Circumstances:
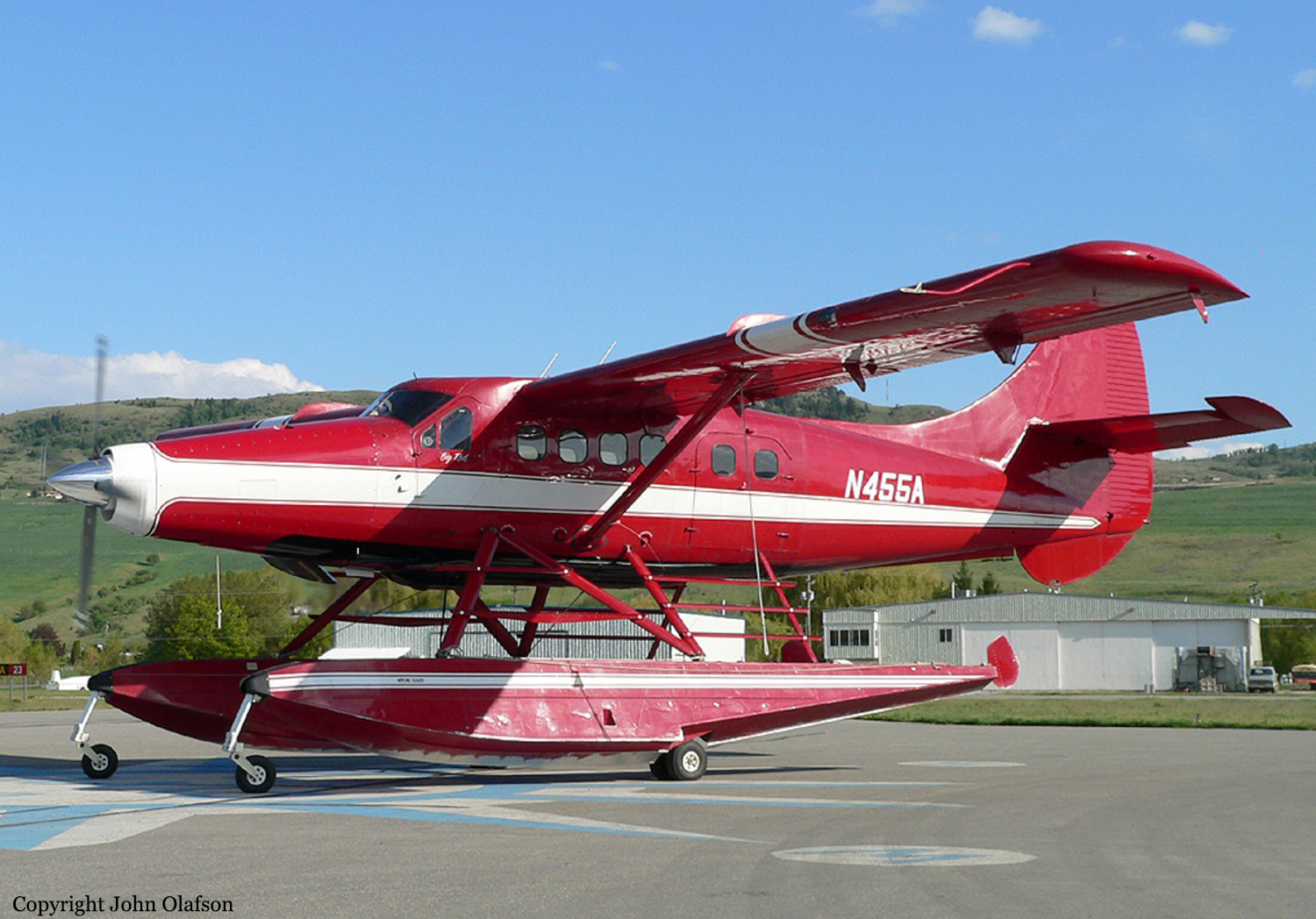
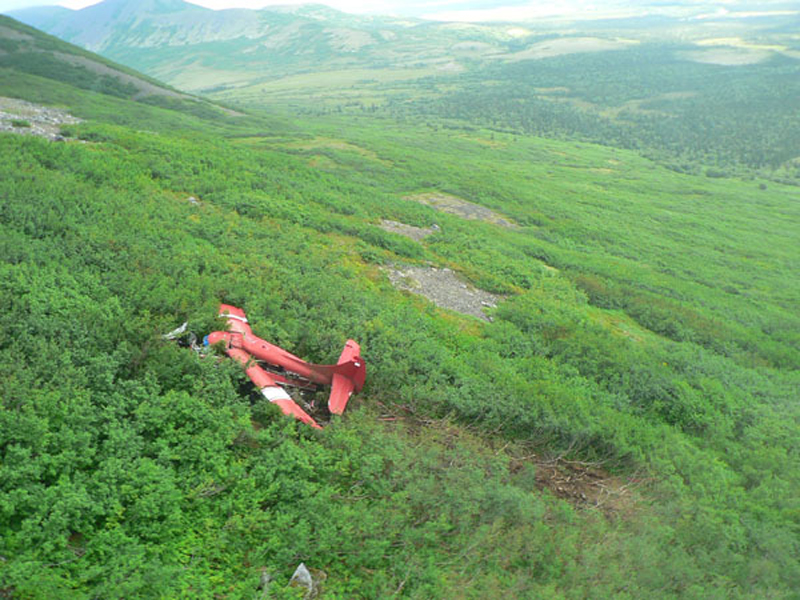
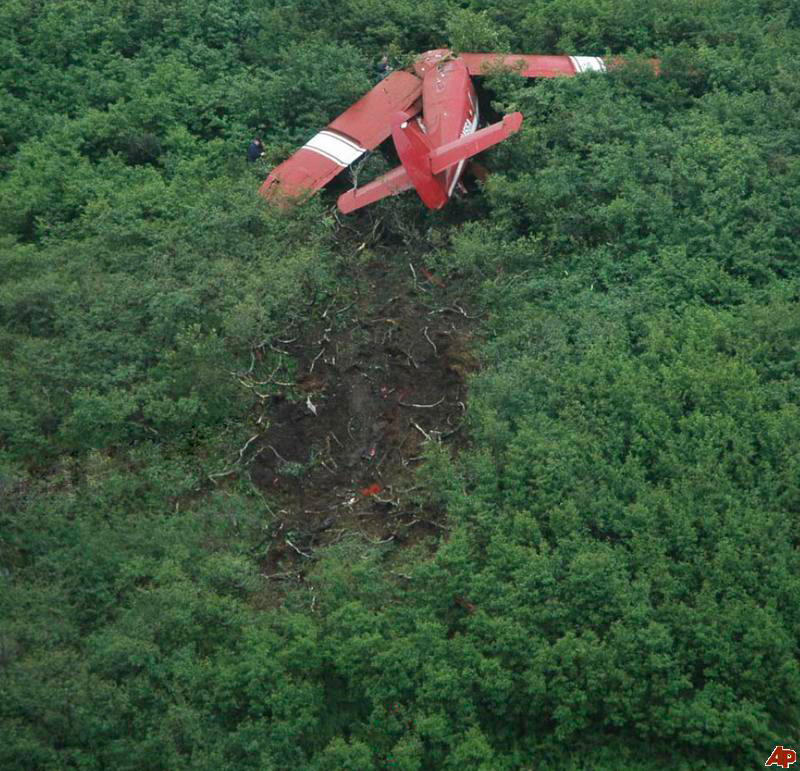
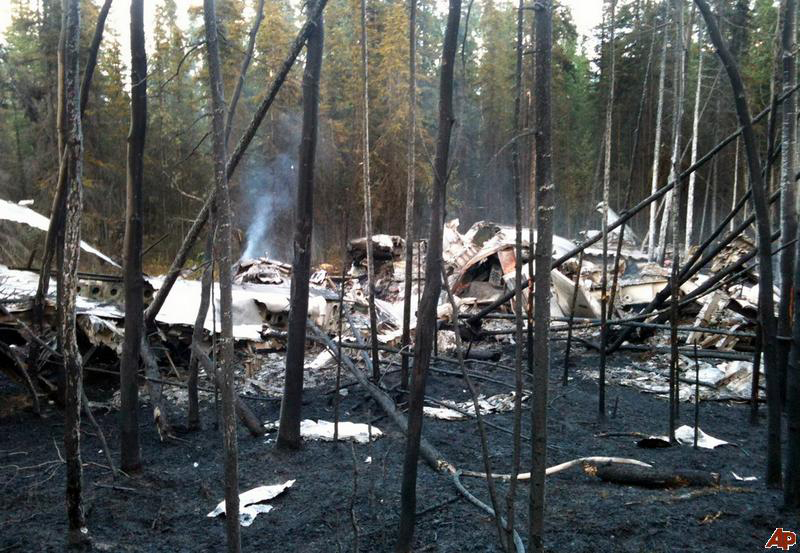
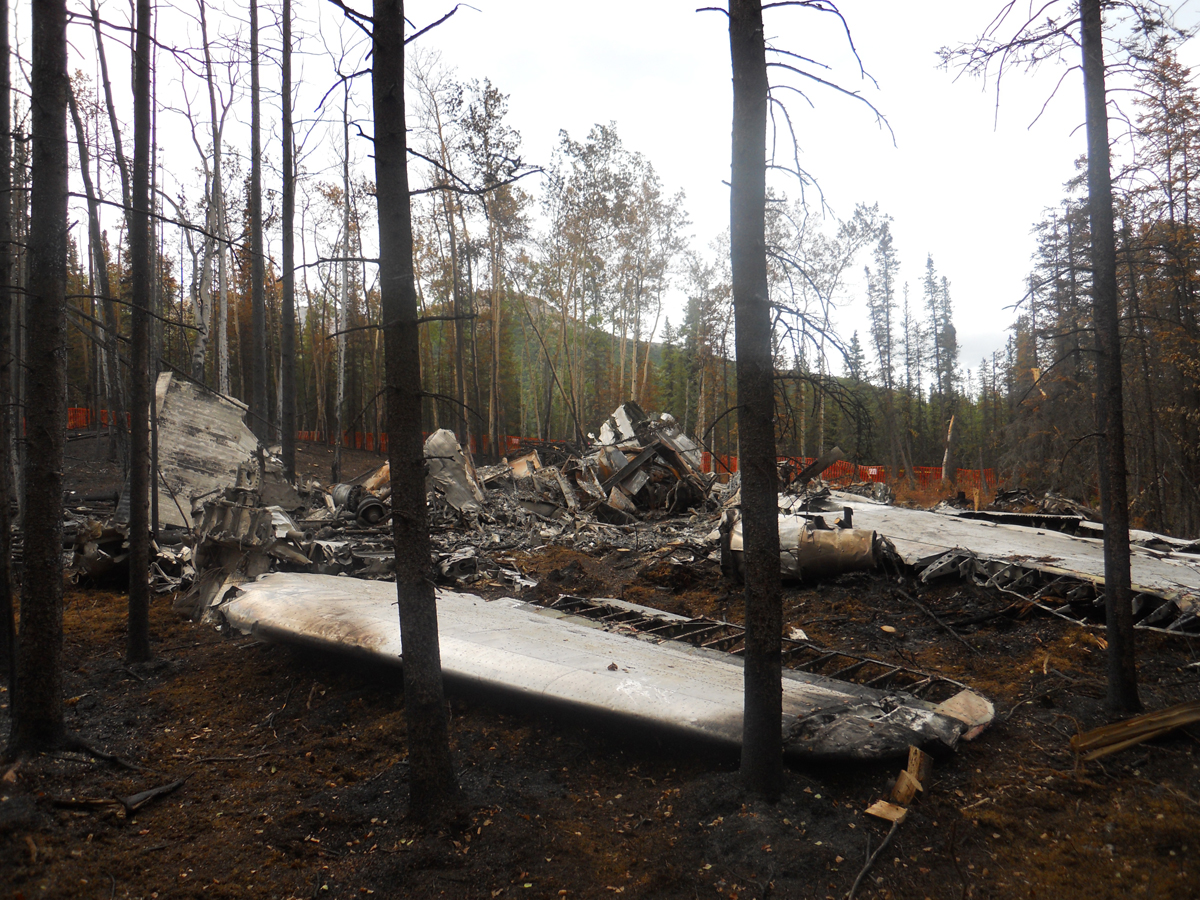
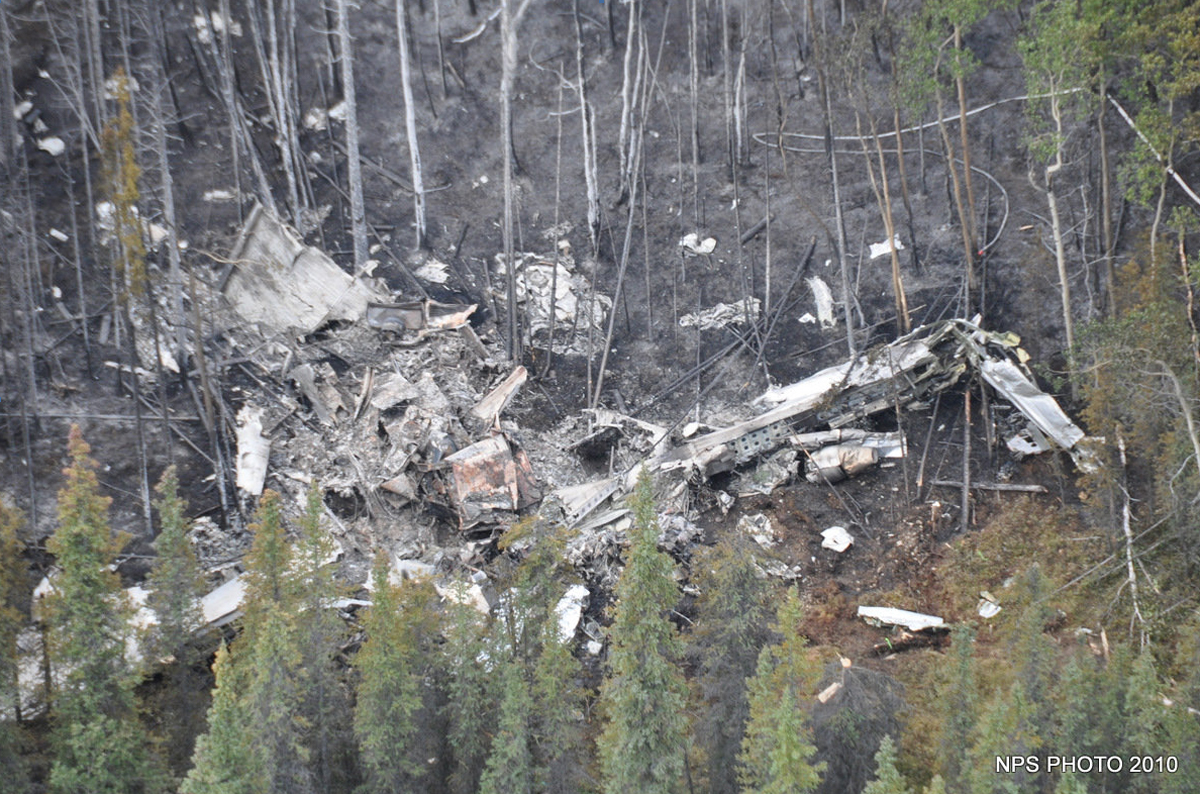
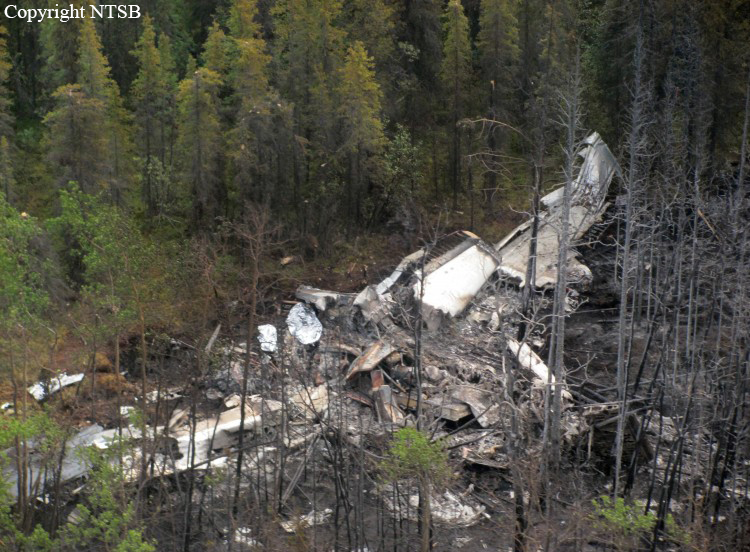
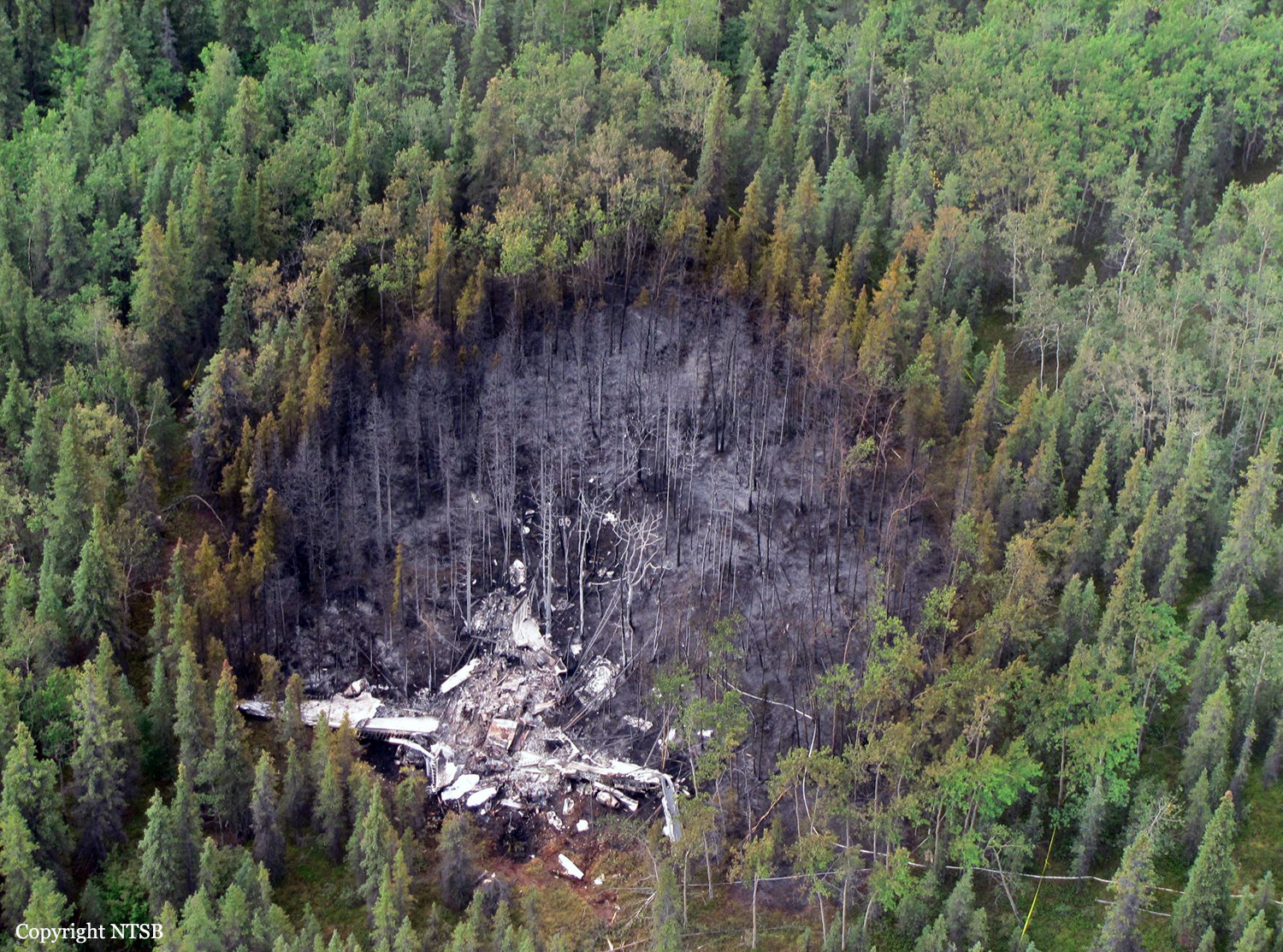
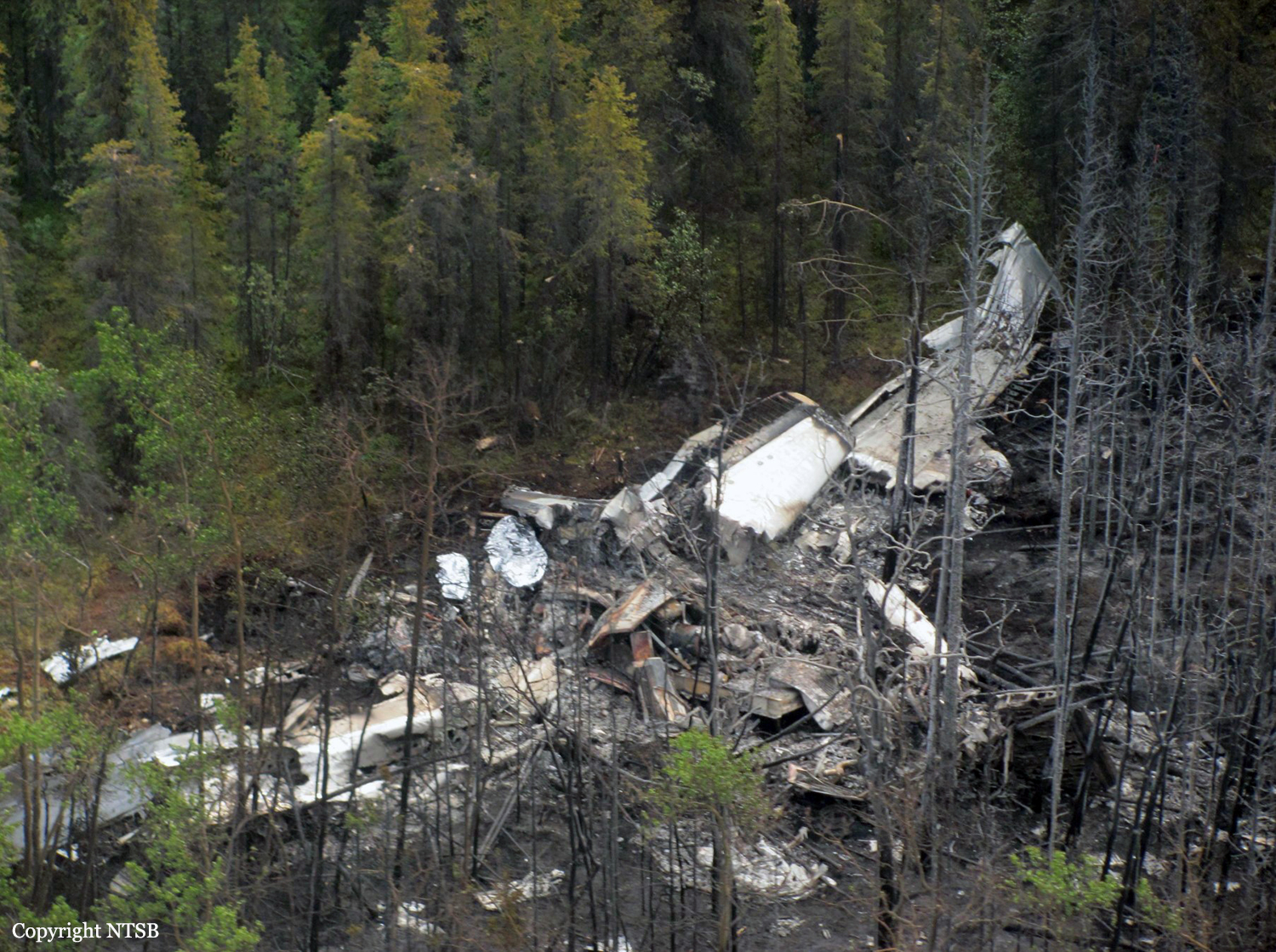
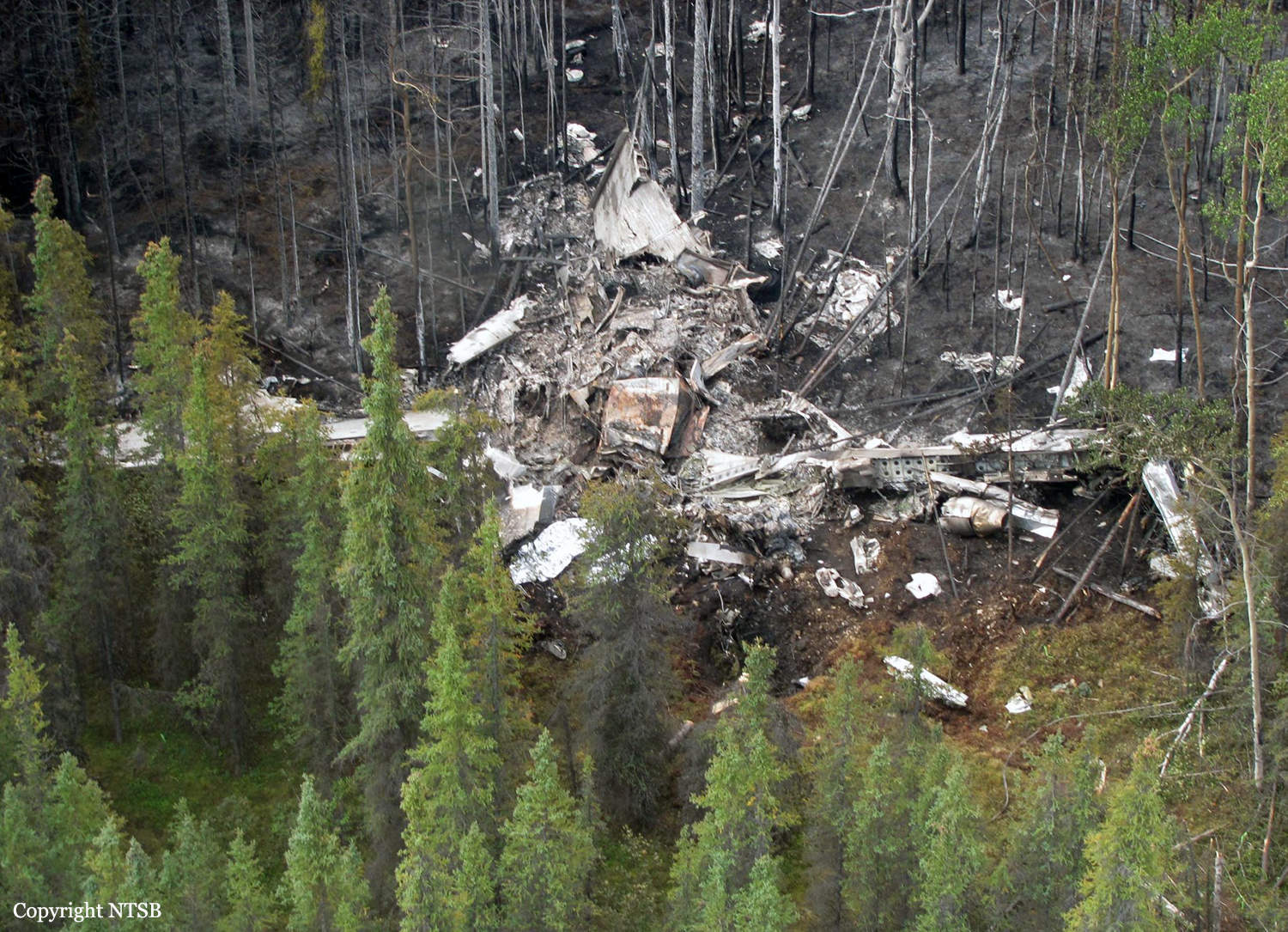
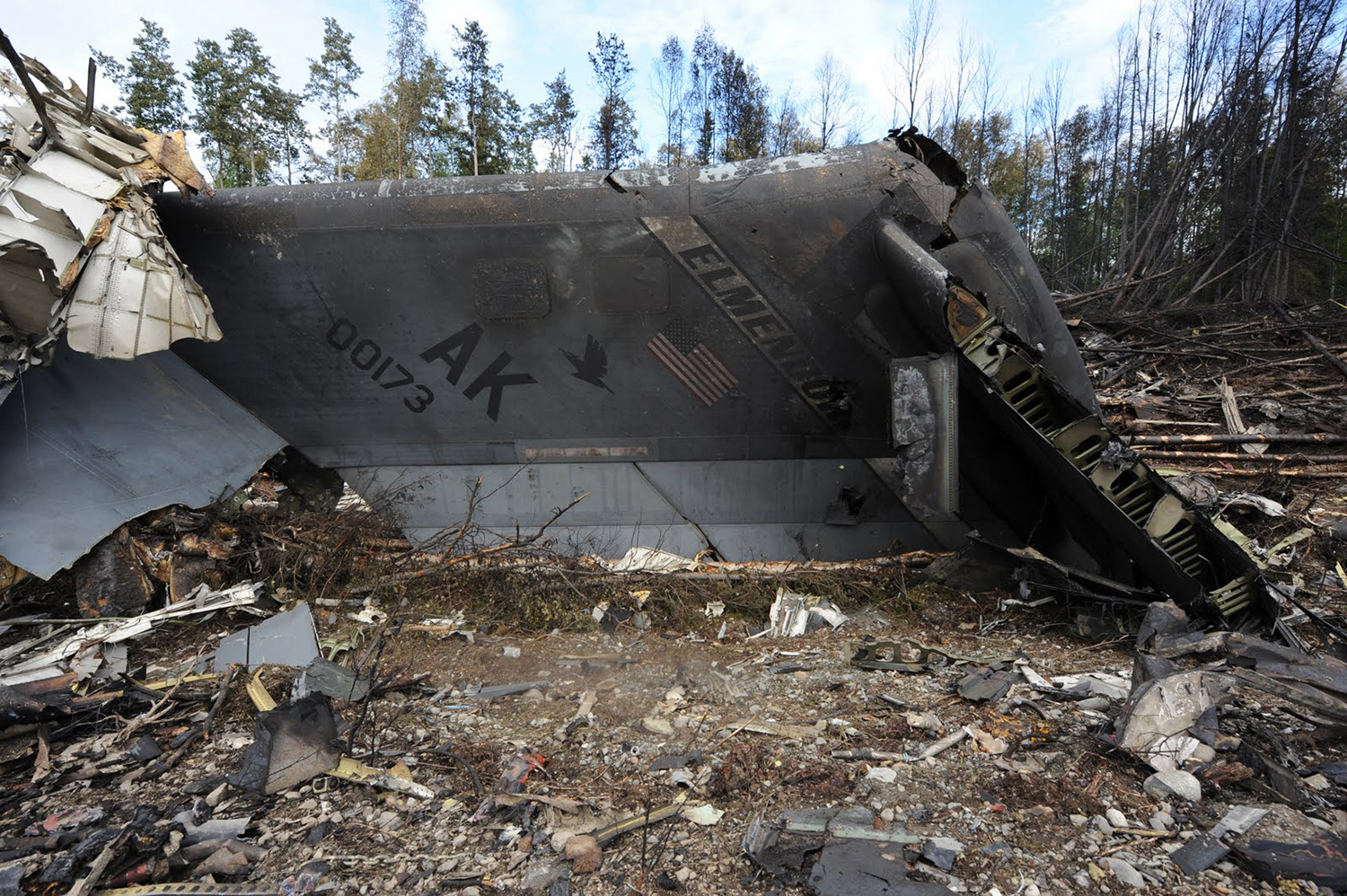
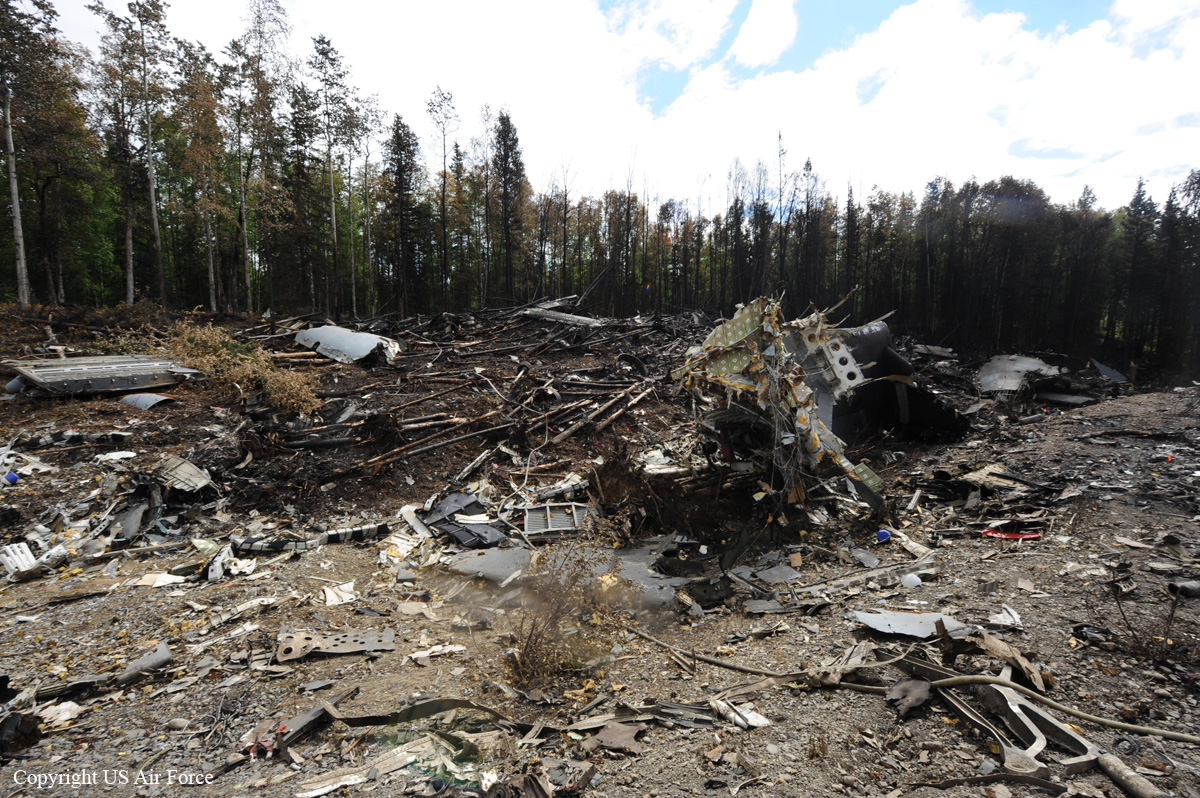
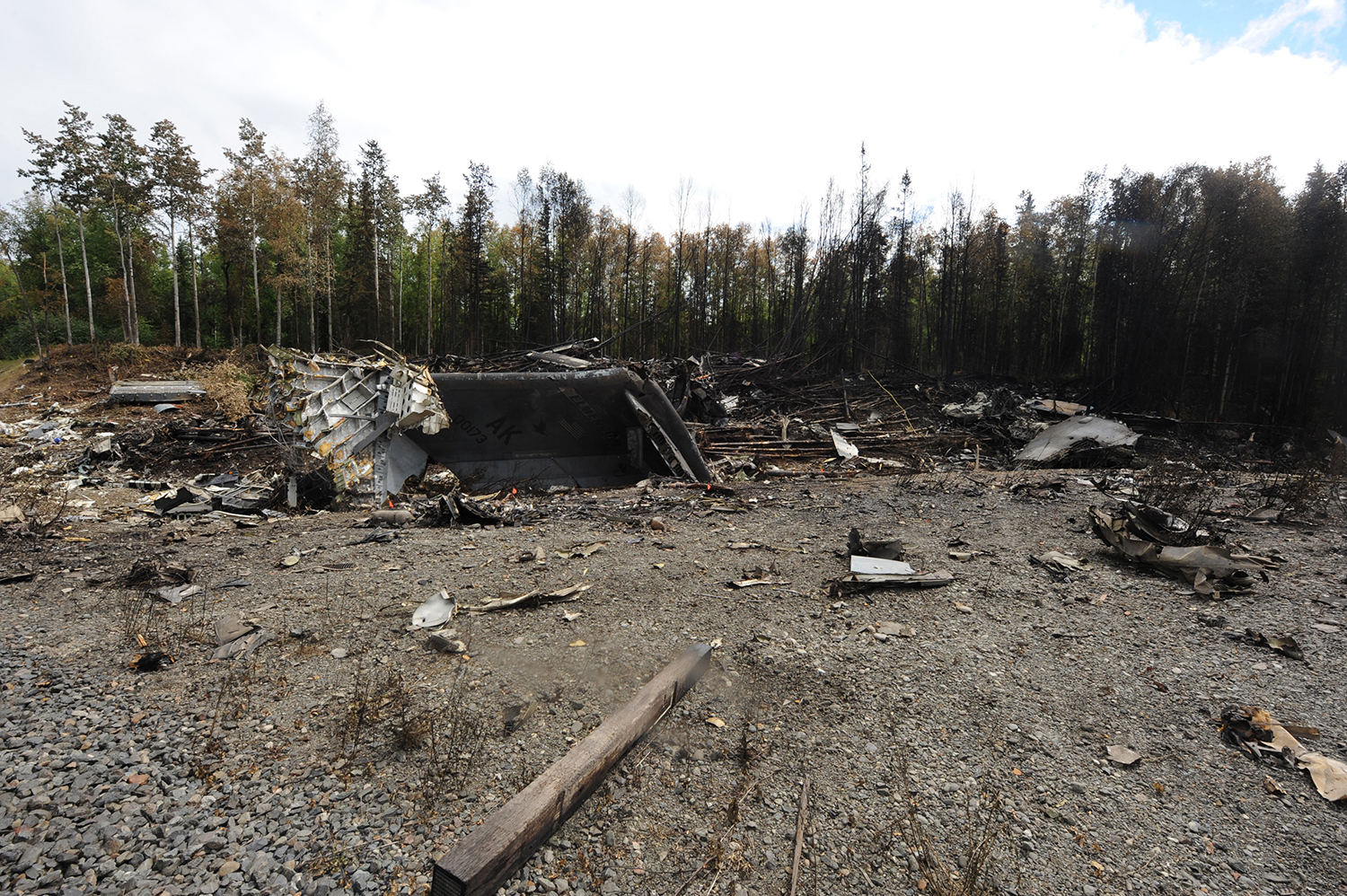
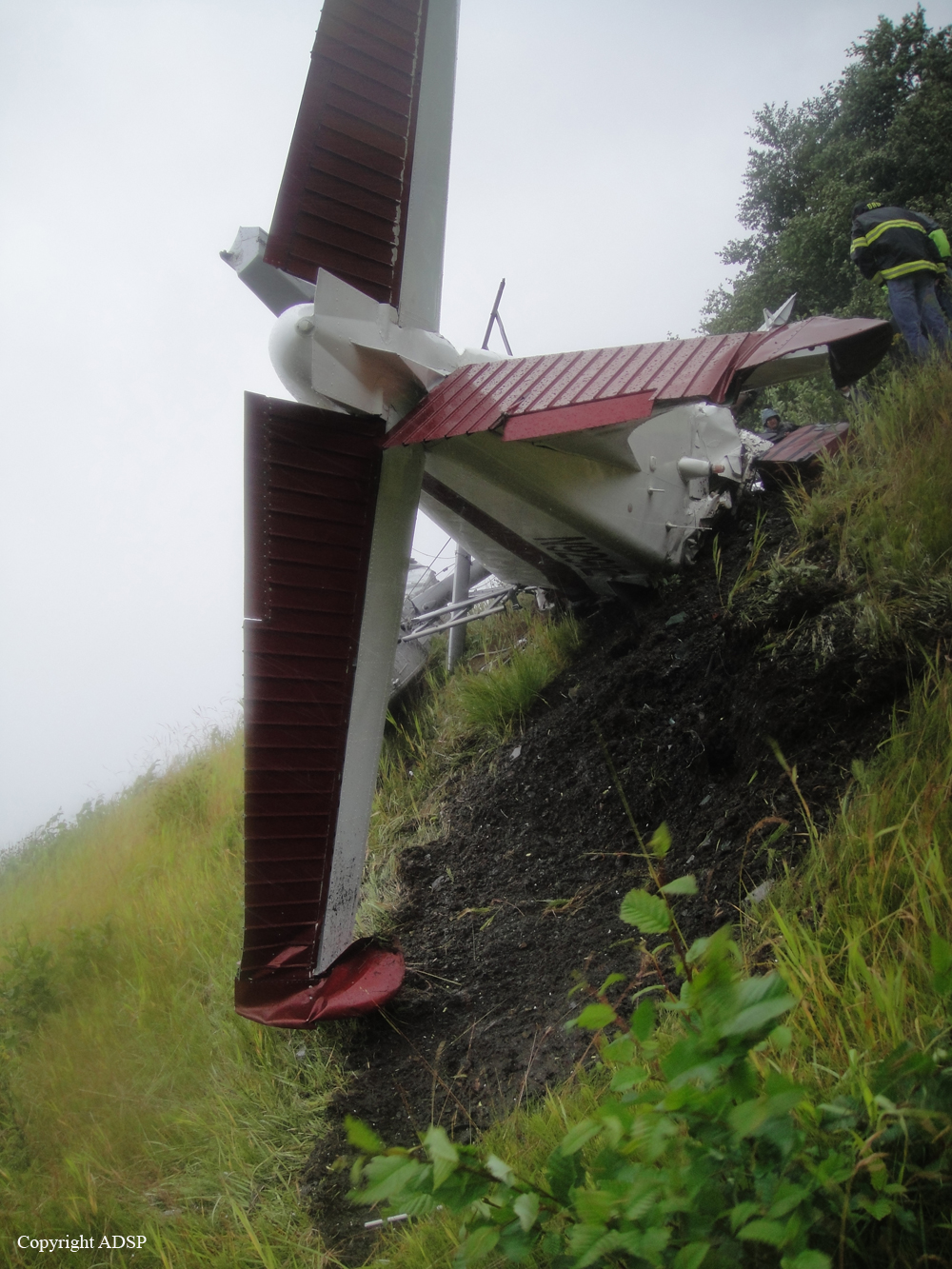
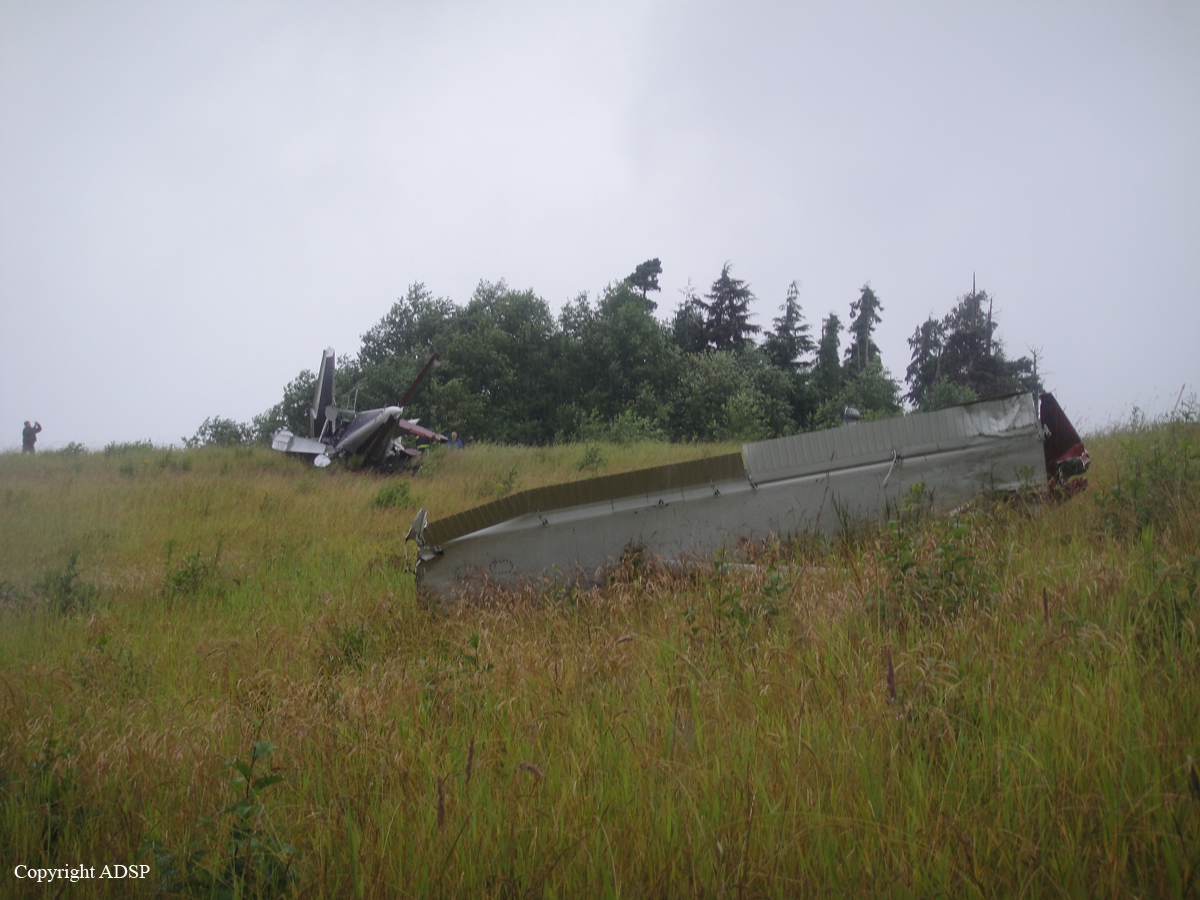
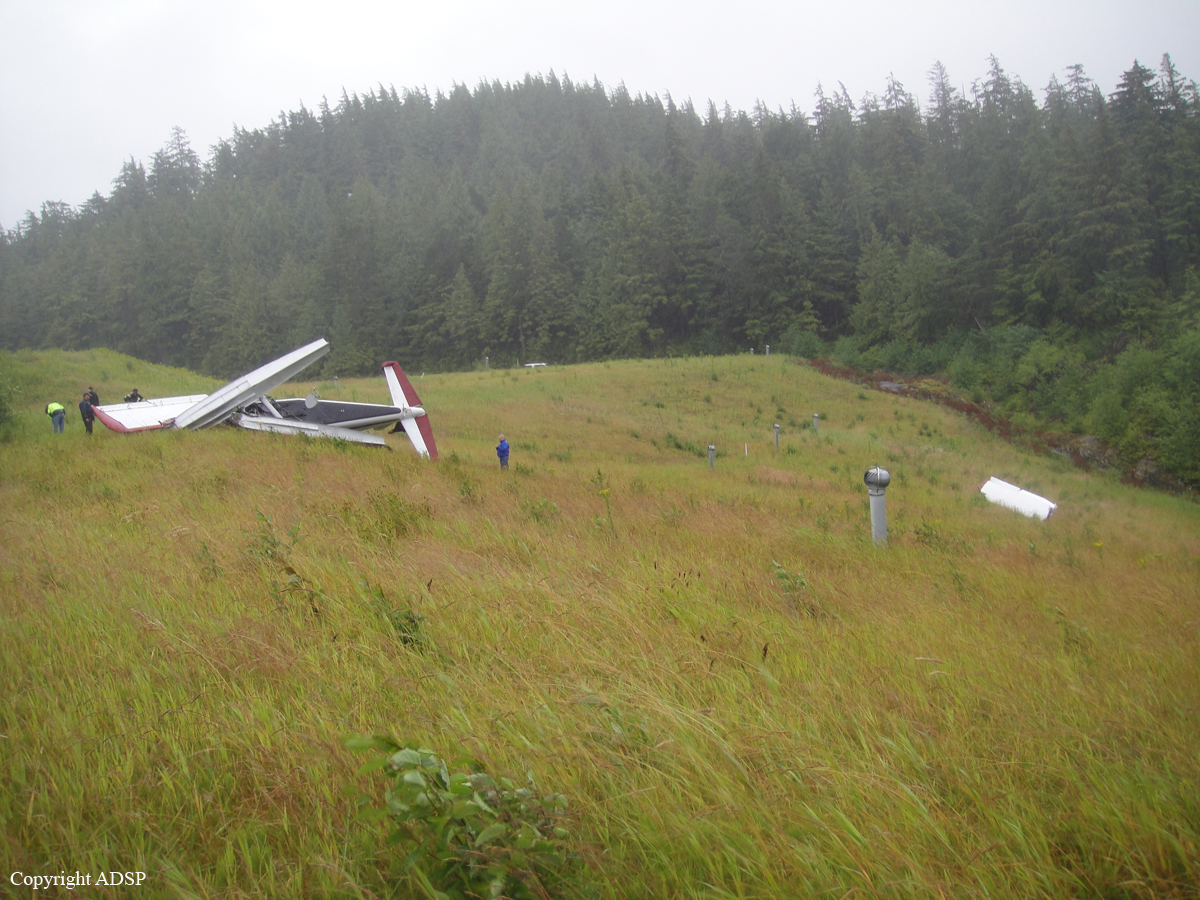
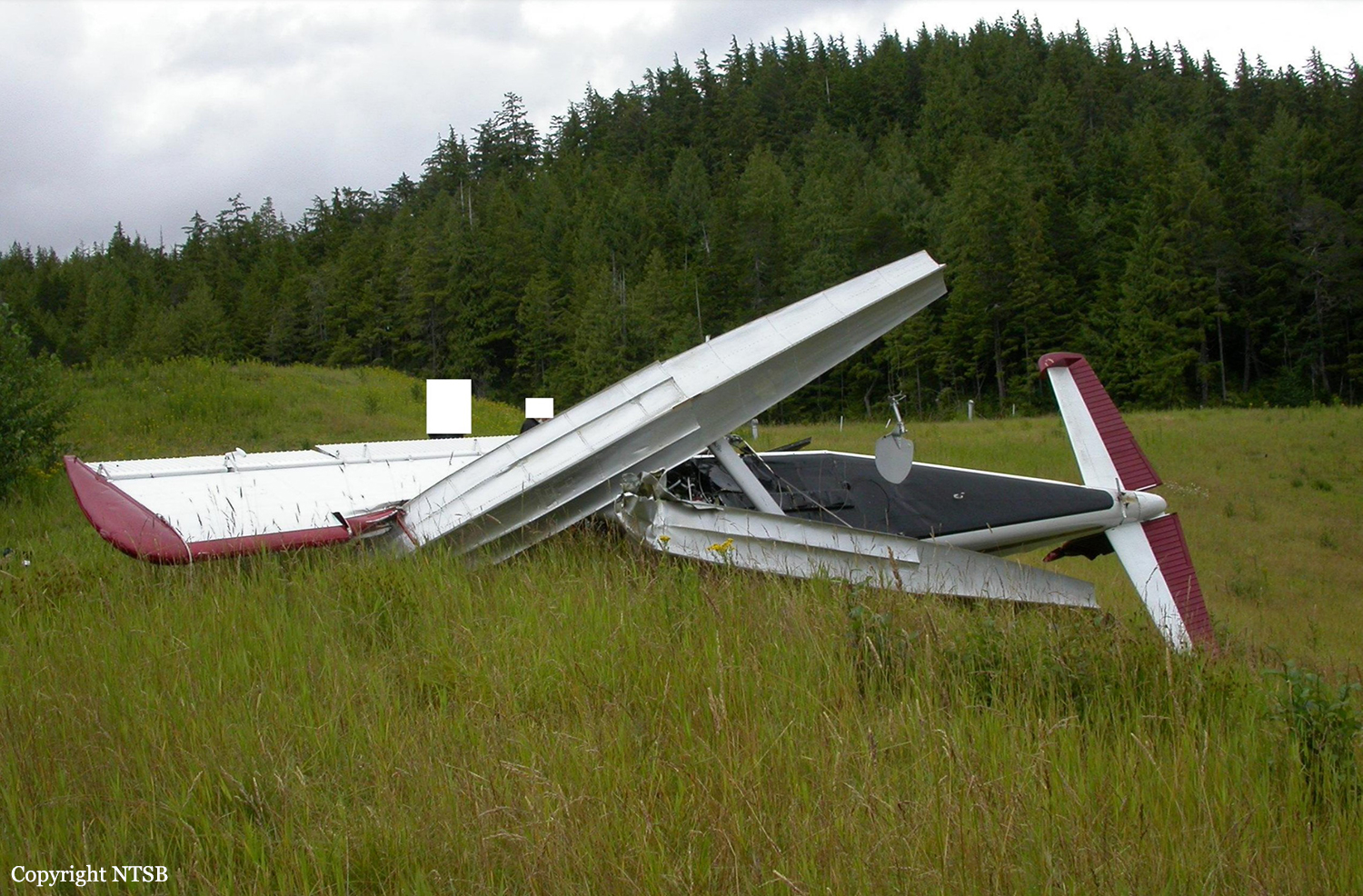
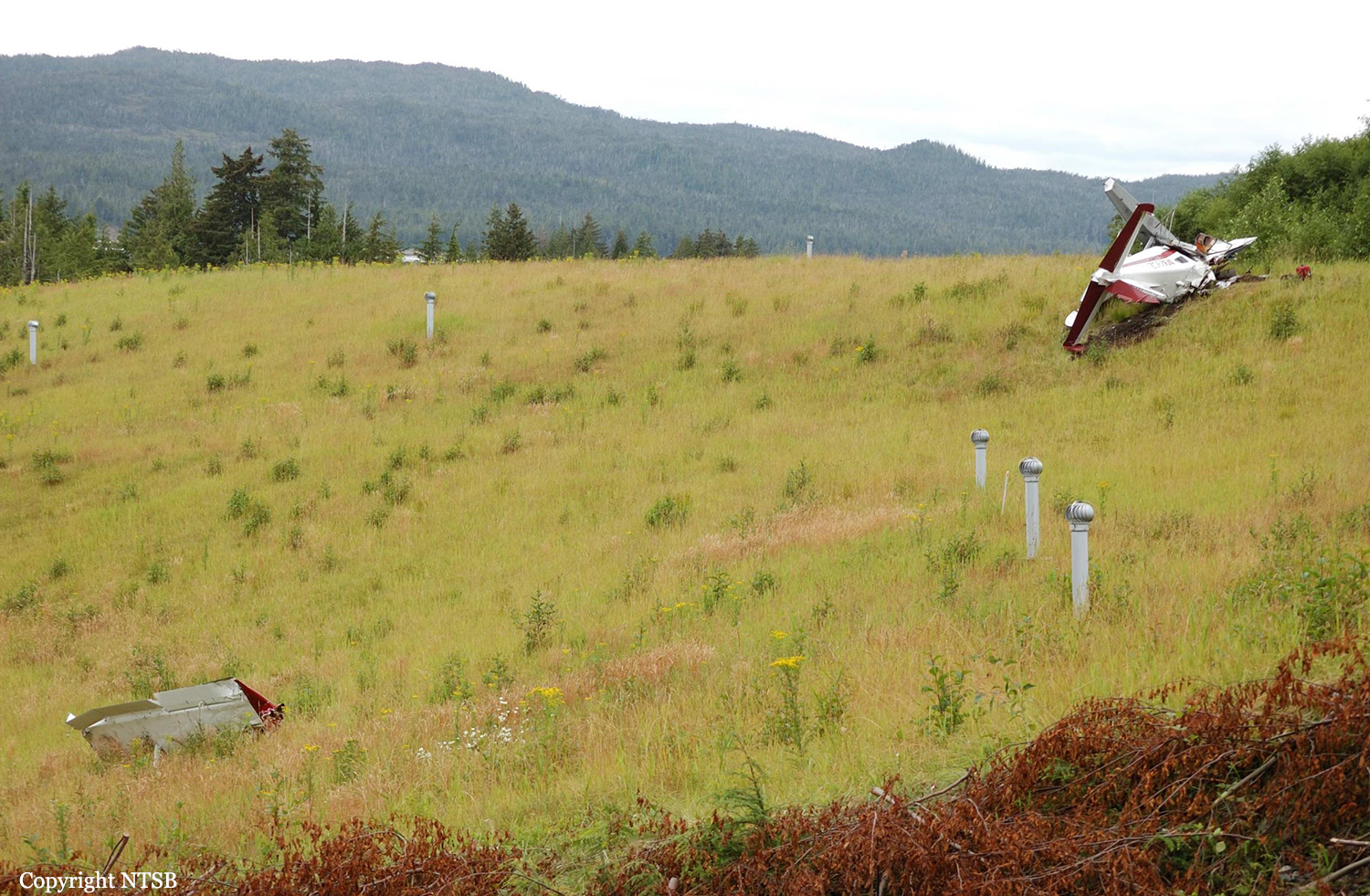
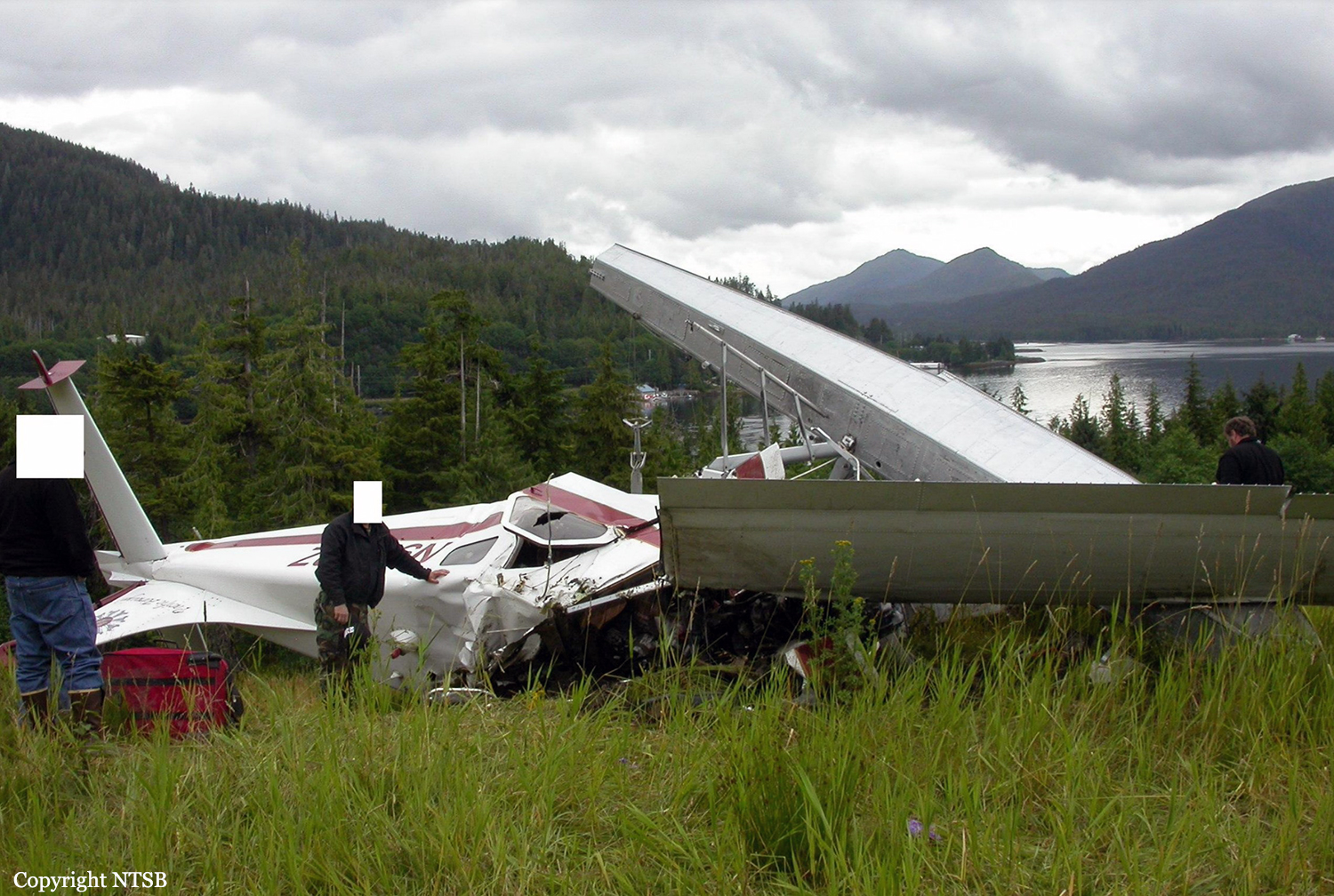
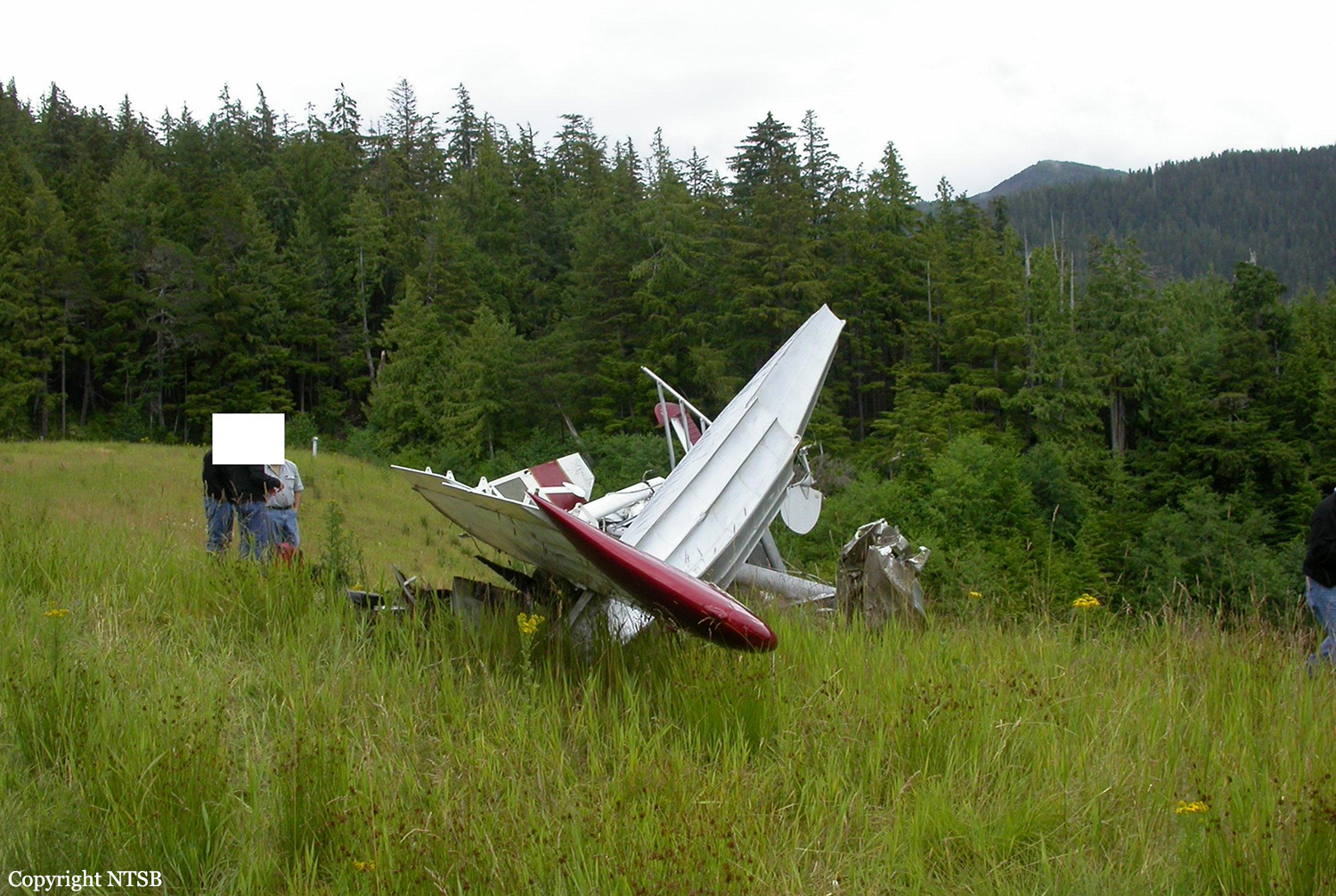
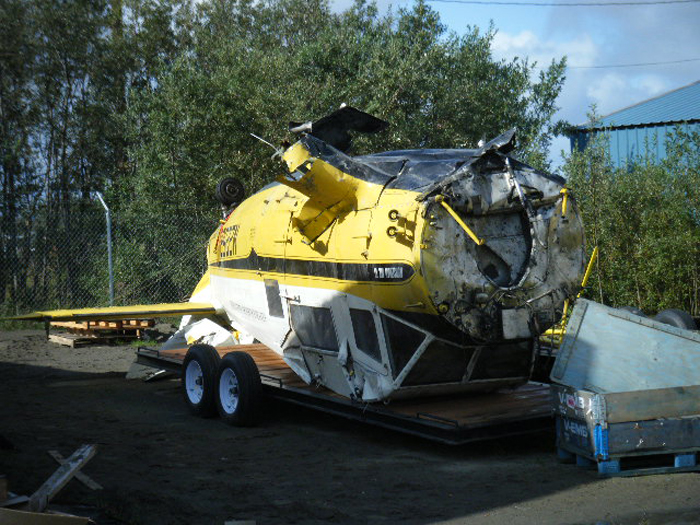
On August 9, 2010, about 1442 Alaska daylight time, a single-engine, turbine-powered, amphibious float-equipped de Havilland DHC-3T airplane, N455A, impacted mountainous, tree-covered terrain about 10 nautical miles (nm) northeast of Aleknagik, Alaska. The airline transport pilot and four passengers received fatal injuries, and four passengers received serious injuries. The airplane sustained substantial damage, including deformation and breaching of the fuselage. The flight was operated by GCI Communication Corp. (GCI), of Anchorage, Alaska, under the provisions of 14 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 91. About the time of the accident, meteorological conditions that met the criteria for marginal visual flight rules (MVFR) were reported at Dillingham Airport (DLG), Dillingham, Alaska, about 18 nm south of the accident site. No flight plan was filed. The flight departed about 1427 from a GCI-owned private lodge on the shore of Lake Nerka and was en route to a remote sport fishing camp about 52 nm southeast on the Nushagak River. According to GCI lodge personnel, the purpose of the flight was to transport the lodge guests to the fishing camp for an afternoon of fishing. The GCI lodge manager stated that the accident pilot had flown previously that morning in the accident airplane to DLG, where he dropped off another GCI pilot and then returned to the lodge. Sky Connect tracking system data for the accident airplane showed that, on that previous trip, the accident pilot departed the lodge for DLG about 0902 and returned about 1120. A review of DLG flight service station (FSS) recordings revealed that, about 1105, during the return flight from DLG to the lodge, the accident pilot filed a pilot report (PIREP) in which he reported ceilings at 500 feet, visibility of 2 to 3 miles in light rain, and “extremely irritating…continuous light chop” turbulence that he described as “kind of that shove-around type stuff rather than just bumps.” According to GCI lodge personnel, when the pilot returned to the lodge, he stated that the weather was not conducive for a flight to the fishing camp because of the turbulence and low ceilings. Passengers from the accident flight and GCI personnel indicated during postaccident interviews that, by the time that they had lunch about 1300, the weather had improved, and the group discussed with the pilot the option of going to the fishing camp. One passenger characterized the conversation as casual and stated that no pressure was placed on the pilot to make the flight or to depart by a certain time. The GCI lodge manager and some passengers stated that they thought that the pilot checked the weather on the computer during lunch, and the guest party co-host (one of GCI’s senior vice presidents) stated that the pilot informed him about 1400 that he was comfortable taking the group to the fishing camp if the group wanted to go. The GCI lodge manager stated that, before the airplane departed, he sent an e-mail to the fishing camp to indicate that the guests were coming, and personnel there informed him that the pilot had already contacted them. The lodge manager stated that he went down to the dock to help push the airplane off and that, when the flight departed, he could see all of Jackknife Mountain across the lake. (The mountain’s highest peak, which is about 3 nm from the dock, is depicted as 2,326 feet above mean sea level [msl] on an aviation sectional chart, and the elevation of Lake Nerka is depicted as about 40 feet msl on a topographical map.) He stated that the weather included broken ceilings about 2,000 feet above ground level (agl) with some blue patches in the sky and good visibility. The flight route from the lodge to the fishing camp traversed Class G airspace; 14 CFR 91.155 specifies that, for daytime flights below 1,200 feet agl, the flight must be flown clear of clouds and in conditions that allow at least 1 mile flight visibility. During a postaccident interview, the passenger who was in the right cockpit seat stated that, when the airplane departed, the visibility was “fine.” He stated that the pilot went a different direction during takeoff (compared to the passenger’s experiences during previous flights to the fishing camp) and that the pilot said it was to avoid “wind and weather.” The passenger described the weather as cloudy above with light turbulence. He stated that the airplane stayed below the clouds and that he noticed water “running across” the outside of the windshield before he fell asleep about 10 minutes into the flight. Another passenger, who was seated in the second seat behind the pilot on the left side of the airplane, stated that some fog was present beneath the airplane but that he did not think that the airplane flew into any clouds. He estimated that he fell asleep about 3 to 4 minutes after departure. The passenger who was in the first seat behind the pilot on the left side of the airplane stated in an initial interview that he could not see well out his side window and that he had no indication of the weather; however, in a subsequent interview, he stated that, once the airplane was airborne, he could not see the ground and could see only “white-out” conditions outside the airplane. He stated in the subsequent interview that he did not know if the airplane had climbed into clouds initially or if it had entered clouds at some point along the way. The passenger who was in the third seat behind the pilot on the left side of the airplane stated that the pilot kept the airplane below the cloud ceiling and flew along the tree line, followed streams, and maneuvered to avoid terrain. The passenger stated that the airplane banked into a left turn (he said that the bank angle was not unusual) and then immediately impacted terrain. Neither he nor the other passenger who was awake at the time of impact recalled noticing any unusual maneuvering, unusual bank or pitch angles, or change in engine noises that would indicate any problem before the airplane impacted terrain. The wreckage was found at an elevation of about 950 feet msl in steep, wooded terrain in the Muklung Hills, about 16 nm southeast of the GCI lodge. Figure 1 shows the accident site (view looking north-northwest).