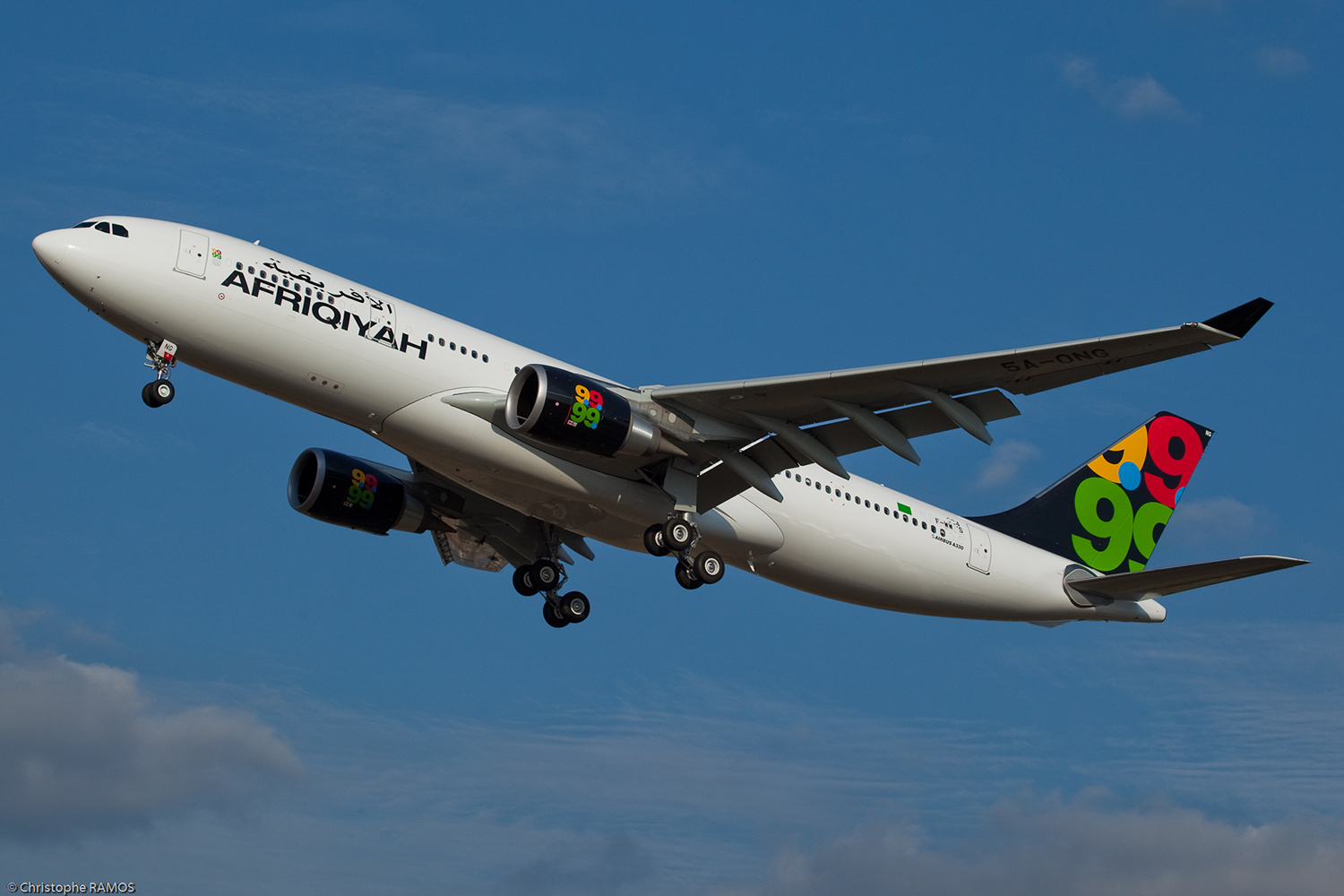
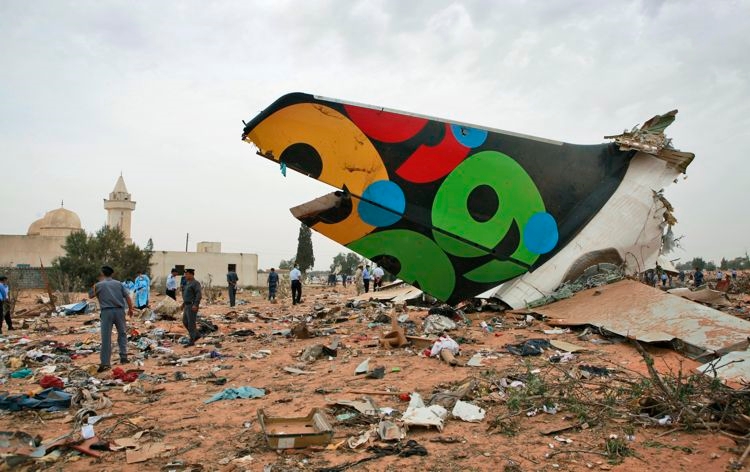
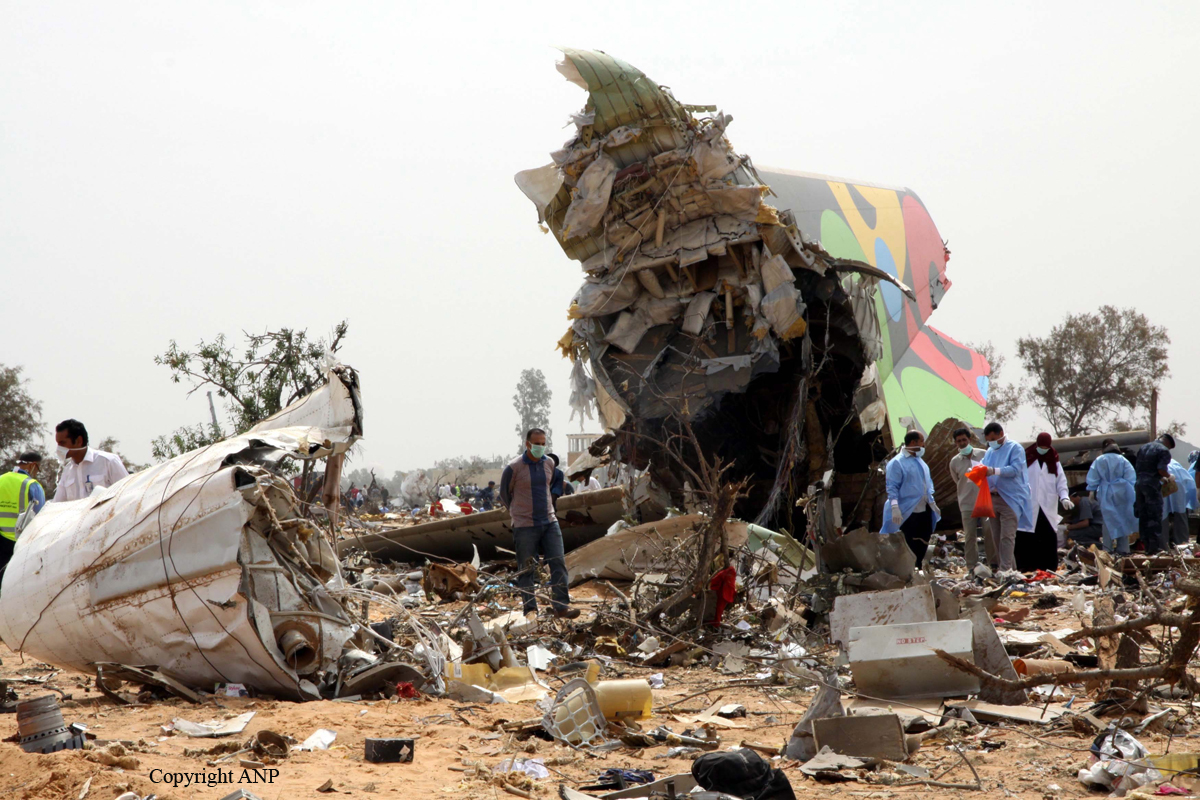
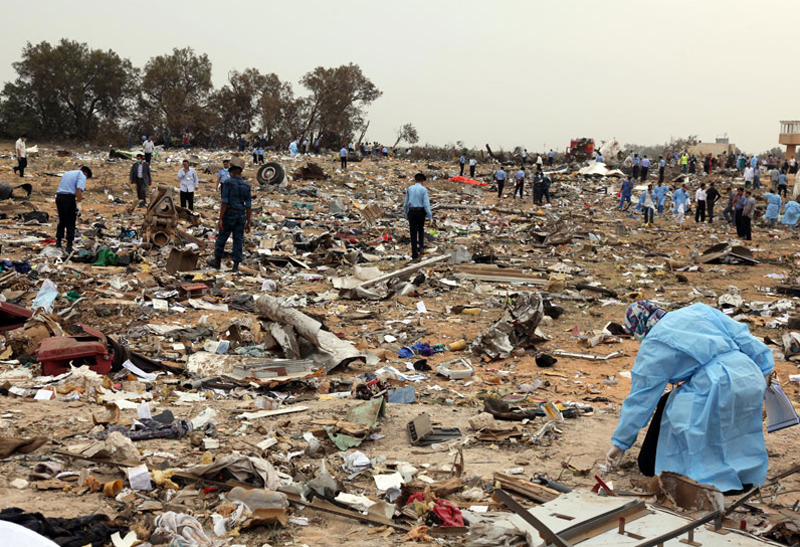
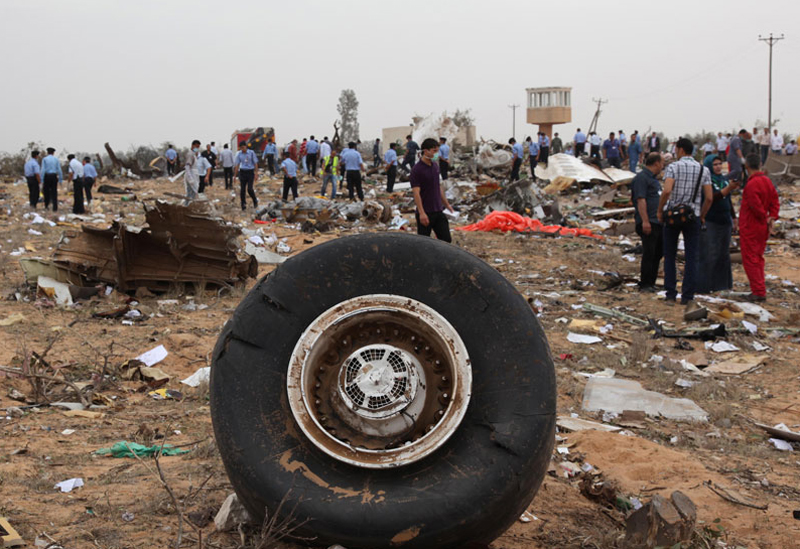
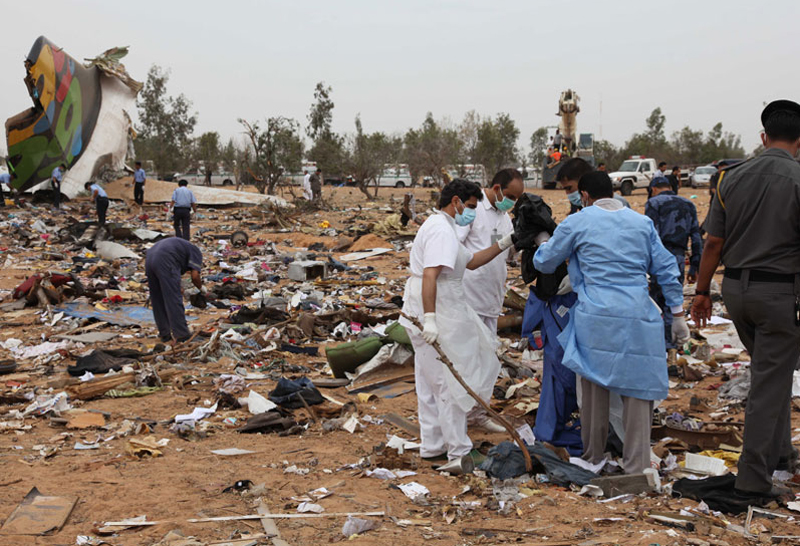
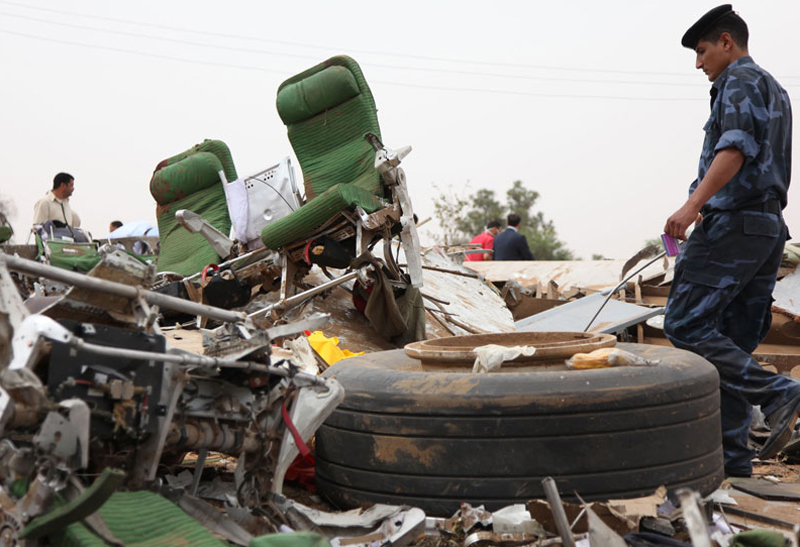
Crash of an Airbus A330-202 in Tripoli: 103 killed
Date & Time:
May 12, 2010 at 0601 LT
Registration:
5A-ONG
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Johannesburg - Tripoli - London
MSN:
1024
YOM:
2009
Flight number:
AAW771
Crew on board:
11
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
93
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
103
Captain / Total hours on type:
516.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
516
Aircraft flight hours:
2175
Aircraft flight cycles:
572
Circumstances:
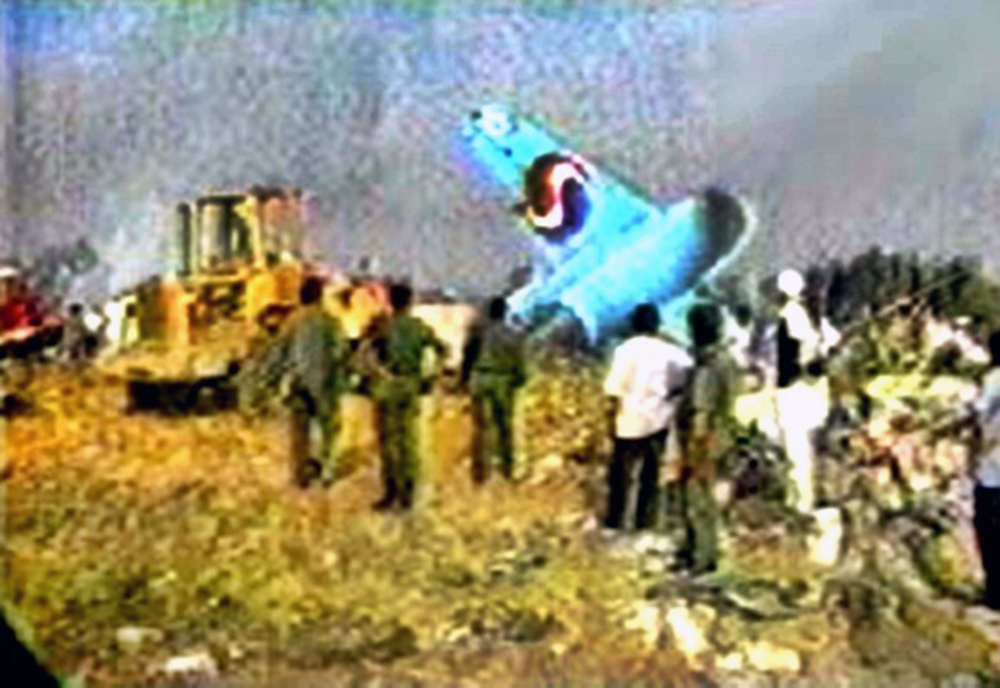
The aircraft was on a schedule flight from O. R. Tambo International Airport - Johannesburg (South Africa) to London, with an intermediate stop at Tripoli international Airport, Libya. The Aircraft took off on May 11th 2010 at 19:25 UTC as flight number 8U771/AAW771. There were three cockpit crew, eight cabin crew, and 93 passengers on board, with fifty thousand kg of fuel during takeoff role and the Aircraft mass was 187,501 kg. During final approach towards runway 09 at Tripoli international Airport, the crew announced go-around and initiated the miss approach procedure with the knowledge and confirmation of Tripoli tower. During the missed approach phase, the Aircraft responded to the crew’s inputs, velocity and altitude increased above the MDA, then the aircraft descended dramatically until collided with the ground about 1,200 meters from the threshold of the runway 09 and 150 meters to the right of its centerline, impact and post impact fire caused complete destruction to the Aircraft. A boy aged 8 was injured while 103 other occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
A final approach carried out in common managed guidance mode should have relieved the crew of their tasks. The limited coordination and cooperation between the two crew members, especially the change into vertical selected guidance mode by the PF, probably led to a lack of a common action plan. The lack of feedback from the 28 April 2010 flight, flown by the same crew on the same aircraft, did not allow them to anticipate the potential risks associated with managing non-precision approaches. The pilots’ performance was likely impaired because of fatigue, but the extent of their impairment and the degree to which it contributed to the performance deficiencies that occurred during the flight cannot be conclusively determined. During the go-around, the crew was surprised not to acquire visual references. On one hand the crew feared exceeding the aircraft’s speed limits in relation to its configuration, and on the other hand they were feeling the effects of somatogravic illusion due to the aircraft acceleration. This probably explains the aircraft handling inputs, mainly nose-down inputs, applied during the go-around. These inputs were not consistent with what is expected in this flight phase. The degraded CRM did not make it possible for either crew member to identify and recover from the situation before the collision with the ground, even when the TAWS warnings were activated close to the ground.
Based on elements from the investigation, the accident resulted from:
- The lack of common action plan during the approach and a final approach continued below the MDA, without ground visual reference acquired.
- The inappropriate application of flight control inputs during a go- around and on the activation of TAWS warnings,
- The lack of monitoring and controlling of the flight path.
These events can be explained by the following factors:
- Limited CRM on approach that degraded during the missed approach. This degradation was probably amplified by numerous radio-communications during the final approach and the crew’s state of fatigue,
- Aircraft control inputs typical in the occurrence of somatogravic perceptual illusions,
- Inappropriate systematic analysis of flight data and feedback mechanism within the AFRIQIYAH Airways.
- Non adherence to the company operation manual, SOP and standard terminology.
In addition, the investigation committee found the following as contributing factors to the accident:
- Weather available to the crew did not reflect the actual weather situation in the final approach segment at Tripoli International Airport.
- In adequacy of training received by the crew.
- Occupancy of tower frequency by both air and ground movements control.
Based on elements from the investigation, the accident resulted from:
- The lack of common action plan during the approach and a final approach continued below the MDA, without ground visual reference acquired.
- The inappropriate application of flight control inputs during a go- around and on the activation of TAWS warnings,
- The lack of monitoring and controlling of the flight path.
These events can be explained by the following factors:
- Limited CRM on approach that degraded during the missed approach. This degradation was probably amplified by numerous radio-communications during the final approach and the crew’s state of fatigue,
- Aircraft control inputs typical in the occurrence of somatogravic perceptual illusions,
- Inappropriate systematic analysis of flight data and feedback mechanism within the AFRIQIYAH Airways.
- Non adherence to the company operation manual, SOP and standard terminology.
In addition, the investigation committee found the following as contributing factors to the accident:
- Weather available to the crew did not reflect the actual weather situation in the final approach segment at Tripoli International Airport.
- In adequacy of training received by the crew.
- Occupancy of tower frequency by both air and ground movements control.
Final Report: