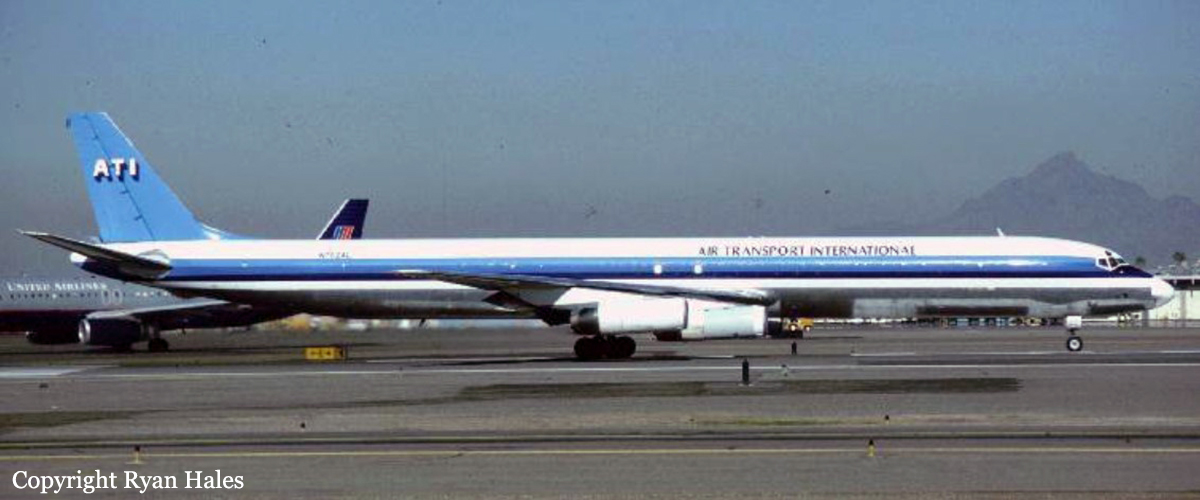
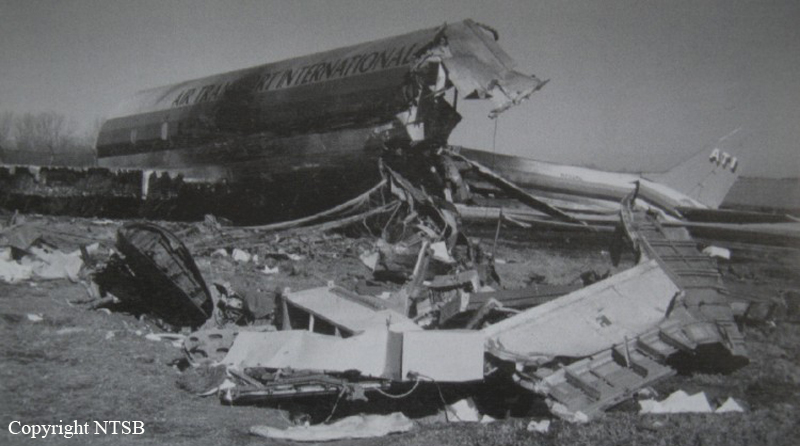
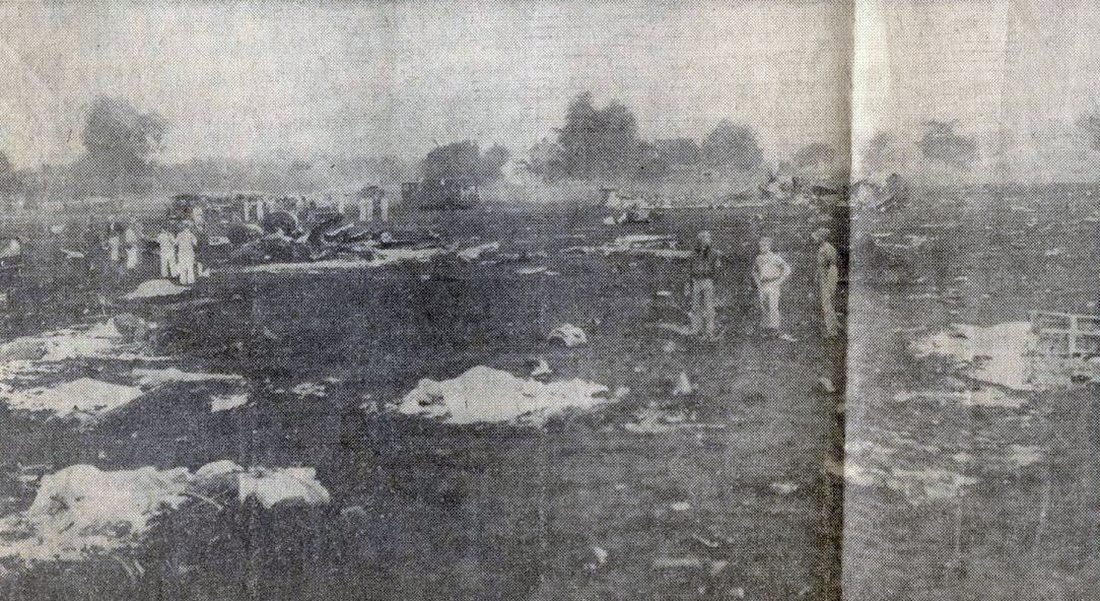
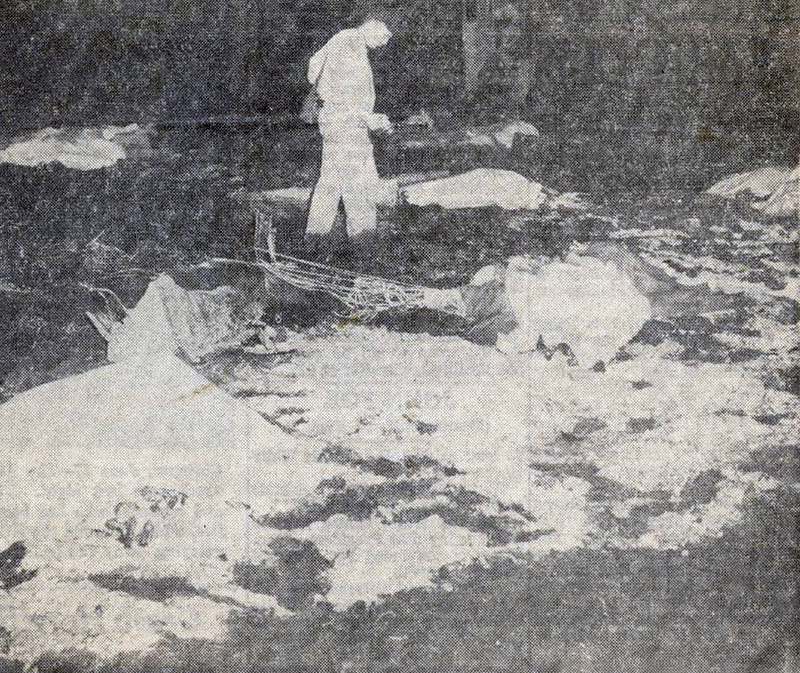
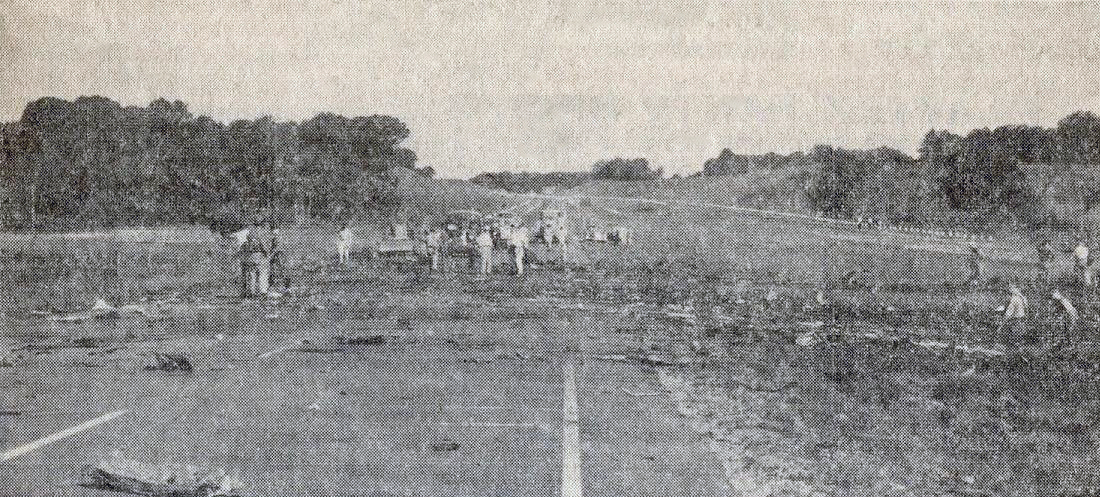
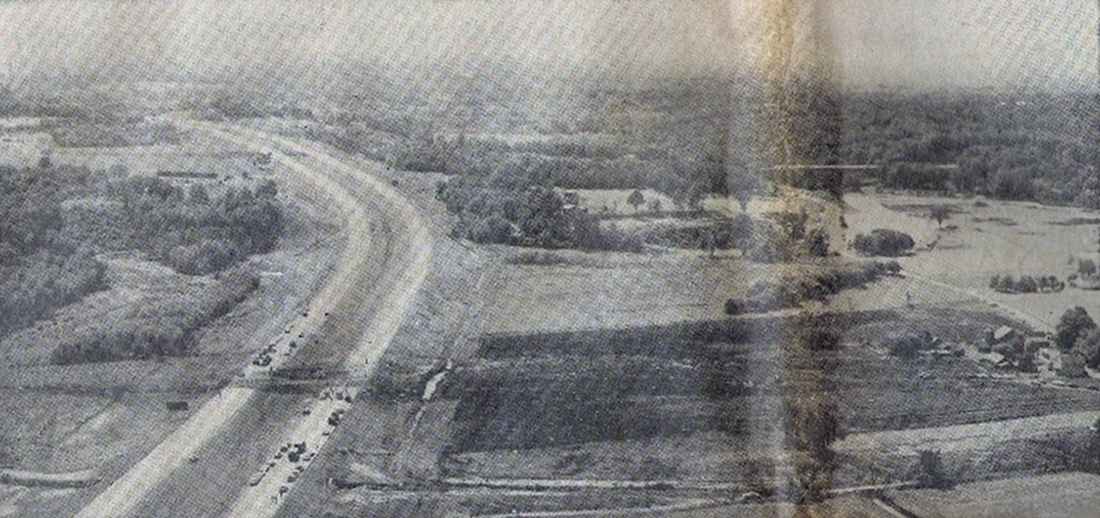
Crash of a Douglas DC-8-63CF in Kansas City: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 16, 1995 at 2027 LT
Registration:
N782AL
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kansas City - Westover
MSN:
45929
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Captain / Total hours on type:
4483.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
218
Aircraft flight hours:
77096
Aircraft flight cycles:
22404
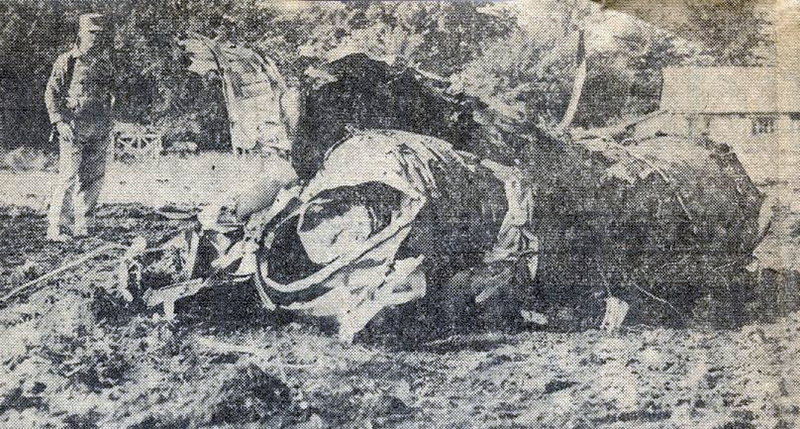
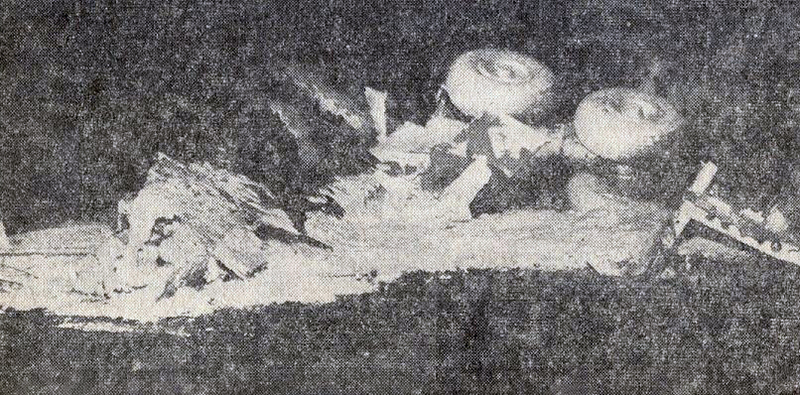
Circumstances:
The airplane crashed immediately after liftoff during a three-engine takeoff. Flightcrew had shortened rest break; rest periods not required for ferry flights. Flight crew fatigue from lack of rest, sleep, and disruption of circadian rhythms. Flightcrew did not have adequate, realistic training in three-engine takeoff techniques or procedures. Flight crew did not adequately understand three-engine takeoff procedures, including significance of vmcg. Flight engineer improperly determined vmcg speed, resulting in value 9 knots too low. During first takeoff attempt, captain applied power to asymmetrical engine too soon, was unable to maintain directional control, and rejected the takeoff. Captain agreed to modify procedure by allowing flight engineer to advance throttle, a deviation of prescribed procedure. FAA oversight of operator was inadequate because the poi and geographic inspectors were unable to effectively monitor domestic crew training and international operations. Existing far part 121 flight time limits & rest requirements that pertained to the flights that the flightcrew flew prior to the ferry flights did not apply to the ferry flights flown under far part 91. Current one-engine inoperative takeoff procedures do not provide adequate rudder availability for correcting directional deviations during the takeoff roll compatible with the achievement of maximum asymmetric thrust at an appropriate speed greater than ground minimum control speed. All three crew members were killed.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of the following factors:
- The loss of directional control by the pilot in command during the takeoff roll, and his decision to continue the takeoff and initiate a rotation below the computed rotation airspeed, resulting in a premature liftoff, further loss of control and collision with the terrain.
- The flightcrew's lack of understanding of the three-engine takeoff procedures, and their decision to modify those procedures.
- The failure of the company to ensure that the flightcrew had adequate experience, training, and rest to conduct the nonroutine flight. Contributing to the accident was the inadequacy of Federal Aviation Administration oversight of air transport international and federal aviation administration flight and duty time regulations that permitted a substantially reduced flightcrew rest period when conducting a non revenue ferry flight under 14 code of federal regulations part 91.
- The loss of directional control by the pilot in command during the takeoff roll, and his decision to continue the takeoff and initiate a rotation below the computed rotation airspeed, resulting in a premature liftoff, further loss of control and collision with the terrain.
- The flightcrew's lack of understanding of the three-engine takeoff procedures, and their decision to modify those procedures.
- The failure of the company to ensure that the flightcrew had adequate experience, training, and rest to conduct the nonroutine flight. Contributing to the accident was the inadequacy of Federal Aviation Administration oversight of air transport international and federal aviation administration flight and duty time regulations that permitted a substantially reduced flightcrew rest period when conducting a non revenue ferry flight under 14 code of federal regulations part 91.
Final Report: