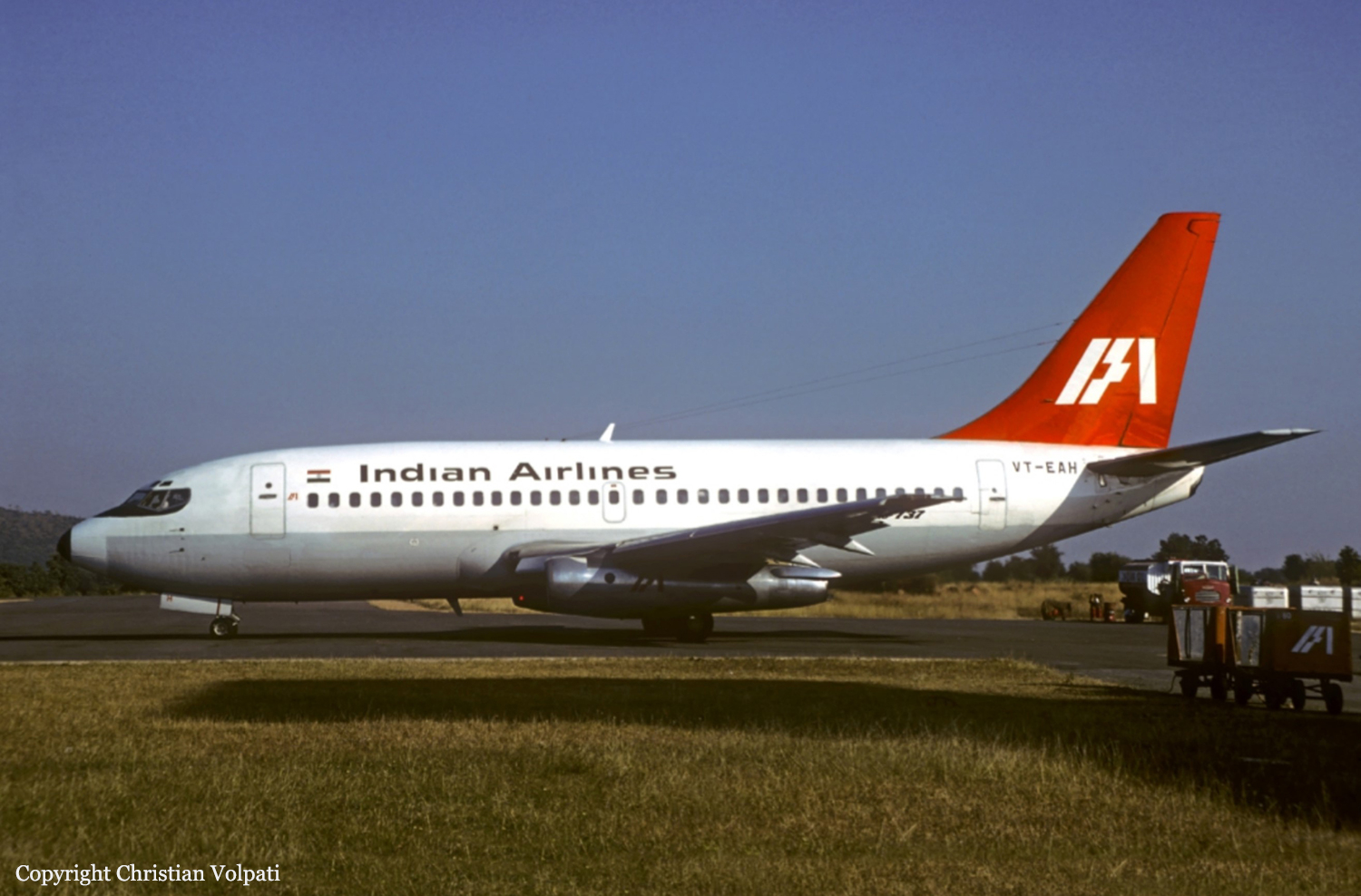
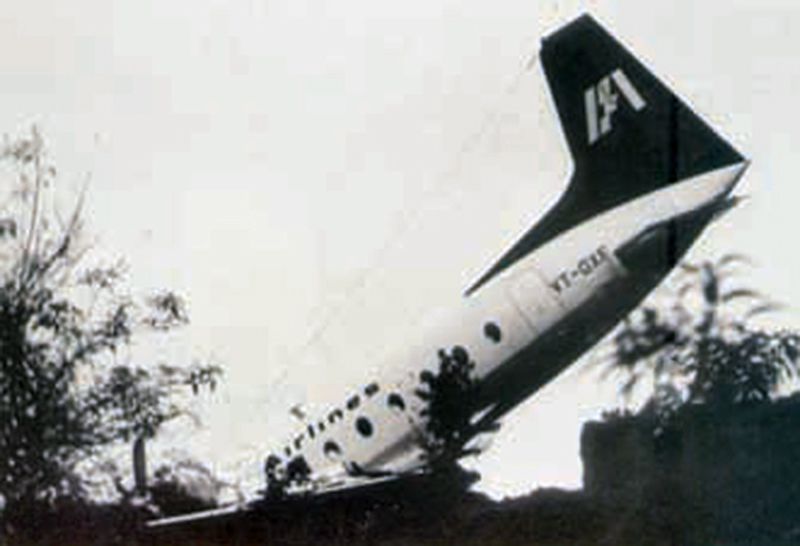
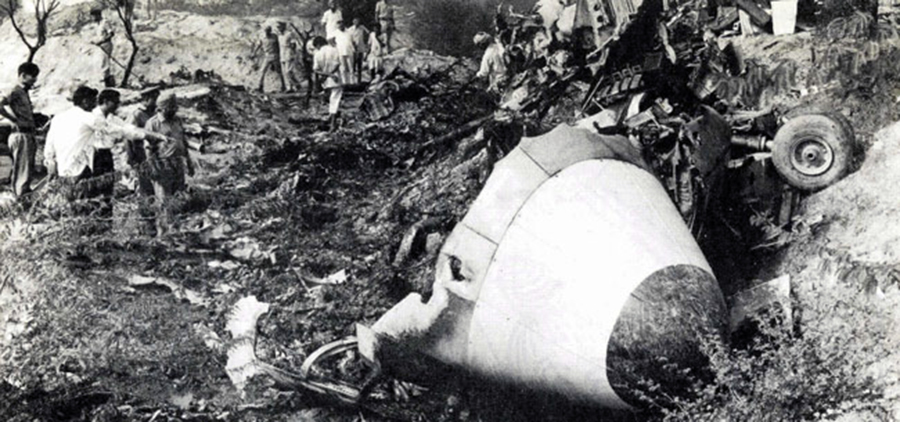
Crash of a Boeing 737-2A8 in Ahmedabad: 133 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 19, 1988 at 0653 LT
Registration:
VT-EAH
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bombay - Ahmedabad
MSN:
20481
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
IC113
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
129
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
133
Aircraft flight hours:
42750
Aircraft flight cycles:
47520
Circumstances:
Indian Airlines B-737 aircraft VT-EAH was operating scheduled flight IC113 (Bombay - Ahmedabad sector) on 19-10-1988. There were 135 occupants on board including 6 crew members. Aircraft contacted Ahmedabad Approach Control at 0620LT. Ahmedabad weather as per Metar of 0540LT was passed to the aircraft and again at 0625LT (speci) of 0610LT was passed to the aircraft and then visibility has been reduced from 6 km to 3 km. Clearance to descend to FL150 was given at 0632LT and the aircraft was further cleared to FL55, 25 DME at 0636LT. At 0641LT, the aircraft was advised to report over Ahmedabad VOR and 'Speci' of 0640LT was also transmitted to the aircraft as per the same the winds were calm, visibility 2 km in haze and was 1010. QNH was correctly read back by the aircraft. The pilot decided to carry localiser-DME approach for runway 23 and reported overhead Ahmedabad. The aircraft went outbound and reported turning inbound. This was the last transmission from the aircraft and thereafter contact with the ATC was lost at 0650:53. The aircraft was found crashed at a distance of 2,540 meters from the beginning of runway 23 on the extended centre line of the runway in a paddy field at about 0653LT. Out of 135 persons on board, 133 received fatal injuries. The remaining two were seriously injured. The aircraft was destroyed due to post impact fire.
Probable cause:
The cause of the accident is attributed to error on part of the pilot-in-command as well as copilot due to non adherence to laid down procedures under poor visibility conditions. Both pilot and copilot failed to follow approved procedures, directives, instructions, etc. Weather was considered as a contributing factor.