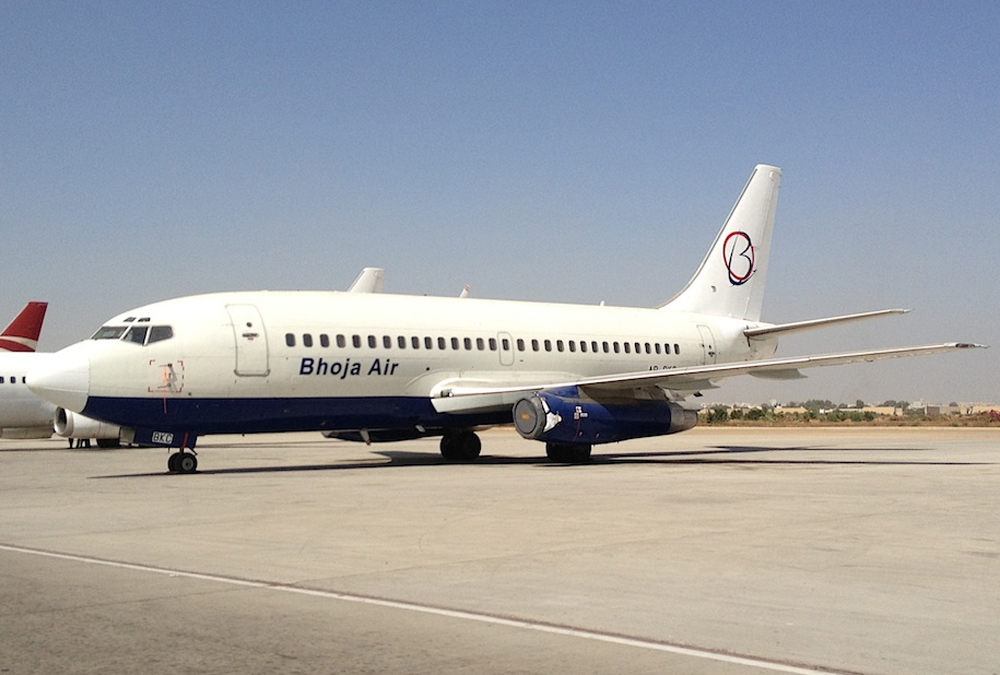
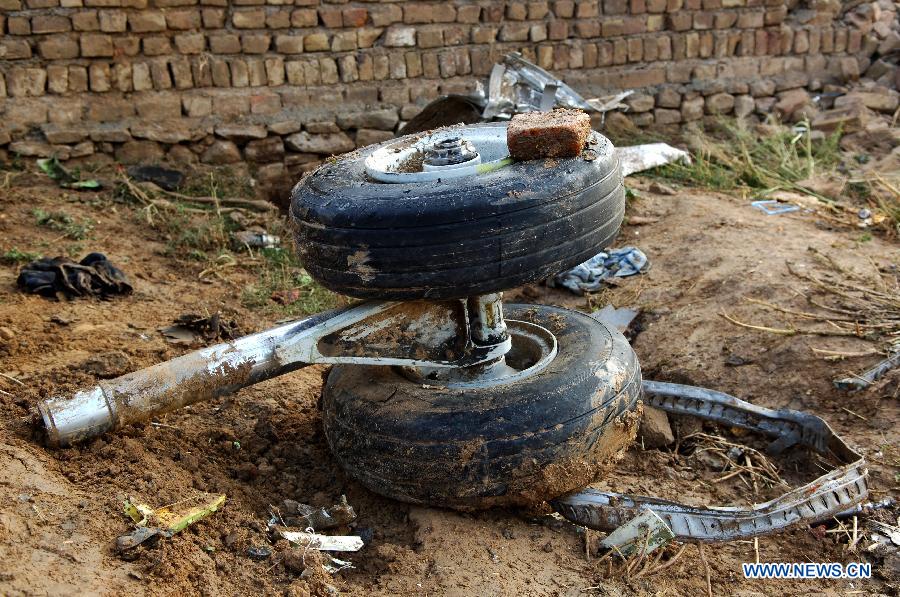
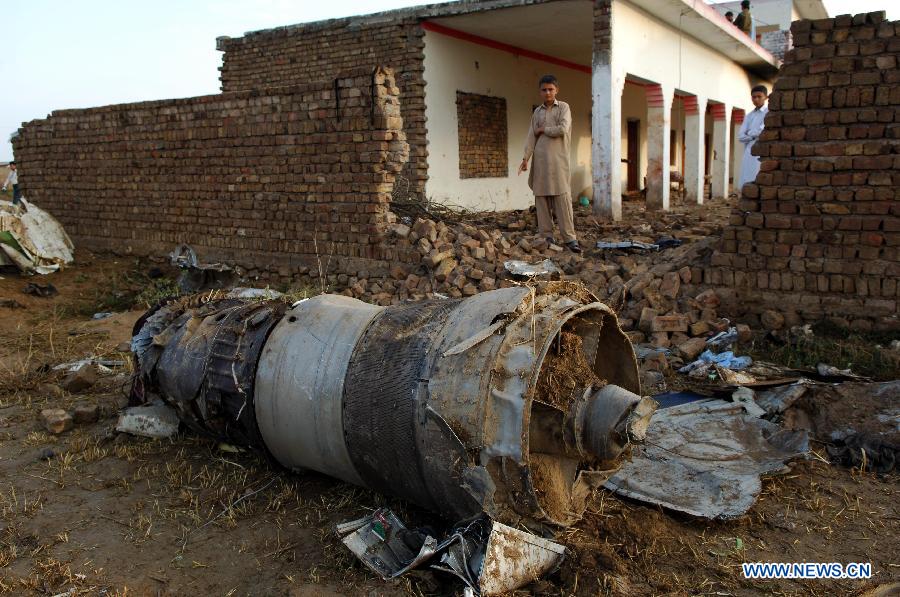
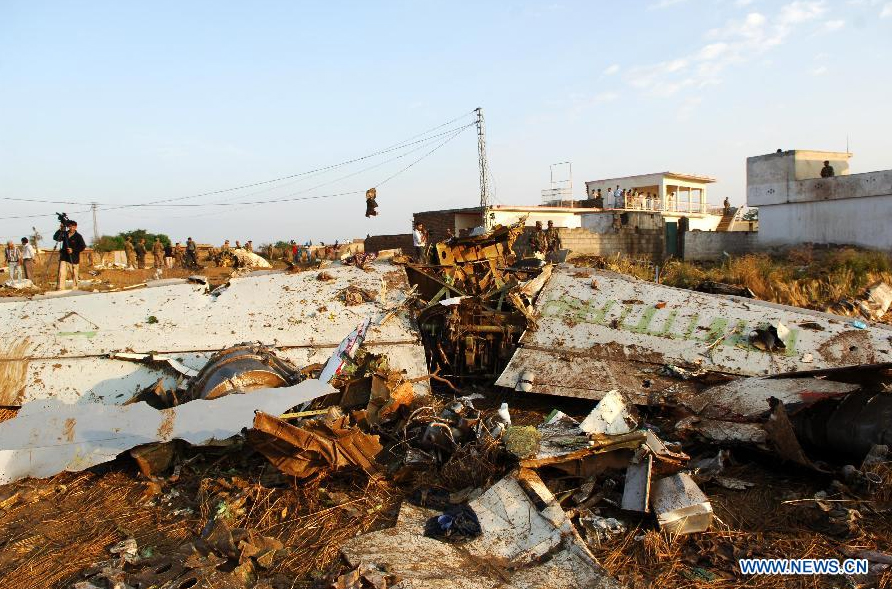
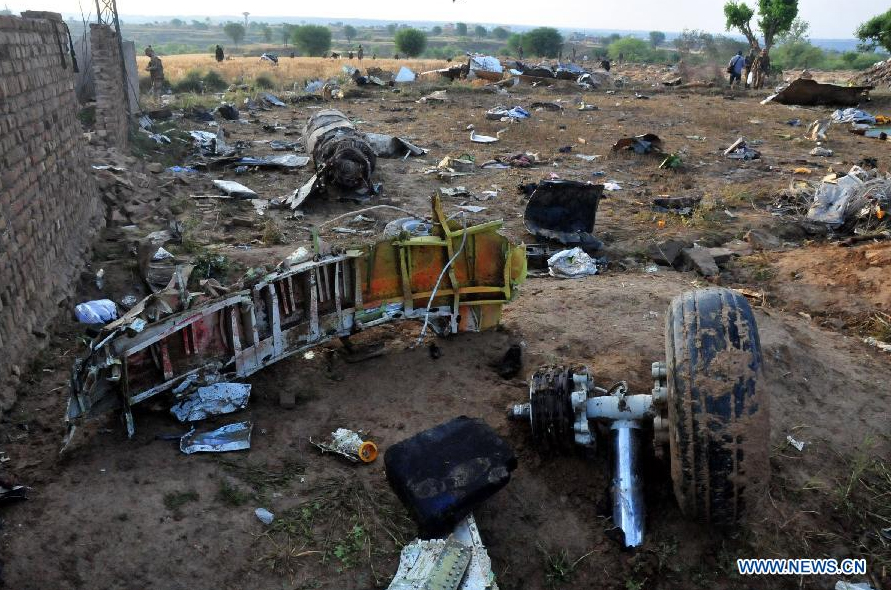
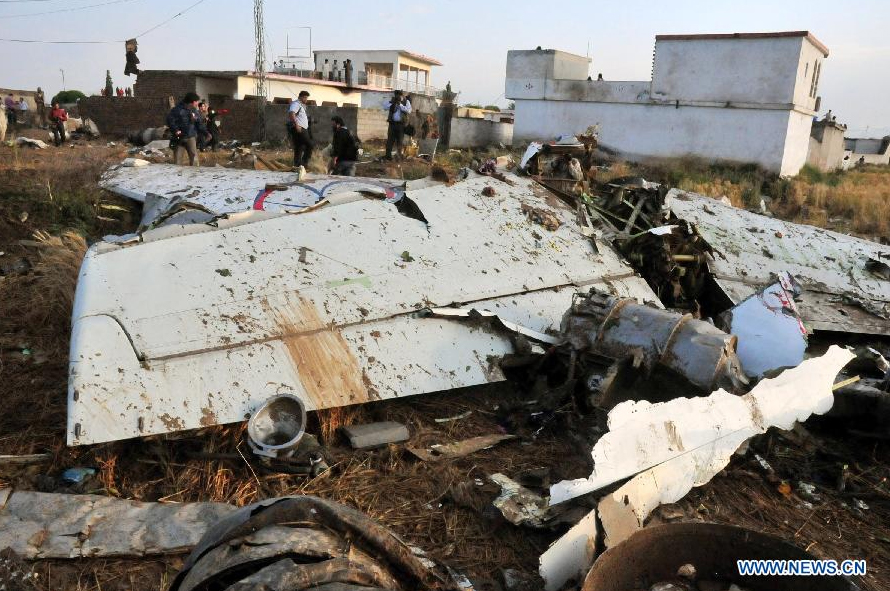
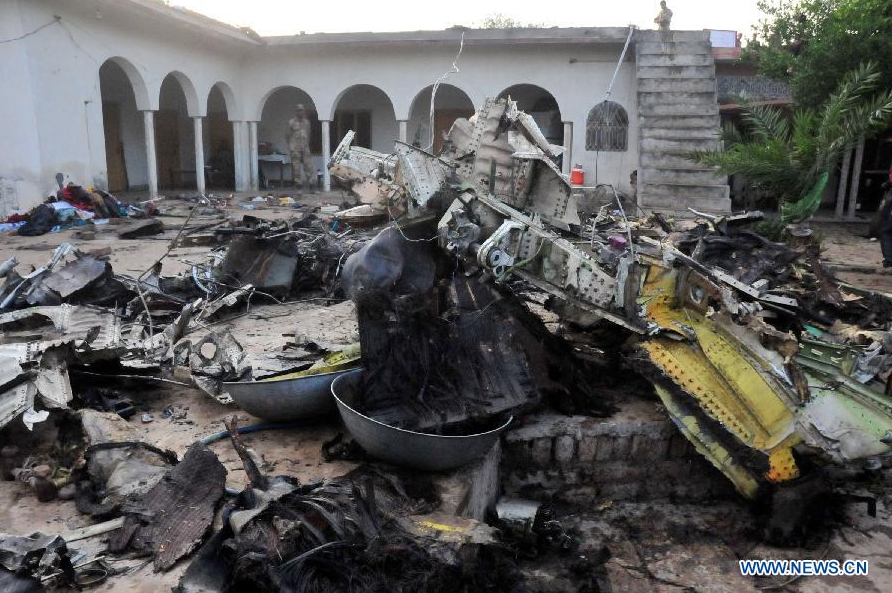
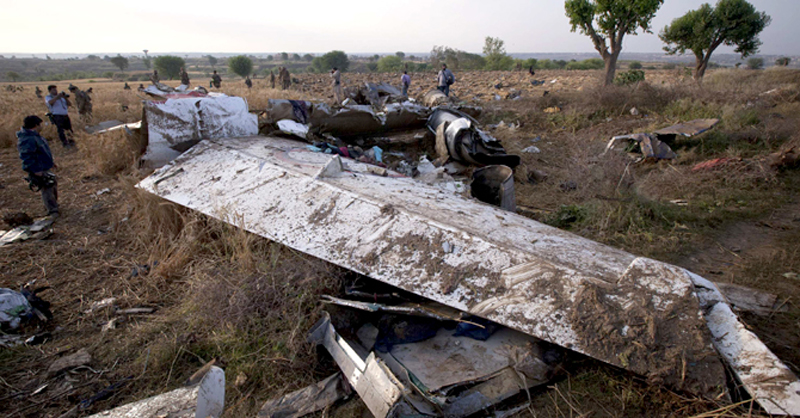
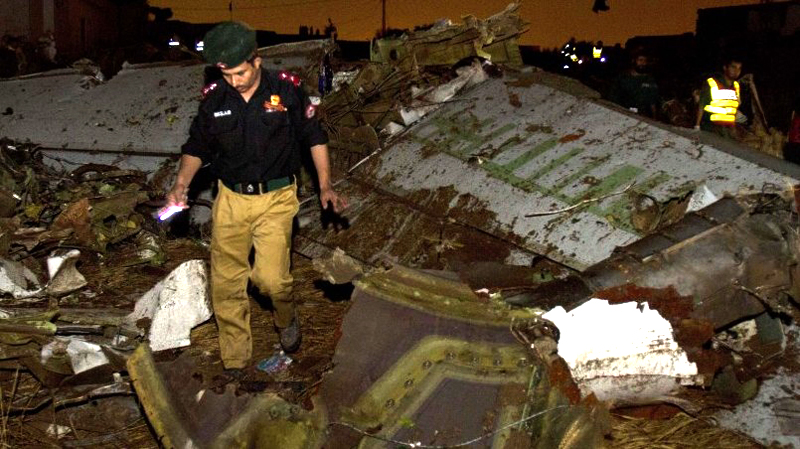
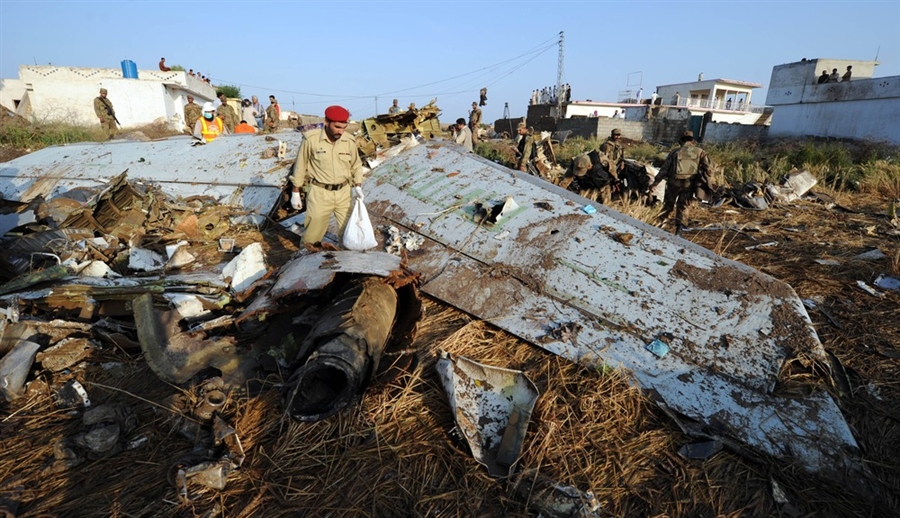
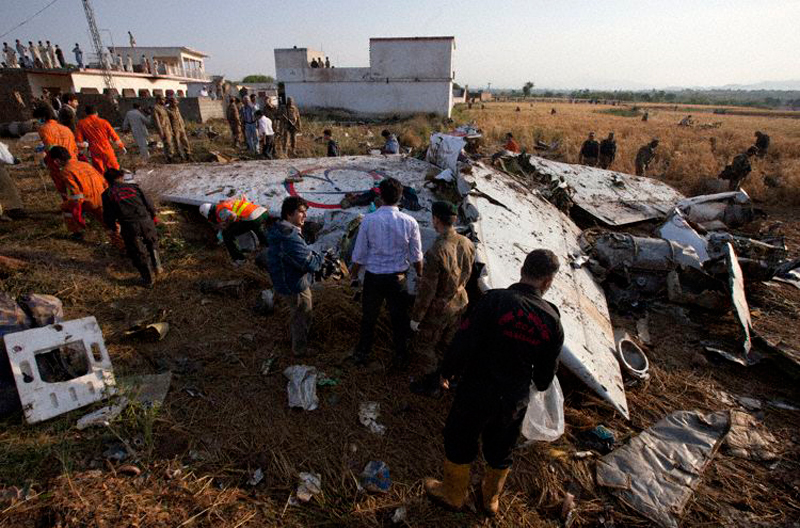
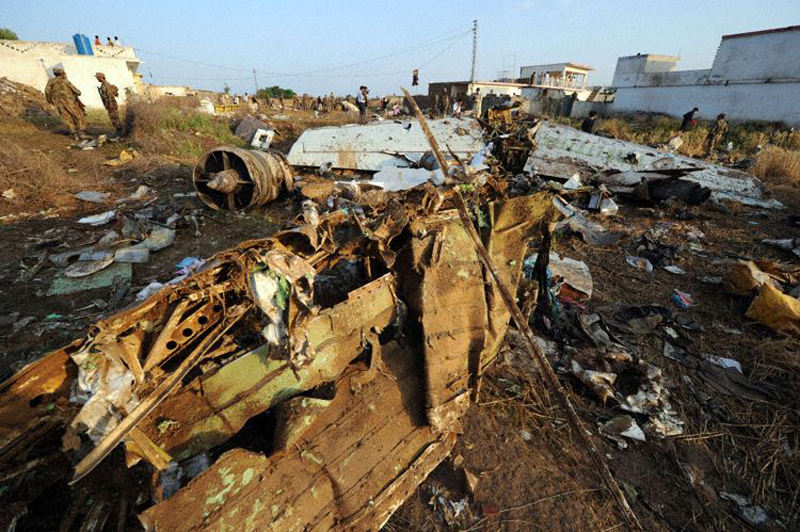
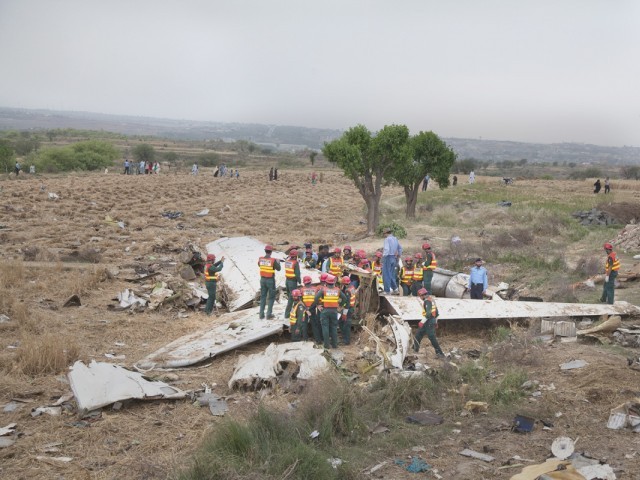
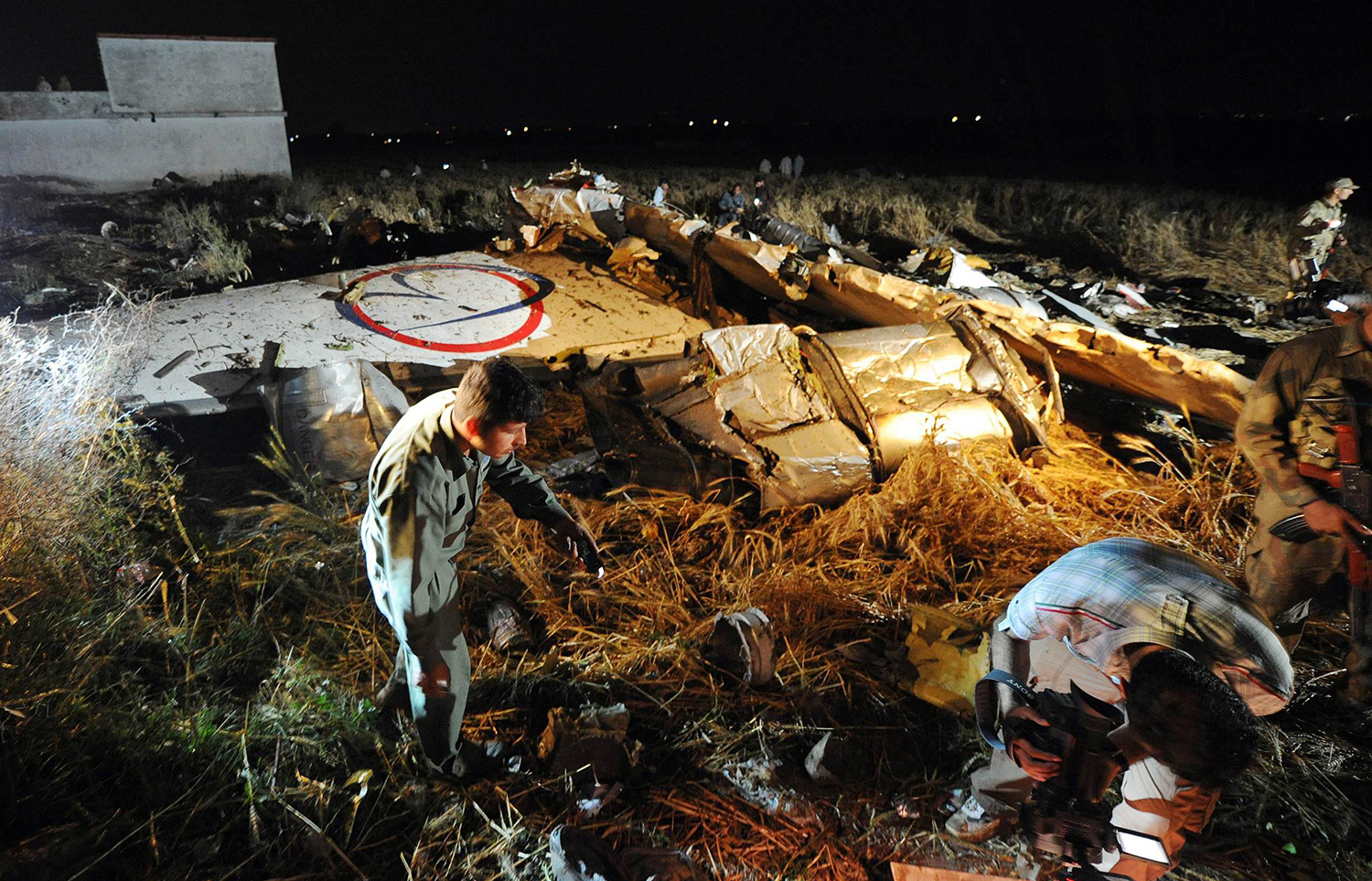
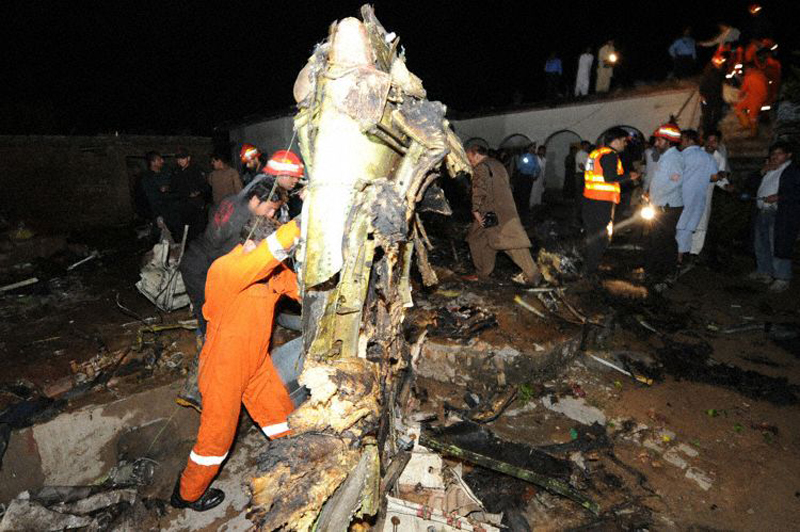
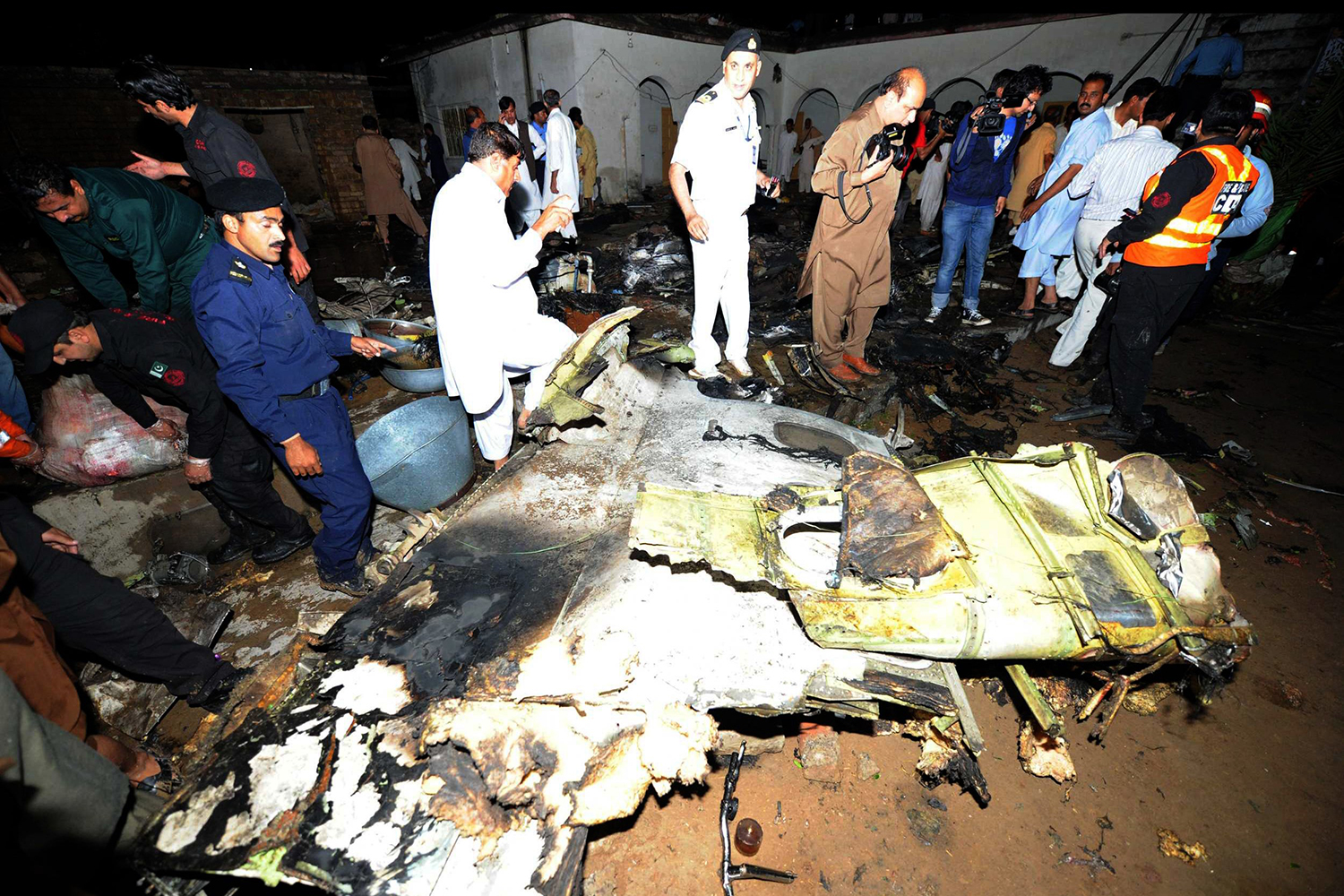
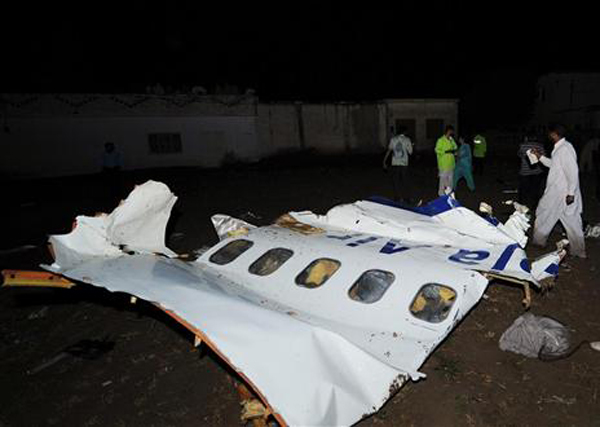
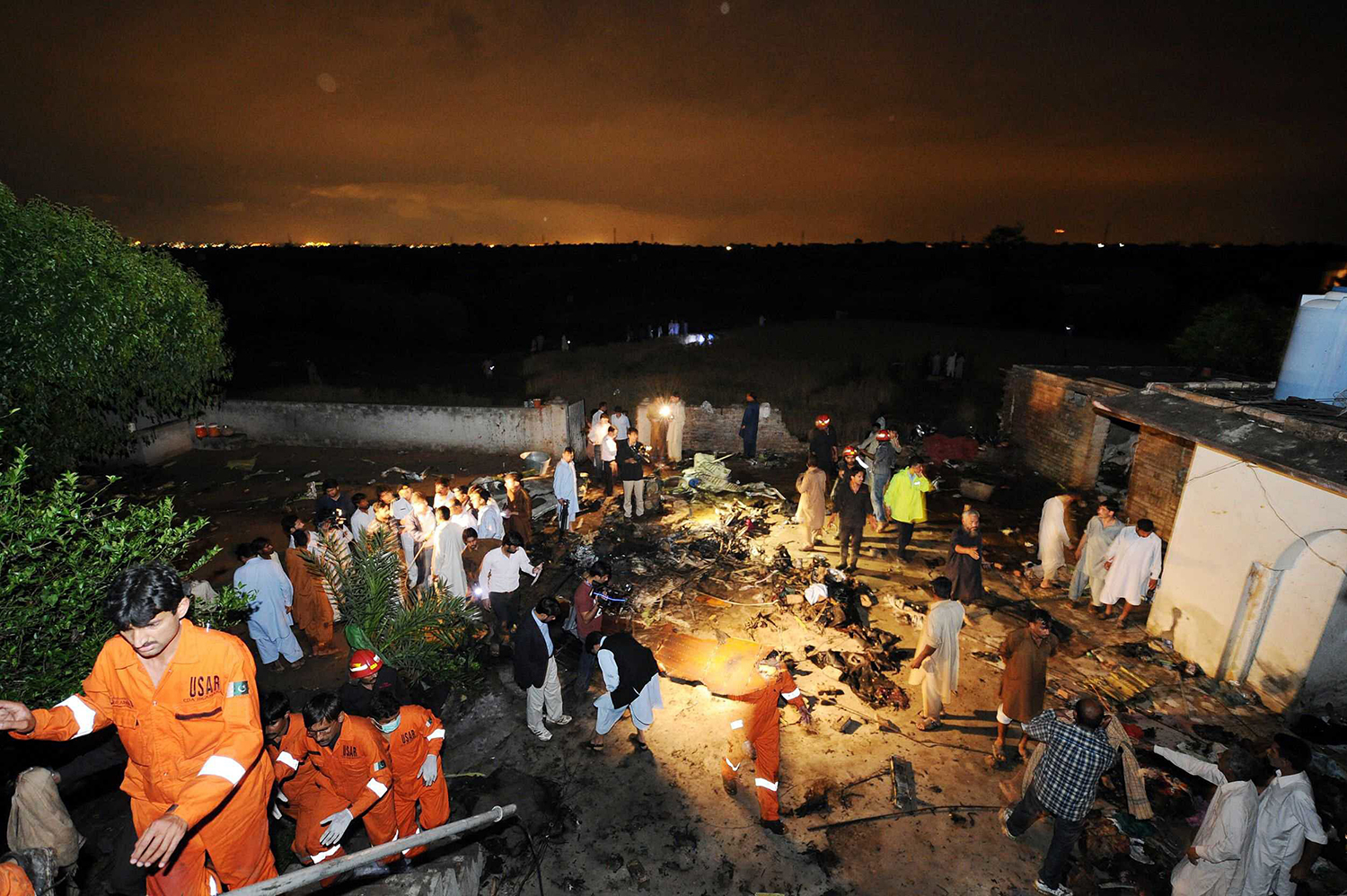
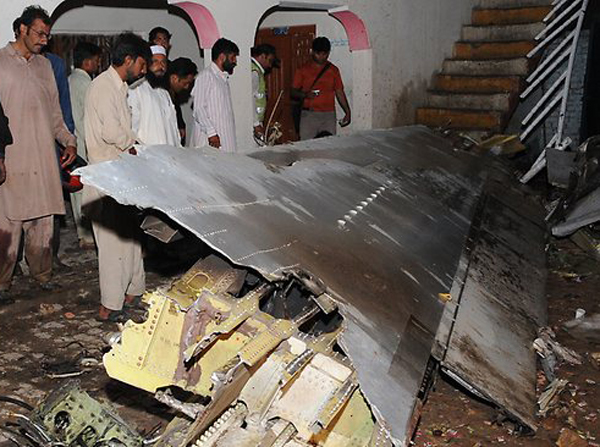
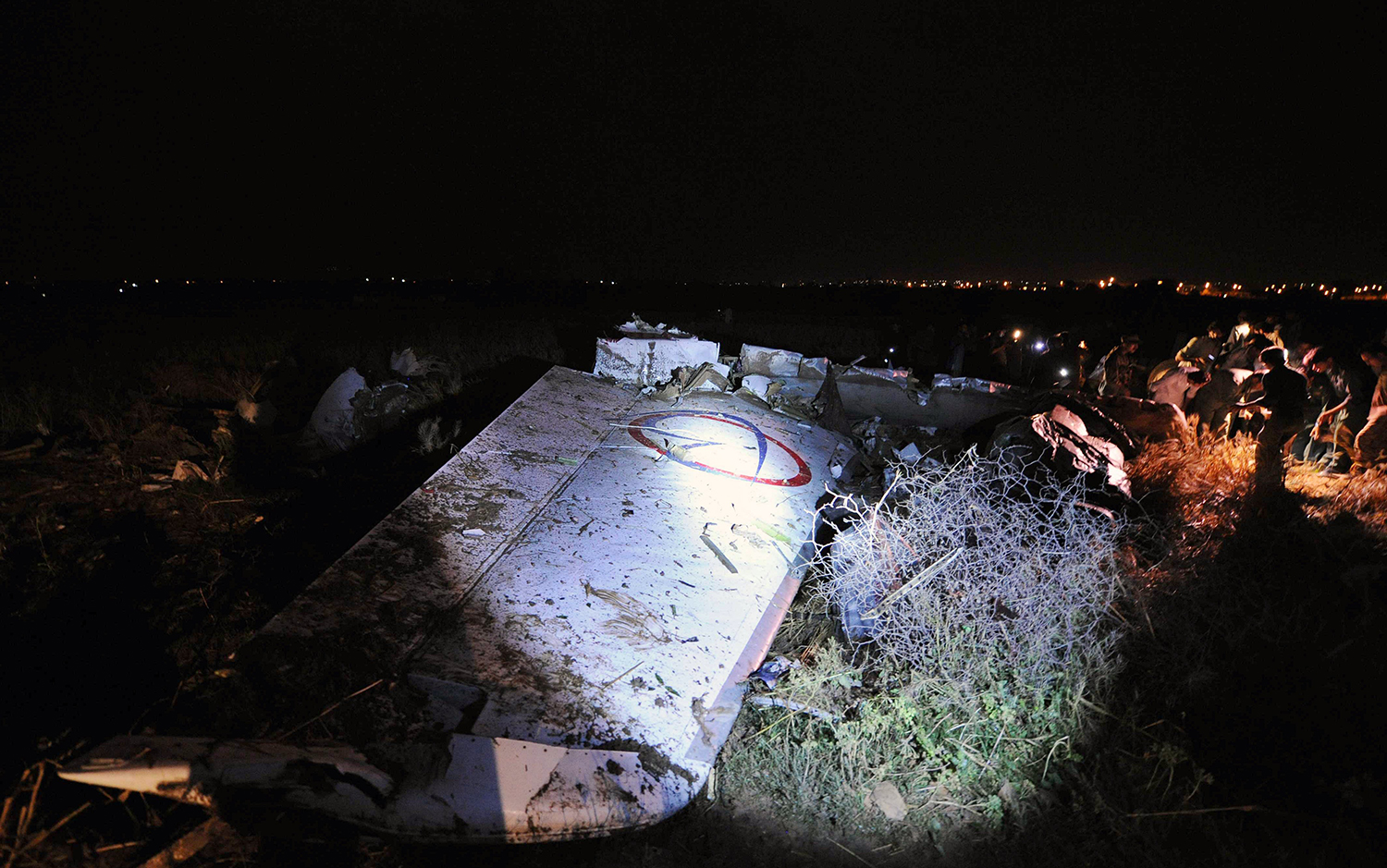
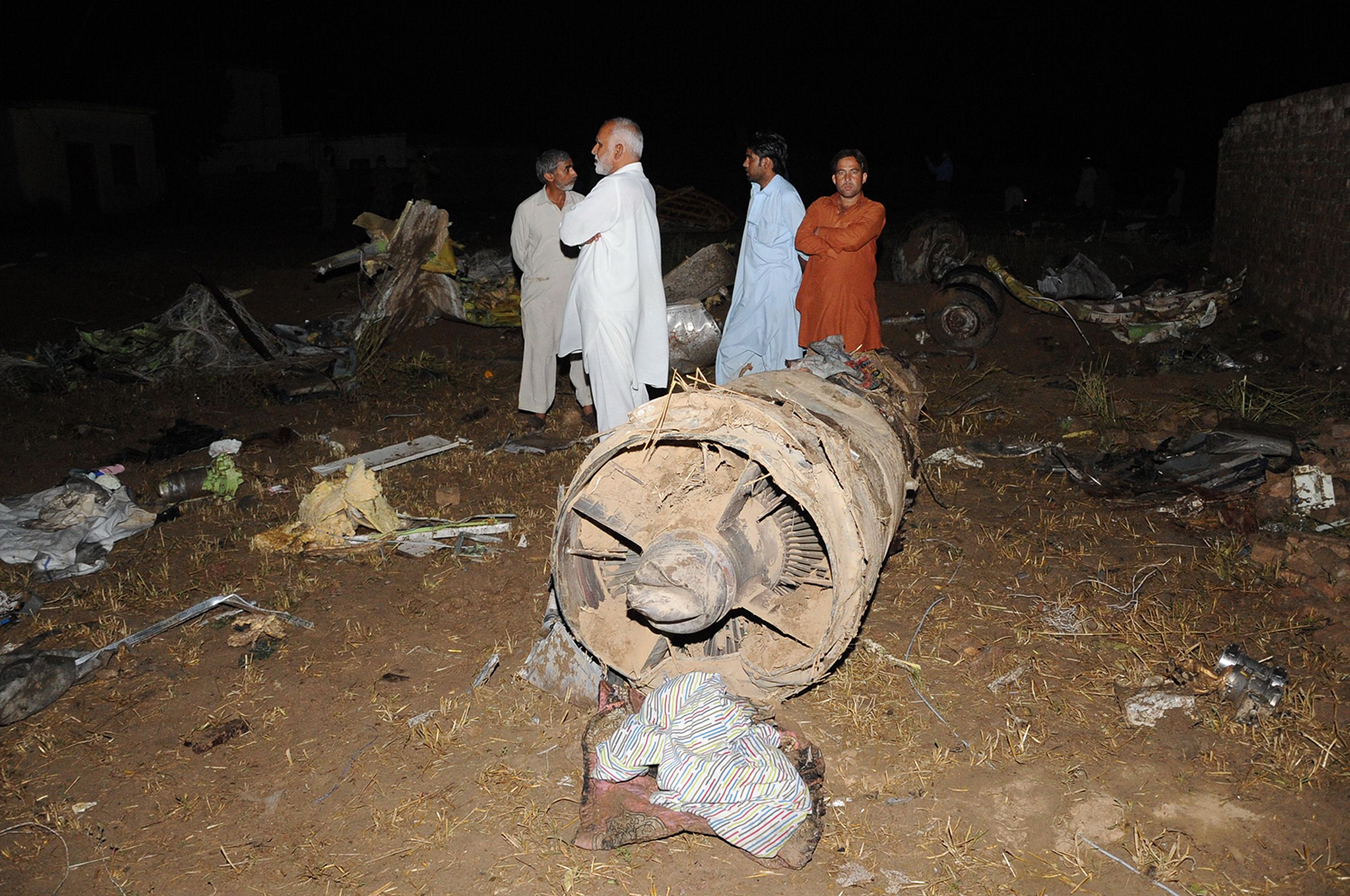
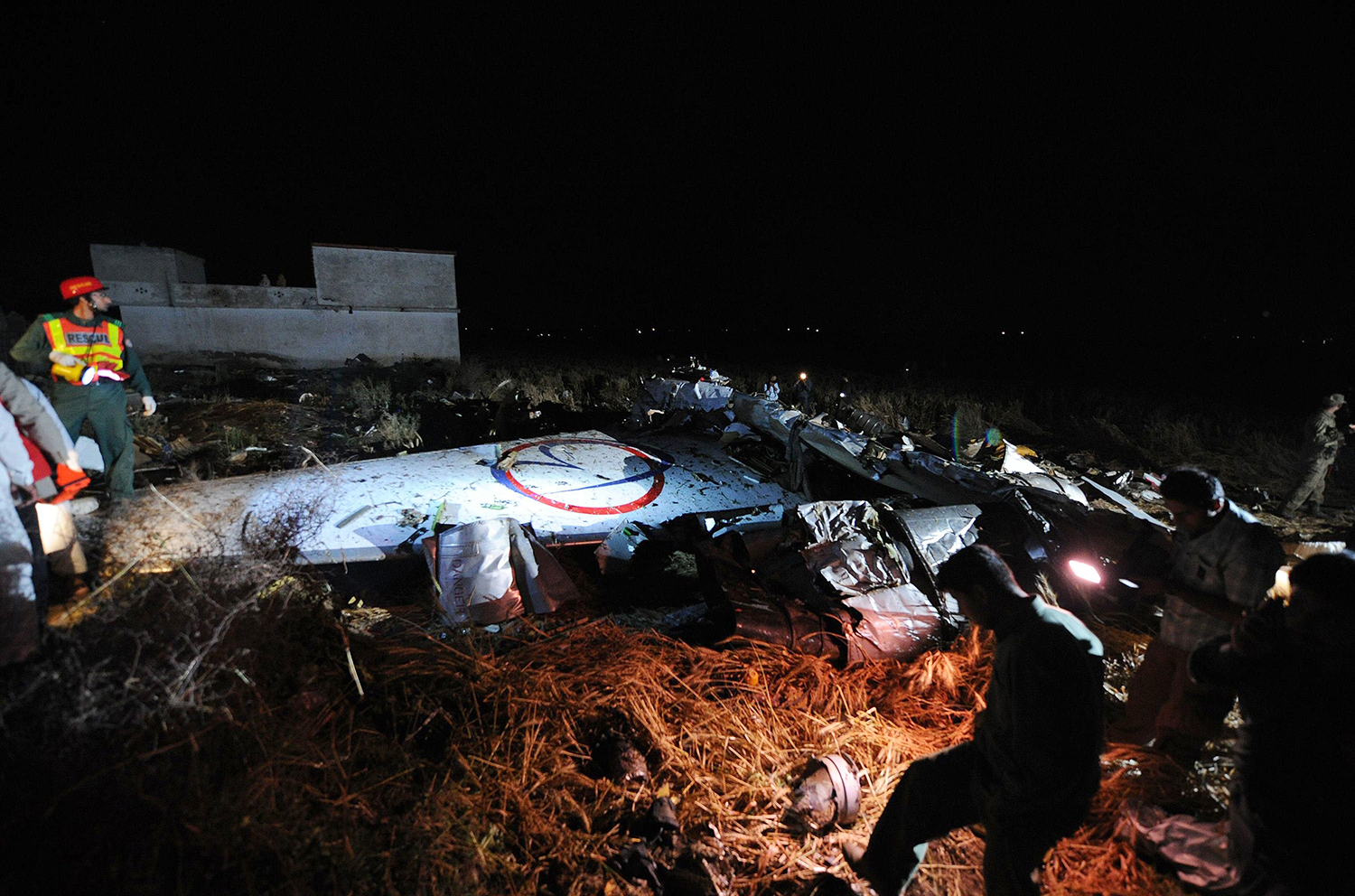
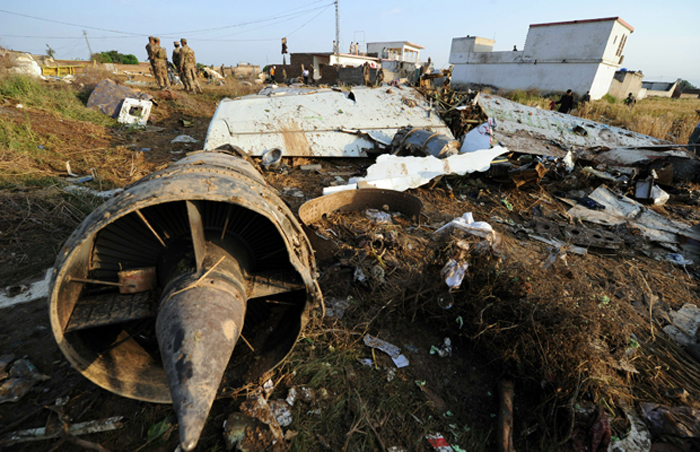
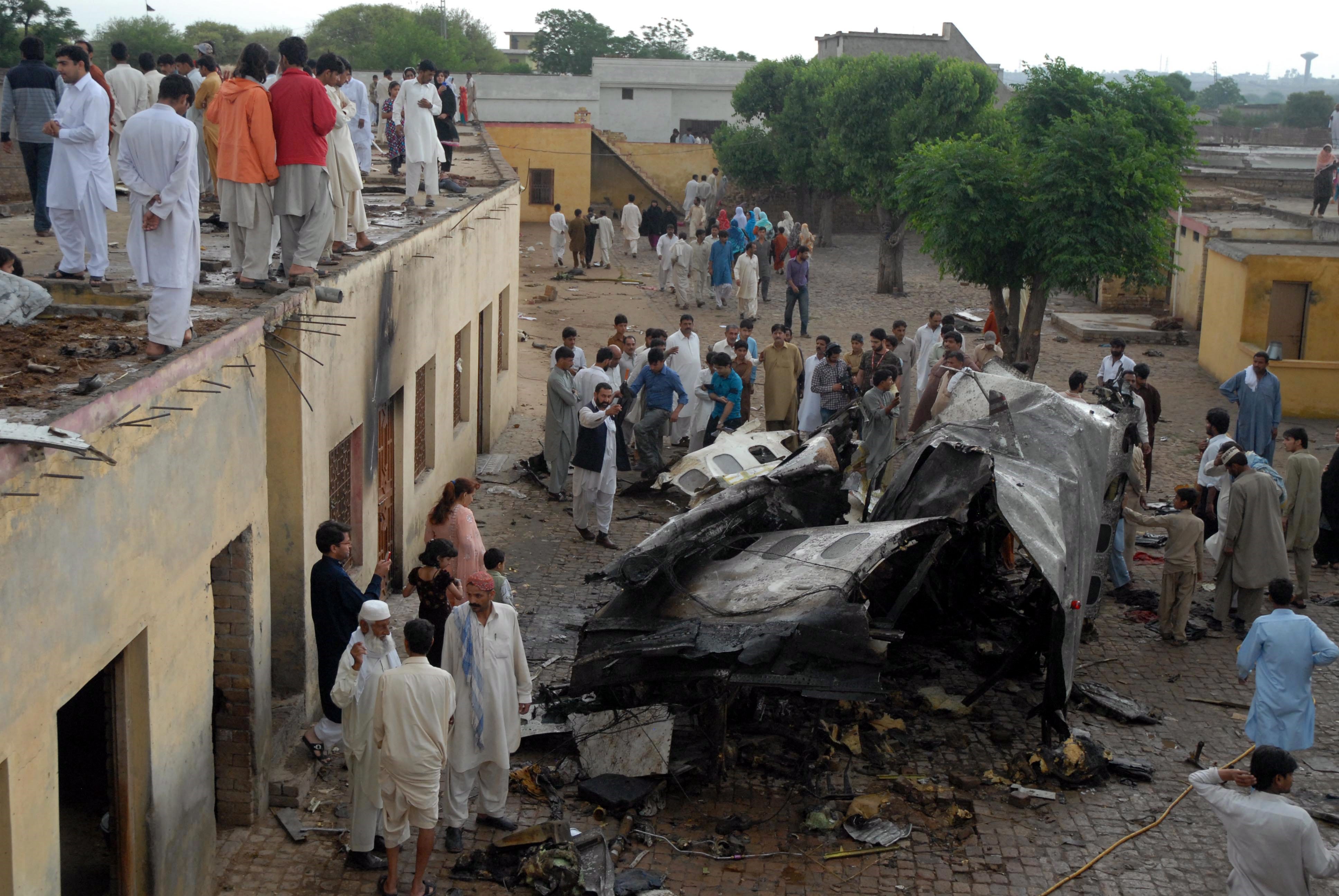
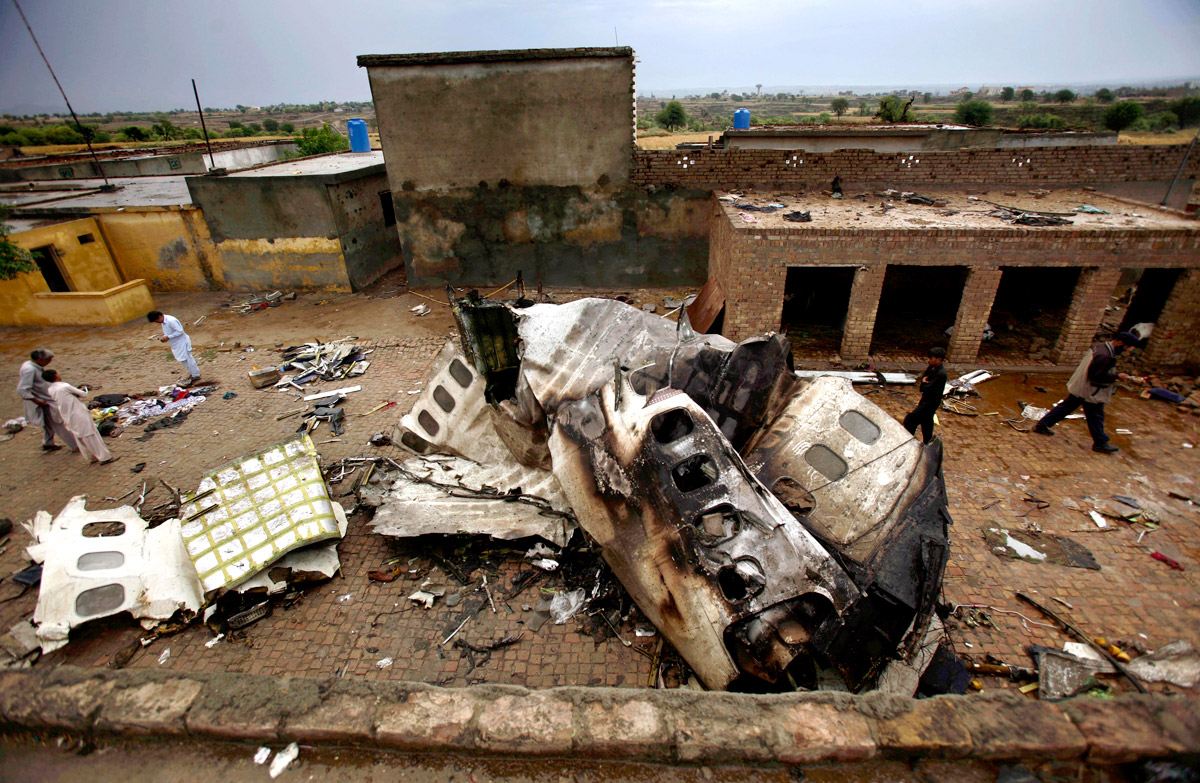
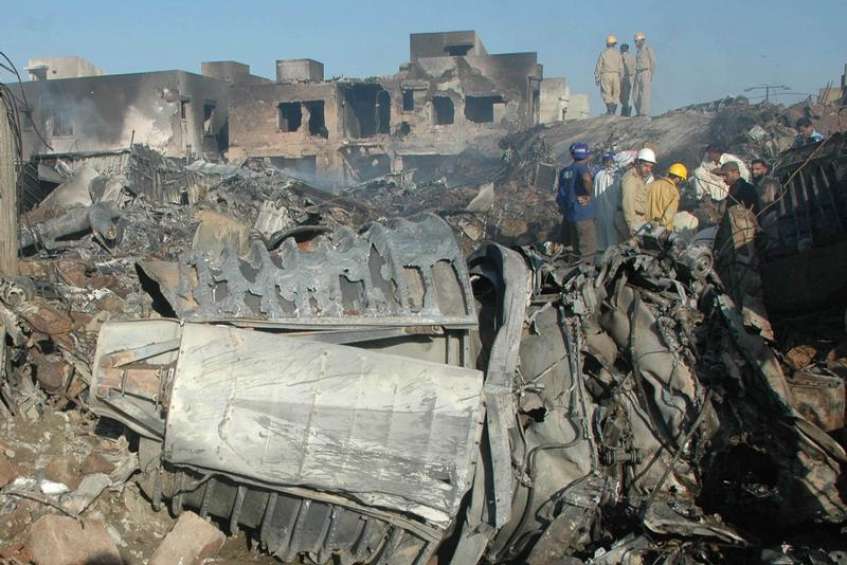
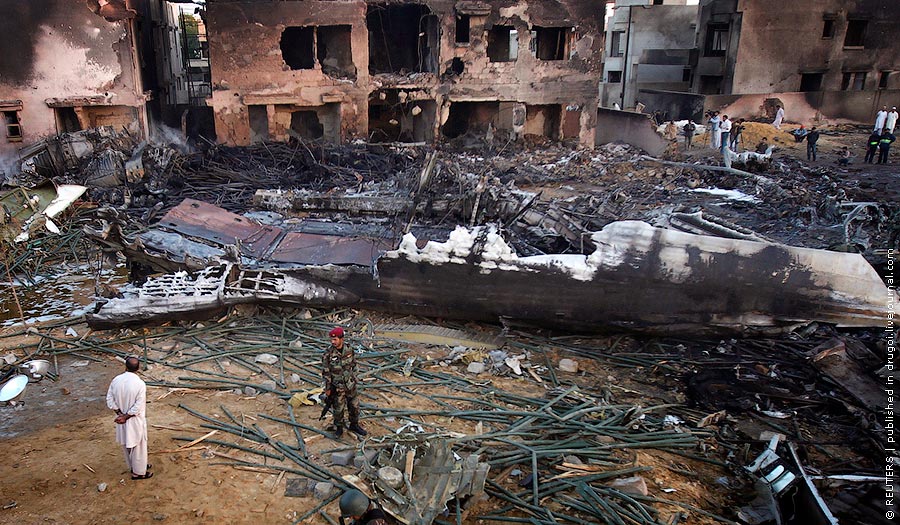
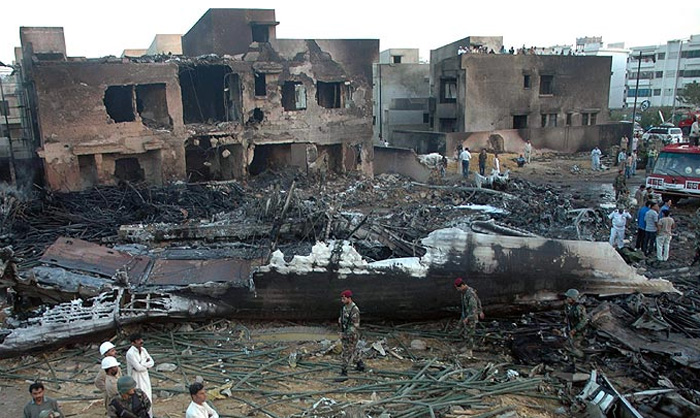
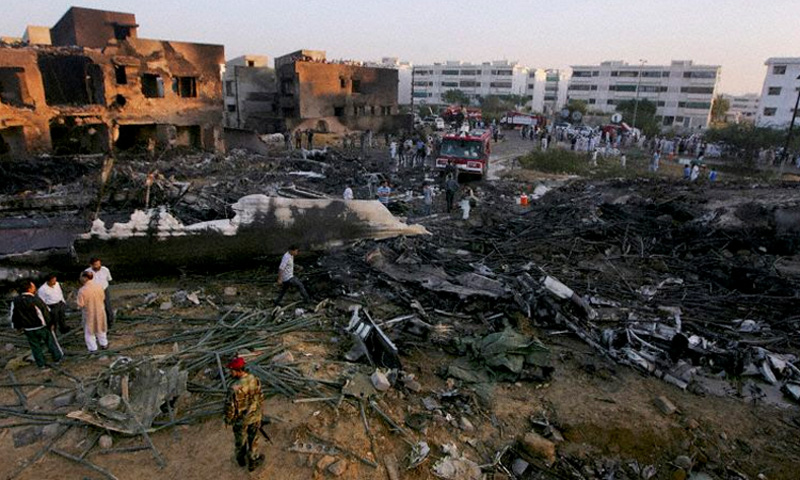
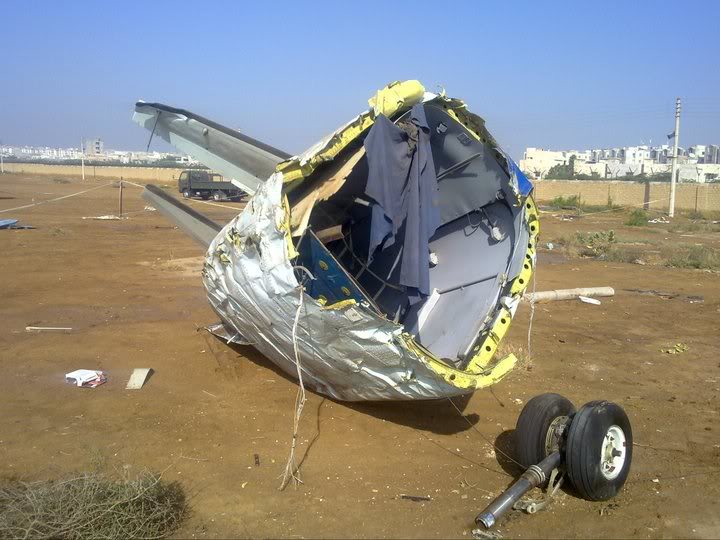
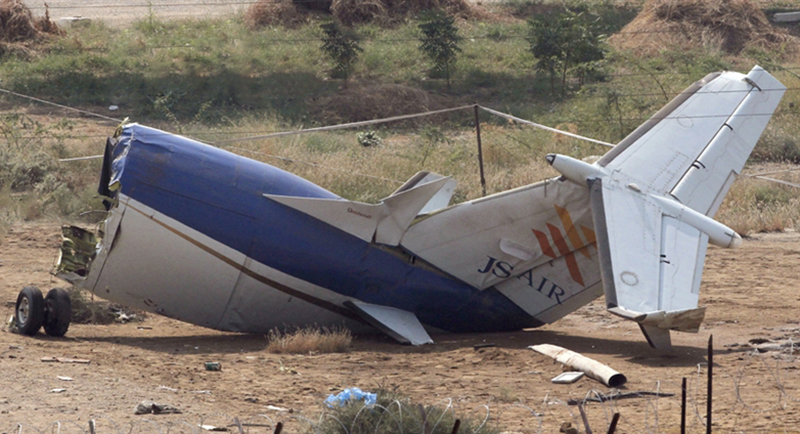
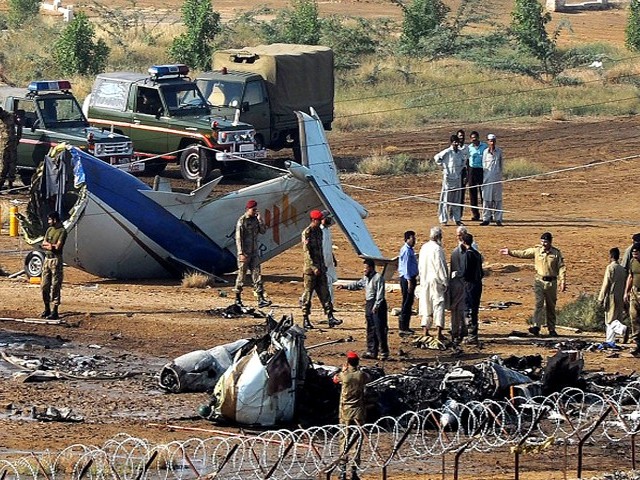
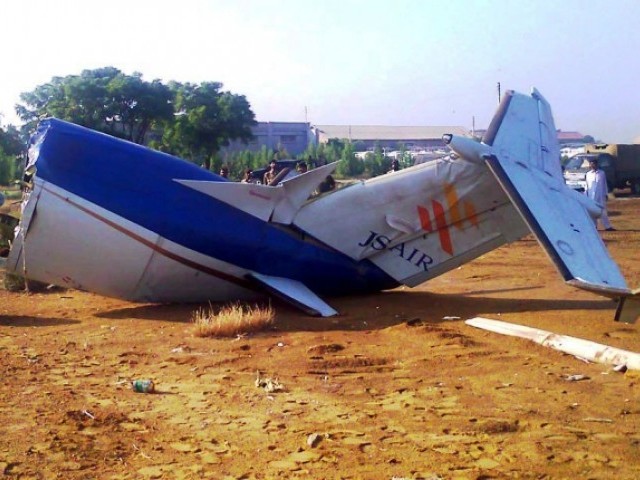
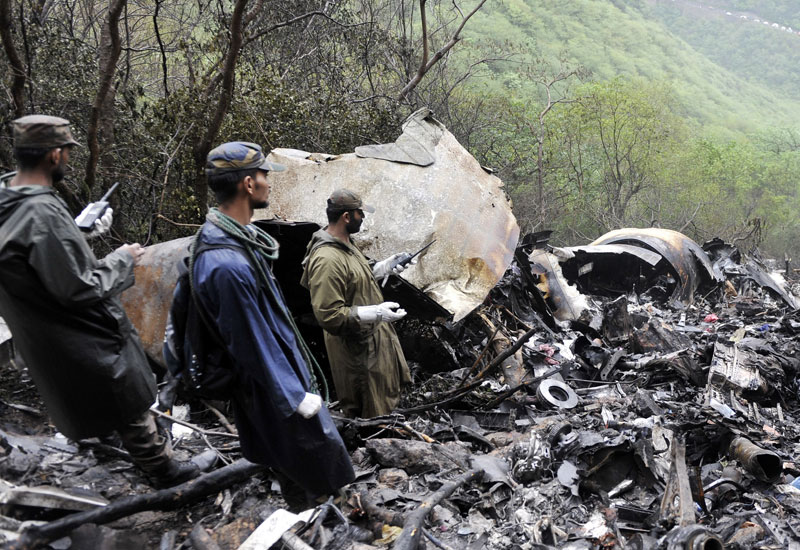
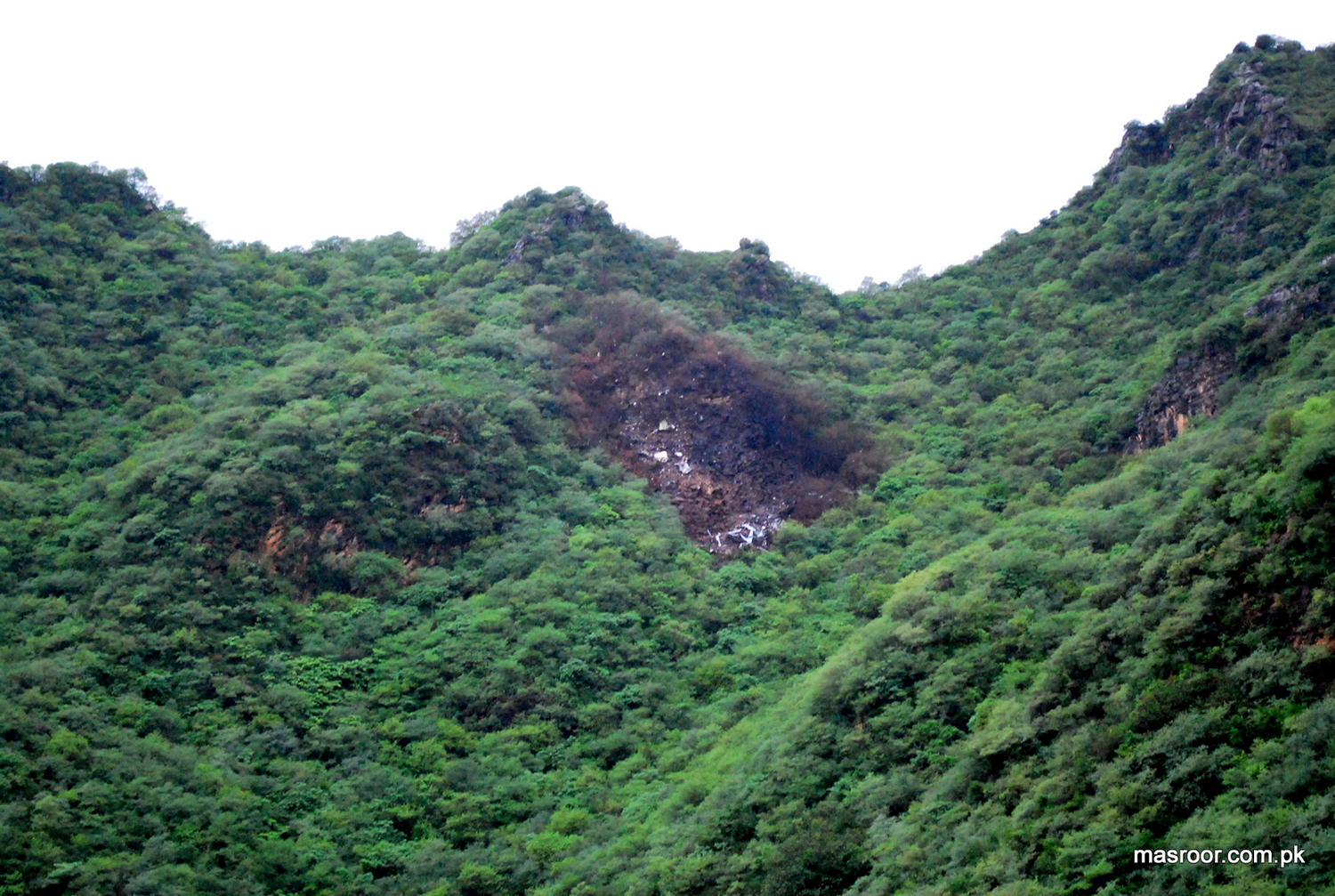
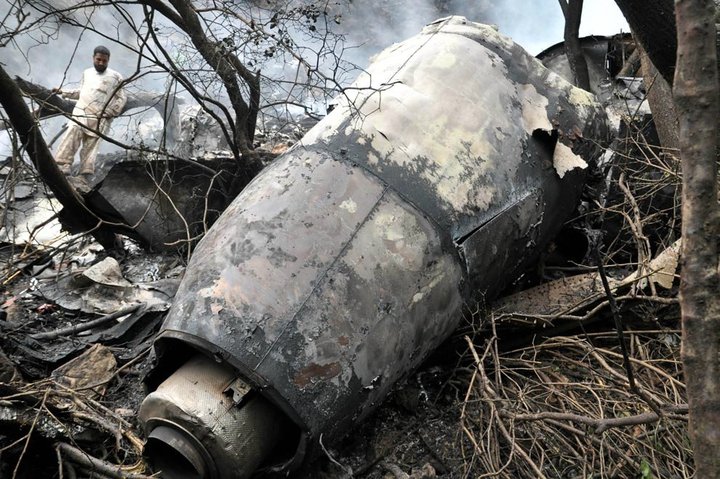
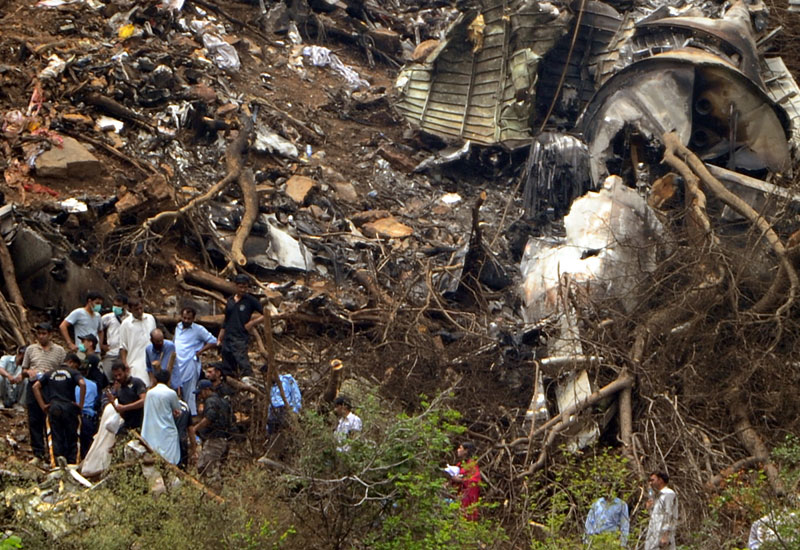
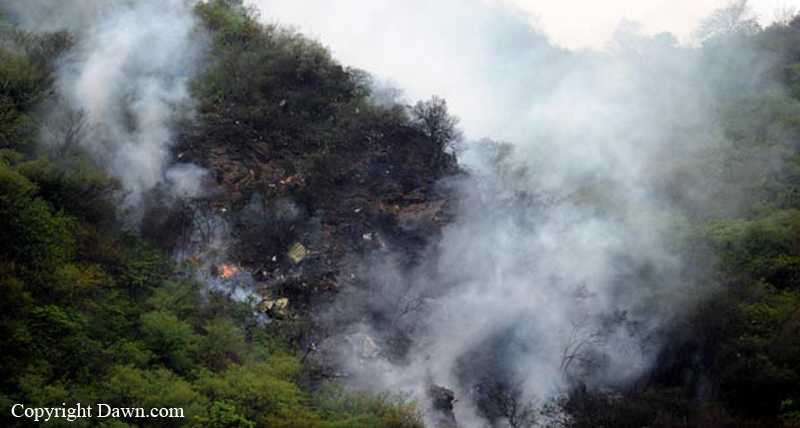
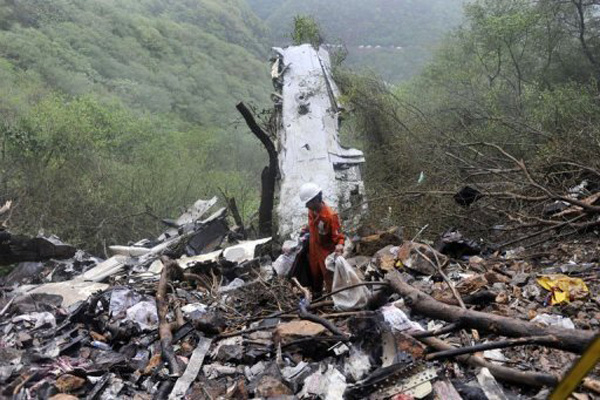
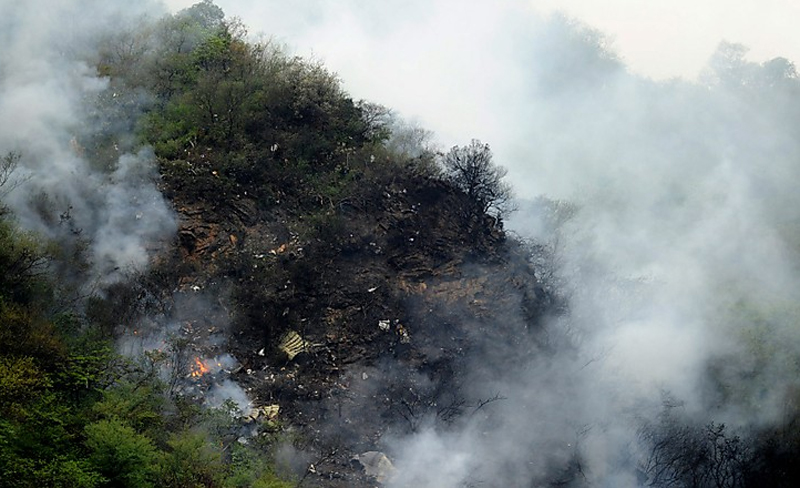
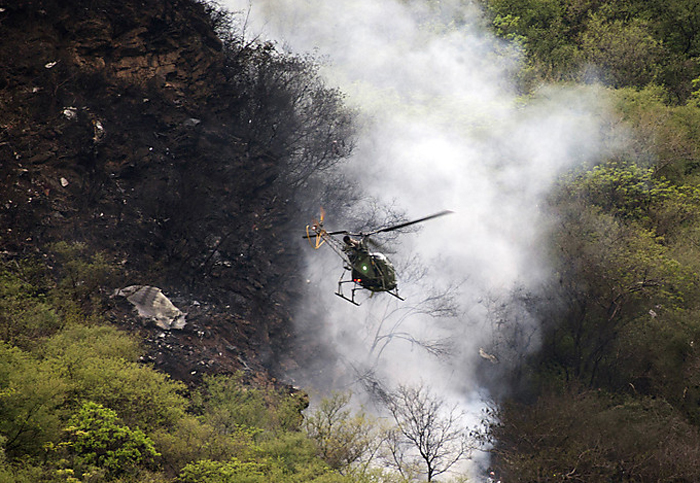
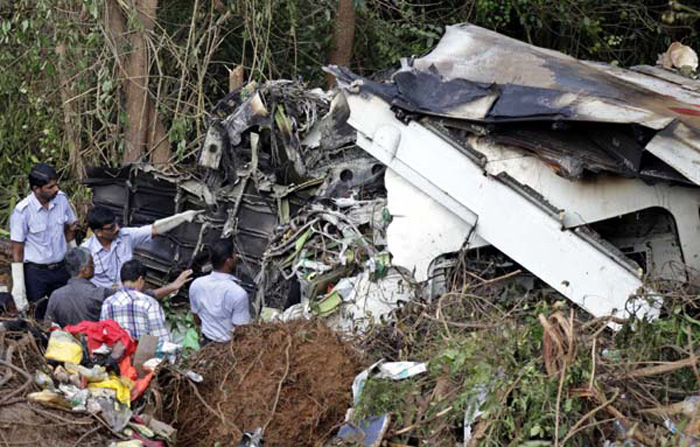
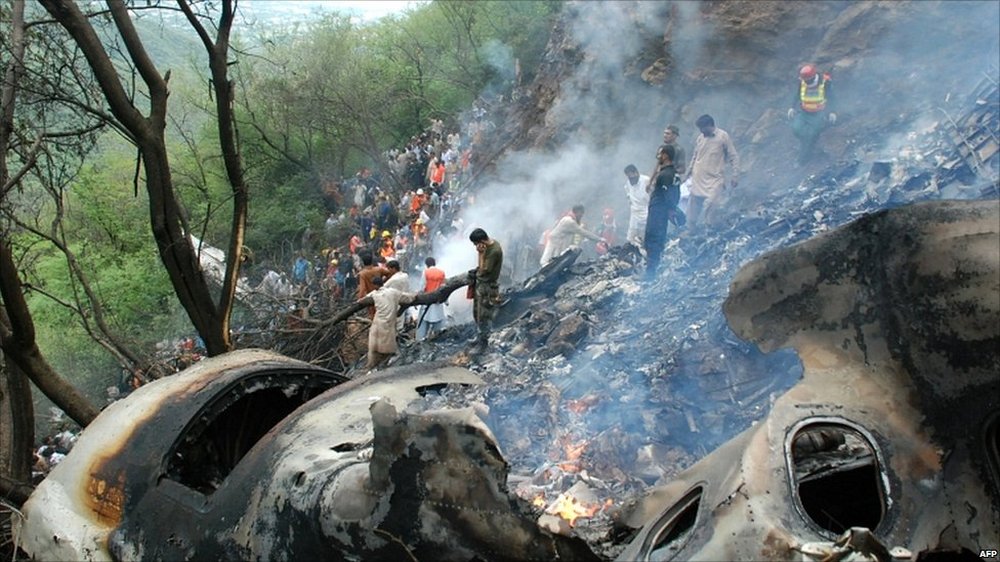
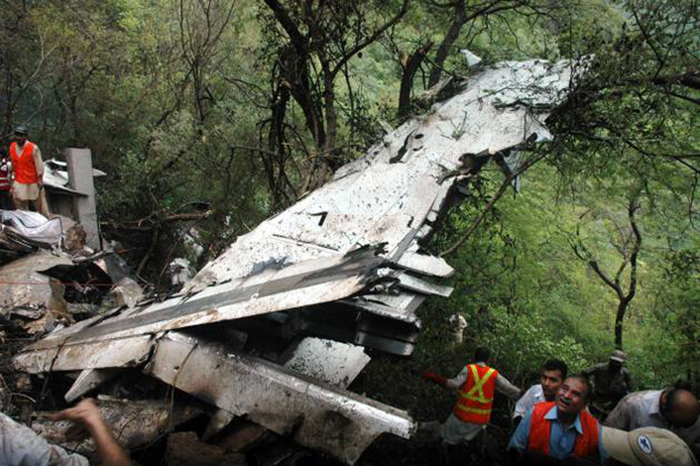
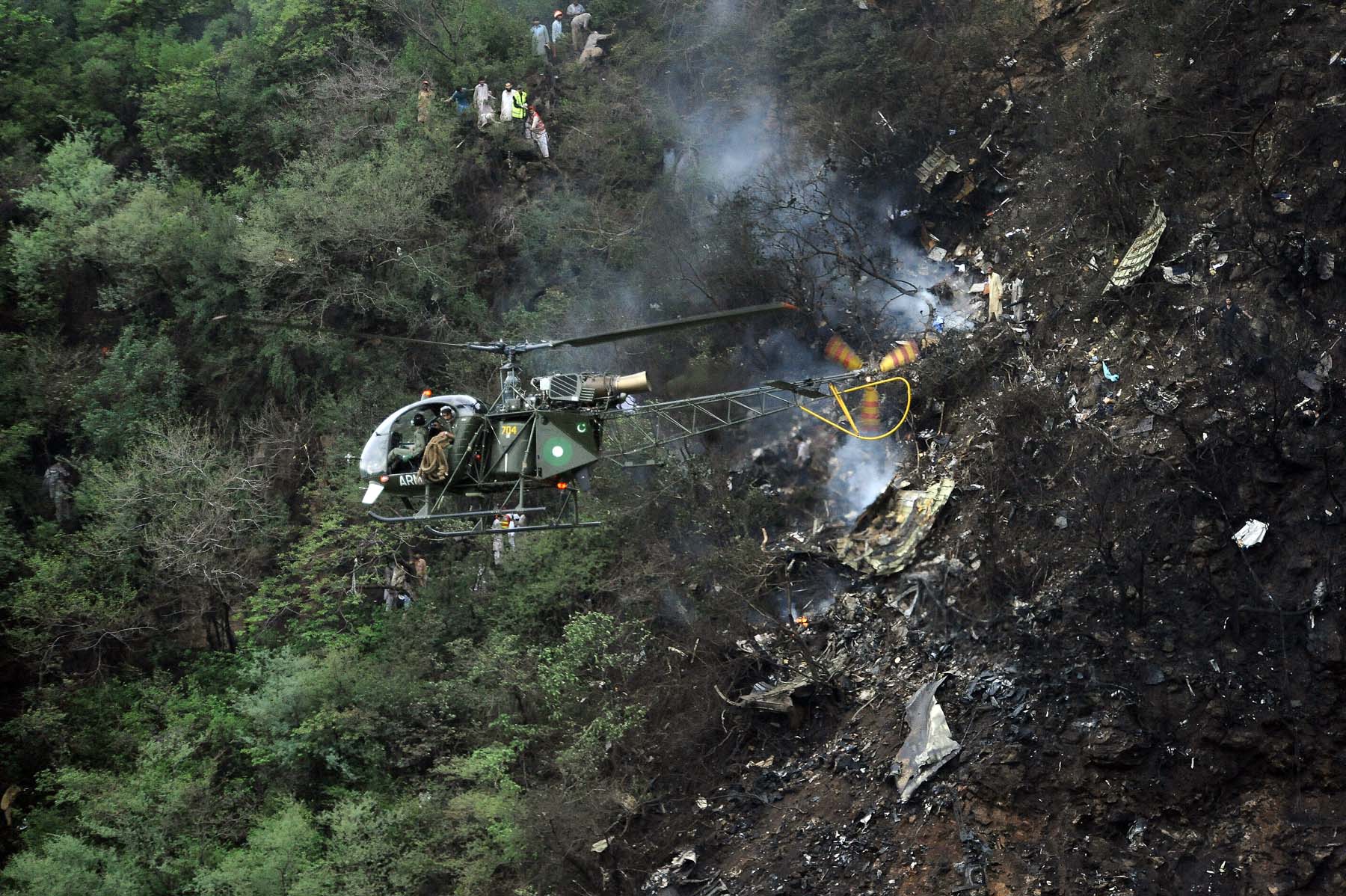
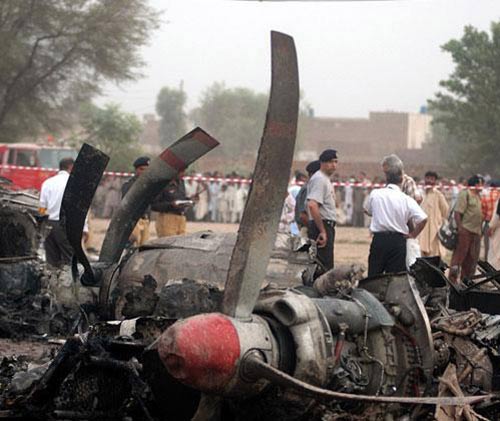
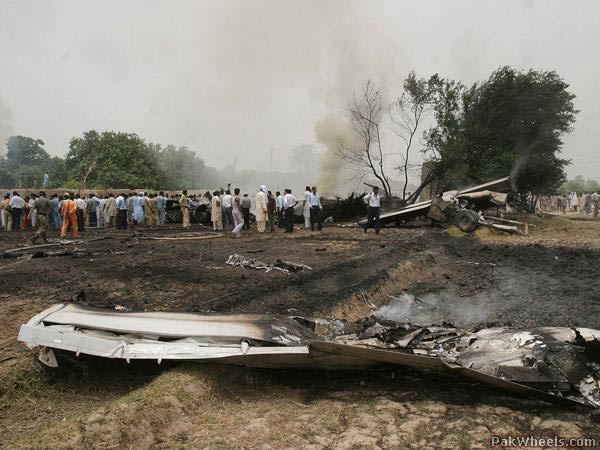
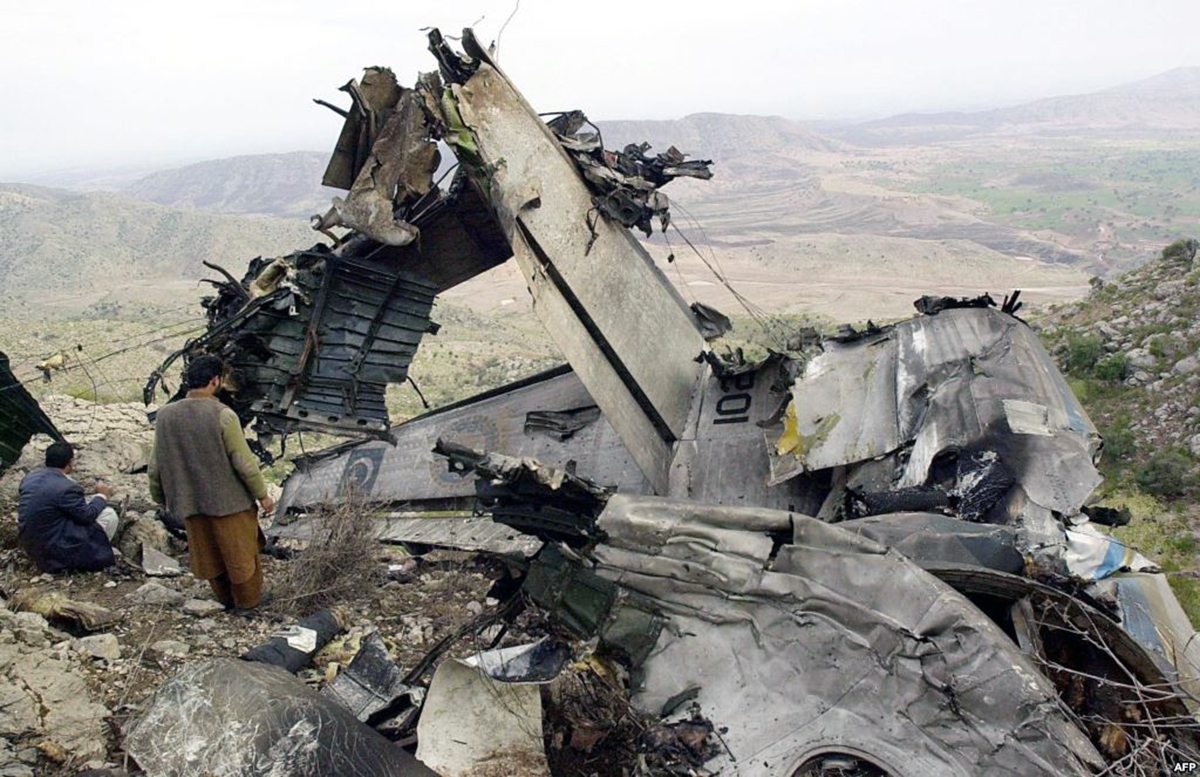
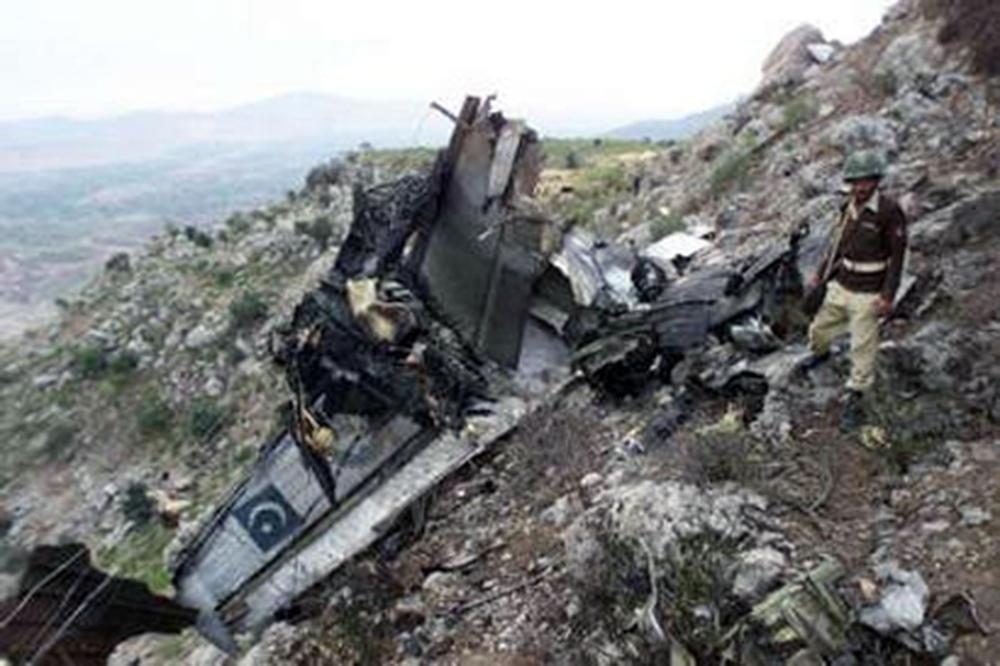
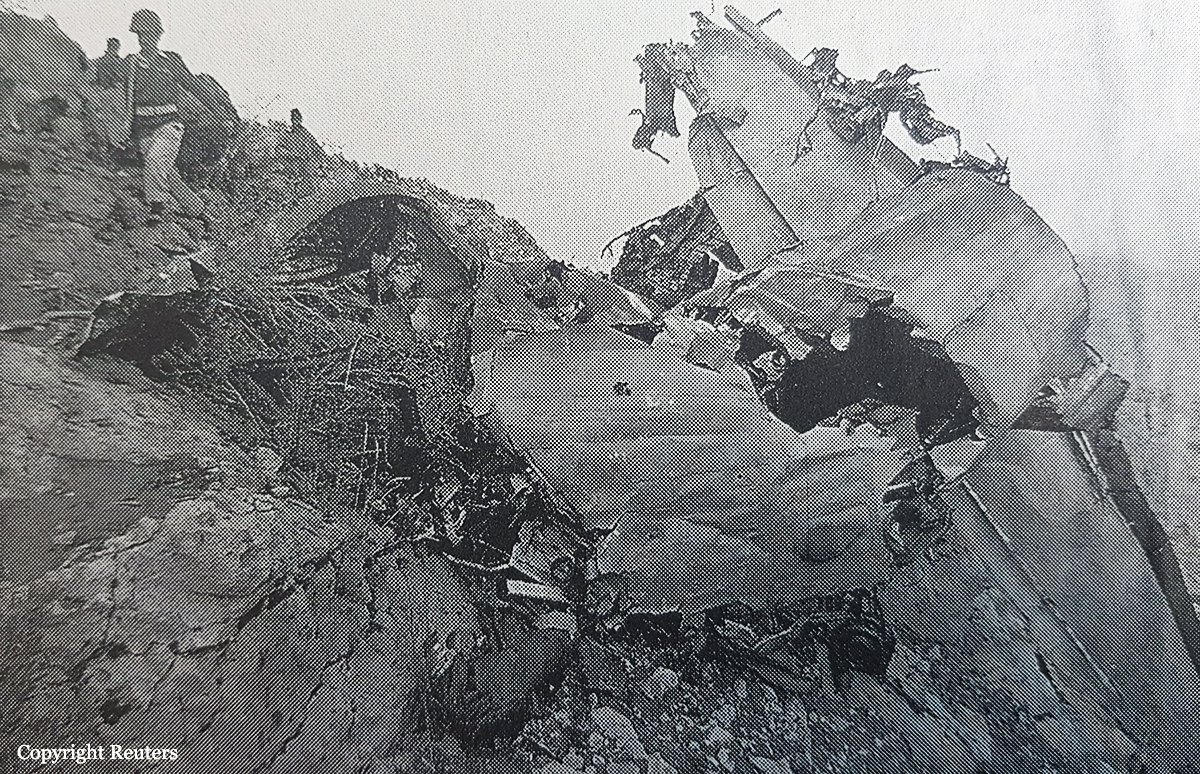
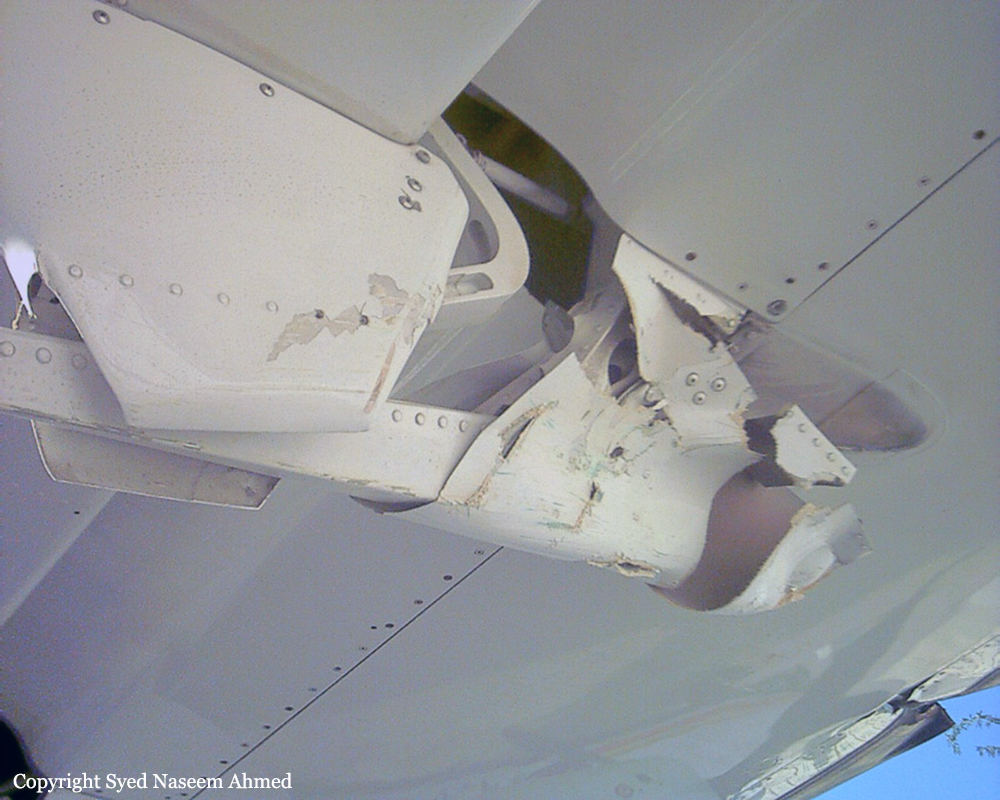
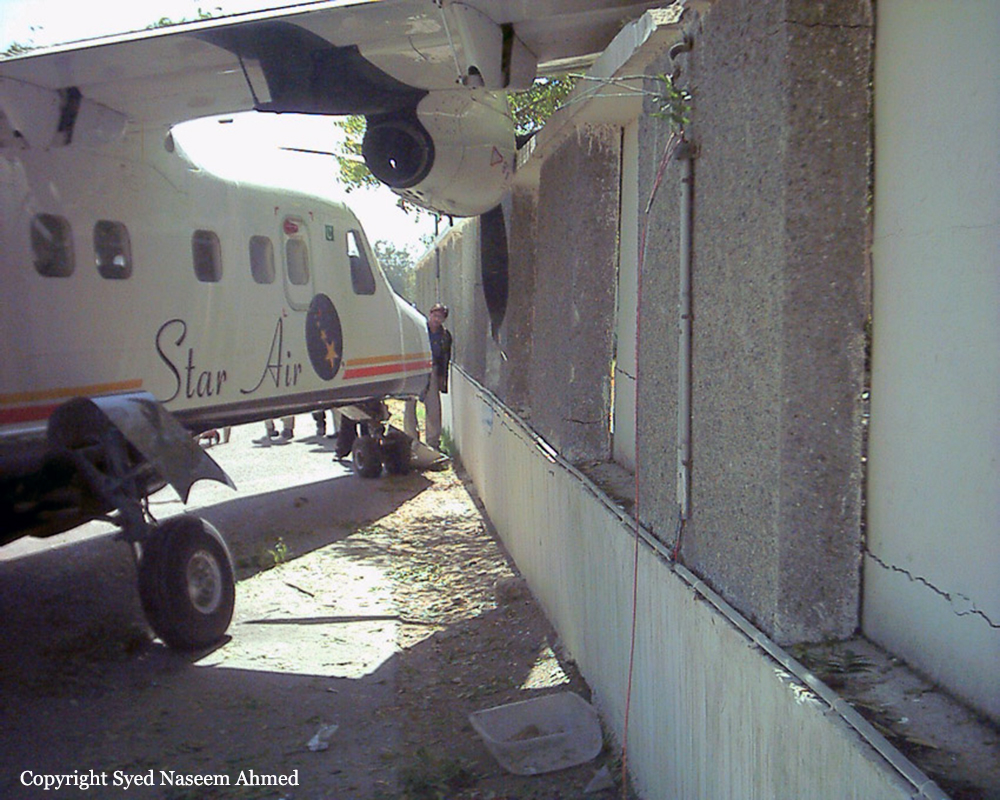
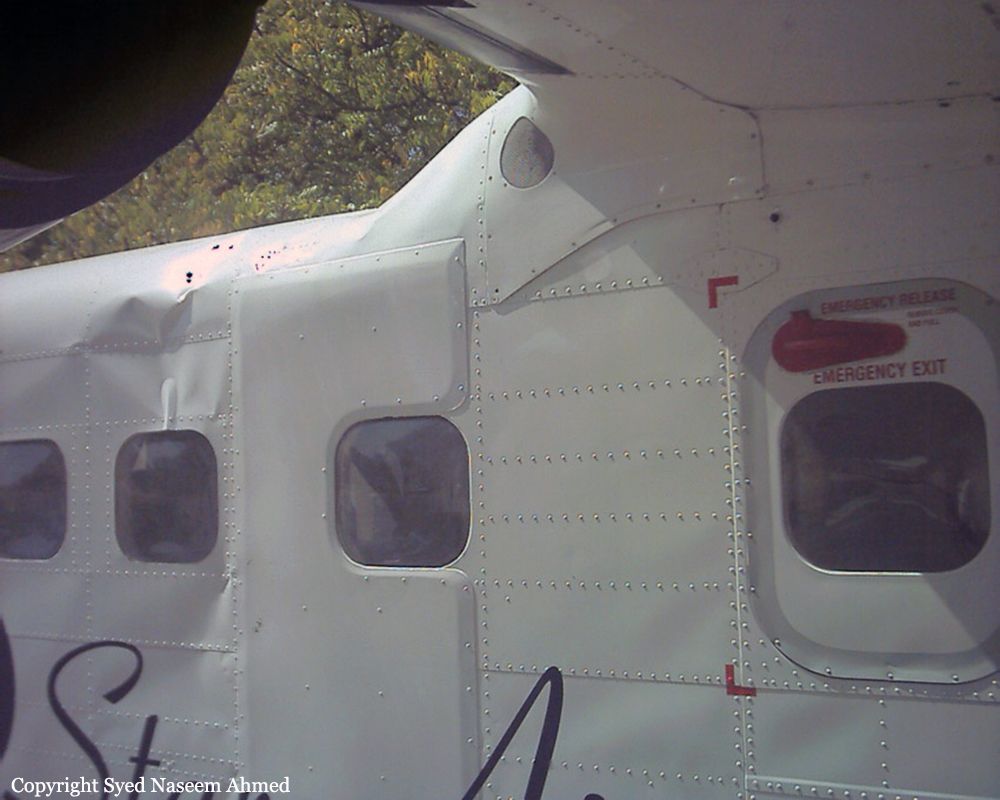
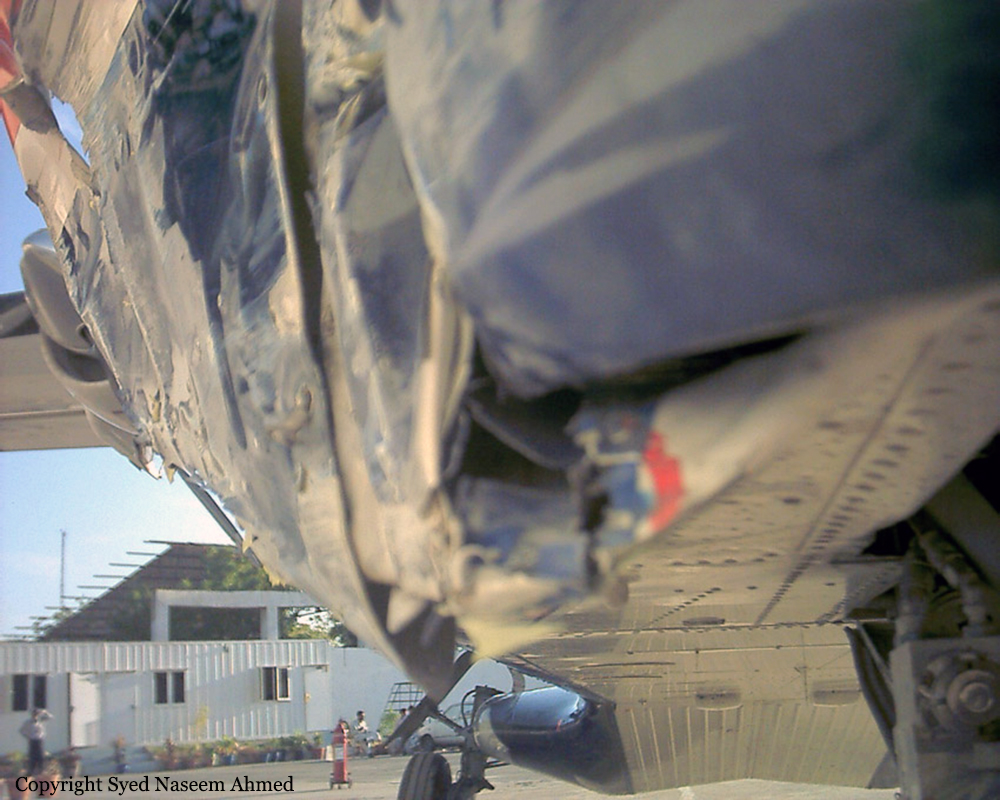
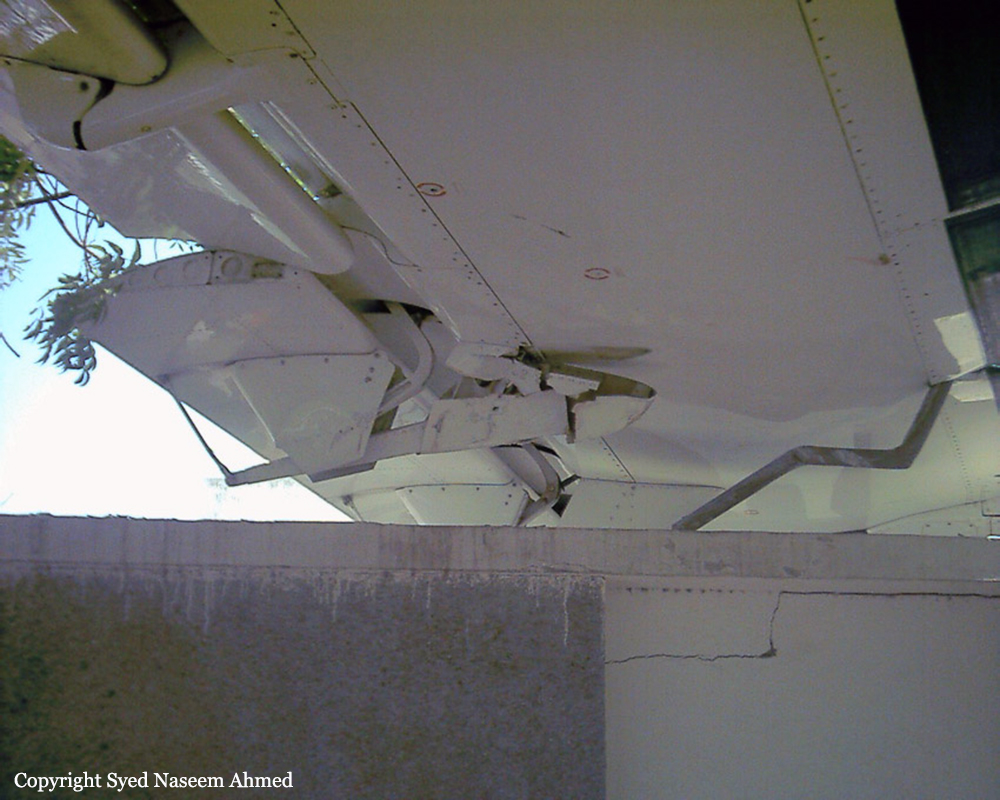
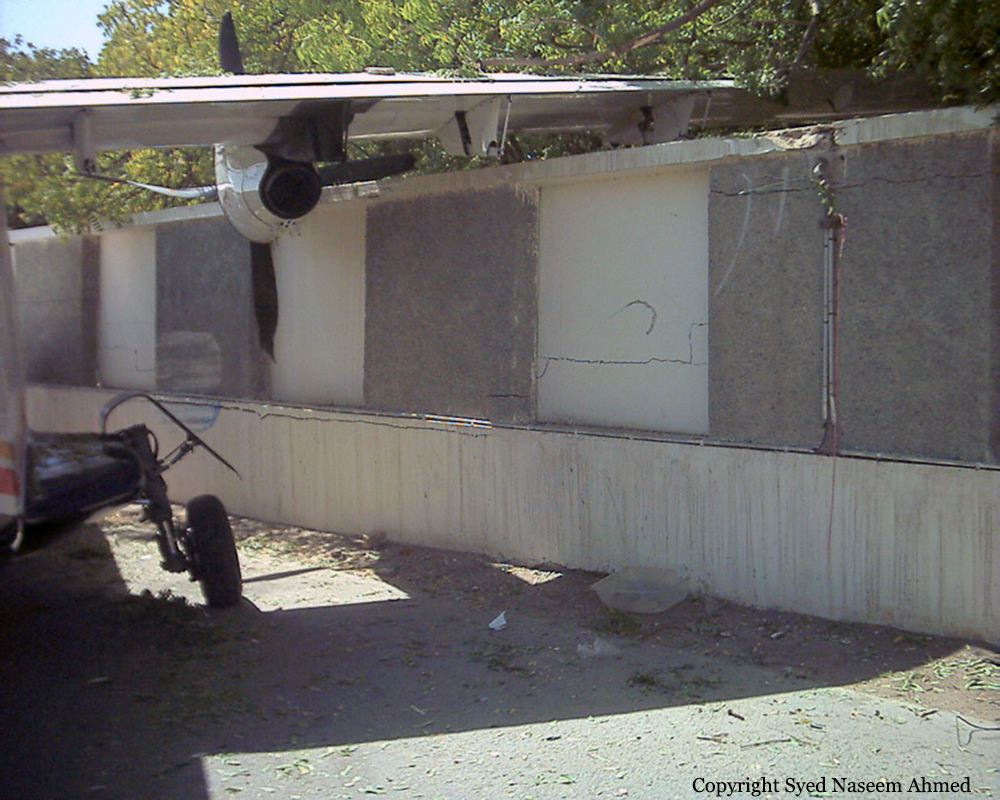
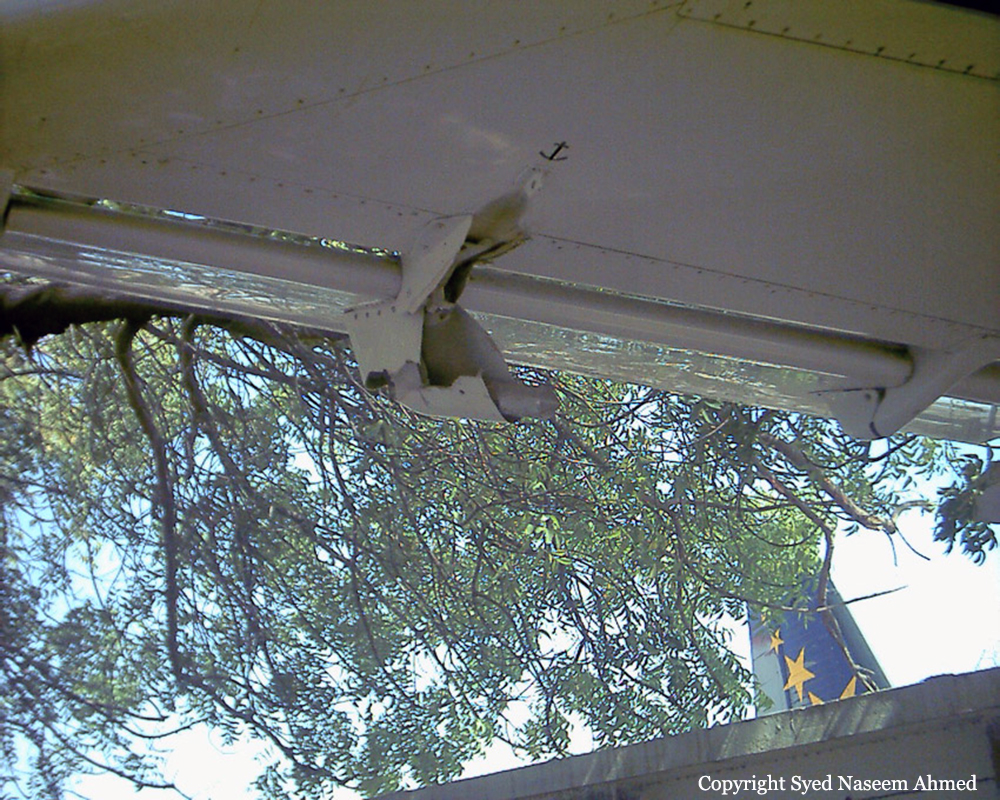
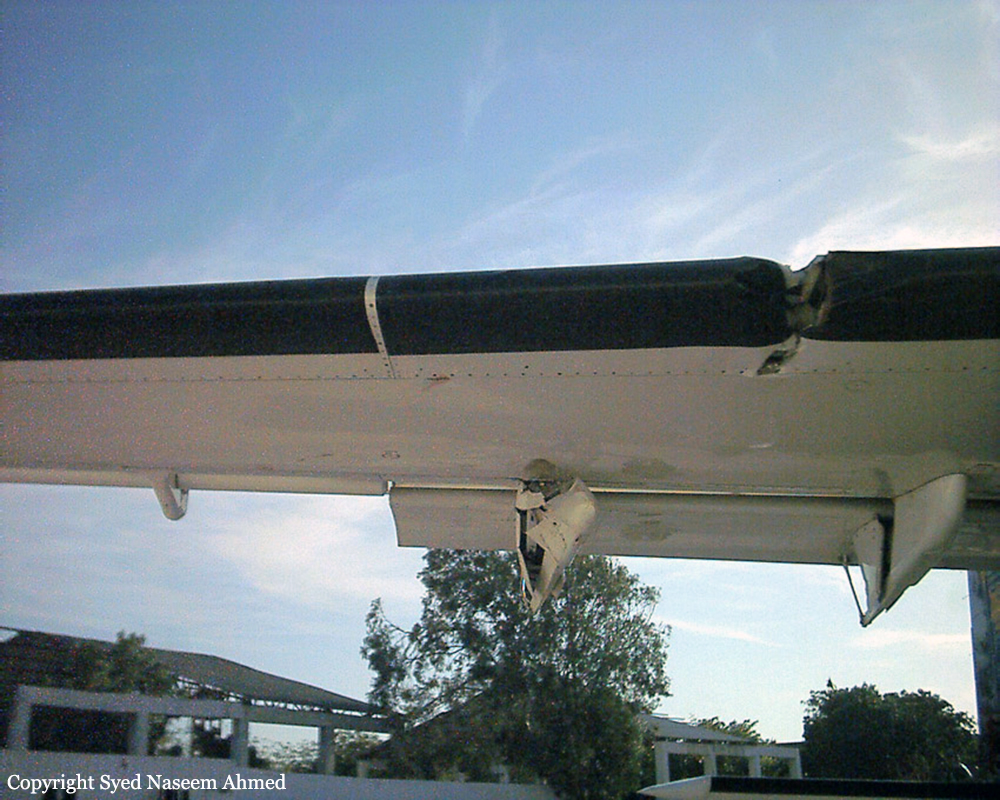
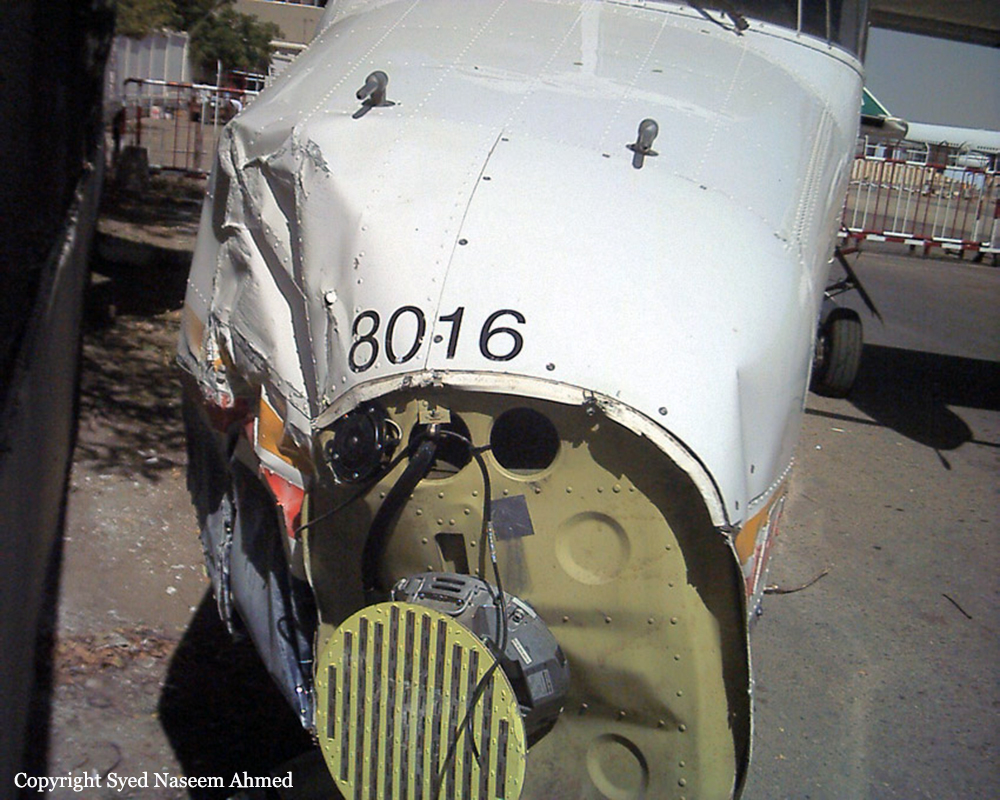
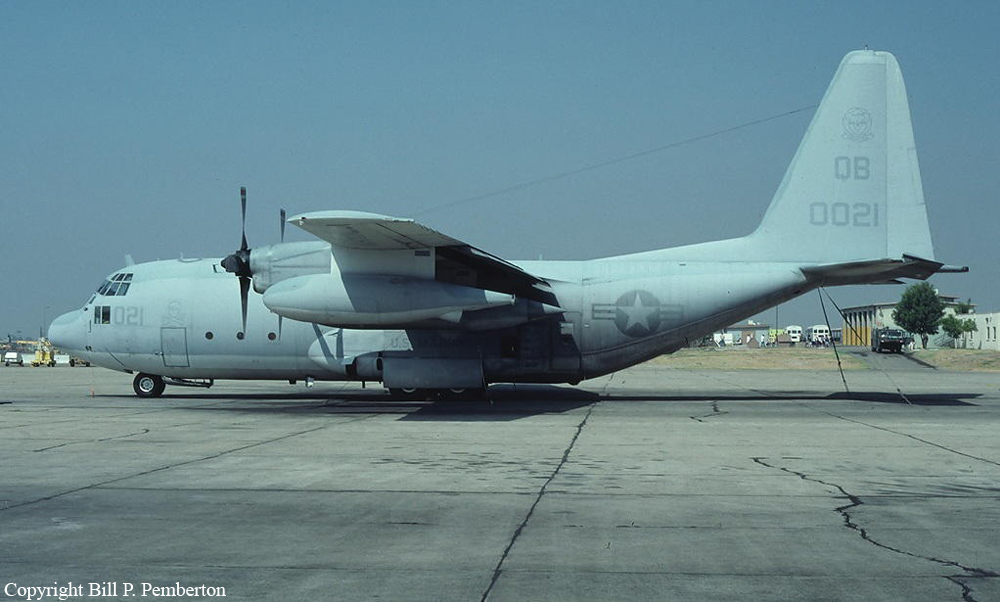
Crash of a Boeing 737-236 in Islamabad: 127 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 20, 2012 at 1840 LT
Registration:
AP-BKC
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Karachi - Islamabad
MSN:
23167/1074
YOM:
1984
Flight number:
BHO213
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
121
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
127
Captain / Total hours on type:
2027.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
750
Aircraft flight hours:
46933
Aircraft flight cycles:
37824
Circumstances:
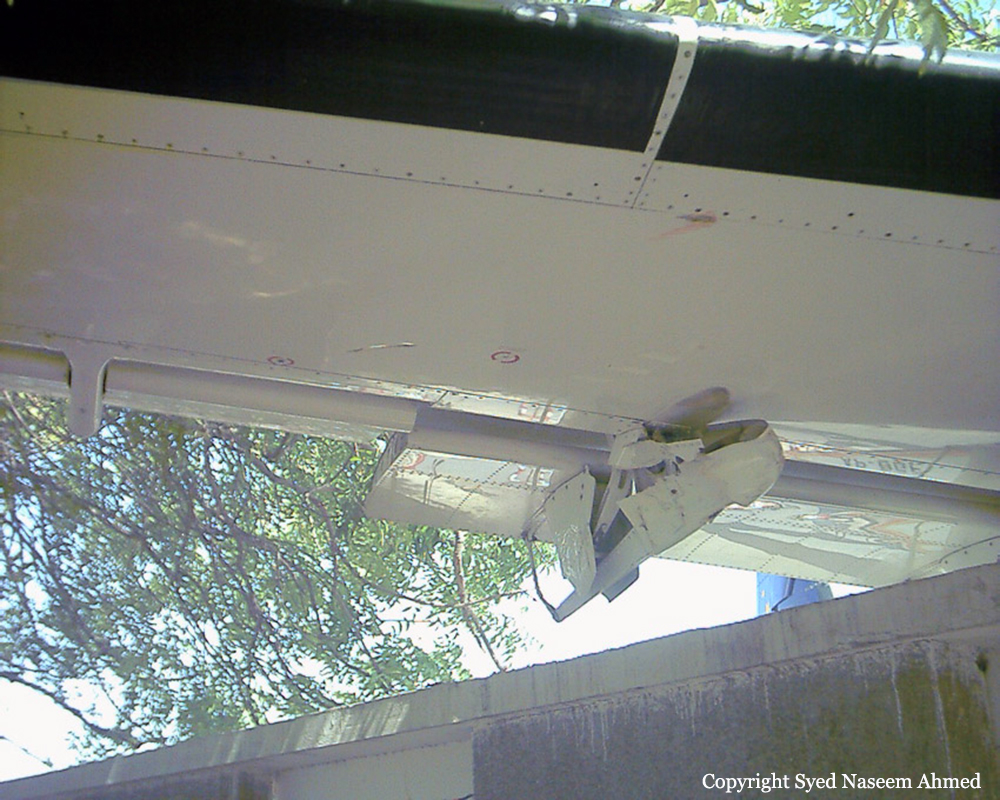
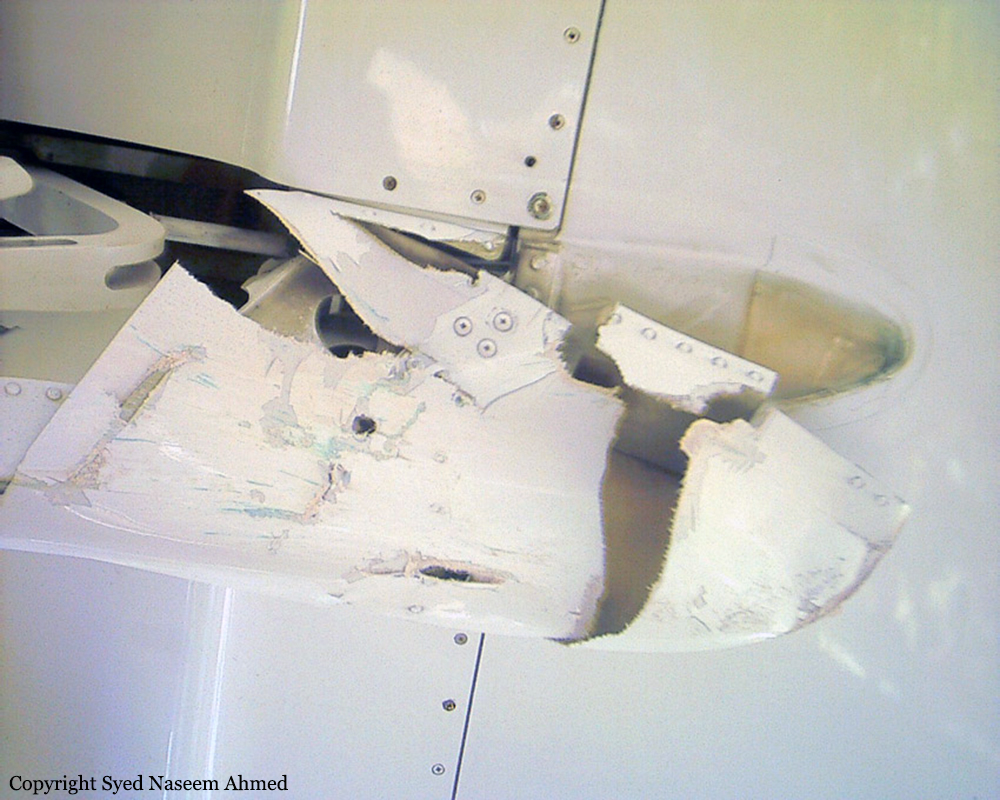
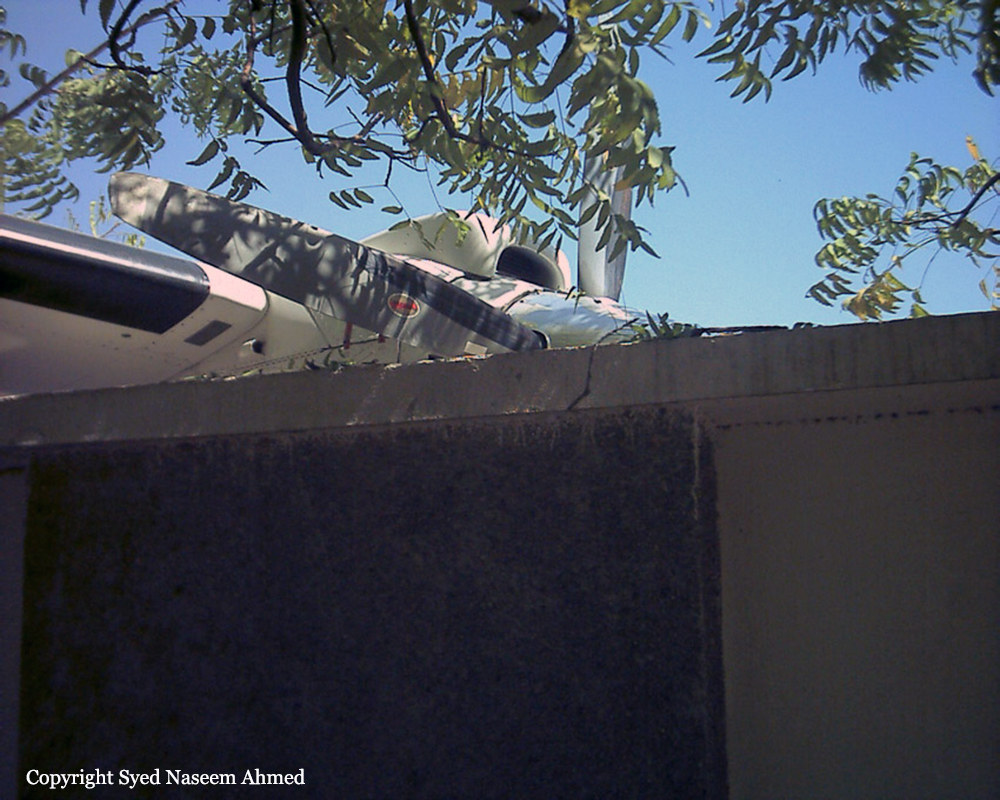
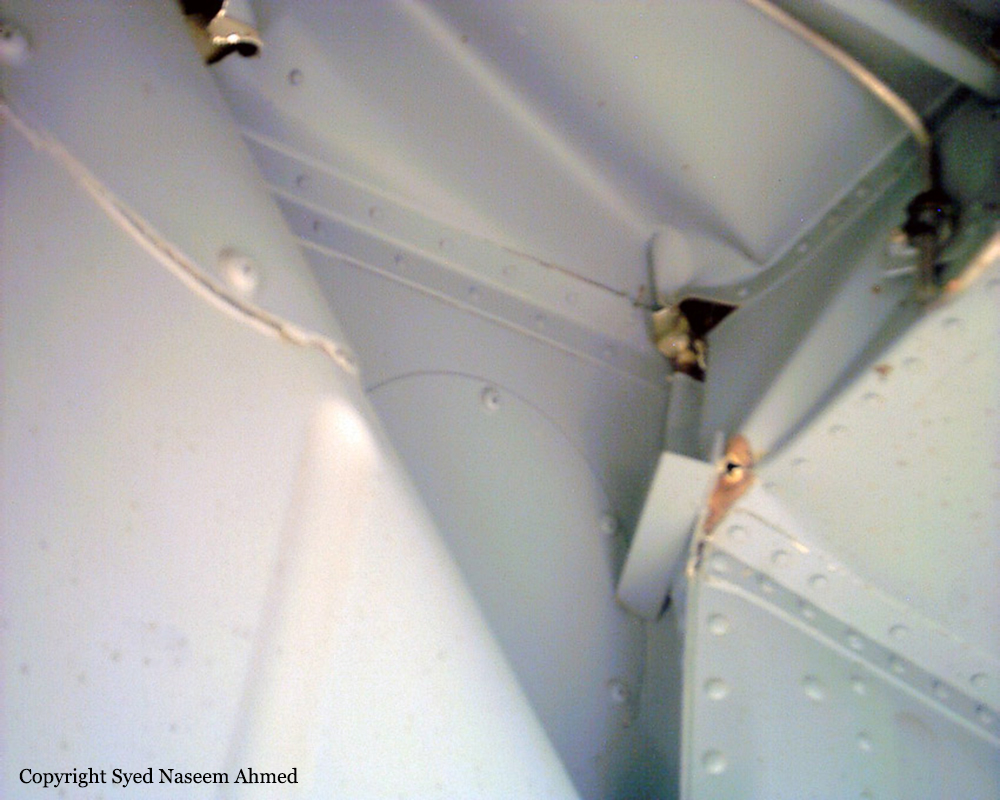
On 20th April, 2012, M/s Bhoja Air Boeing 737-236A Reg # AP-BKC was scheduled to fly domestic Flight BHO-213 from Jinnah International Airport (JIAP) Karachi to Benazir Bhutto International Airport (BBIAP) Islamabad. The aircraft had 127 souls onboard including 06 flight crew members. The Mishap Aircraft (MA) took off for Islamabad at 1705 hrs Pakistan Standard Time (PST) from Karachi. The reported weather at Islamabad was thunderstorm with gusty winds. During approach for landing at BBIAP, Islamabad (OPRN), Flight BHO-213 was cleared by Islamabad Approach Radar for an Instrument Landing System (ILS) approach for Runway 30. The MA, while established on ILS (aligned with Runway 30 at prescribed altitude), at 6 miles to touchdown was asked by the Approach Radar to change over to Air Traffic Control (ATC) Tower frequency for final landing clearance. The cockpit crew came on ATC Tower frequency and flight was cleared to land at BBIAP, Islamabad, but the cockpit crew did not respond to the landing clearance call. The ATC Tower repeated the clearance but there was no response. After a few minutes, a call from a local resident was received in ATC Tower, stating that an aircraft had crashed close to Hussain Abad (A population around 4 nm short of runway 30 BBIAP, Islamabad). It was later confirmed that Flight BHO-213 had crashed and all 127 souls onboard (121 passengers + 6 flight crew) had sustained fatal injuries along with complete destruction of aircraft.
Probable cause:
Factors Leading to the Accident:
- The aircraft accident took place as a result of combination of various factors which directly and indirectly contributed towards the causation of accident. The primary causes of accident include, ineffective management of the basic flight parameters such as airspeed, altitude, descent rate attitude, as well as thrust management. The contributory factors include the crew’s decision to continue the flight through significant changing winds associated with the prevailing weather conditions and the lack of experience of the crew to the airplane’s automated flight deck.
- The reasons of ineffective management of the automated flight deck also include Bhoja Air’s incorrect induction of cockpit crew having experience of semi automated aircraft, inadequate cockpit crew simulator training and absence of organizational cockpit crew professional competence and monitoring system.
- The incorrect decision to continue for the destination and not diverting to the alternate aerodrome despite the presence of squall line and very small gaps observed by the Captain between the active weather cells is also considered a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
- The operator’s Ops Manual (CAA Pakistan approved) clearly states to avoid active weather cells by 5 to 10 nm which was violated by the cockpit crew is also considered a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
- FO possessed average professional competence level and was due for his six monthly recurrent simulator training for Boeing 737-200 aircraft (equipped with a semi-automated flight deck). Bhoja Air requested an extension for his recurrent simulator training on 07th March, 2012. As per the existing laid down procedures of CAA Pakistan, two months extension was granted for recurrent simulator training on 09th March, 2012. The extension was granted for Boeing 737-200 aircraft, whereas the newly inducted Boeing 737-236A aircraft was equipped with automated flight deck. It is important to note that Bhoja Air did not know this vital piece of information till their cockpit crew went for simulator training to South Africa. This critical information regarding automation of the newly inducted Boeing 737-236A was not available with Flight Standard Directorate CAA, Pakistan as the information was not provided by the Bhoja Air Management.
- Therefore it is observed that due to the ignorance of Bhoja Air Management and CAA Pakistan, the said extension in respect of FO for simulator training was initially requested by former and subsequently approved by the latter. This resulted in absence of variance type training conformance of FO because of which he did not contribute positively in recovering the aircraft out of unsafe set of conditions primarily due to lack of automation knowledge, proper training and relying on captain to take remedial actions. This is also considered as one of the contributory factors in causation of accident.
- The Captain’s airline flying experience on semi automated flight deck aircraft and his selection for automated aircraft without subsequent training and monitoring to enhance his professional competence and skill, is one of the factors in causation of the accident.
- None of the cockpit crew member challenged the decision of each other to continue for the destination despite violation of Ops Manual instructions which is against the essence of CRM training.
- After experiencing the extremely adverse weather conditions, the cockpit crew neither knew nor carried out the Boeing recommended QRH and FCOM / Ops Manual procedures to handle the abnormal set of conditions / situations due to non availability of customized Boeing documents for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series).
Finalization:
- The ineffective automated flight deck management in extreme adverse weather conditions by cockpit crew caused the accident. The ineffective automated flight deck management was due to various factors including; incorrect selection of cockpit crew on account of their inadequate flying experience, training and competence level for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series), absence of formal simulator training in respect of FO for handling an automated flight deck, non-existence of cockpit crew professional competence / skill level monitoring system at operator level (Bhoja Air).
- The cockpit crew incorrect decision to continue the flight for destination and non- adherence to Boeing recommended QRH and FCOM remedial actions / procedures due to non-availability of customized aircraft documents (at Bhoja Air) for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series) contributed towards the causation of accident. The inability of CAA Pakistan to ensure automated flight deck variance type training and monitoring requirements primarily due to incorrect information provided by the Bhoja Air Management was also a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
- The aircraft accident took place as a result of combination of various factors which directly and indirectly contributed towards the causation of accident. The primary causes of accident include, ineffective management of the basic flight parameters such as airspeed, altitude, descent rate attitude, as well as thrust management. The contributory factors include the crew’s decision to continue the flight through significant changing winds associated with the prevailing weather conditions and the lack of experience of the crew to the airplane’s automated flight deck.
- The reasons of ineffective management of the automated flight deck also include Bhoja Air’s incorrect induction of cockpit crew having experience of semi automated aircraft, inadequate cockpit crew simulator training and absence of organizational cockpit crew professional competence and monitoring system.
- The incorrect decision to continue for the destination and not diverting to the alternate aerodrome despite the presence of squall line and very small gaps observed by the Captain between the active weather cells is also considered a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
- The operator’s Ops Manual (CAA Pakistan approved) clearly states to avoid active weather cells by 5 to 10 nm which was violated by the cockpit crew is also considered a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
- FO possessed average professional competence level and was due for his six monthly recurrent simulator training for Boeing 737-200 aircraft (equipped with a semi-automated flight deck). Bhoja Air requested an extension for his recurrent simulator training on 07th March, 2012. As per the existing laid down procedures of CAA Pakistan, two months extension was granted for recurrent simulator training on 09th March, 2012. The extension was granted for Boeing 737-200 aircraft, whereas the newly inducted Boeing 737-236A aircraft was equipped with automated flight deck. It is important to note that Bhoja Air did not know this vital piece of information till their cockpit crew went for simulator training to South Africa. This critical information regarding automation of the newly inducted Boeing 737-236A was not available with Flight Standard Directorate CAA, Pakistan as the information was not provided by the Bhoja Air Management.
- Therefore it is observed that due to the ignorance of Bhoja Air Management and CAA Pakistan, the said extension in respect of FO for simulator training was initially requested by former and subsequently approved by the latter. This resulted in absence of variance type training conformance of FO because of which he did not contribute positively in recovering the aircraft out of unsafe set of conditions primarily due to lack of automation knowledge, proper training and relying on captain to take remedial actions. This is also considered as one of the contributory factors in causation of accident.
- The Captain’s airline flying experience on semi automated flight deck aircraft and his selection for automated aircraft without subsequent training and monitoring to enhance his professional competence and skill, is one of the factors in causation of the accident.
- None of the cockpit crew member challenged the decision of each other to continue for the destination despite violation of Ops Manual instructions which is against the essence of CRM training.
- After experiencing the extremely adverse weather conditions, the cockpit crew neither knew nor carried out the Boeing recommended QRH and FCOM / Ops Manual procedures to handle the abnormal set of conditions / situations due to non availability of customized Boeing documents for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series).
Finalization:
- The ineffective automated flight deck management in extreme adverse weather conditions by cockpit crew caused the accident. The ineffective automated flight deck management was due to various factors including; incorrect selection of cockpit crew on account of their inadequate flying experience, training and competence level for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series), absence of formal simulator training in respect of FO for handling an automated flight deck, non-existence of cockpit crew professional competence / skill level monitoring system at operator level (Bhoja Air).
- The cockpit crew incorrect decision to continue the flight for destination and non- adherence to Boeing recommended QRH and FCOM remedial actions / procedures due to non-availability of customized aircraft documents (at Bhoja Air) for Boeing 737-236A (advanced version of Boeing 737-200 series) contributed towards the causation of accident. The inability of CAA Pakistan to ensure automated flight deck variance type training and monitoring requirements primarily due to incorrect information provided by the Bhoja Air Management was also a contributory factor in causation of the accident.
Final Report: