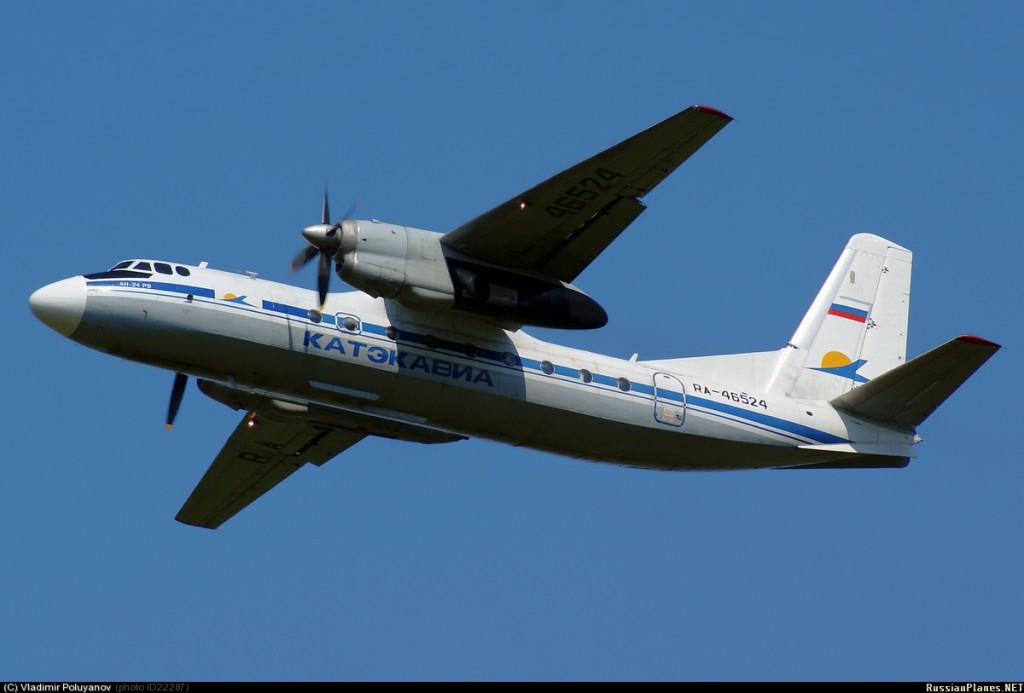
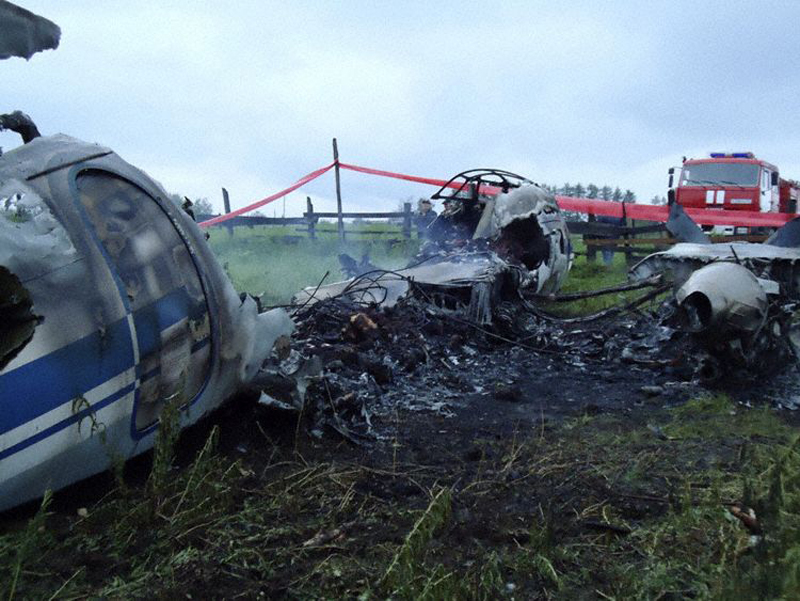
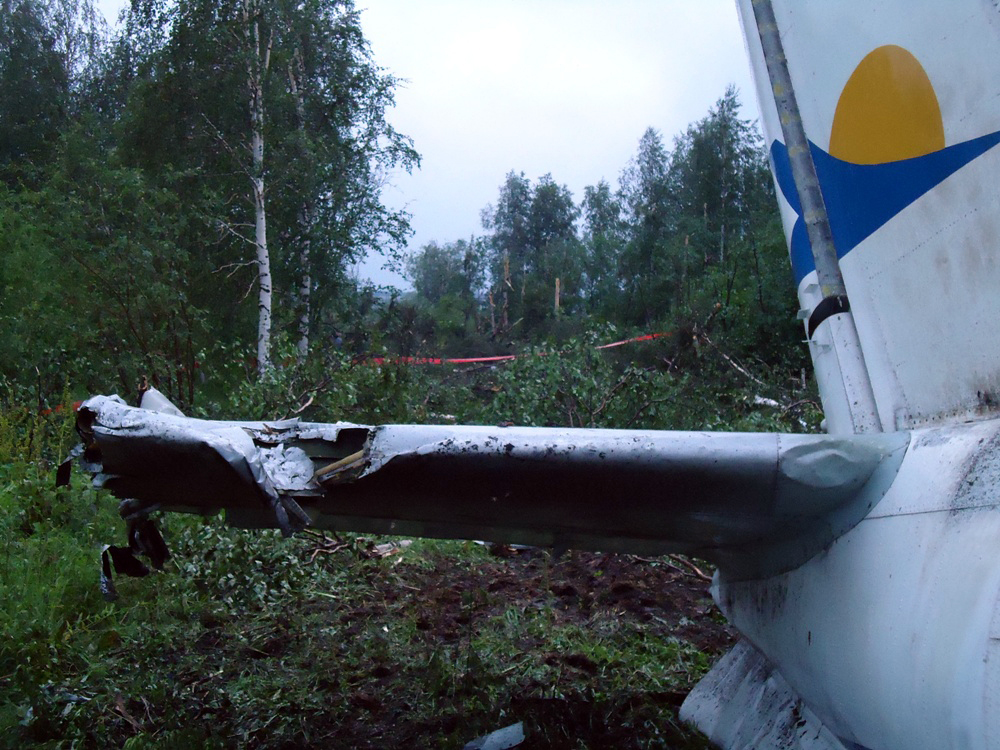
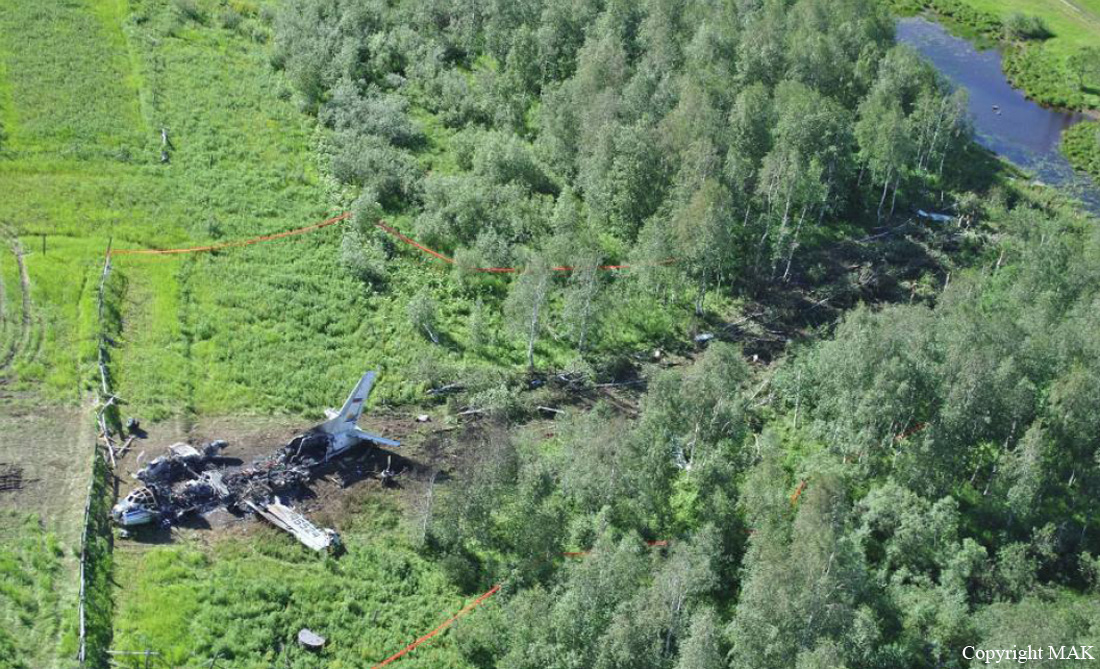
Crash of an Embraer ERJ-190-100LR in Yichun: 44 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 24, 2010 at 2138 LT
Registration:
B-3130
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Harbin - Yichun
MSN:
190-00223
YOM:
2008
Flight number:
VD8387
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
91
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
44
Aircraft flight hours:
5109
Aircraft flight cycles:
4712
Circumstances:
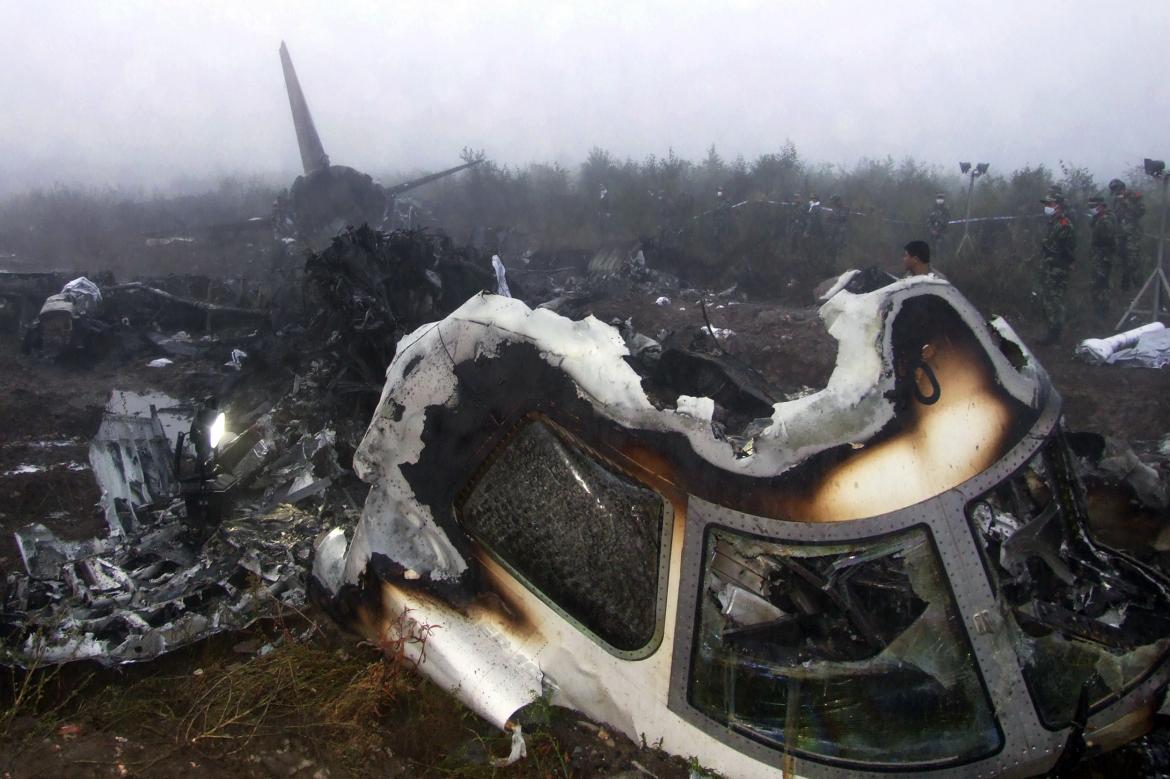
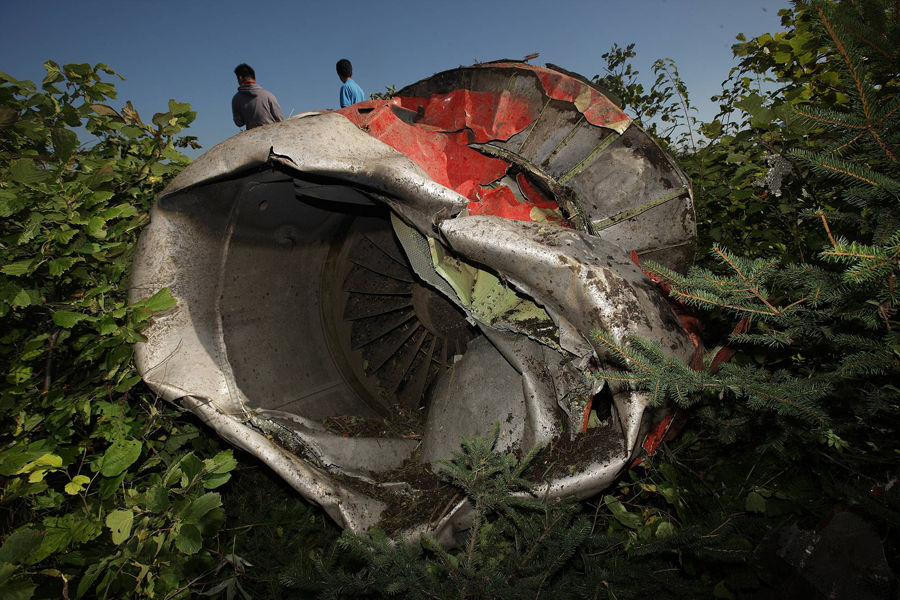
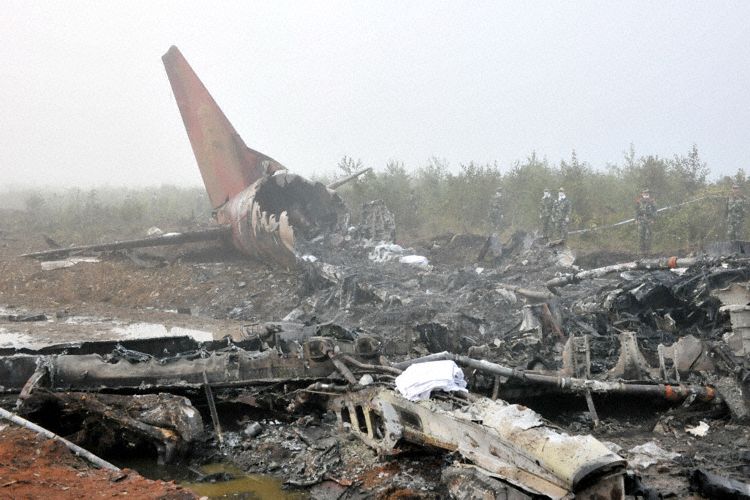
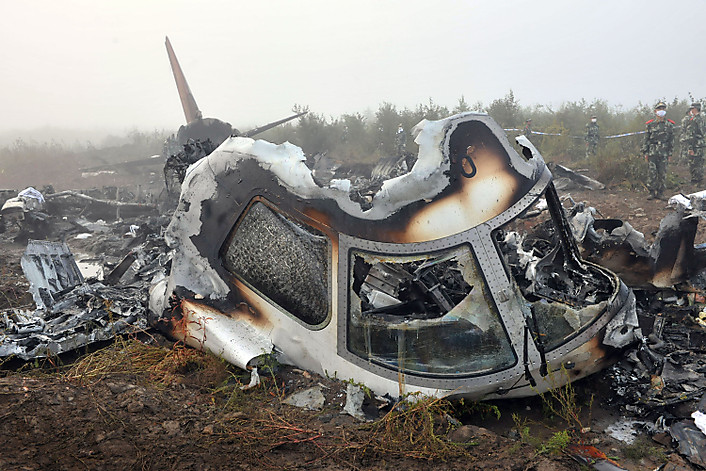
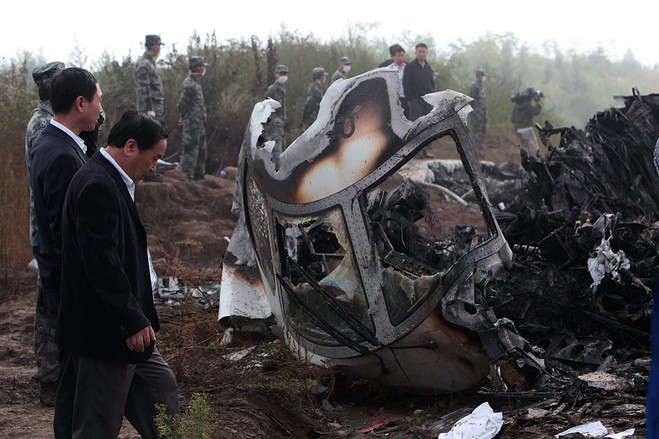
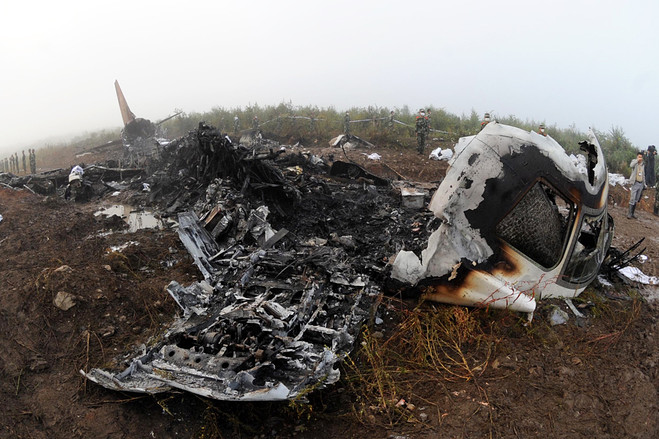
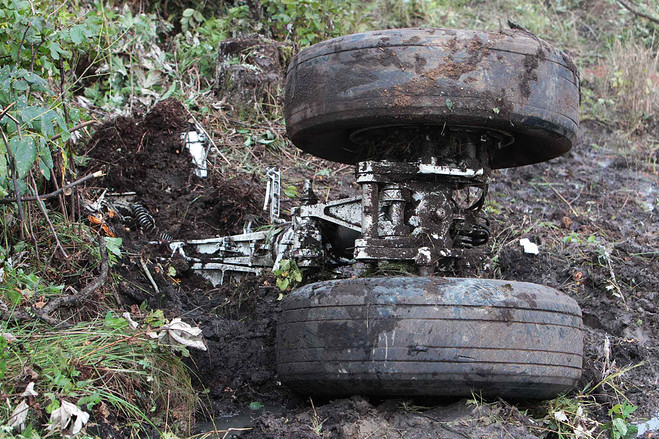
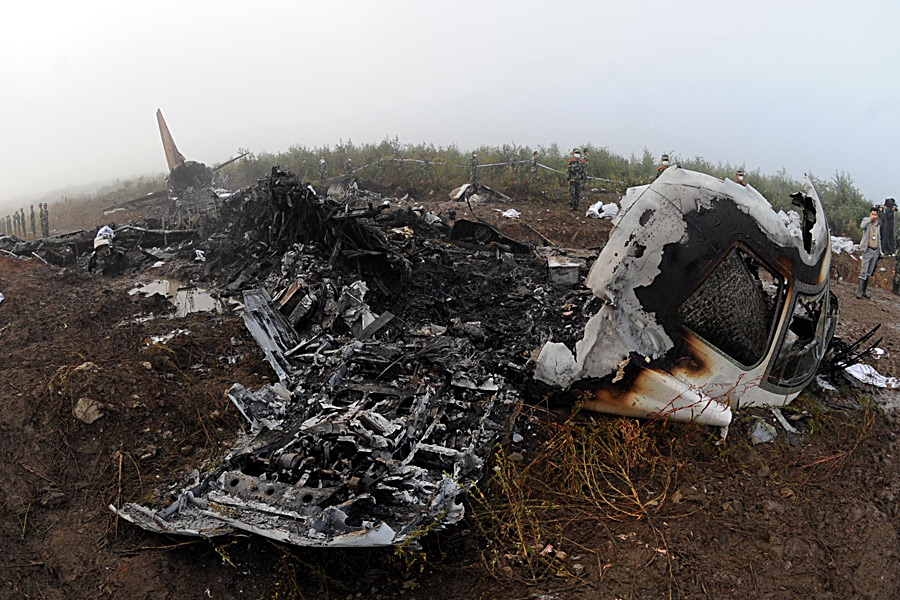
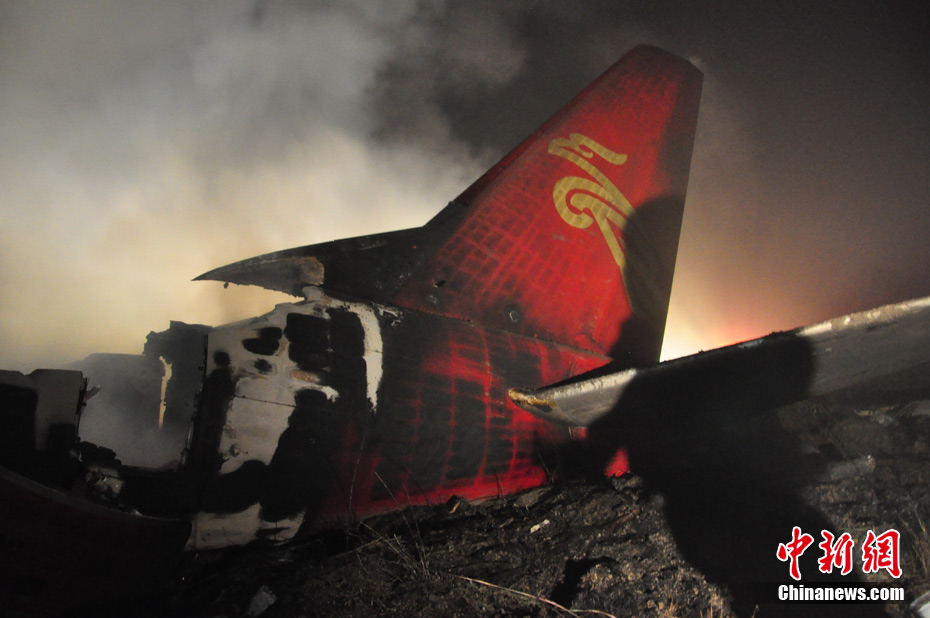
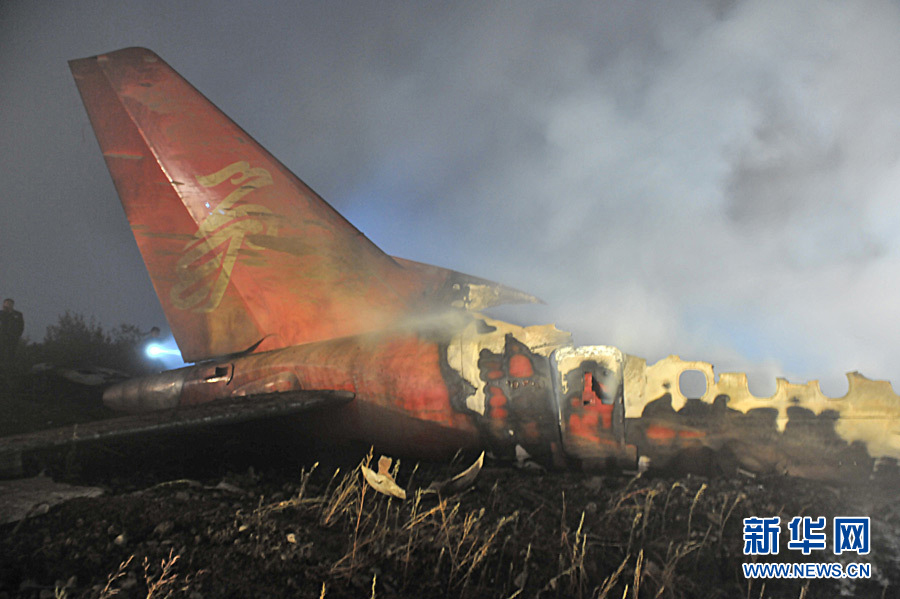
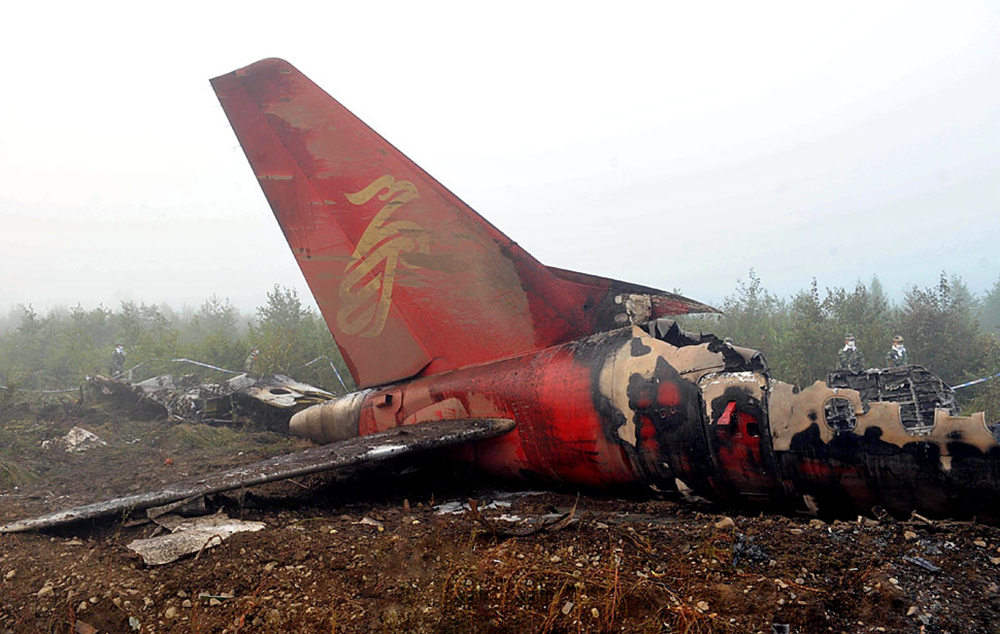
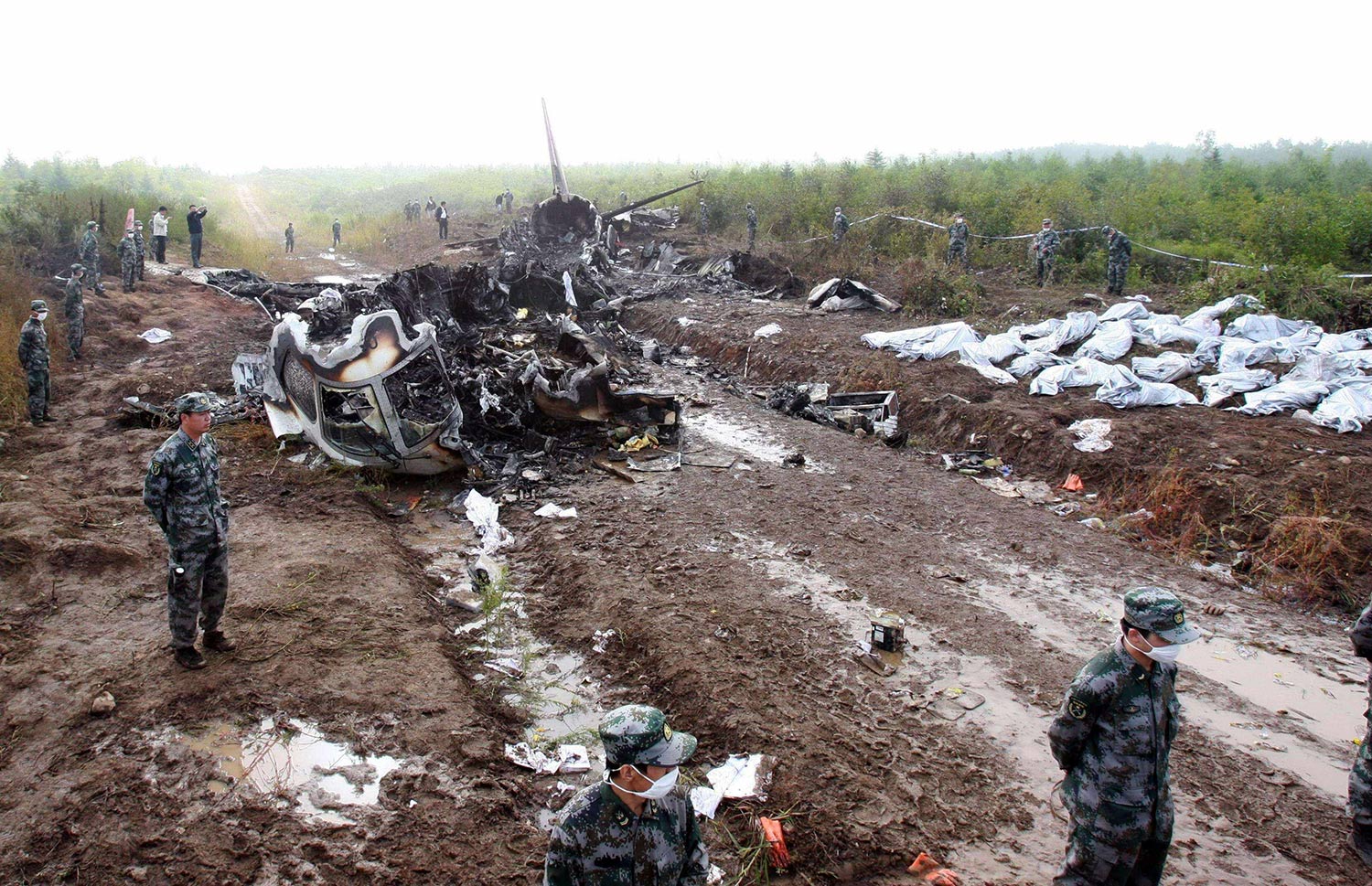
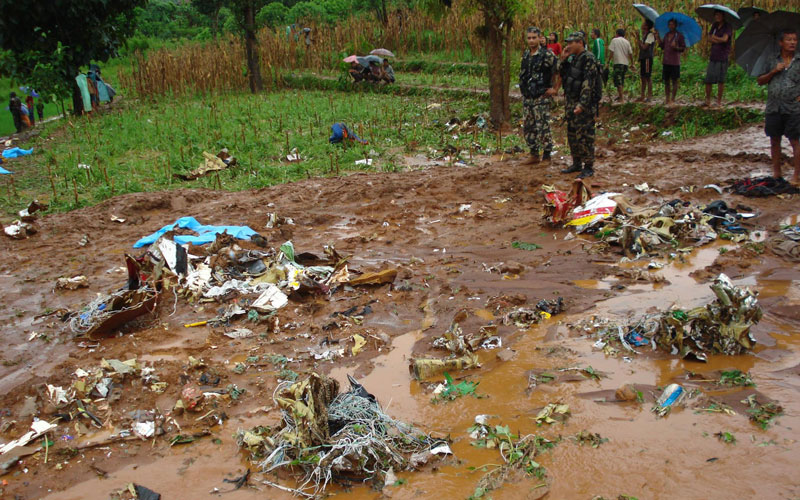
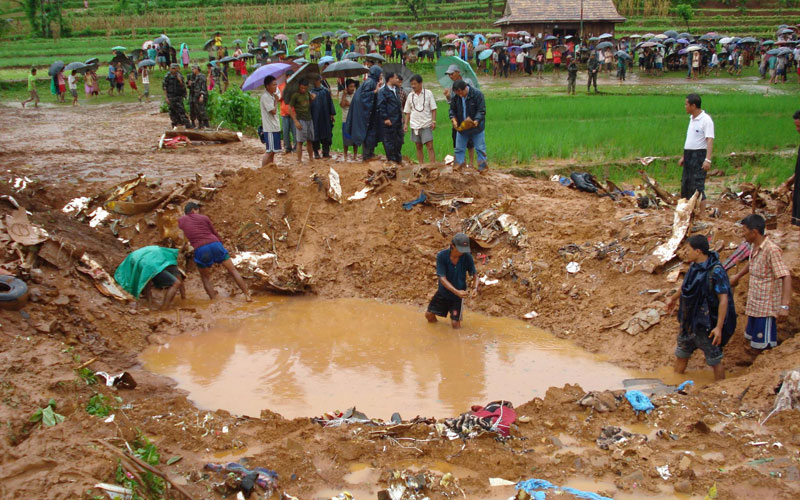
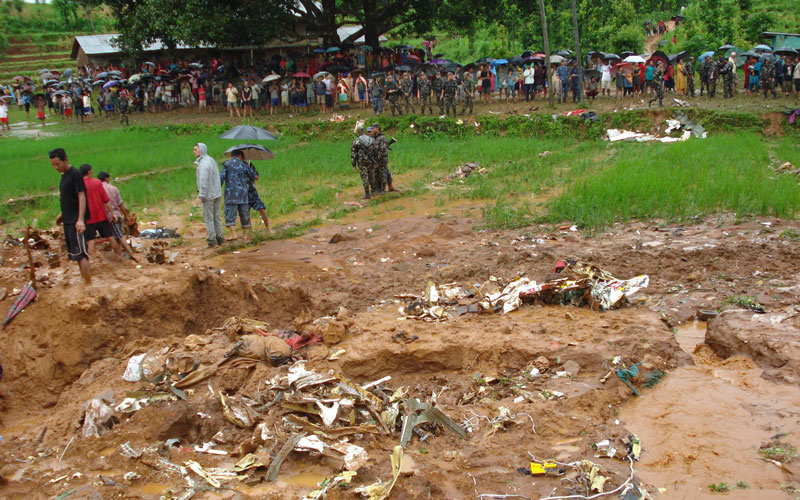
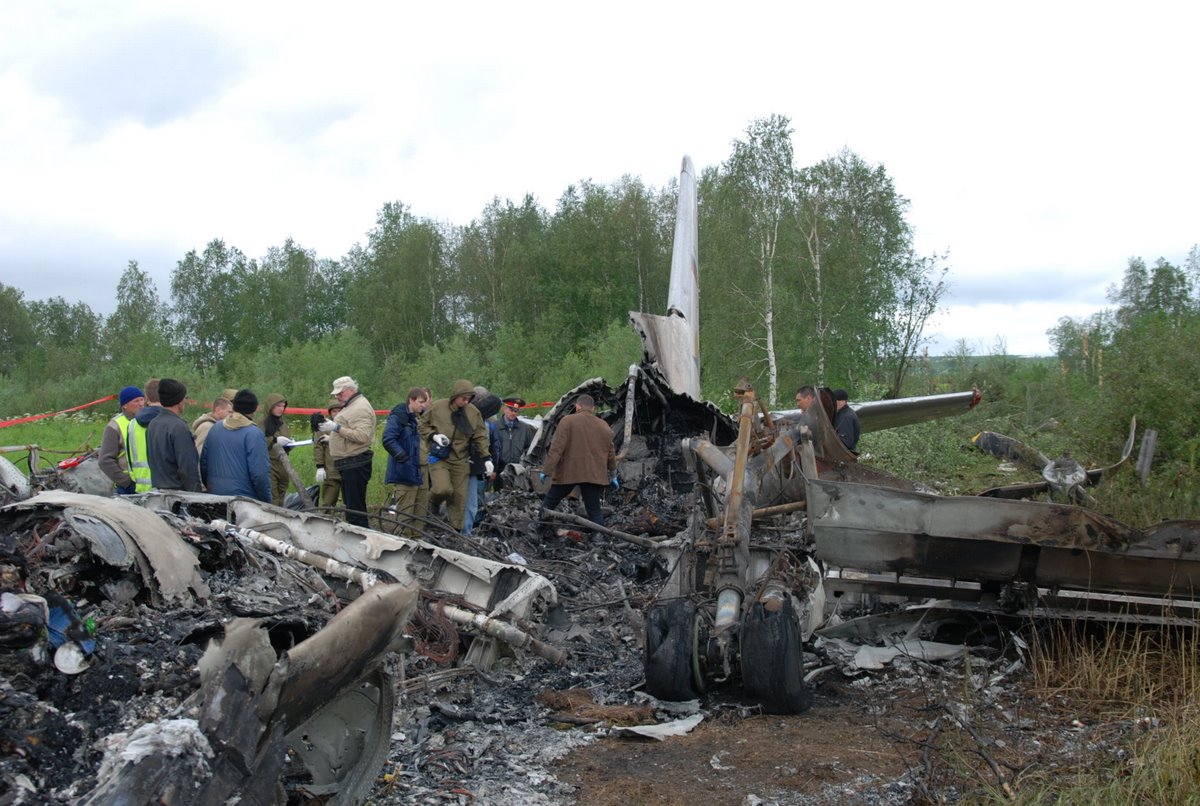
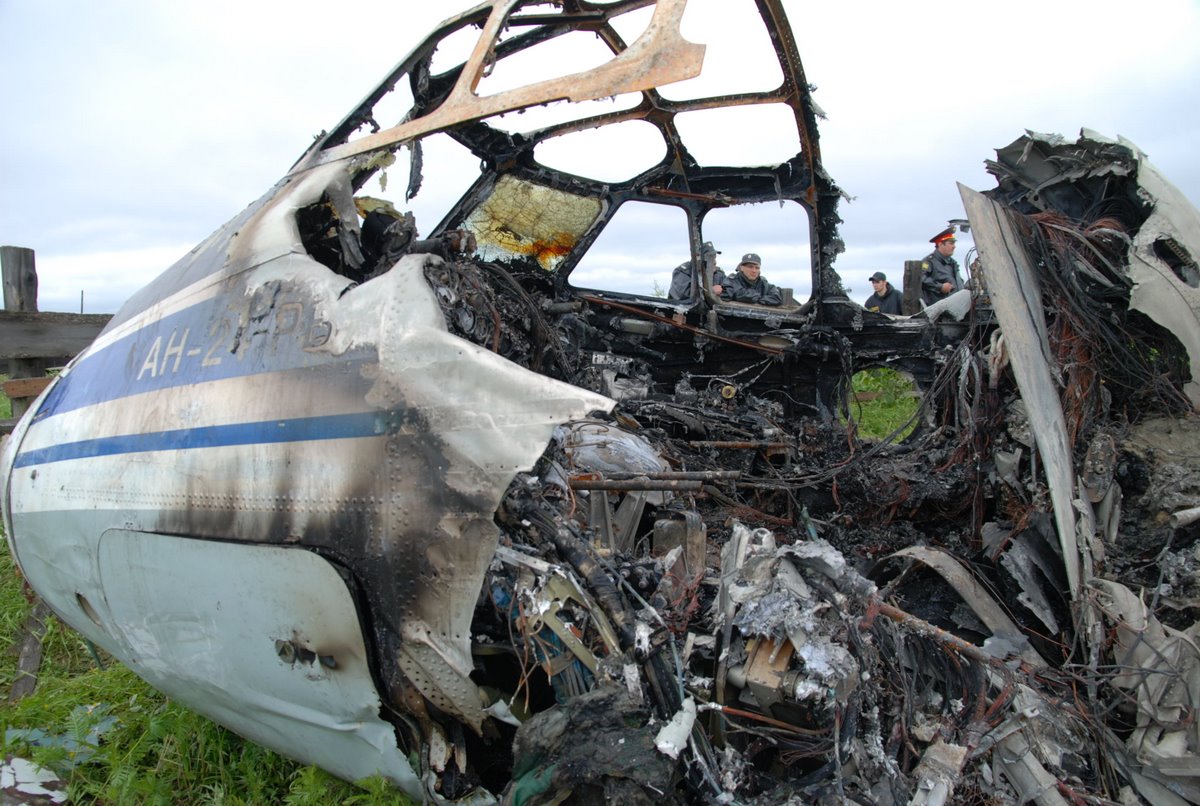
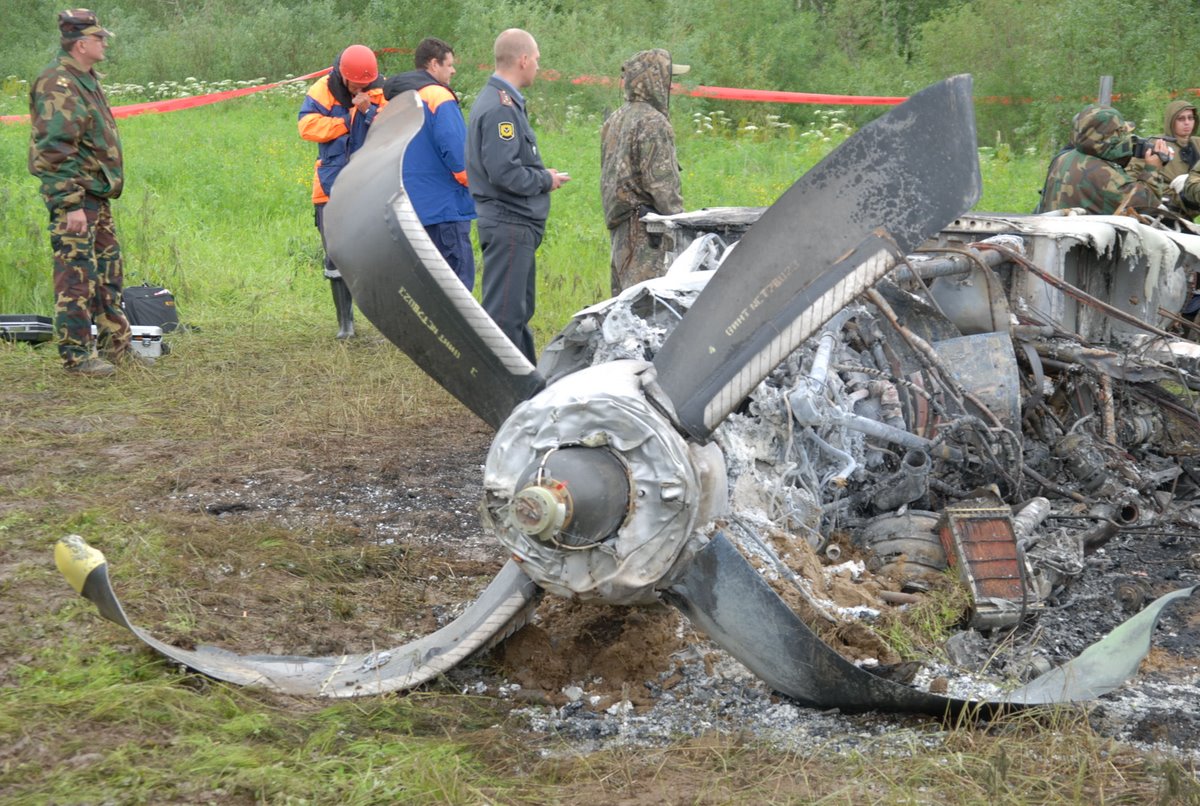
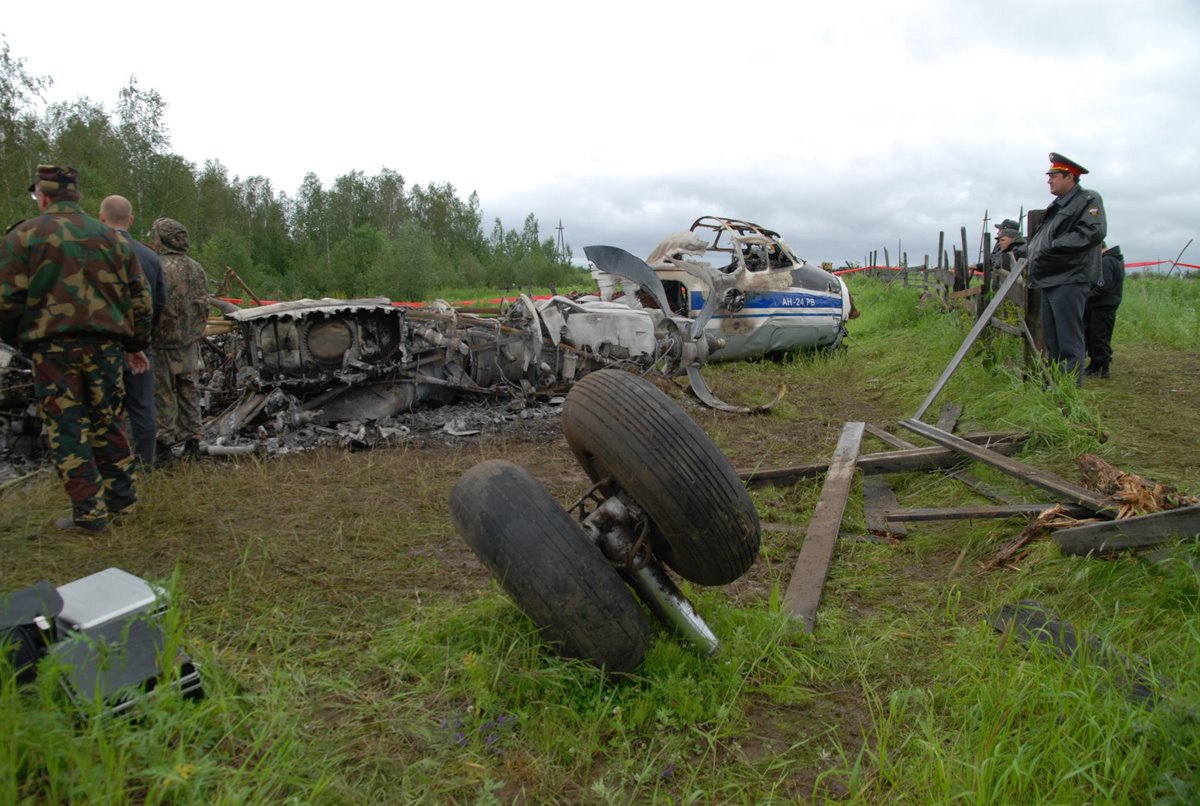
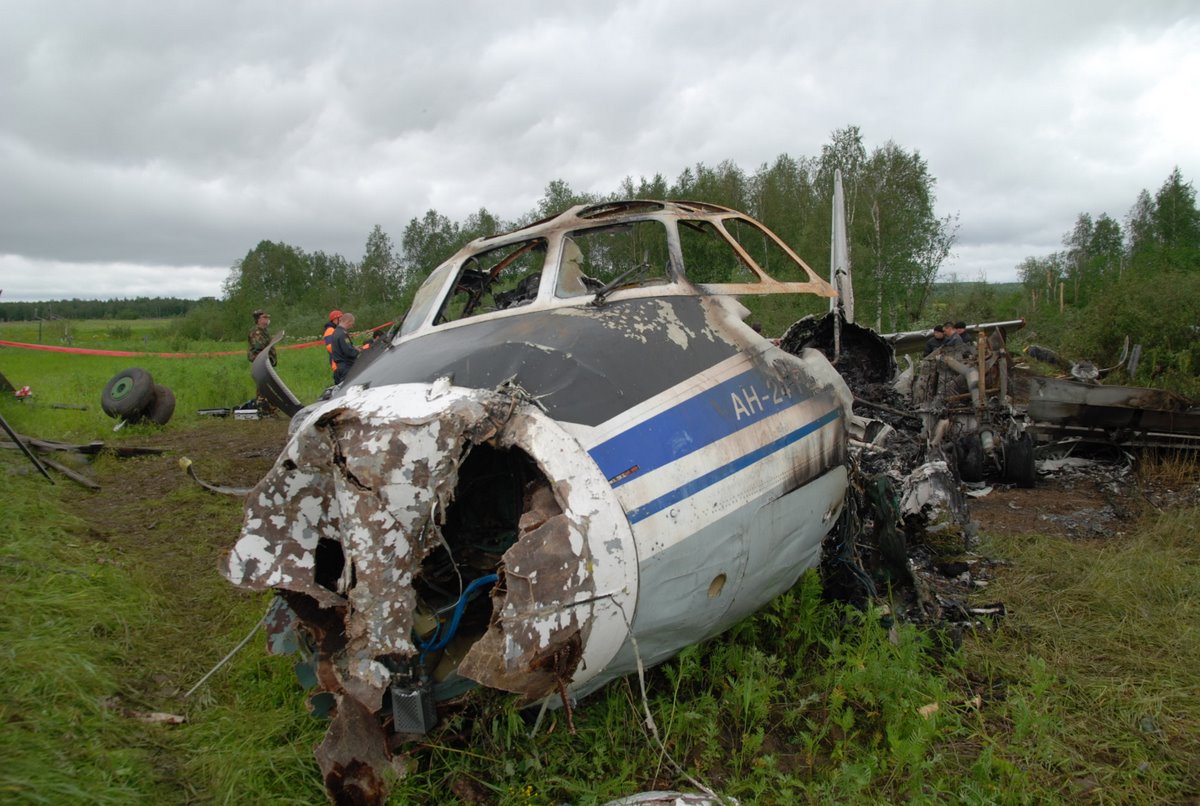
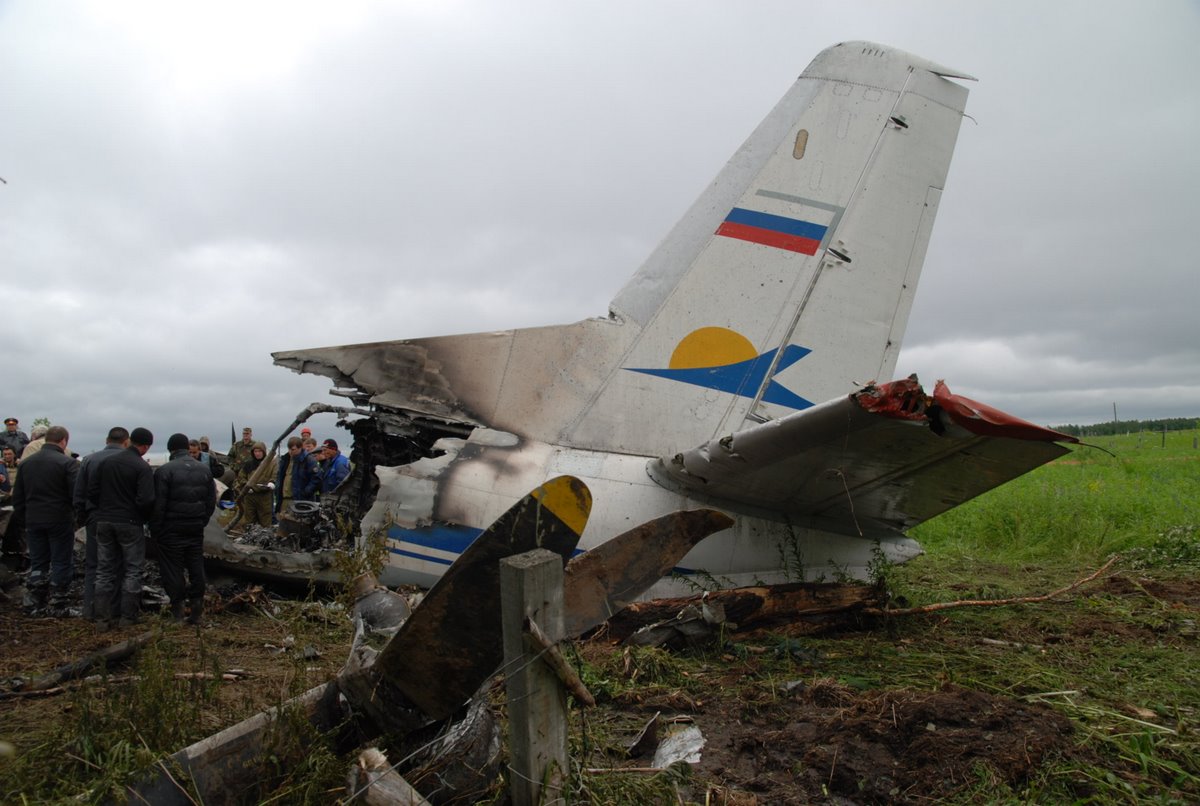
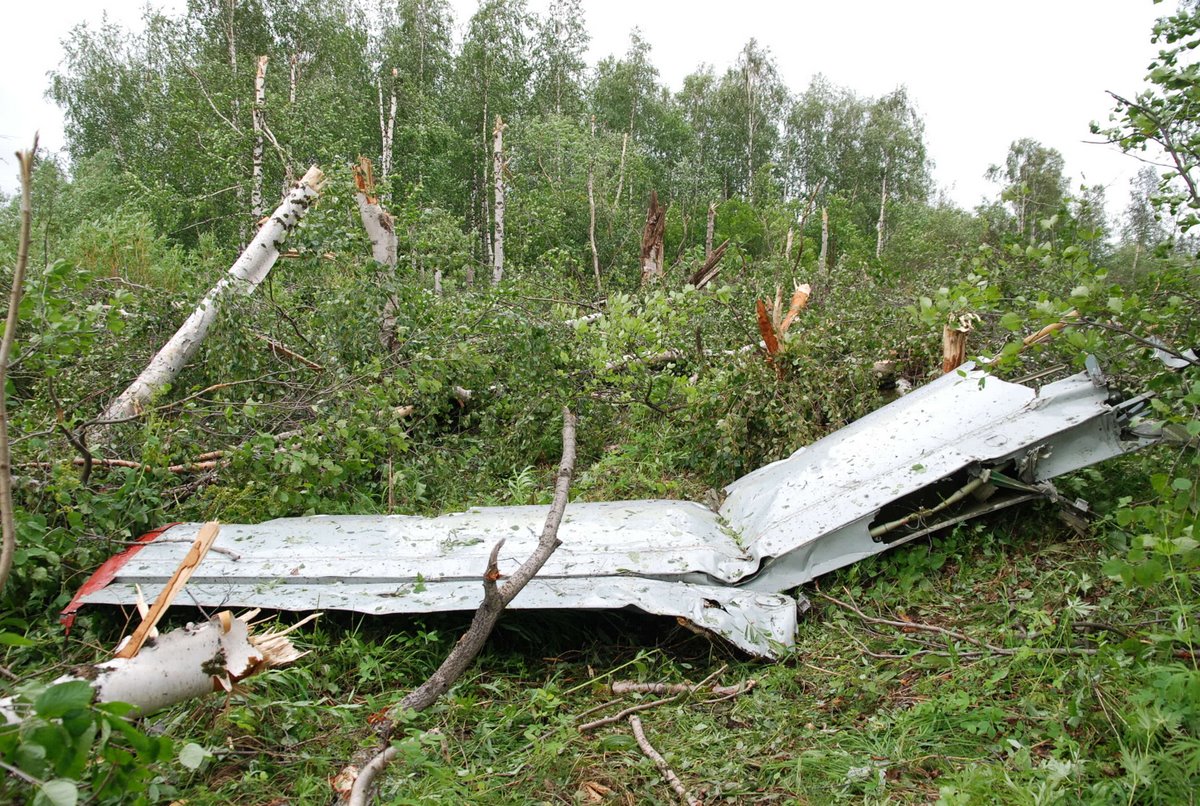
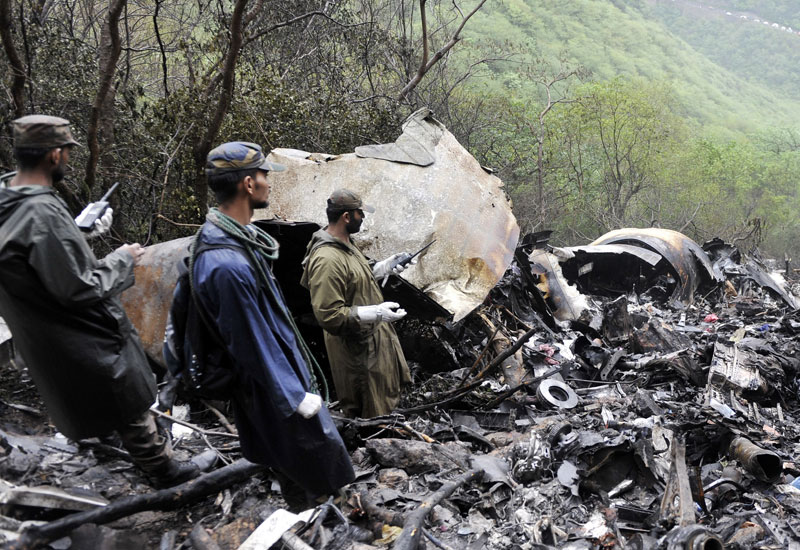
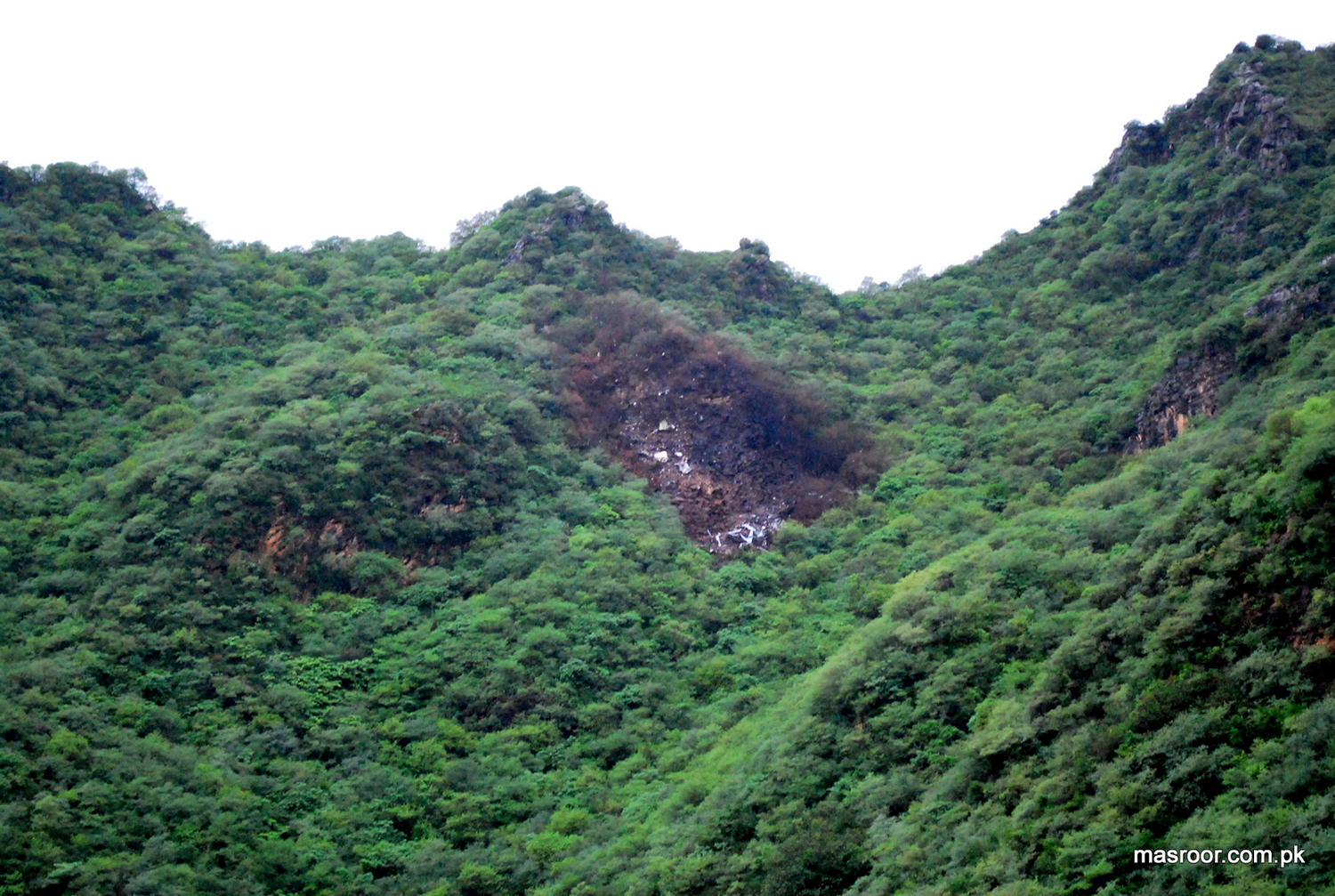
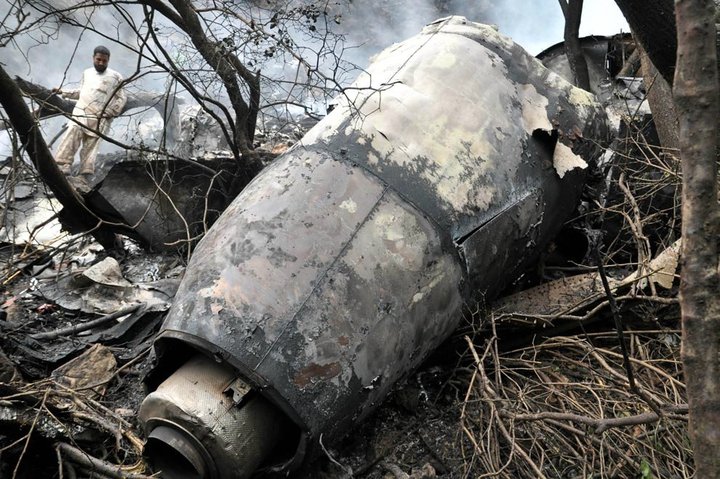
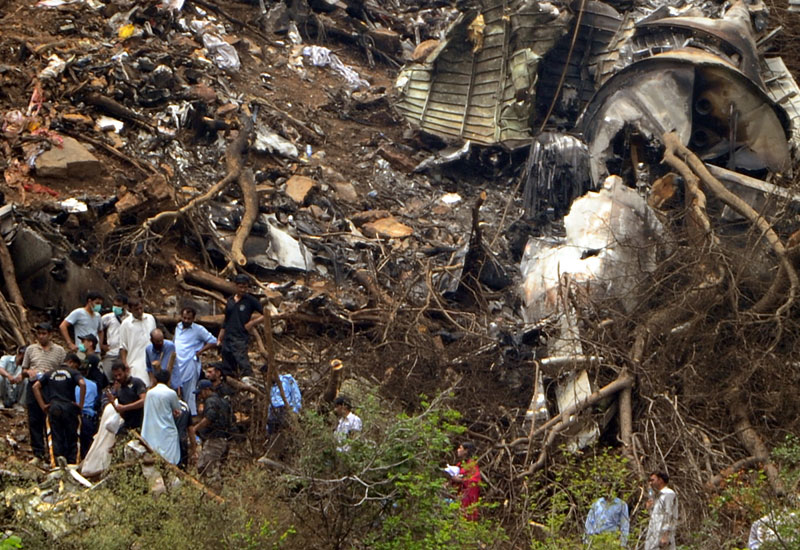
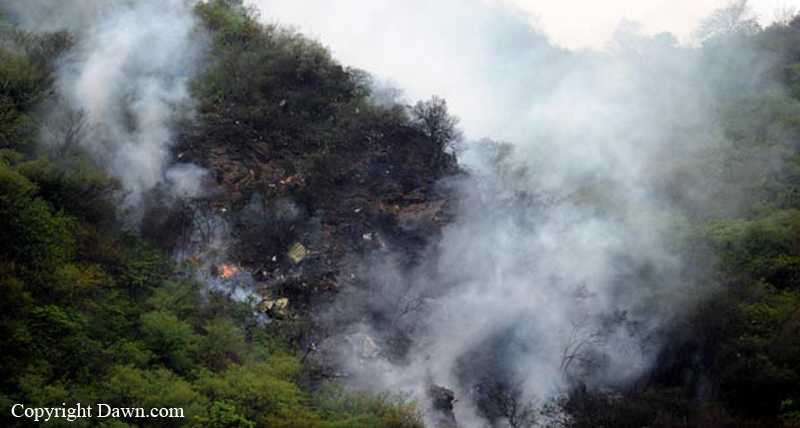
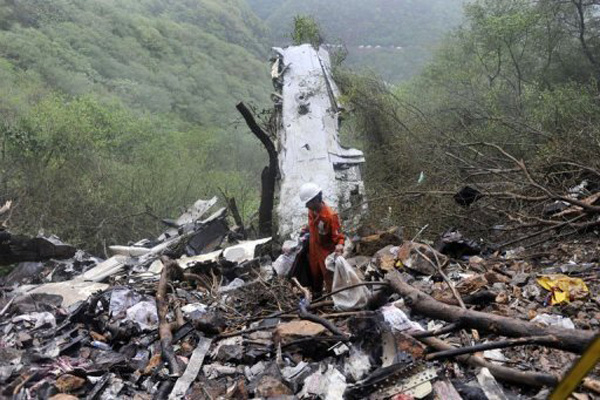
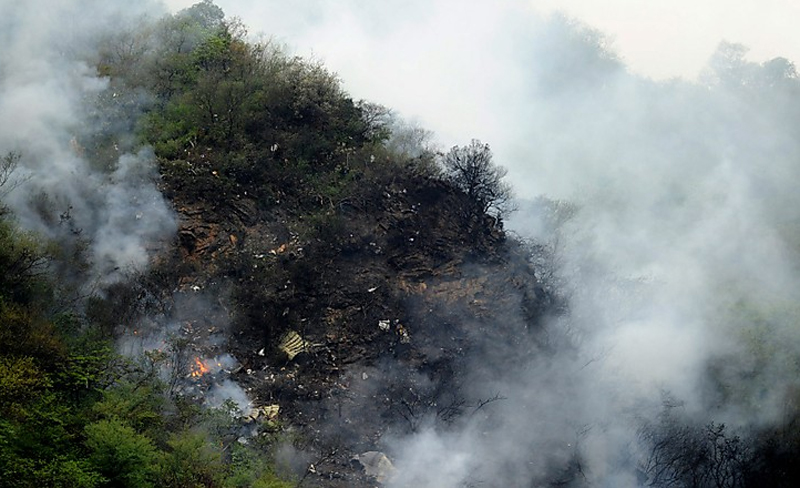
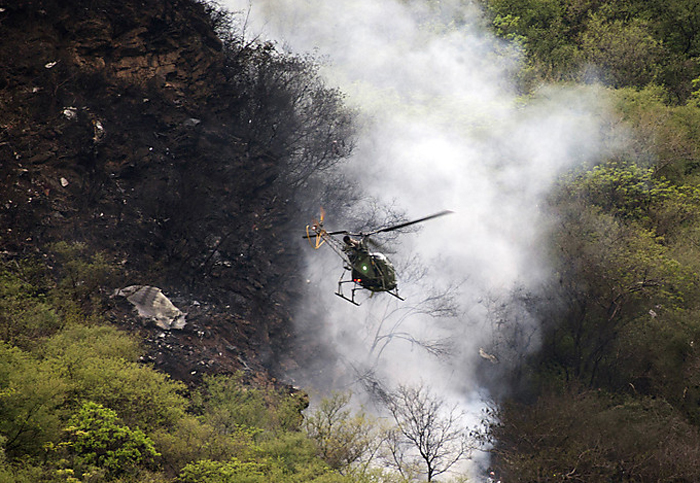
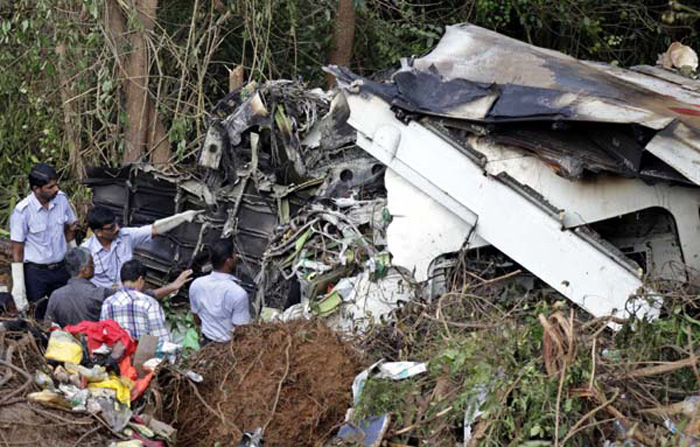
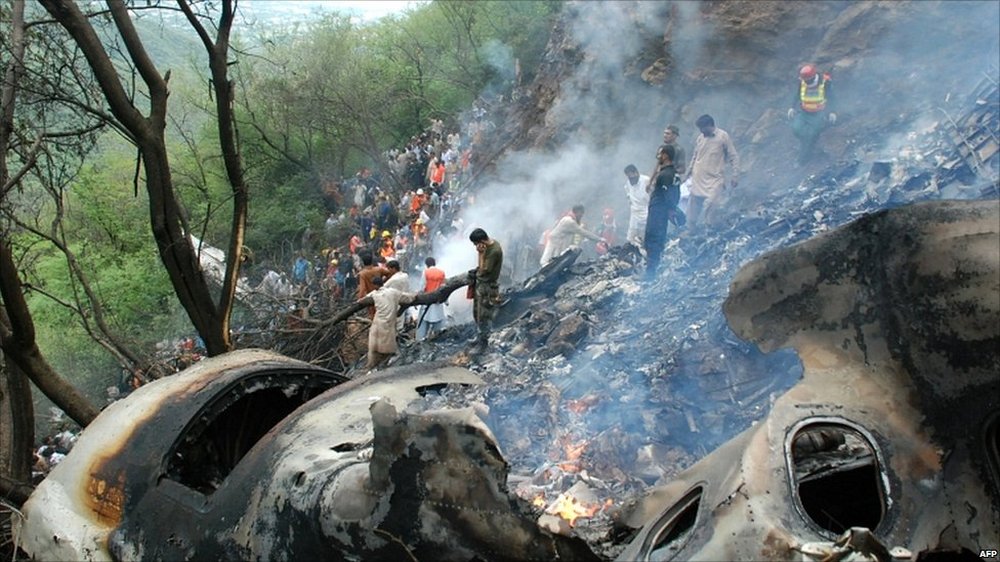
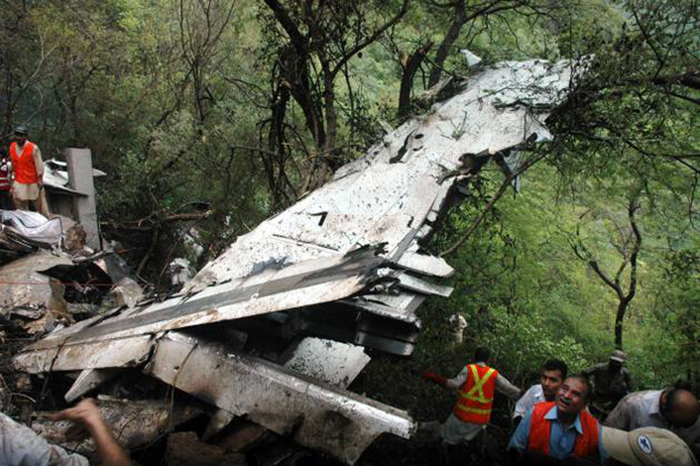
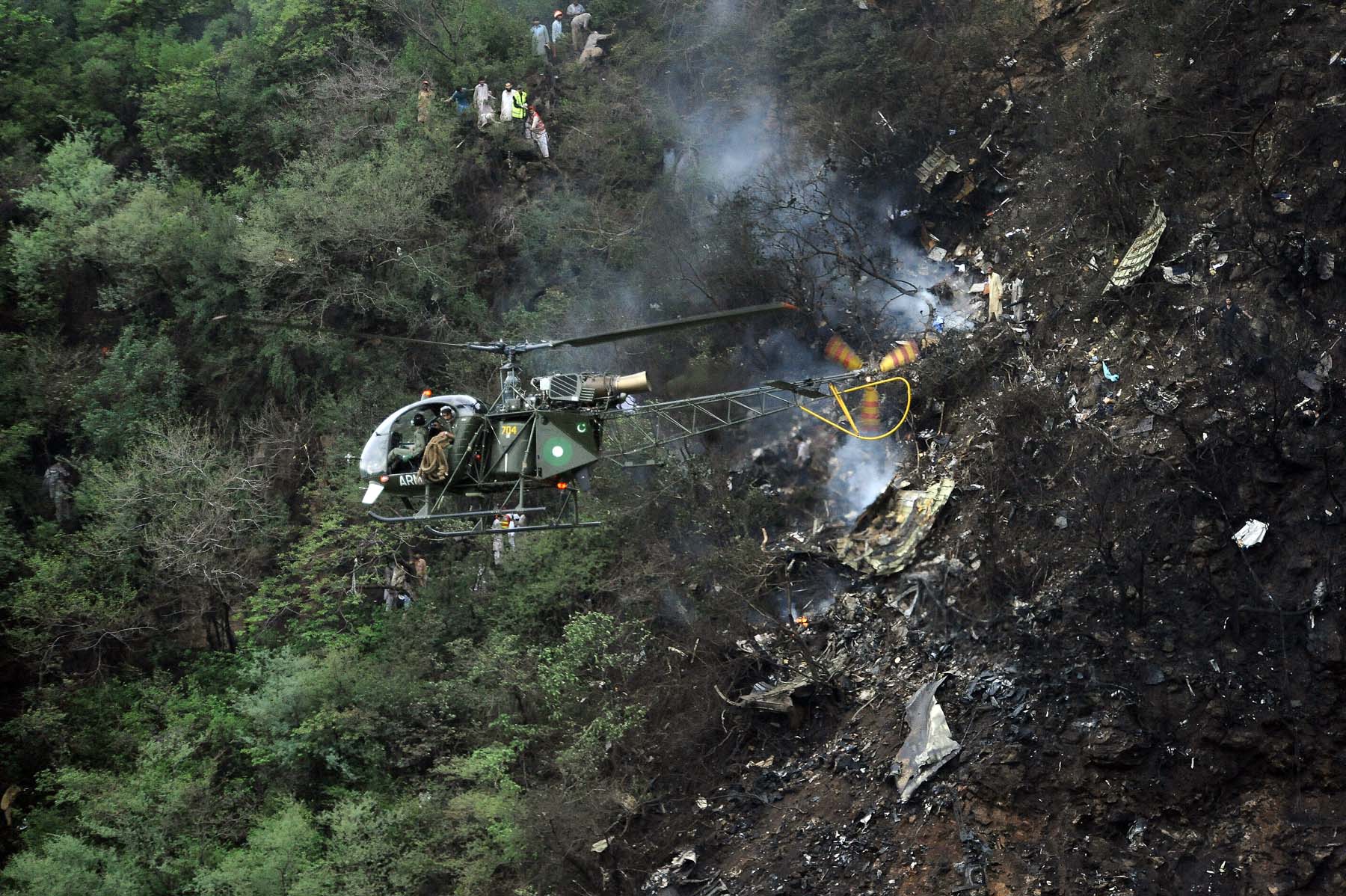
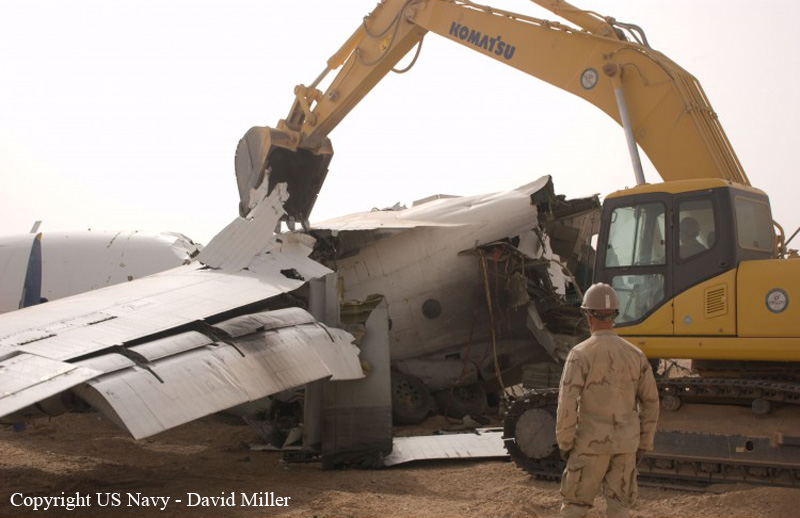
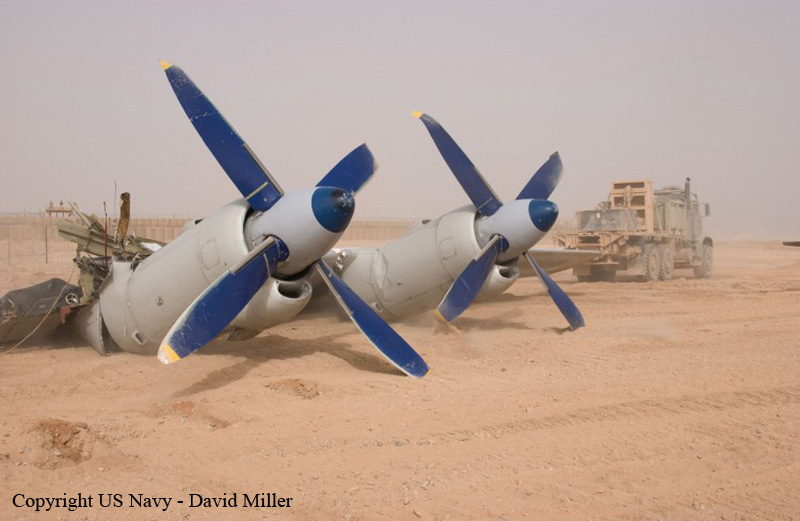
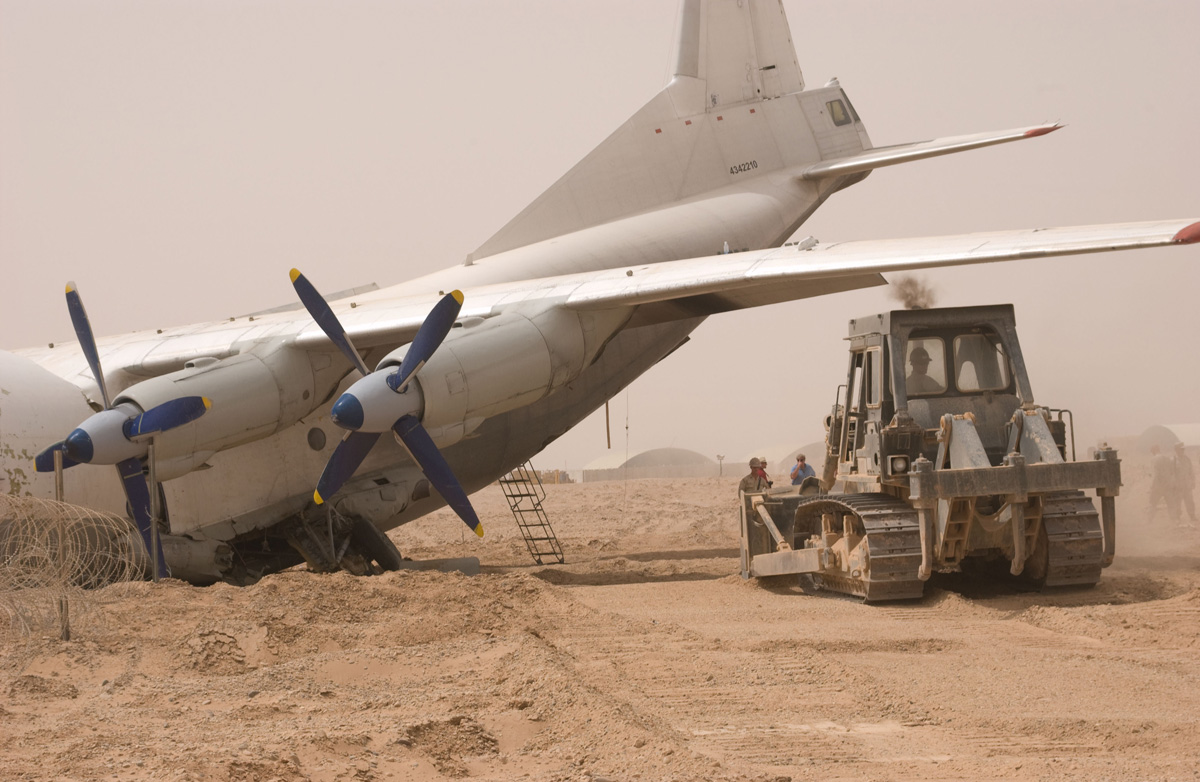
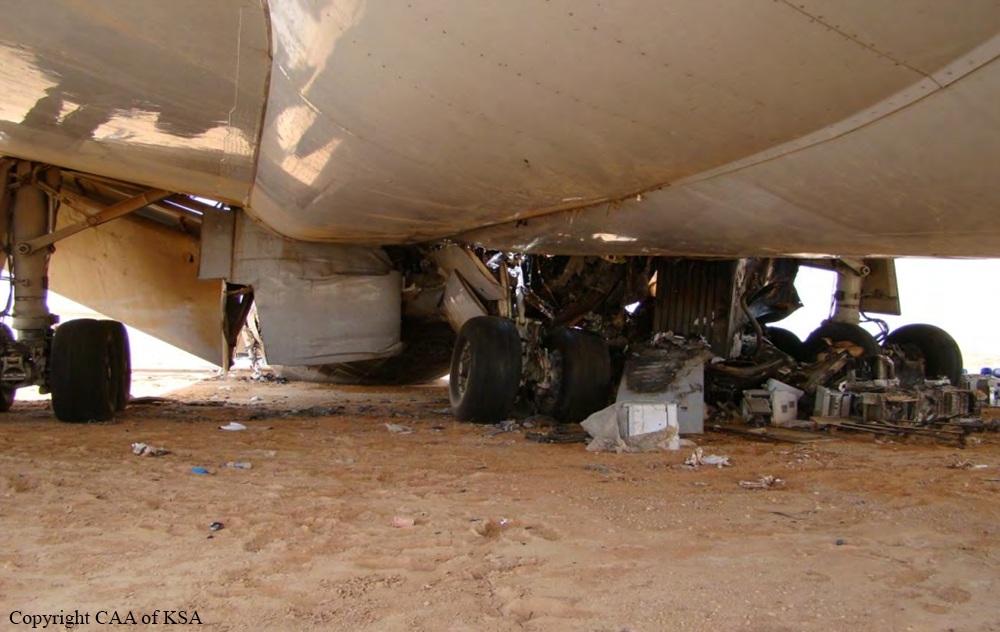
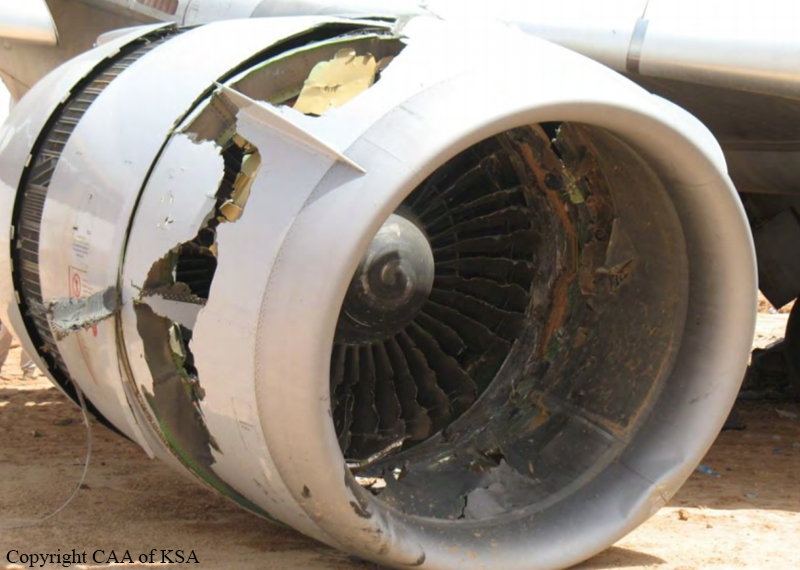
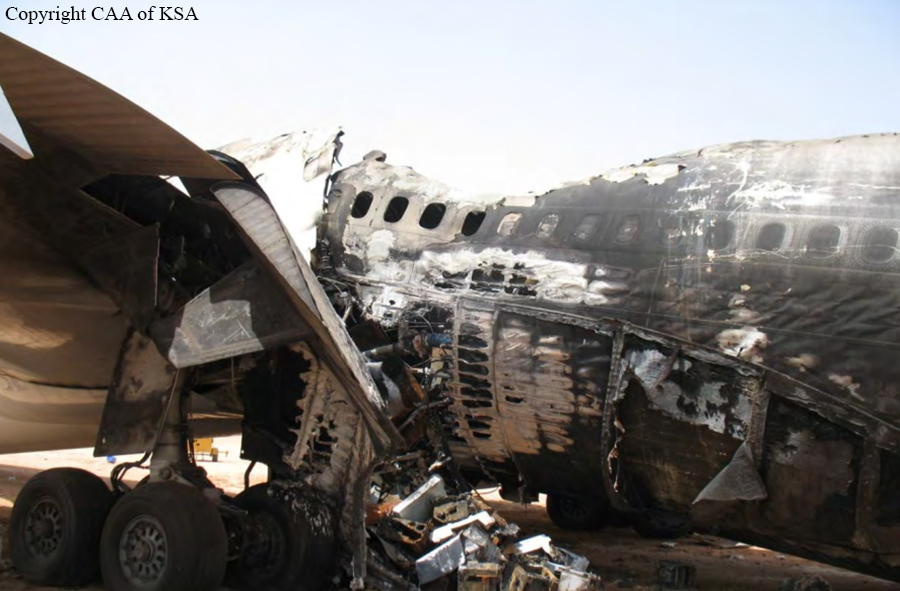
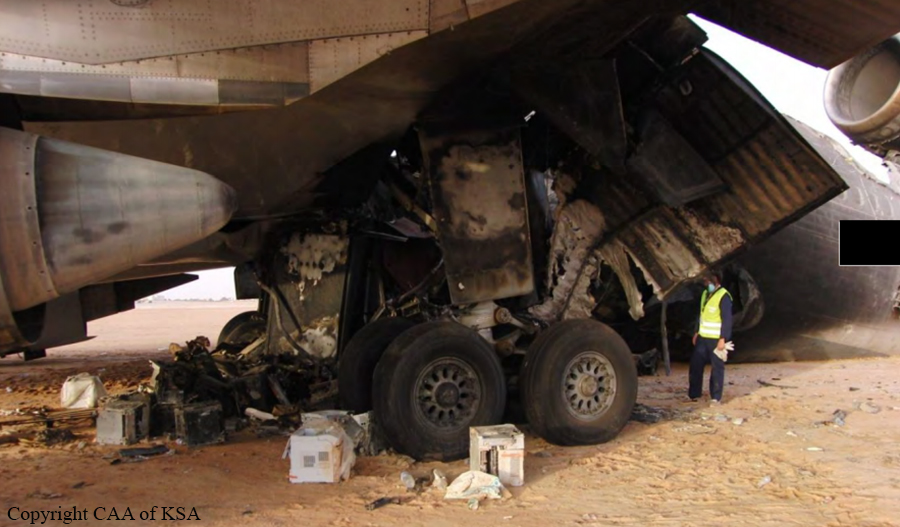
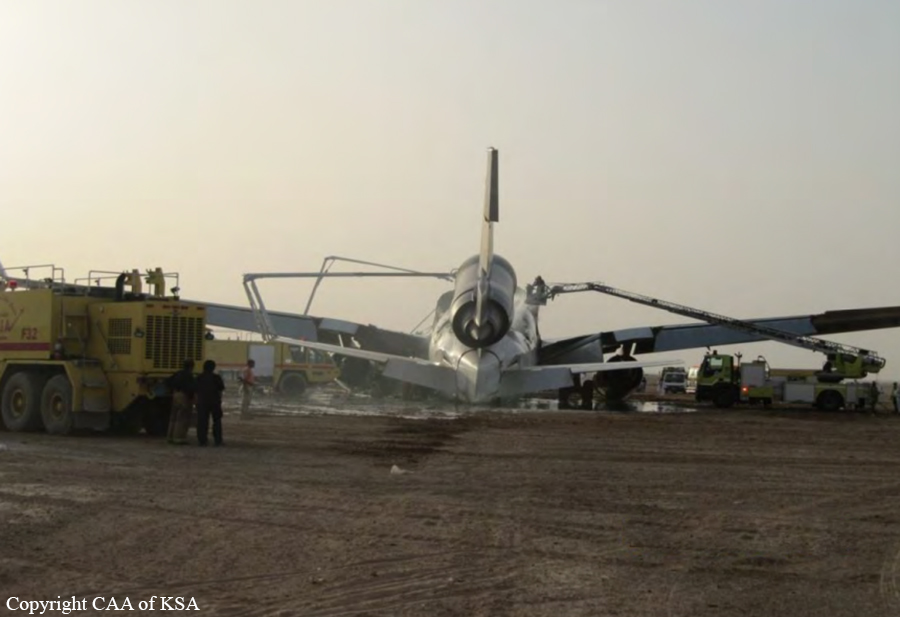
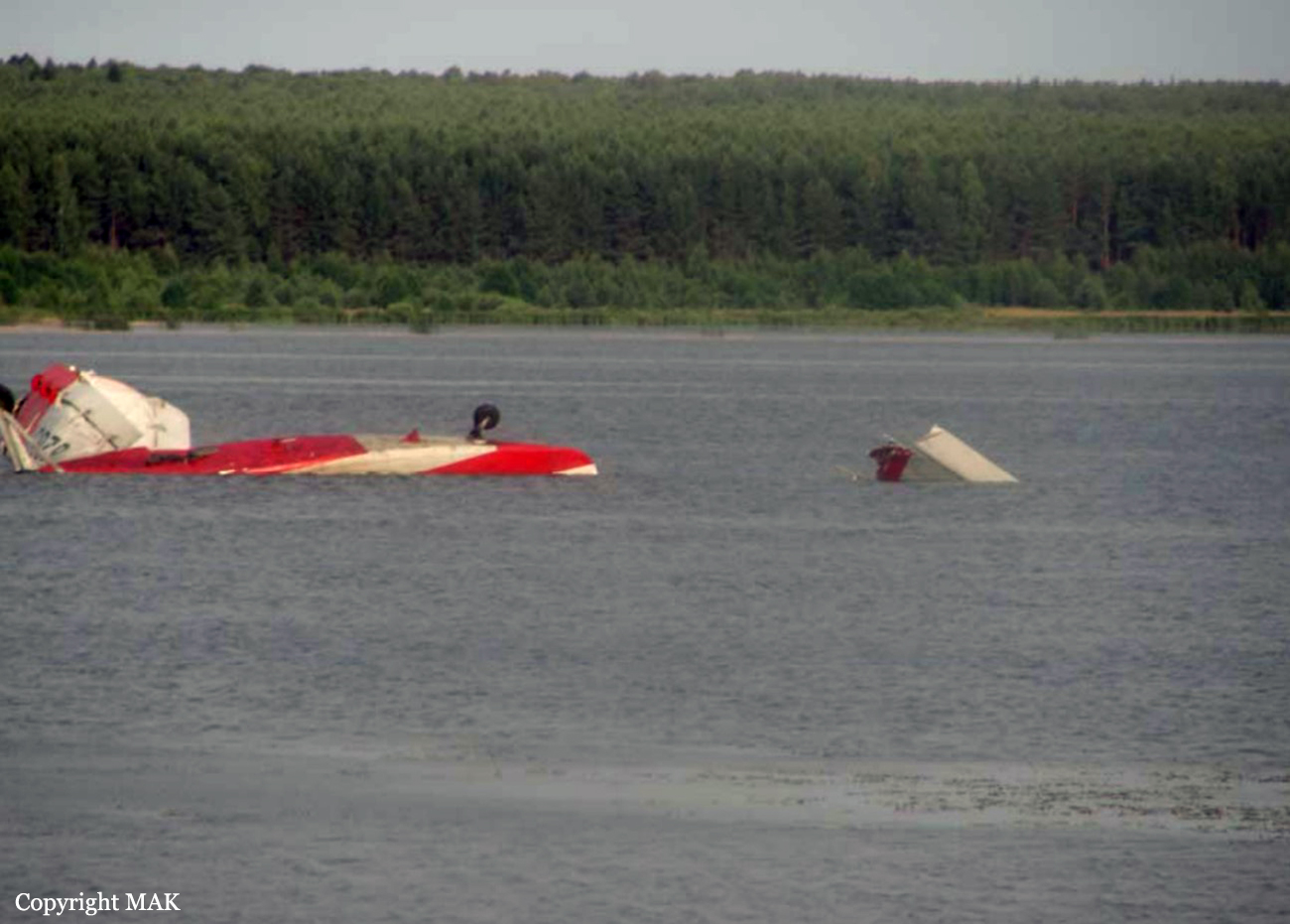
The crew started the approach in poor weather conditions with a visibility reduced at 2,800 metres. On short final, the aircraft was too low and the crew did not establish visual contact with the runway. The aircraft impacted ground 1,110 metres short of runway 30, slid and came to rest in flames 690 meters short of runway. 44 passengers were killed while the aircraft was destroyed by a post crash fire. First fatal accident involving an Embraer 190 and first accident at Yuchin Airport since it was open to traffic in 2009.
Probable cause:
- In violation of the airline's flight operation manual the captain attempted the approach to Yichun below required visibility. The airport reported 2800 meters of visibility while the manual required 3600 meters of visibility to begin the approach
- In violation of regulations by the Civil Aviation Authority the crew descended below minimum descent altitude although the aircraft was operating in fog and visual contact with the runway had not been established
- Despite the aural height announcements and despite not seeing the runway the crew continued the landing in the blind without initiating a go-around resulting in impact with terrain
Contributing factors were:
- The airline's safety management is insufficient:
* part of the flight crew arbitrarily implement the company's operations manual as the company does not follow up outstanding problems. Records suggest frequent deviations from approach profiles, i.e. deviation above or below glide slopes, excessive rates of descents and unstable approaches
* crew rostering and crew cooperation: Each of the crew was flying into Yichun for the first time despite the known safety risks at the airport, the communication and cooperation within the crew was insufficient, the crew members did not monitor each other in order to reduce human errors
* the airline's emergency training did not meet requirements, in particular the cabin crew training did not provide for hands on training on E190 cabin doors and overwing exits. Alternate means by the airline did prove ineffective and did not provide the quality China's Civil Aviation Authority requires thus leaving cabin crew unprepared to meet required cabin crew emergency response capabilities
- Parent company's Shenzhen Airlines oversight insufficient
* Shenzhen Airlines, after having taken over Henan Airlines in 2006, did not provide sufficient funding and technical support affecting the stability and safety of staff and quality management
* Air China, holding stock into Shenzhen Airlines, installed a safety supervisor but failed to address the safety management issues with Shenzhen and Henan Airlines
- No supervision by China's Civil Aviation Authority
* the license to operate the flight from Harbin to Yichun was granted without route validation and without safety management in violation of regulations
* to solve the lack of cabin crew flight attendants were certified although not meeting the relevant requirements for air transport operations
* the regional office of the Civil Aviation Authority did not communicate to their superiors that they had approved the domestic operation of the route from Harbin to Yichun permitting non-standard procedures
- China's Civil Aviation Authority safety management loopholes.
- In violation of regulations by the Civil Aviation Authority the crew descended below minimum descent altitude although the aircraft was operating in fog and visual contact with the runway had not been established
- Despite the aural height announcements and despite not seeing the runway the crew continued the landing in the blind without initiating a go-around resulting in impact with terrain
Contributing factors were:
- The airline's safety management is insufficient:
* part of the flight crew arbitrarily implement the company's operations manual as the company does not follow up outstanding problems. Records suggest frequent deviations from approach profiles, i.e. deviation above or below glide slopes, excessive rates of descents and unstable approaches
* crew rostering and crew cooperation: Each of the crew was flying into Yichun for the first time despite the known safety risks at the airport, the communication and cooperation within the crew was insufficient, the crew members did not monitor each other in order to reduce human errors
* the airline's emergency training did not meet requirements, in particular the cabin crew training did not provide for hands on training on E190 cabin doors and overwing exits. Alternate means by the airline did prove ineffective and did not provide the quality China's Civil Aviation Authority requires thus leaving cabin crew unprepared to meet required cabin crew emergency response capabilities
- Parent company's Shenzhen Airlines oversight insufficient
* Shenzhen Airlines, after having taken over Henan Airlines in 2006, did not provide sufficient funding and technical support affecting the stability and safety of staff and quality management
* Air China, holding stock into Shenzhen Airlines, installed a safety supervisor but failed to address the safety management issues with Shenzhen and Henan Airlines
- No supervision by China's Civil Aviation Authority
* the license to operate the flight from Harbin to Yichun was granted without route validation and without safety management in violation of regulations
* to solve the lack of cabin crew flight attendants were certified although not meeting the relevant requirements for air transport operations
* the regional office of the Civil Aviation Authority did not communicate to their superiors that they had approved the domestic operation of the route from Harbin to Yichun permitting non-standard procedures
- China's Civil Aviation Authority safety management loopholes.