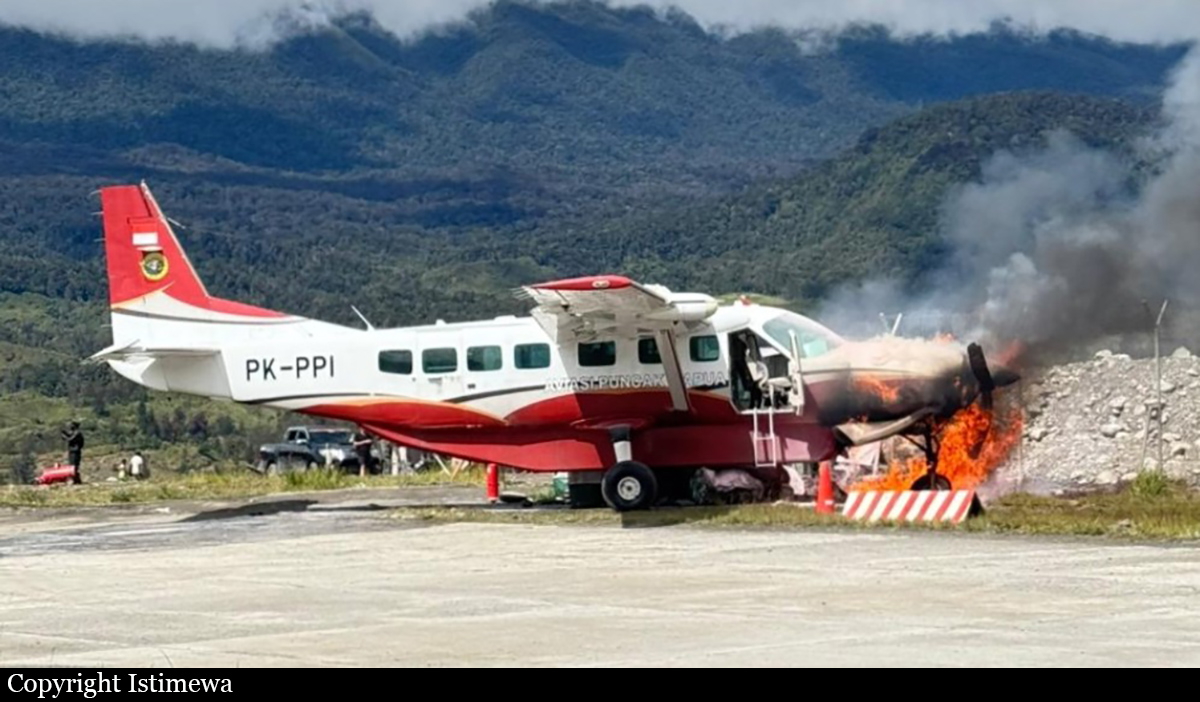
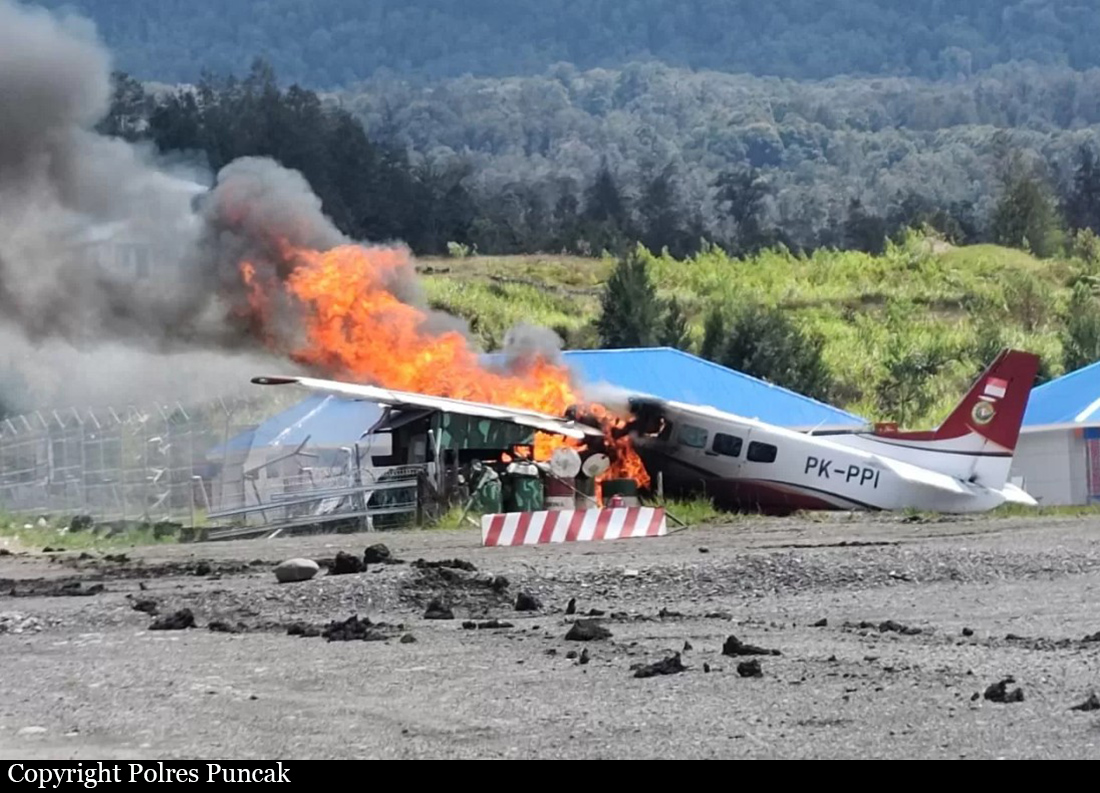
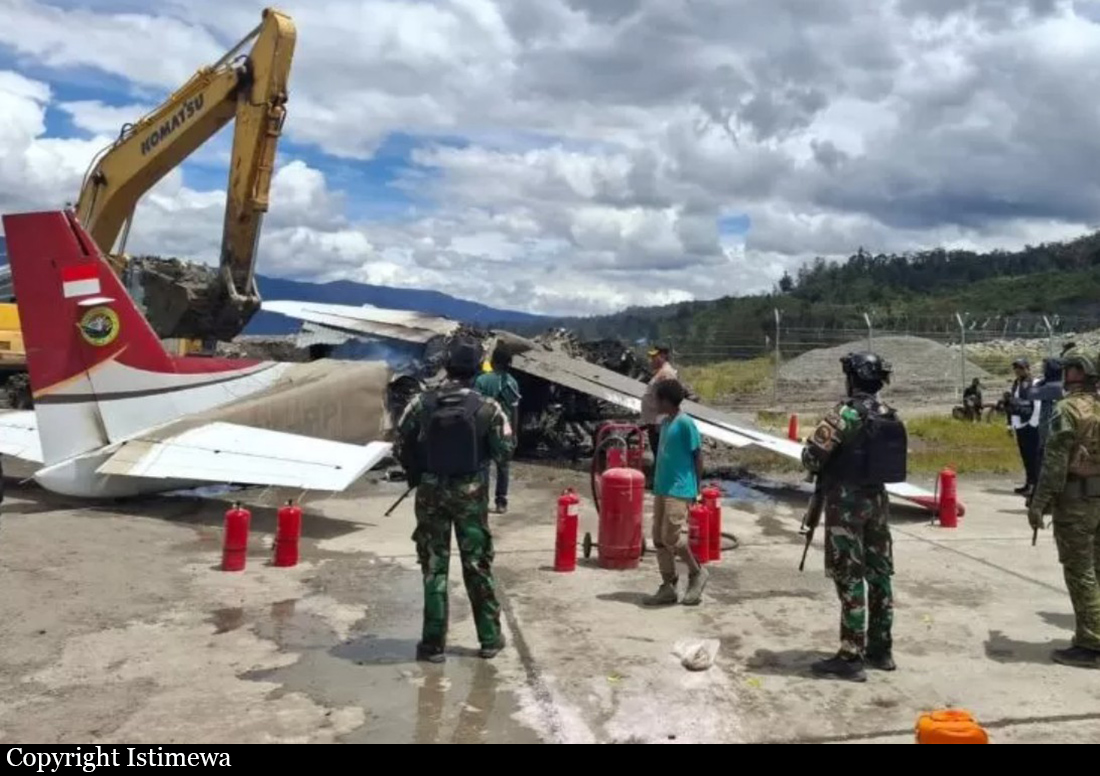
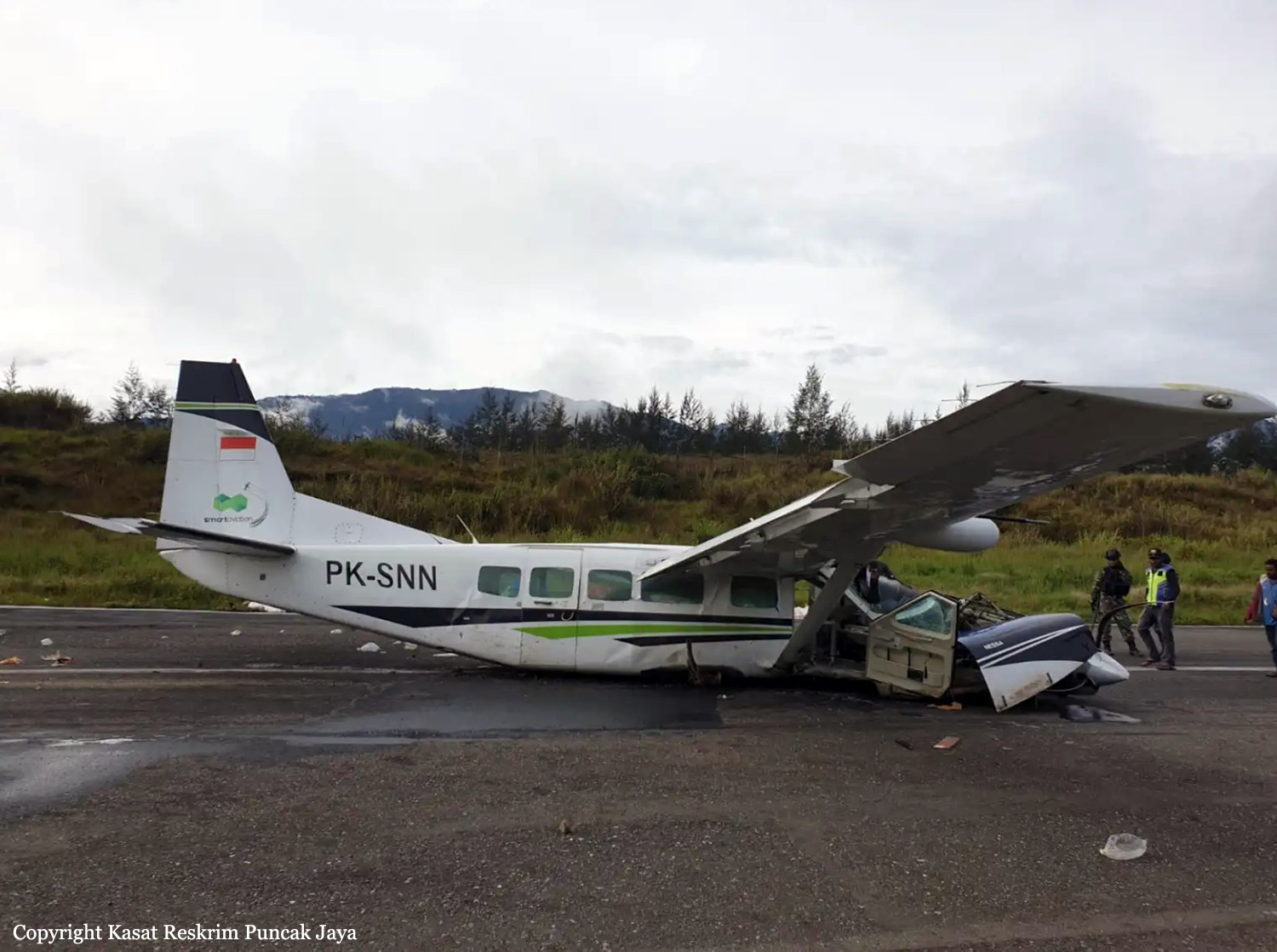
Circumstances:
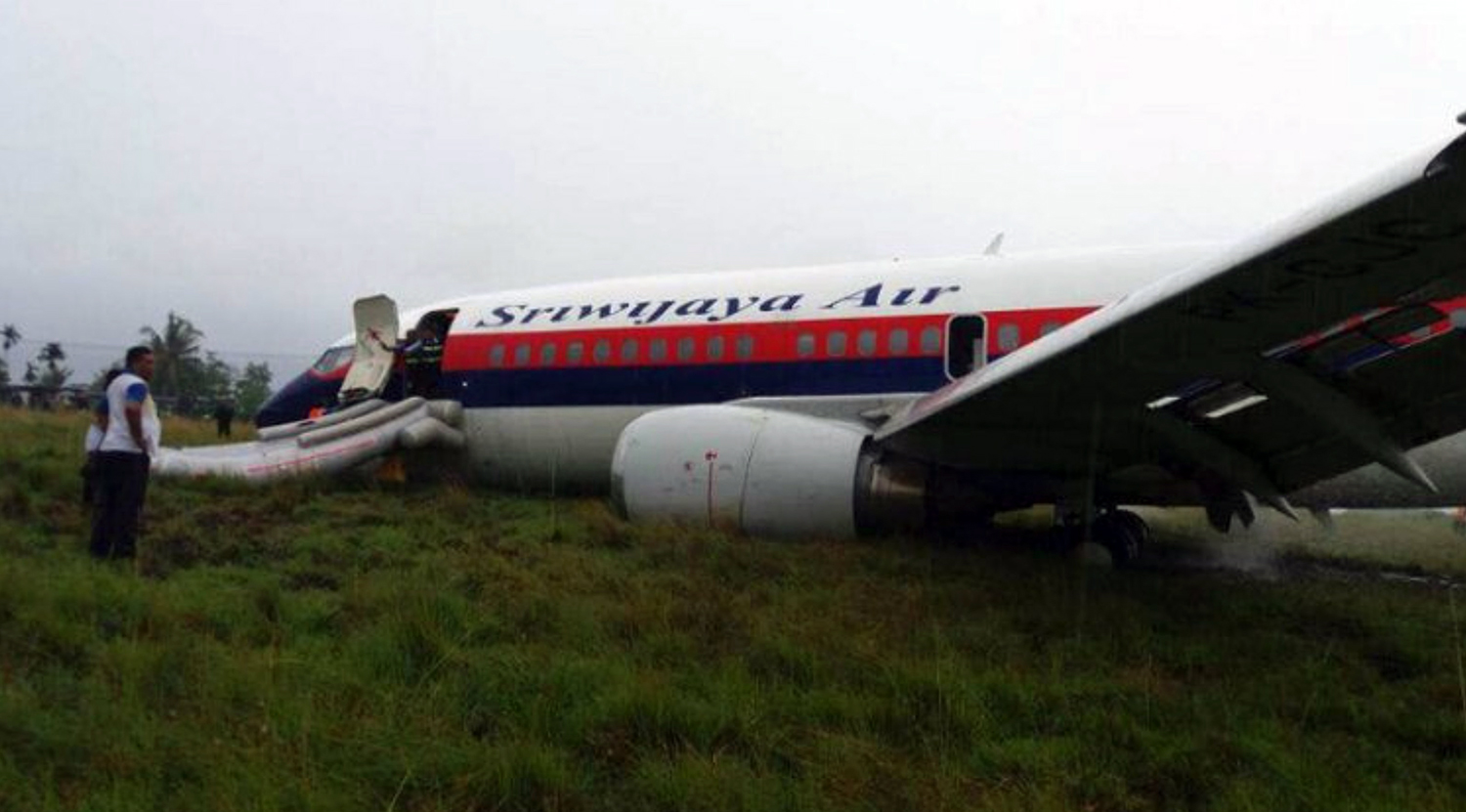
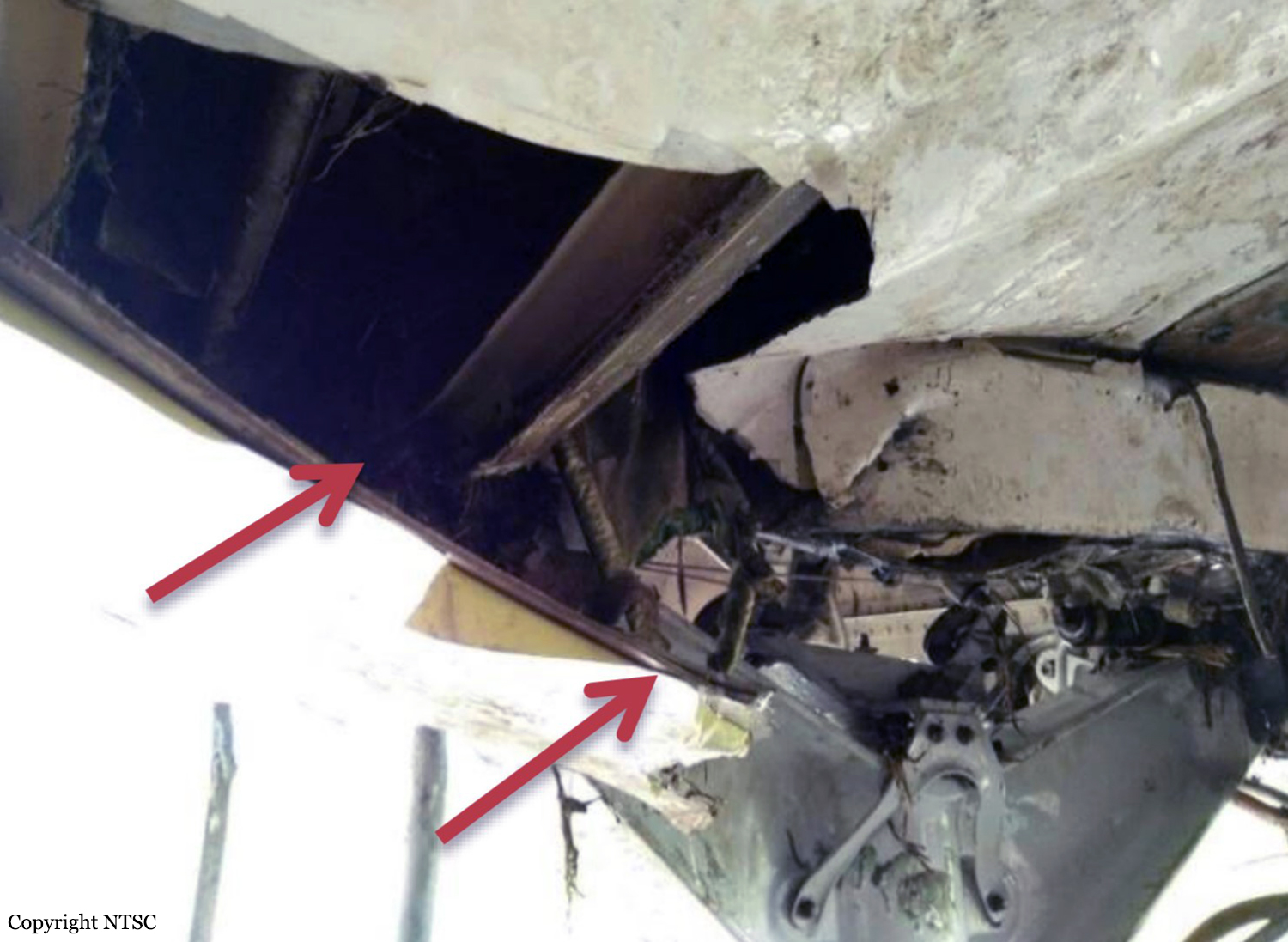
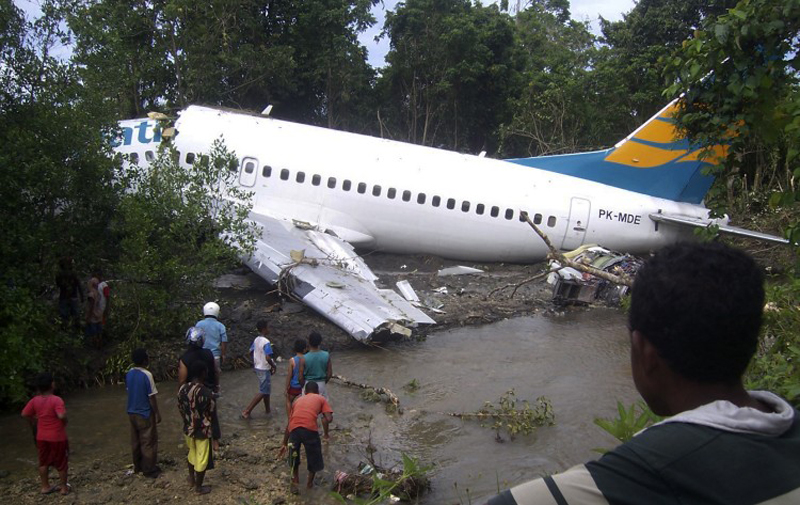
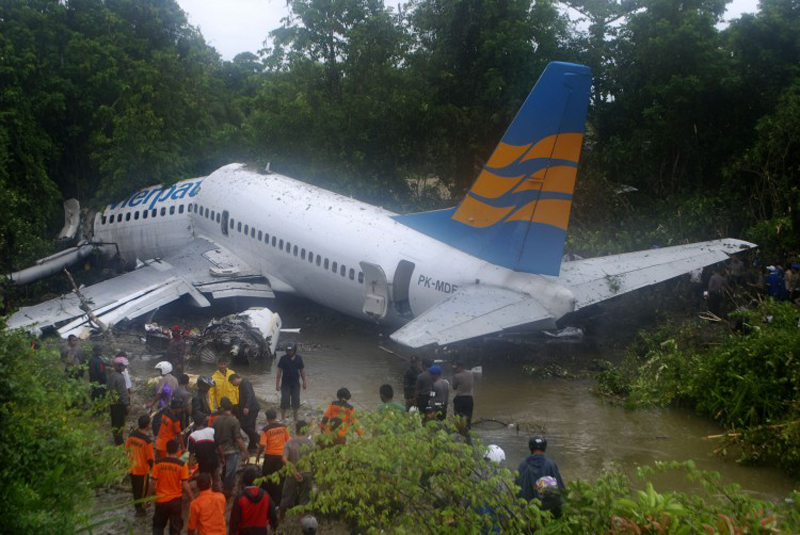
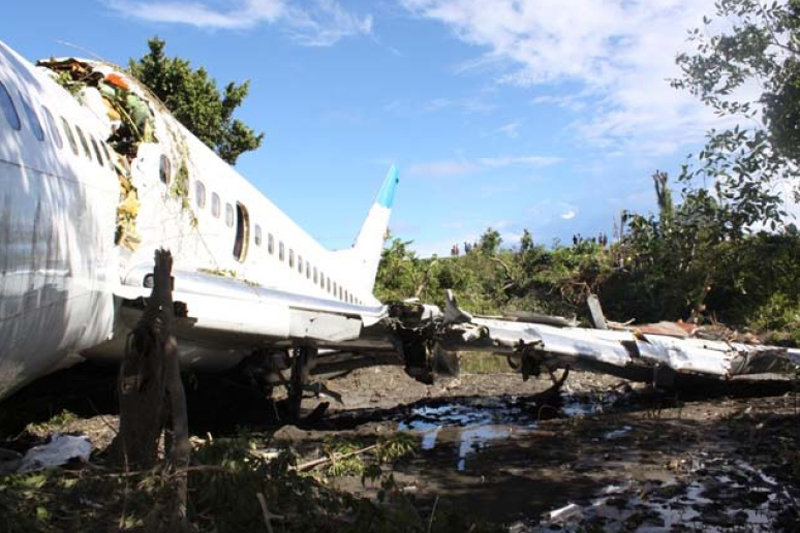
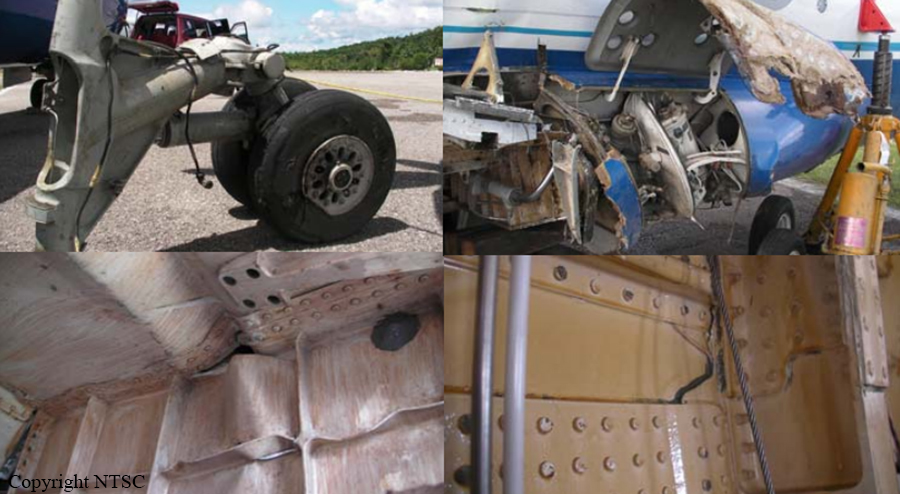
On 13 April 2010, a Boeing B737-300 aircraft registered PK-MDE was being operated by PT. Merpati Nusantara Airline as a scheduled passenger flight MZ 836, from Hasanuddin Airport, Makassar, Sulawesi to Rendani Airport, Manokwari, Papua. It made a transit stop at Domine Eduard Osok Airport, Sorong, Papua. The aircraft departed from Makassar at 2010 UTC and landed at Sorong at 2214 UTC. The scheduled departure time from Sorong was 2235, but due to heavy rain over Manokwari, the departure was delayed for about two hours. The pilot in command was the pilot flying, and the copilot, who also held a command rating on the aircraft, was the support/monitoring pilot. The aircraft subsequently departed Sorong 2 hours and 43 minutes later, at 0118. The observed weather report issued by Badan Meteorologi dan Geofisika (BMG) Manokwari for takeoff and landing at 0100 indicated that the weather was “continuous slight rain, horizontal visibility of 3 to 4 kilometers, cloud overcast cumulus-stratocumulus, westerly wind at 5 knots”. The aircraft’s dispatch release from Sorong indicated that the flight was planned under the Instrument Flight Rules (IFR). The destination, Manokwari, had no published instrument approach procedure. Terminal area operations, including approach and landing, were required to be conducted under the Visual Flight Rules (VFR). At 0146 the crew made the first direct contact with Rendani Radio and reported their position as 14 Nm from Manokwari, and maintaining altitude 10,500 feet. Following this radio contact, Rendani Radio informed the crew that the weather was continuous slight rain, visibility 3 kilometers, cloud overcast with cumulus stratocumulus at 1,400 feet, temperature 24 degrees Celsius, QNH 1012 hectopascals. The transcript of the Rendani Radio communications with the aircraft indicated that controller then instructed the crew to descend and joint right downwind for runway 35, and to report when overhead the airport. Shortly after, the crew reported overhead the airport at 5,000 feet. The controller then instructed the crew to report when they were on final approach for runway 35. The crew acknowledged this instruction. At 0154 the crew reported that they were on final for runway 35. The controller informed them that the wind was calm, runway condition was wet and clear. The crew read back the wind condition and that the runway was clear, but did not mention the wet runway condition. According to the Rendani Airport Administrator’s report to the investigation, the aircraft was observed to make a normal touchdown on the runway at about 0155, about 120 meters from the approach end of runway 35. The report stated that the aircraft’s engine reverser sound was not heard during landing roll. Witnesses on board the aircraft also stated that the aircraft made a smooth landing, and the engine reversers were not heard during the landing roll. During the landing roll, the aircraft veered to the left about 140 meters from the end of runway 35, then overran the departure end of runway 35. At about 0156 it came to a stop 205 meters beyond the end of the runway in a narrow river; the Rendani River. The Observed Weather Report issued by BMG Manokwari for takeoff and landing at 0200 (4 minutes after the accident) indicated that the weather was continuous moderate rain, with a horizontal visibility of 4 kilometers, cloud overcast cumulus stratocumulus, south-westerly wind at 5 knots. The airport rescue and fire fighting unit was immediately deployed to assist the post crash evacuation. Due to the steep terrain 155 meters from the end of runway 35, the rescuers had to turn back and use the airport’s main road to reach the aircraft. The accident site was in an area of shallow muddy water surrounded by mangrove vegetation. The aircraft was substantially damaged. Nearby residents, police and armed forces personnel assisted the evacuation from the aircraft. The Rendani Airport Administrator reported that the passengers and crew members were evacuated and moved from the site by 0230. They were taken to the Manokwari General Hospital, and Manokwari Naval Hospital for further medical treatment.