Circumstances:
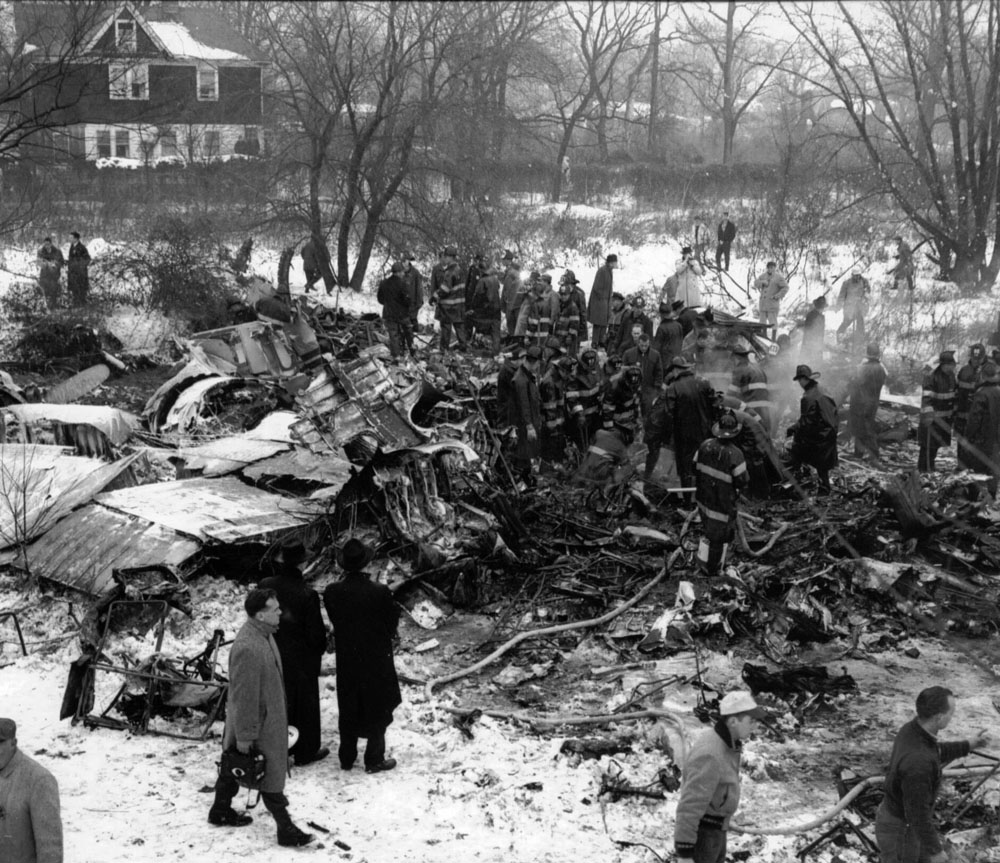
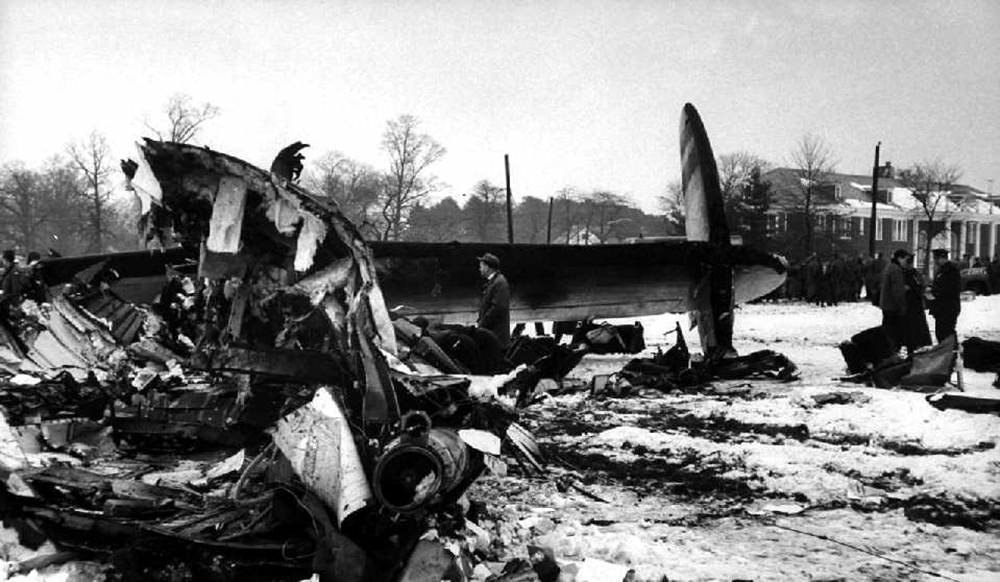
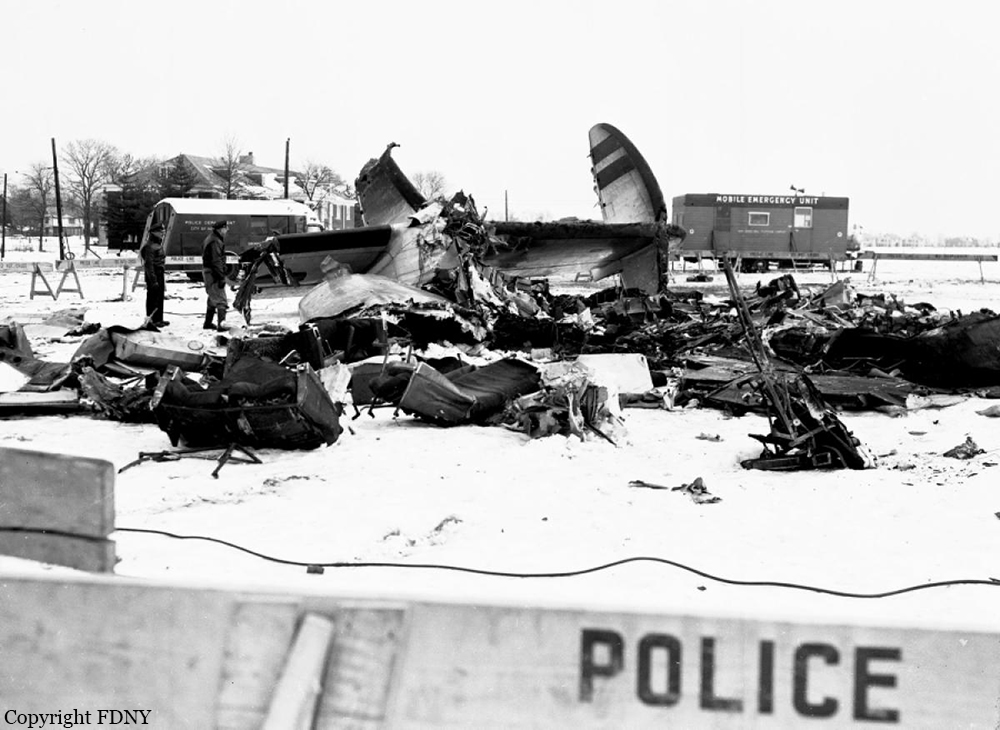
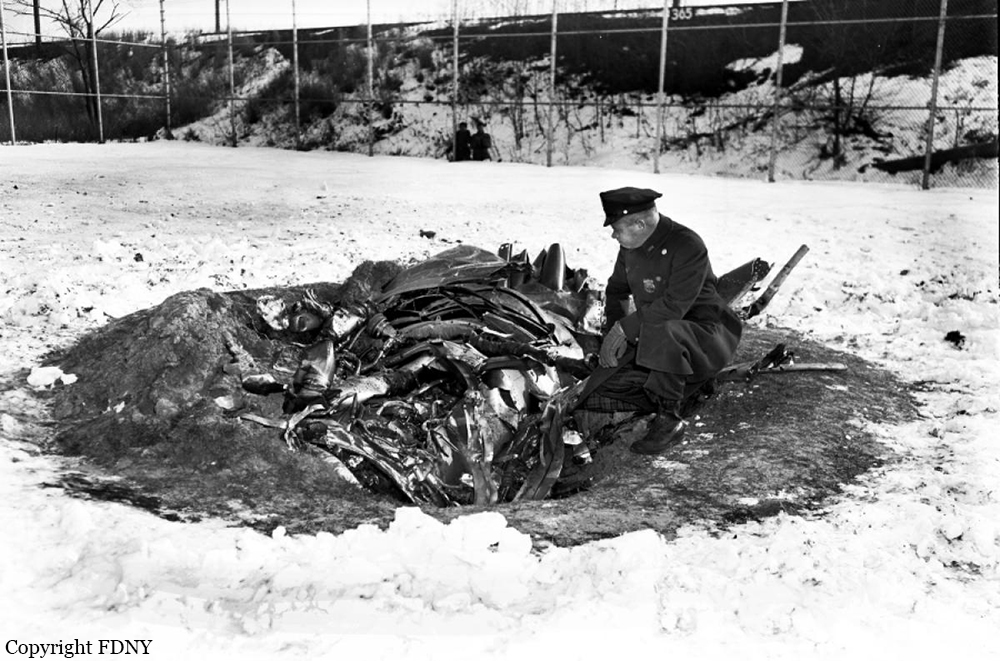
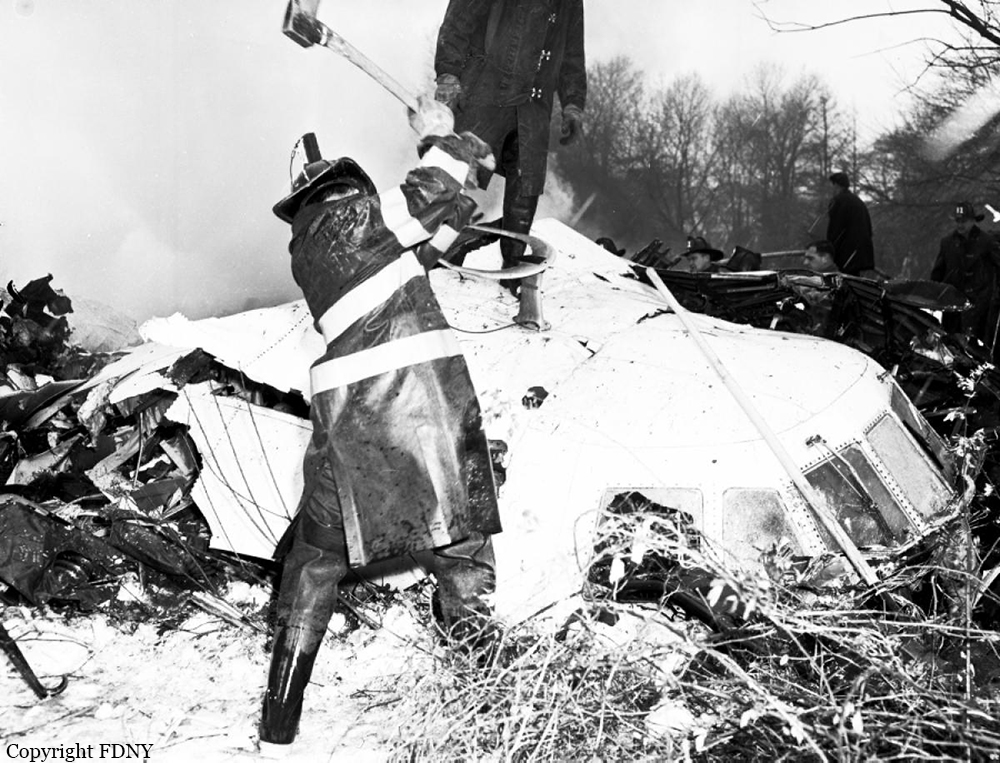
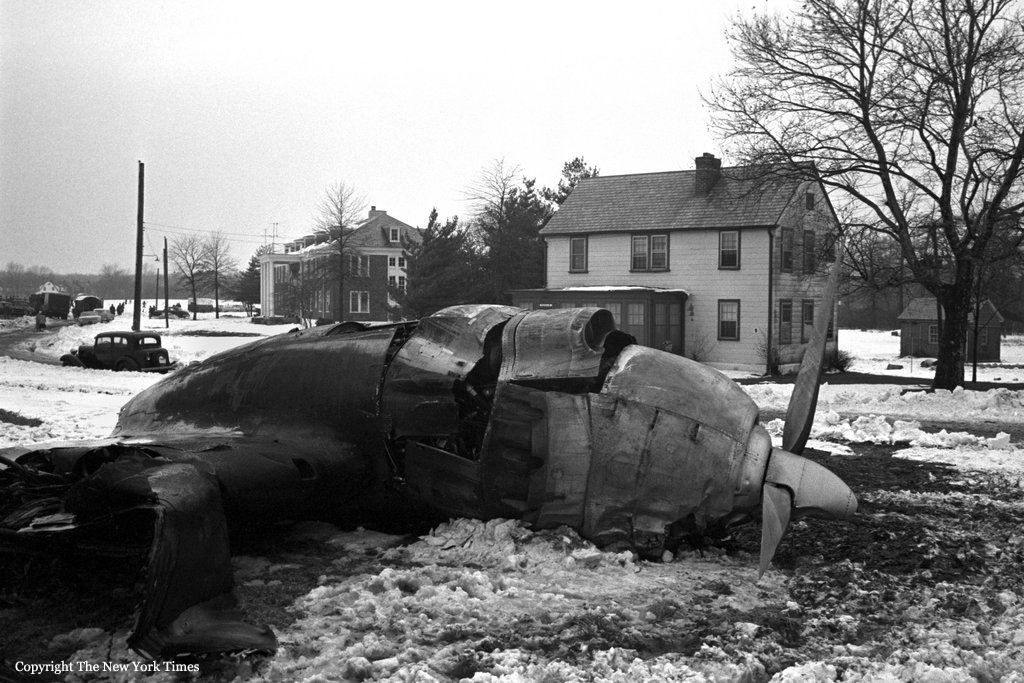
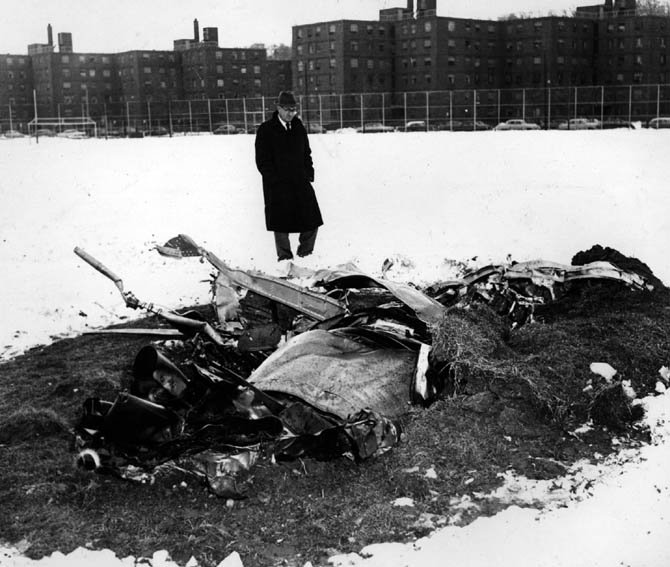
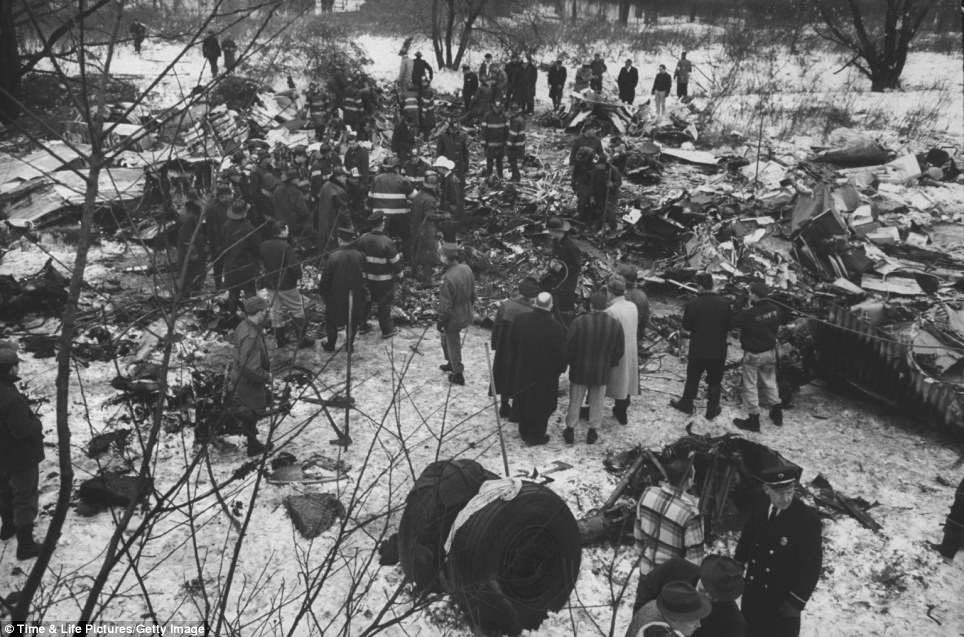
On December 16, 1960, at 1033 e.s.t., a collision between Trans World Airlines Model 1049A Constellation, N6907C, and a United Air Lines DC-8, N8013U, occurred near Miller Army Air Field, Staten Island, New York. Trans World Airlines Flight 266 originated at Dayton, Ohio. The destination was LaGuardia Airport, New York, with one en route stop at Columbus, Ohio United Air Lines Flight 826 was a non-stop service originating at O'Hare Airport, Chicago, Illinois, with its destination New York International Airport, New York. Both aircraft were operating under Instrument Flight Rules. Following the collision the Constellation fell on Miller Army Field, and the DC-8 continued in a northeasterly direction, crashing into Sterling place near Seventh Avenue in Brooklyn, New York. Both aircraft were totally destroyed. All 128 occupants of both aircraft and 6 persons on the ground in Brooklyn were fatally injured. There was considerable damage to property in the area of the ground impact of the DC-8. TWA Flight 266 departed Port Columbus Airport at 0900, operating routinely under Air Traffic Control into the New York area The New York Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) subsequently advised that radar contact had been established and cleared the flight to the Linden. Intersection, Control of the flight was subsequently transferred to LaGuardia Approach Control. When the flight was about over the Linden Intersection, LaGuardia Approach Control began vectoring TWA 266 by radar to the final approach course for a landing on runway 4 at LaGuardia. Shortly thereafter TWA 266 was cleared to descend to 5,000 feet, and was twice advised of traffic in the vicinity on a northeasterly heading. Following the transmission of this information the radar targets appeared to merge on the LaGuardia Approach Control radar scope, and communications with TWA 266 were lost. United Air Lines Flight 826 operated routinely between Chicago and the New York area, contacting the New York ARTCC at 1012 Shortly thereafter the New York Center cleared UAL 826 to proceed from the Allentown, Pa., very high frequency omni directional radio range station (VOR) direct to the Robbinsville, New Jersey, VOR, and thence to the Preston Intersection via Victor Airway 123. At approximately 1021, UAL 826 contacted Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC) to advise their company that the No. 2 receiver accessory unit was inoperative, which would indicate that one of the aircraft's two VHF radio navigational receivers was not functioning. A "fix" is established by the intersection of two radials from two separate radio range stations. With one unit inoperative the cross-bearings necessary can be taken by tuning the remaining receiver from one station to the other. This process consumes considerable time, however, and is not as accurate as the simultaneous display of information on two separate position deviation indicators While UAL 826 advised the company that one unit was inoperative, Air Traffic Control was not advised. At 1025 the New York ARTCC issued a clearance for a new routing which shortened the distance to Preston by approximately 11 miles. As a result, this reduced the amount of time available to the crew to retune the single radio receiver to either the Colt' s Neck, New Jersey, or Solberg, New Jersey, VOR in order to establish the cross-bearing with Victor 123, which would identify the Preston Intersection. In the event the crew would not attempt to retune the single VOR receiver, crossbearings on the Scotland Low Frequency Radiobeacon could be taken with the aircraft direction finding (ADF) equipment. This would be a means of identifying the Preston Intersection but, under the circumstances, would require rapid mental calculation in the interpretation of a display which could be easily misread. Several factors support the conclusion that this occurred. Instructions had been issued to UAL 826 for holding at the Preston Intersection the clearance limit, should holding be necessary. Clearance beyond Preston for an approach to Idlewild Airport would be received from Idlewild Approach Control and the transfer of control of the flight from the New York Center to Idlewild Approach Control would normally take place as the aircraft was approaching Preston. UAL 826 was not receiving radar vectors, but was providing its own navigation. After the flight reported passing through 6,000 feet the New York Center advised that radar service was terminated and instructed the flight to contact Idlewild Approach Control. UAL 826 then called Idlewild Approach Control, stating "United 826 approaching Preston at 5,000." This was the last known transmission from UAL 826. At the time UAL 826 advised it was approaching Preston it had in fact gone on by this clearance limit several seconds before and was several miles past the point at which it should have turned into the holding pattern. This is confirmed by the data obtained from the flight recorder which had been installed in the UAL DC-8, as well as by analysis of the communication tapes At a point approximately 11 miles past the Preston Intersection a collision occurred between TWA 266 and UAL 826. Weather at the altitude of the collision and at the time of the accident was such as to preclude flight by visual means.