Circumstances:
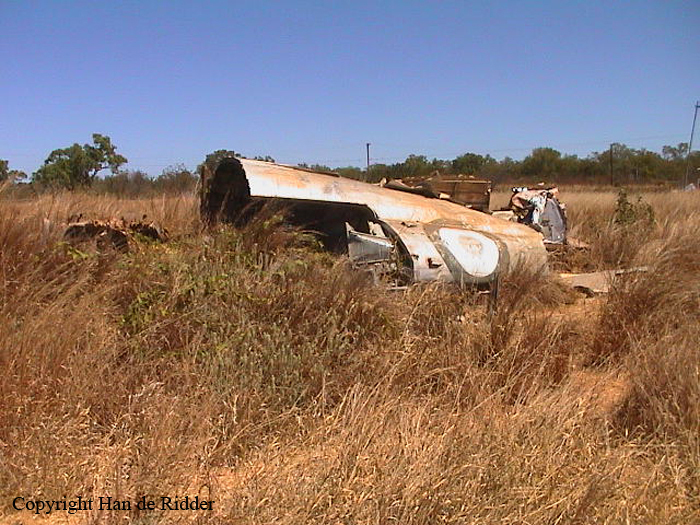
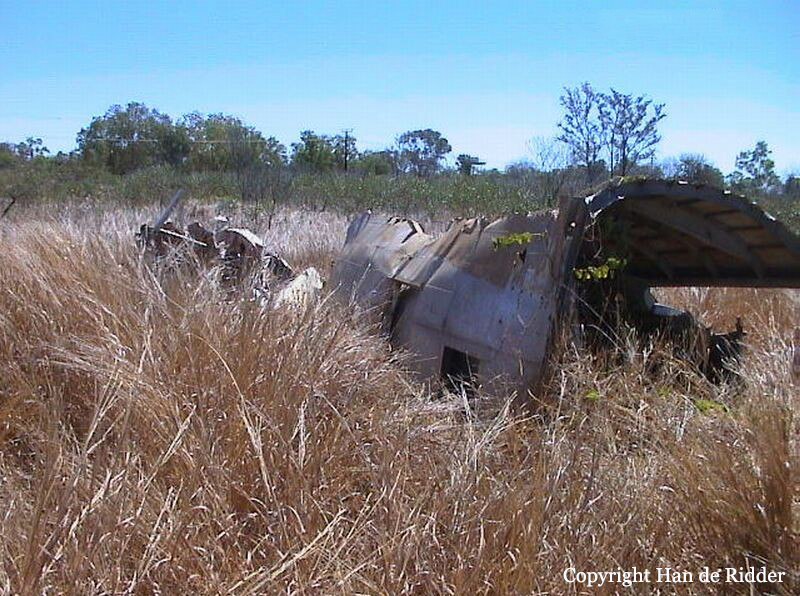
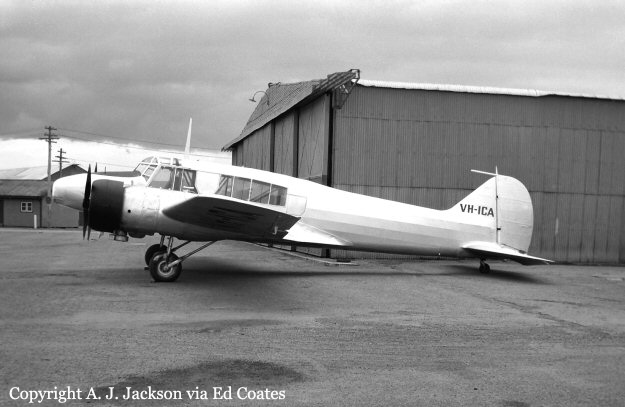
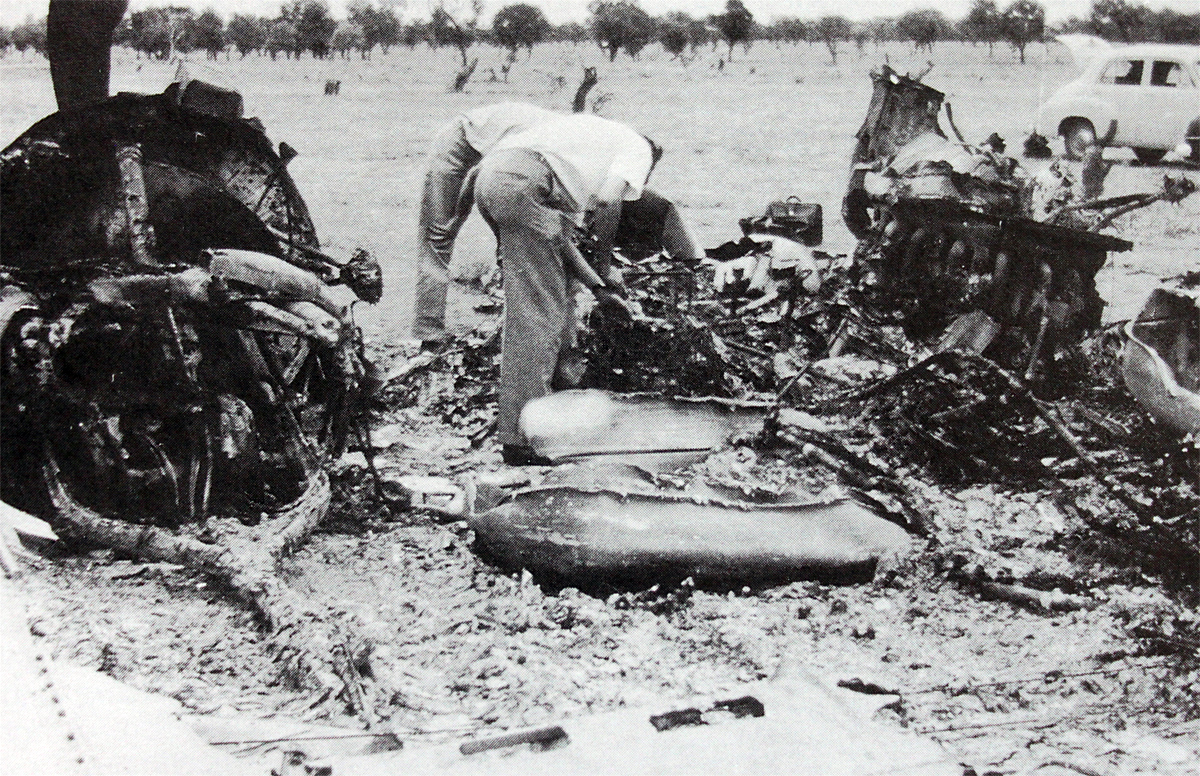
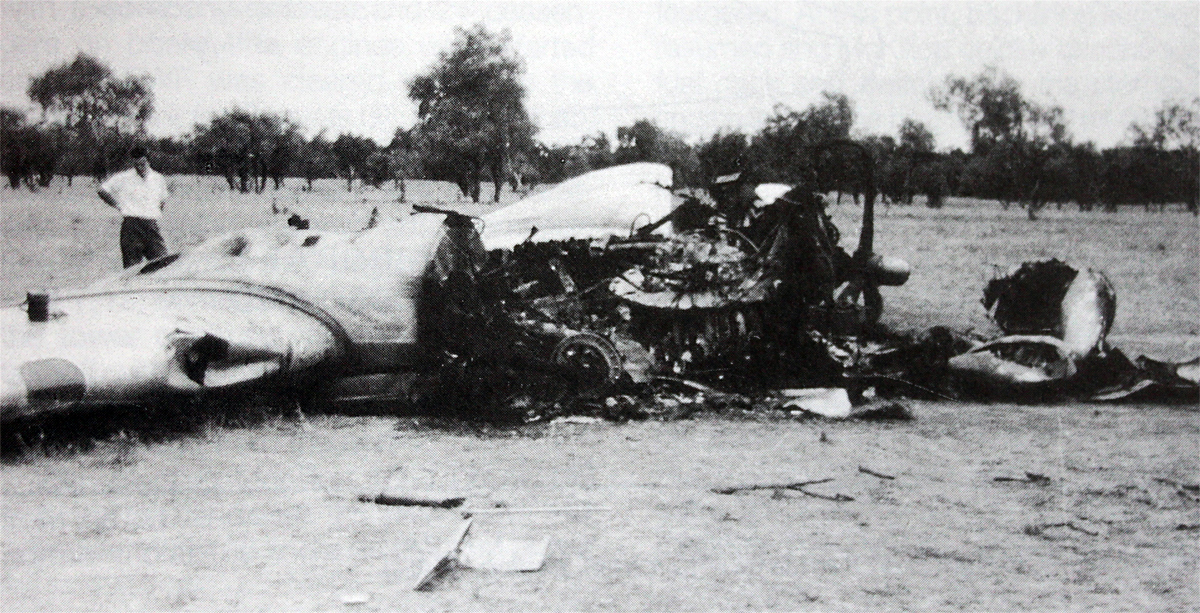
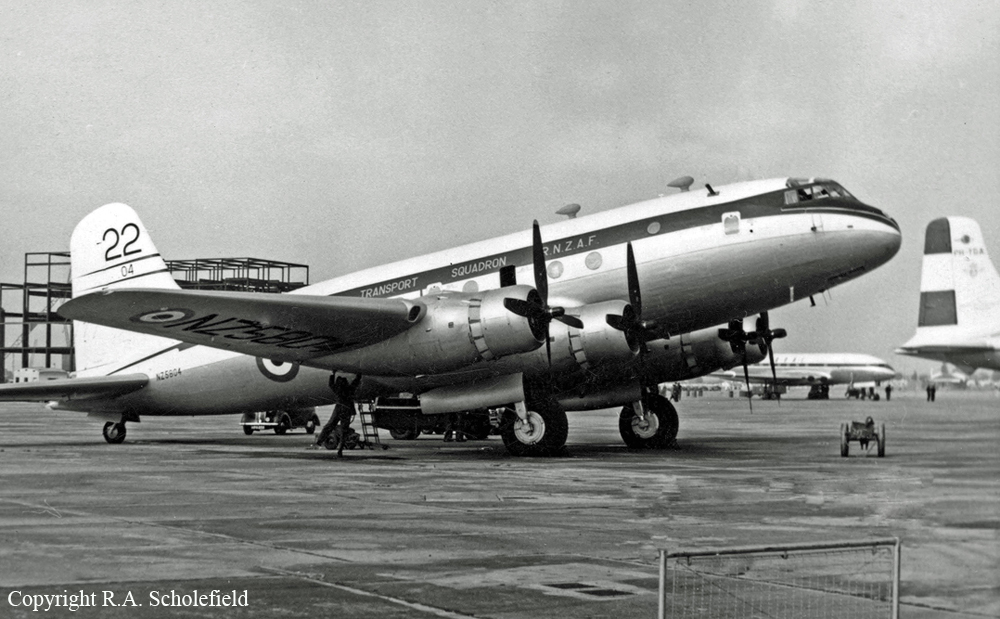
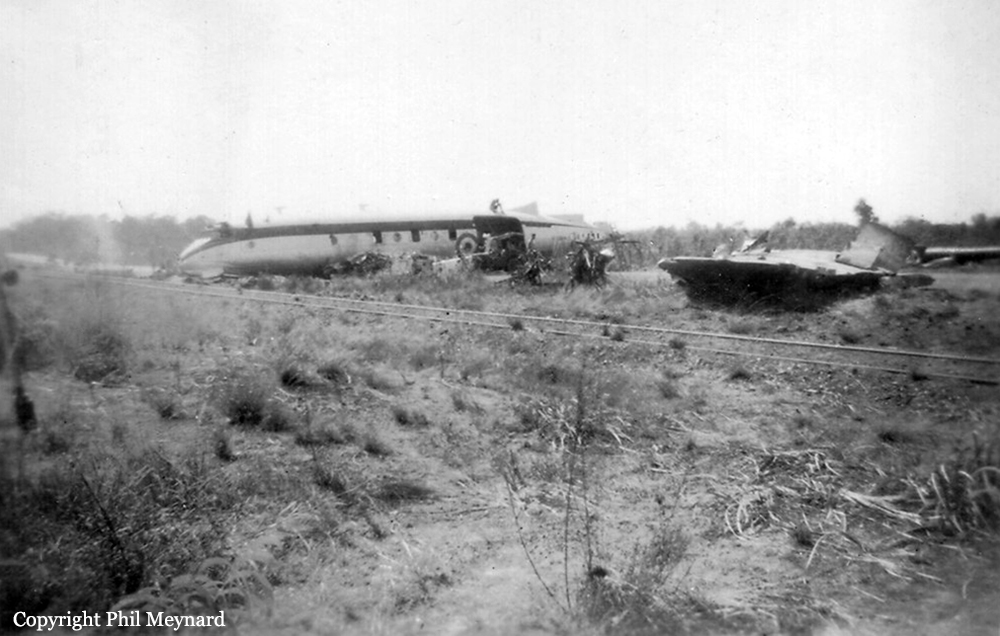
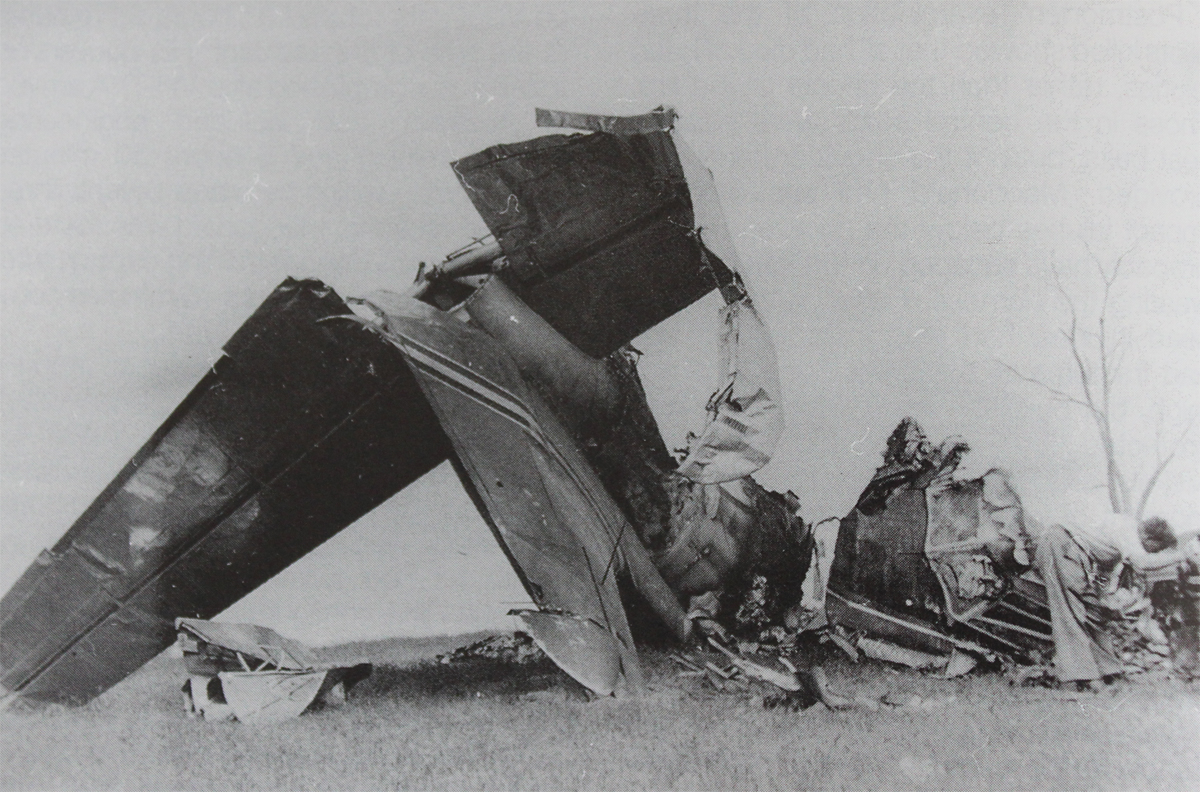
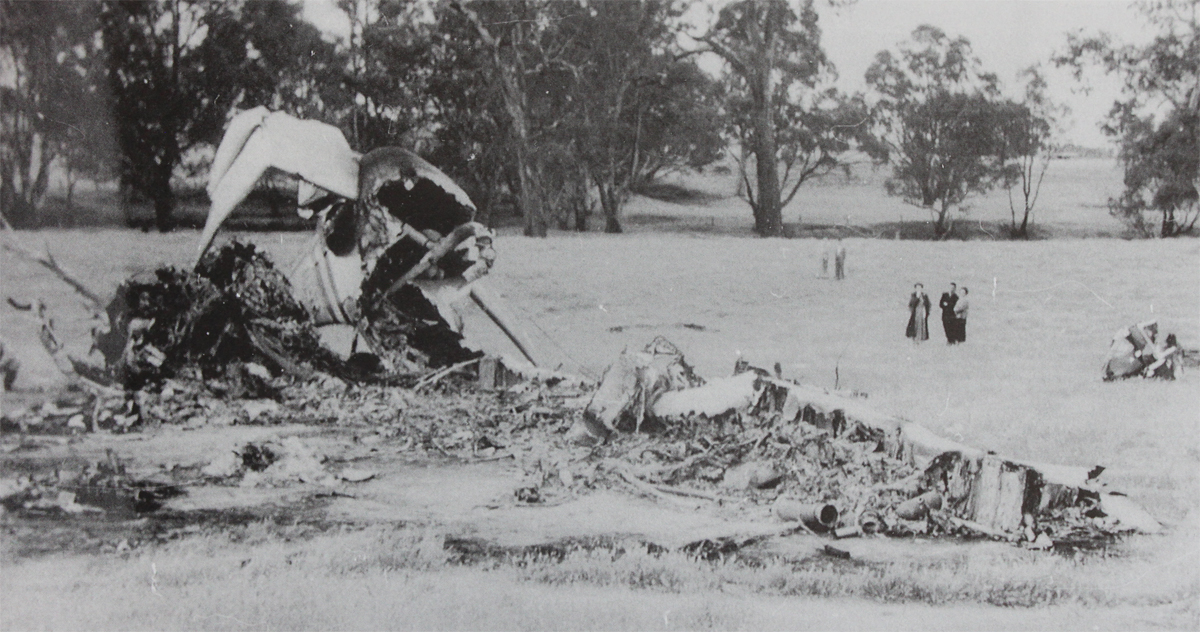
10 Squadron RAAF had received a telephone call late on Good Friday night from the Townsville hospital seeking an emergency evacuation to Brisbane of a critically jaundiced 2 day old baby, Robyn Huxley. As most of the Squadron's air crew were on leave or stand-down over Easter, the Commanding Officer of 10 Squadron, Wing Commander John Costello decided to pilot the Squadron's only serviceable aircraft, A73-64, for the evacuation flight. The crew consisted of the new Commanding Officer Wing Commander Costello who had flown Sunderlands during the war against the German U Boats in the Atlantic, the Senior Navigation Officer, Squadron Leader Finlay, who was a wartime Pathfinder navigator, the squadron Chief Signaler, Flight Lieutenant Cater, and the squadron Senior Engineering Officer, Squadron Leader Mason. The baby girl and nurse Mafalda Gray were positioned in the long-nosed section of the Lincoln bomber. The aircraft took off from Garbutt airfield at 00.30 am on Saturday 9 April 1955. The aircraft encountered some cloud and rain as it approached southern Queensland. The aircraft had to fly at a relatively low altitude to ensure the baby had a comfortable flight. At 4.05 am the aircraft contacted Brisbane Air Traffic Control to advise that they were flying in cloud at 6,000 feet. They advised that they would arrive in Brisbane in about 10 minutes time and sought a clearance to reduce altitude to 5,000 feet. Brisbane Air Traffic Control advised that they were cleared to drop to 5,000 feet and if they wished they could drop to 4,000 feet for the approach to Eagle Farm airfield. A short time later Brisbane Air Traffic Control contacted them with weather information and asked them to confirm when they had obtained a visual fix on the town of Caboolture. No further reports were heard from the Lincoln bomber. There were no low clouds in the Brisbane area at that time. Some time later, reports came in that an aircraft, later confirmed as a Lincoln, was heard to circle over the town of Bell at about 3.30 am. Bell is located about 18 miles north east of Dalby. Clearly A73-64 was well off course. The weather south of Bell was overcast with scattered rain. At 4.14 am some members of the Brisbane Bushwalking Club heard a large aircraft fly overhead followed by the noise of an impact and some large explosions. By their estimation it had slammed into a nearby mountain in the Main Range region of the Border Ranges near Emu Vale. This was later confirmed to be Mount Superbus, the highest mountain (1,375 meters) in southern Queensland. A small group from the Bushwalking club was dispatched immediately to Emu Vale to notify the relevant authorities. Five hours later a Canberra bomber from Amberley airbase was able to confirm the location of the still burning wreckage of Lincoln, A73-64 just below the summit of Mount Superbus. Ground rescue crews were dispatched to the site. They quickly confirmed that there were no survivors.
Crew (10th Squadron):
W/Cdr John Peter Costello, pilot,
S/Ldr Charles Surtees Mason, copilot,
S/Ldr John Watson Finlay, navigator,
F/Lt William George Stanley Cater, signaler.
Passengers:
Baby Robyn Huxley,
Sister Mafalda Gray.
Source: http://www.ozatwar.com/ozcrashes/superbus.htm