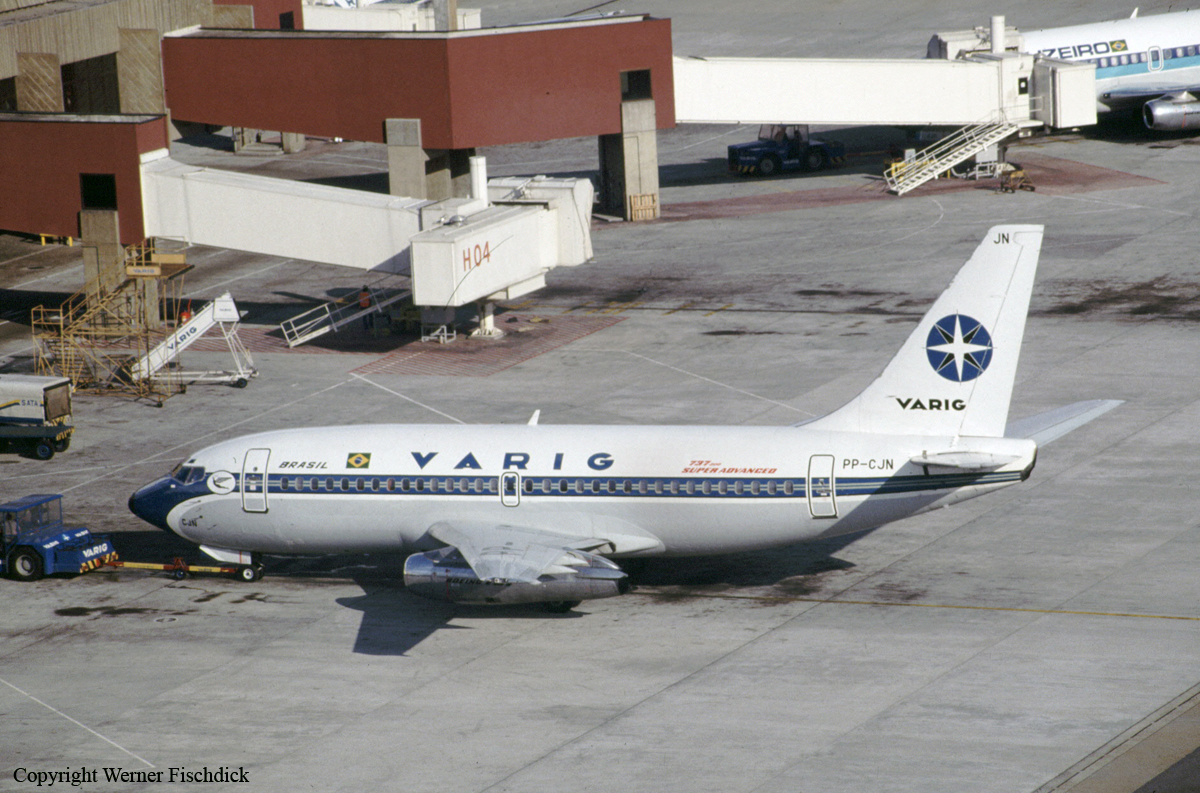
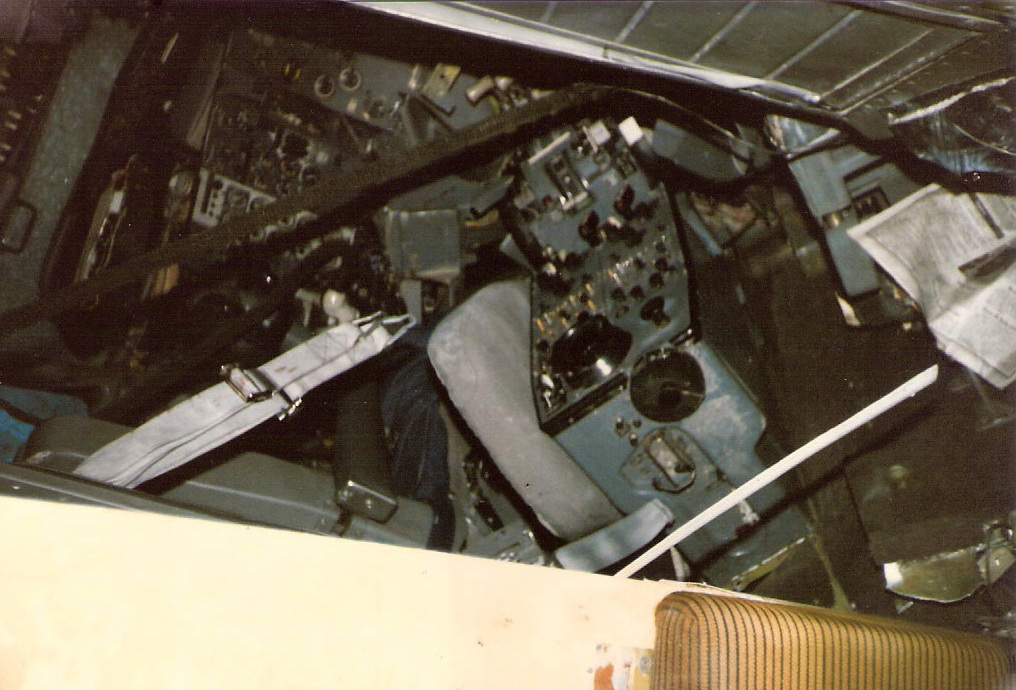
Crash of a Boeing 737-2C3 in Goiânia
Date & Time:
Sep 16, 2001 at 1053 LT
Registration:
PP-CJN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
São Paulo – Goiânia
MSN:
21012
YOM:
1974
Flight number:
RG2240
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
62
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Aircraft flight hours:
68500
Aircraft flight cycles:
65500
Circumstances:
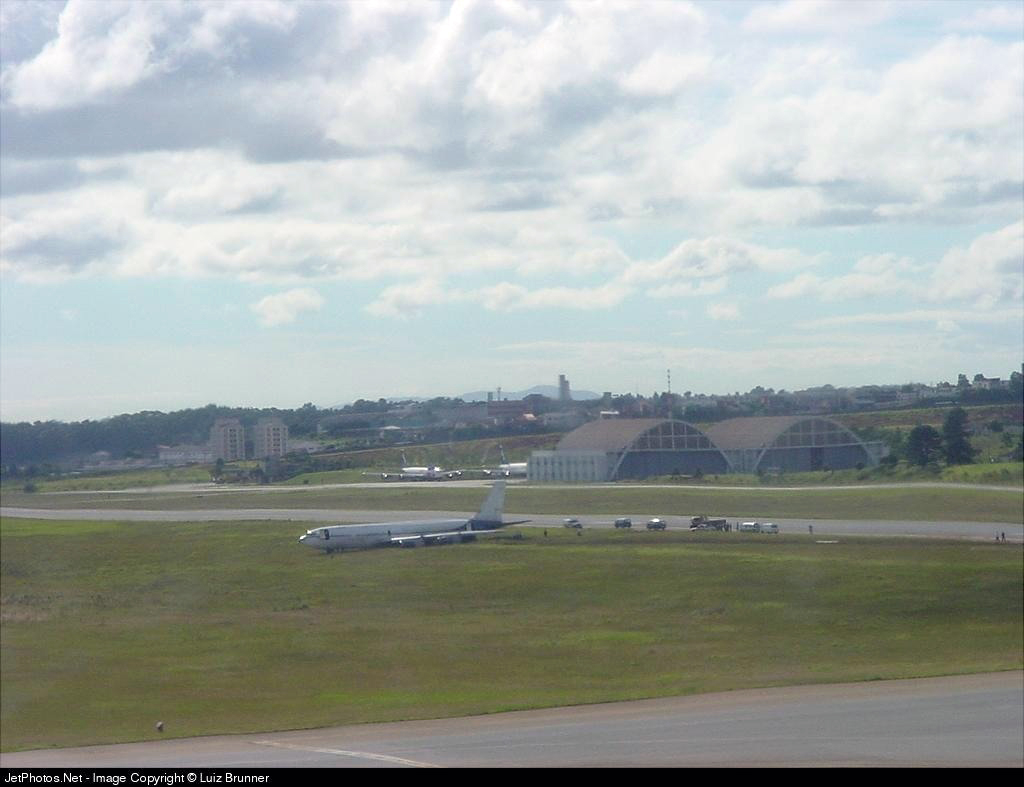
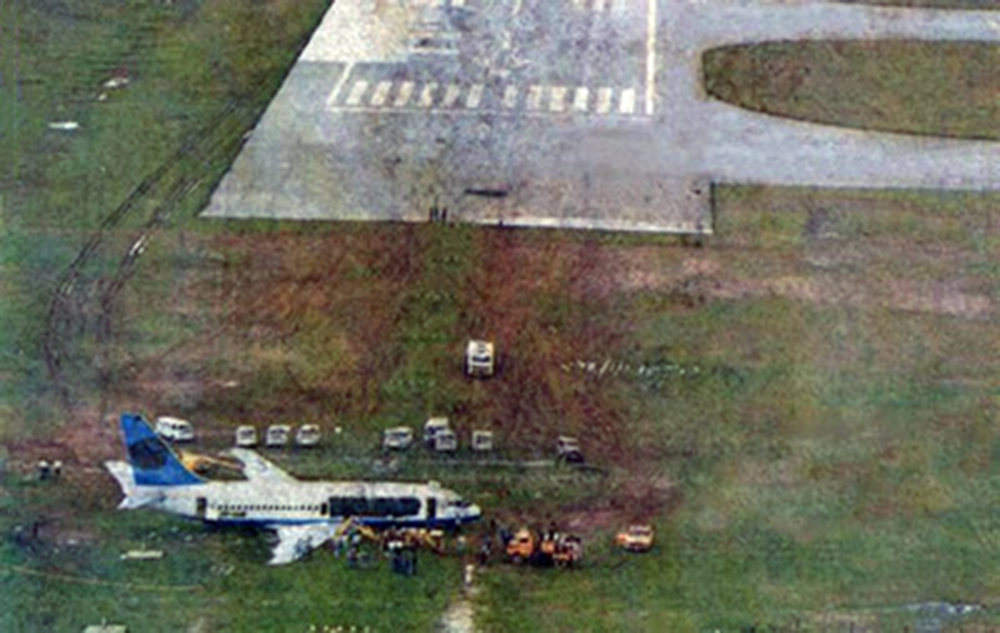
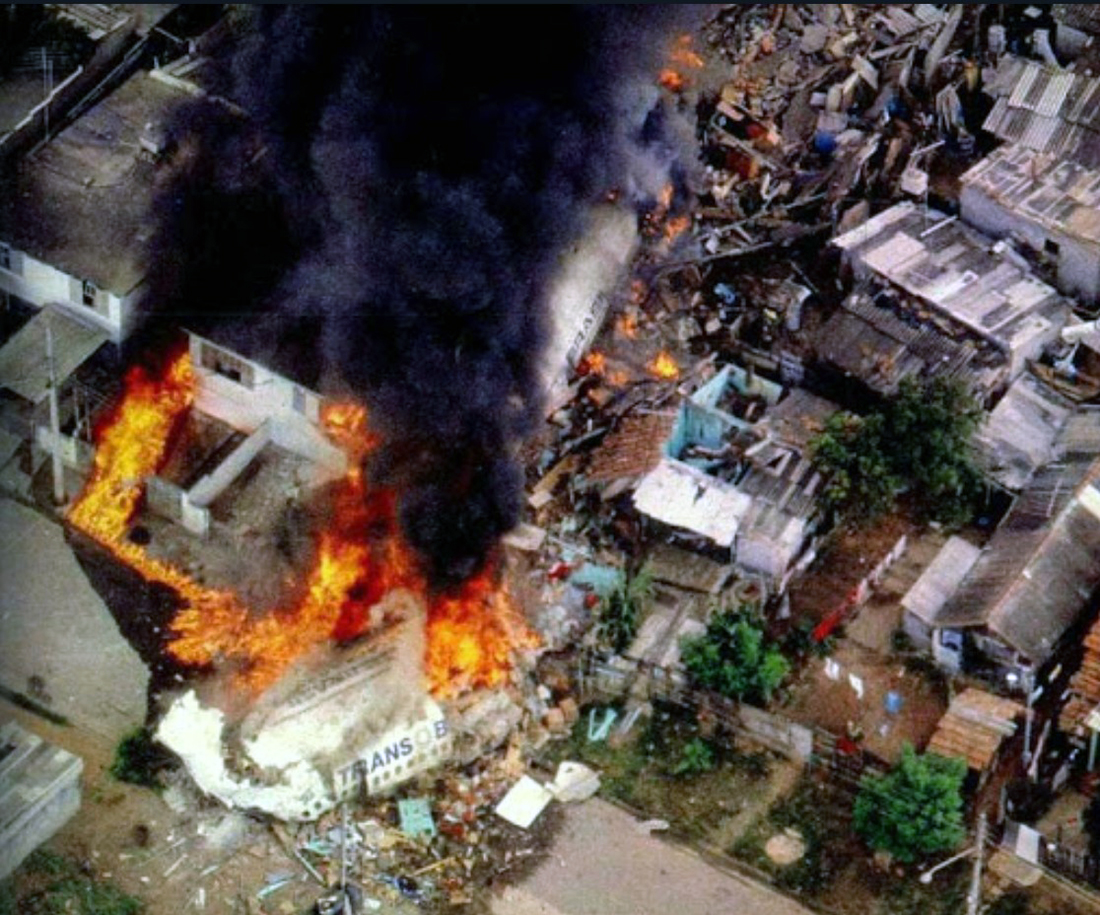
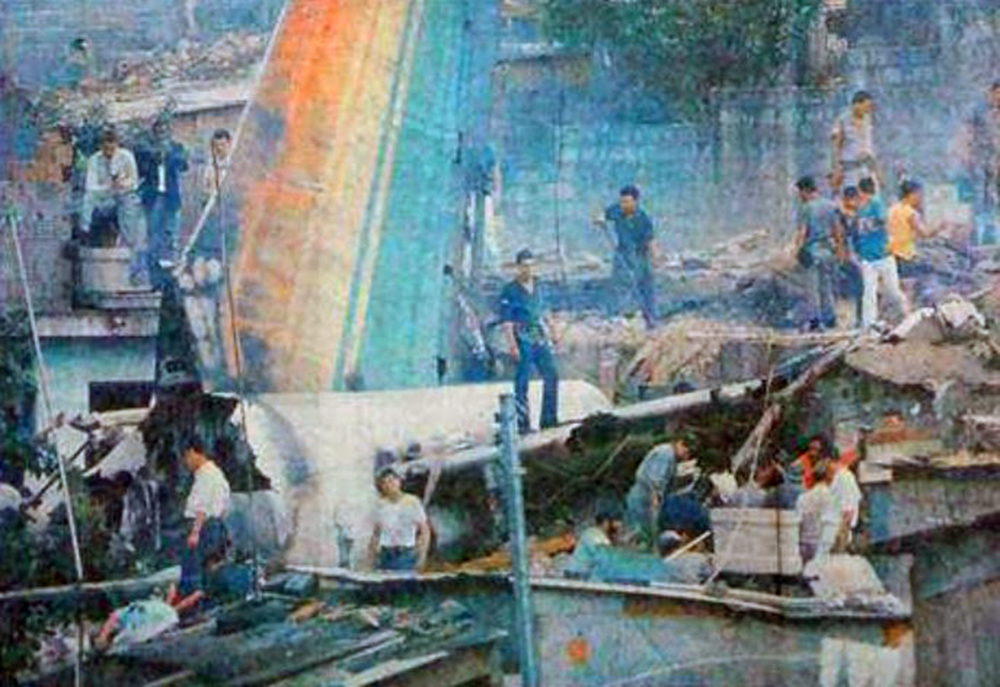
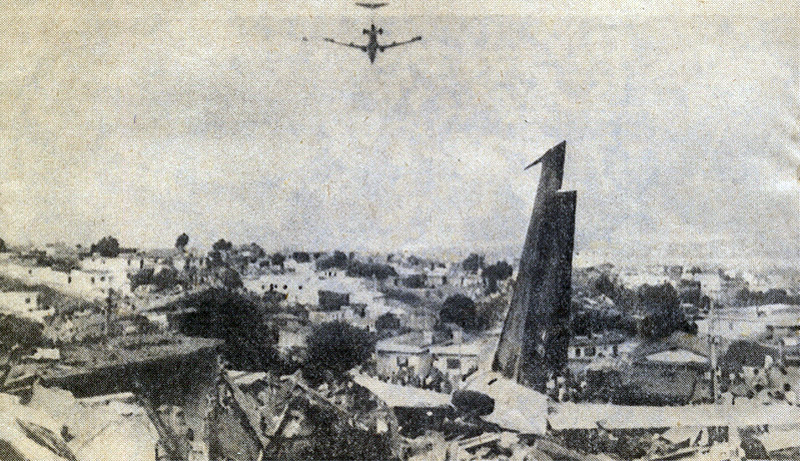
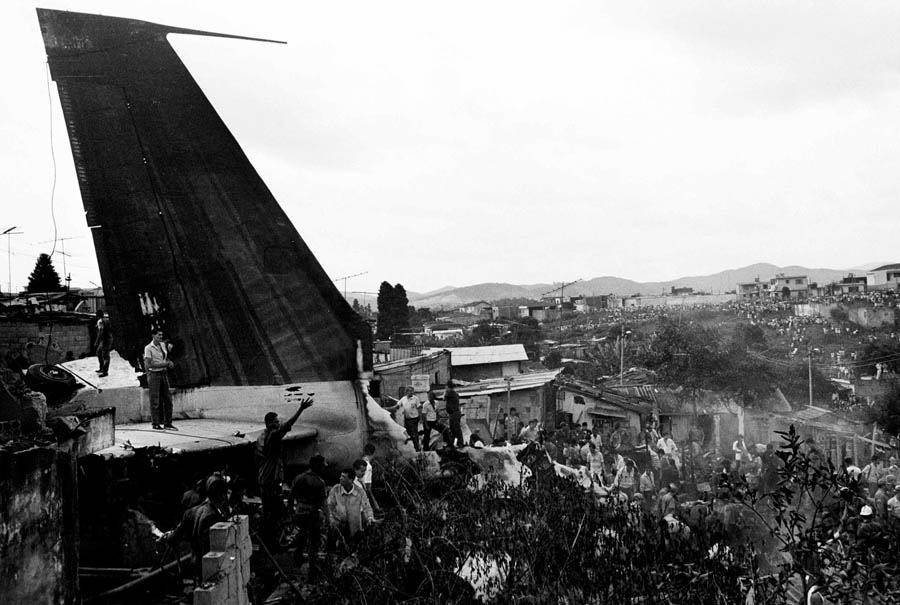
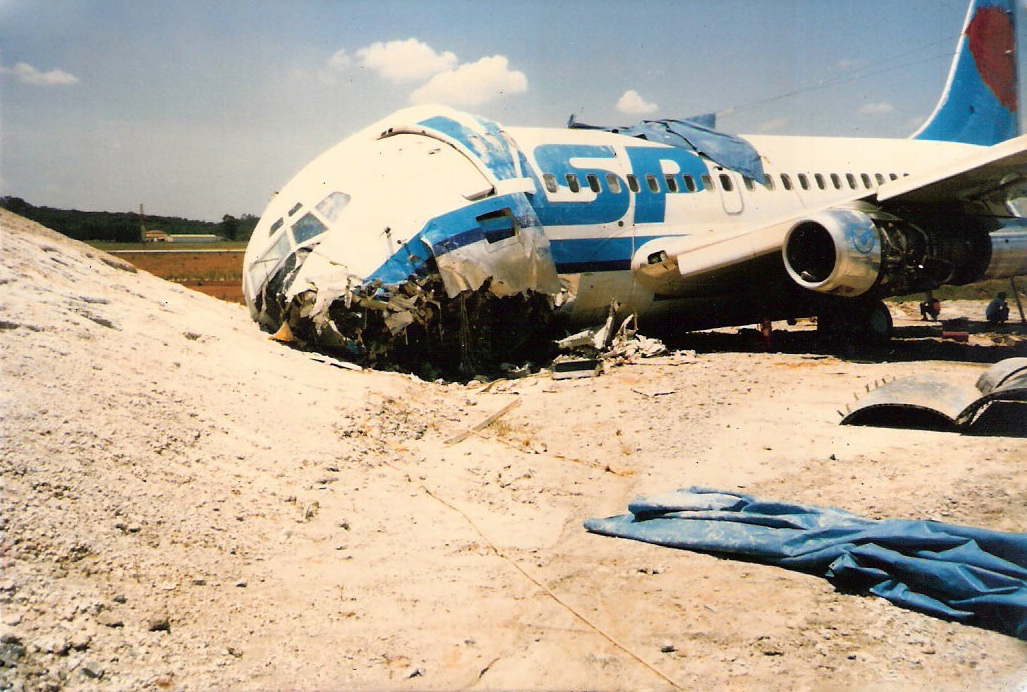
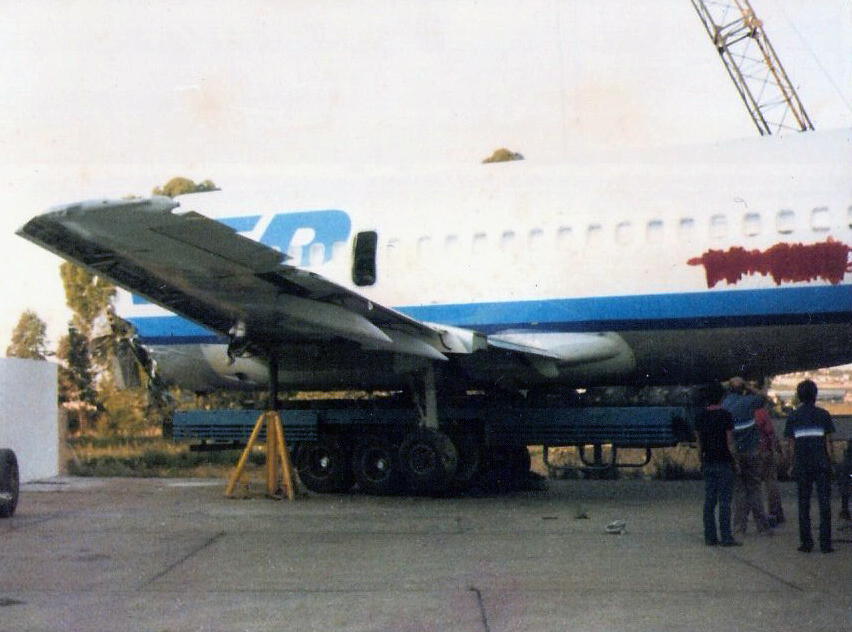
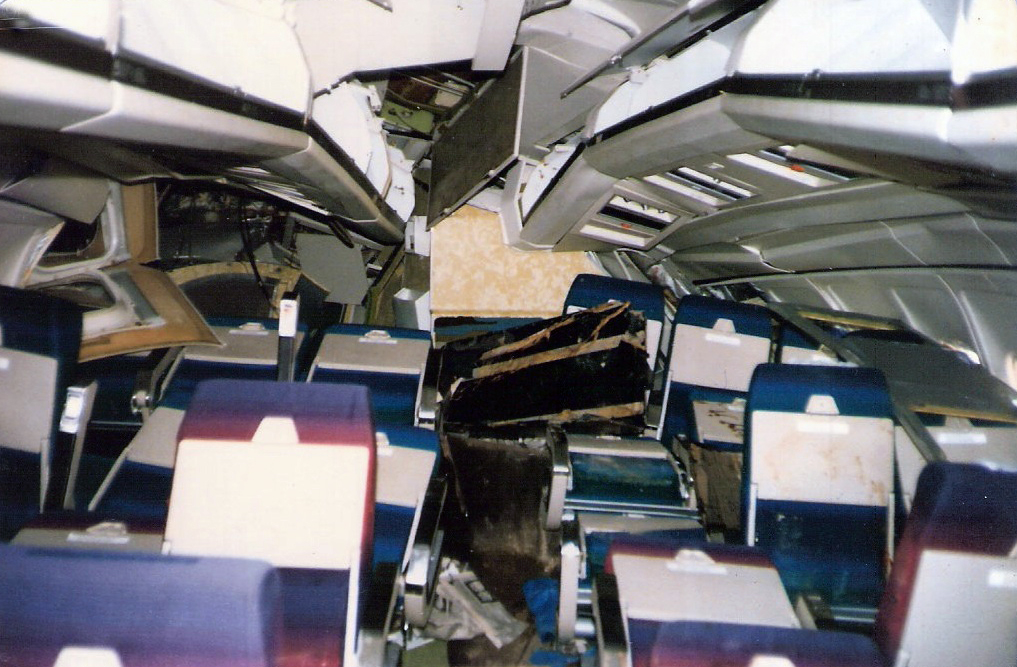
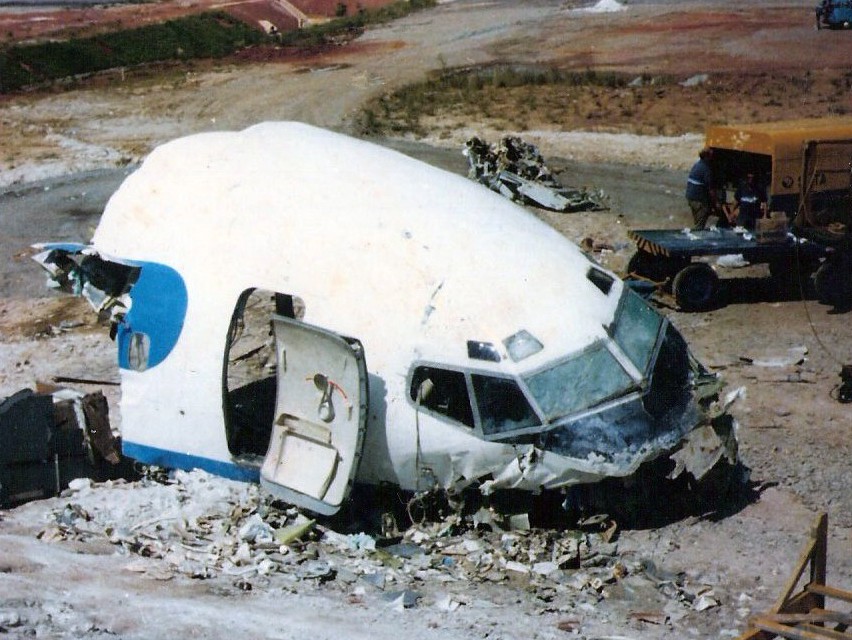
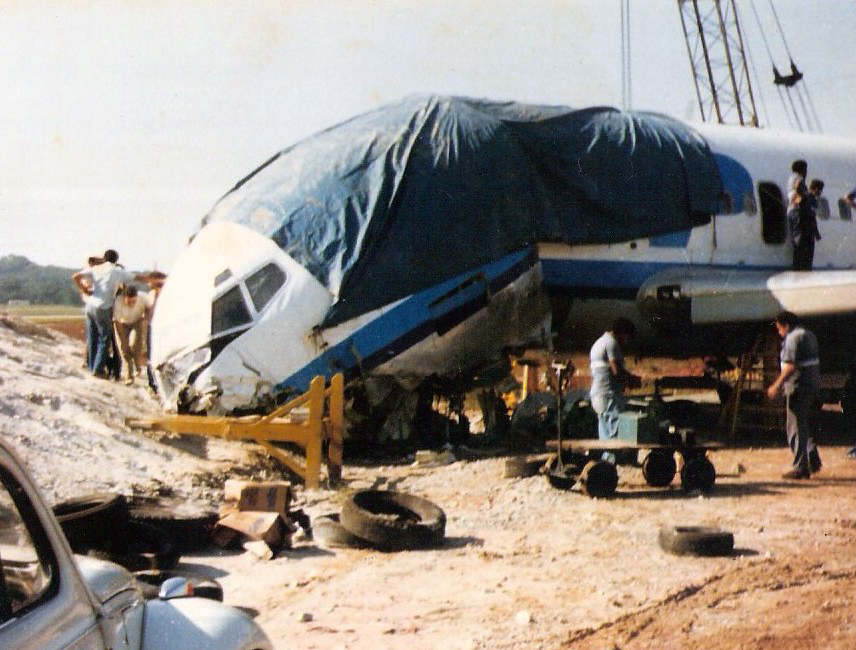
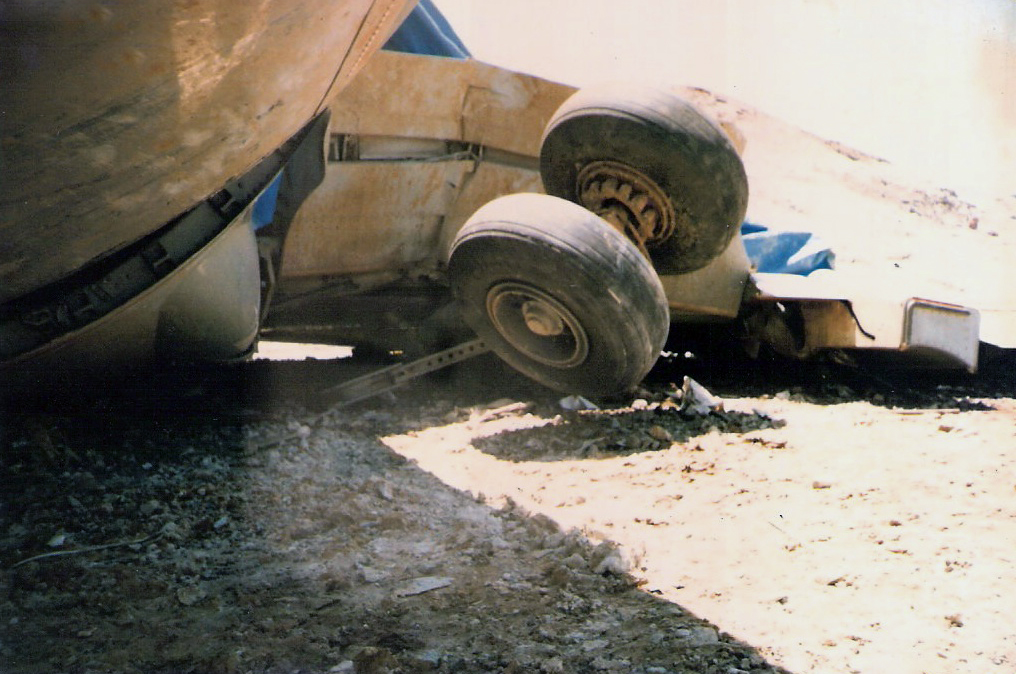
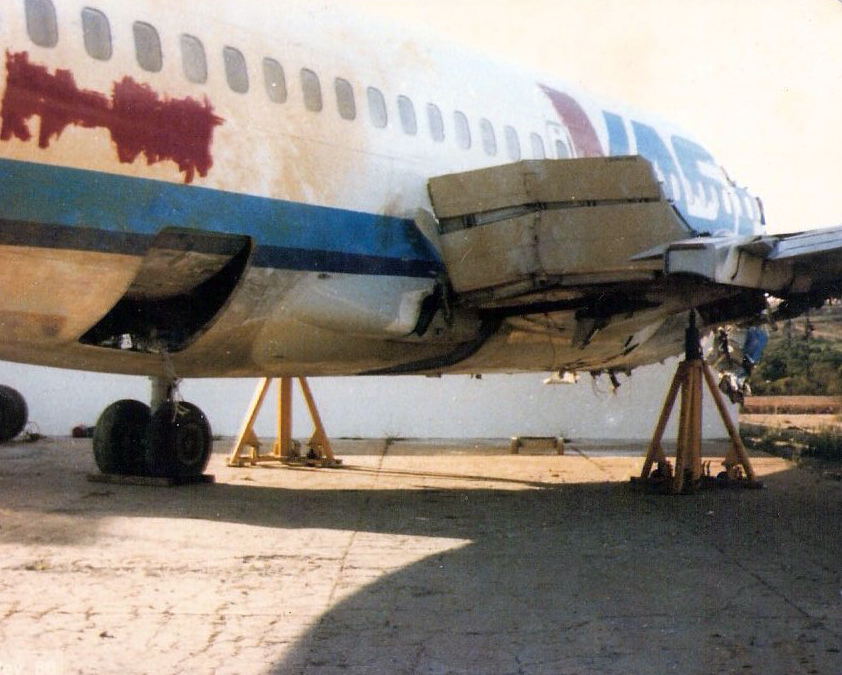
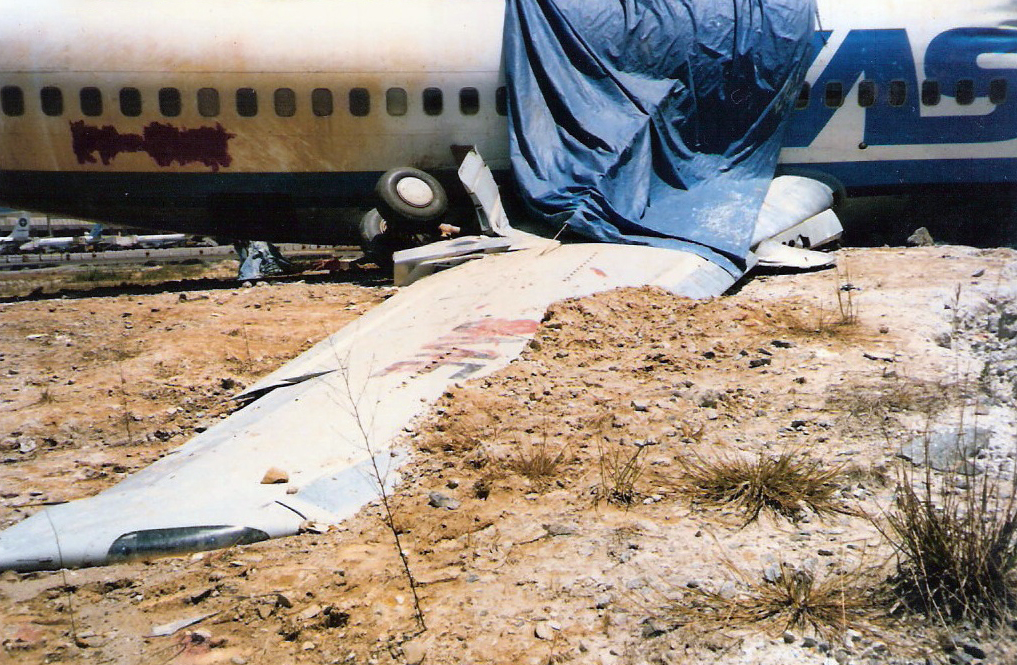
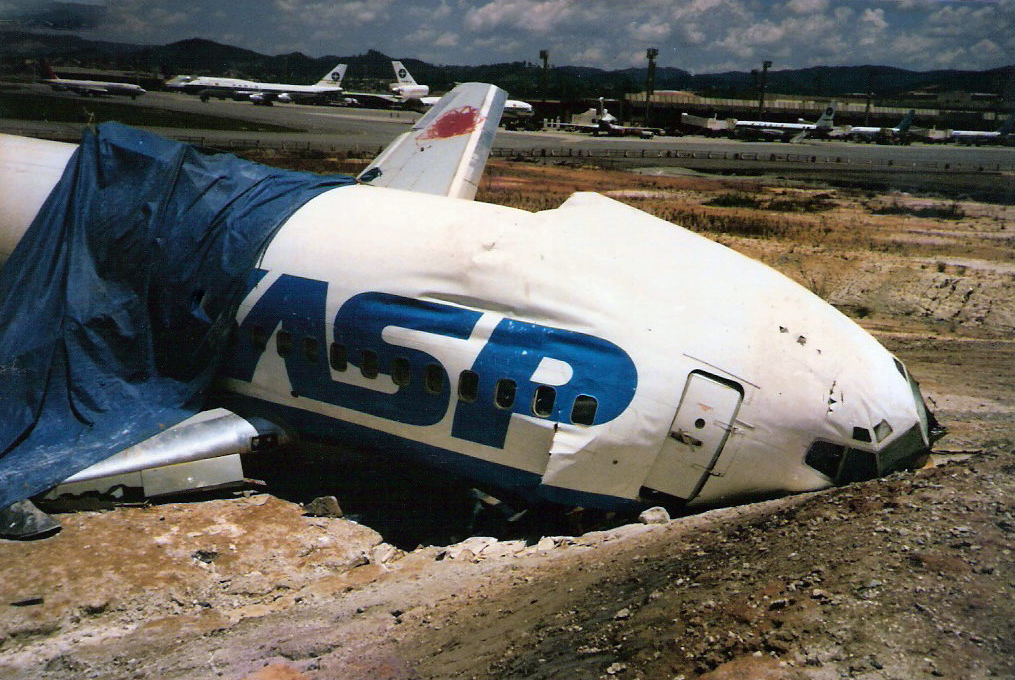
On final approach to Goiânia-Santa Genoveva Airport, the crew encountered poor weather conditions with a limited visibility due to rain. The aircraft landed about 500 metres past the runway threshold but as it was misaligned, the right main gear touched down on the left side of the runway. The crew attempted to steer the plane back onto the runway when the right main gear collapsed. The aircraft went out of control, lost its right engine then its nose gear and came to rest on the runway. All 67 occupants evacuated safely.
Probable cause:
Wrong approach configuration on part of the crew who continued the approach while the aircraft was not properly aligned with the runway centerline.