Crash of a Boeing 737-2R4C in New Delhi: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 8, 1994 at 1454 LT
Registration:
VT-SIA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
New Delhi - New Delhi
MSN:
21763
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Captain / Total hours on type:
2821.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
166
Aircraft flight hours:
25947
Aircraft flight cycles:
2861
Circumstances:
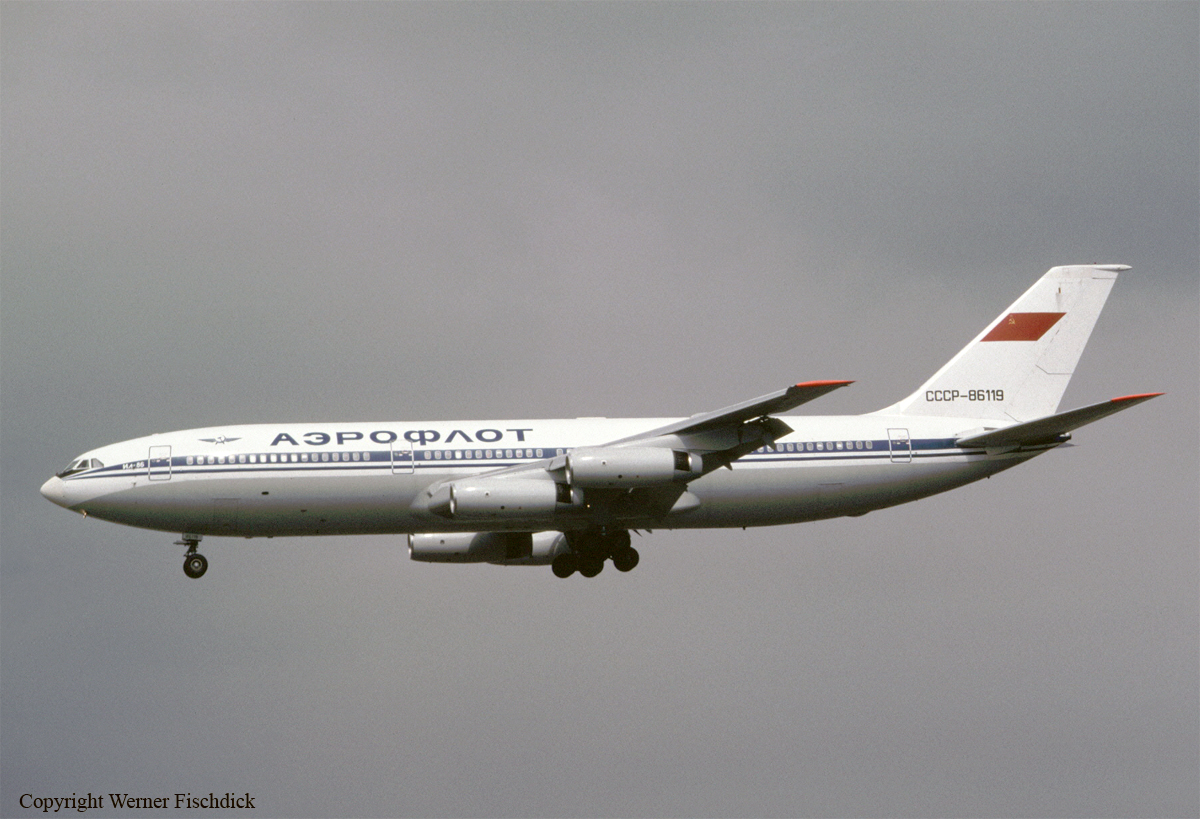
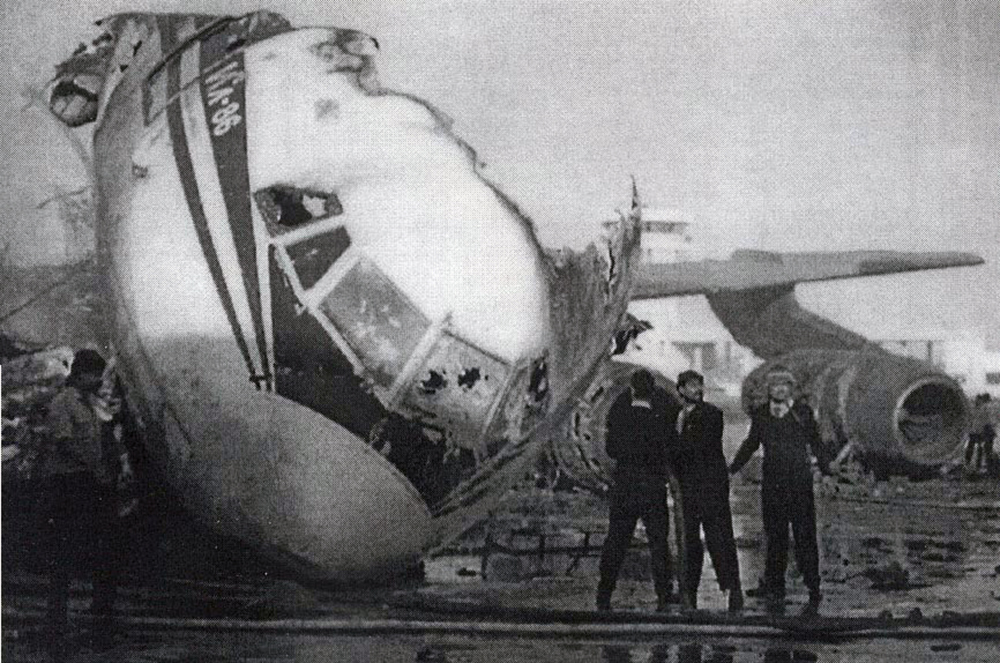
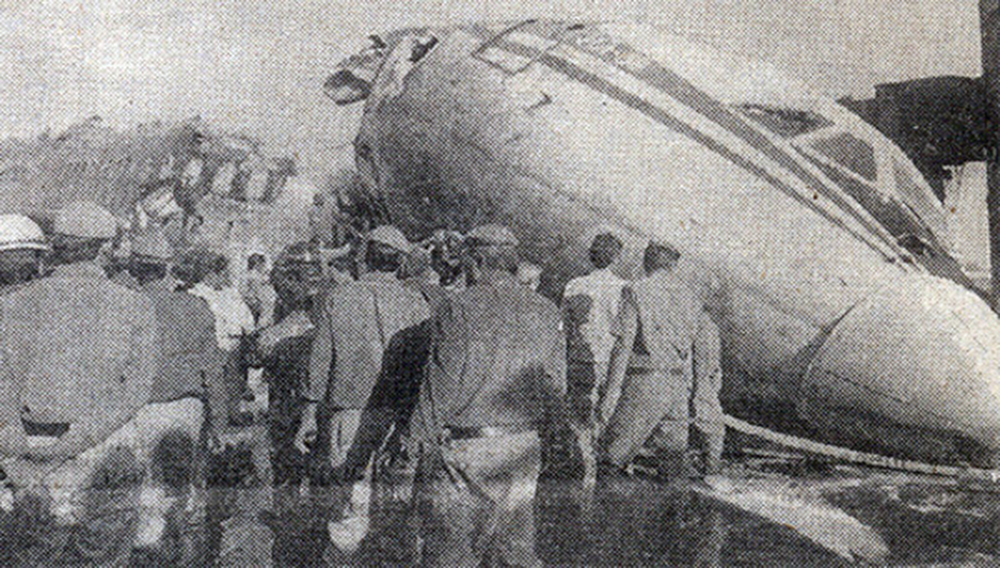
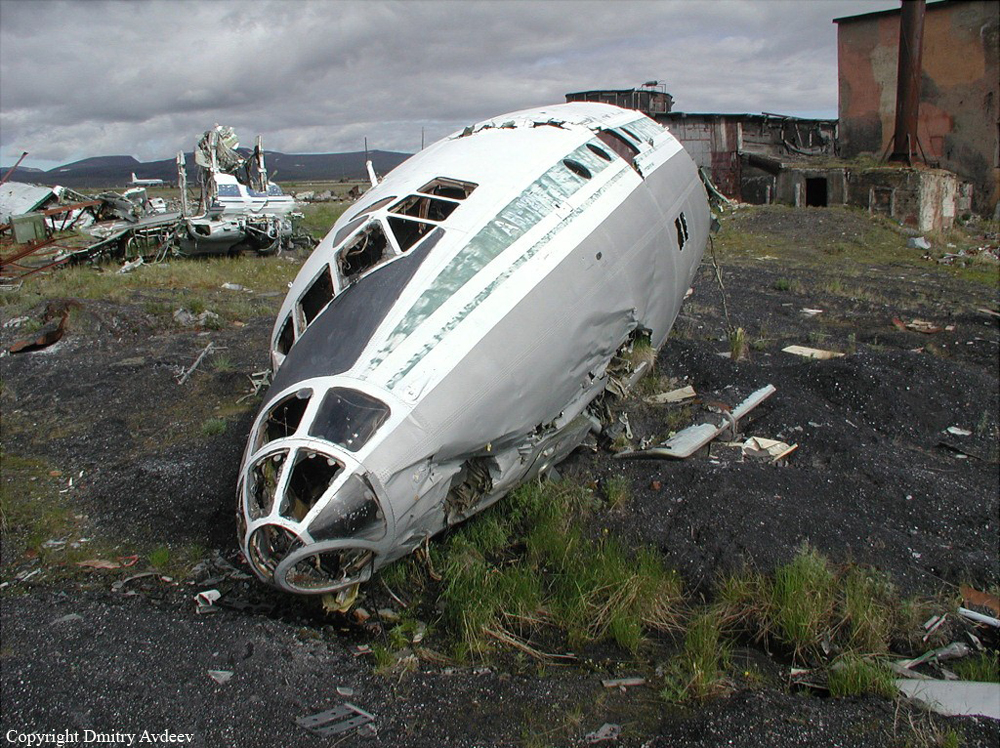
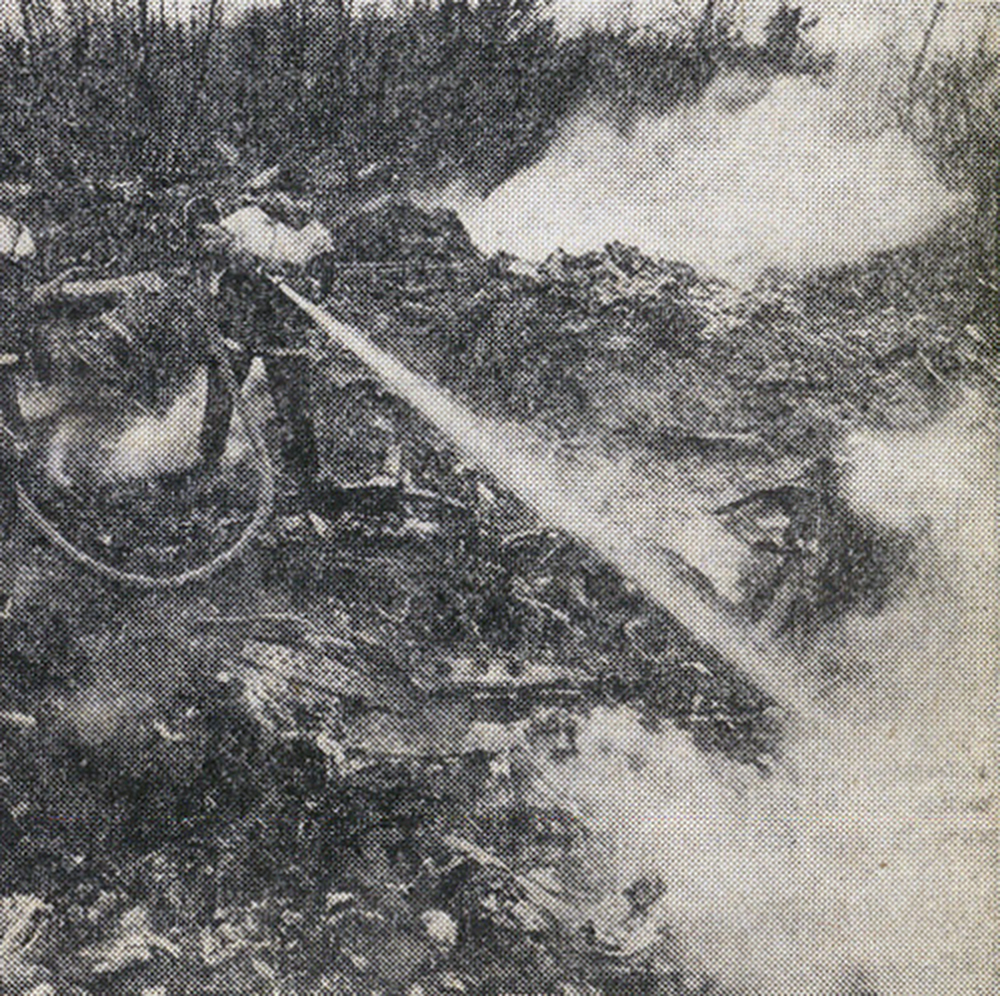
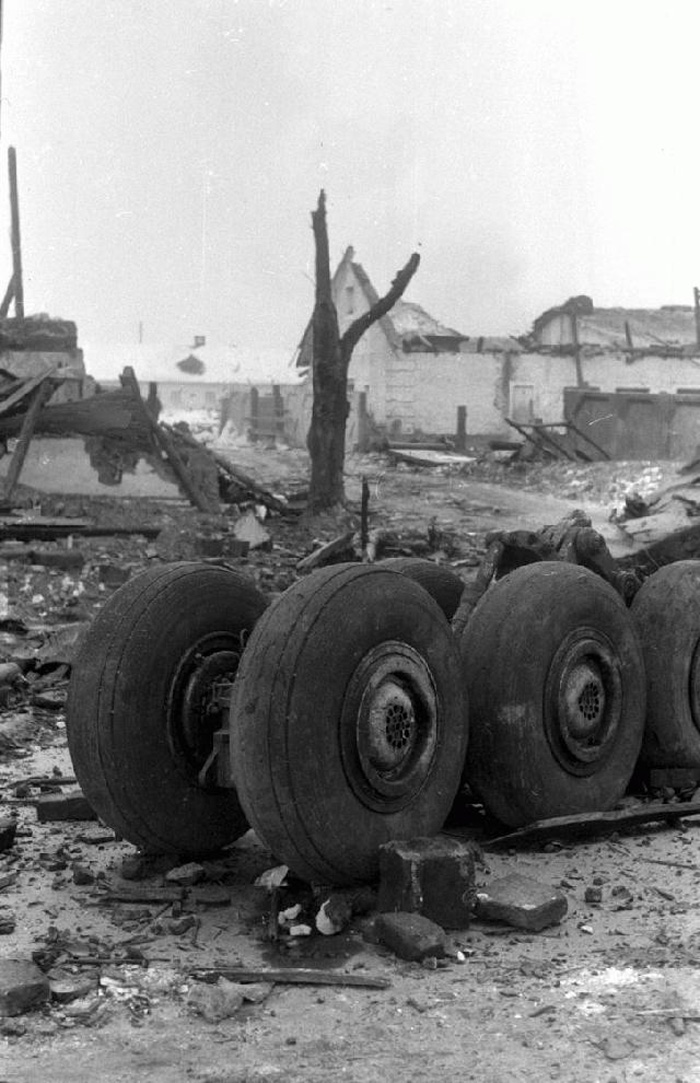
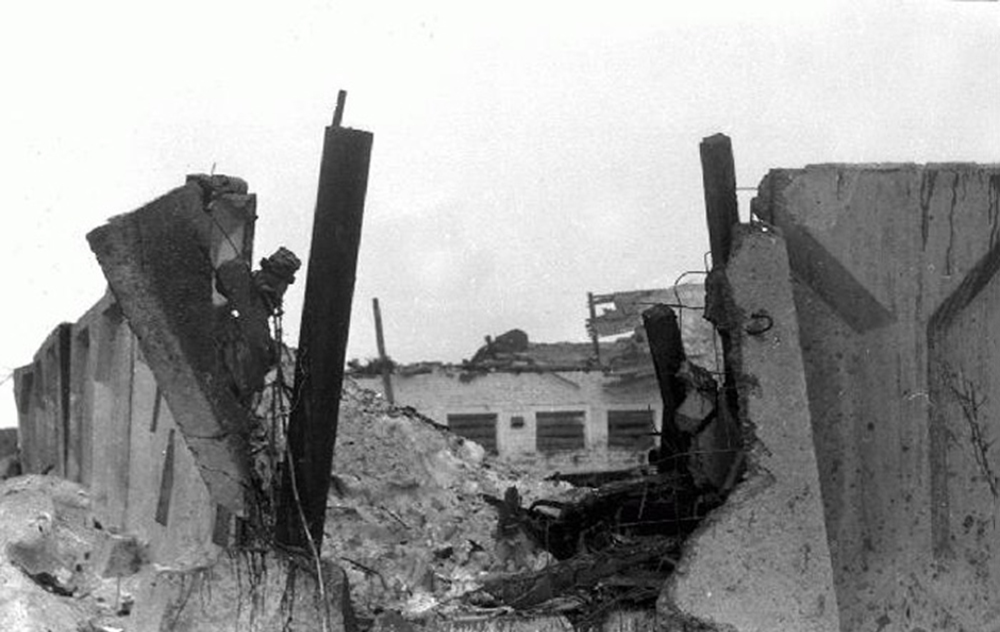
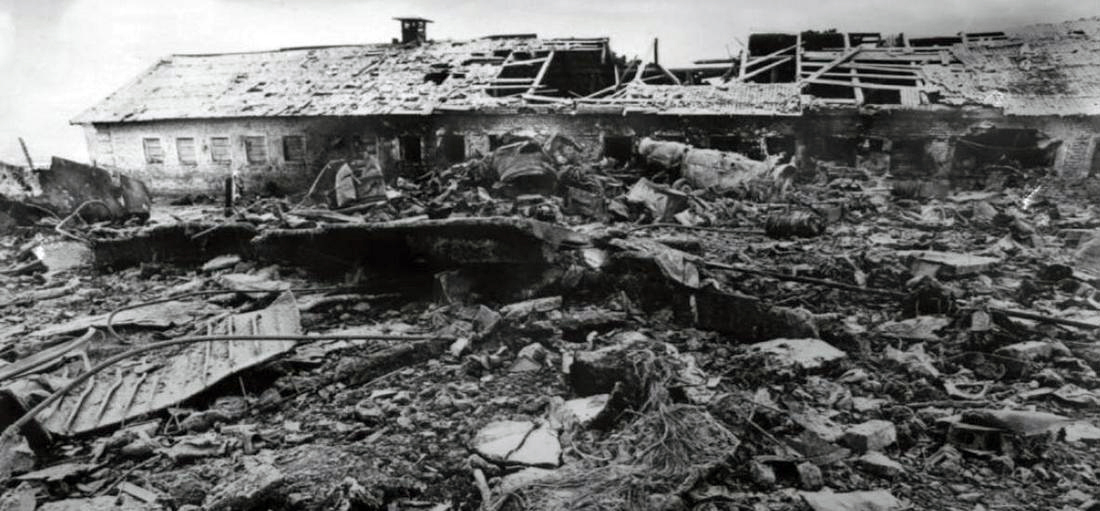
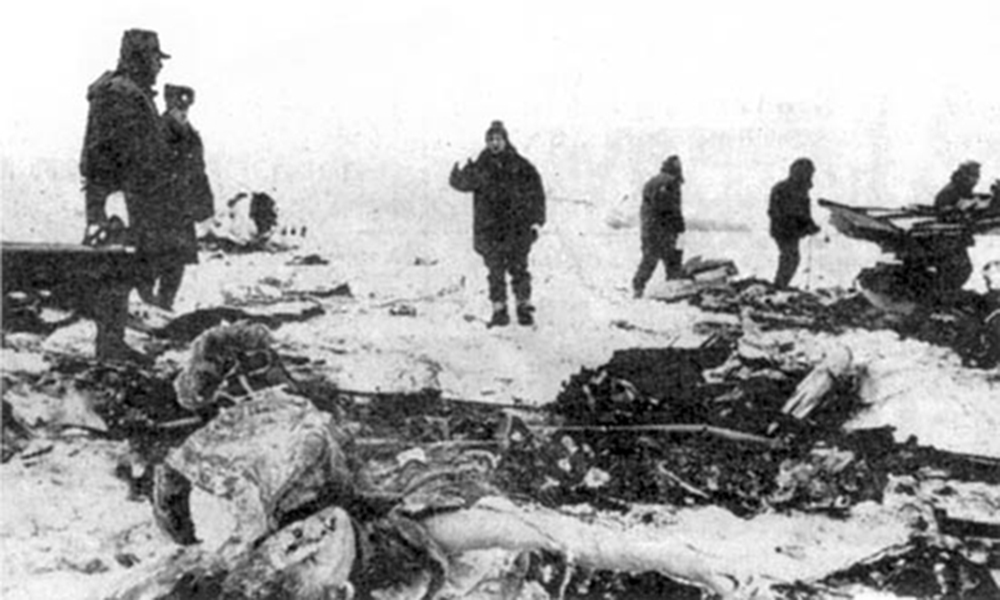
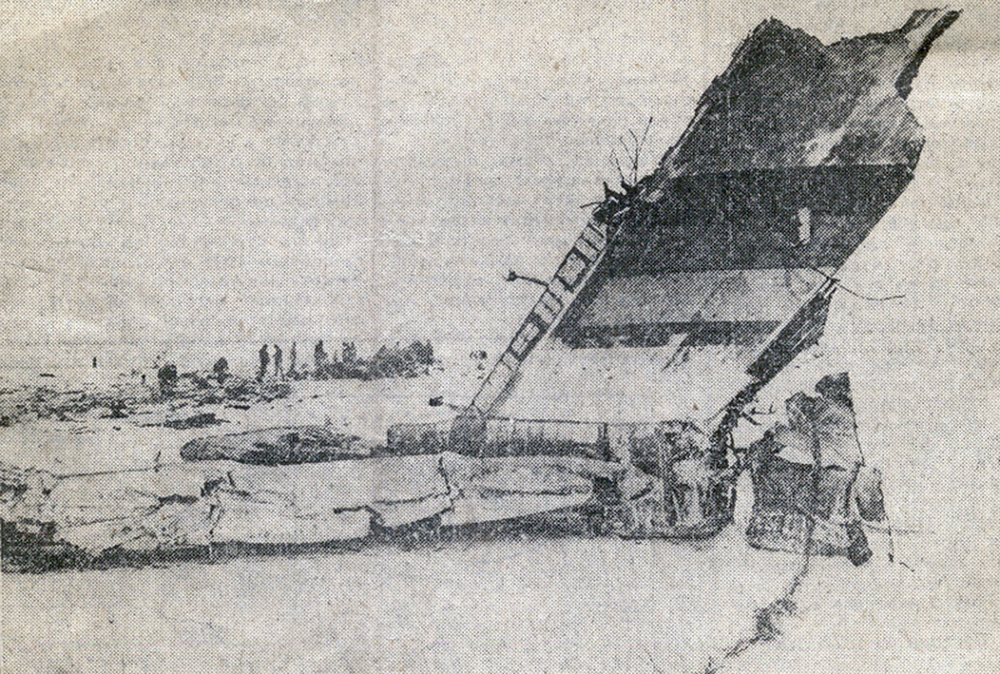
The aircraft was engaged in a local training flight at New Delhi-Indira Gandhi Airport, carrying one instructor and three trainee pilots. Five circuits and landings were completed uneventfully and during the sixth touch-and-go exercice, after take off from runway 28, the aircraft took a left turn and crashed on the international apron. The aircraft collided with an Aeroflot Ilyushin II-86 registered RA-86119 that was parked on the apron, bay n°45. Both aircraft were destroyed by fire. All four crew members on board the Boeing 737 were killed as well as four people on board the II-86 and one on the ground.
Probable cause:
Loss of control after rotation due to application of wrong rudder by trainee pilot during engine failure exercice. The instructor did not guard/block the rudder control and give clear commands as instructor so as to obviate the application of wrong rudder control by the trainee pilot.
Final Report: