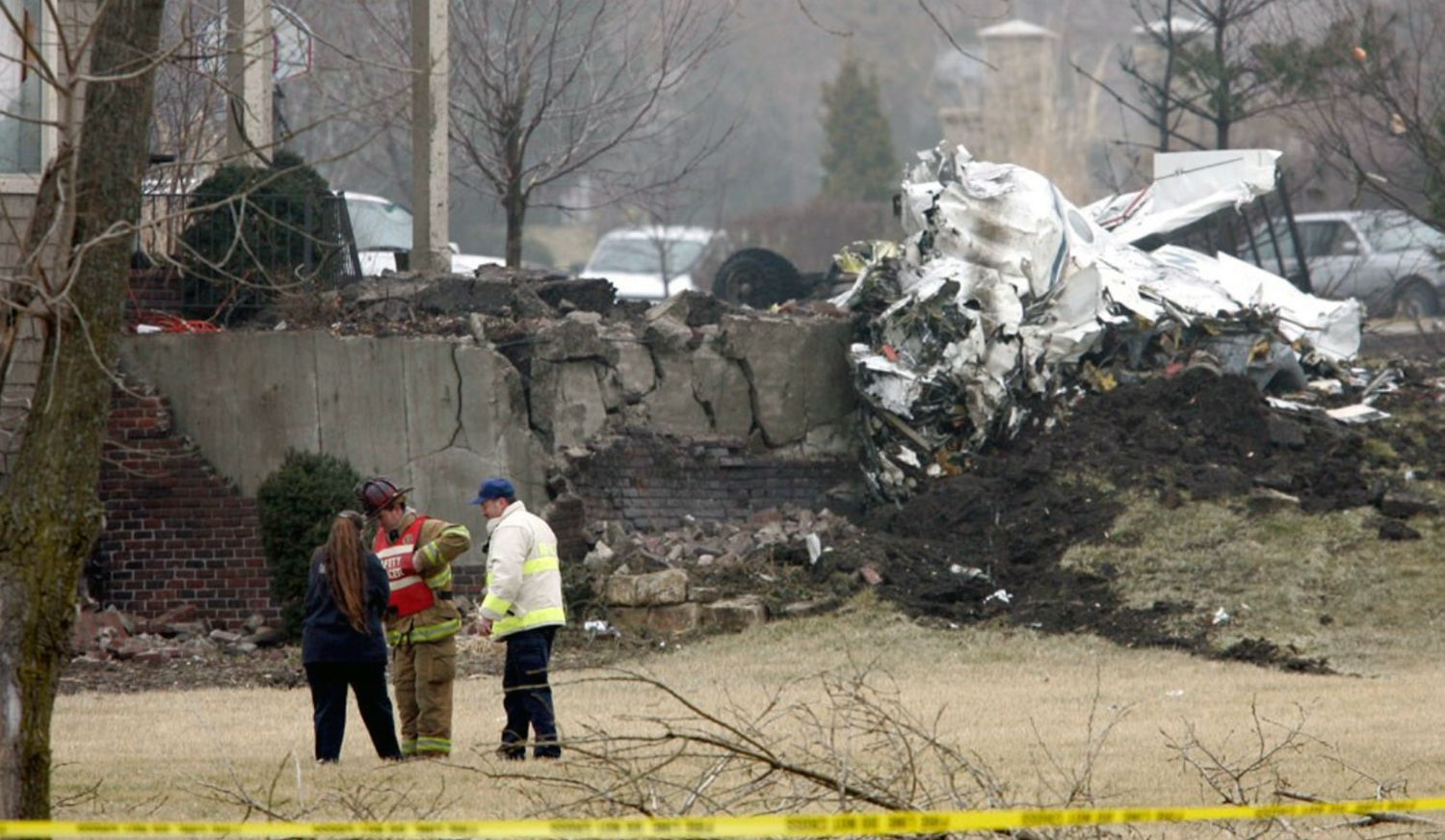
Crash of a Cessna 421C Golden Eagle III in Olathe: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 21, 2005 at 0943 LT
Registration:
N844JK
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Olathe – Zephyrhills
MSN:
421C-0681
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Aircraft flight hours:
2957
Circumstances:
The airplane received substantial damage on impact with trees, terrain, and a residence about one mile from the departure airport during instrument meteorological conditions. The airport elevation was 1,096 feet mean sea level. The personal flight was operating on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan with a filed equipment suffix designating that the airplane was equipped with a Global Positioning System. Airplane records indicate that the airplane was equipped with a GPS but was not approved for IFR navigation. The pilot was issued a departure clearance to 3,000 feet and heading of 130 degrees. Radar data indicates that the airplane leveled off at an altitude approximately 2,000 feet during a 32 second period while executing a right turn to the assigned heading. Witnesses reported that the airplane impacted terrain in a right wing nose low attitude. Wreckage distribution and ground scarring was indicative of a high-speed impact with terrain. No anomalies that would have precluded normal operation of the airplane were noted. The calculated airplane weight was approximately 597 lbs above the maximum gross weight of the airplane.
Probable cause:
The pilot's failure to maintain adequate altitude/clearance during cruise flight, resulting in collision with trees. Contributing factors were the low altitude and low ceiling.
Final Report: