Country
Crash of a Boeing 747-168B in Charkhi Dadri: 312 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 12, 1996 at 1840 LT
Registration:
HZ-AIH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
New Delhi - Dhahran - Jeddah
MSN:
22748
YOM:
1982
Flight number:
SV763
Crew on board:
23
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
289
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
312
Captain / Total hours on type:
104.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1952
Aircraft flight hours:
40035
Aircraft flight cycles:
14927
Circumstances:
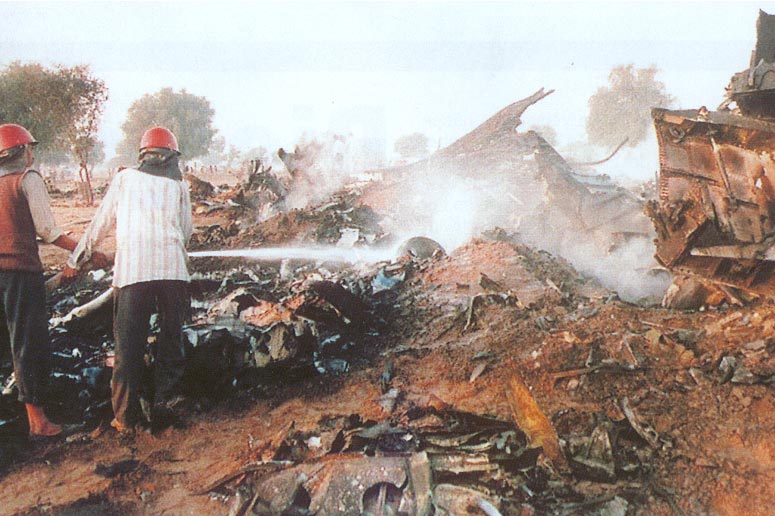
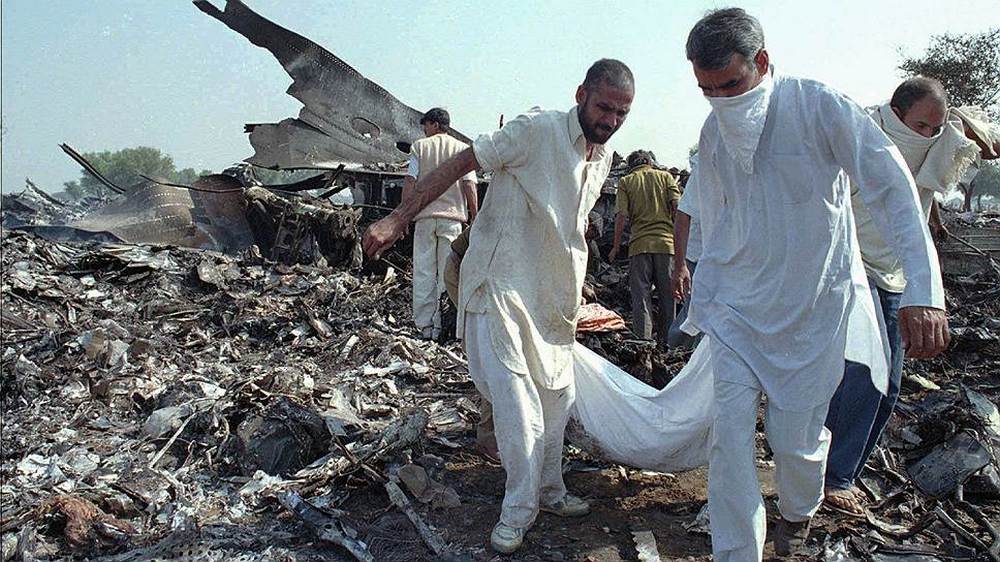
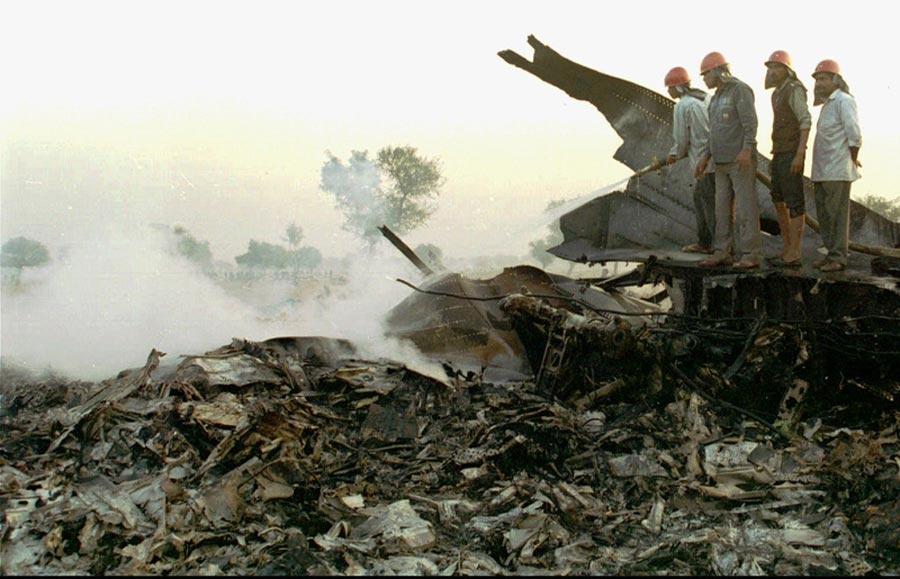
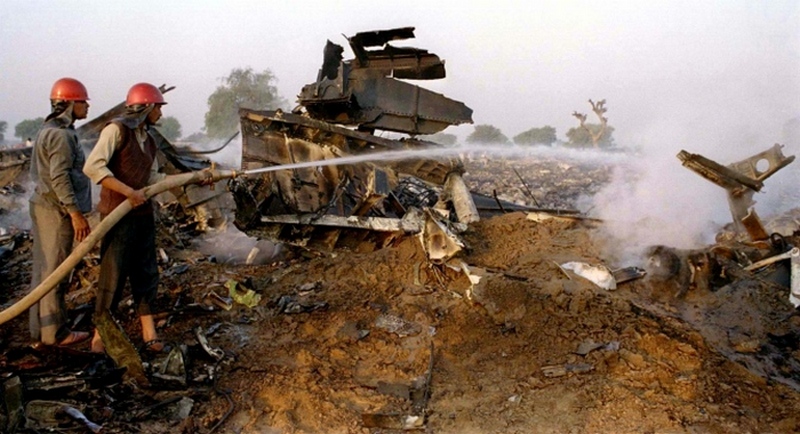
The aircraft departed New Delhi-Indira Gandhi Airport at 1833LT on a flight to Jeddah with an intermediate stop in Dhahran, carrying 289 passengers and 23 crew members. After takeoff, the crew was instructed to climb to FL140 via route G452. Seven minutes after takeoff, while cruising at an altitude of 14,000 feet, the aircraft collided with a Kazakhstan Airlines (Kazair) Ilyushin II-76TD that was descending to New Delhi Airport. Registered UN-76435, it was completing flight KZA1907 from Shymkent with 27 passengers and 10 crew members on board. After the collision, both aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed in an open field located about 3 km Charkhi Dadri, some 80 km west of New Delhi-Indira Gandhi Airport. Both aircraft were destroyed by impact forces and a post crash fire and all 349 occupants in both aircraft were killed.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the collision was the consequence of the failure of the Kazair crew to follow the assigned altitude of 15,000 feet while approaching New Delhi. The crew of the Kazair II-76 was instructed by ATC to continue the descent to Indira Gandhi Airport via the same route G452 but at an altitude of 15,000 feet (14,000 feet for the Saudia B747). For unknown reasons, the Kazair crew continued the descent below FL150 without clearance until both aircraft faced each other and collided. During the minutes preceding the accident, both Kazair and Saudia crew have been informed by ATC about other traffic.
Final Report:







Crash of a Boeing 747-131 off East Moriches: 230 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 17, 1996 at 2031 LT
Registration:
N93119
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
New York – Paris
MSN:
20083
YOM:
1971
Flight number:
TW800
Crew on board:
18
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
212
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
230
Captain / Total hours on type:
5490.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
4700
Aircraft flight hours:
93303
Aircraft flight cycles:
16869
Circumstances:
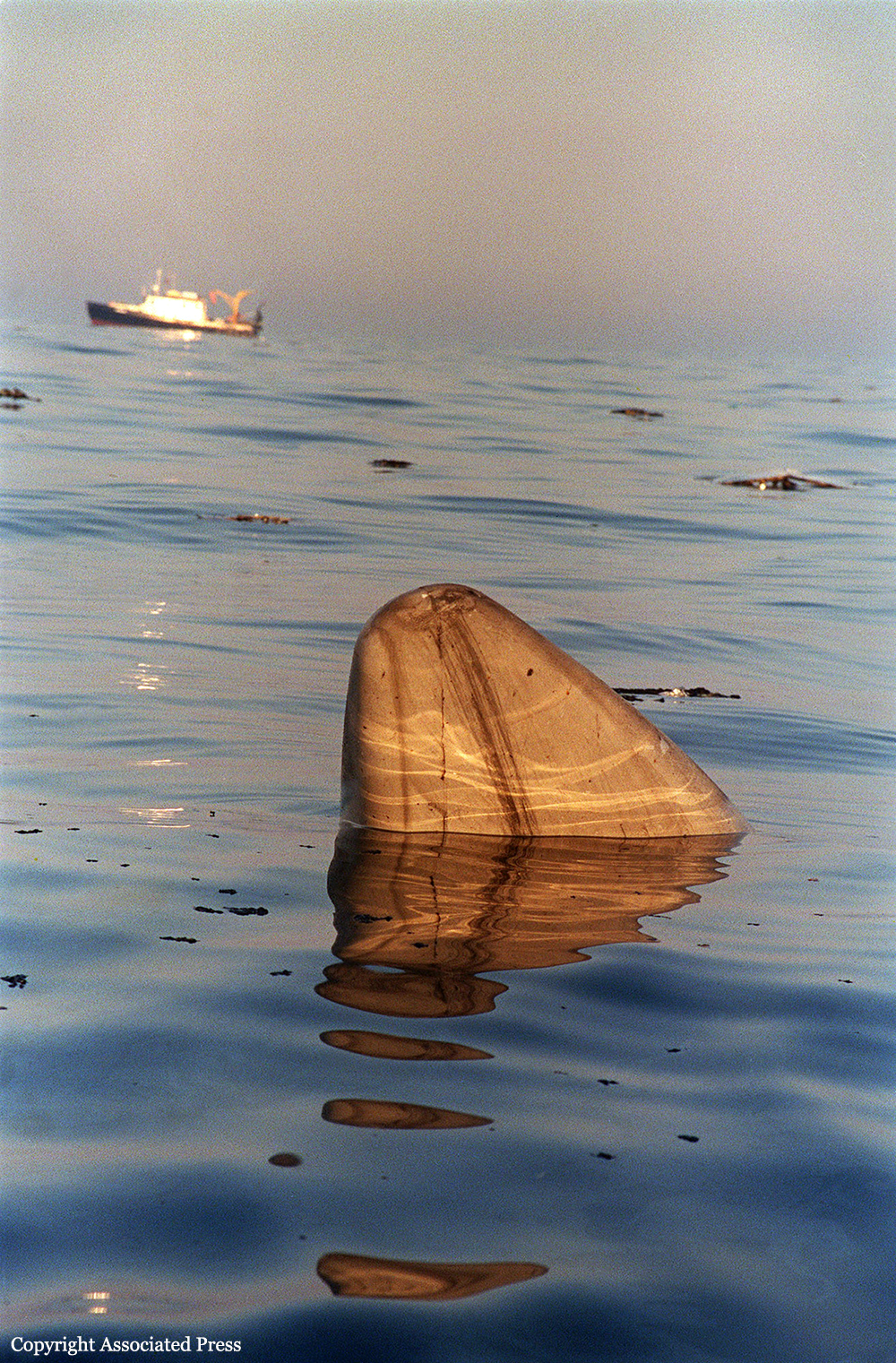
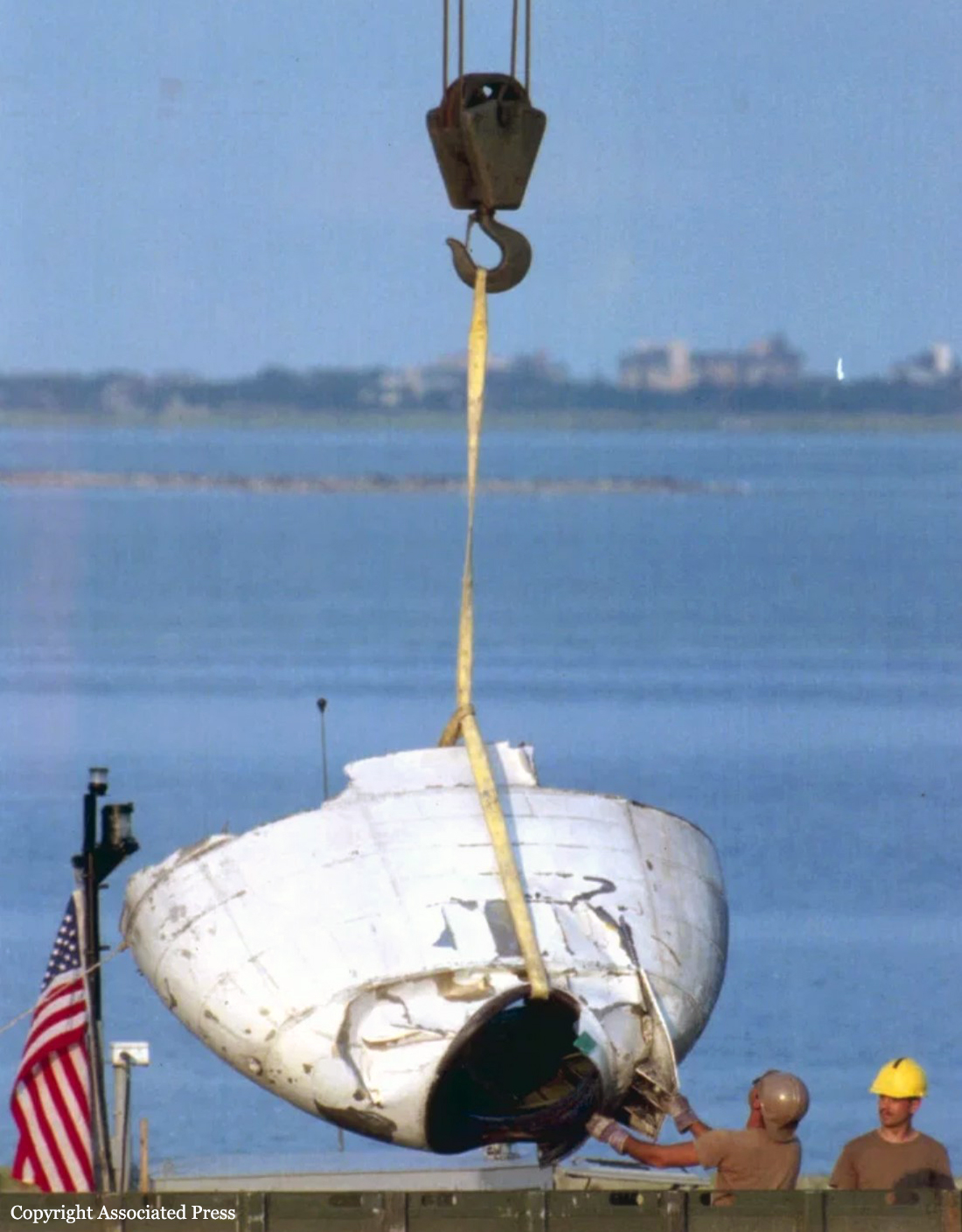
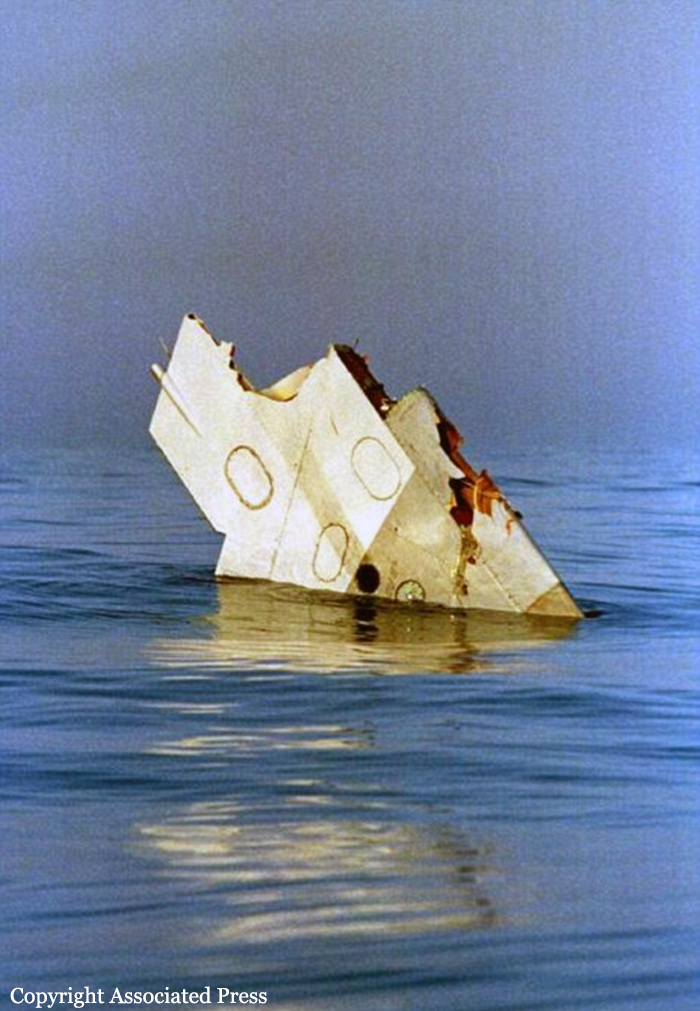
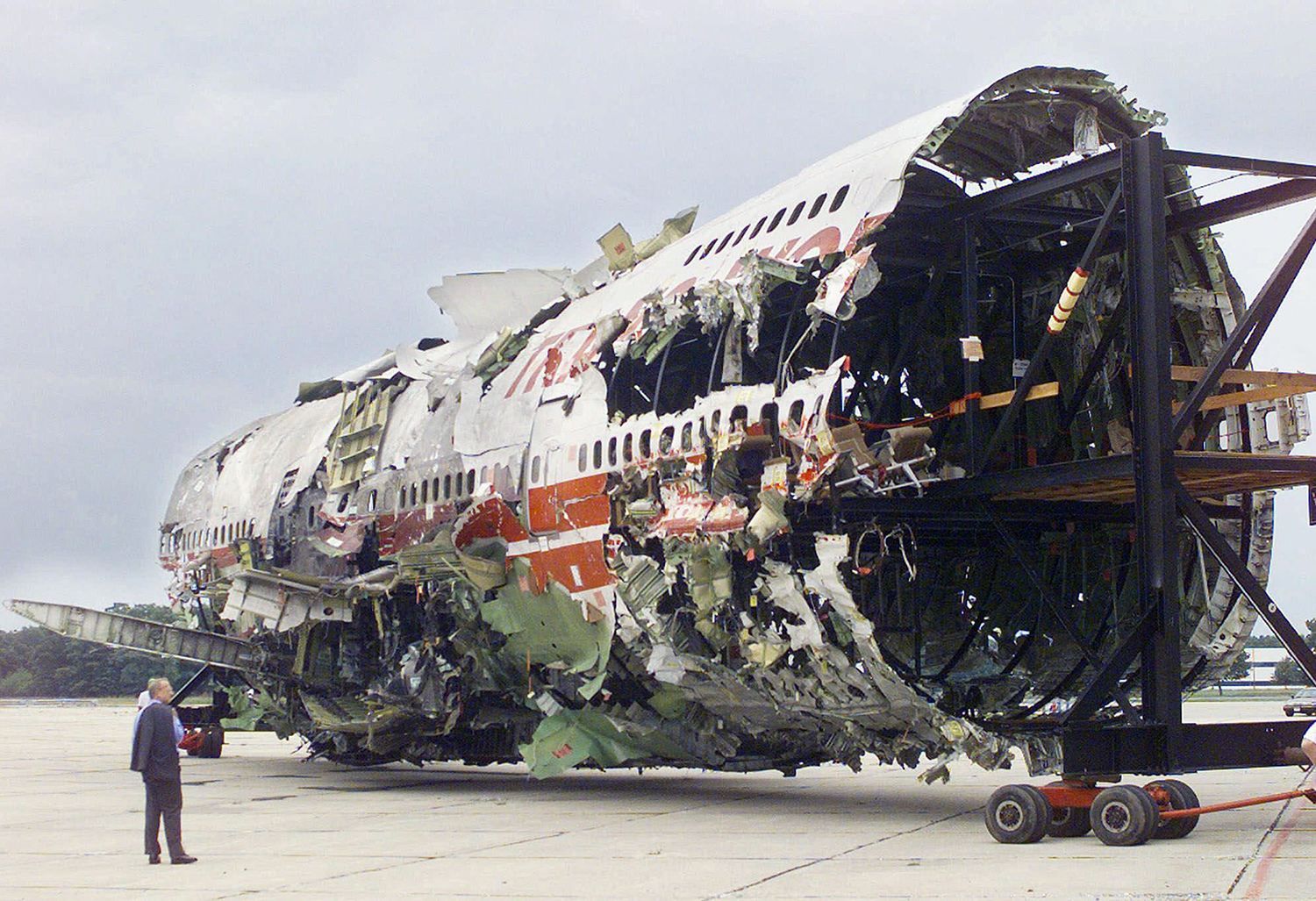
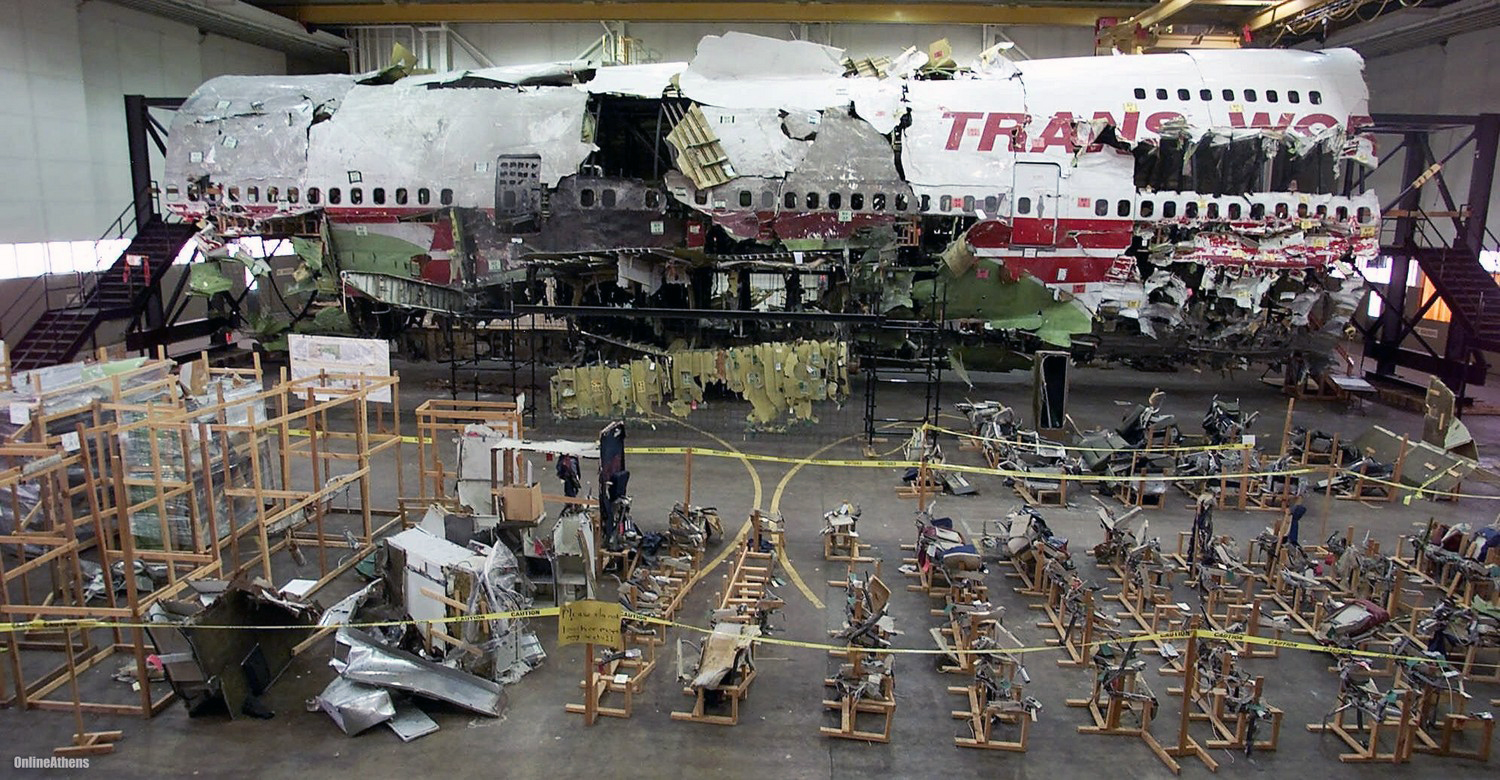
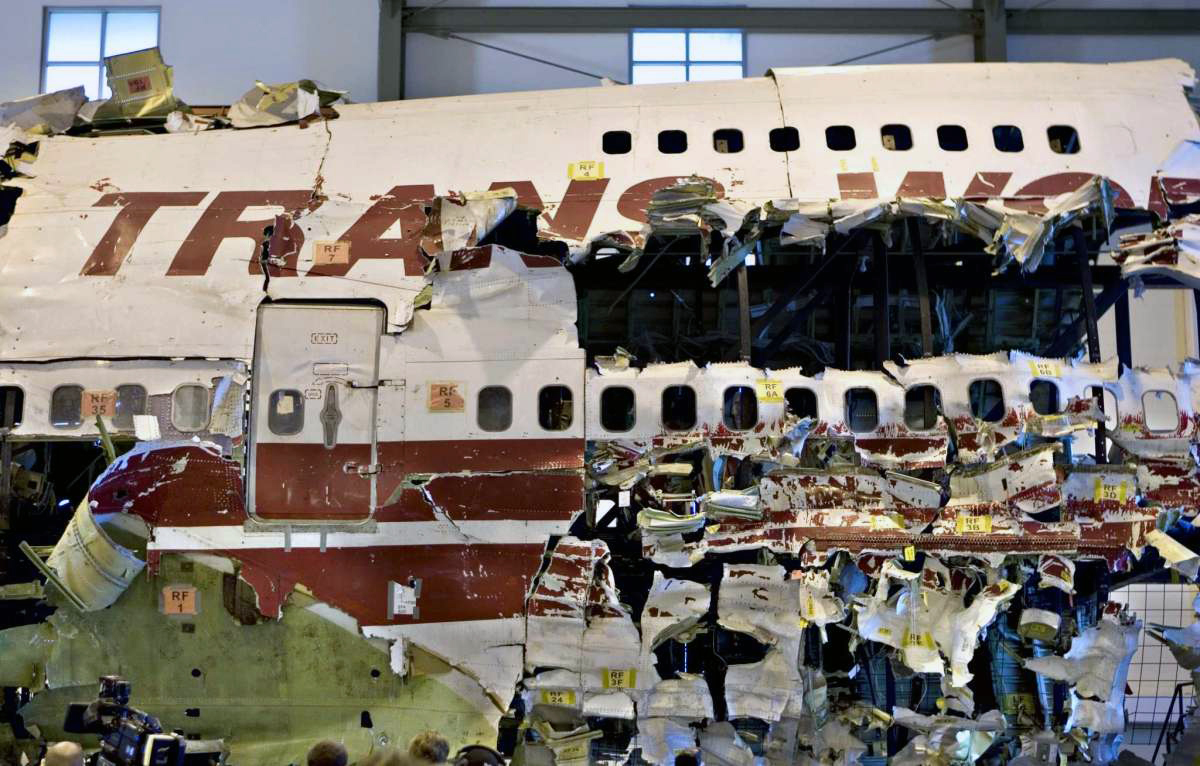
On July 17, 1996, about 2031 eastern daylight time, Trans World Airlines, Inc. (TWA) flight 800, a Boeing 747-131, N93119, crashed in the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York. TWA flight 800 was operating under the provisions of 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 121 as a scheduled international passenger flight from John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), New York, New York, to Charles De Gaulle International Airport, Paris, France. The flight departed JFK about 2019, with 2 pilots, 2 flight engineers, 14 flight attendants, and 212 passengers on board. All 230 people on board were killed, and the airplane was destroyed. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed for the flight, which operated on an instrument flight rules flight plan. The investigation revealed that the crash occurred as the result of a fuel/air explosion in the airplane's center wing fuel tank (CWT) and the subsequent in-flight breakup of the airplane. The investigation further revealed that the ignition energy for the CWT explosion most likely entered the CWT through the fuel quantity indication system wiring; neither the ignition energy release mechanism nor the location of the ignition inside the CWT could be determined from the available evidence. There was no evidence of a missile or bomb detonation.
Probable cause:
An explosion of the center wing fuel tank (CWT), resulting from ignition of the flammable fuel/air mixture in the tank. The source of ignition energy for the explosion could not be determined with certainty, but, of the sources evaluated by the investigation, the most likely was a short circuit outside of the CWT that allowed excessive voltage to enter it through electrical wiring associated with the fuel quantity indication system. Contributing factors to the accident were the design and certification concept that fuel tank explosions could be prevented solely by precluding all ignition sources and the design and certification of the Boeing 747 with heat sources located beneath the CWT with no means to reduce the heat transferred into the CWT or to render the fuel vapor in the tank non flammable.
Final Report:
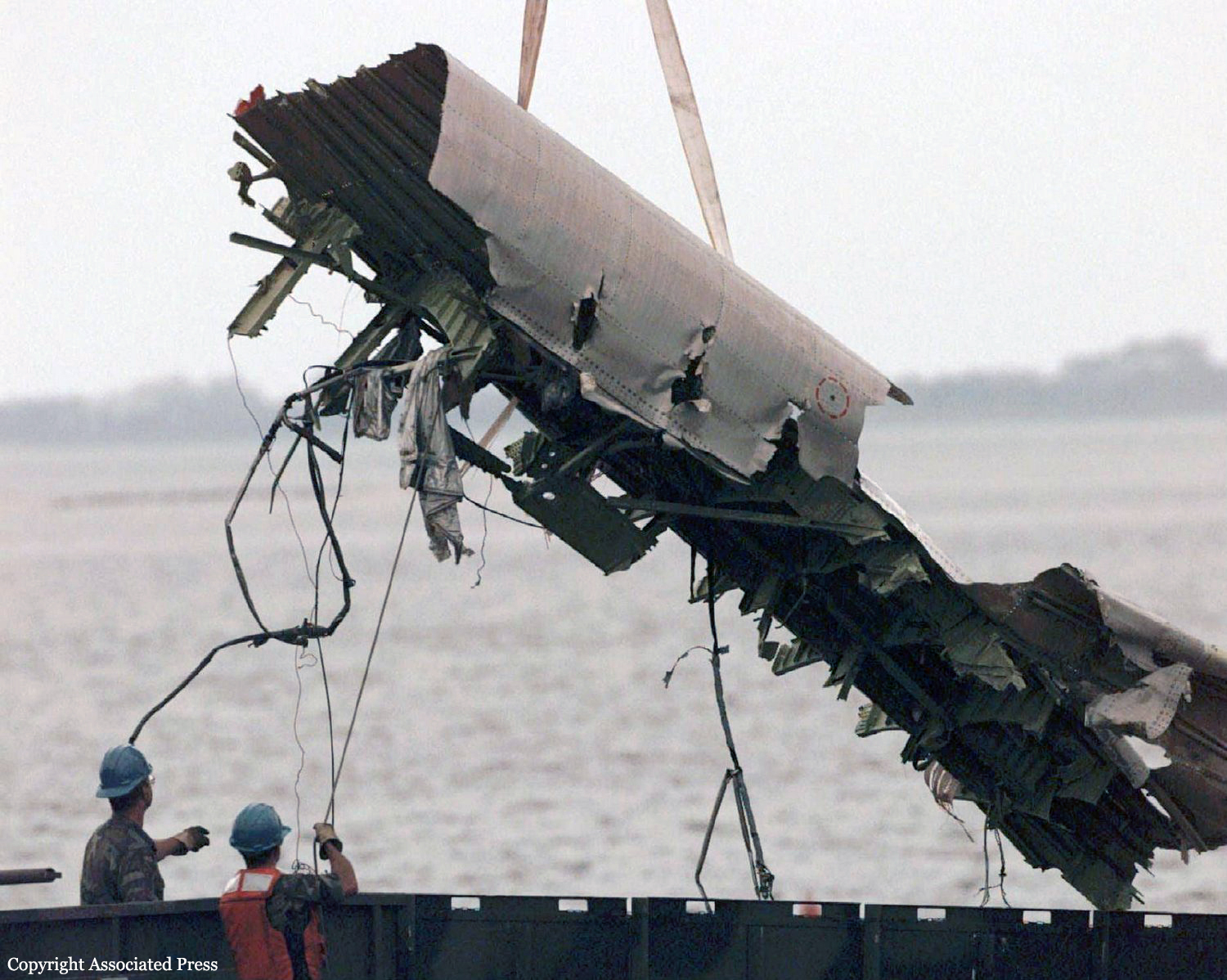
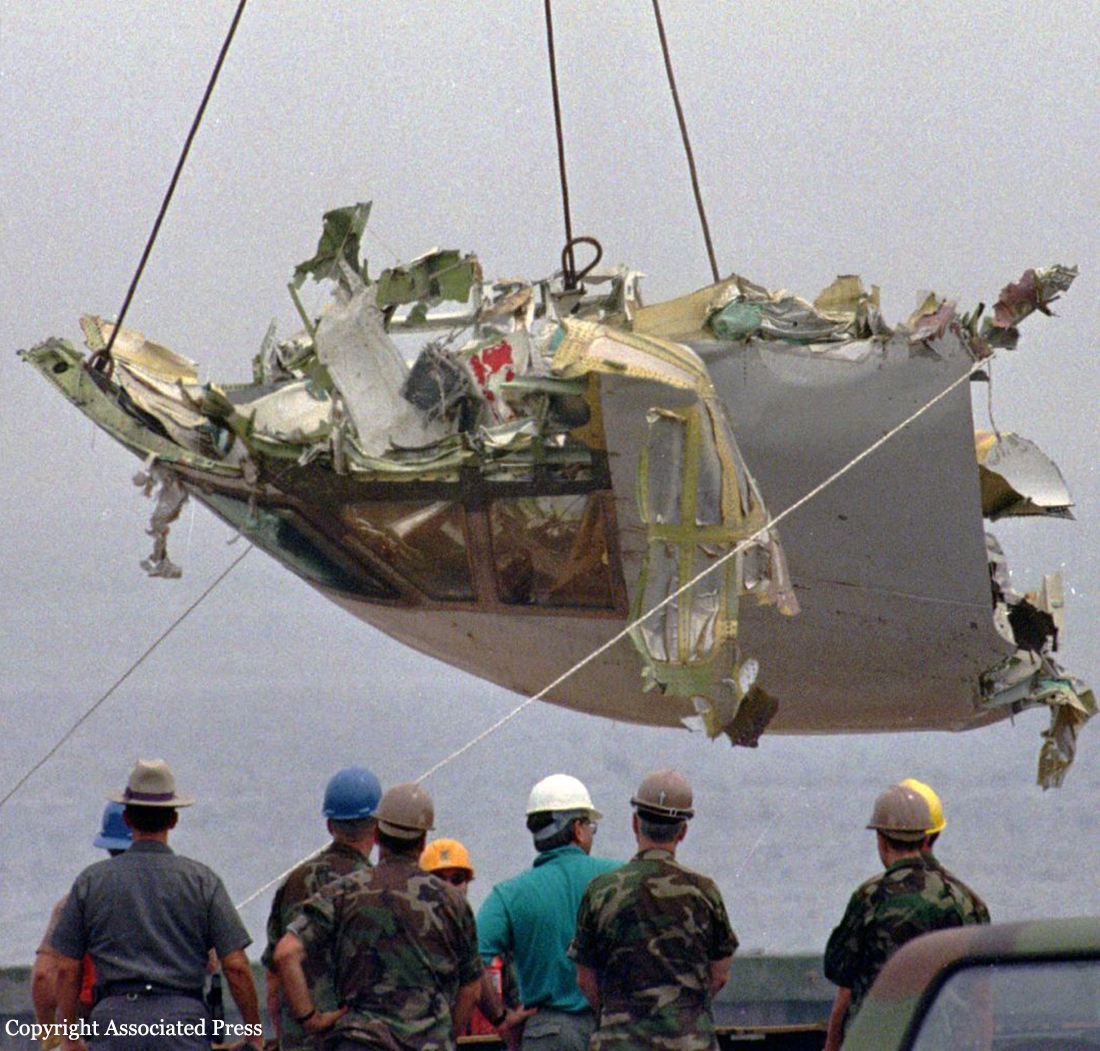
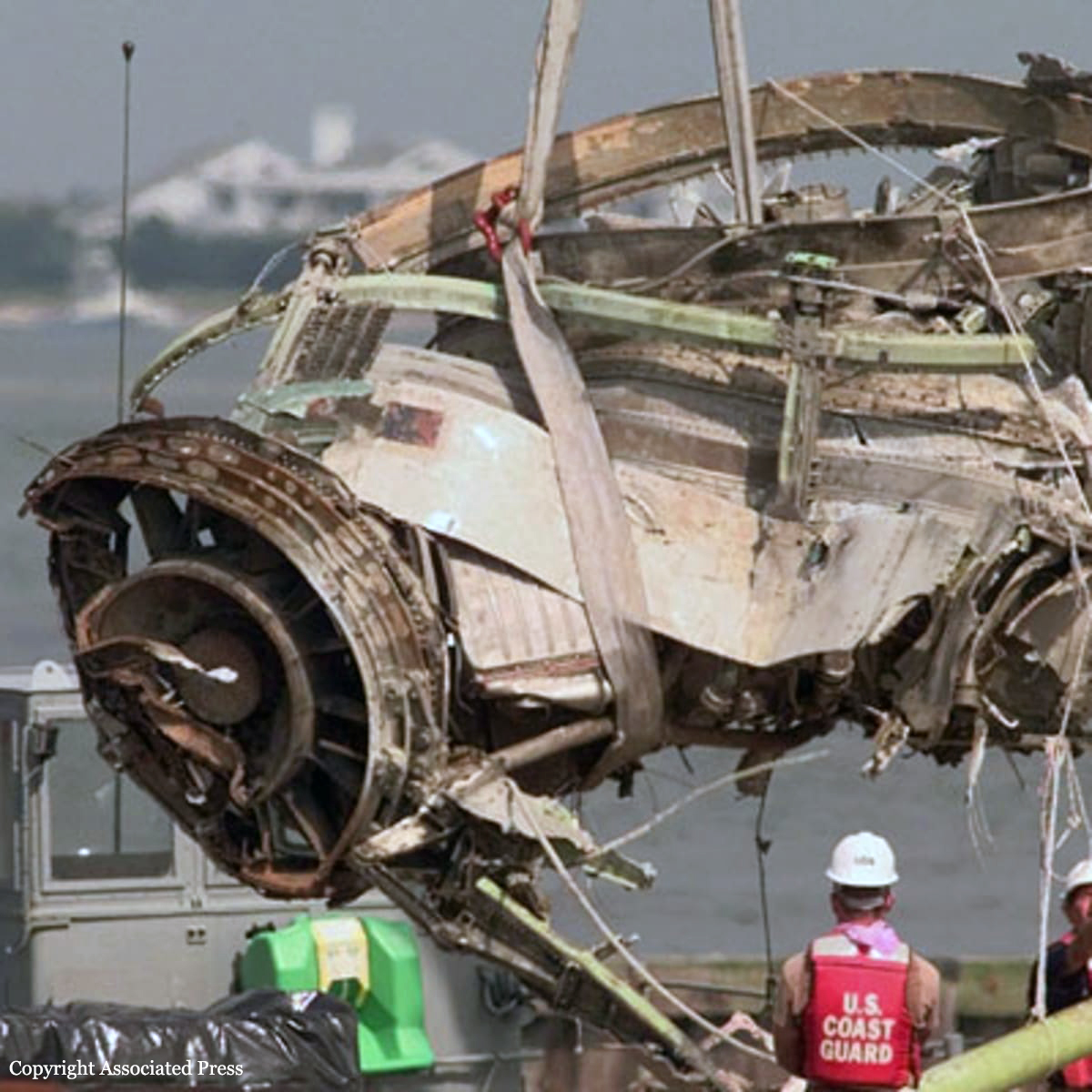




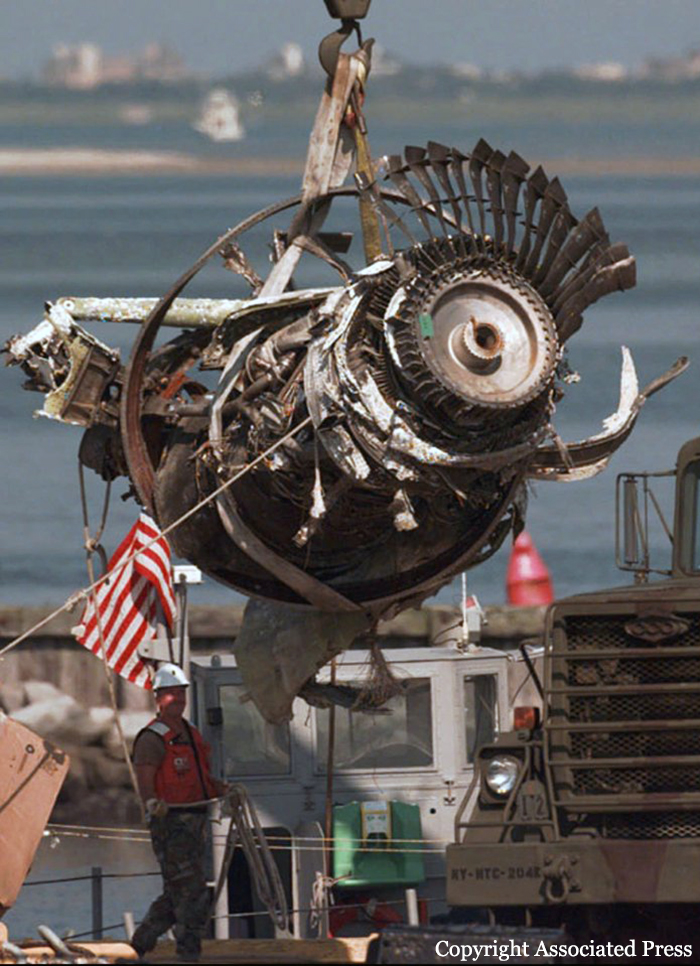






Crash of a Boeing 747-136 in New York
Date & Time:
Dec 20, 1995 at 1136 LT
Registration:
N605FF
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
New York - Miami
MSN:
20271
YOM:
1971
Flight number:
FF041
Crew on board:
17
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
451
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2905.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
4804
Aircraft flight hours:
90456
Aircraft flight cycles:
17726
Circumstances:
The captain initiated a takeoff on runway 04L, which was covered with patches of ice and snow. The wind was from 330 degrees at 11 knots. Before receiving an 80-knot call from the 1st officer, the airplane began to veer to the left. Subsequently, it went off the left side of the runway and collided with signs and an electric transformer. Investigation revealed evidence that the captain had overcontrolled the nosewheel steering through the tiller, then applied insufficient or untimely right rudder inputs to effect a recovery. The captain abandoned an attempt to reject the takeoff, at least temporarily, by restoring forward thrust before the airplane departed the runway. The current Boeing 747 operating procedures provide inadequate guidance to flightcrews regarding the potential for loss of directional control at low speeds on slippery runways with the use of the tiller. Current Boeing 747 flight manual guidance was inadequate about when a pilot should reject a takeoff following some indication of a lack of directional control response. Improvements in the slippery runway handling fidelity of flight simulators used for Boeing 747 pilot training were considered to be both needed and feasible.
Probable cause:
The captain's failure to reject the takeoff in a timely manner when excessive nosewheel steering tiller inputs resulted in a loss of directional control on a slippery runway. Inadequate Boeing 747 slippery runway operating procedures developed by Tower Air, Inc., and the Boeing Commercial Airplane Group and the inadequate fidelity of B-747 flight training simulators for slippery runway operations contributed to the cause of this accident. The captain's reapplication of forward thrust before the airplane departed the left side of the runway contributed to the severity of the runway excursion and damage to the airplane.
Final Report:


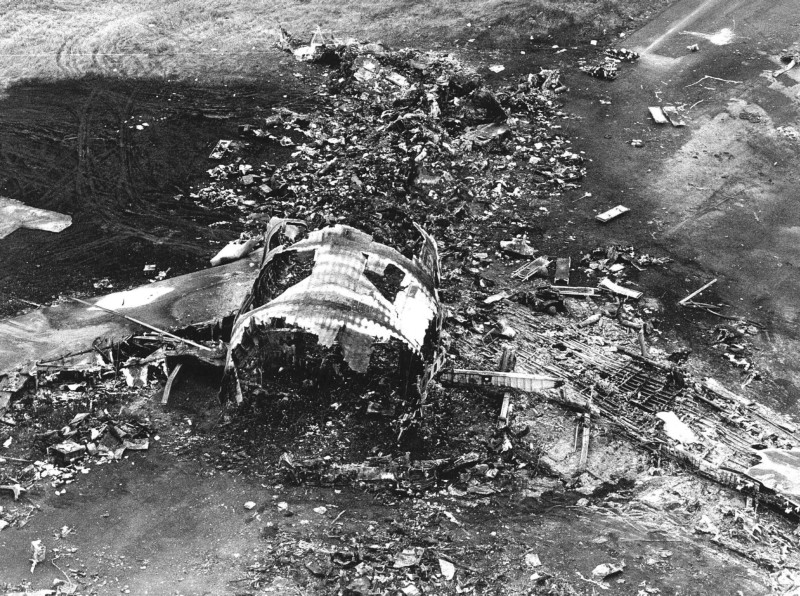
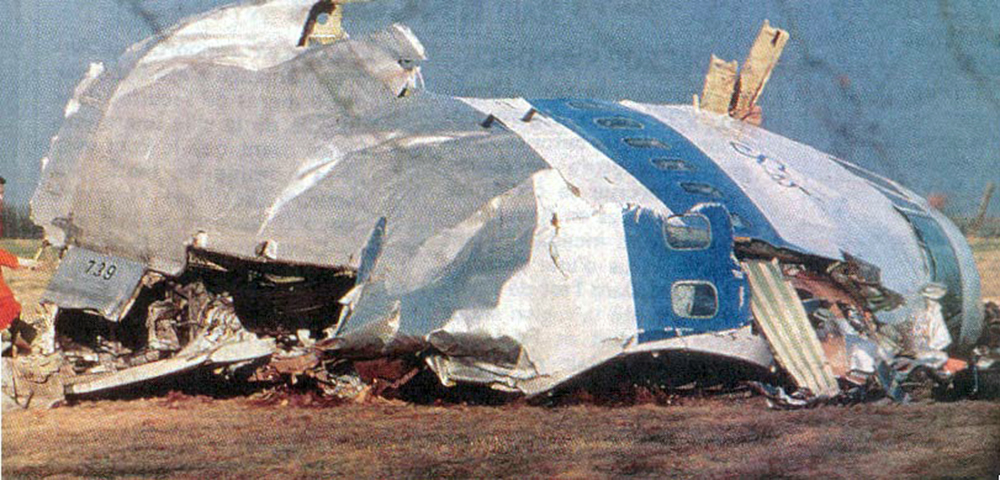
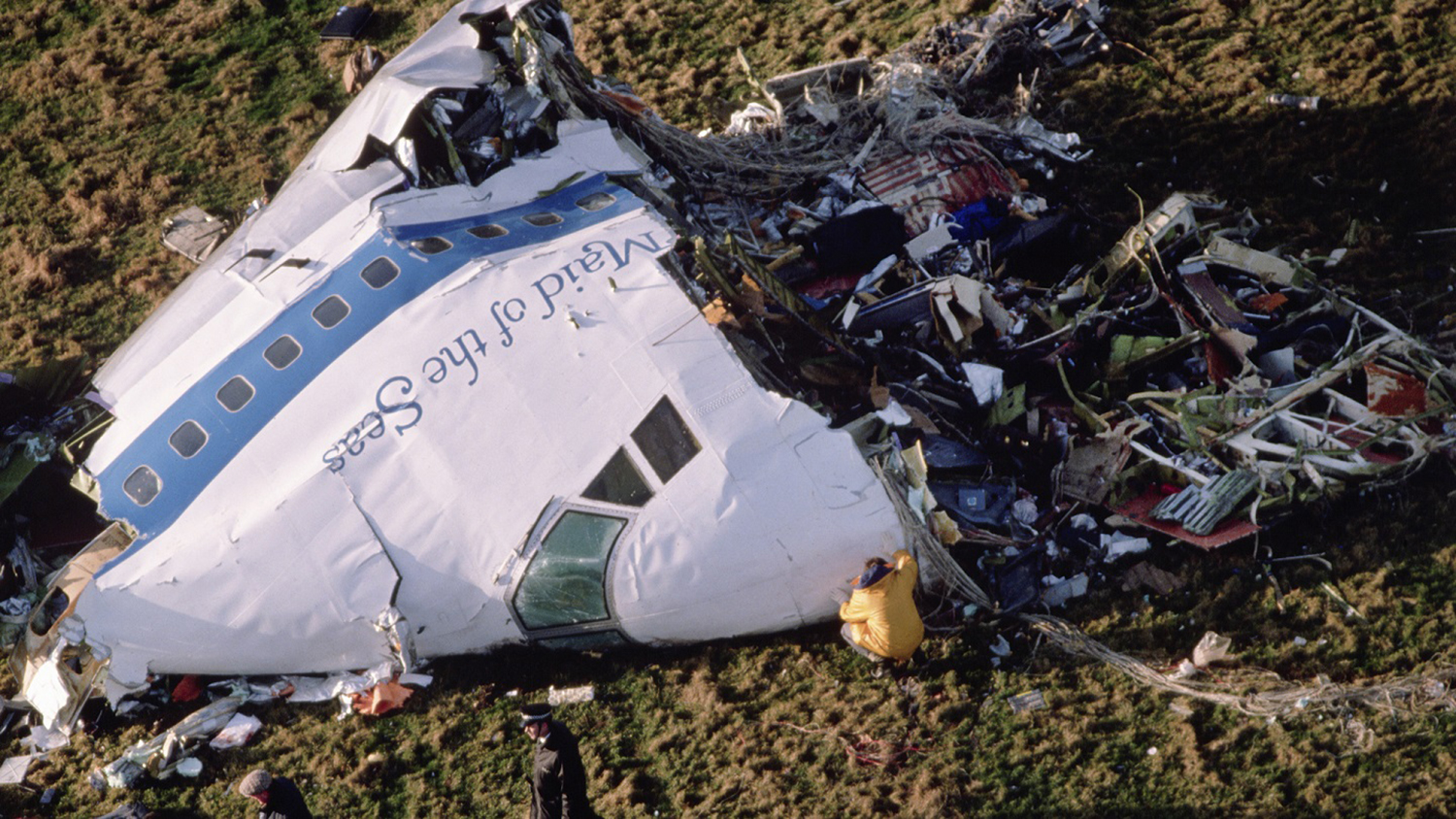
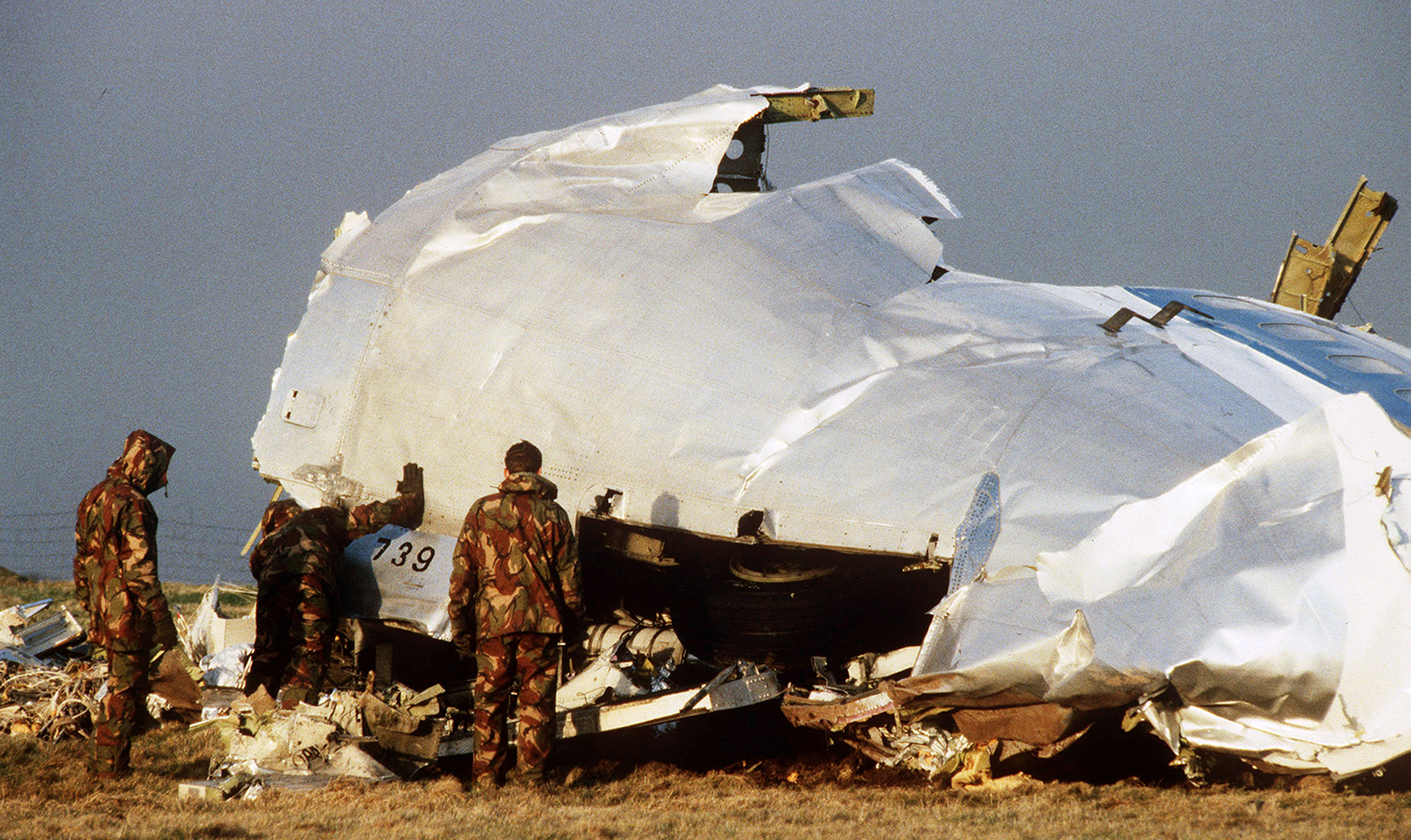
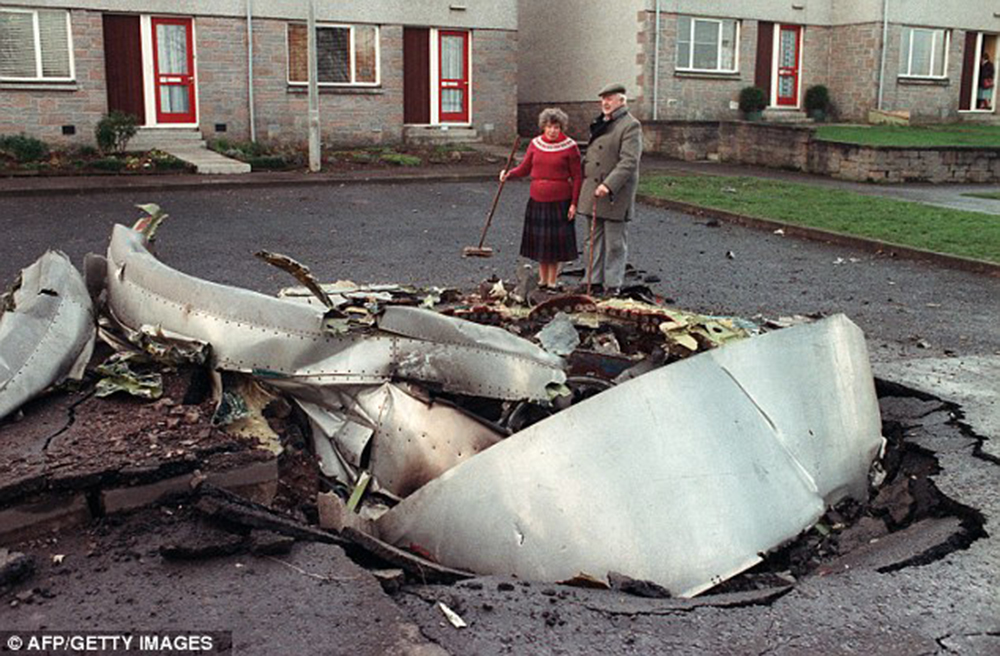
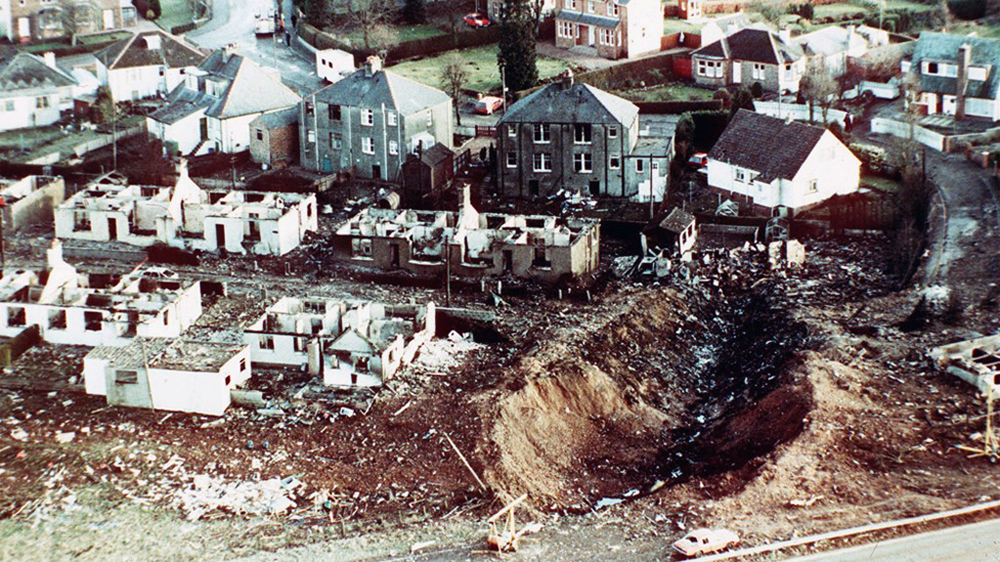
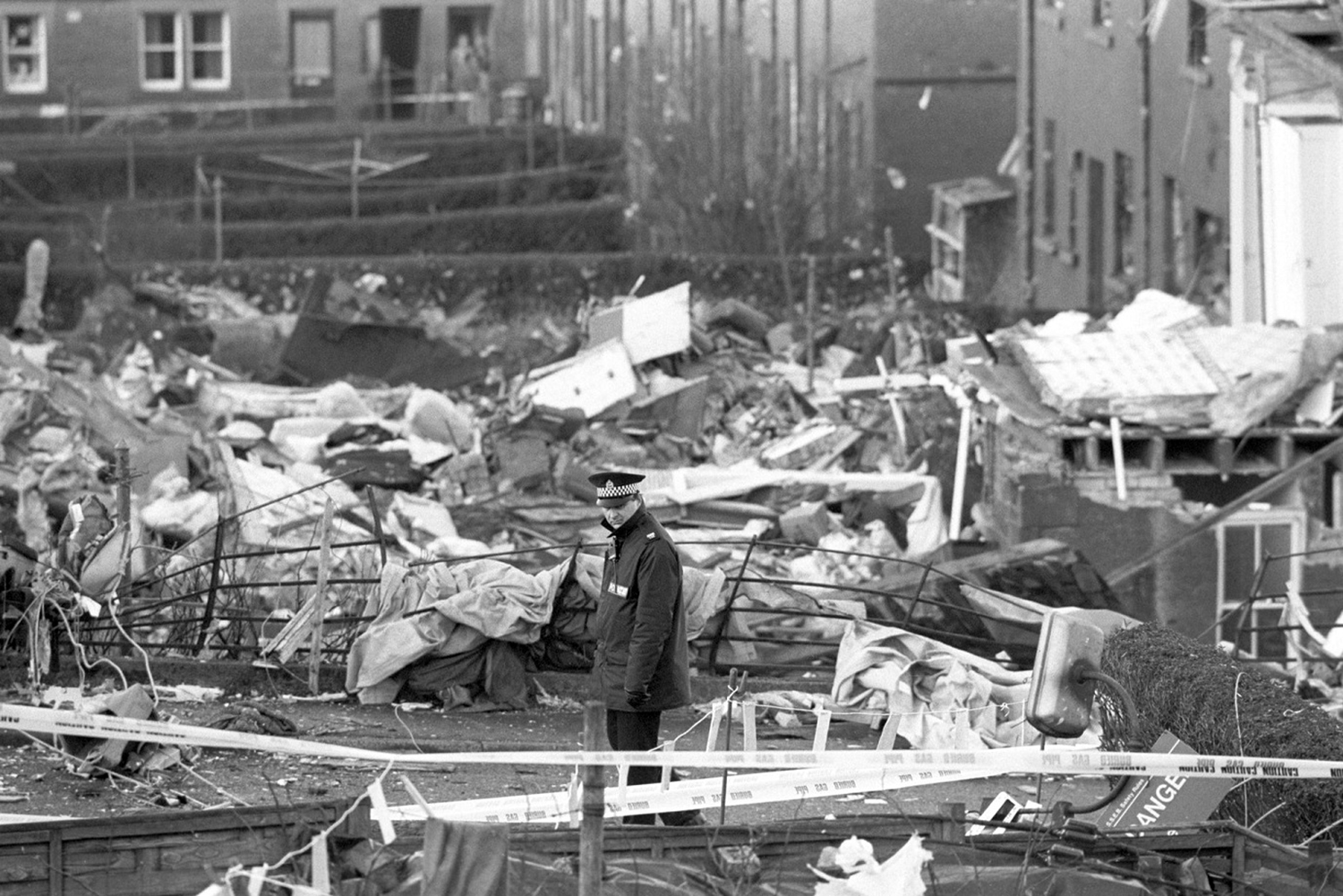
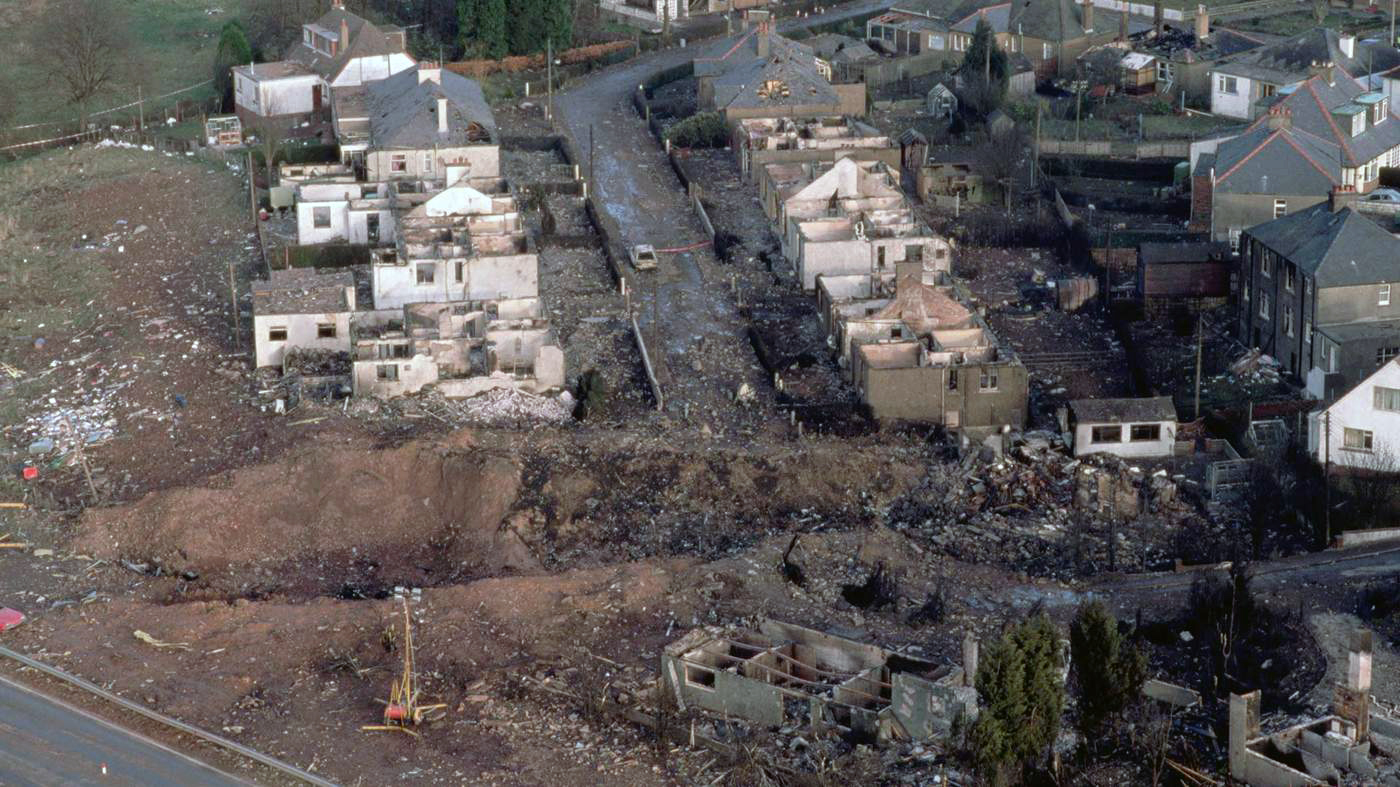
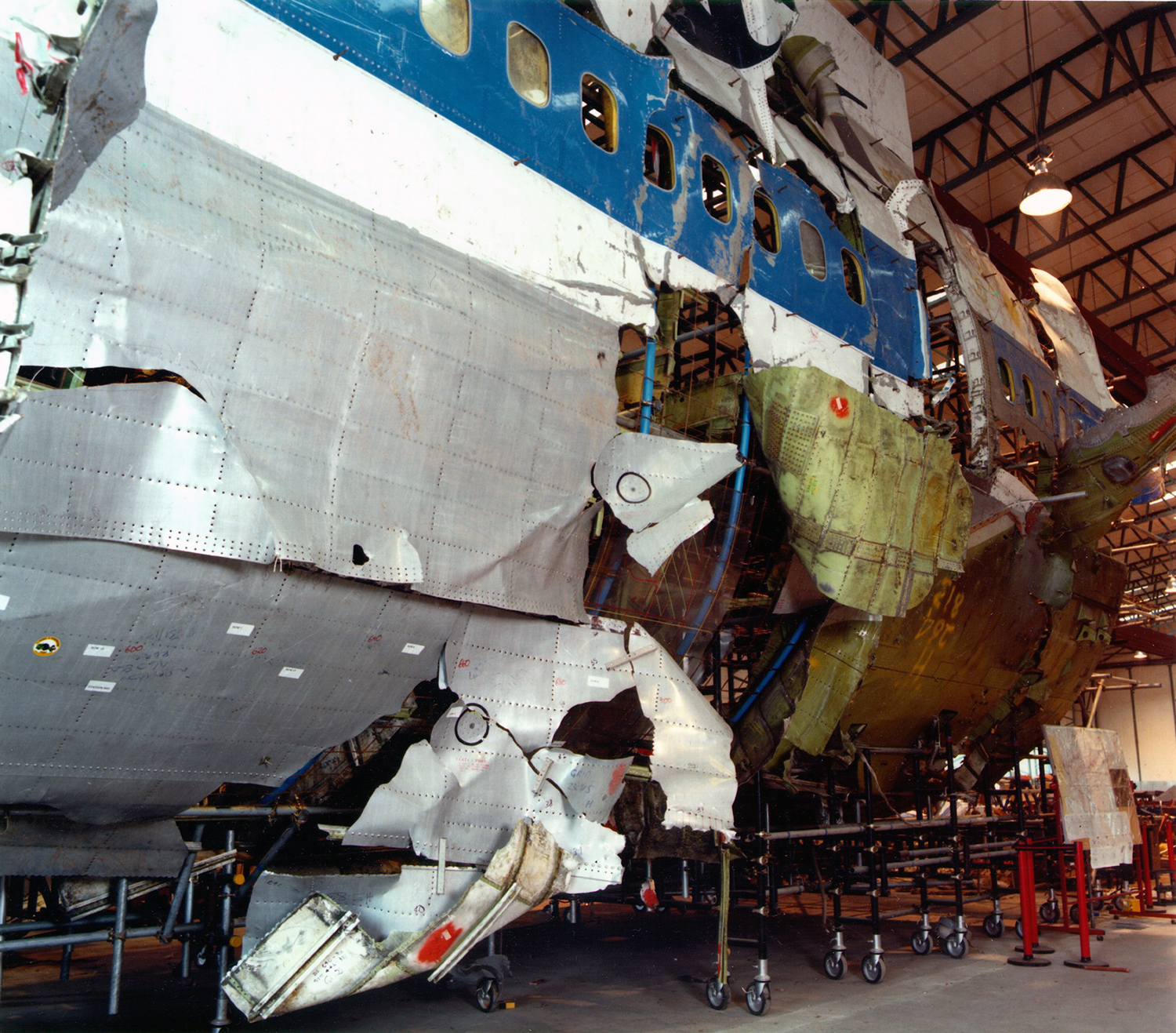
Crash of a Boeing 747-121A in Lockerbie: 270 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 21, 1988 at 1903 LT
Registration:
N739PA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
London - New York
MSN:
19646
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
PA103
Crew on board:
16
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
243
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
270
Captain / Total hours on type:
4107.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
5517
Aircraft flight hours:
72464
Aircraft flight cycles:
16497
Circumstances:
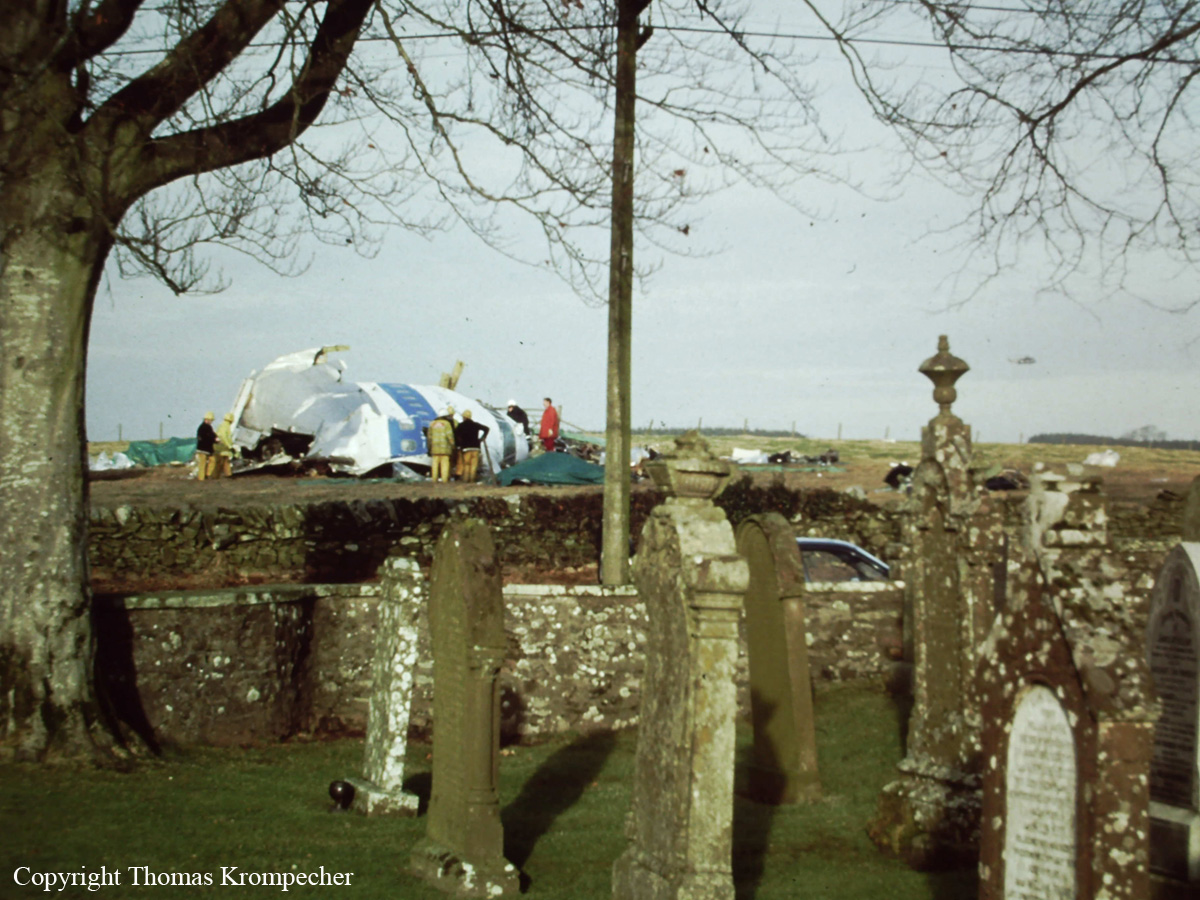
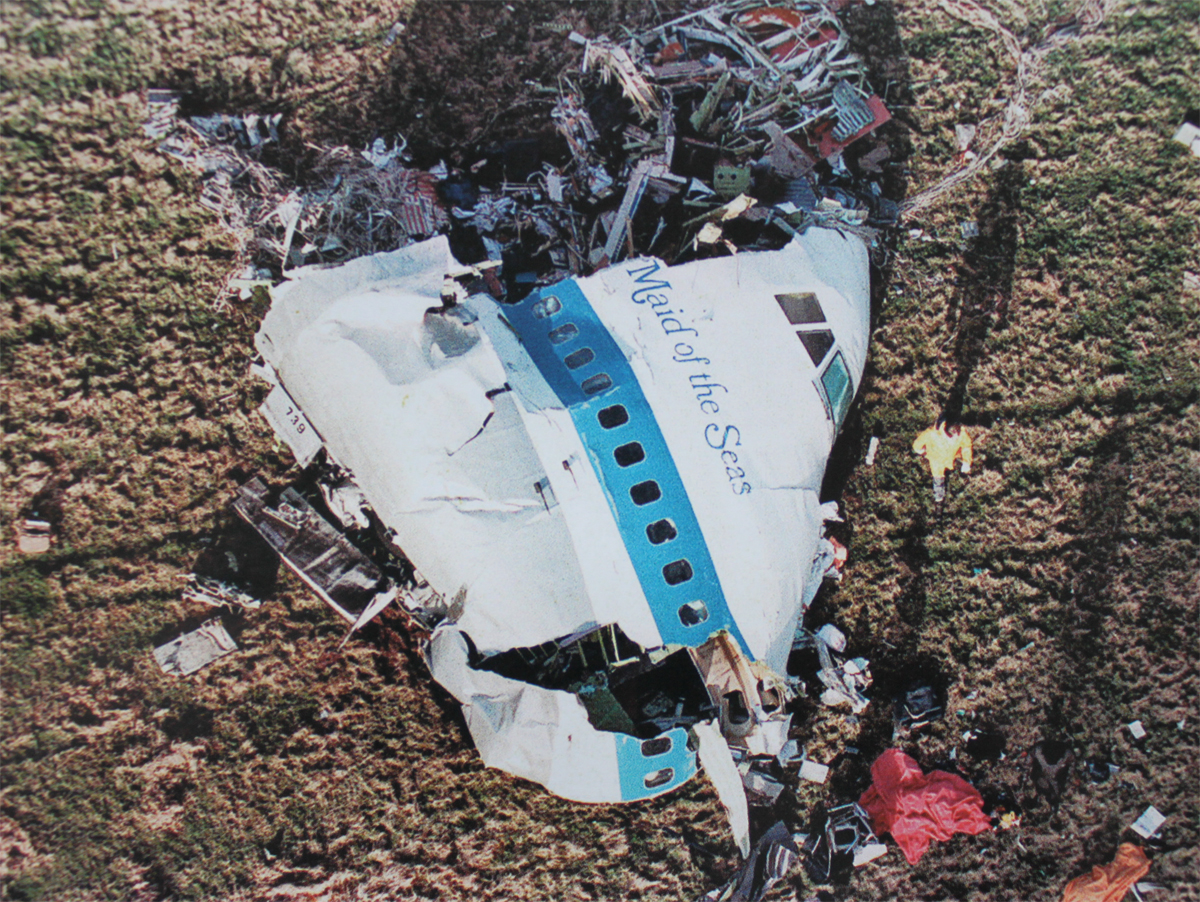
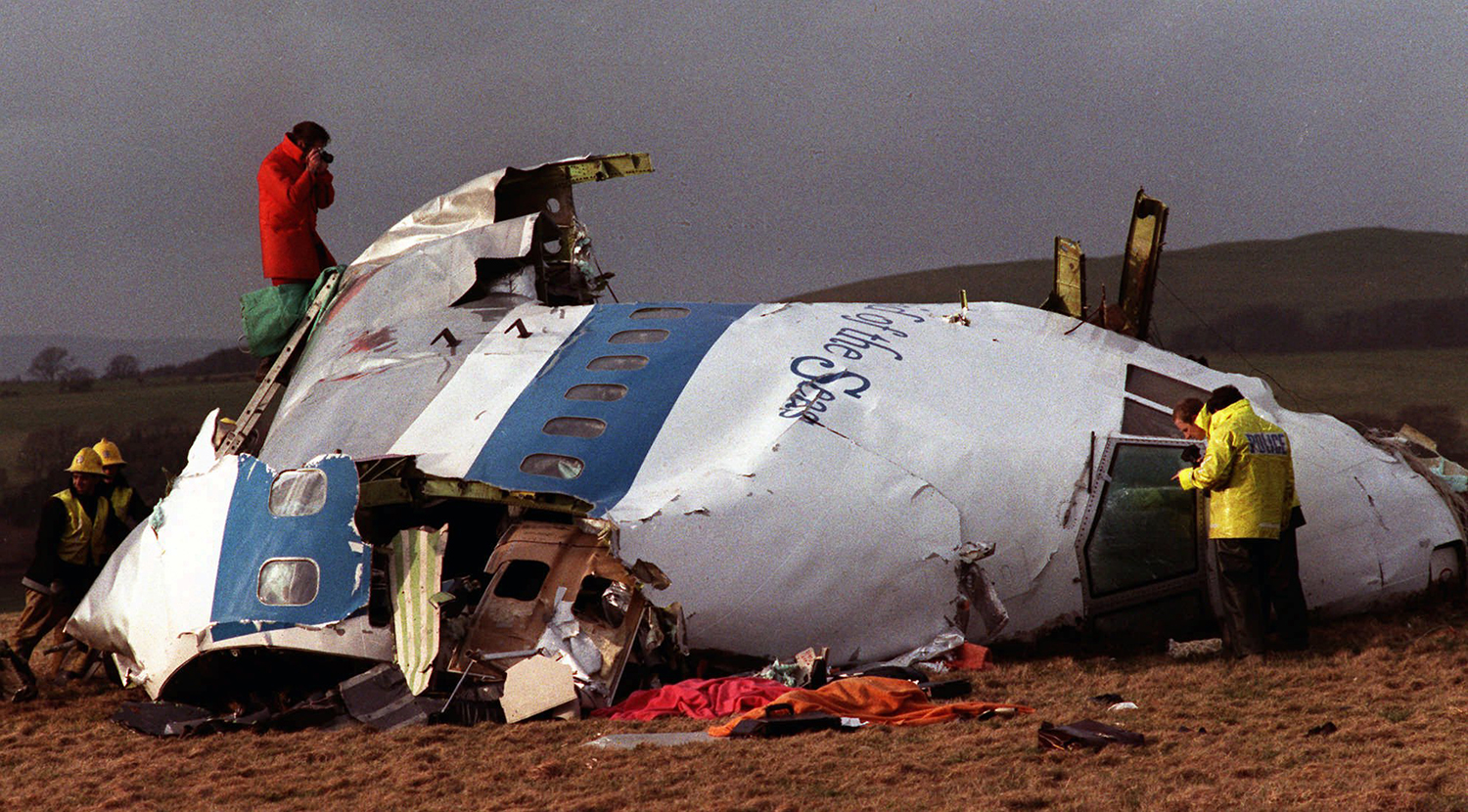
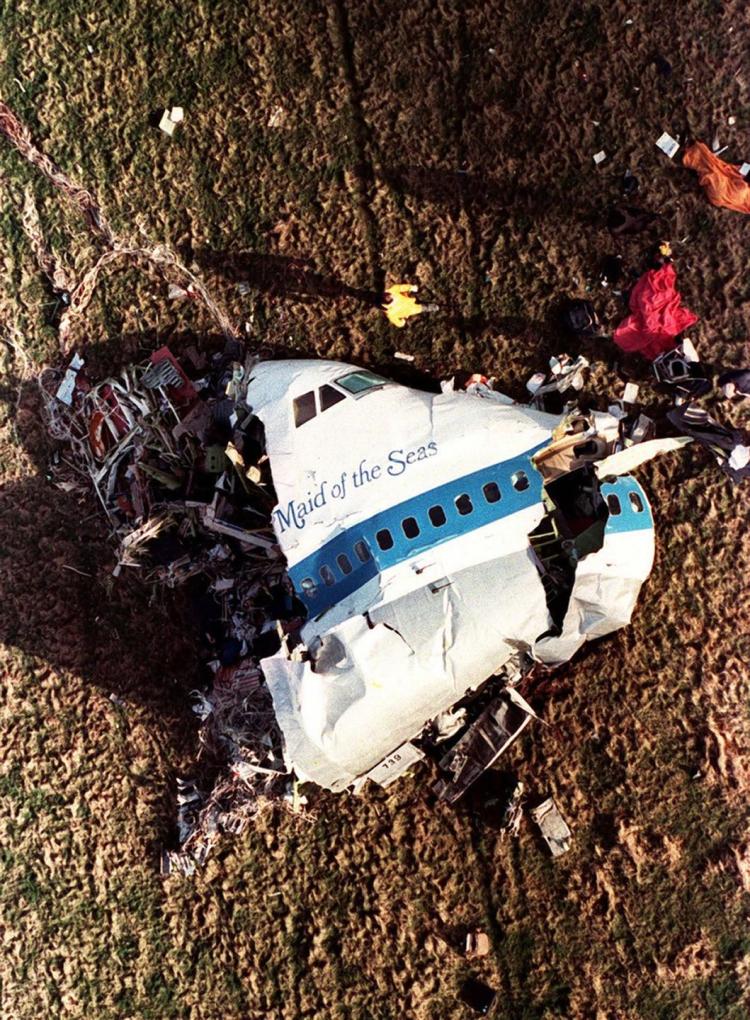
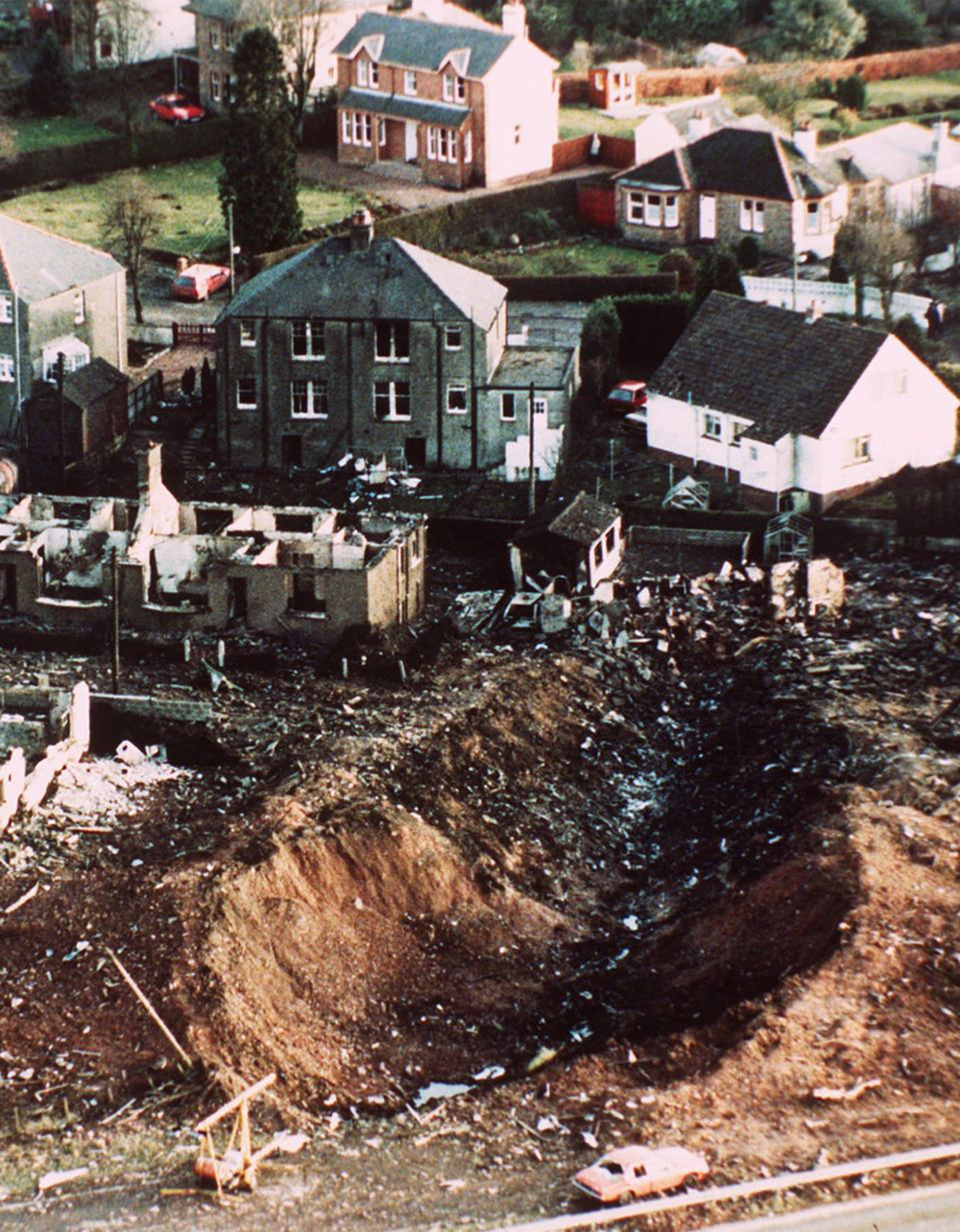
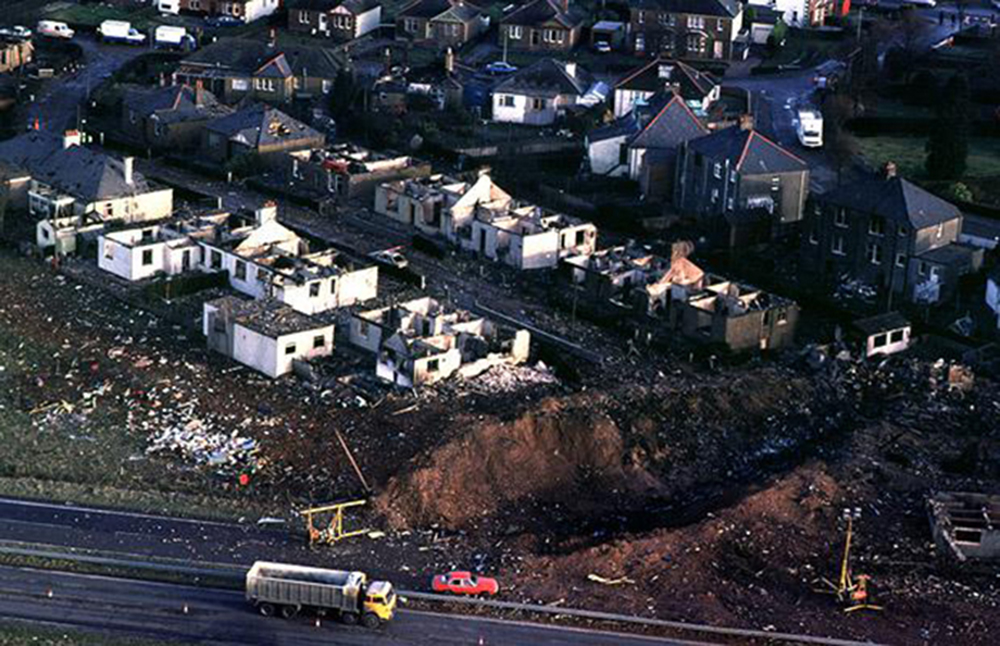
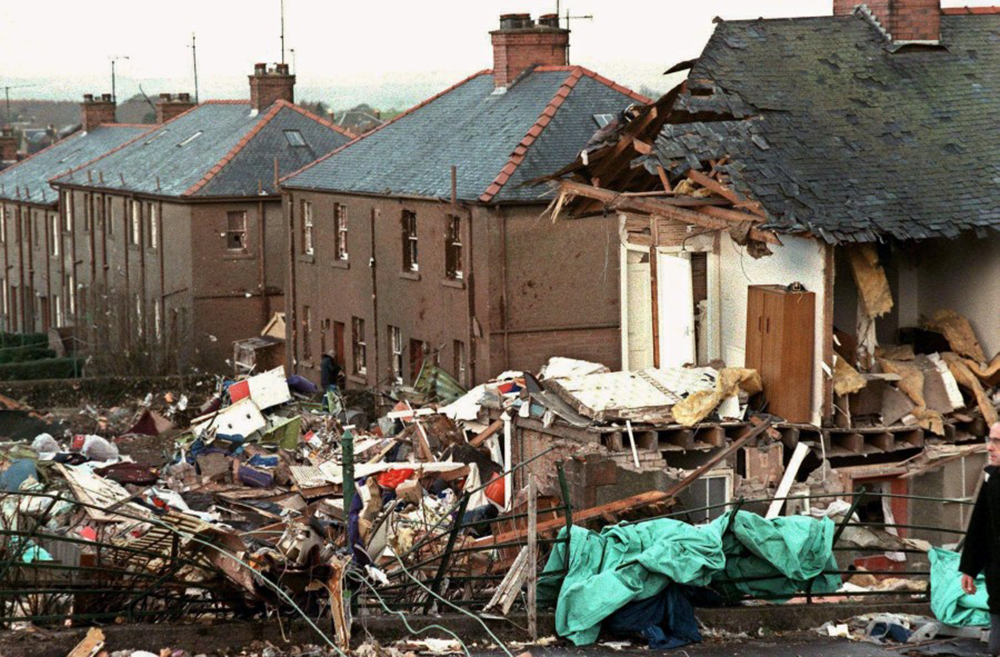
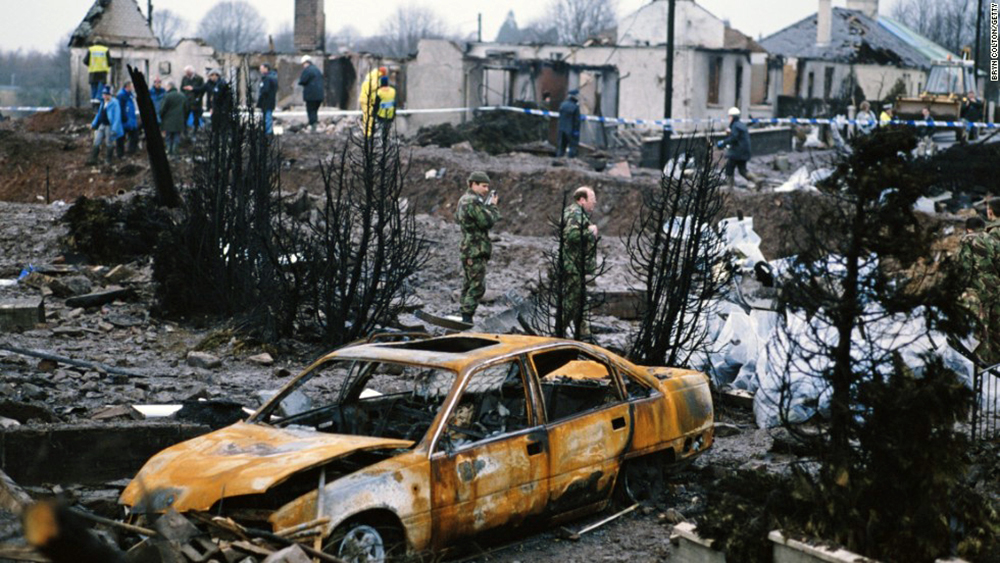
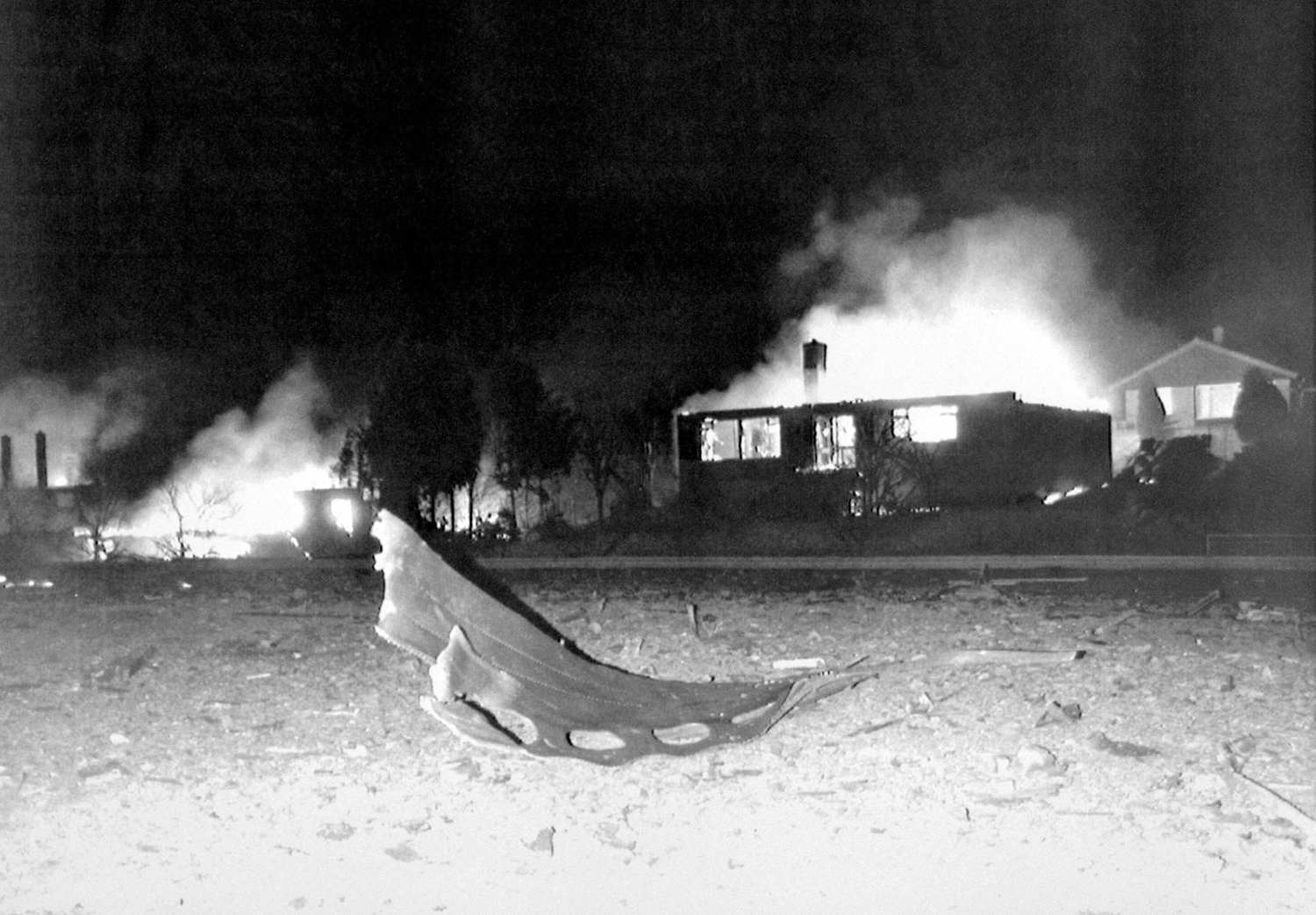
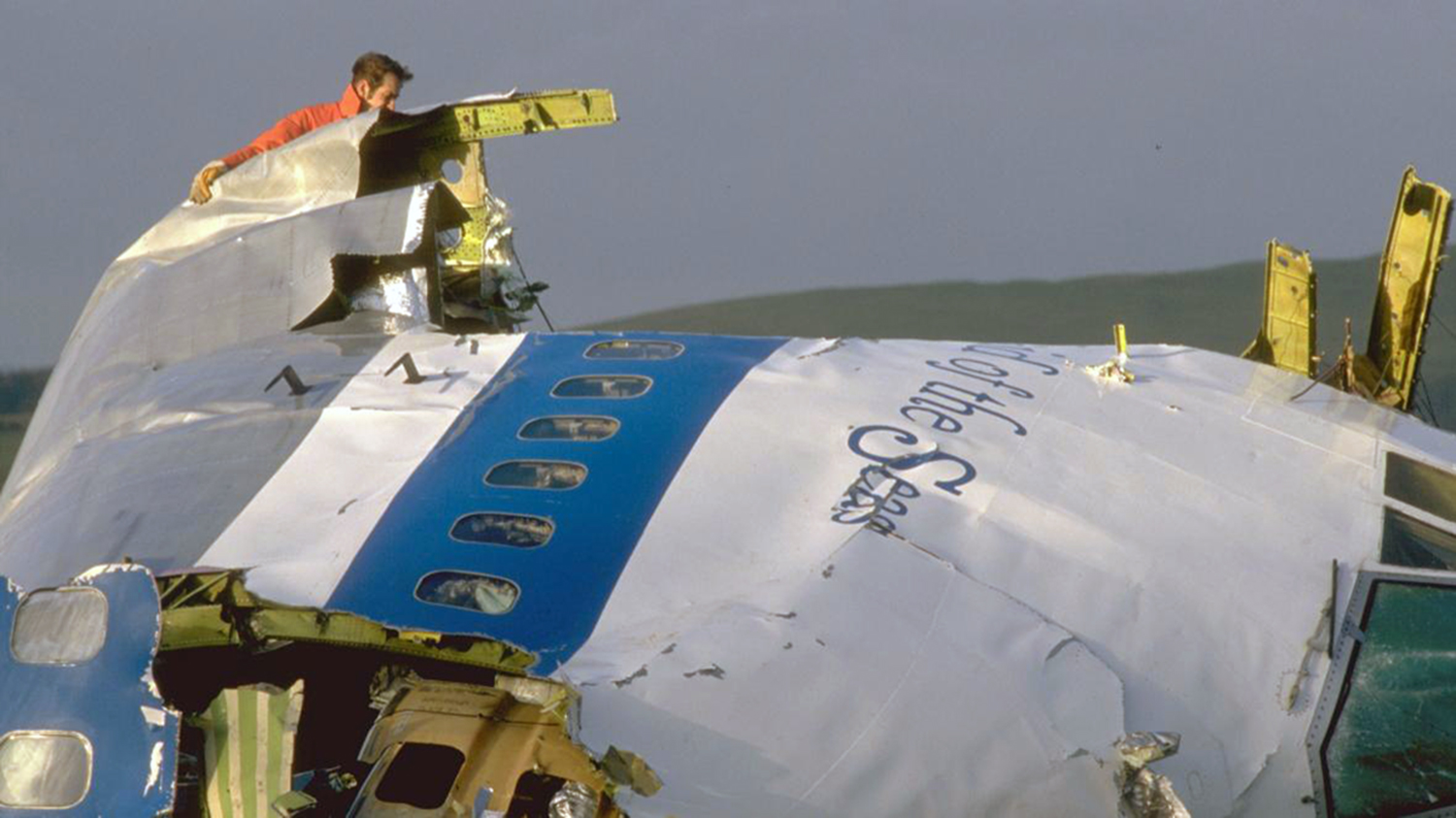
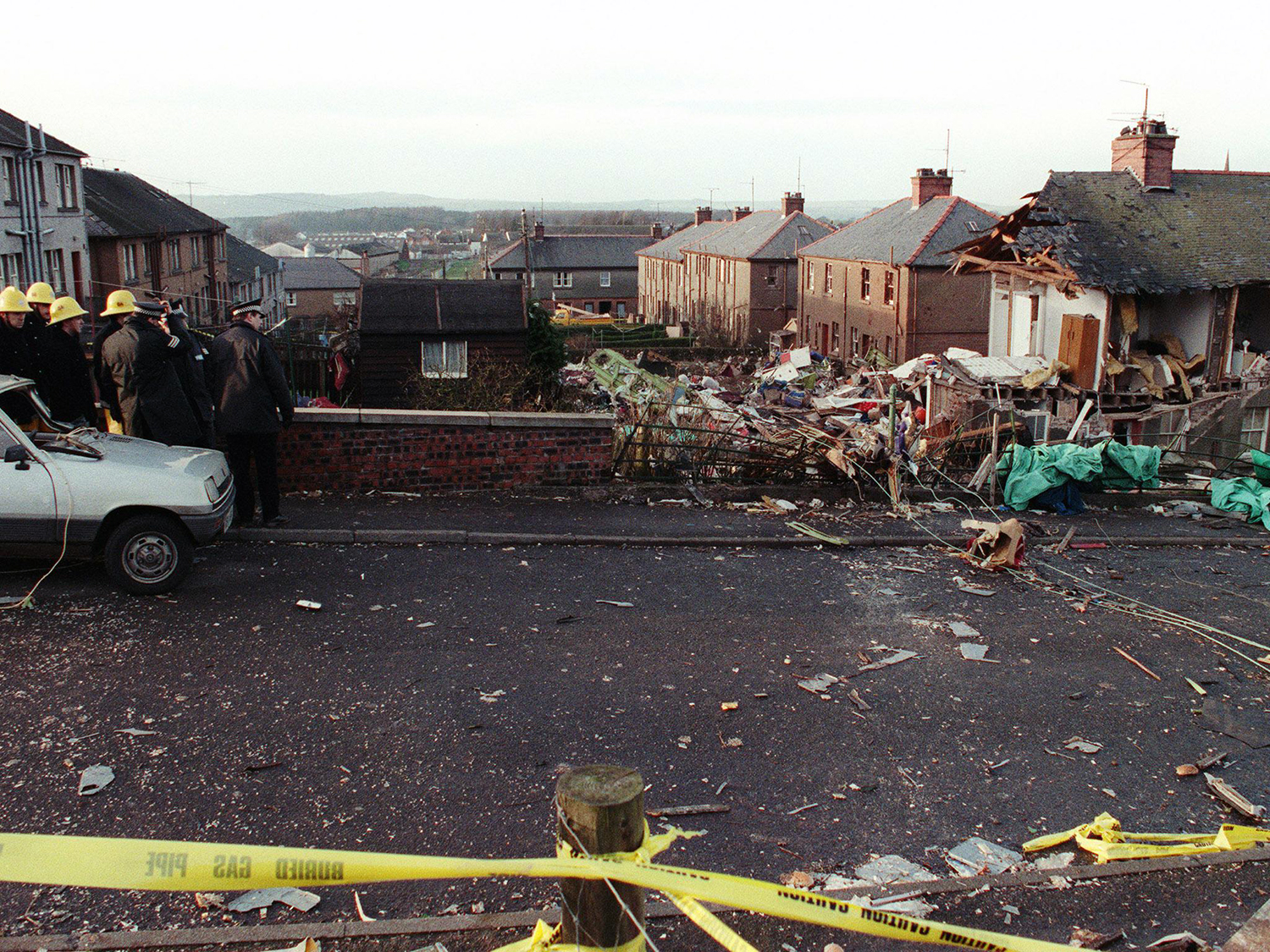
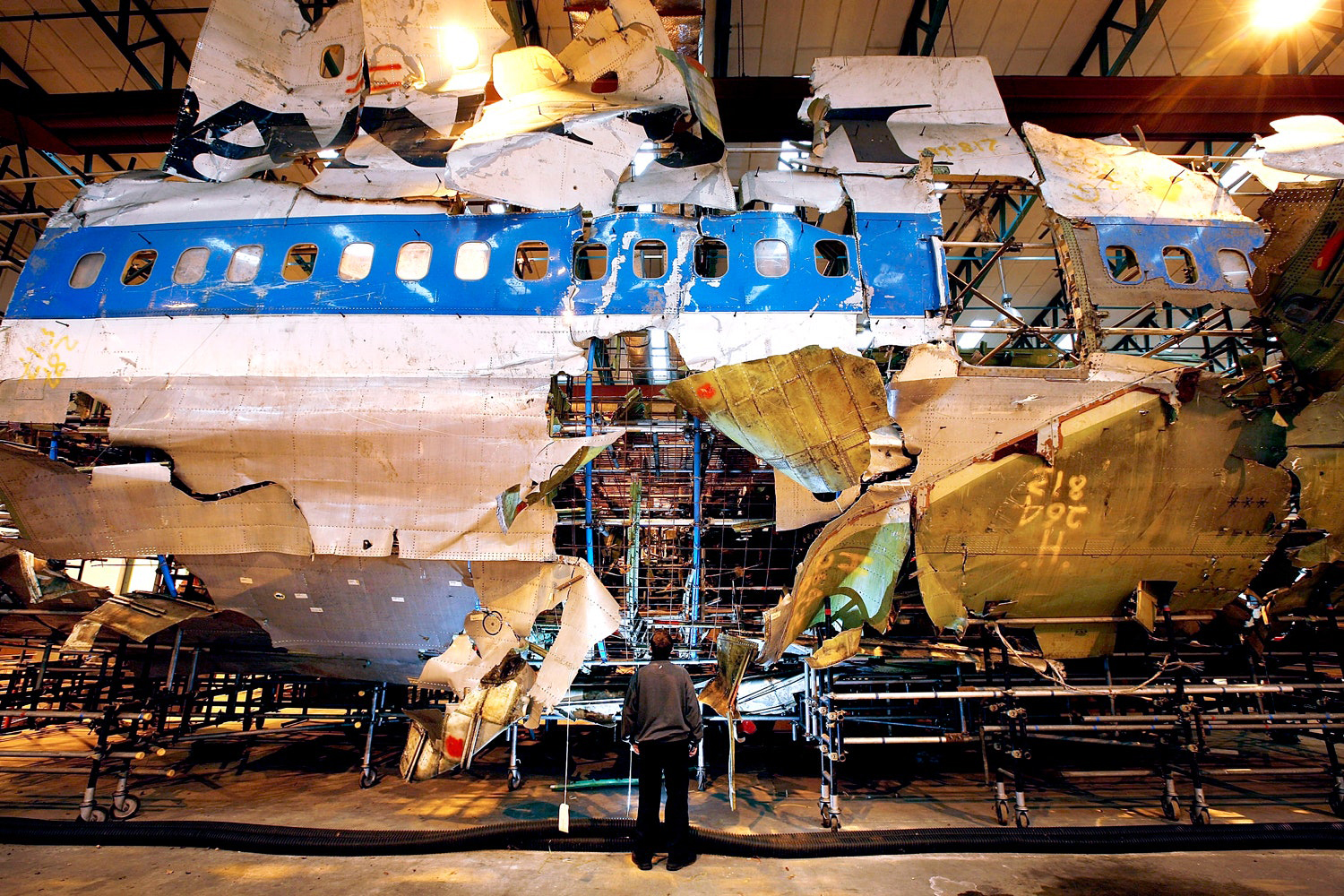
Flight PA103 departed London-Heathrow runway 27R for New York at 18:25. The aircraft levelled off at FL310, 31 minutes later. At 19:03 Shanwick Oceanic Control transmitted an oceanic clearance. At that time an explosion occurred in the aircraft's forward cargo hold at position 4L. The explosive forces produced a large hole in the fuselage structure and disrupted the main cabin floor. Major cracks continued to propagate from the large hole while containers and items of cargo ejected through the hole, striking the empennage, left- and right tail plane. The forward fuselage and flight deck area separated when the aircraft was in a nose down and left roll attitude, peeling away to the right at Station 800. The nose section then knocked the no. 3 engine off its pylon. The remaining aircraft disintegrated while it was descending nearly vertically from 19000 feet to 9000 feet. A section of cabin floor and baggage hold (from approx. Station 1241-1920) fell onto housing at Rosebank Terrace, Lockerbie. The main wing structure struck the ground with a high yaw angle at Sherwood Crescent, Lockerbie causing a massive fire. The Semtex bomb which caused the explosion had probably been hidden in a radio cassette player and was transferred to PA103 from a Pan Am Boeing 727 flight, arriving from Frankfurt. After a three-year joint investigation by the Dumfries and Galloway Constabulary and the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation indictments for murder were issued on November 13, 1991, against Abdel Basset Ali al-Megrahi, a Libyan intelligence officer and the head of security for Libyan Arab Airlines (LAA), and Lamin Khalifah Fhimah, the LAA station manager in Luqa Airport, Malta. United Nations sanctions against Libya and protracted negotiations with the Libyan leader Colonel Muammar al-Gaddafi secured the handover of the accused on April 5, 1999. On January 31, 2001, Megrahi was convicted of murder by a panel of three Scottish judges, and sentenced to 27 years in prison. Fhimah was acquitted.
Probable cause:
The in-flight disintegration of the aircraft was caused by the detonation of an improvised explosive device located in a baggage container positioned on the left side of the forward cargo hold at aircraft station 700.
Final Report:
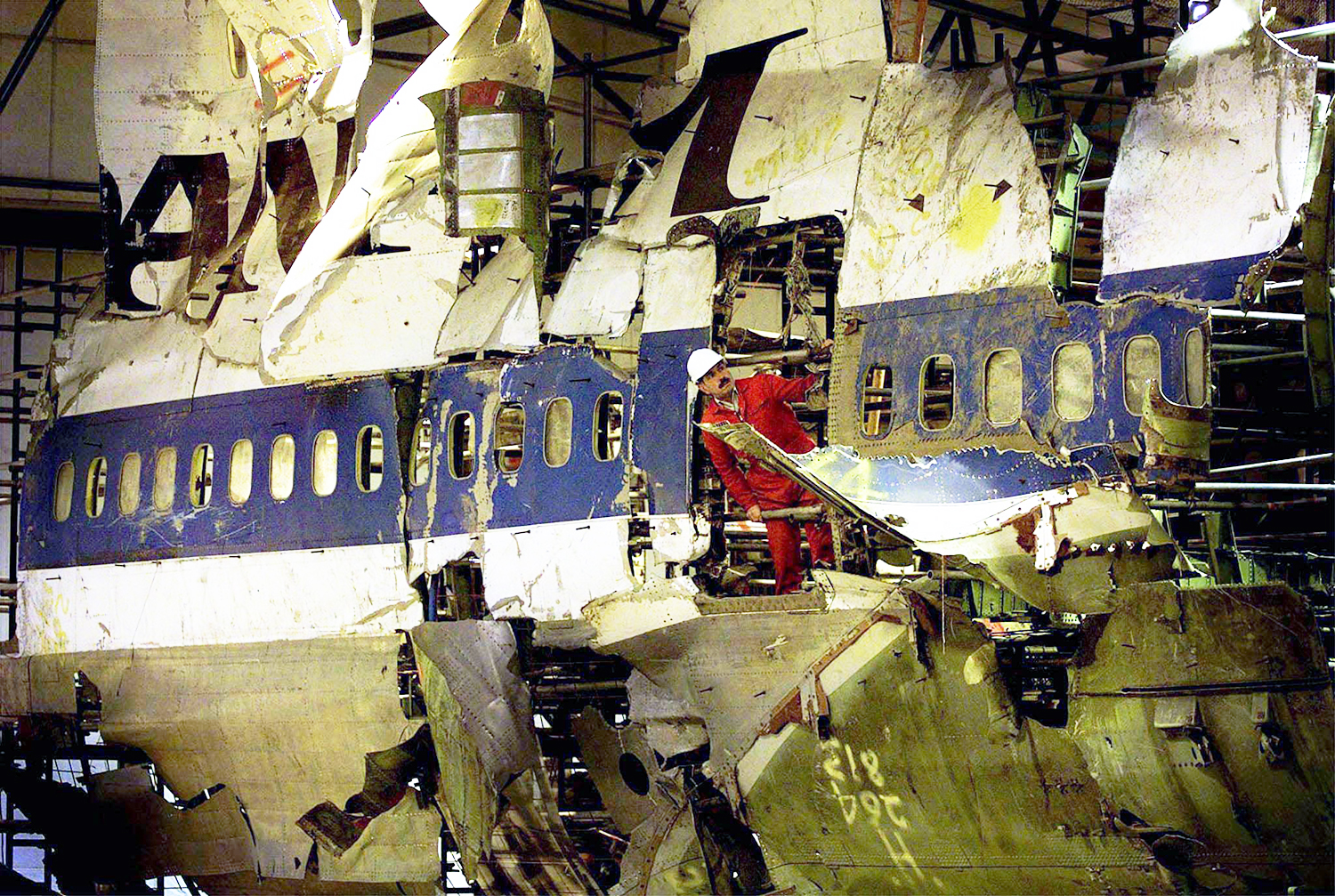
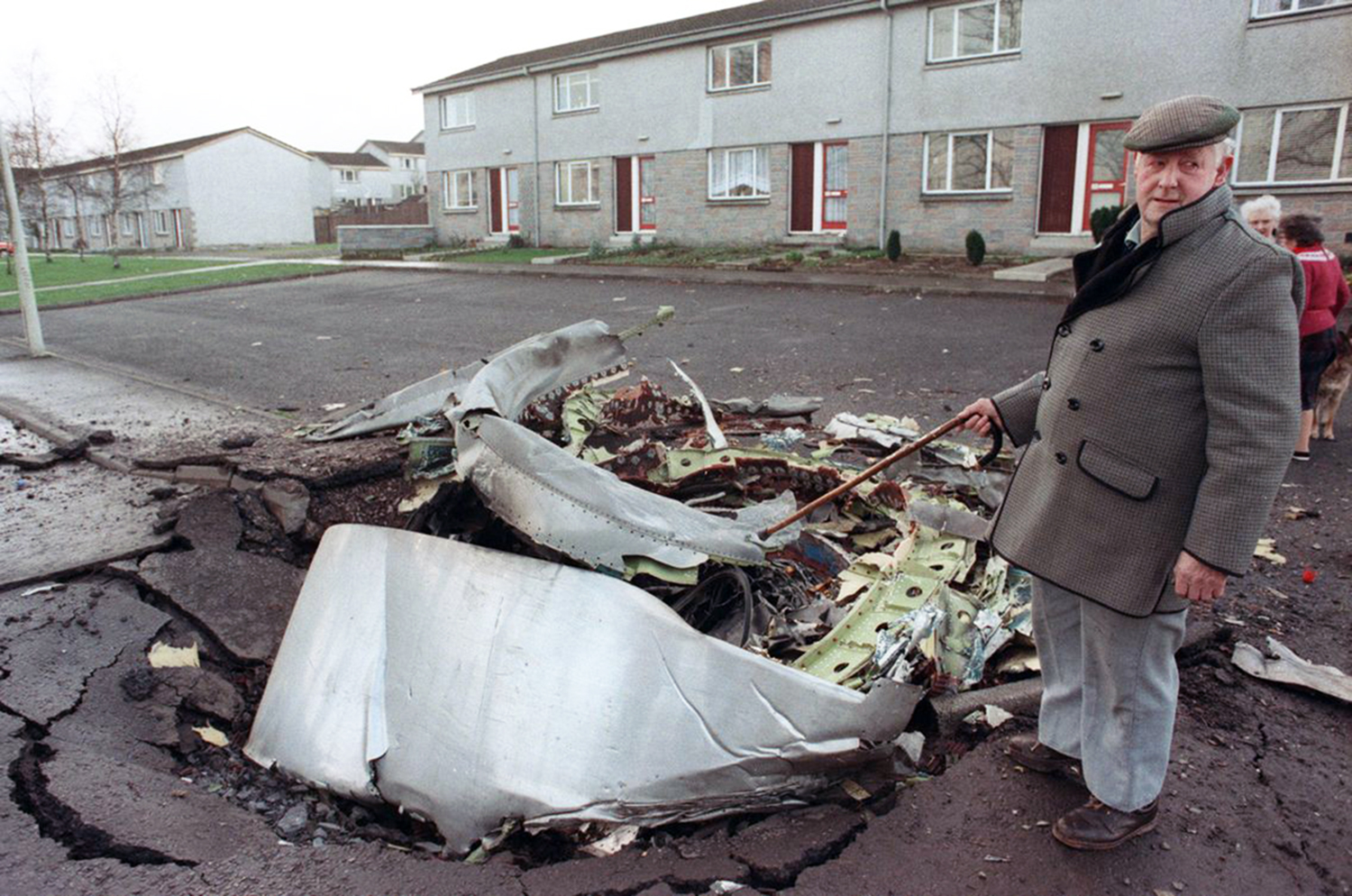
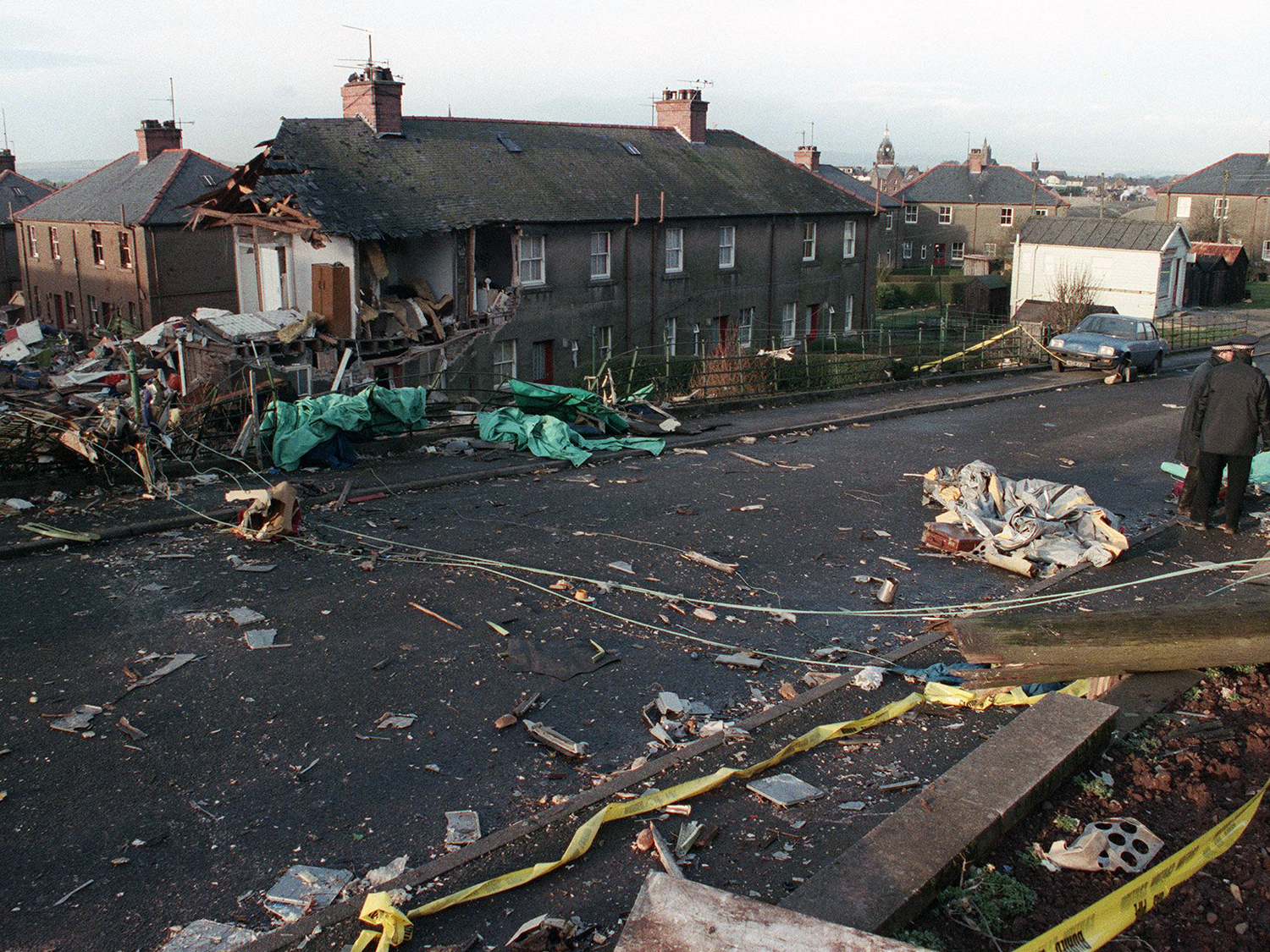


























Crash of a Boeing 747-121 in Karachi
Date & Time:
Aug 4, 1983 at 0438 LT
Registration:
N738PA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
New Delhi – Karachi – London – New York
MSN:
19645
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
PA073
Crew on board:
16
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
227
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Aircraft flight hours:
53324
Circumstances:
Flight PA073 was cleared to land on runway 25R of Karachi International Airport (KHI), Pakistan. The approach speed just prior to touchdown was 152 knots. After touchdown reverse thrust was applied on engines n°1, 2 and 3. Engine No.4 which had an unserviceable reverser was left in forward idle. Seventy knots was called and some three seconds later reverse power was decreased. At this stage EPR on n°4 engine increased rapidly. The aircraft veered to the left of the centerline at about 7400 feet from the approach end of runway 25R and departed the runway edge at 8000 feet from the approach end of runway 25R with 2,500 feet of runway remaining. Shortly before the aircraft departed the runway, the pilot flying (copilot) reported that he had no brakes and no nose wheel steering. The captain stated that he got on the brakes and tiller at this time to assist. After departing the runway surface the aircraft travelled 380 feet through soft mud before it came to rest at a point about 2100 feet from the end of runway 25R, heading about 160 degrees on the Southern side of the runway with the tail of the aircraft 120 feet from the runway edge. Shortly after the aircraft departed the runway, the nose gear struck a VASI light installation and its concrete base causing the nose gear to collapse backwards and to the left, resulting in total destruction of the VASI light installation and damage to the forward cargo hold, floor of the first class section and the stairway leading to the upper deck. Damage to the aircraft was substantial and it was not repaired. All 243 occupants evacuated safely.
Source: ASN
Source: ASN
Probable cause:
Loss of directional control as the result of inadvertent application of forward thrust on n°4 engine at the time the pilot flying was coming out of reverse thrust on engines n°1, 2 and 3 during the landing roll, and subsequent failure of the crew to recognize the asymmetric power condition. Contributing were failure of the crew to monitor the engines, and failure to follow specified procedures during the landing.
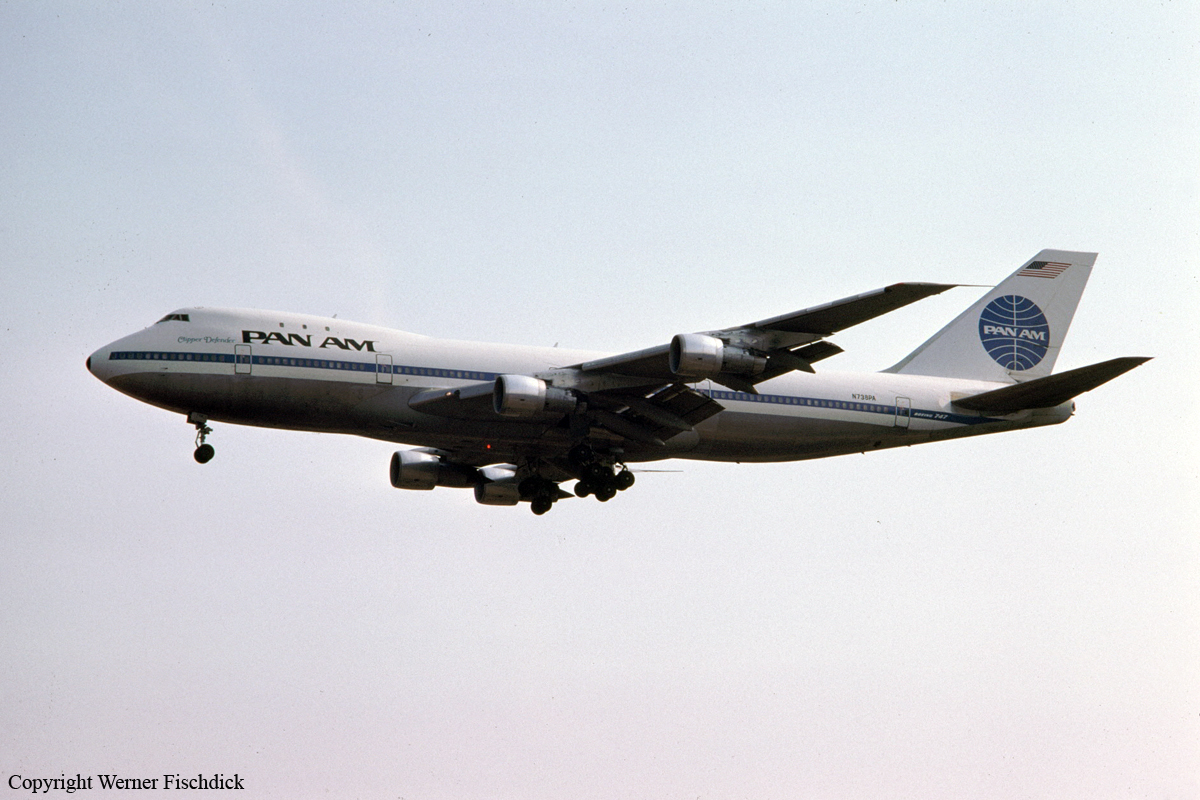

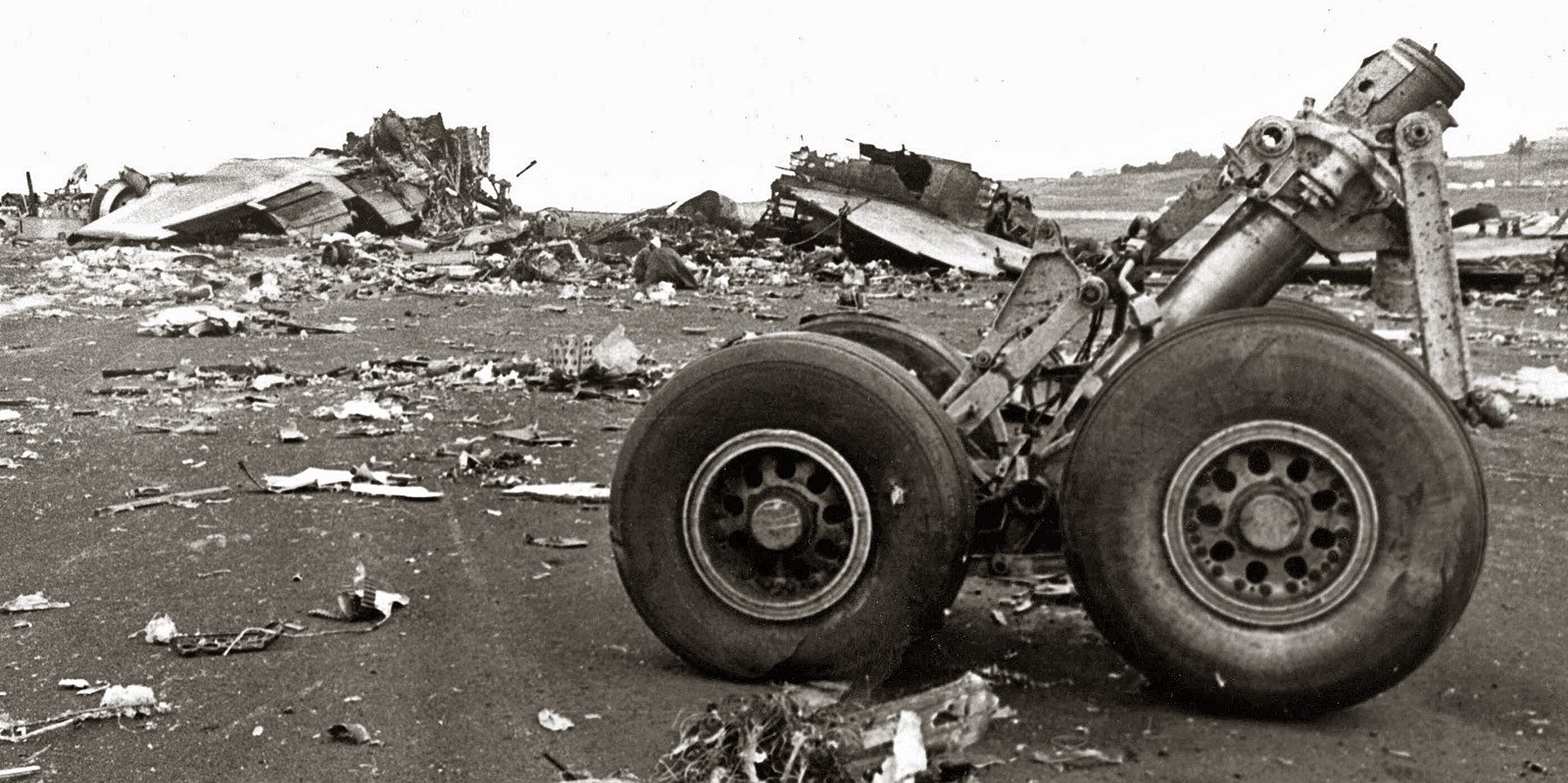
Crash of a Boeing 747-121 in Tenerife: 335 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 27, 1977 at 1706 LT
Registration:
N736PA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Los Angeles – New York – Las Palmas
MSN:
19643
YOM:
1969
Flight number:
PA1736
Crew on board:
16
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
380
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
335
Captain / Total hours on type:
564.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2796
Aircraft flight hours:
25725
Aircraft flight cycles:
7195
Circumstances:
The KLM Boeing 747, registration PH-BUF, took off from Schipol Airport (Amsterdam) at 0900 hours on 27 March 1977, en route to Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. This flight was part of the Charter Series KL4805/4806 Amsterdam-Las Palmas (Canary Islands) - Amsterdam operated by KLM on behalf of the Holland International Travel Group (H.I.N.T.), Rijswijk-Z.H. The Boeing 747 registration N736PA, flight number 1736, left Los Angeles International Airport, California, United States, on 26 March 1977, local date, at 0129Z hours, arriving at John F. Kennedy International Airport at 0617Z hours. After the aeroplane was refuelled and a crew change effected, it took off for Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (Spain) at 0742Z. While the aeroplanes were en route to Las Palmas, a bomb exploded in the airport passenger terminal. On account of this incident and of a warning regarding a possible second bomb, the airport was closed. Therefore, KLM 4805 was diverted to Los Rodeos (Tenerife) Airport, arriving at 1338Z on 27 March 1977. For the same reason, PAA1736 proceeded to the same airport, which was its alternate, landing at 1415. At first the KLM passengers were not allowed to leave the aeroplane, but after about twenty minutes they were all transported to the terminal building by bus. On alighting from the bus, they received cards identifying them as passengers in transit on Flight KL 4805. Later, all the passengers boarded KLM 4805 expect the H.I.N.T. Company guide, who remained in Tenerife. When Las Palmas Airport was opened to traffic once more, the PAA 1736 crew prepared to proceed to Las Palmas, which was the flight's planned destination. When they attempted to taxi on the taxiway leading to runway 12, where they had been parked with four other aeroplanes on account of the congestion caused by the number of flights diverted to Tenerife, they discovered that it was blocked by KLM Boeing 747, Flight 4805, which was located between PAA 1736 and the entrance to the active runway. The first officer and the flight engineer left the aeroplane and measured the clearance left by the KLM aircraft, reaching the conclusion that it was insufficient to allow PAA 1736 to pass by, obliging them to writ until the former had started to taxi. The passengers of PAA 1736 did not leave the aeroplane during the whole time that it remained in the airport. KLM 4805 called the tower at 1656 requesting permission to taxi. It was authorized to do so and at 1658 requested to backtrack on runway 12 for take-off on runway 30. The tower controller first cleared the KLM flight to taxi to the holding position for runway 30 by taxiing down the main runway and leaving it by the (third) taxiway to its left. KLM 4805 acknowledged receipt of this message from the tower, stating that it was at that moment taxiing on the runway, which it would leave by the first taxiway in order to proceed to the approach end of runway 30. The tower controller immediately issued an amended clearance, instructing it to continue to taxi to the end of the runway, where it should proceed to backtrack. The KLM flight confirmed that it had received the message, that it would backtrack, and that it was taxiing down tile main runway. The tower signalled its approval, whereupon KLM 4805 immediately asked the tower again if what they had asked it to do was to turn left on taxiway one. The tower replied in the negative and repeated that it should continue on to the end of the runway and there backtrack. Finally, at 1659, KLM 4805 replied, "O.K., sir." At 1702, the PAA aeroplane called the tower to request confirmation that it should taxi down the runway. The tower controller confirmed this, also adding that they should leave the runway by the third taxiway to their left. At 1703:00, in reply to the tower controller's query to KLM 4805 as to how many runway exits they had passed, the latter confirmed that at that moment they were passing by taxiway C4. The tower controller told KLM 4805, "O.K., at the end of the runway make one eighty and report ready for ATC clearance ." In response to a query from KLM 4805, the tower controller advised both aeroplanes - KLM 4805 and PAA 1736 - that the runway centre line lights were out of service. The controller also reiterated to PAA 1736 that they were to leave the main runway via the third taxiway to their left and that they should report leaving the runway. At the times indicated, the following conversations took place between the tower and the KLM 4805 and PAA 1736 aeroplanes. Times taken from KLM CVR.
1705:44.6 KLM 4805: The KLM four eight zero five is now ready for take-off and we are waiting for our ATC clearance. (1705:50.77).
1705:53.41 Tower: KLM eight seven zero five you are cleared to the Papa Beacon, climb to and maintain flight level nine zero, right turn after take-off, proceed with heading four zero until intercepting the three two five radial from Las Palmas VOR. (1706 :08.09).
1706:09.61 KLM 4805: Ah - Roger, sir, we are cleared to the Papa Beacon, flight level nine zero until intercepting the three two five. We are now (at take-off). (1706:17.79).
1706:18.19 Tower : O.K..... Stand by for take-off, I will call you. (1706: 21.79).
Note: A squeal starts at: 1706:19.39 The squeal ends at: 1706:22.06
1706:21.92 PAA 1736: Clipper one seven three six. (1706 : 23.39).
1706:25.47 Tower: Ah - Papa Alpha one seven three six report the runway clear. (1706: 28.89).
1706:29.59 PAA 1736: O.K., will report when we're clear. (1706:30.69).
1706:31.69 Tower: Thank you.
Subsequently, KLM 4805, which had released its brakes to start take-off run 20 seconds before this communication took place, collided with the PAA aeroplane. The control tower received no further communications from PAA 1736, nor from KLM 4805. There were no eyewitnesses to the collision. All 248 occupants on board the KLM 747 were killed. Among the 396 people on board the Pan Am 747, 335 were killed (among them nine crew members) and 61 others were injured.
1705:44.6 KLM 4805: The KLM four eight zero five is now ready for take-off and we are waiting for our ATC clearance. (1705:50.77).
1705:53.41 Tower: KLM eight seven zero five you are cleared to the Papa Beacon, climb to and maintain flight level nine zero, right turn after take-off, proceed with heading four zero until intercepting the three two five radial from Las Palmas VOR. (1706 :08.09).
1706:09.61 KLM 4805: Ah - Roger, sir, we are cleared to the Papa Beacon, flight level nine zero until intercepting the three two five. We are now (at take-off). (1706:17.79).
1706:18.19 Tower : O.K..... Stand by for take-off, I will call you. (1706: 21.79).
Note: A squeal starts at: 1706:19.39 The squeal ends at: 1706:22.06
1706:21.92 PAA 1736: Clipper one seven three six. (1706 : 23.39).
1706:25.47 Tower: Ah - Papa Alpha one seven three six report the runway clear. (1706: 28.89).
1706:29.59 PAA 1736: O.K., will report when we're clear. (1706:30.69).
1706:31.69 Tower: Thank you.
Subsequently, KLM 4805, which had released its brakes to start take-off run 20 seconds before this communication took place, collided with the PAA aeroplane. The control tower received no further communications from PAA 1736, nor from KLM 4805. There were no eyewitnesses to the collision. All 248 occupants on board the KLM 747 were killed. Among the 396 people on board the Pan Am 747, 335 were killed (among them nine crew members) and 61 others were injured.
Probable cause:
The KLM aircraft had taken off without take-off clearance, in the absolute conviction that this clearance had been obtained, which was the result of a misunderstanding between the tower and the KLM aircraft. This misunderstanding had arisen from the mutual use of usual terminology which, however, gave rise to misinterpretation. In combination with a number of other coinciding circumstances, the premature take-off of the KLM aircraft resulted in a collision with the Pan Am aircraft, because the latter was still on the runway since it had missed the correct intersection.
Final Report: