Circumstances:
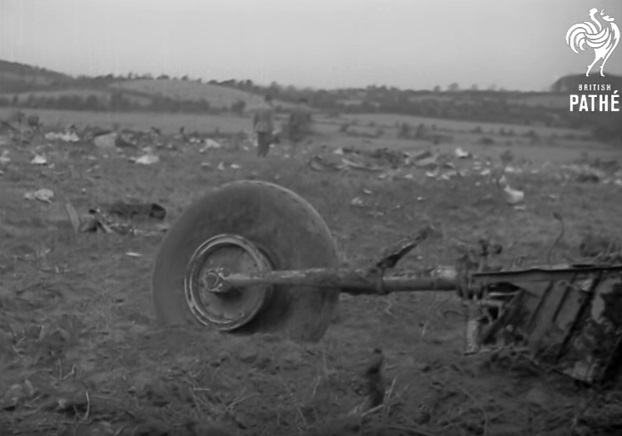
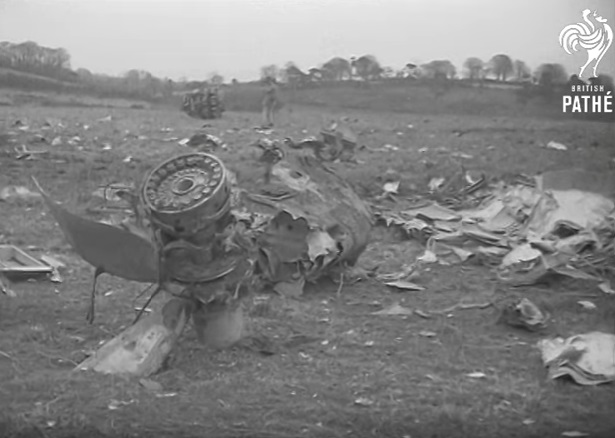
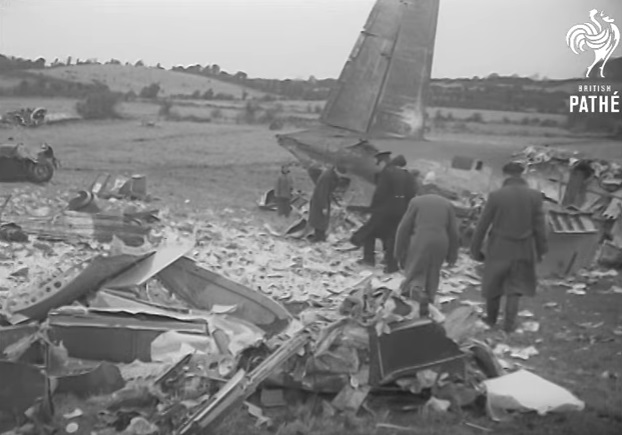
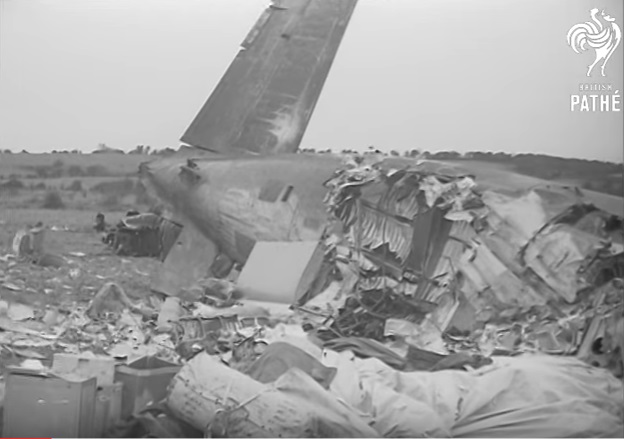
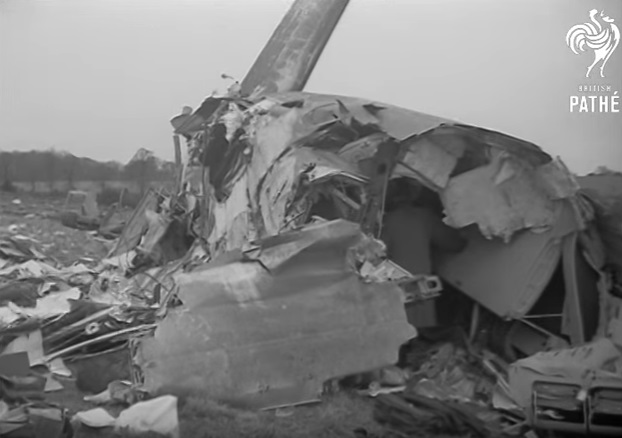
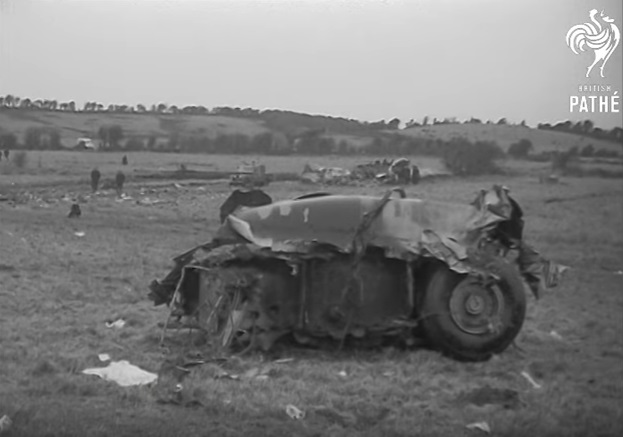
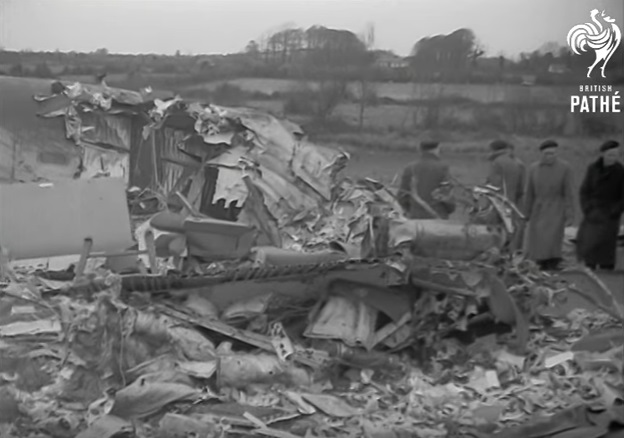
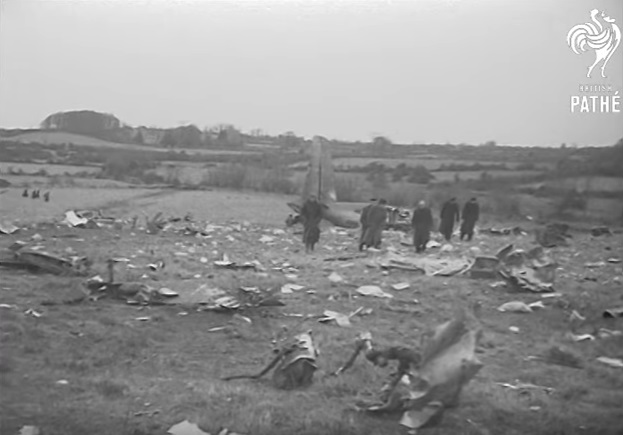
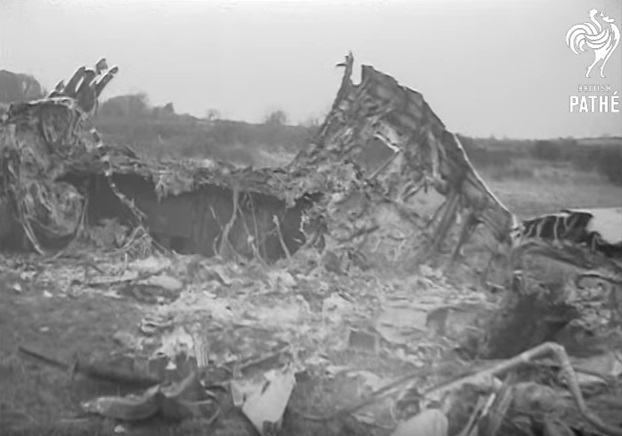
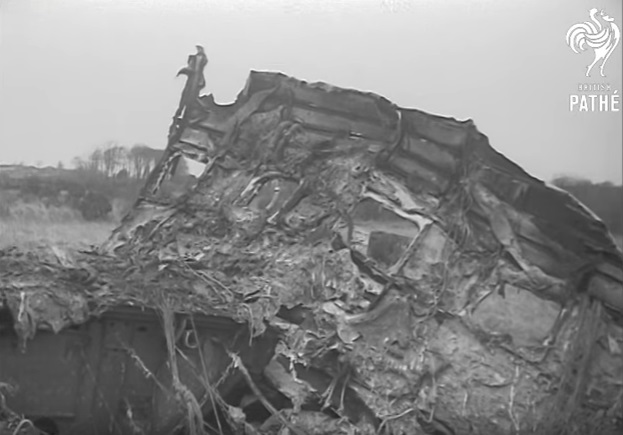
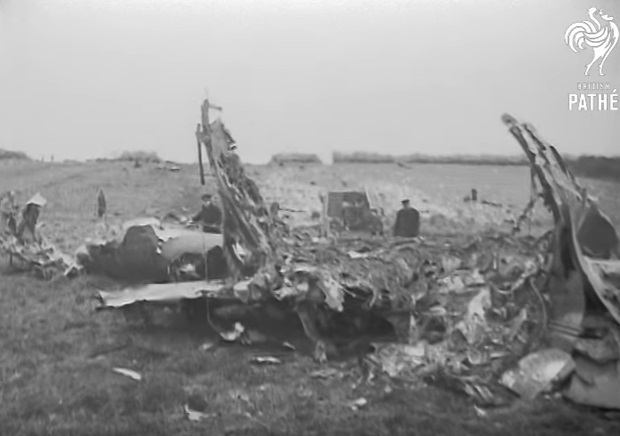
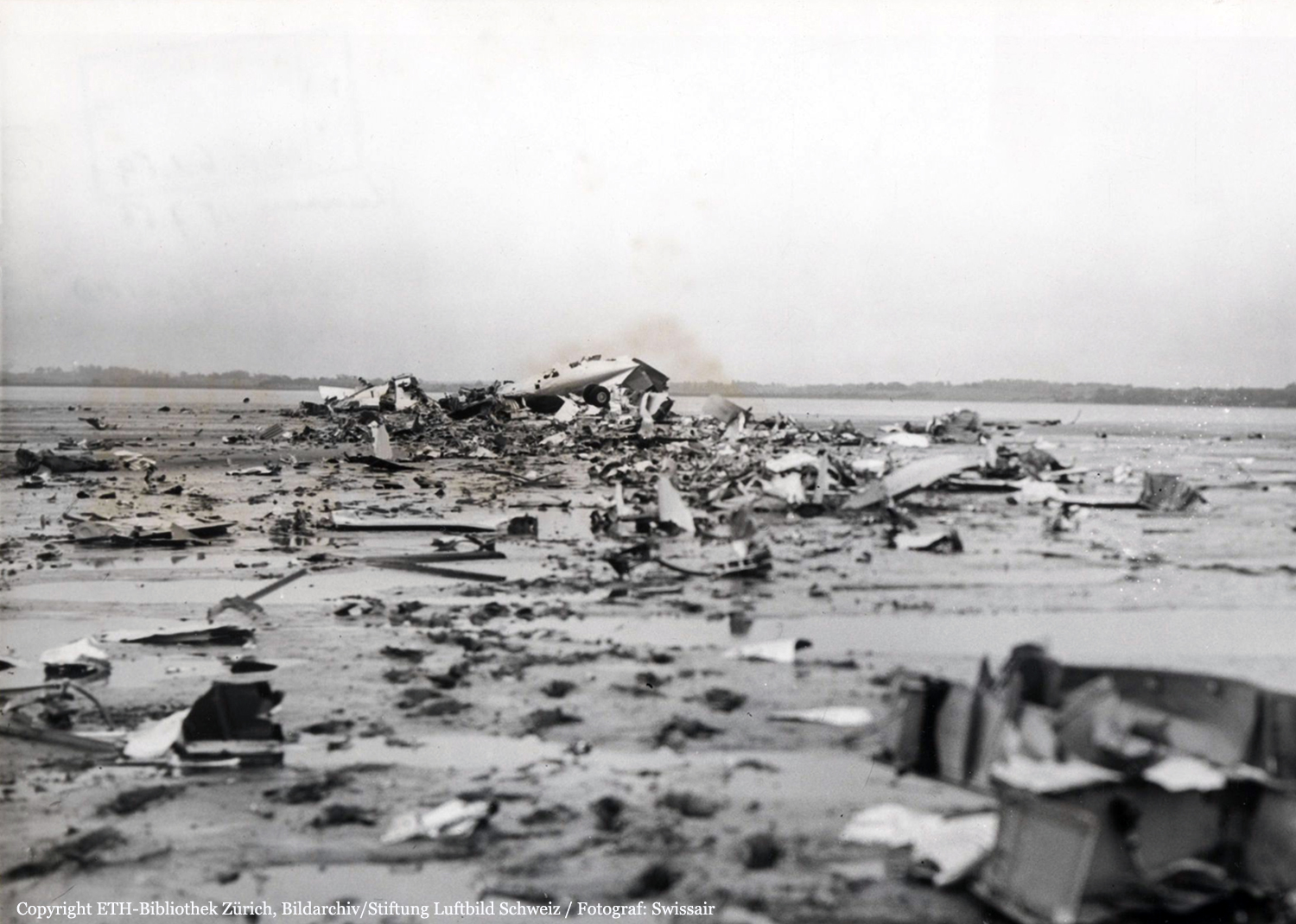
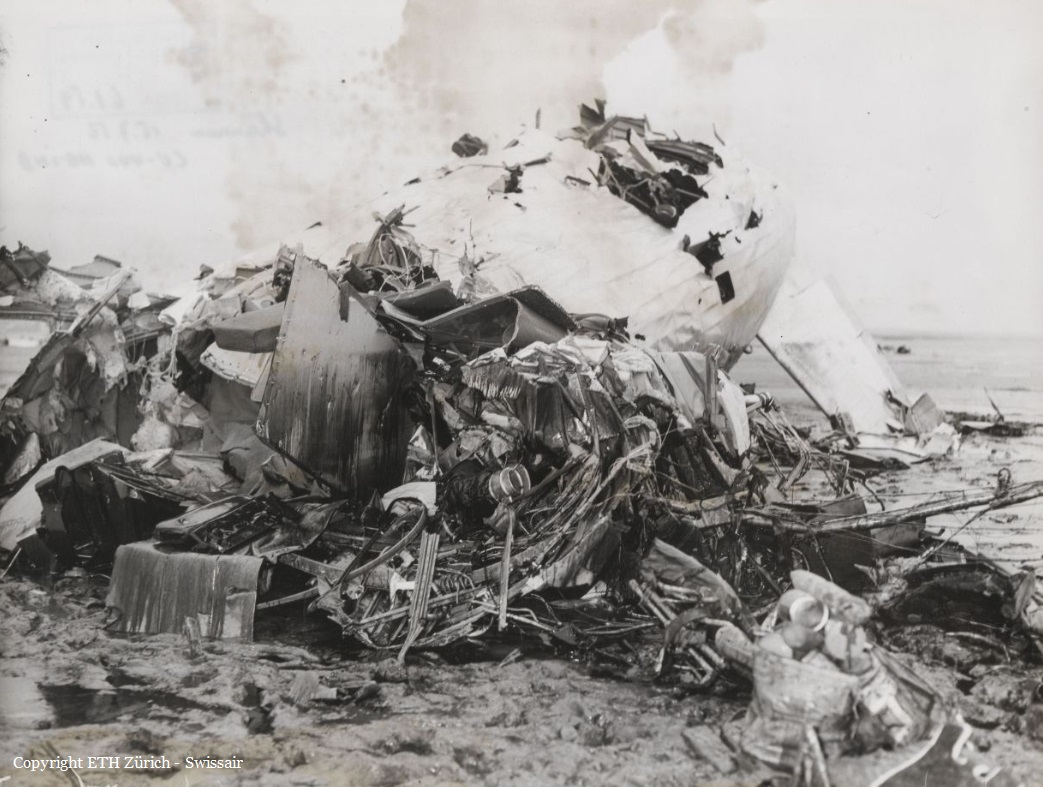
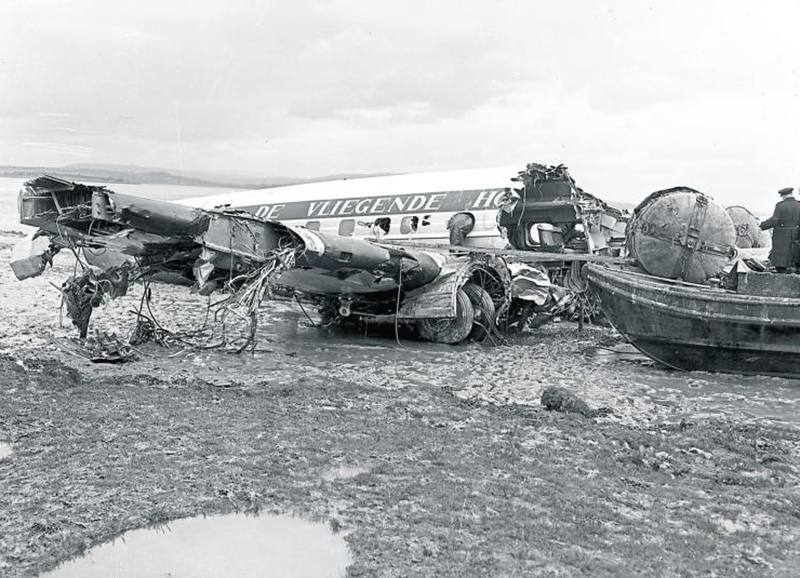
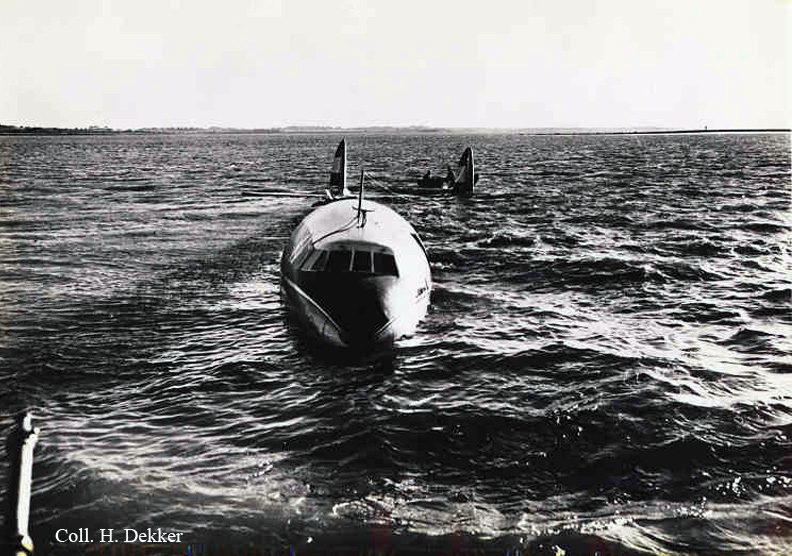
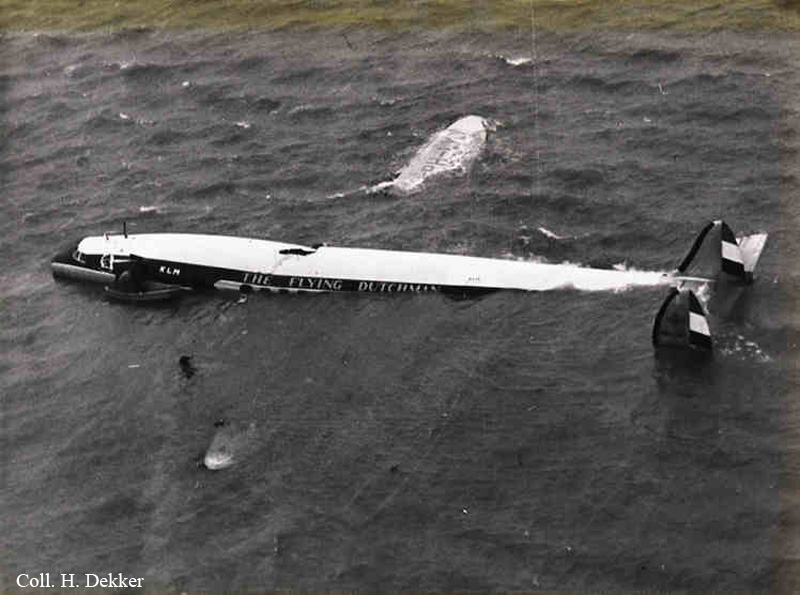
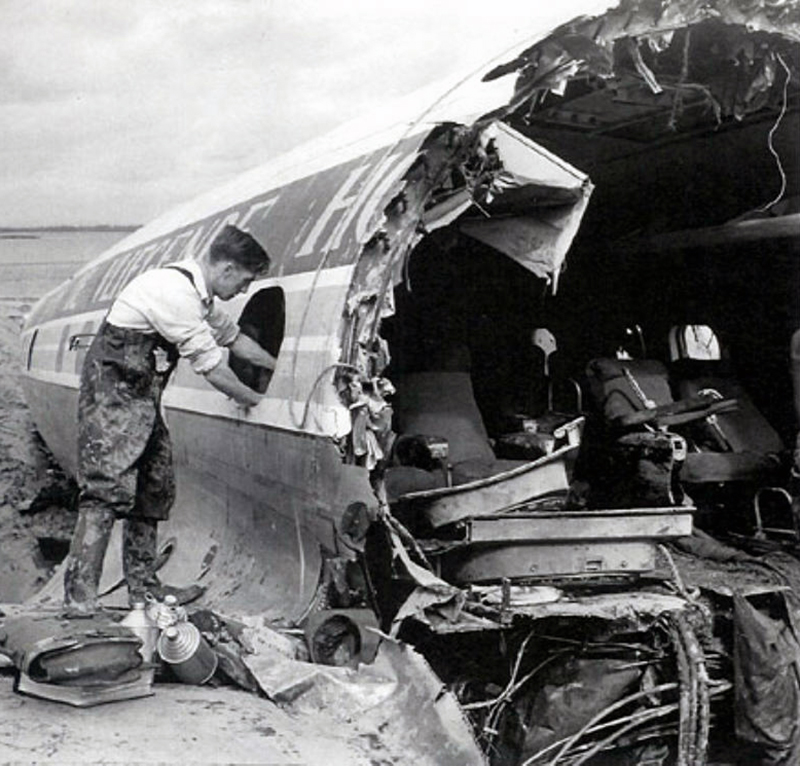
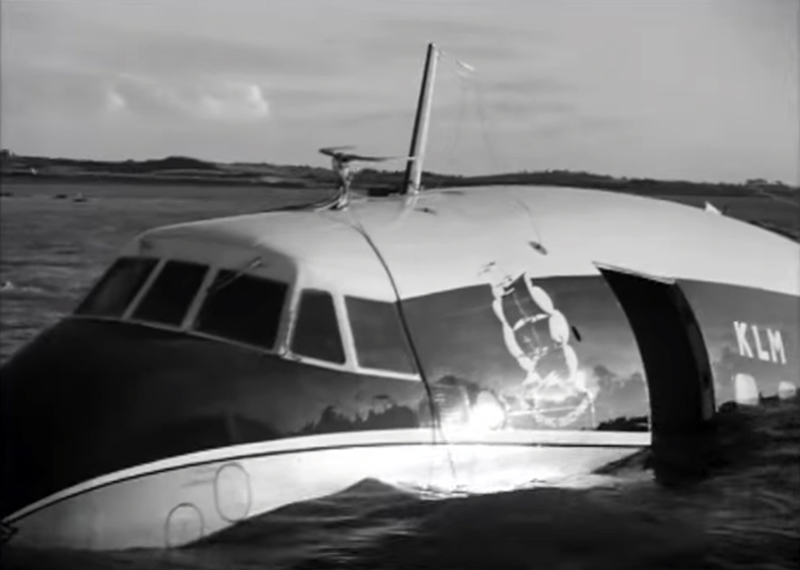
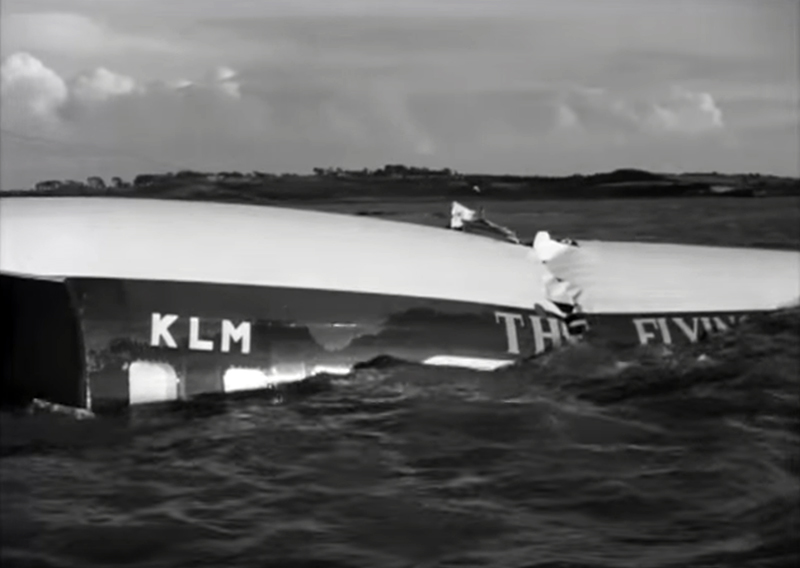
Pan American's Flight 1-10, originating in San Francisco, California, April 10, 1948, was scheduled to fly around the world to New York, New York. In accordance with company practice the flight changed to a different aircraft, NC-88858, at the Pan American Airways' base in Calcutta, India. The flight took off from Calcutta, April 13, 1948, and continued without incident via Damascus, Syria, and Istanbul, Turkey, to Brussels, Belgium. During a night landing approach at Brussels the fluorescent lighting on the left or pilot side of the cockpit went out. Since the only other lighting immediately available was a chart light which was focused on the automatic direction finder indicator, the flight instruments could not be read, and the remainder of the landing approach was accomplished without visual reference to the flight instruments. An examination was made of the fluorescent lights after the landing. They appeared to operate normally, so the flight departed from Brussels, continuing without difficulty until on the final landing approach into London. When the power was reduced the same pilot's fluorescent lights again went out. This time the chart light was focused on the airspeed indicator. The approach was continued, and the landing was accomplished without incident. A faulty rheostat switch was found to be the cause of the fluorescent light failure, but since a spare switch could not be located, it was not changed at London. An entry describing the defect was placed in the aircraft's Form C, the airplane flight log, and the captain and the flight engineer of the new crew were informed by the company's maintenance supervisor of the condition. Though no actual maintenance was accomplished, the lights again appeared to be operating normally, so the captain, F. C. Jakel, decided to take-off, departing from London at 0035, April 15, 1948, for Shannon. At this time available weather forecasts indicated that at the estimated time of the flight's arrival at Shannon the ceiling there would be 700 feet with a higher cloud layer at 1,000 feet, and visibility 4 miles. At 0159, April 15, 1948, the flight reported being at an altitude of 4,500 feet, contact, over the Limerick Junction fan marker, located 25 statute miles southeast from the Shannon Airport, and requested permission to make a practice approach to the field with the use of the instrument landing system. Shannon Tower cleared the flight for this approach. The tower advised that 3 hours previously the instrument landing system equipment on the airport had been reported faulty, but that it had since been serviced and was operating normally according to its monitoring board, though not flight-checked. At 0210, the flight reported that it was proceeding to the outer marker, 5.2 statute miles northeast of the Shannon Airport, and also made a report, routine for Pan American flights, "mechanical condition okay." In response Shannon Tower advised the flight that the weather over the field was "fog patches, 3 miles visibility, cloud base 400 feet, sky 6/10 covered, wind from 325 degrees at 4 miles per hour." The flight was instructed to land on runway 23, the runway for which the instrument landing system was projected. It was also requested to report when making the 180 degree procedure turn for the inbound instrument approach to the field, and when over the outer marker. The requested position reports were not received by the tower, but at 0220 the flight did report a "missed approach," 2 and advised that it was going around for a second approach. At this time the flight was observed through a break in the clouds by the Shannon Tower, which was the first time that the aircraft had been seen in the vicinity of the Shannon Airport. The aircraft was reported as 500 feet above the ground, over, and in line with runway 23. Power was heard being increased, and the aircraft was observed turning left. On the second approach, at 0227, the flight reported making its 180 degree procedure turn and was cleared for landing by the tower. One minute later, weather conditions at the field were transmitted to the flight as "fog patches, visibility 2 1/2 miles, 6/10 cloud base 400 feet, 4/10 cloud base 300 feet, wind 325 degrees, 3 miles per hour, altimeter 30.29." The flight reported approaching the outer marker at 0231 at which time the tower advised that another flight which had just taken off had reported a ceiling of 500 feet when northwest of the field. Flight 1-10 acknowledged this information, which was the last communication received The aircraft was not observed at any time during the second approach until after it struck the ground. The aircraft struck the ground 2,380 feet northeast of the approach end of runway 23, and directly in line with that runway. Flames followed immediately after impact, and consumed a great portion of the wreckage. A passenger survived while 30 other occupants were killed.