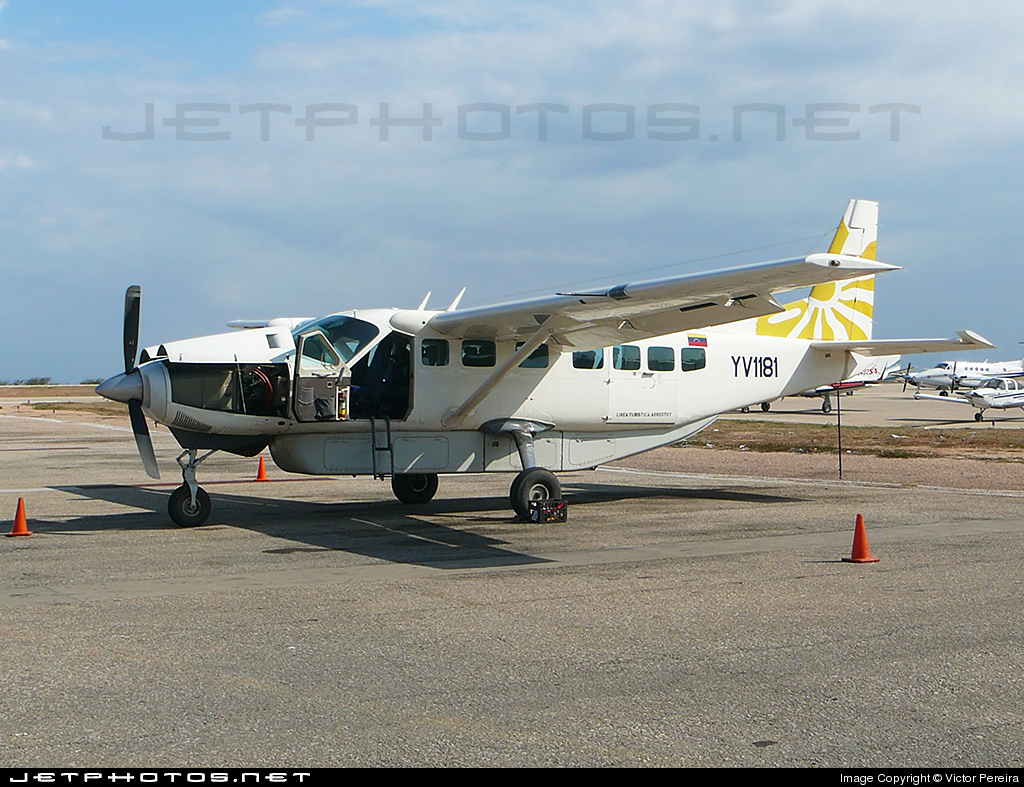
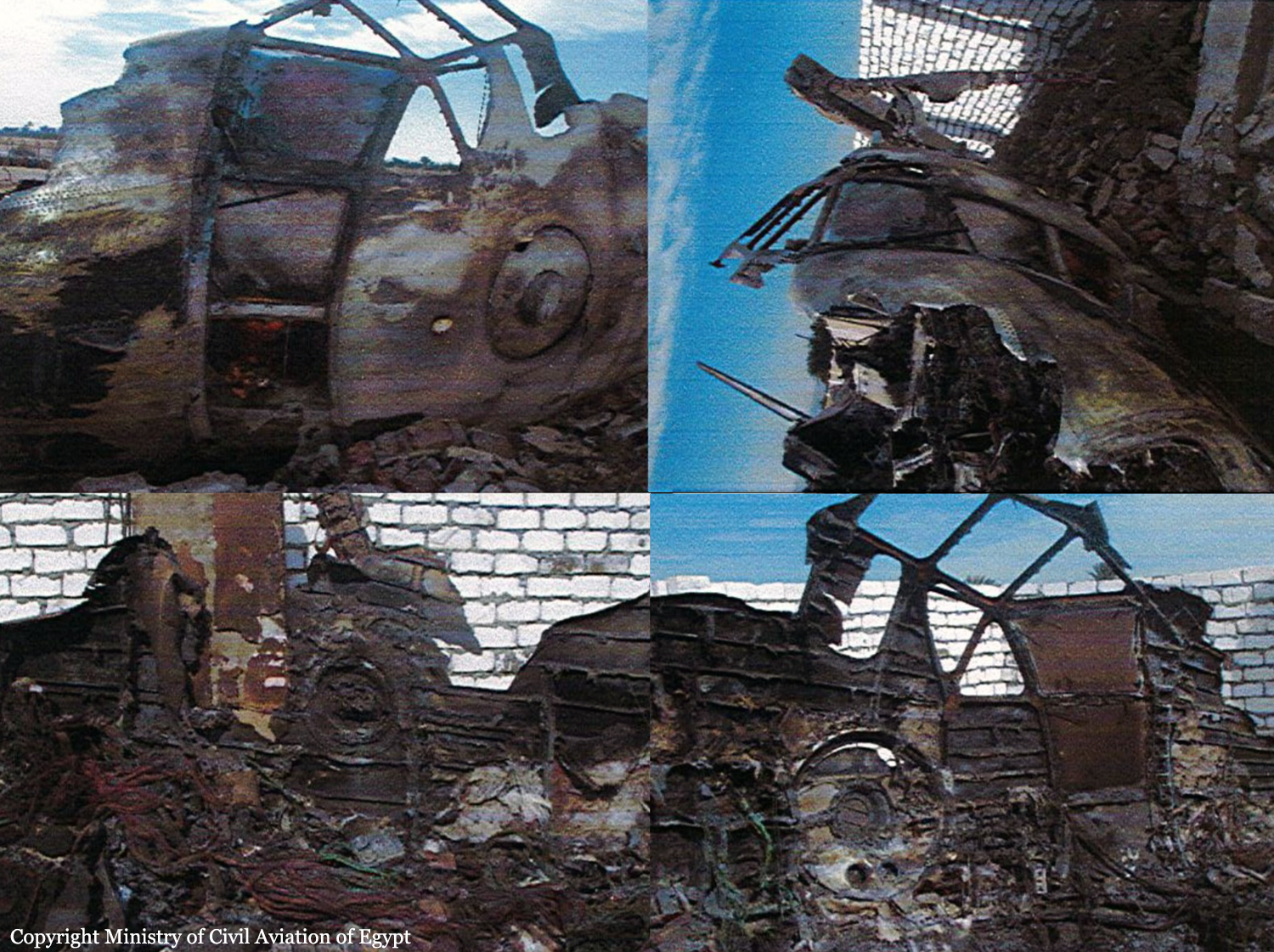Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Canaima: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 17, 2009 at 1545 LT
Registration:
YV1181
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Canaima – Ciudad Bolívar
MSN:
208B-0695
YOM:
1998
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
10
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
1021.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
59
Aircraft flight hours:
15753
Circumstances:
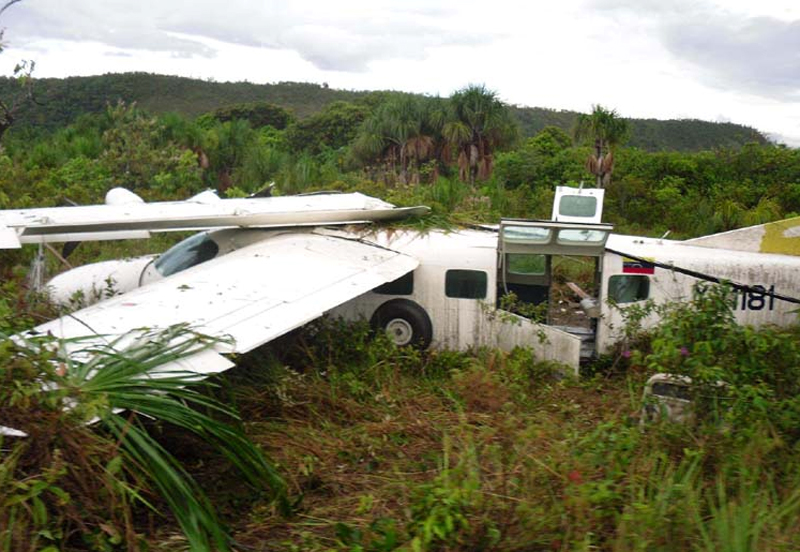
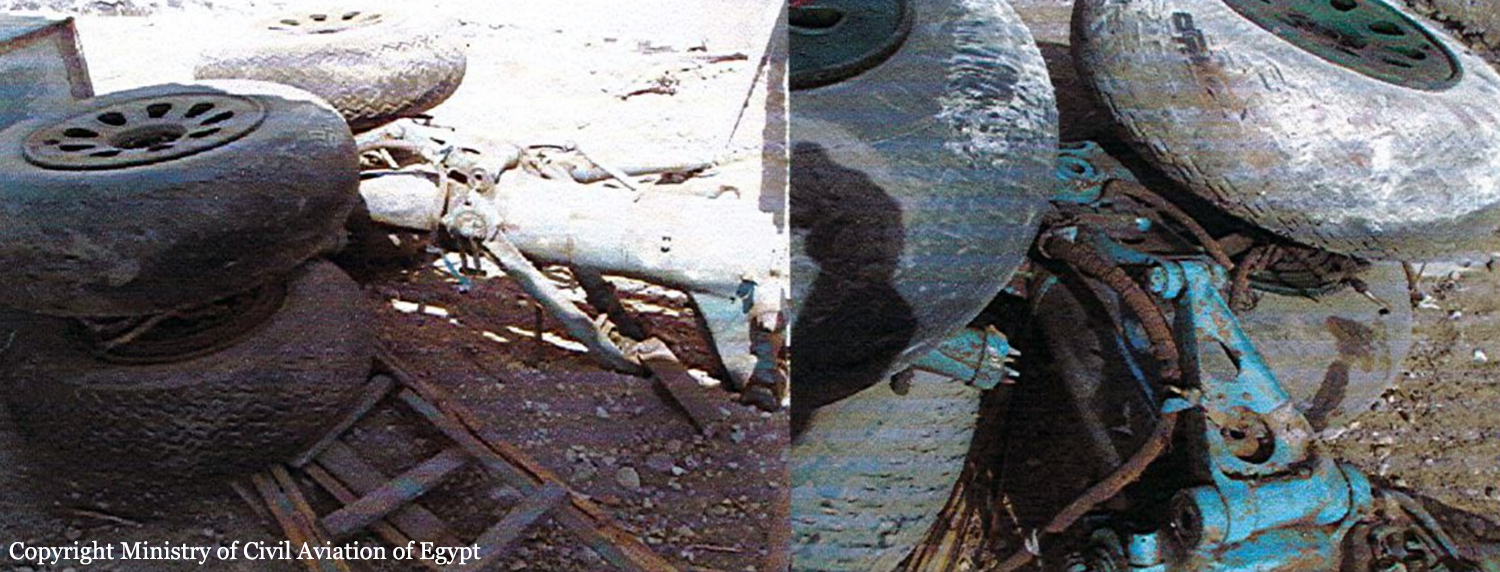
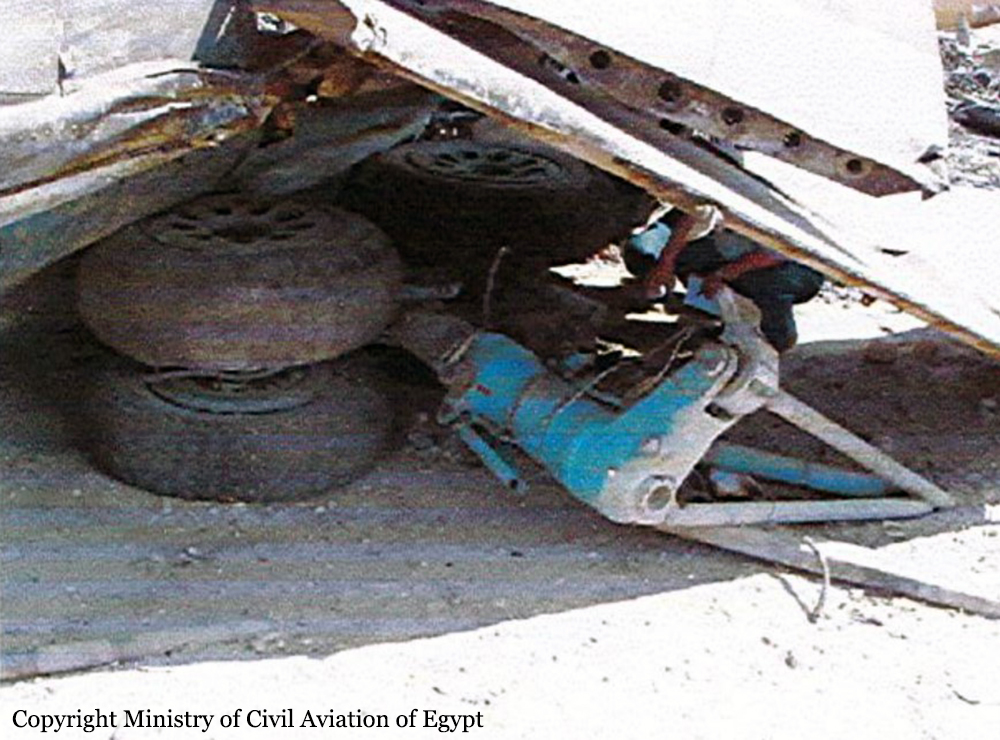
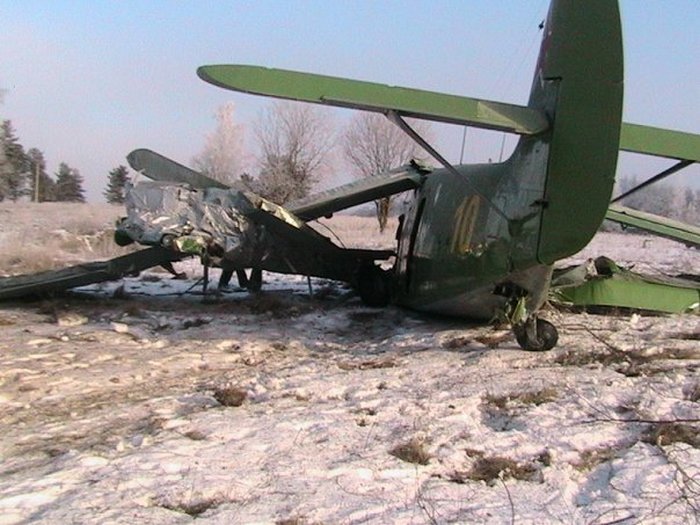
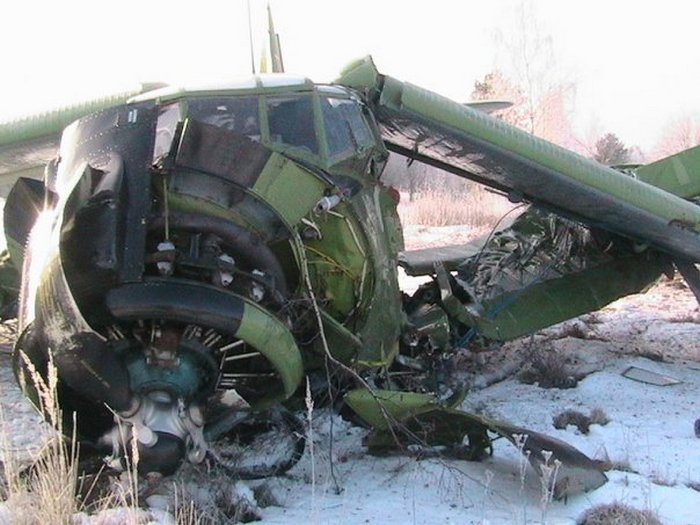
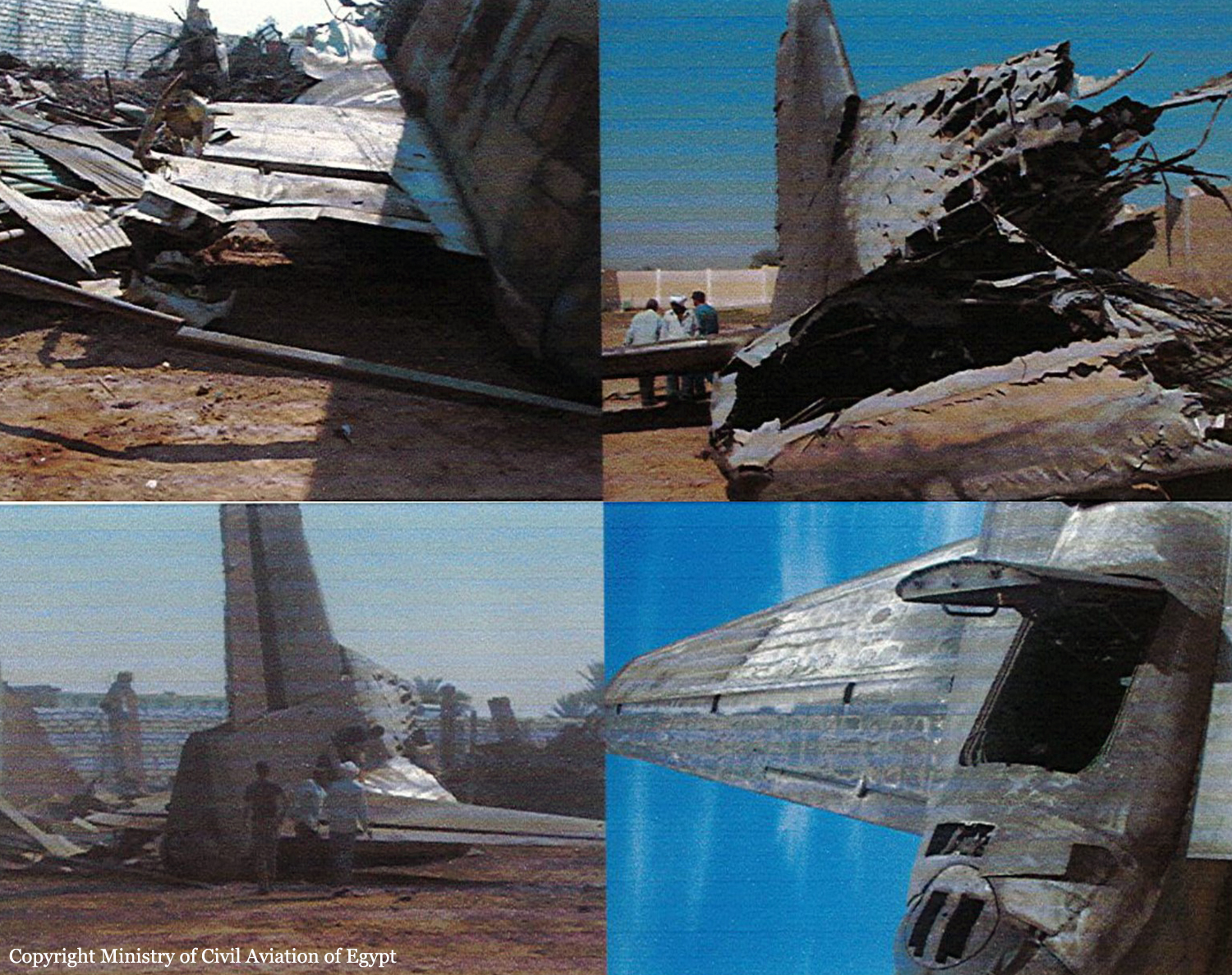
After takeoff from runway 36 at Canaima Airport, while in initial climb, the single engine aircraft encountered difficulties to gain height. It collided with power lines and crashed in bushes located 80 metres past the runway end. A young boy aged 6 was killed while all other occupants were injured, seven seriously. The aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
The accident occurred as a result of the inability of the aircraft to take off, affected by the tailwind and water puddles that covered part of the runway, which did not allow speed to build up, crashing into the ground. It is considered that the most likely cause of the accident was mismanagement by the crew, in the sense of failing to make adequate planning and analysis, coupled with overconfidence and lack of identification of hazardous conditions at that time of takeoff. Based on our [JIAAC] investigations, we can infer that there were several contributing causes for the occurrence of this accident. In this order, we can state the following:
- Adverse weather and tailwind conditions associated with the phenomenon.
- Incorrect management by the crew to use only the last third of the runway with the meteorological conditions prevailing at that time.
- Failure of the aerodrome administration to identify and correct poor drainage of the runway.
- Failure of the Autoridad Aeronáutica to monitor safety.
- Rejection by the crew of the concatenated form in which the factors involved in this event developed.
After all the analysis to different causes involved in this accident, we can point to as the main Causal Factor: Human Factor, due to the mismanagement by the flight crew upon takeoff in these conditions. Physical and Material factors included everything related to the prevailing weather conditions, road conditions and lack of services at the aerodrome by the authorities; all of them are considered Contributing Factors.
- Adverse weather and tailwind conditions associated with the phenomenon.
- Incorrect management by the crew to use only the last third of the runway with the meteorological conditions prevailing at that time.
- Failure of the aerodrome administration to identify and correct poor drainage of the runway.
- Failure of the Autoridad Aeronáutica to monitor safety.
- Rejection by the crew of the concatenated form in which the factors involved in this event developed.
After all the analysis to different causes involved in this accident, we can point to as the main Causal Factor: Human Factor, due to the mismanagement by the flight crew upon takeoff in these conditions. Physical and Material factors included everything related to the prevailing weather conditions, road conditions and lack of services at the aerodrome by the authorities; all of them are considered Contributing Factors.
Final Report: