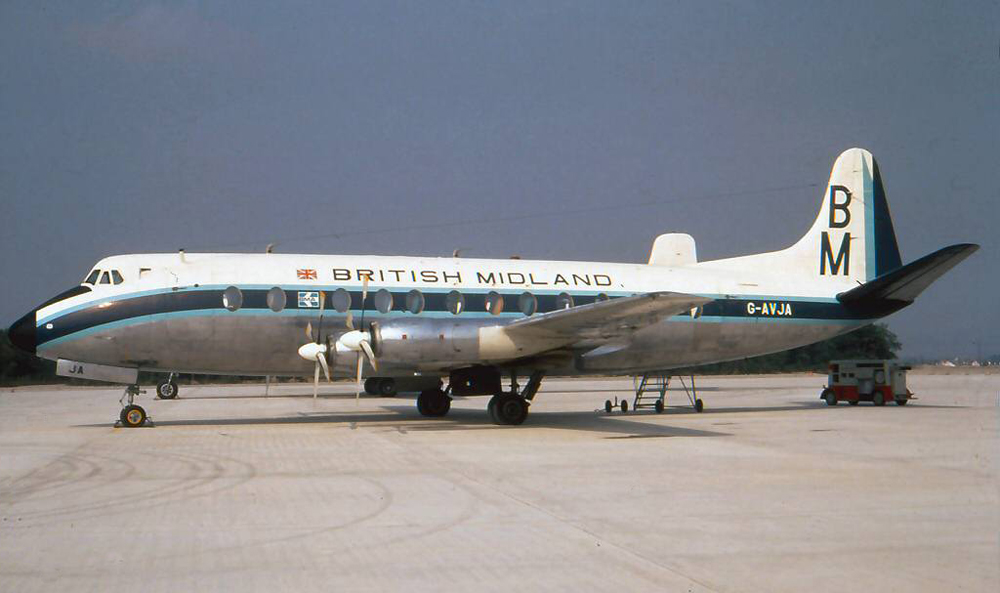
Ground collision with a Fokker F27 in Edinburgh
Date & Time:
Feb 2, 2008 at 2115 LT
Registration:
TC-MBG
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Edinburgh - Coventry
MSN:
10459
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2745.00
Circumstances:
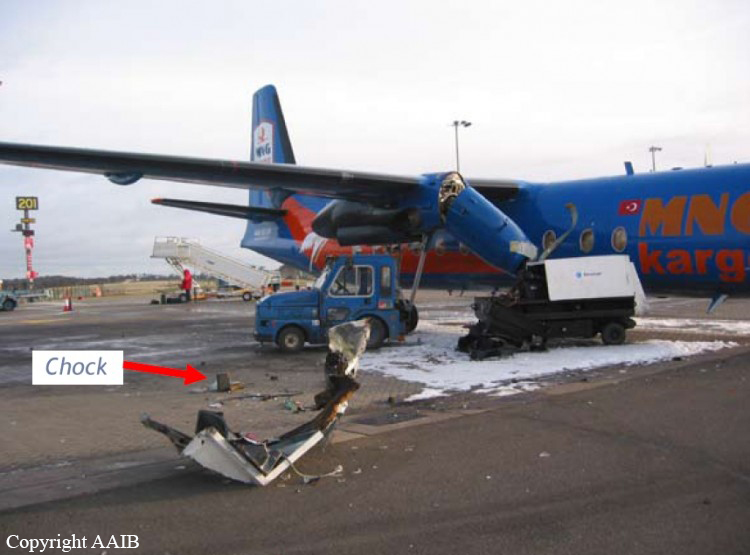
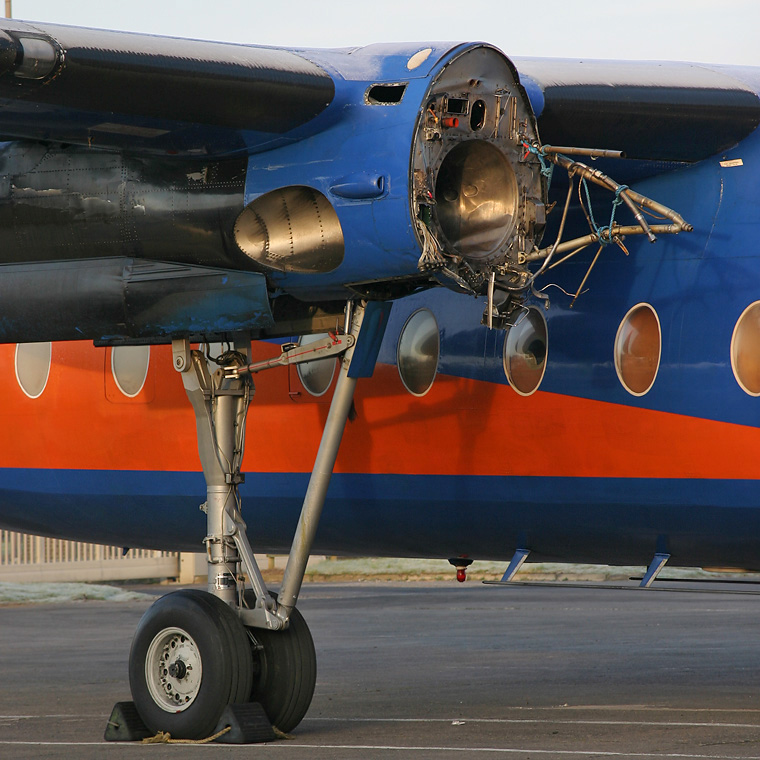
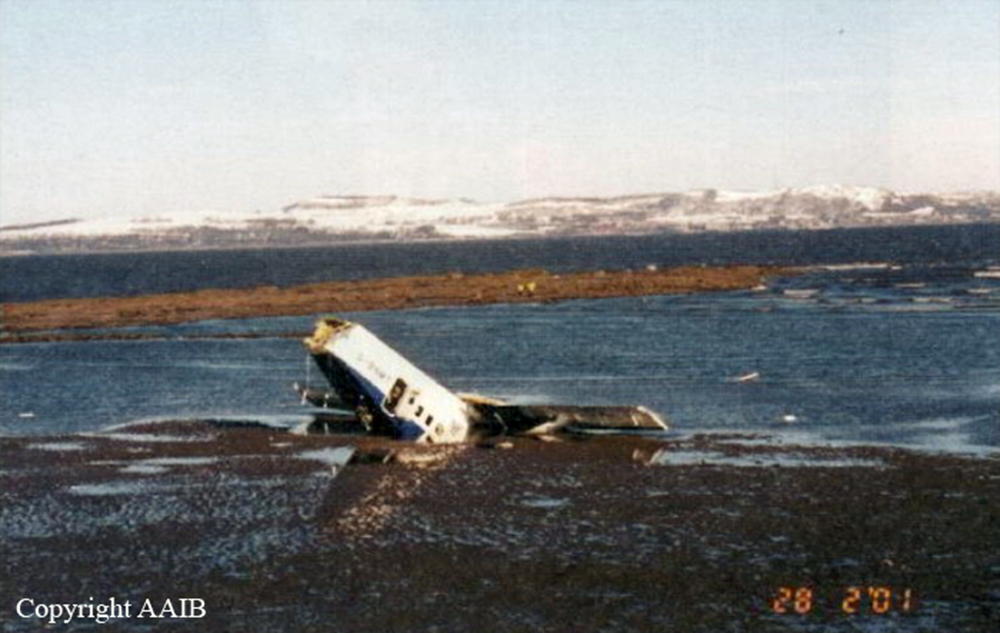
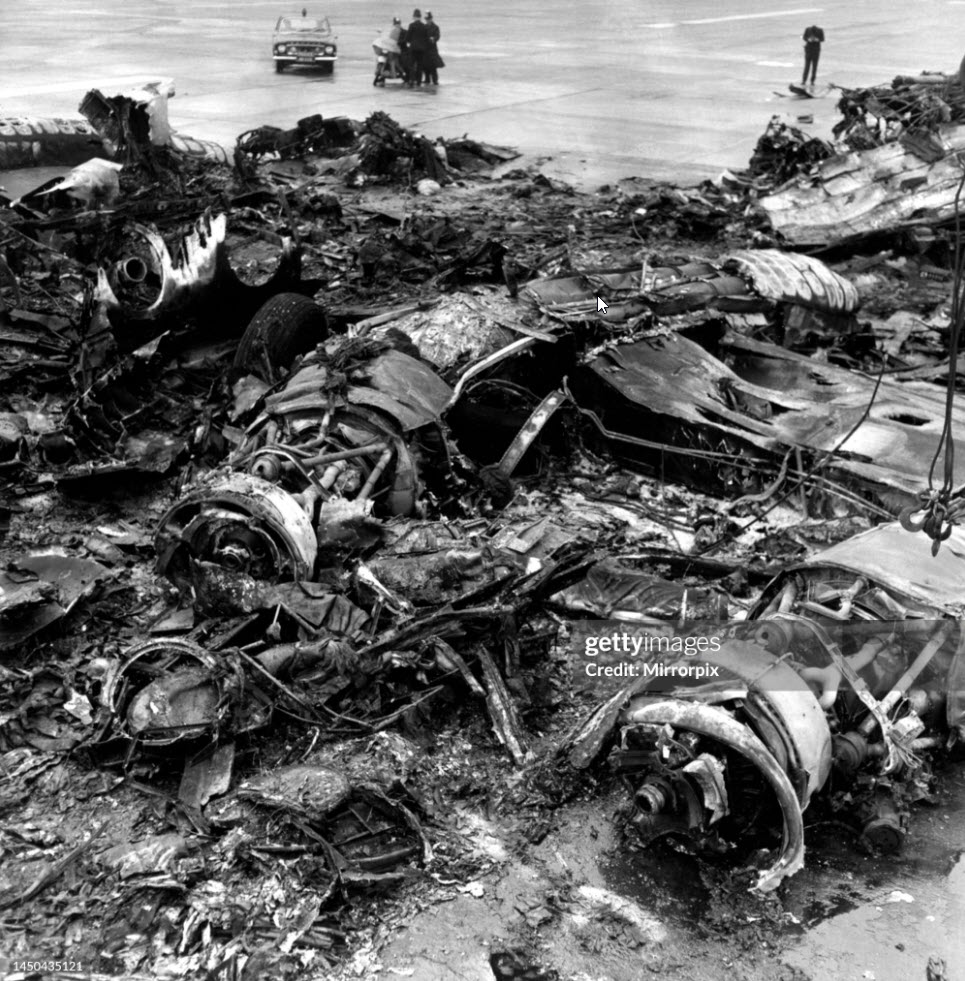
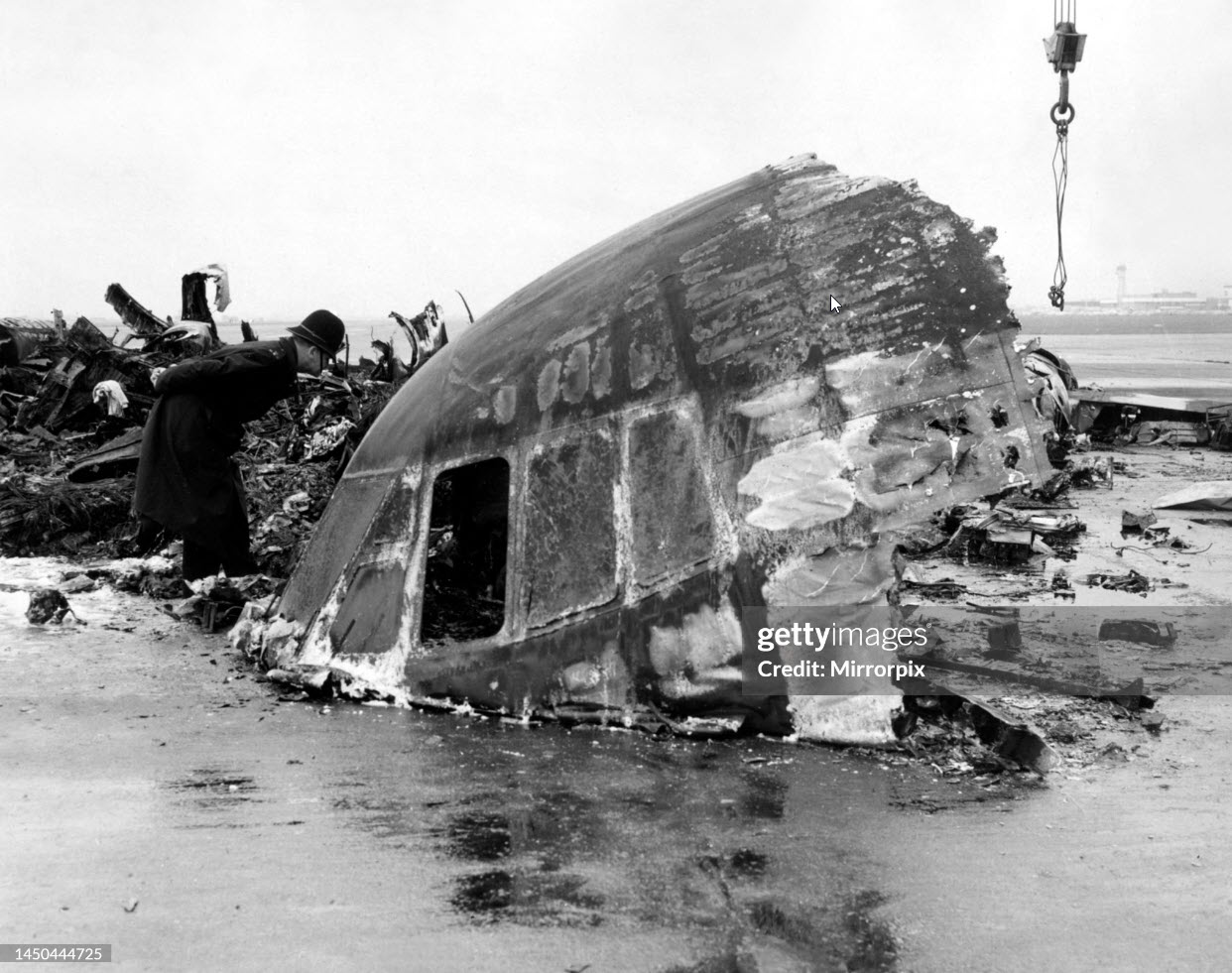
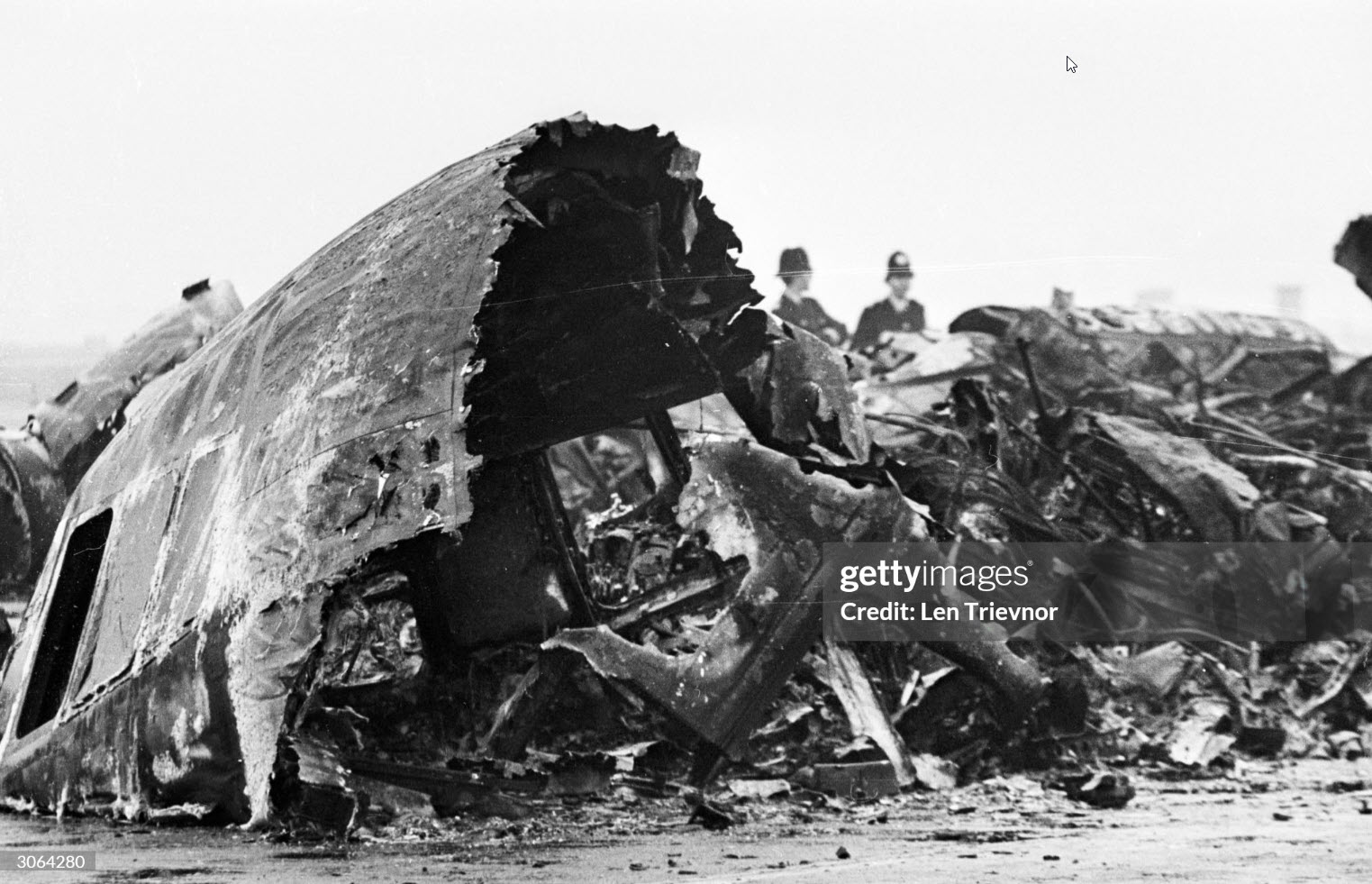
The aircraft was scheduled to operate a night cargo flight from Edinburgh to Coventry. The weather conditions at Edinburgh Airport were wintry with snowfall, which required the aircraft to be de-iced. Shortly after both engines had been started, the commander signalled to the marshaller to remove the Ground Power Unit (GPU) from the aircraft, which was facing nose out from its stand, down a slight slope. As the marshaller went to assist his colleague to remove the GPU to a safe distance prior to the aircraft taxiing off the stand, the aircraft started to move forward slowly, forcing them to run to safety. The flight crew, who were looking into the cockpit, were unaware that the aircraft was moving. It continued to move forward until its right propeller struck the GPU, causing substantial damage to the GPU, the propeller and the engine. The ground crew were uninjured. No cause as to why the aircraft moved could be positively identified.
Probable cause:
The aircraft moved forward inadvertently after engine start, causing its right propeller to strike a GPU. Possible explanations include that the parking brake was not set, the chocks had slipped from the nosewheel, or the chocks were removed prematurely. There was insufficient evidence to determine which of these scenarios was the most likely. Contributory factors were: the aircraft was facing down a slight downslope, the ramp was slippery due to the weather conditions and the flight crew increased engine speed to top up the pneumatic system pressure. The airport operator’s instructions contained in MDD 04/07 required aircraft facing nose-out on North Cargo Apron stands to be towed onto the taxiway centreline, prior to starting engines. Had these instructions been complied with, the accident would probably have been avoided.
Final Report: