Date & Time:
Jan 15, 2009 at 2110 LT
Operator:
Schedule:
Makhachkala - Nizhny Novgorod
Crew fatalities:
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Circumstances:
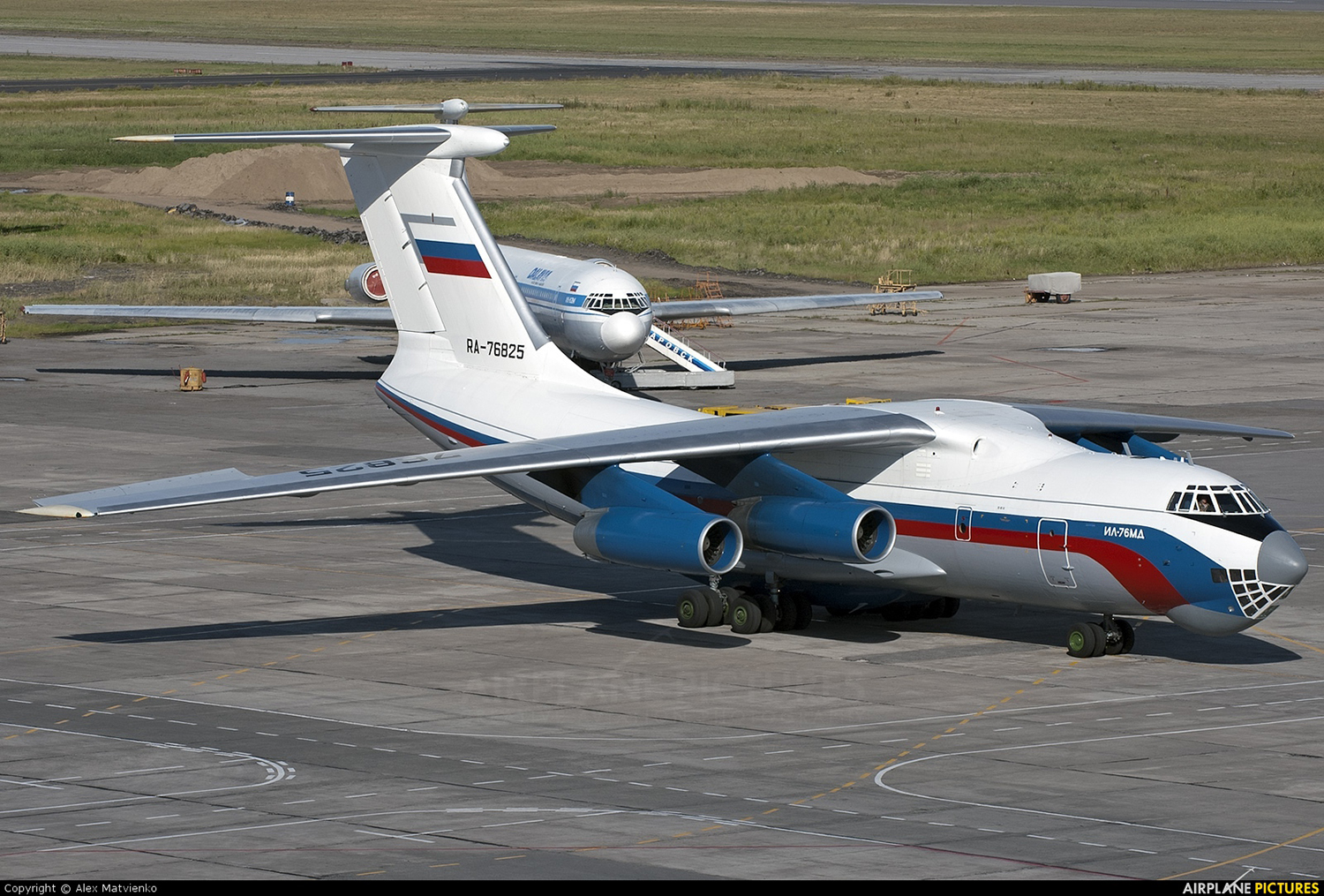
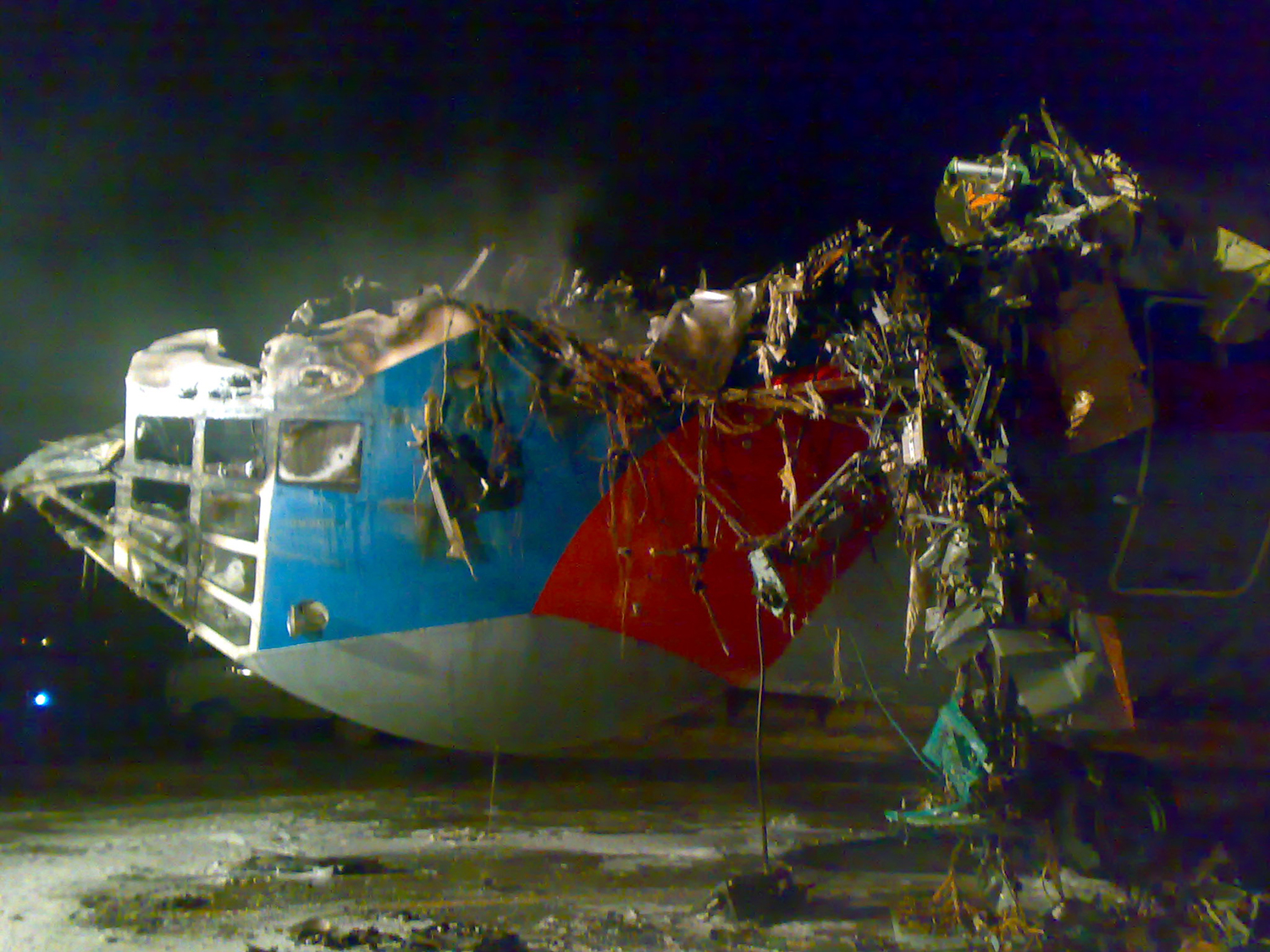
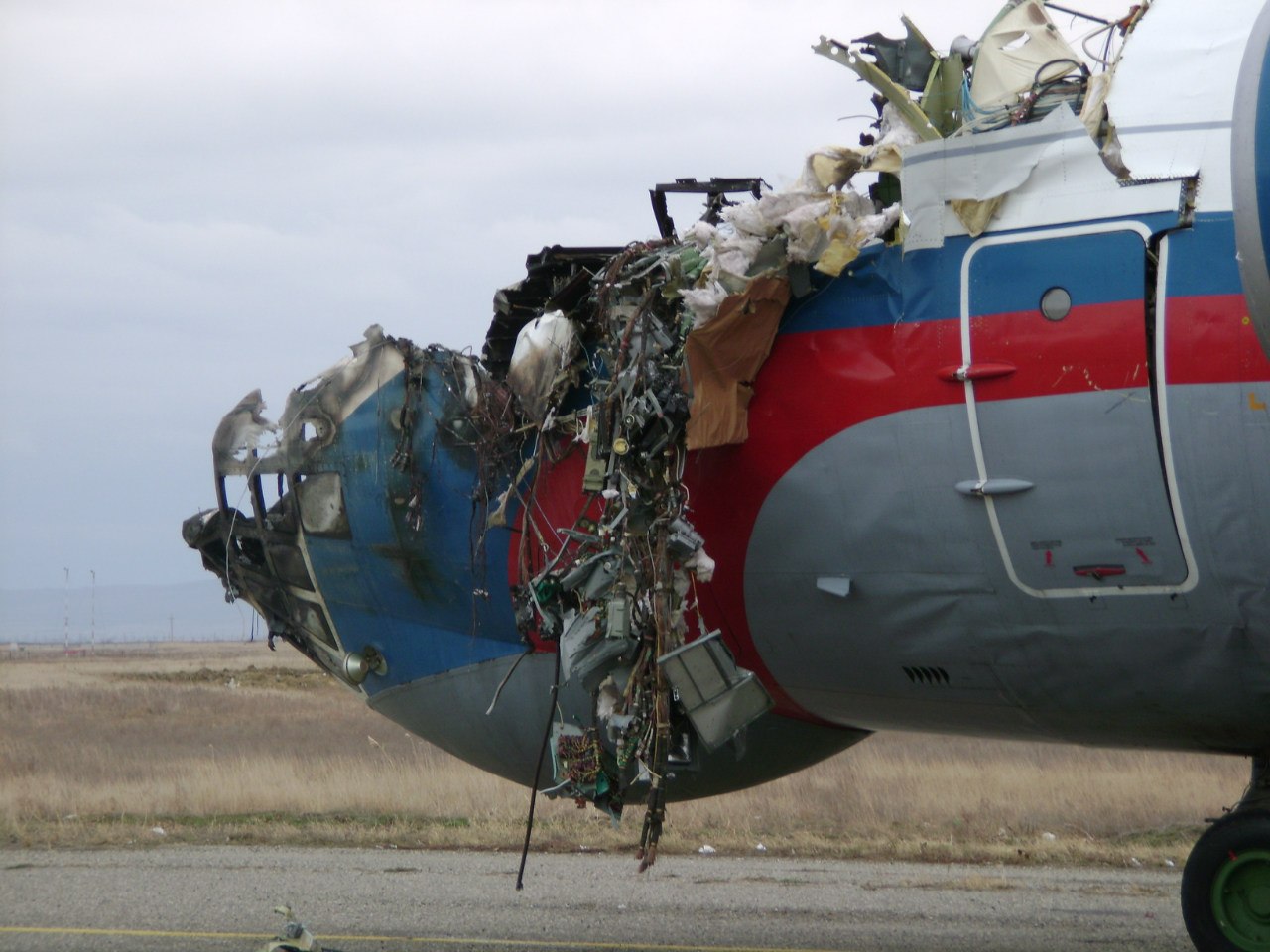
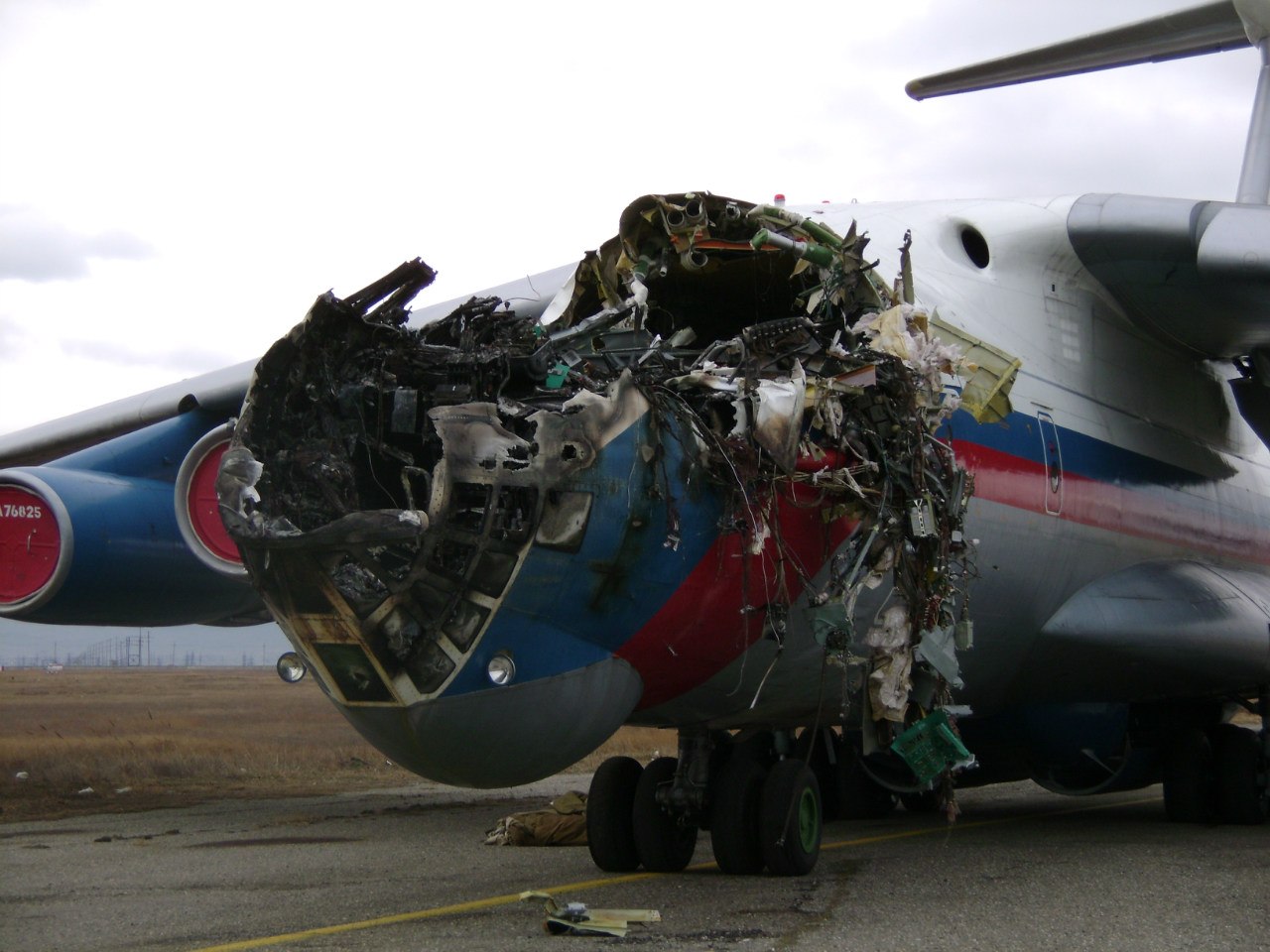
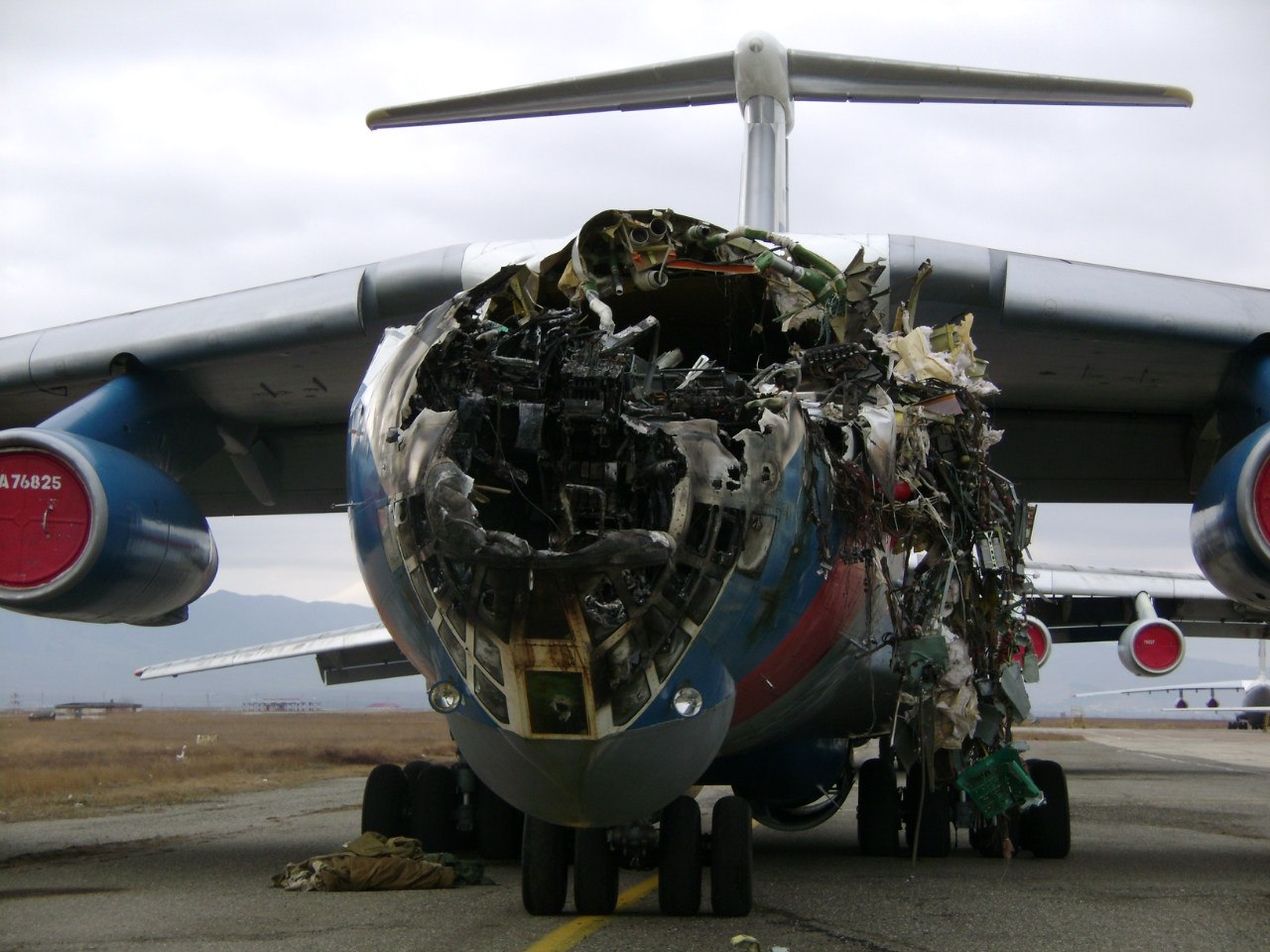
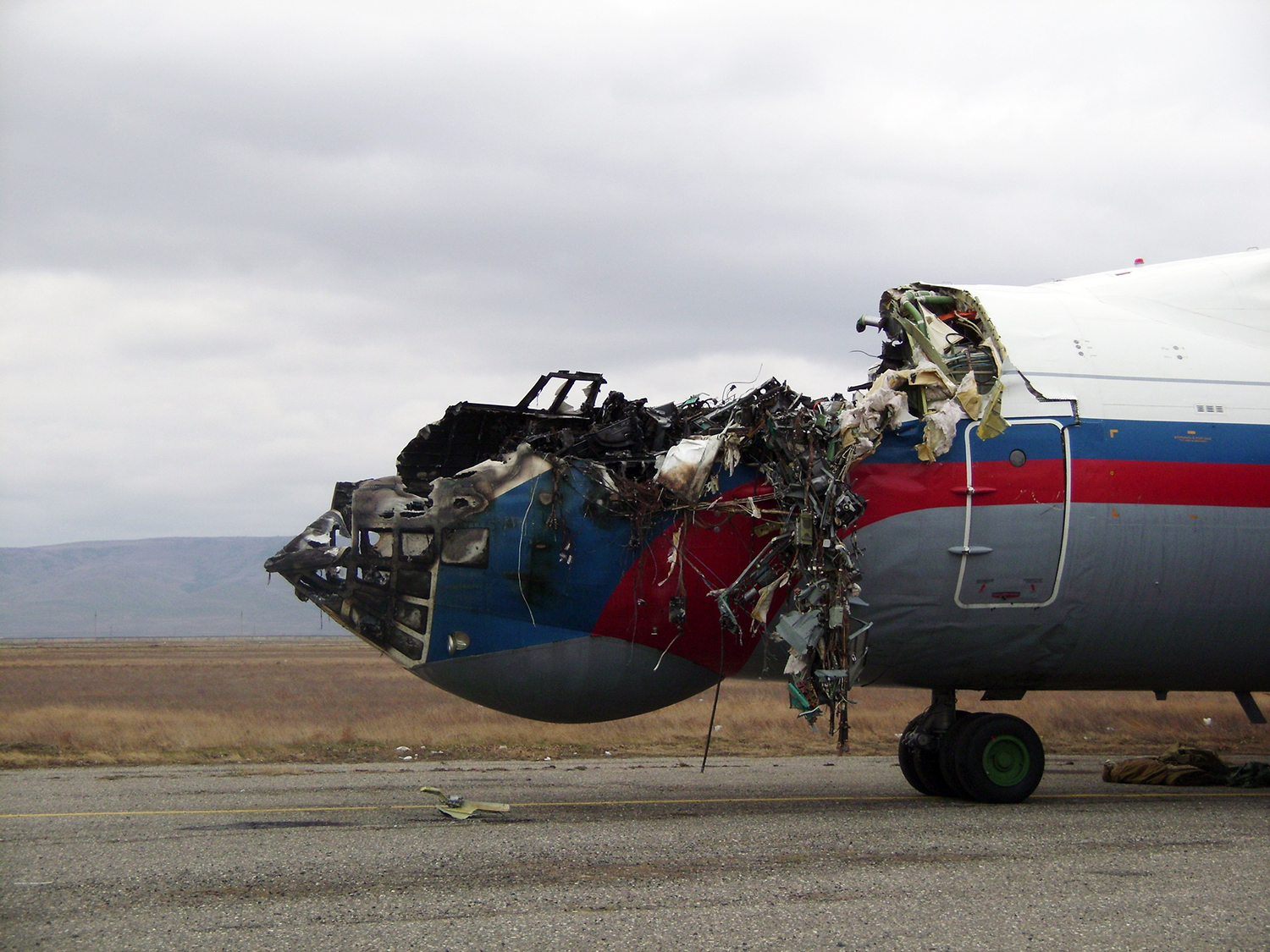
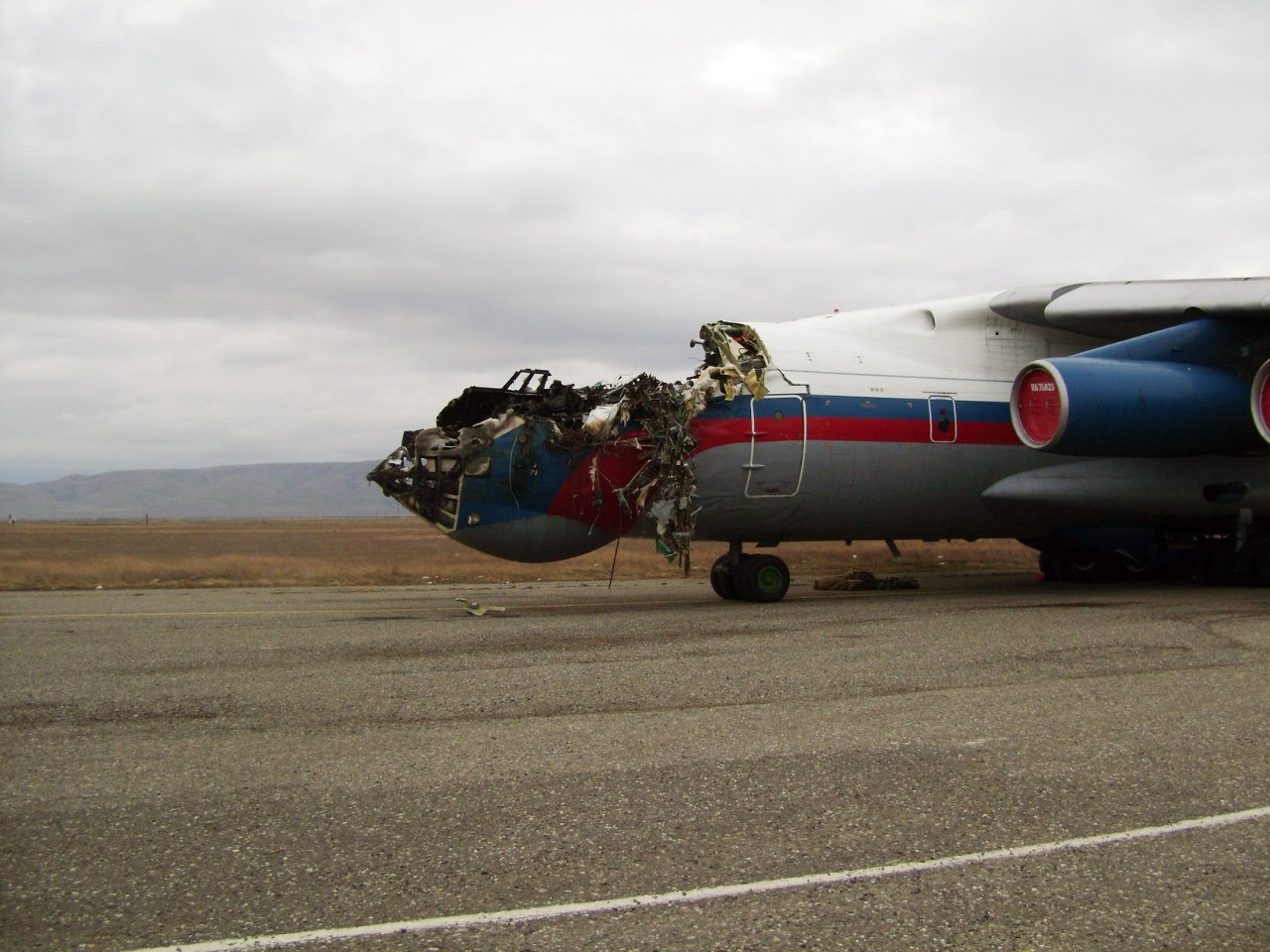
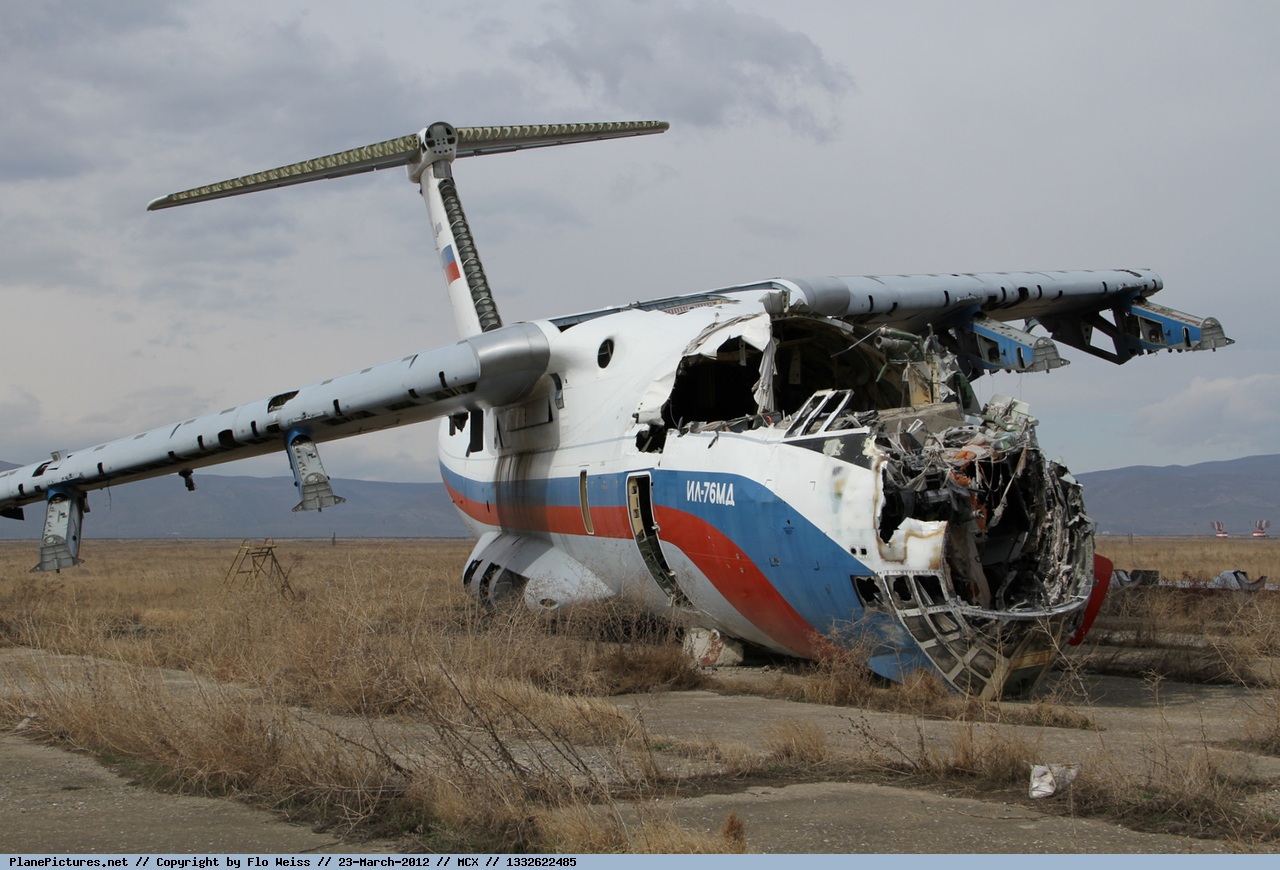
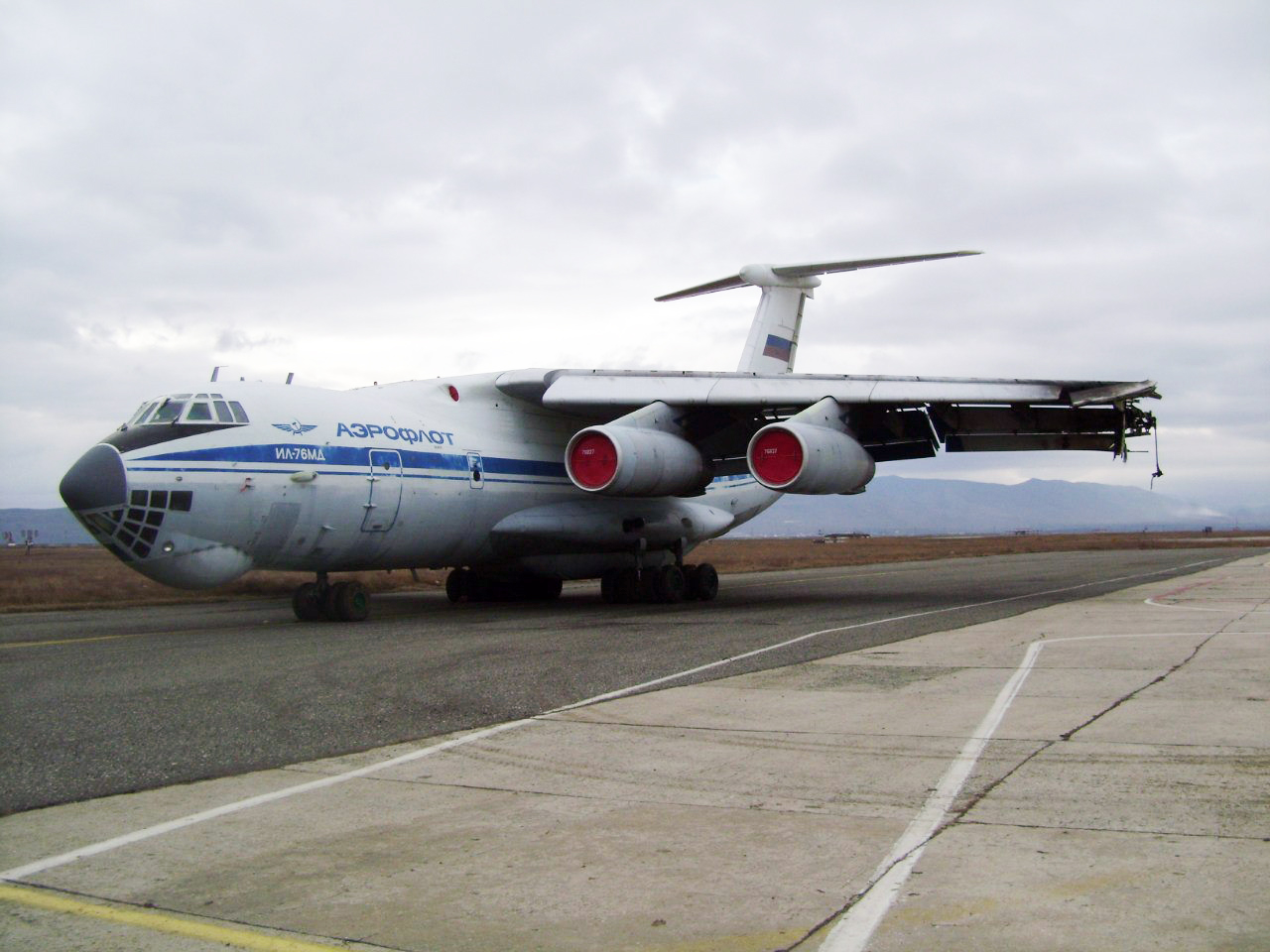
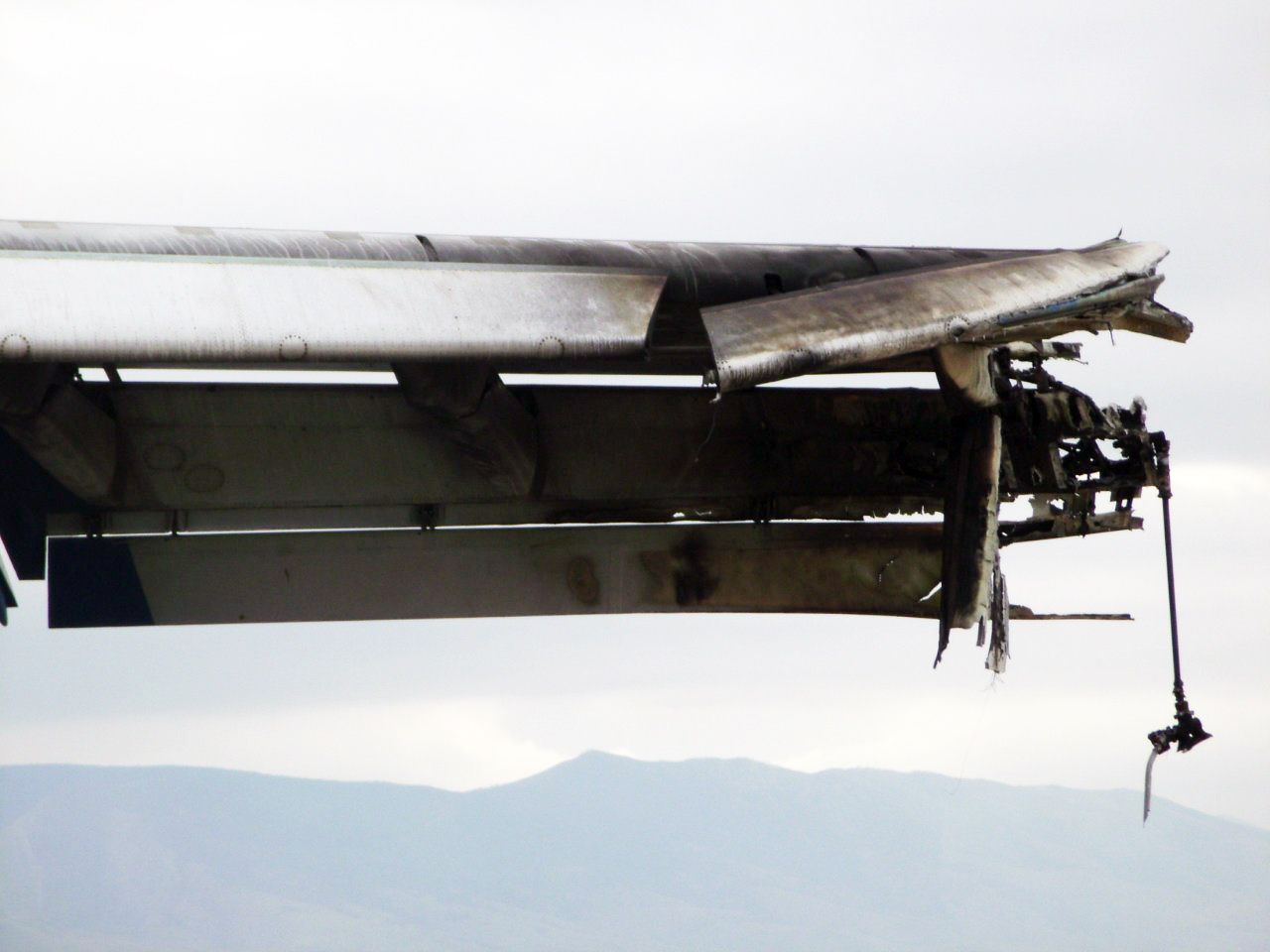
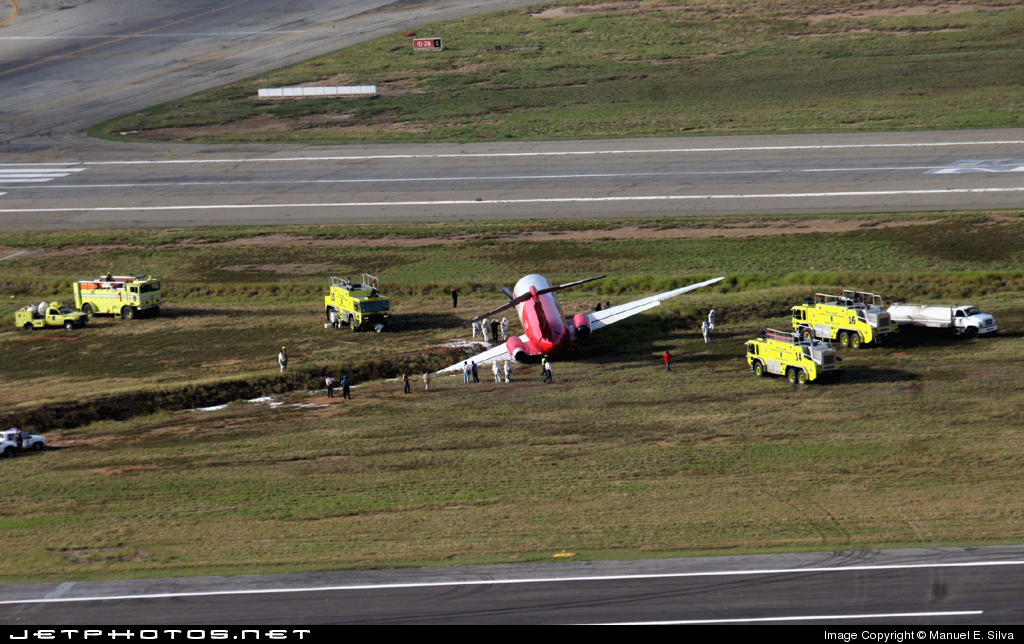
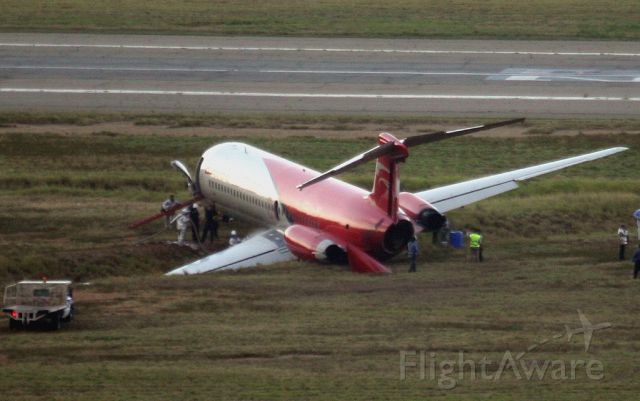
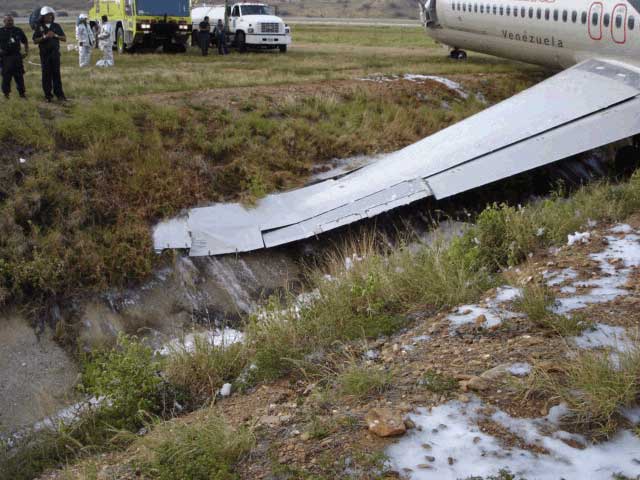
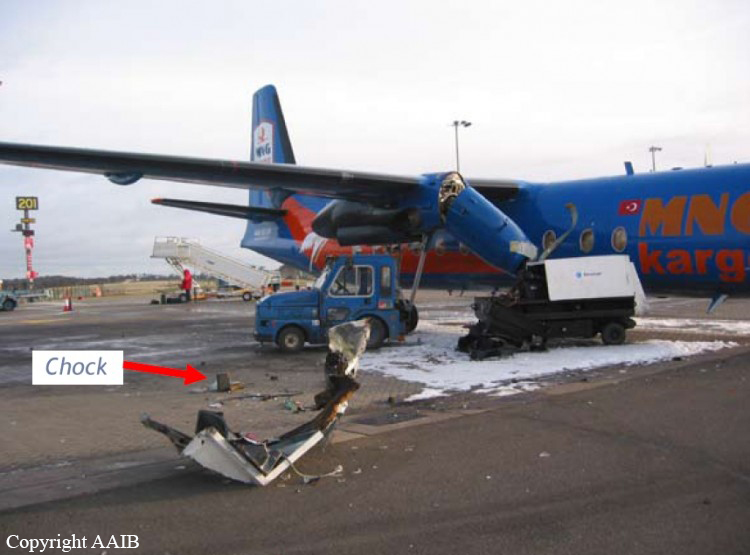
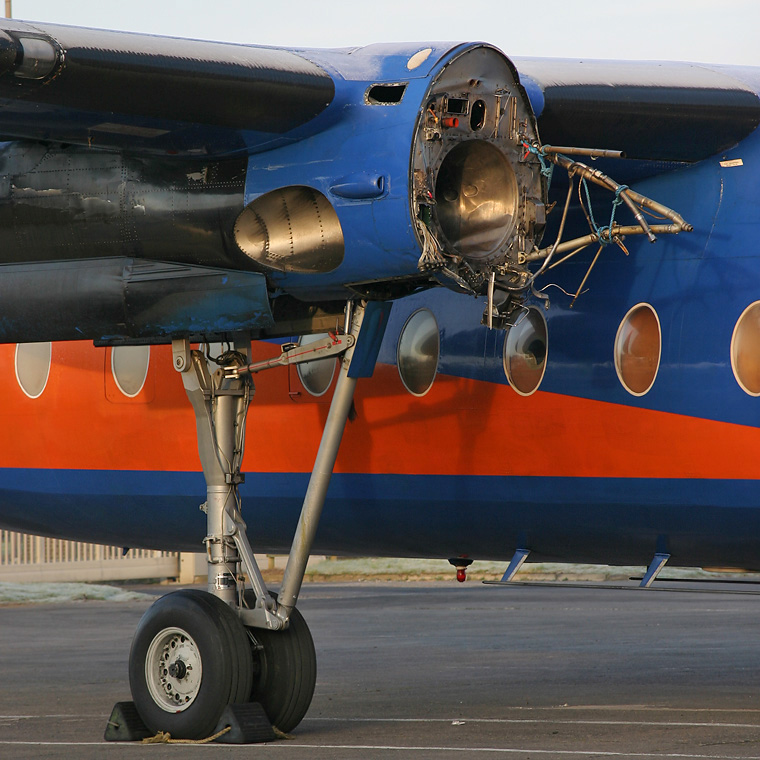
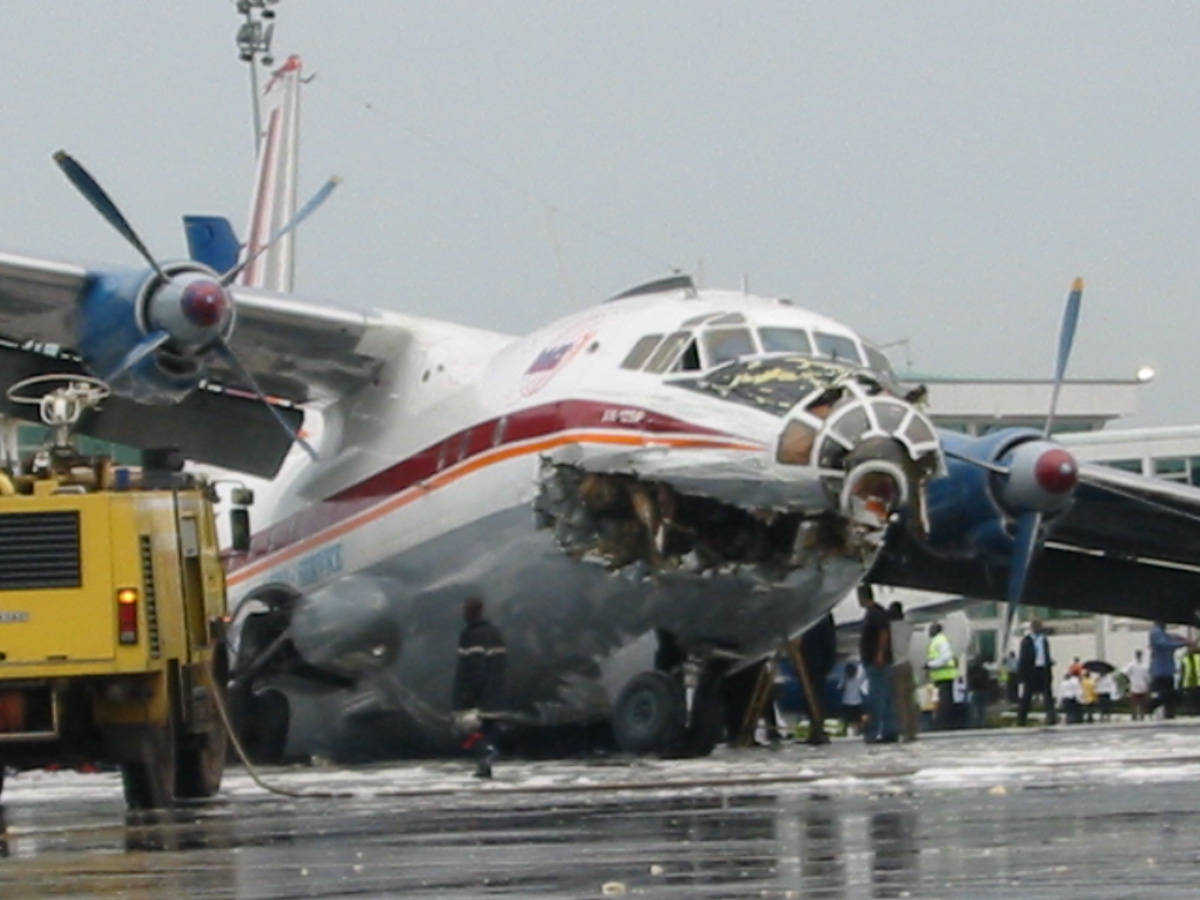
The aircraft was dispatched to Makhachkala to deliver troops, military equipment and cargo with 7 crew members on board. Ready for the next trip to Nizhny Novgorod, the crew was cleared to taxi to the holding point of runway 14. At that time, the visibility was poor due to the night and foggy conditions. A second Ilyushin II-76MD registered RA-76827 was on approach to runway 14 with 25 passengers and a crew of six on board. On final approach, the navigator informed the crew that the headlights should be switched on but no actions was taken. In a visibility lower than 800 metres, the aircraft landed on the left part of the runway, 530 metres past the runway threshold. Almost immediately after touchdown, the airplane veered off runway to the left, rolled for about 512 metres when its left wing collided with the cockpit of the II-76 registered RA-76825 that was waiting at a position located 41 metres past the holding position markings. RA-76827 continued to roll parallel to the runway and eventually stopped 1'876 metres past the runway 14 threshold with only minor damage, and no one on board was injured. The cockpit of RA-76825 was totally destroyed and four crew members were killed while three others were injured.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of the combination of the following factors:
- Poor piloting techniques on part of the landing crew,
- Rules violation on part of the captain of the taxiing aircraft,
- Errors and violations of procedures by air traffic control at Makhachkala Airport,
- Shortcomings in flight technical support at Makhachkala airport,
- After touchdown on the left side of runway 14, 530 metres after threshold, RA-76827 skidded to the left and veered off runway into soft ground. After a course of 512 metres, the left wing tip impacted the cockpit of RA-76825 that was holding at a position located 41 metres beyond the holding position marking. The presence of the aircraft beyond the holding position marking was due to non-compliant ground markings, uncoordinated actions by air traffic controllers and the fact that the captain failed to report his position to ATC,
- Shortcomings and irregularities in the organization of meteorological services at Makhachkala airport, which resulted in unsatisfactory meteorological information transmitted to the crews, leading to a landing in below minima weather conditions,
- Shortcomings in the organization of flight operations at 675 OSAP procedure, which led to a mismatch between the crew's actual level of preparedness and the complexity of the flight mission,
- An overestimation by the captain of his level of preparedness,
- The failure of the captain to divert to the alternate airport,
- A lack of discipline on part of the captain who decided to complete the landing procedure with the headlights off.
Final Report: