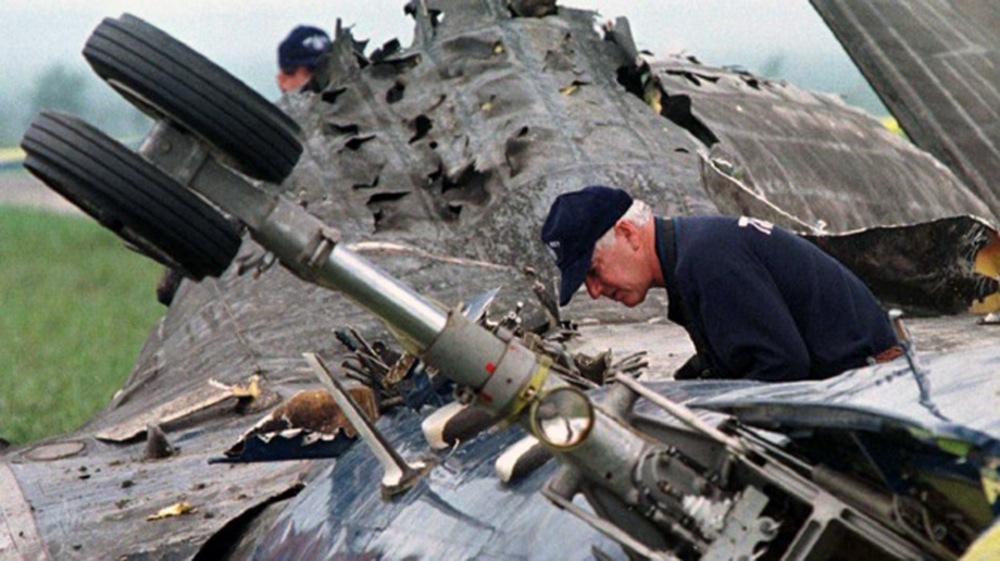
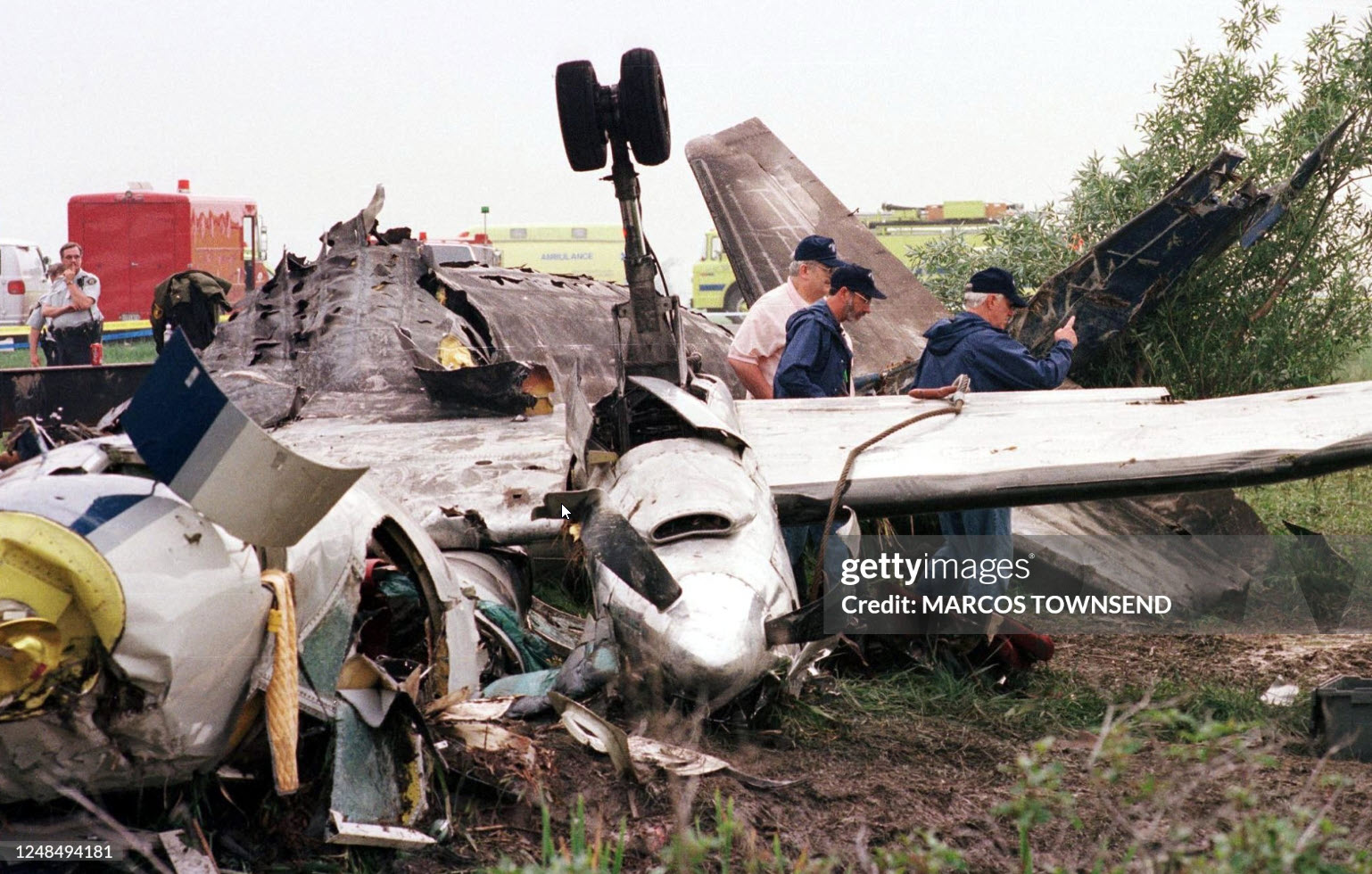
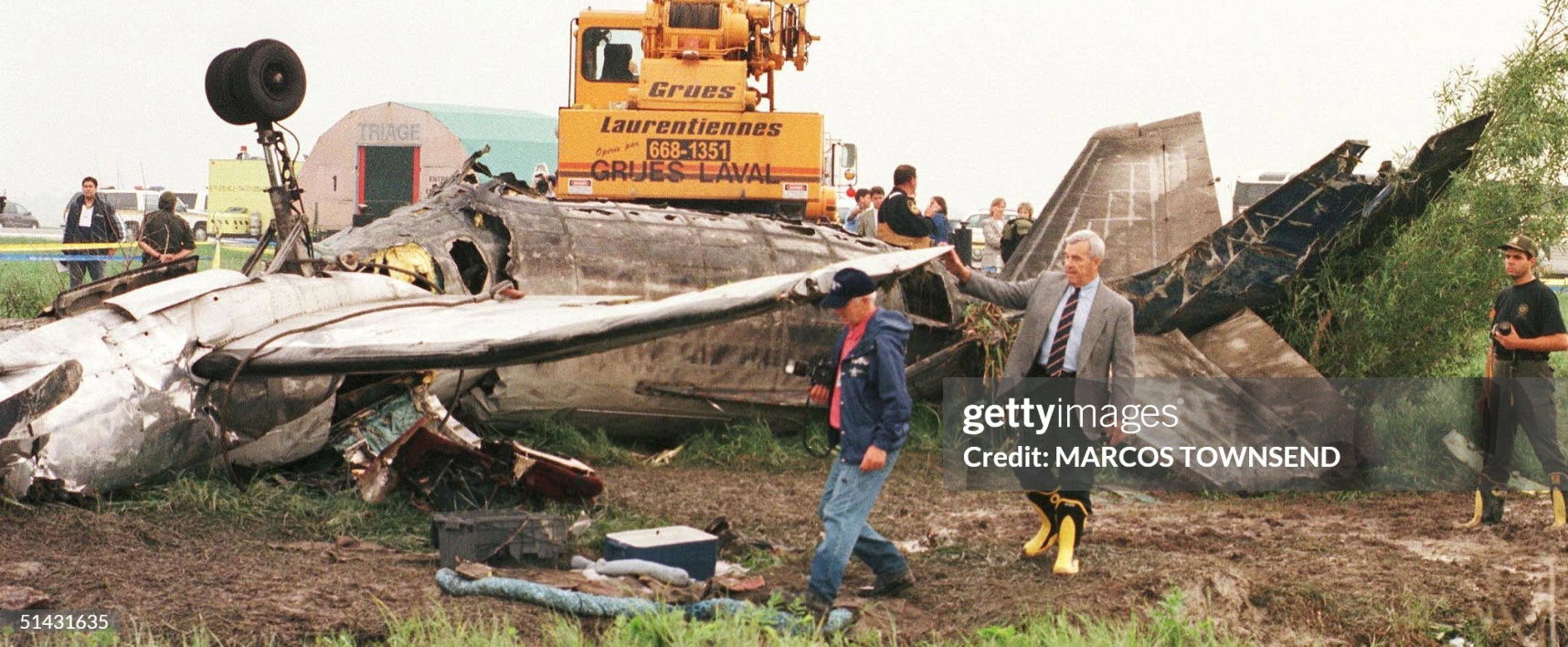
Crash of a Swearingen SA226AC Metro II in Montreal: 11 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 18, 1998 at 0728 LT
Registration:
C-GQAL
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Montreal - Peterborough
MSN:
TC-233
YOM:
1977
Flight number:
PRO420
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
9
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
11
Captain / Total hours on type:
4200.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
93
Aircraft flight hours:
28931
Circumstances:
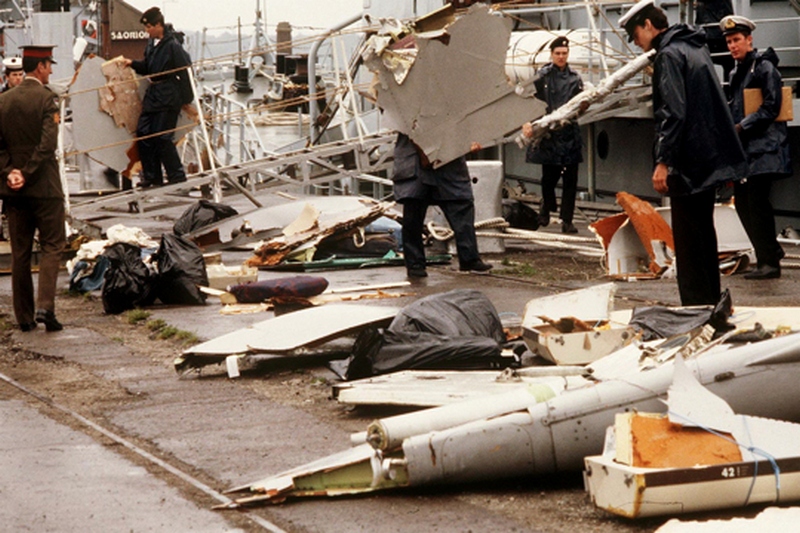
On the morning of 18 June 1998, Propair 420, a Fairchild-Swearingen Metro II (SA226-TC), C-GQAL, took off for an instrument flight rules flight from Dorval, Quebec, to Peterborough, Ontario. The aircraft took off from Runway 24 left (L) at 0701 eastern daylight time. During the ground acceleration phase, the aircraft was pulling to the left of the runway centreline, and the right rudder was required to maintain take-off alignment. Two minutes later, Propair 420 was cleared to climb to 16 000 feet above sea level (asl). At 0713, the crew advised the controller of a decrease in hydraulic pressure and requested to return to the departure airport, Dorval. The controller immediately gave clearance for a 180° turn and descent to 8000 feet asl. During this time, the crew indicated that, for the moment, there was no on-board emergency. The aircraft initiated its turn 70 seconds after receiving clearance. At 0713:36, something was wrong with the controls. Shortly afterward came the first perceived indication that engine trouble was developing, and the left wing overheat light illuminated about 40 seconds later. Within 30 seconds, without any apparent checklist activity, the light went out. At 0718:12, the left engine appeared to be on fire, and it was shut down. Less than one minute later, the captain took the controls. The flight controls were not responding normally: abnormal right aileron pressure was required to keep the aircraft on heading. At 0719:19, the crew advised air traffic control (ATC) that the left engine was shut down, and, in response to a second suggestion from ATC, the crew agreed to proceed to Mirabel instead of Dorval. Less than a minute and a half later, the crew informed ATC that flames were coming out of the 'engine nozzle'. Preparations were made for an emergency landing, and the emergency procedure for manually extending the landing gear was reviewed. At 0723:10, the crew informed ATC that the left engine was no longer on fire, but three and a half minutes later, they advised ATC that the fire had started again. During this time, the aircraft was getting harder to control in roll, and the aileron trim was set at the maximum. Around 0727, when the aircraft was on short final for Runway 24L, the landing gear lever was selected, but only two gear down indicator lights came on. Near the runway threshold, the left wing failed upwards. The aircraft then rotated more than 90° to the left around its longitudinal axis and crashed, inverted, on the runway. The aircraft immediately caught fire, slid 2500 feet, and came to rest on the left side the runway. When the aircraft crashed, firefighters were near the runway threshold and responded promptly. The fire was quickly brought under control, but all occupants were fatally injured.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
- The crew did not realize that the pull to the left and the extended take-off run were due to the left brakes' dragging, which led to overheating of the brake components.
- Dragging of the left brakes was most probably caused by an unidentified pressure locking factor upstream of the brakes on take-off. The dragging caused overheating and leakage, probably at one of the piston seals that retain the brake hydraulic fluid.
- When hydraulic fluid leaked onto the hot brake components, the fluid caught fire and initiated an intense fire in the left nacelle, leading to failure of the main hydraulic system.
- When the L WING OVHT light went out, the overheating problem appeared corrected; however, the fire continued to burn.
- The crew never realized that all of the problems were associated with a fire in the wheel well, and they did not realize how serious the situation was.
- The left wing was weakened by the wing/engine fire and failed, rendering the aircraft uncontrollable.
Findings as to Risk:
- Numerous previous instances of brake overheating or fire on SA226 and SA227 aircraft had the potential for equally tragic consequences. Not all crews flying this type of aircraft are aware of its history of numerous brake overheating or fire problems.
- The aircraft flight manual and the emergency procedures checklist provide no information on the possibility of brake overheating, precautions to prevent brake overheating, the symptoms that could indicate brake problems, or actions to take if overheated brakes are suspected.
- More stringent fire-blocking requirements would have retarded combustion of the seats, reducing the fire risk to the aircraft occupants.
- A mixture of the two types of hydraulic fluid lowered the temperature at which the fluid would ignite, that is, below the flashpoint of pure MIL-H-83282 fluid.
- The aircraft maintenance manual indicated that the two hydraulic fluids were compatible but did not mention that mixing them would reduce the fire resistance of the fluid.
Other Findings:
- The master cylinders were not all of the same part number, resulting in complex linkage and master cylinder adjustments, complicated overall brake system functioning, and difficult troubleshooting of the braking system. However, there was no indication that this circumstance caused residual brake pressure.
- The latest recommended master cylinders are required to be used only with specific brake assembly part numbers, thereby simplifying adjustments, functioning, and troubleshooting.
- Although the emergency checklist for overheating in the wing required extending the landing gear, the crew did not do this because the wing overheat light went out before the crew initiated the checklist.
- The effect of the fire in the wheel well made it difficult to move the ailerons, but the exact cause of the difficulty was not determined.
- The crew did not realize that the pull to the left and the extended take-off run were due to the left brakes' dragging, which led to overheating of the brake components.
- Dragging of the left brakes was most probably caused by an unidentified pressure locking factor upstream of the brakes on take-off. The dragging caused overheating and leakage, probably at one of the piston seals that retain the brake hydraulic fluid.
- When hydraulic fluid leaked onto the hot brake components, the fluid caught fire and initiated an intense fire in the left nacelle, leading to failure of the main hydraulic system.
- When the L WING OVHT light went out, the overheating problem appeared corrected; however, the fire continued to burn.
- The crew never realized that all of the problems were associated with a fire in the wheel well, and they did not realize how serious the situation was.
- The left wing was weakened by the wing/engine fire and failed, rendering the aircraft uncontrollable.
Findings as to Risk:
- Numerous previous instances of brake overheating or fire on SA226 and SA227 aircraft had the potential for equally tragic consequences. Not all crews flying this type of aircraft are aware of its history of numerous brake overheating or fire problems.
- The aircraft flight manual and the emergency procedures checklist provide no information on the possibility of brake overheating, precautions to prevent brake overheating, the symptoms that could indicate brake problems, or actions to take if overheated brakes are suspected.
- More stringent fire-blocking requirements would have retarded combustion of the seats, reducing the fire risk to the aircraft occupants.
- A mixture of the two types of hydraulic fluid lowered the temperature at which the fluid would ignite, that is, below the flashpoint of pure MIL-H-83282 fluid.
- The aircraft maintenance manual indicated that the two hydraulic fluids were compatible but did not mention that mixing them would reduce the fire resistance of the fluid.
Other Findings:
- The master cylinders were not all of the same part number, resulting in complex linkage and master cylinder adjustments, complicated overall brake system functioning, and difficult troubleshooting of the braking system. However, there was no indication that this circumstance caused residual brake pressure.
- The latest recommended master cylinders are required to be used only with specific brake assembly part numbers, thereby simplifying adjustments, functioning, and troubleshooting.
- Although the emergency checklist for overheating in the wing required extending the landing gear, the crew did not do this because the wing overheat light went out before the crew initiated the checklist.
- The effect of the fire in the wheel well made it difficult to move the ailerons, but the exact cause of the difficulty was not determined.
Final Report: