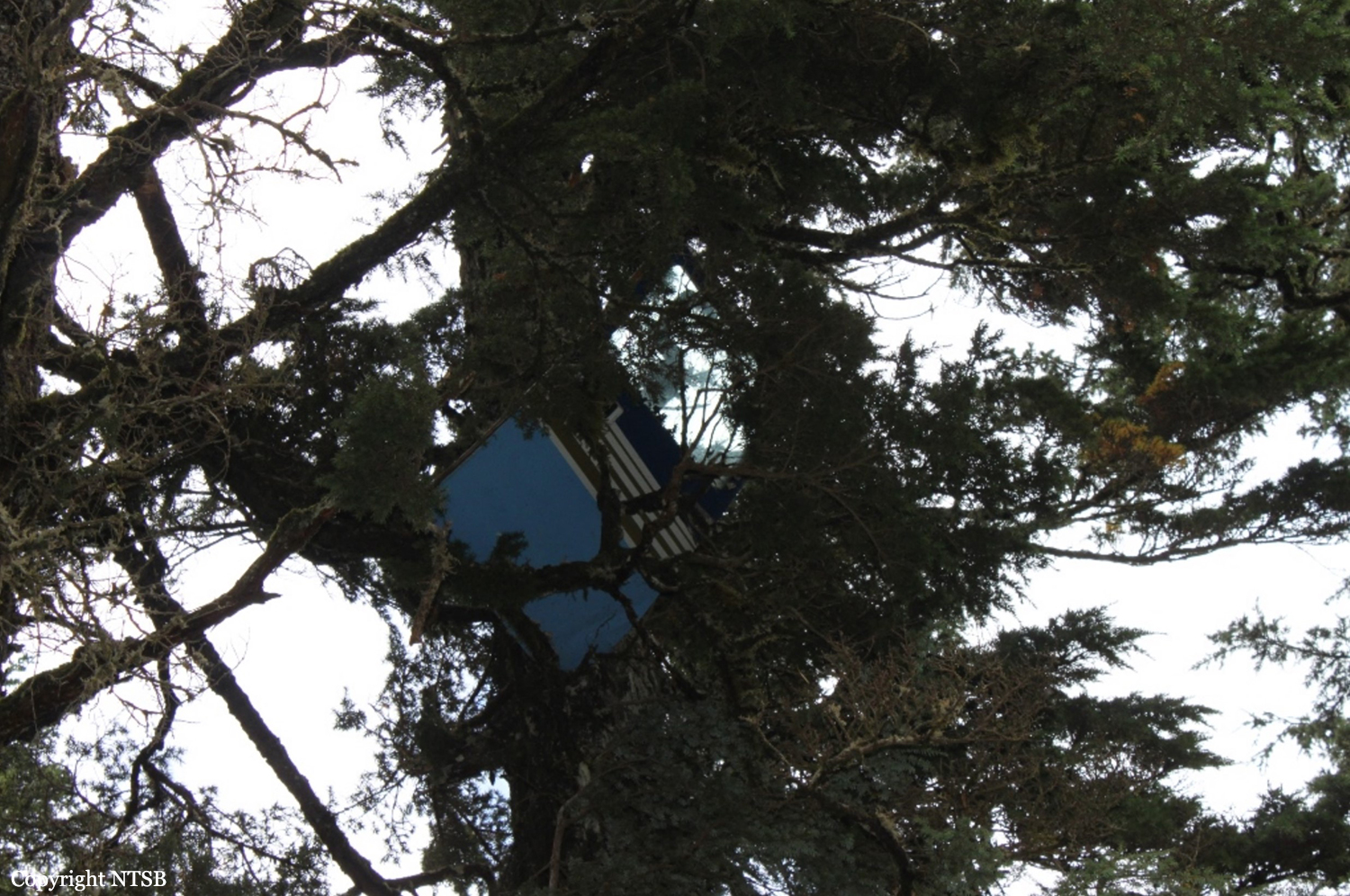
The company flight coordinator on duty when the pilot got her "duty-on" briefing reported that, during the "duty-on" briefing, he informed the commercial pilot that most flights to the intended destination had been cancelled in the morning due to poor weather conditions and that one pilot had turned around due to weather. No record was found indicating that the pilot used the company computer to review weather information before the flight nor that she had received or retrieved any weather information before the flight. If she had obtained weather information, she would have seen that the weather was marginal visual flight rules to instrument flight rules conditions, which might have affected her decision to initiate the flight. The pilot subsequently departed for the scheduled commuter flight with four passengers on board; the flight was expected to be 20 minutes long. Review of automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast data transmitted by the airplane showed that the airplane's flight track was farther north than the typical track for the destination and that the airplane did not turn south toward the destination after crossing the channel. Data from an on board multi-function display showed that, as the airplane approached mountainous terrain on the west side of the channel, the airplane made a series of erratic pitch-and-roll maneuvers before it impacted trees and terrain. Post-accident examination of the airframe and engine revealed no mechanical malfunctions or anomalies that would have precluded normal operation. One of the passengers reported that, after takeoff, the turbulence was "heavy," and there were layers of fog and clouds and some rain. Based on the weather reports, the passenger statement regarding the weather, and the flight's erratic movement just before impact, it is likely that the flight encountered instrument meteorological conditions as it approached the mountainous terrain and that the pilot then lost situational awareness and flew into trees and terrain. According to the company's General Operations Manual (GOM), operational control was delegated to the flight coordinator for the accident flight, and the flight coordinator and pilot-in-command (PIC) were jointly responsible for preflight planning, flight delay, and flight release, which included completing the flight risk assessment (FRA) process. This process required the PIC to fill out an FRA form and provide it to the flight coordinator before flight. However, the pilot did not fill out the form. The GOM stated that one of the roles of the flight dispatcher (also referred to as "flight coordinator") was to assist the pilot in flight preparation by gathering and disseminating pertinent information regarding weather and any information deemed necessary for the safety of flight. It also stated that the dispatcher was to assist the PIC as necessary to ensure that all items required for flight preparation were accomplished before each flight. However, the flight coordinator did not discuss all the risks and weather conditions associated with the flight with the pilot, which was contrary to the GOM. When the flight coordinator who was on duty at the time the airplane was ready to depart did not receive a completed FRA, he did not stop the flight from departing, which was contrary to company policy. By not completing an FRA, it is likely the total risks associated with the accident flight were not adequately assessed. Neither the pilot nor the flight coordinator should have allowed the flight to be released without having completed an FRA form, which led to a loss of operational control and the failure to do so likely contributed to the accident. Interviews with company personnel and a review of a sampling of FRA forms revealed that company personnel, including the flight coordinators, lacked a fundamental knowledge of operational control theory and practice and operational practices (or lack thereof), which led to a loss of operational control for the accident flight. The company provided no formal flight coordinator training nor was a formal training program required. All of the company's qualified flight coordinators were delegated operational control and, thus, were required by 14 Code of Federal Regulations Section 119.69 to be qualified through training, experience, and expertise and to fully understand aviation safety standards and safe operating practice with respect to the company's operation and its GOM. However, the company had no formal method of documenting these requirements; therefore, it lacked a method of determining its flight coordinators' qualifications. In post-accident interviews, the previous Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) principal operations inspector (POI), who became the frontline manager over the certificate, stated that the company used the minimum regulatory standard when it came to ceiling and visibility requirements and that the company did not have any company minimums in place. He further stated that a cloud ceiling of 500 ft and 2 miles visibility would not allow for power-off glide to land even though the company was required to meet this regulation. When asked if he believed the practice of allowing the pilot to decide when to fly was adequate, he said it was not and there should have been route altitudes. However, no action was taken to change SeaPort's operations. The POI at the time of the accident stated that she was also aware that the company was operating contrary to federal regulatory standards for gliding distance to shore. A review of FAA surveillance activities of the company revealed that the POI provided surveillance of the company following the accident, including an operational control inspection, and noted deficiencies with the company's operational procedures; however, the FAA did not hold the company accountable for correcting the identified operational deficiencies. If the FAA had conducted an investigation or initiated an enforcement action pertaining to the company's apparent disregard of the regulatory standard for maintaining glide distance before the accident similar to the inspection conducted following the accident, it is plausible the flight would not have departed or continued when glide distance could not be maintained. The FAA's failure to ensure that the company corrected these deficiencies likely contributed to this accident which resulted, in part, from the company's failure to comply with its GOM and applicable federal regulations, including required glide distance to shore. The company was the holder of a Medallion Shield until they voluntarily suspended the Shield status but retained the "Star" status and continued advertising as a Shield carrier. Medallion stated in an email "With this process of voluntarily suspension, there will be no official communication to the FAA…" Given that Medallion advertises that along with the Shield comes recognition by the FAA as an operator who incorporates higher standards of safety, it seems contrary to safety that they would withhold information pertaining to a suspension of that status.