Crash of a Canadair RegionalJet CRJ-100ER in Kigali: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 12, 2009 at 1315 LT
Registration:
5Y-JLD
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Kigali - Entebbe
MSN:
7197
YOM:
1997
Flight number:
WB205
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
11
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
1110.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
533
Aircraft flight hours:
17140
Aircraft flight cycles:
17025
Circumstances:
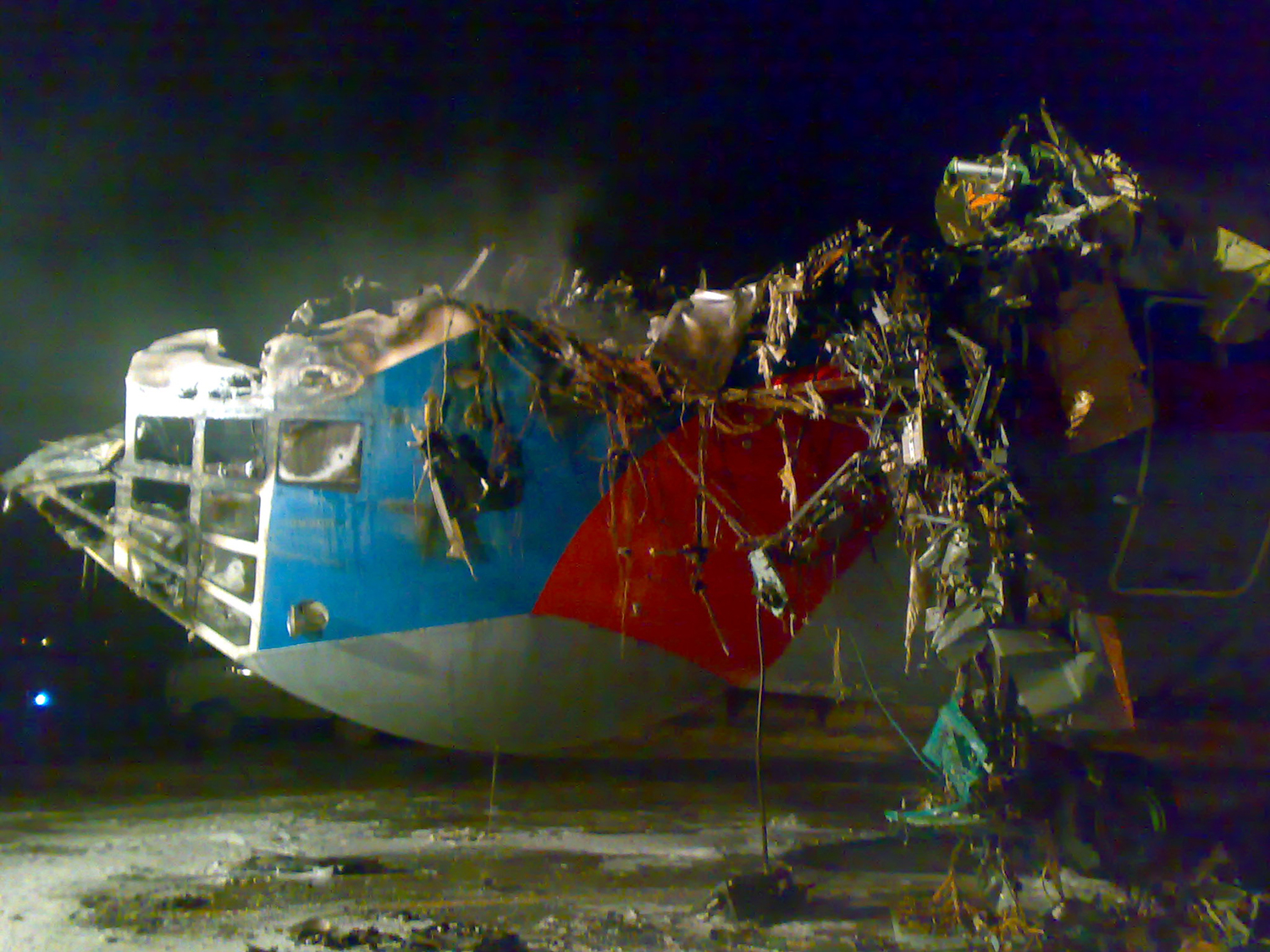
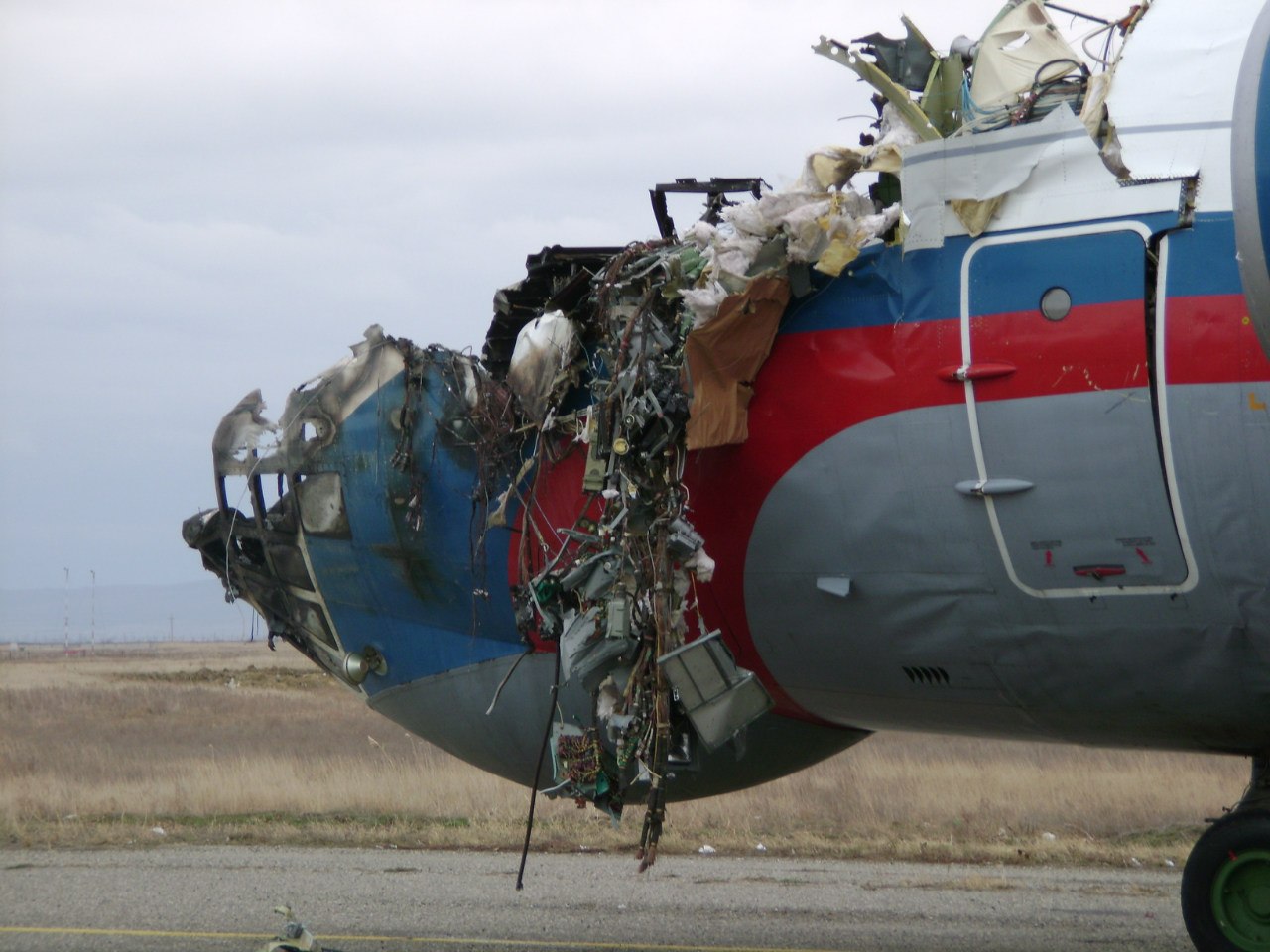
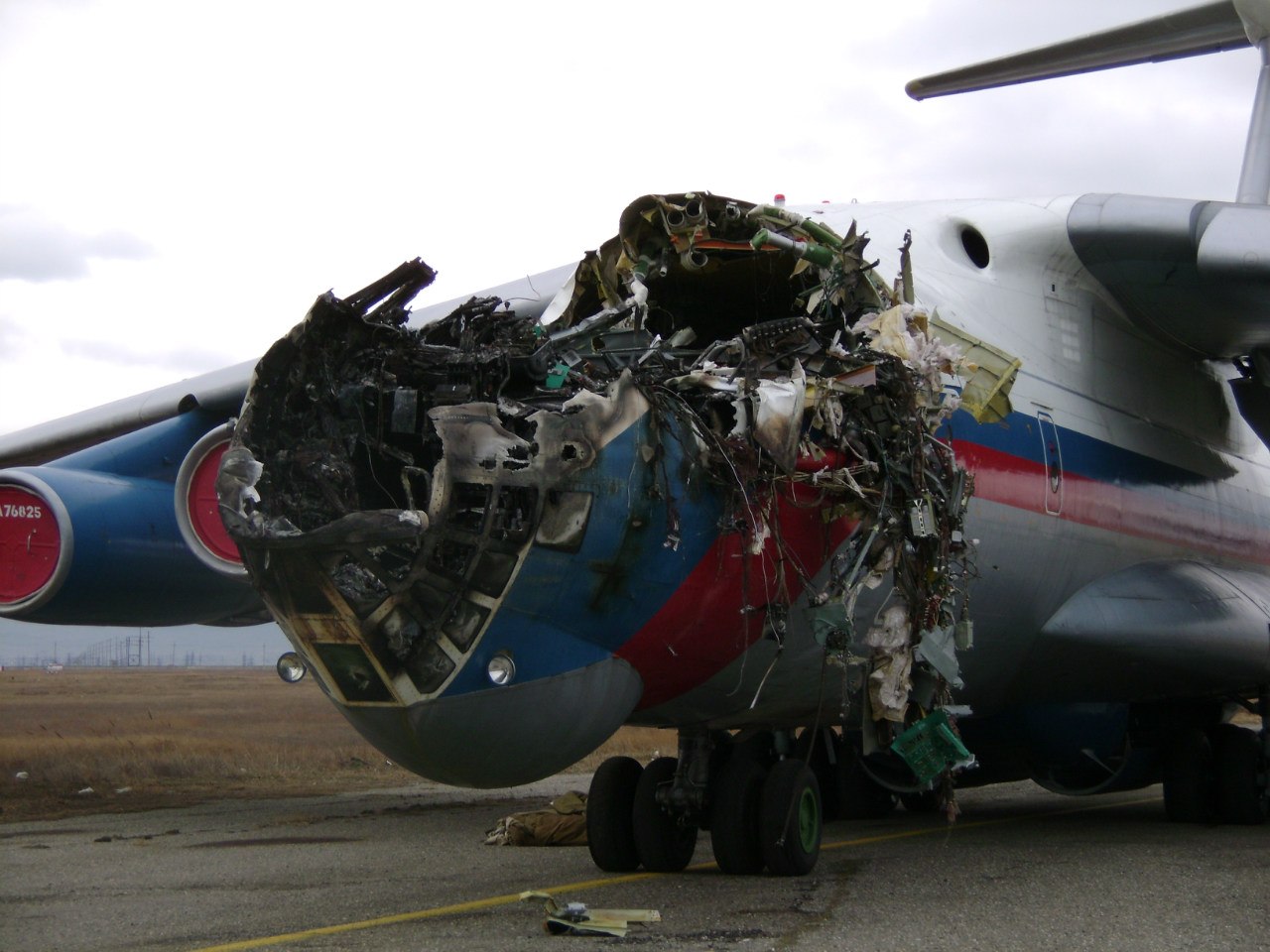
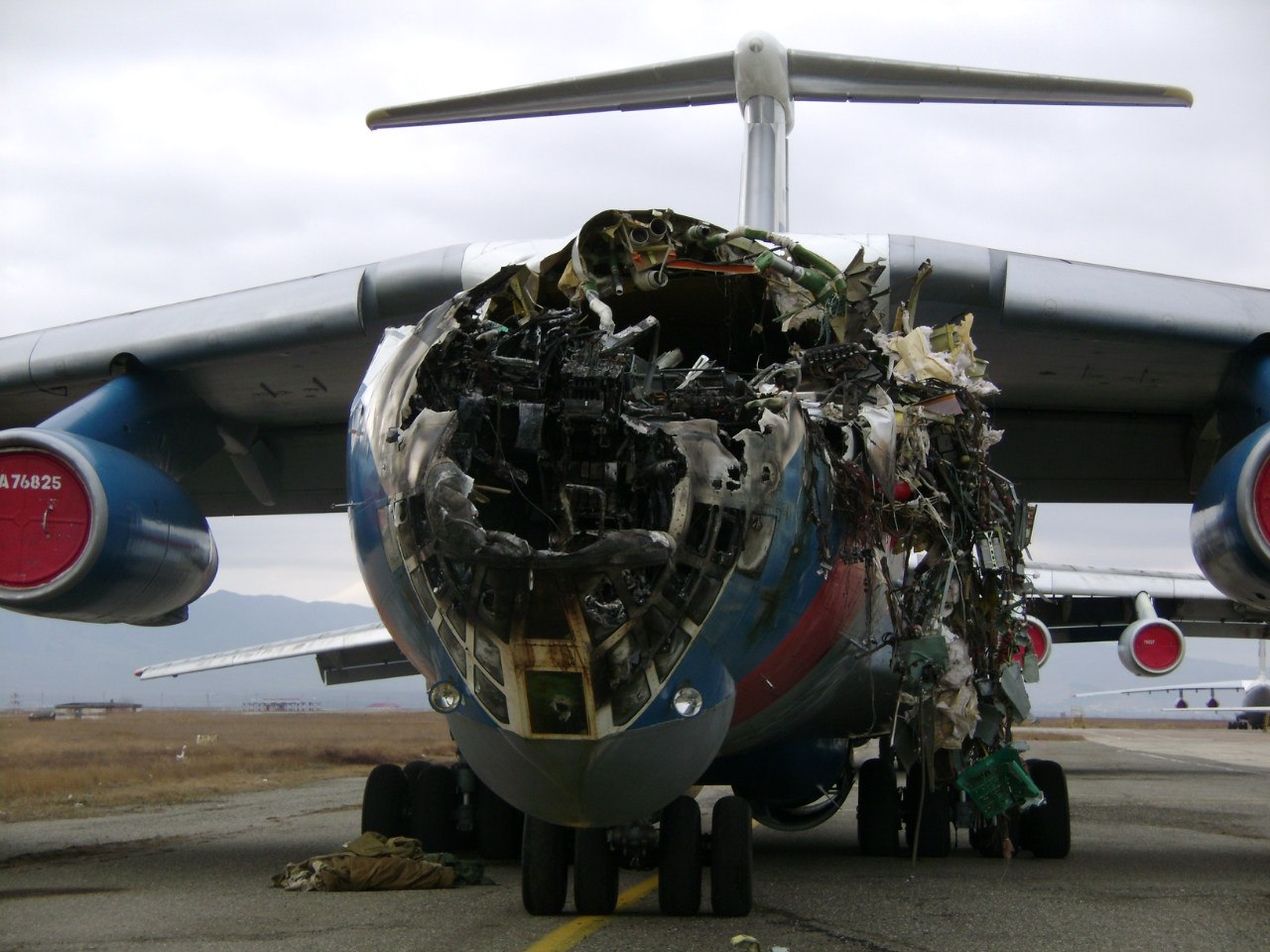
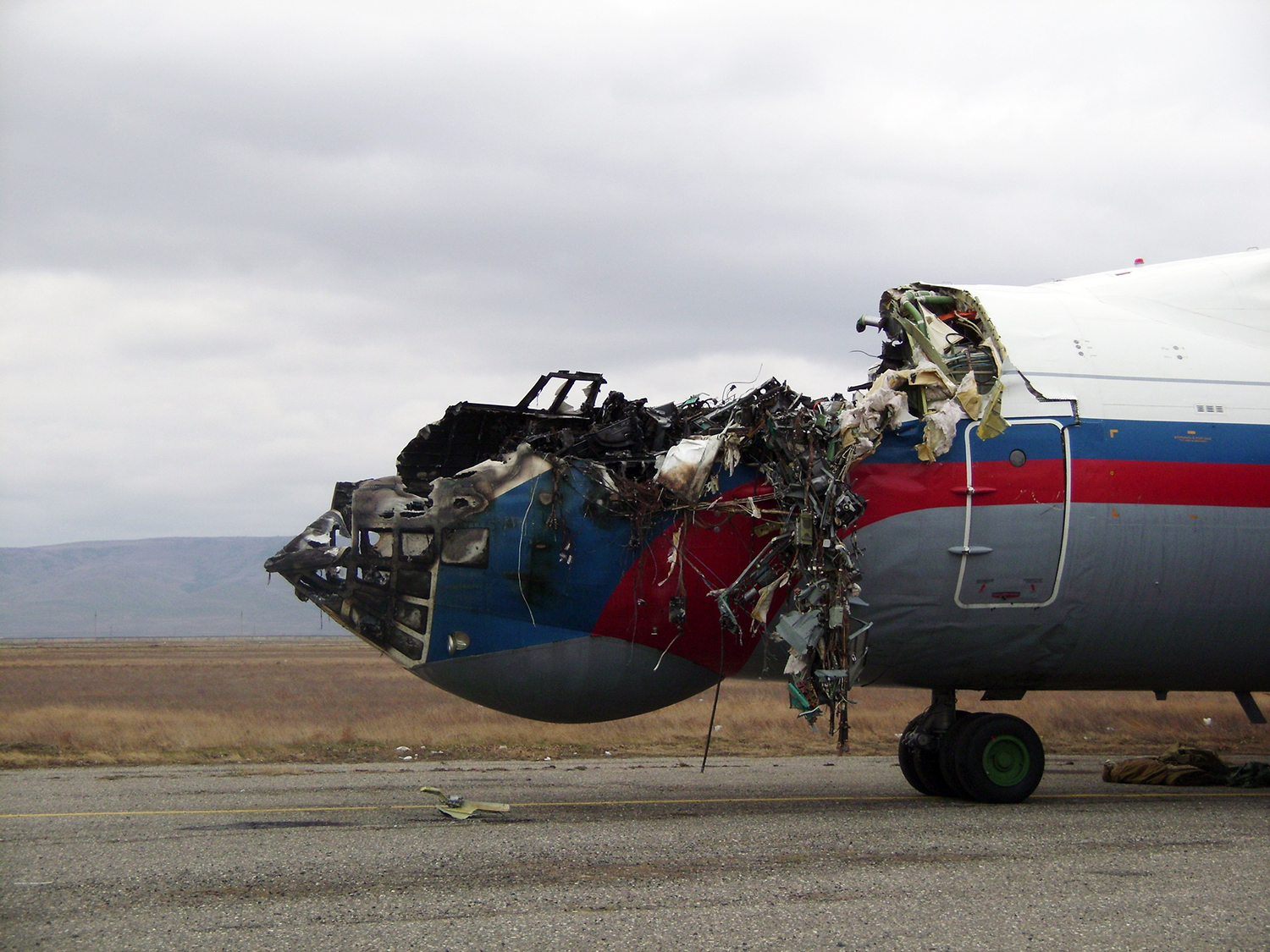
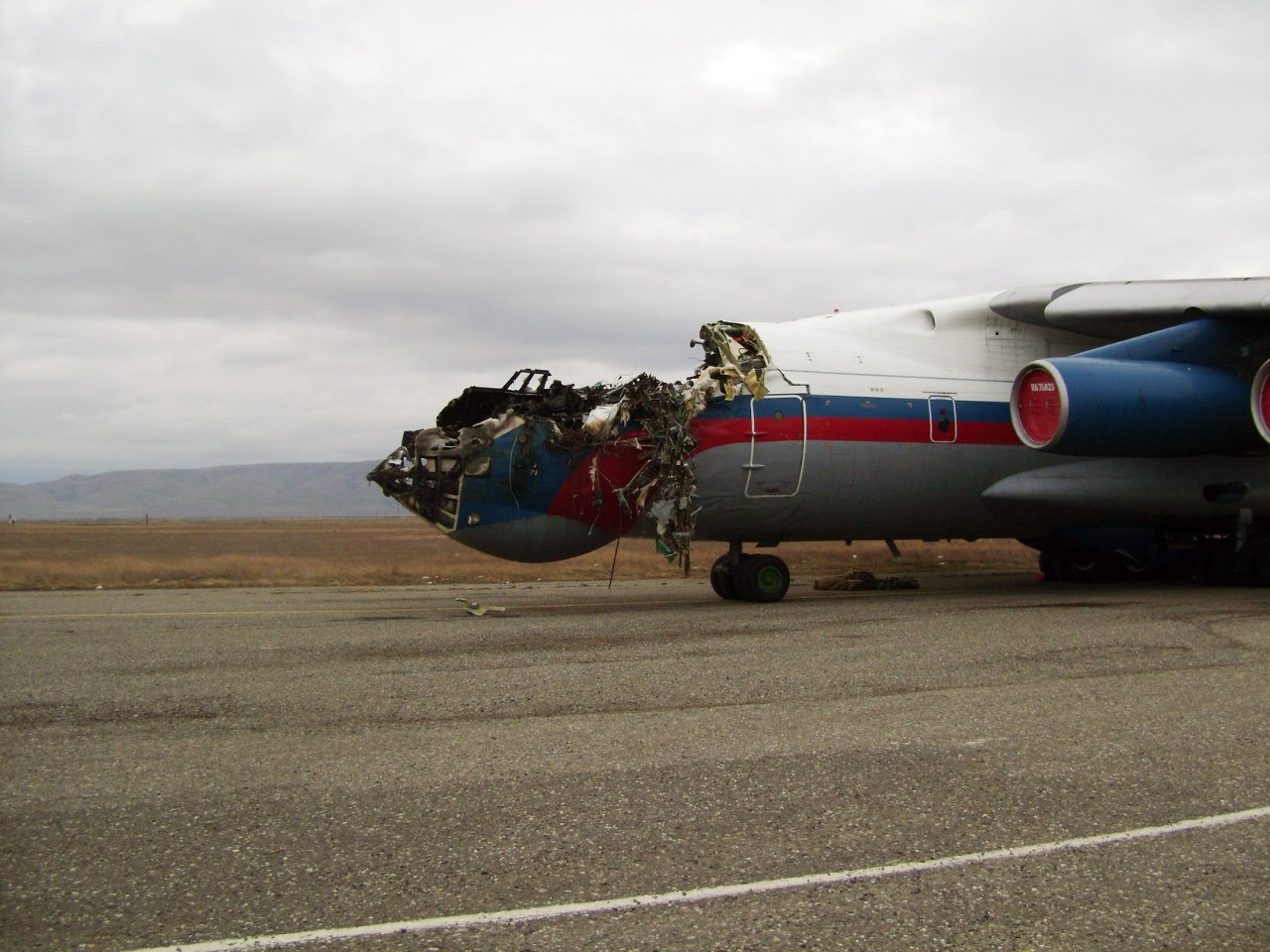
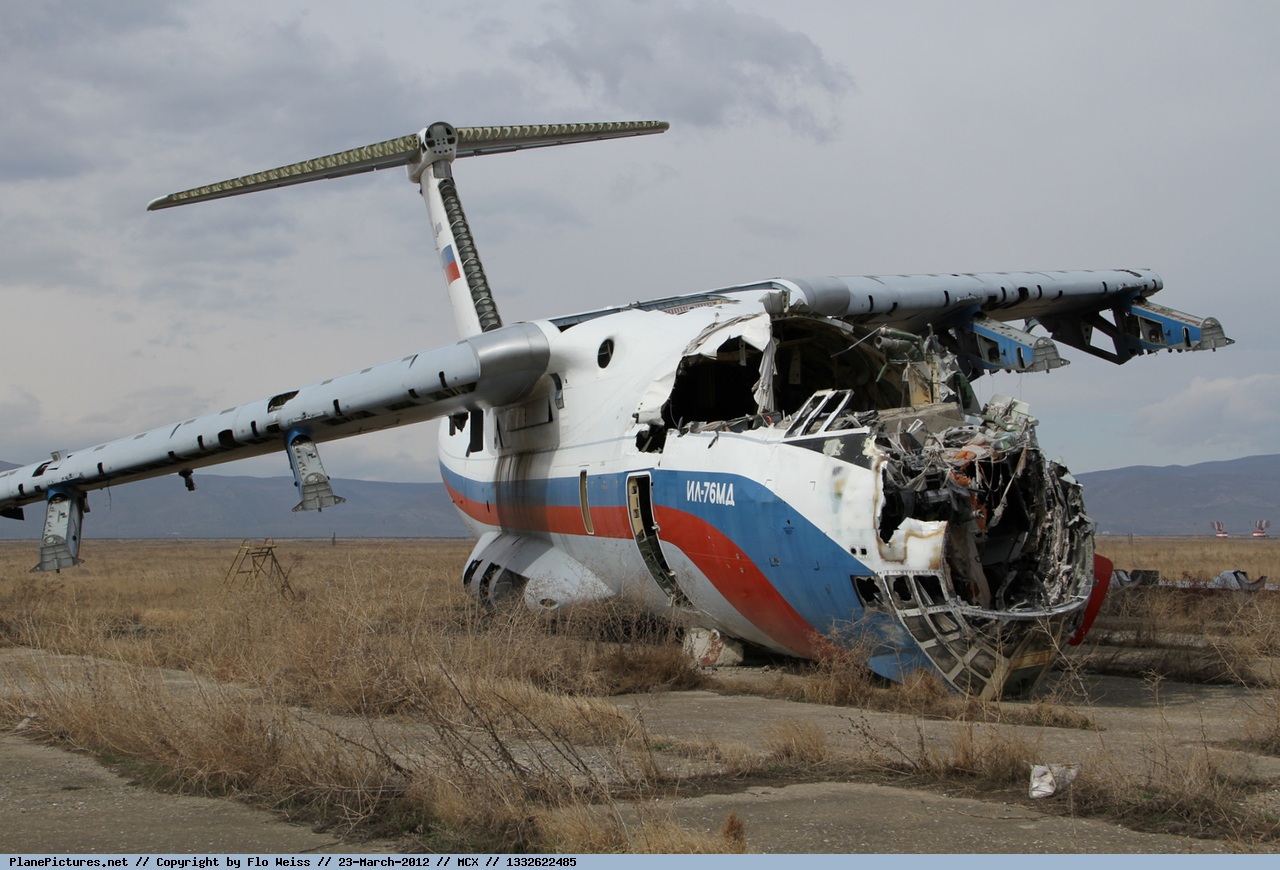
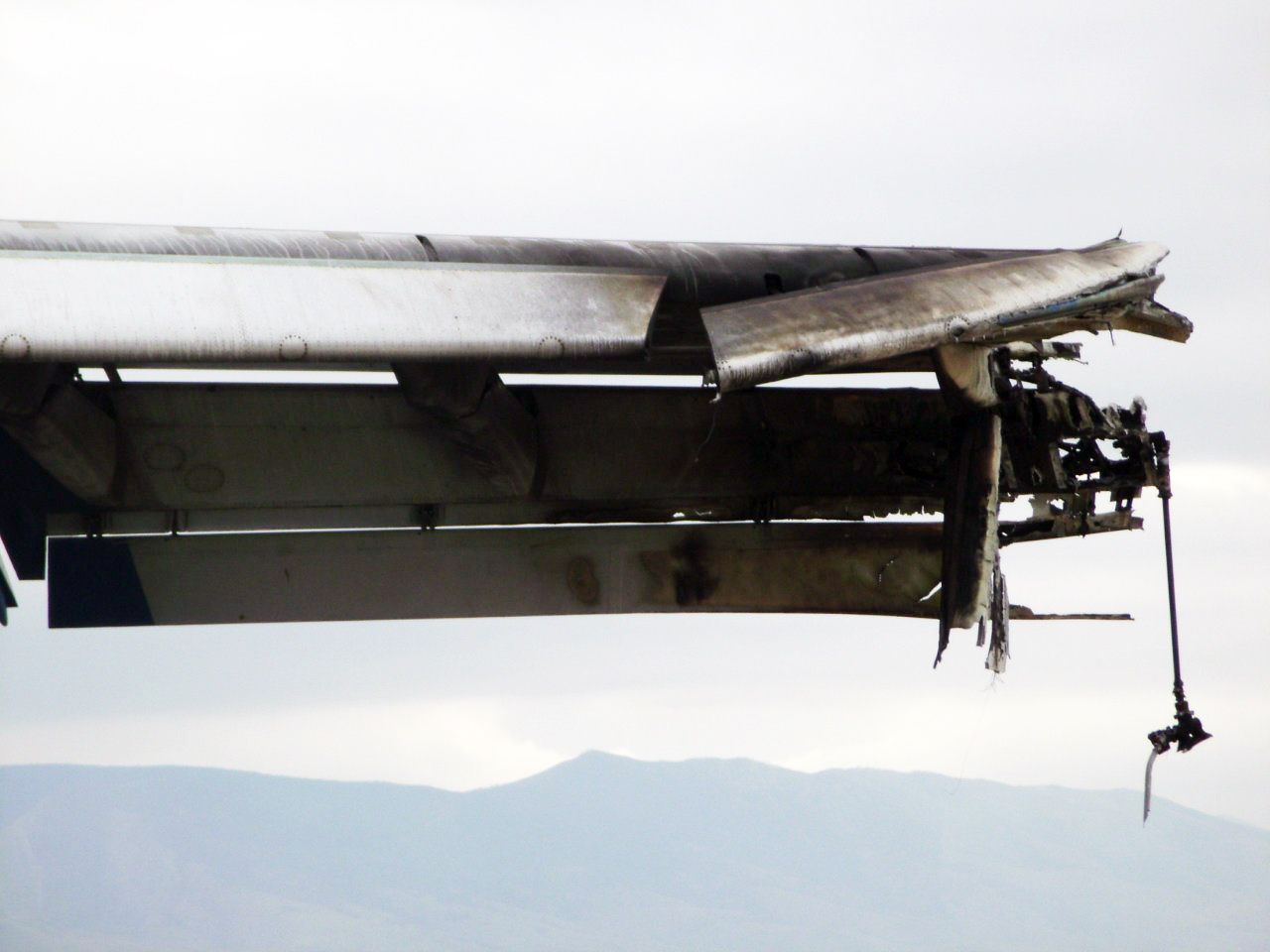
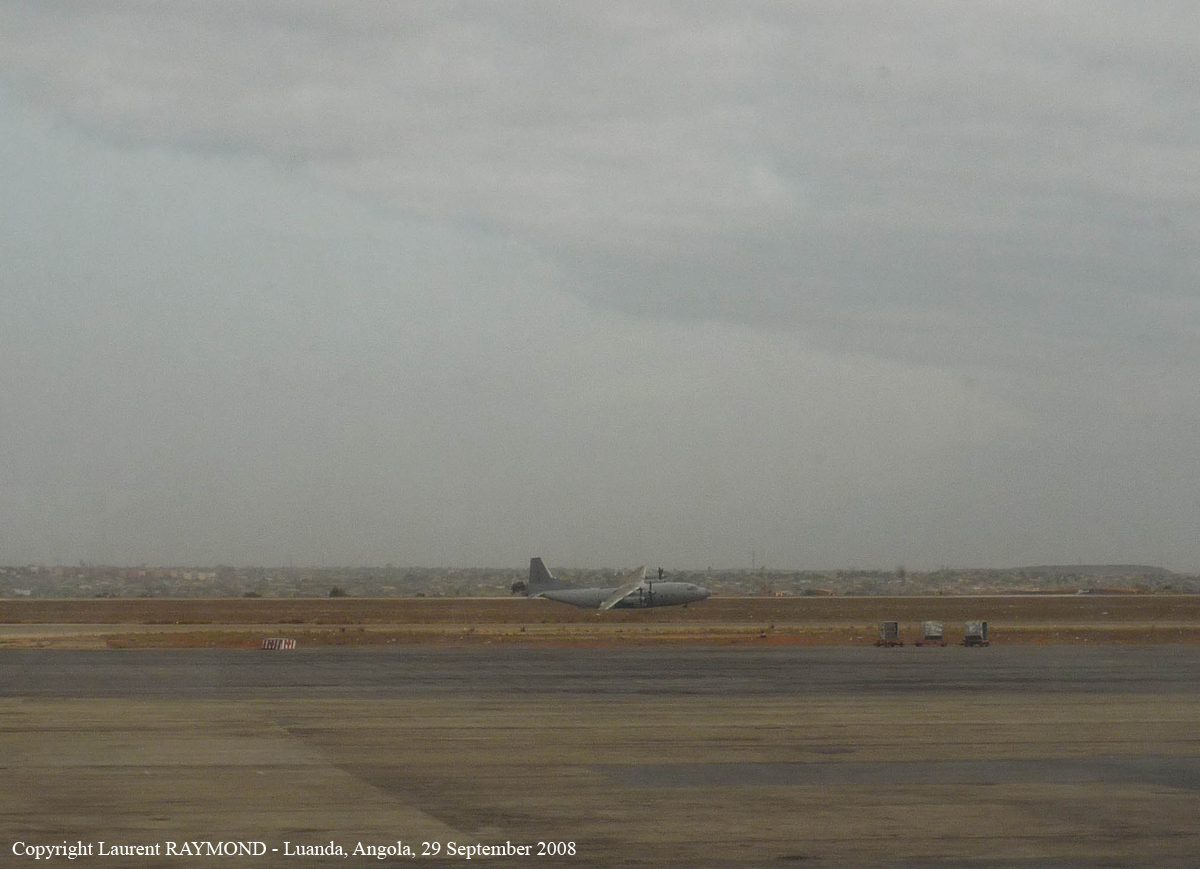
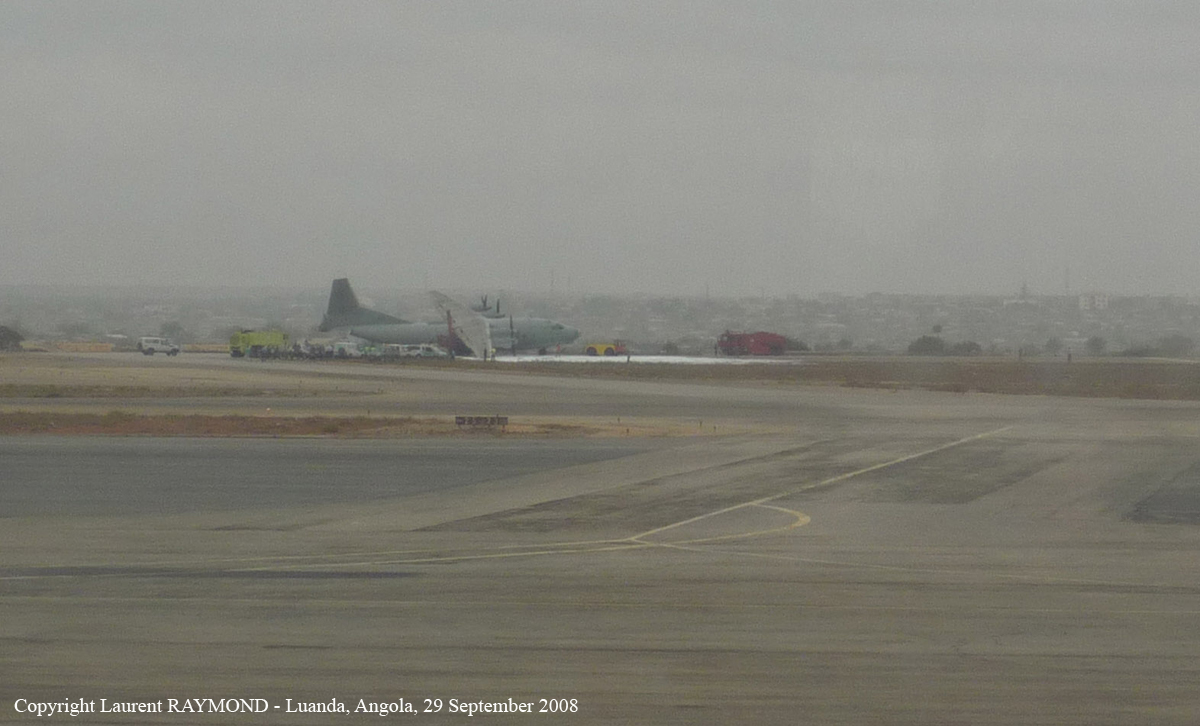
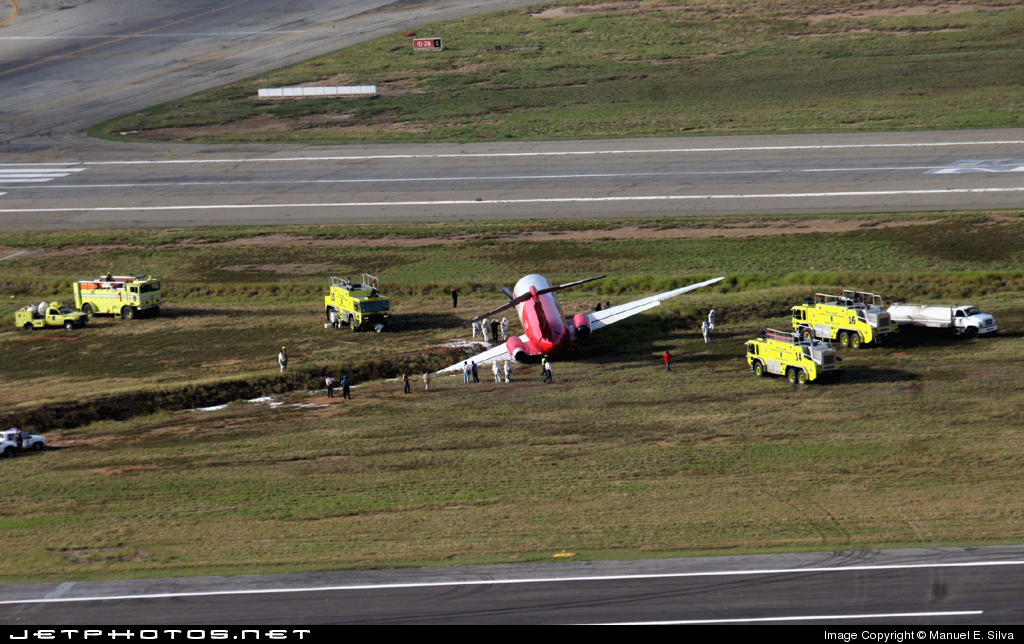
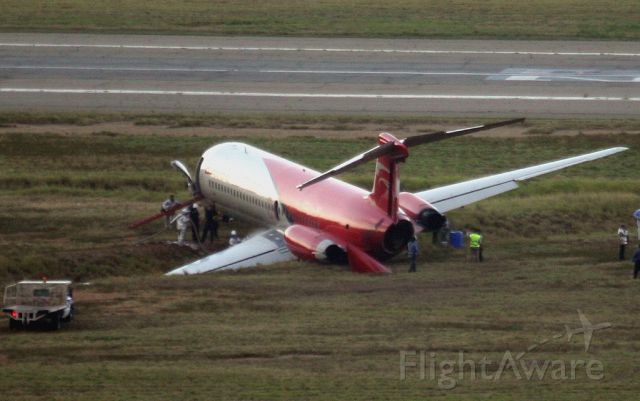
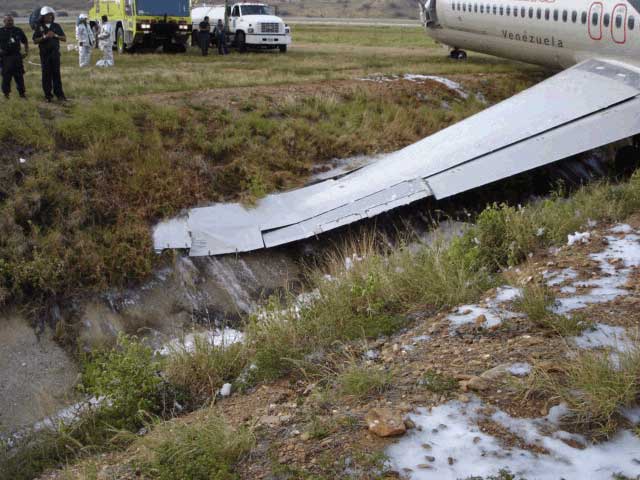
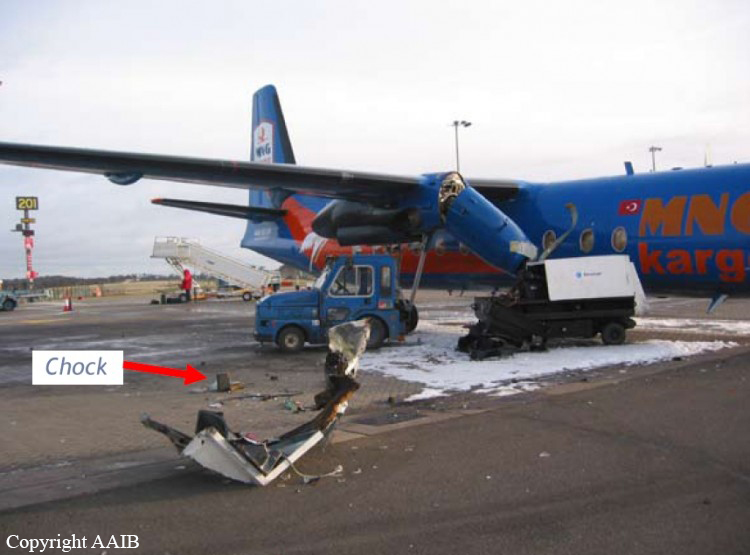
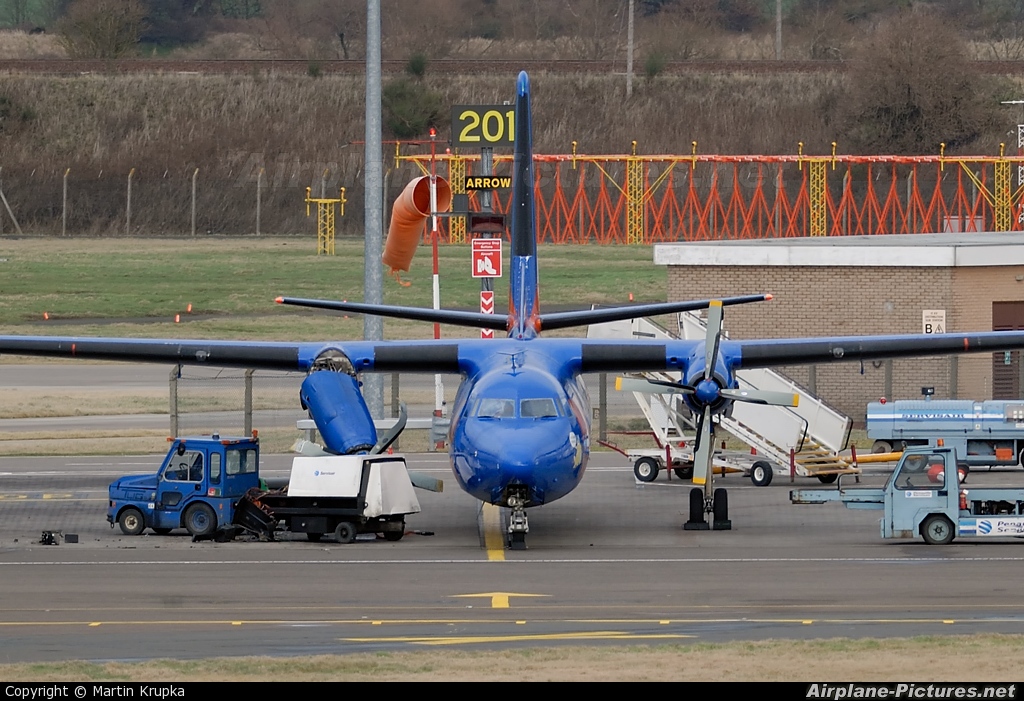
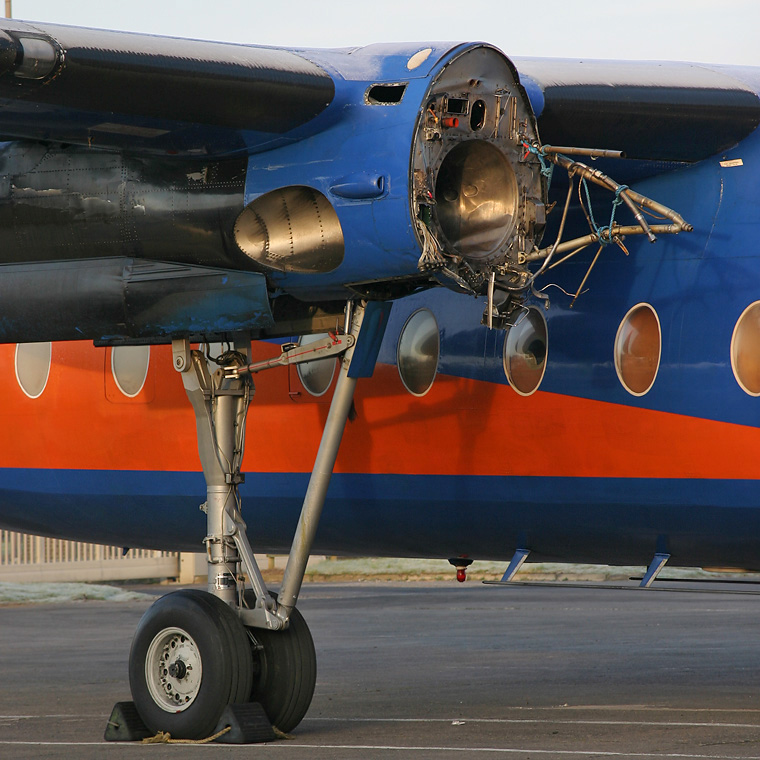
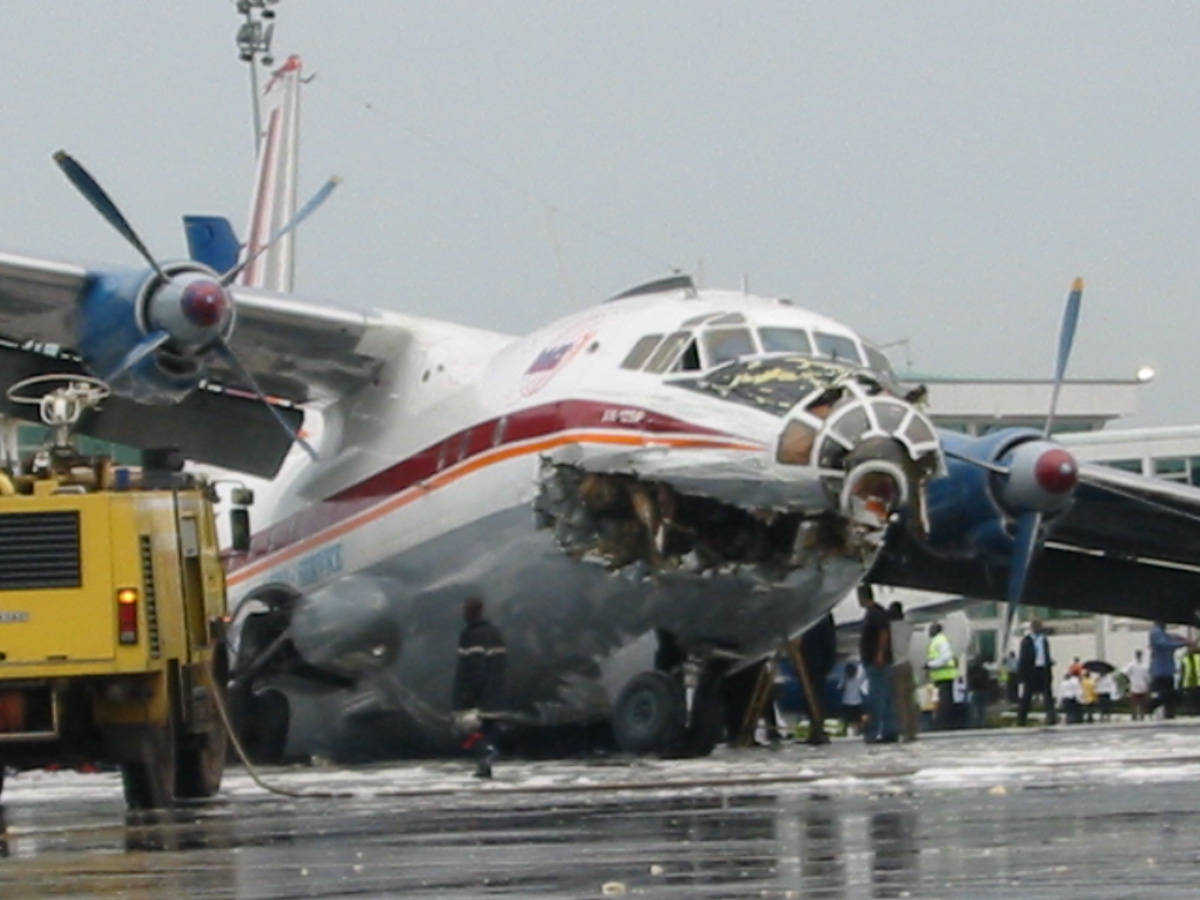
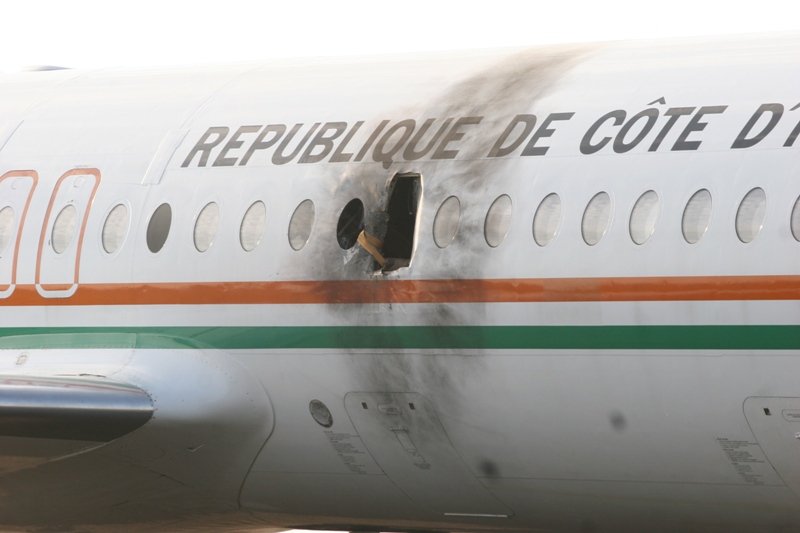
Shortly after takeoff, when the Copilot pulled back the thrust levers of both engines to the desired positions, the thrust lever on left engine could not move and the engine remained in full power. The Pilot in Command (PIC) then informed Air Traffic Controller (ATC) that the aircraft had a technical problem and requested to return to the airport. The crew managed to land safely with the Copilot and accompanying company maintenance engineer struggling to control the left engine which was on high power setting and the PIC controlling the aircraft using only the right hand engine. The aircraft taxied to parking bay number 4 with the left engine still in full power. The captain applied the parking brake and the aircraft stopped for a while and before putting on the chocks, the aircraft started moving forward at a high speed through the jet blast fence and crashed into Control Tower building. A passenger was killed, six people were injured, three seriously.
Probable cause:
The flight crew’s failure to identify corrective action and their lack of knowledge of applicable airplane and engine systems in response to a jammed thrust lever, which resulted in the number 1 engine operating at high power and the airplane configured in an unsafe condition that led to the need to apply heavy braking during landing. Also causal was the flightcrew failure to recognize the safety hazard that existed from overheated brakes and the potential consequence on the braking action needed to park the airplane. Contributing factors included the possible failure by maintenance crew to correctly stow the upper core cowl support strut after maintenance, Flight crew’s failure to follow standard operating procedures, the company’s failure to be availed to manufacturer safety literature on the subject, and the susceptibility of the cowl core support shaft to interfere with the throttle control mechanism when the core strut is not in its stowed position.
Final Report: