Crash of a Douglas C-47A-85-DL in Croydon: 12 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 25, 1947 at 1141 LT
Registration:
VP-YFD
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Croydon – Rome – Salisbury
MSN:
19979
YOM:
1944
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
18
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
12
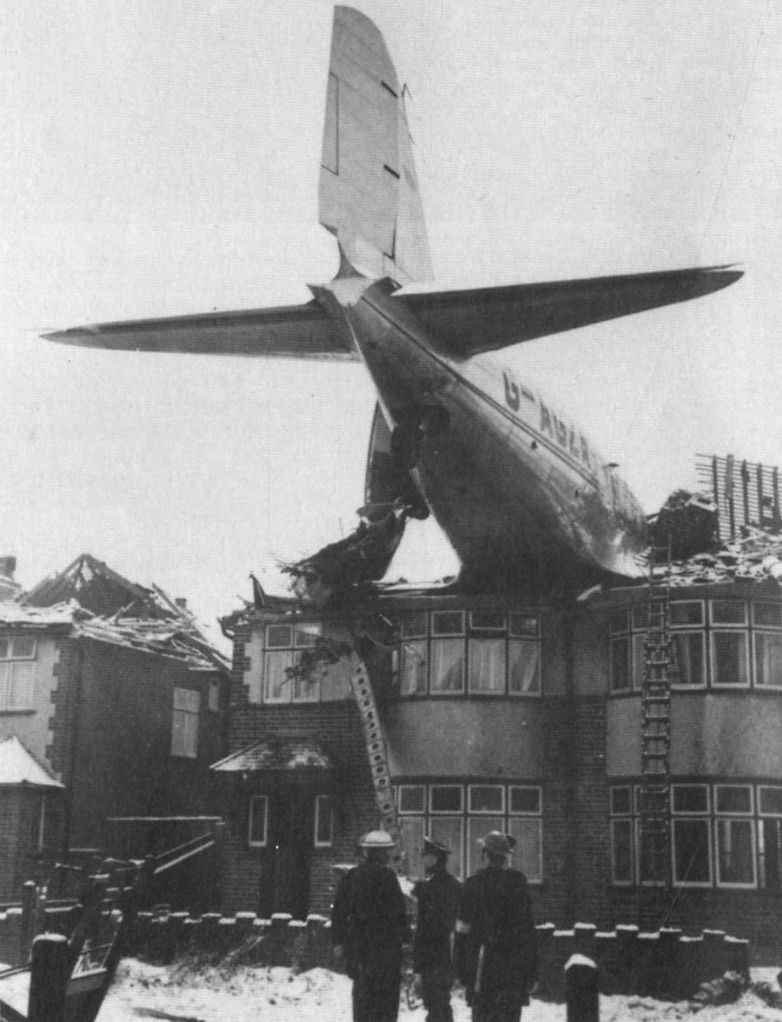
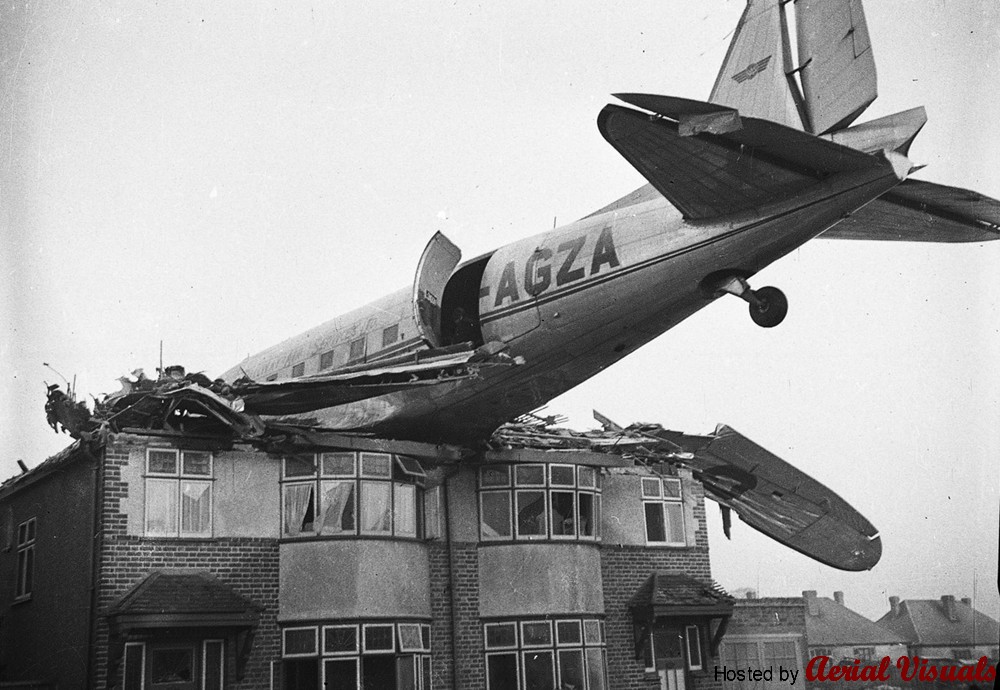
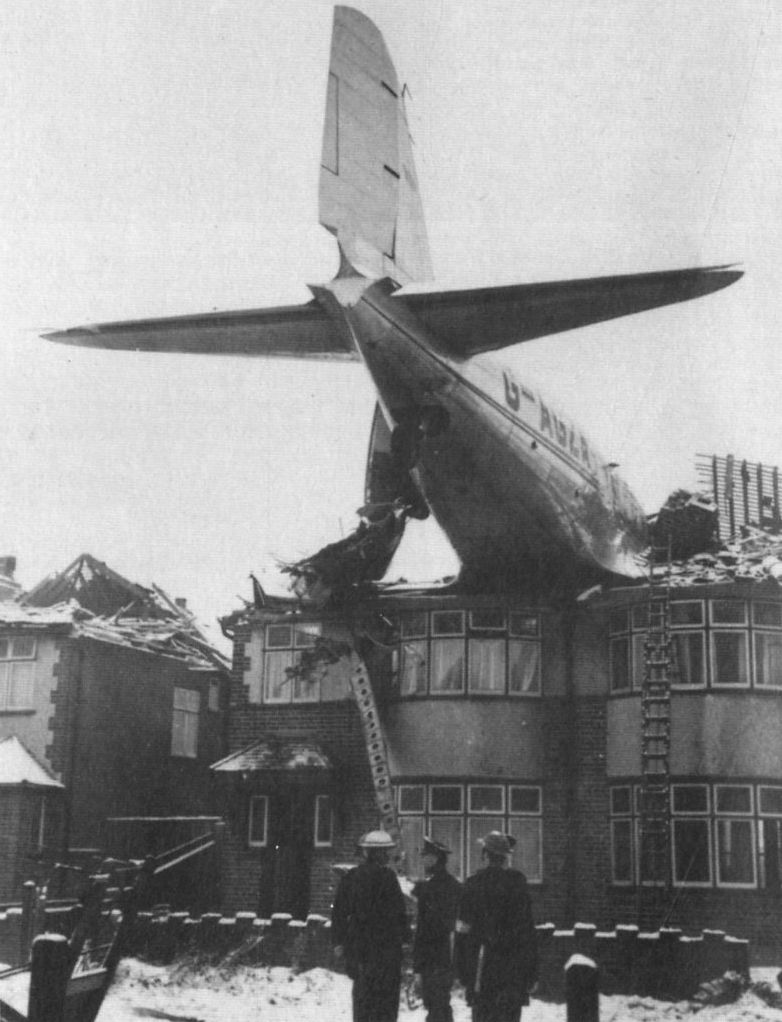
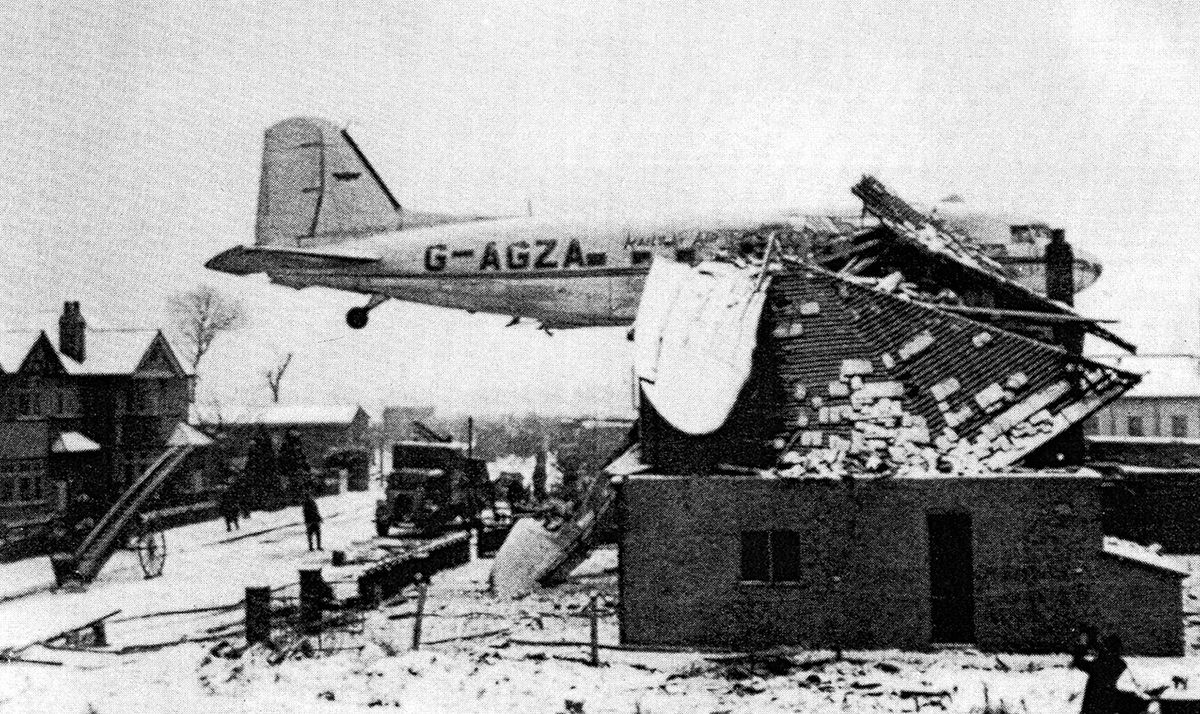
Circumstances:
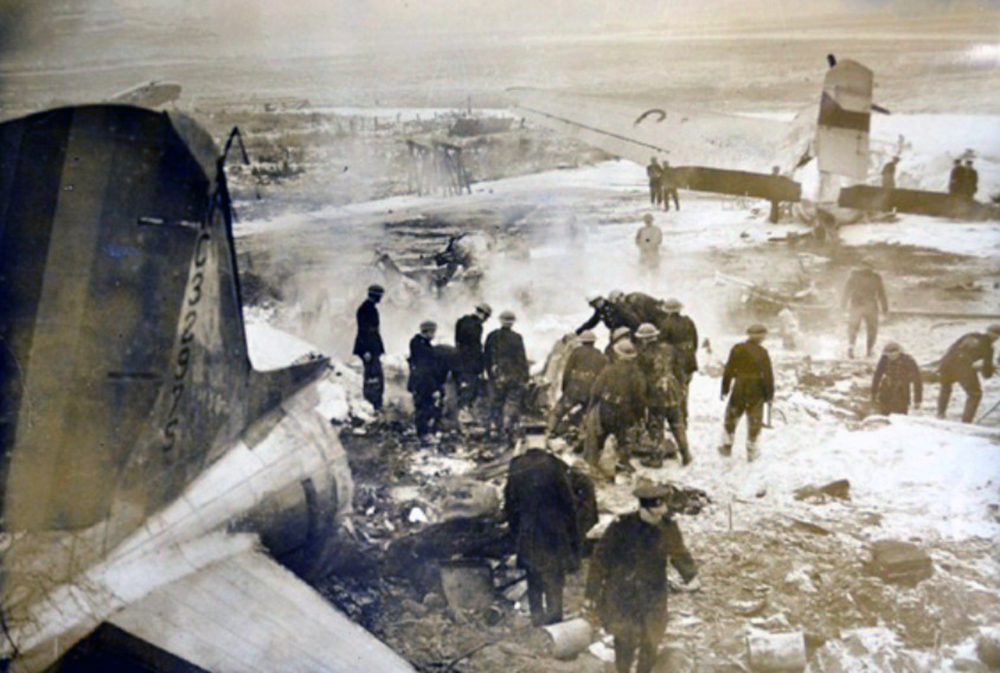
Shortly after takeoff from runway 12, while climbing to a height of some 100 feet in snow falls, the aircraft banked right, stalled and crashed on a parked CSA C-47 registered OK-WDB. Two technicians were working on the Czech C-47 for a maintenance control. Both aircraft were destroyed by fire. While both technicians were slightly injured, 11 people on board the VP-YFD were injured while 12 others were killed, among them the captain, Edward Spencer, founder and owner of this company based in Salisbury, Rhodesia. The aircraft was still registered NC32975.
Probable cause:
On rotation, the aircraft was in stall conditions due to the combination of several factors such as heavy weight, fuselage, wings and empennage covered by snow, poor techniques on part of the pilot, poor judgement and fatigue on part of the crew.
The Ministry of Civil Aviation instituted "an inspection of Certificates of Airworthiness, Certificates of Safety and crew licences" at airfields under their control to ensure these documents were in order. The aircraft did not have a CofA, nor a valid Certificate of Safety, and no member of crew held a Navigators licence nor a licence to sign a Certificate of Safety.
The Ministry of Civil Aviation instituted "an inspection of Certificates of Airworthiness, Certificates of Safety and crew licences" at airfields under their control to ensure these documents were in order. The aircraft did not have a CofA, nor a valid Certificate of Safety, and no member of crew held a Navigators licence nor a licence to sign a Certificate of Safety.