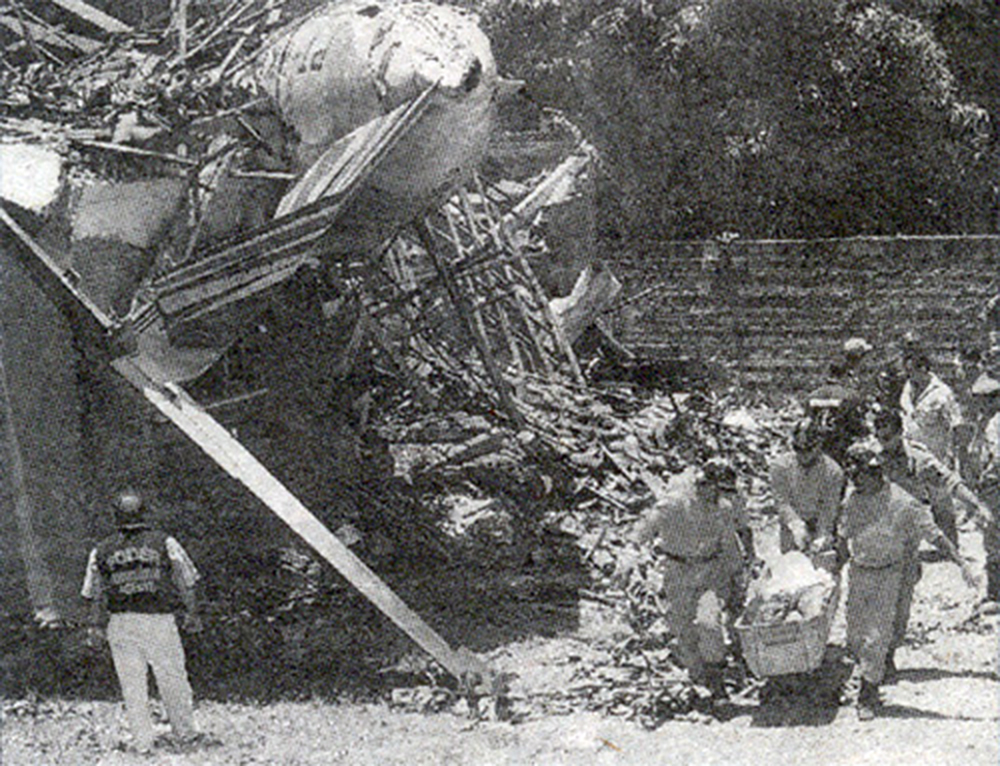Crash of a Rockwell Shrike Commander 500S in Fortaleza
Date & Time:
Jul 2, 2002 at 1640 LT
Registration:
PT-KZD
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Fortaleza - Fortaleza
MSN:
500-3140
YOM:
1972
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2900.00
Aircraft flight hours:
9960
Circumstances:
The twin engine aircraft departed Fortaleza-Pinto Martins Airport on a local post maintenance test flight (50 hours), carrying two passengers and one pilot. After takeoff, while climbing to a height of 200 feet, the power on the left engine fluctuated. The pilot modified the position of the fuel selector but the situation did not change. As the aircraft was losing height, the pilot shut down the left engine and feathered its propeller when the aircraft rolled to the left, causing the left wing to struck a concrete wall. Out of control, the aircraft struck the roof of a house, then a second one and eventually crashed on a third residence. All three occupants were injured as well as one people on the ground.
Probable cause:
The fuel pump and the servo-injectors had faults which certainly contributed to the accident as the left engine was not properly supplied with fuel.
Final Report: