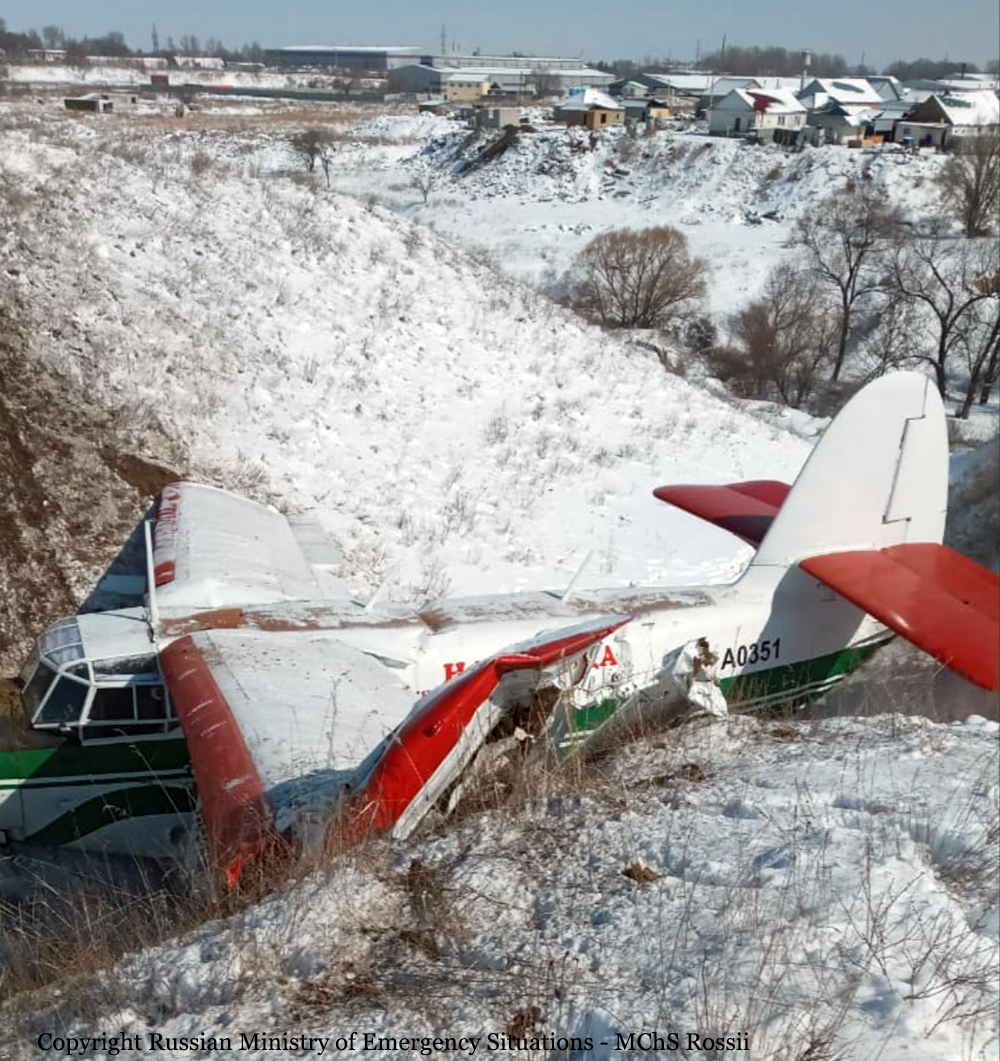
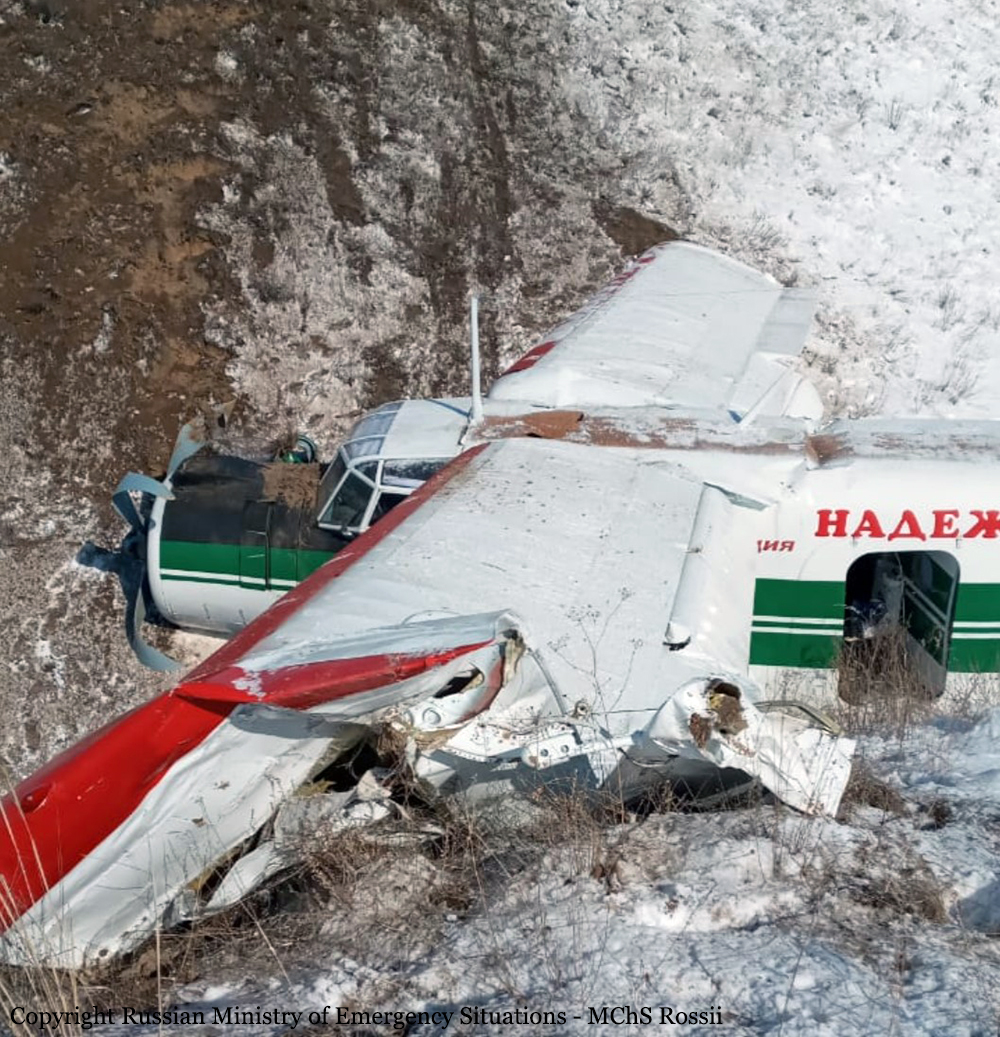
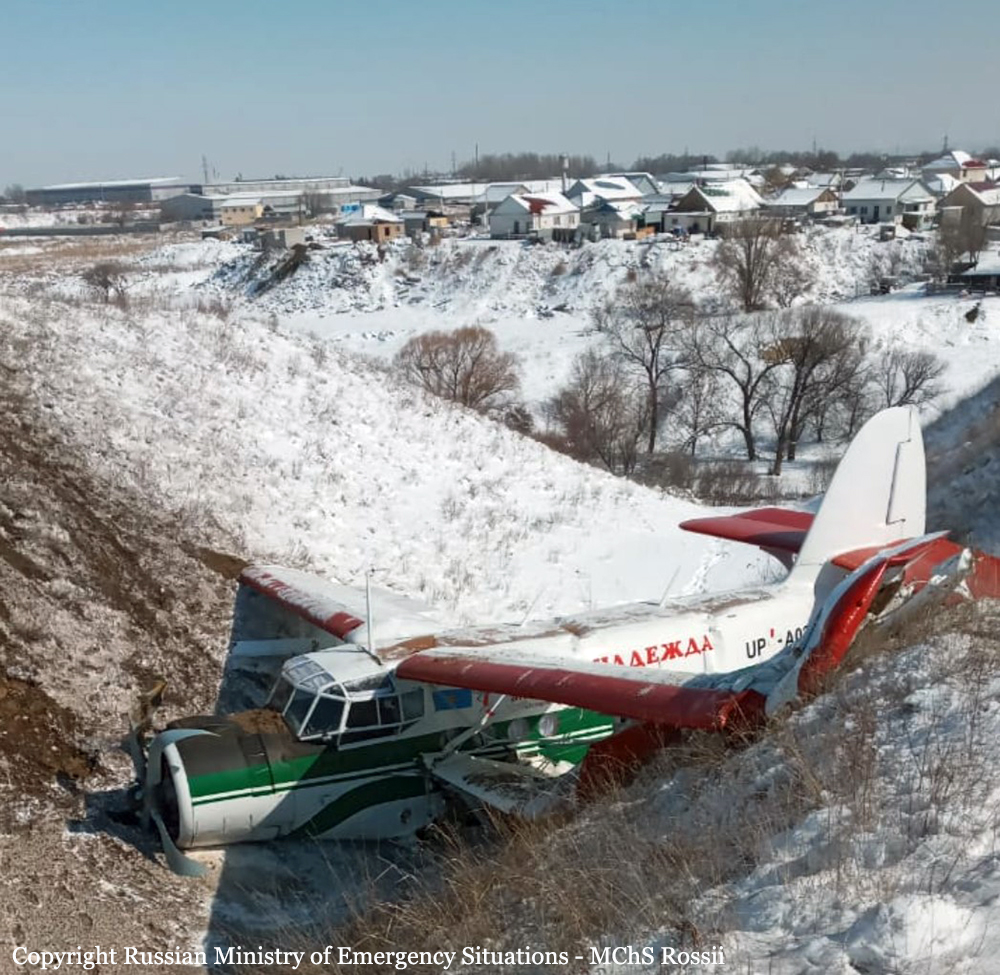
Circumstances:
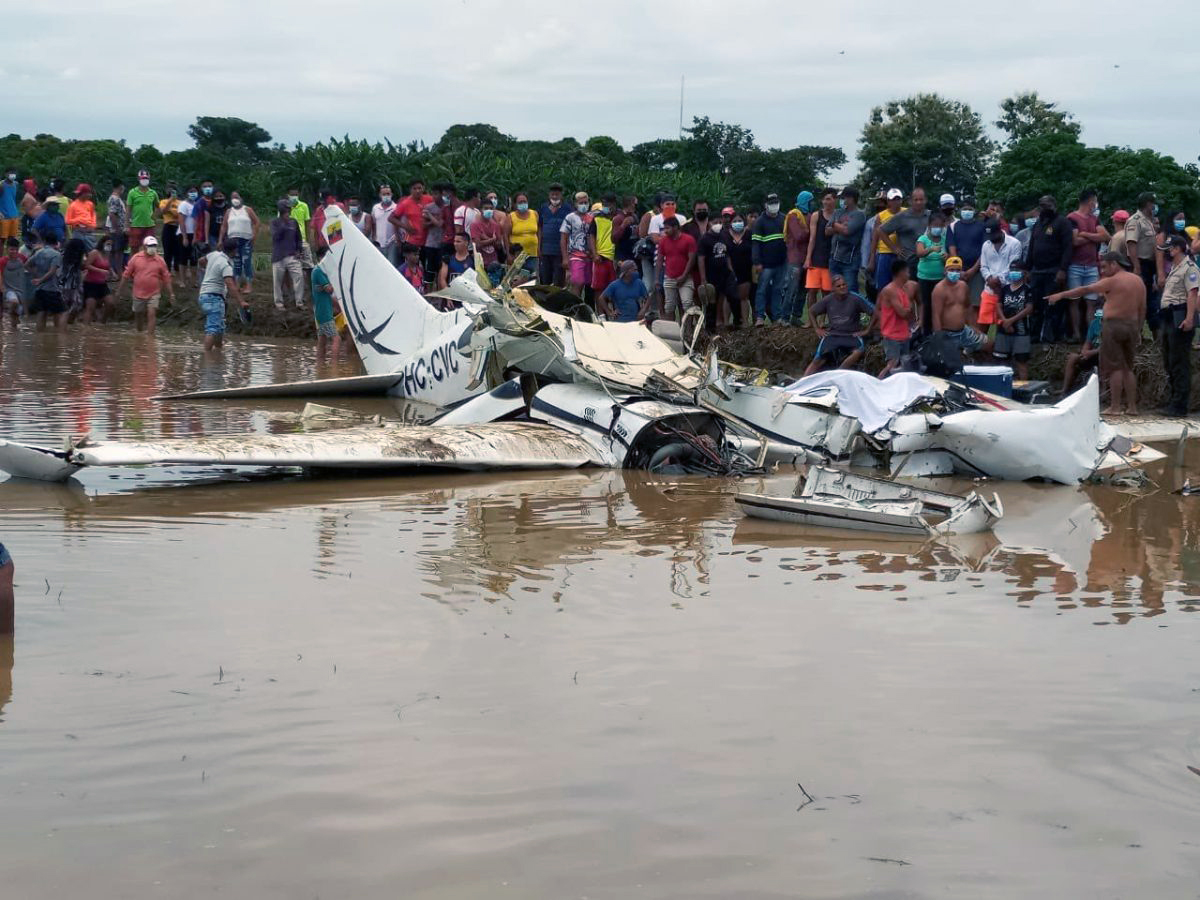
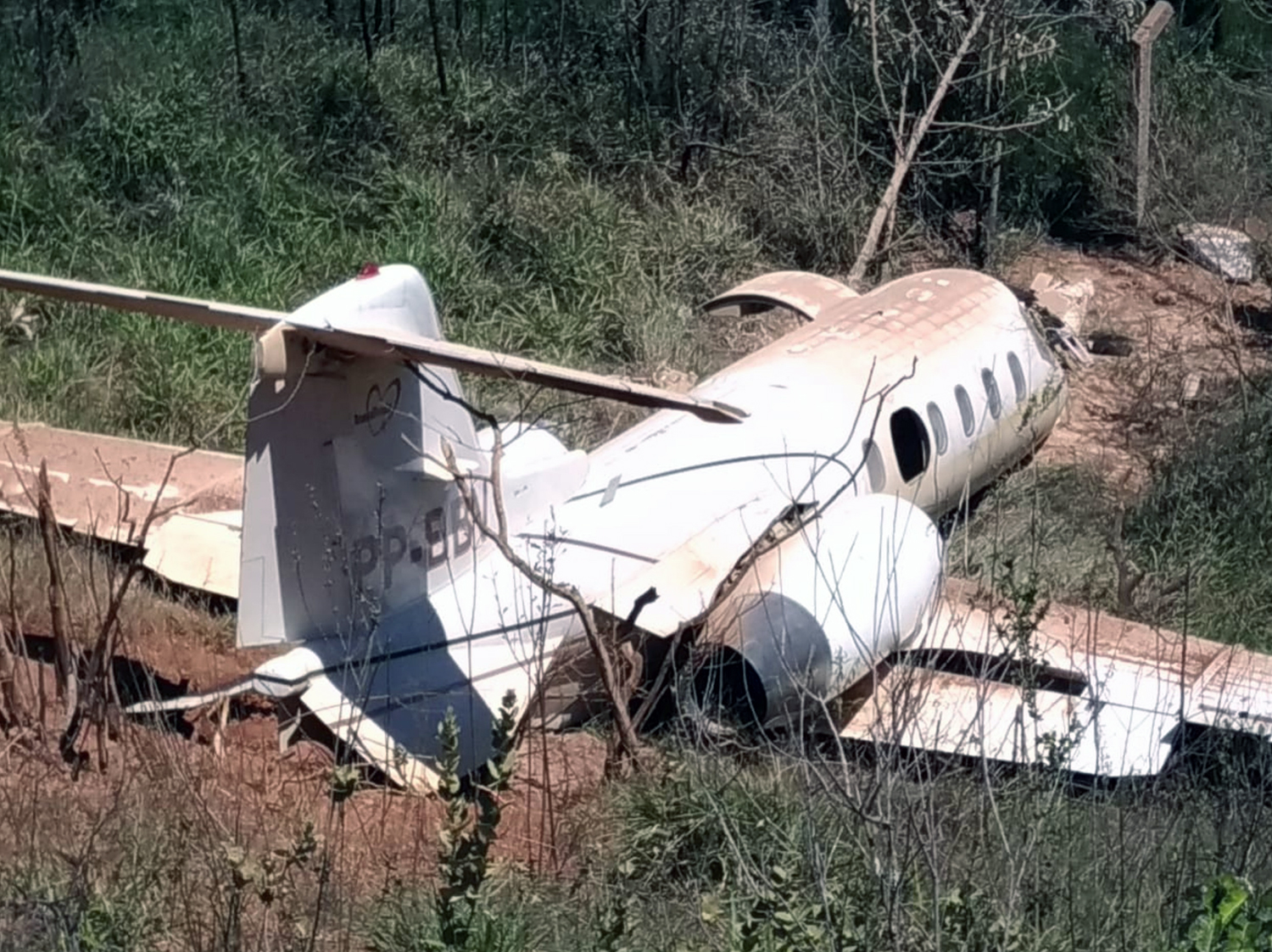
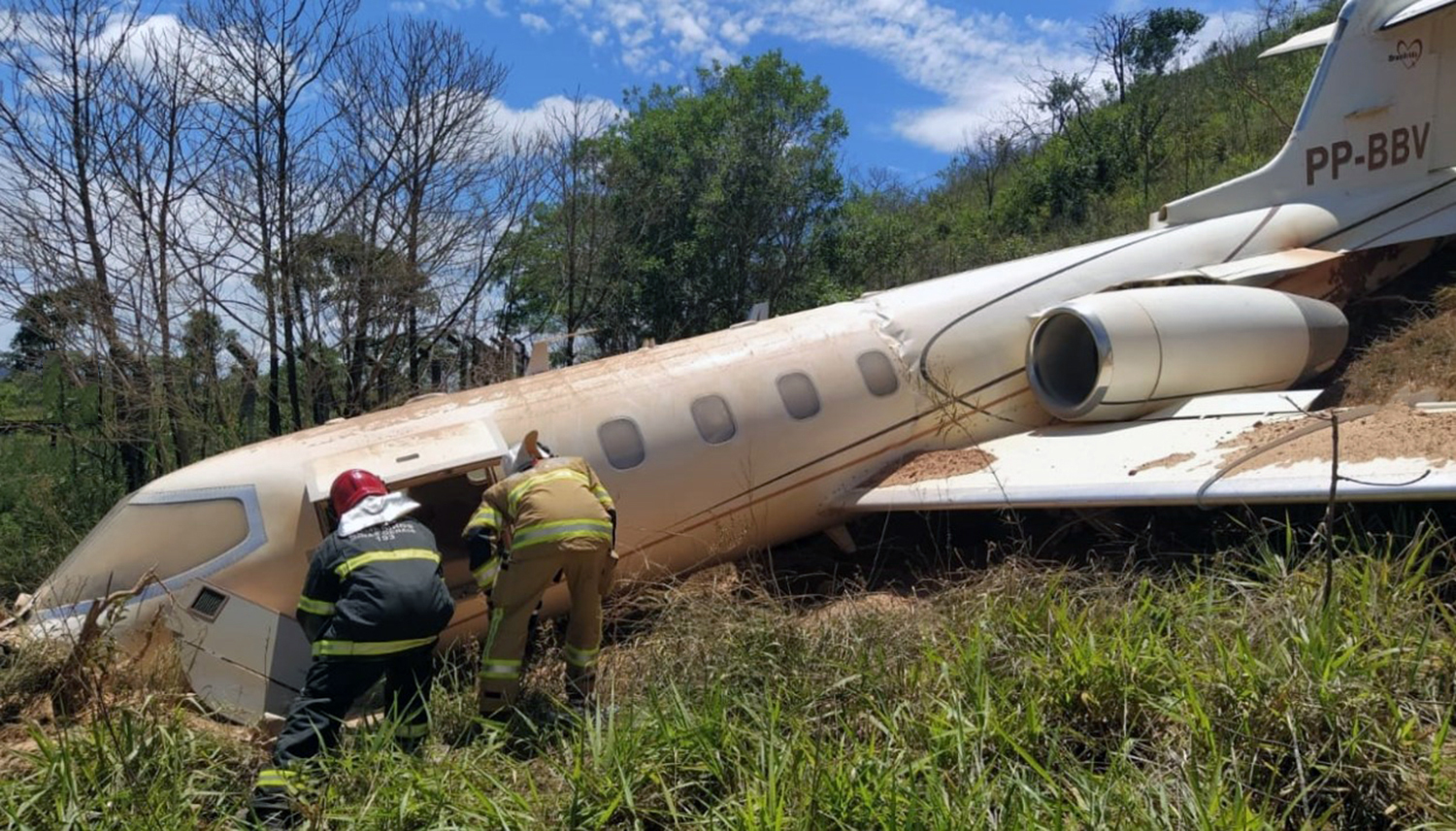
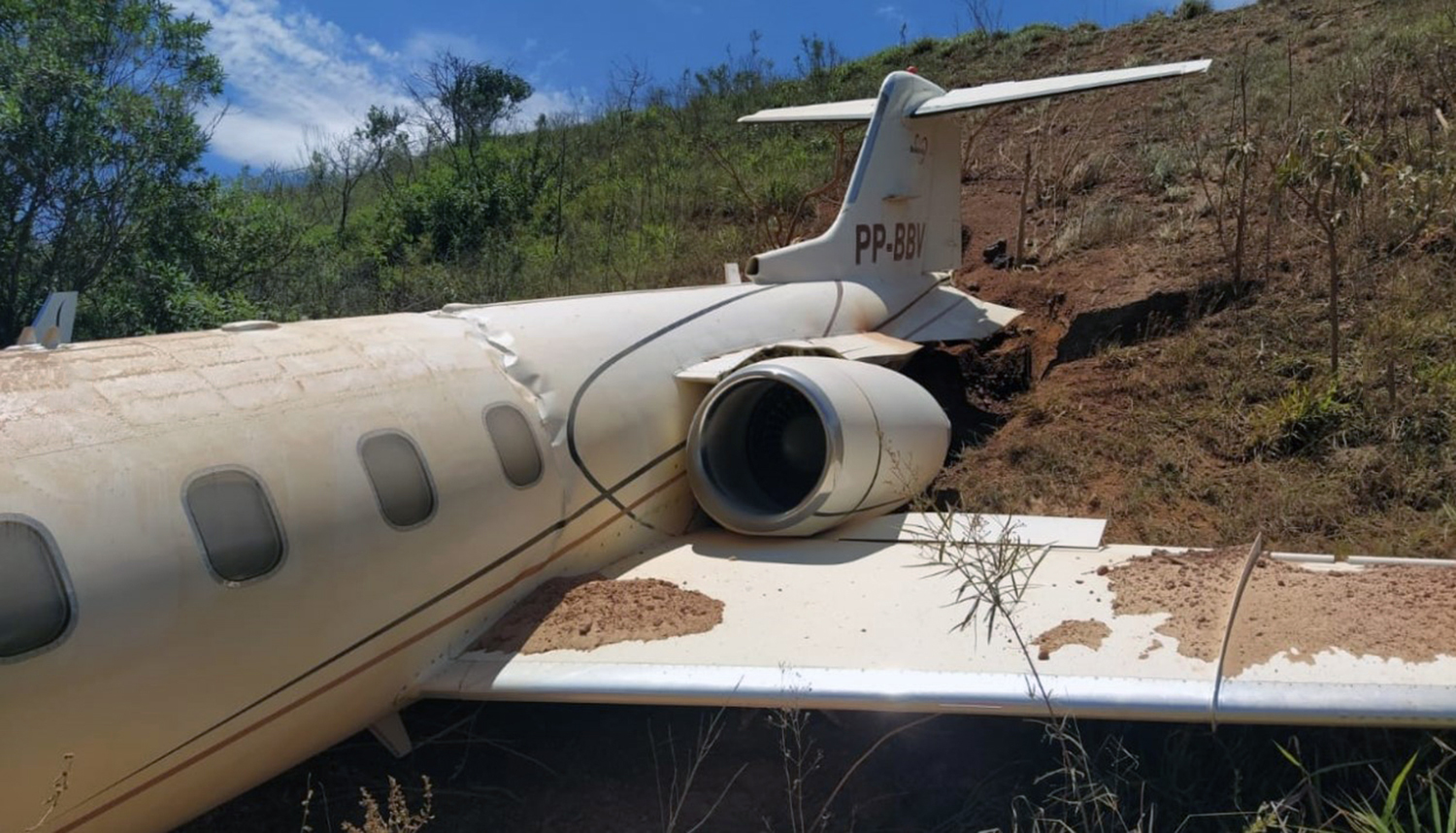
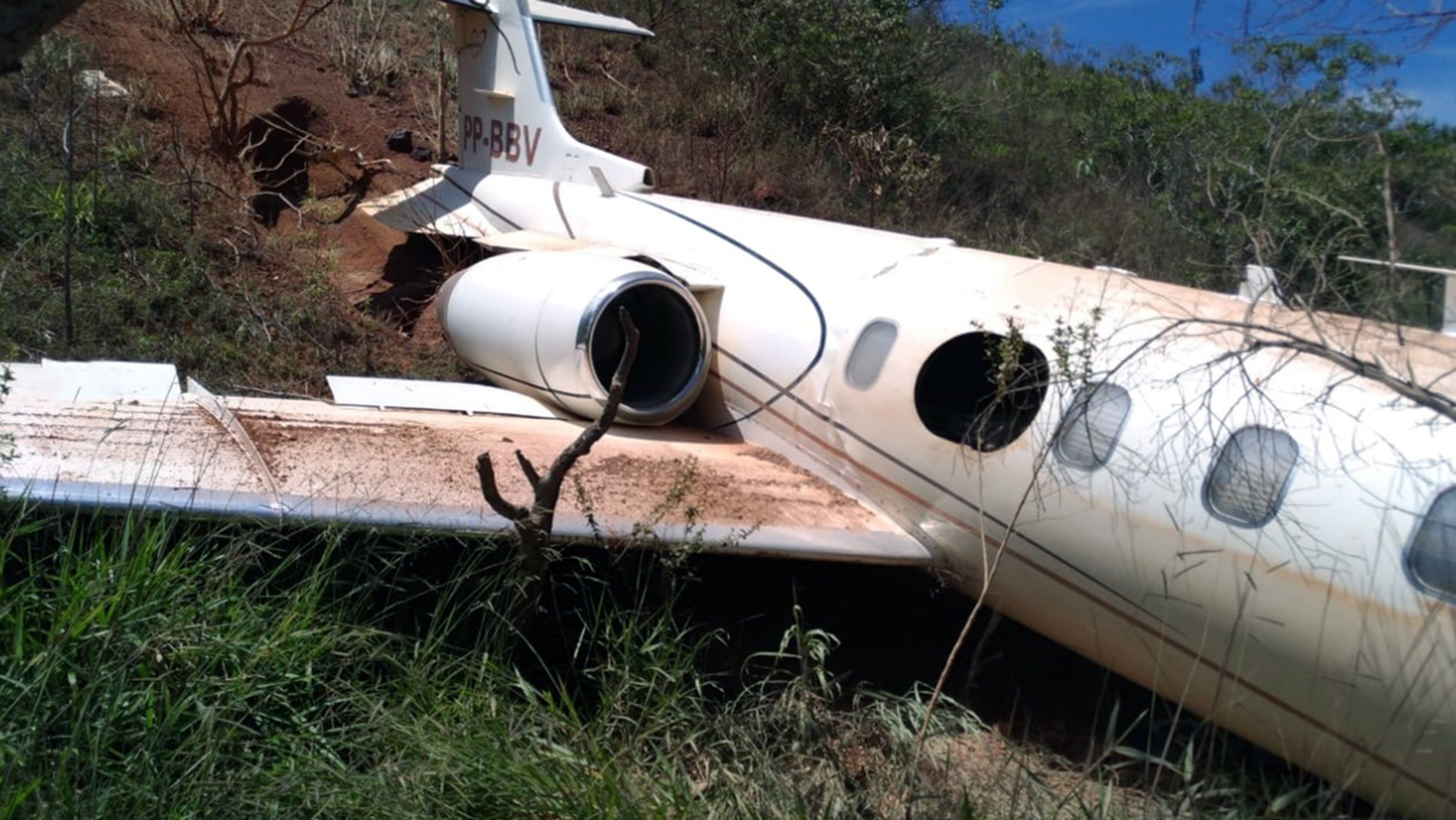
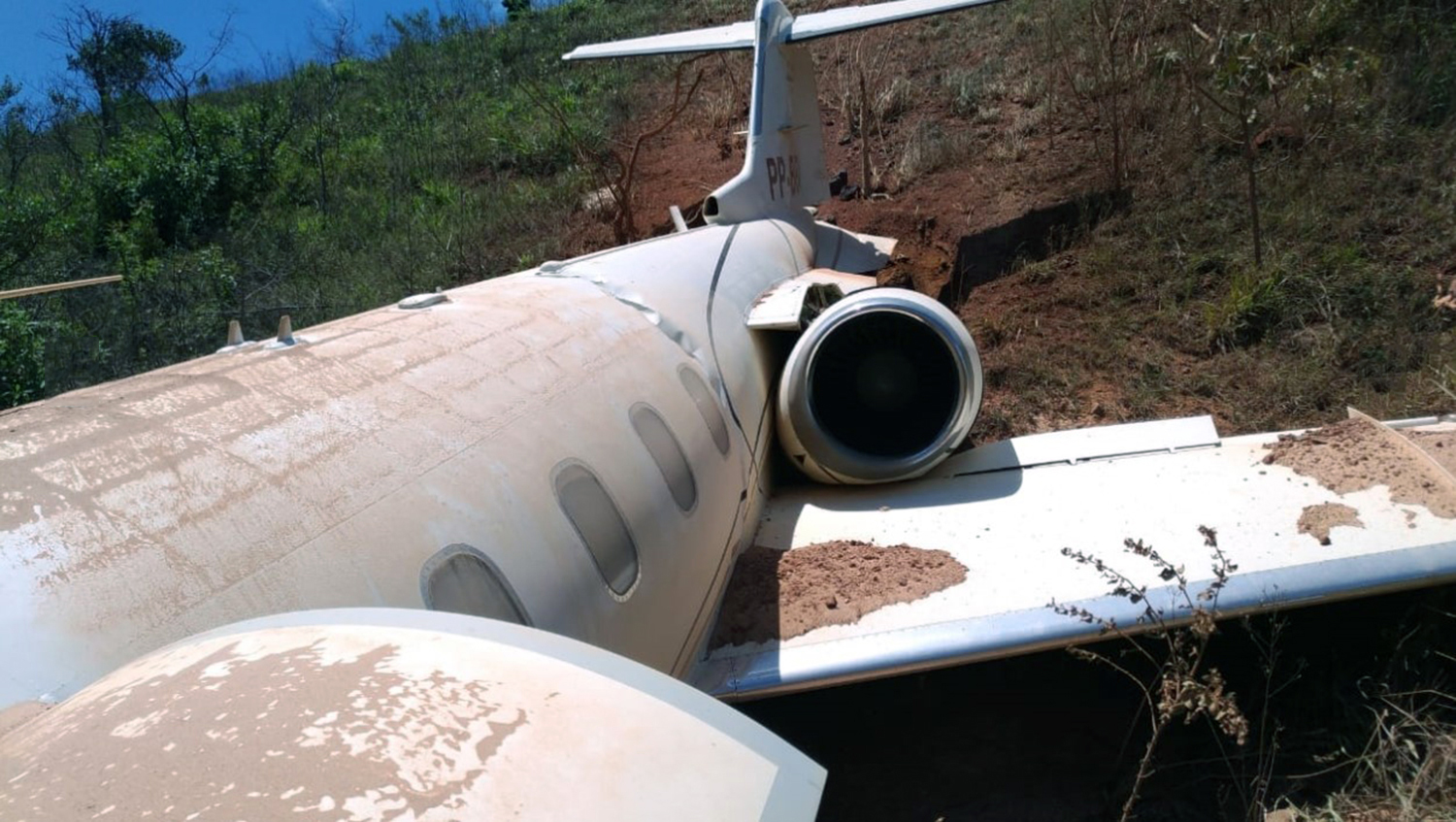
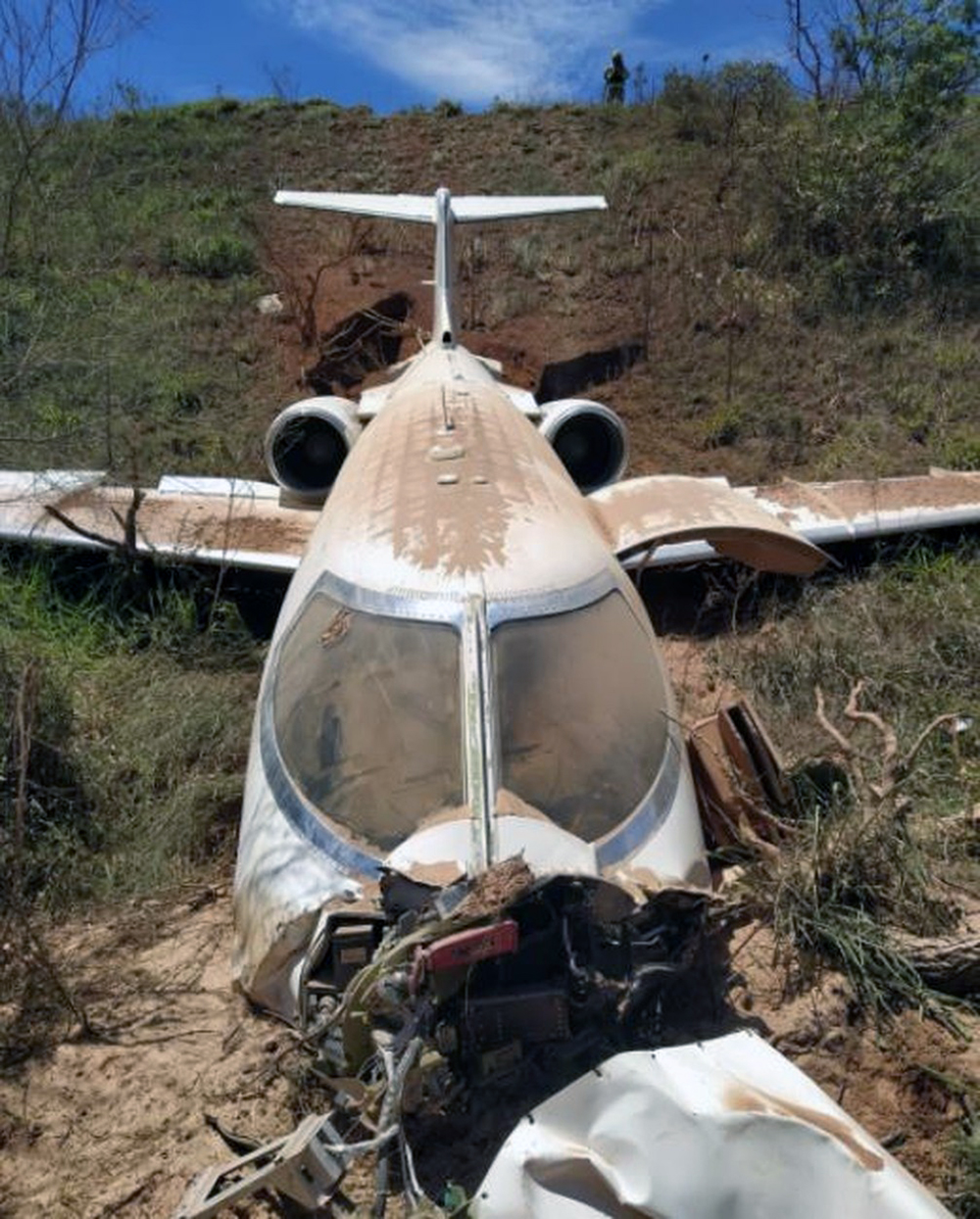
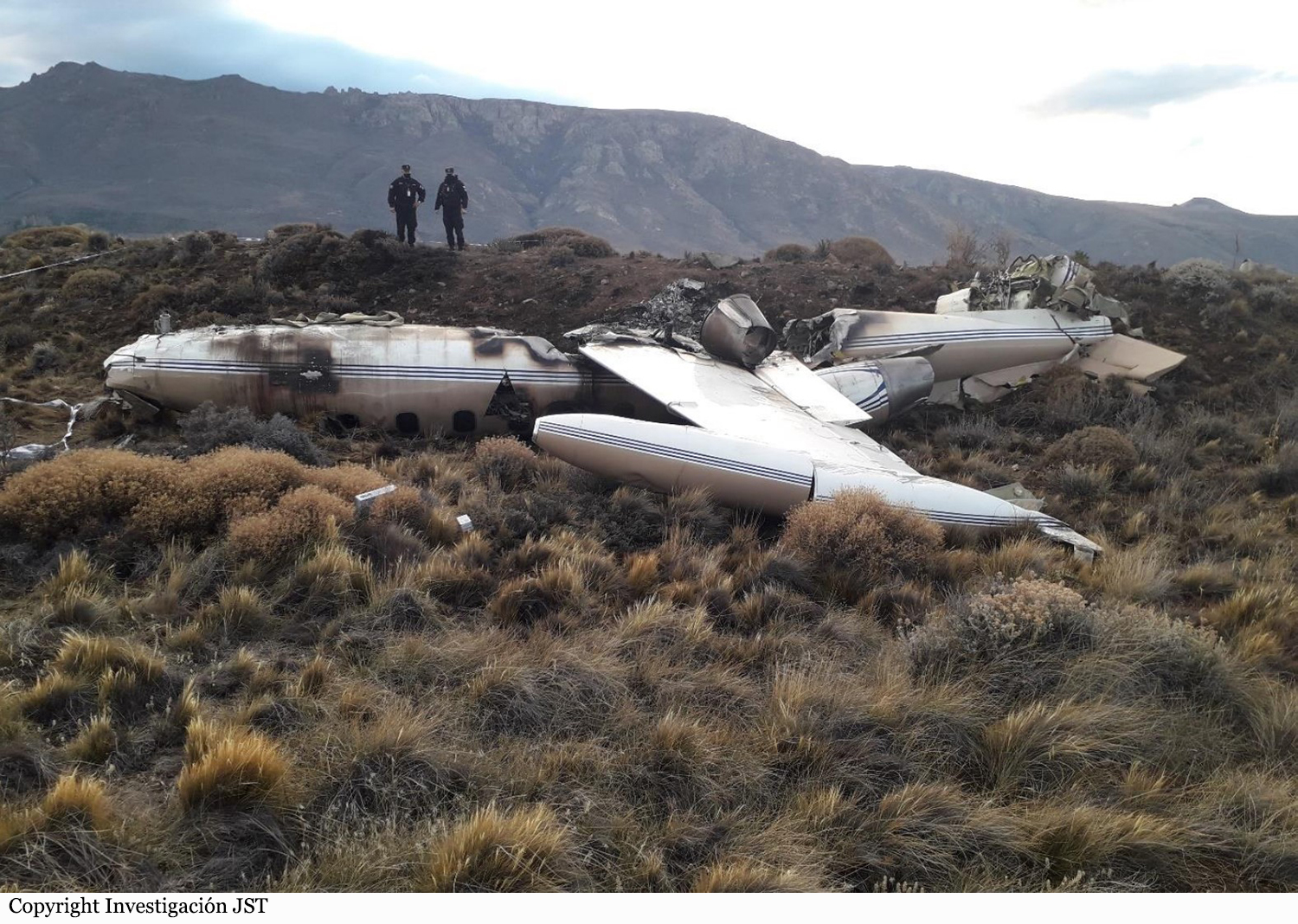
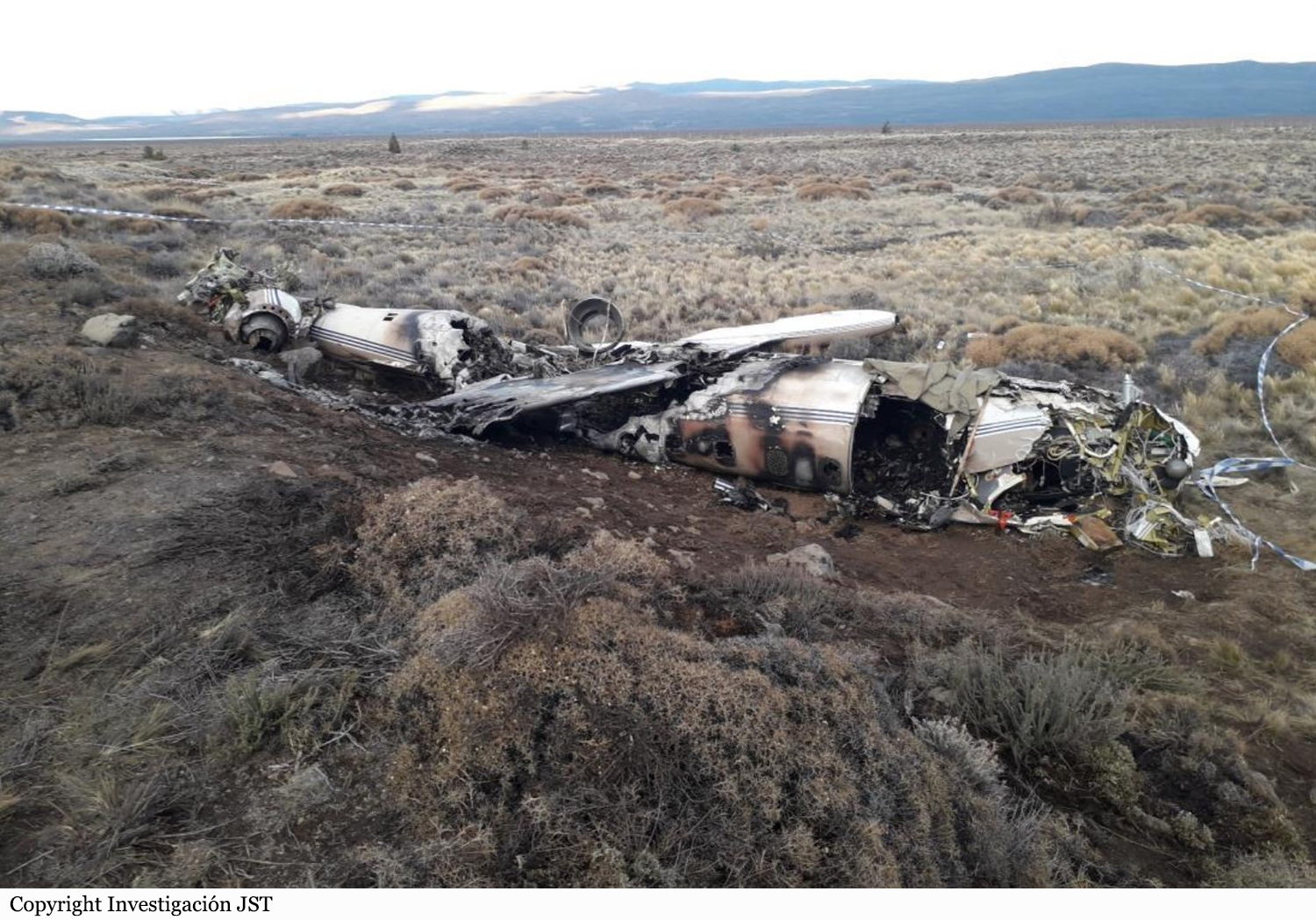
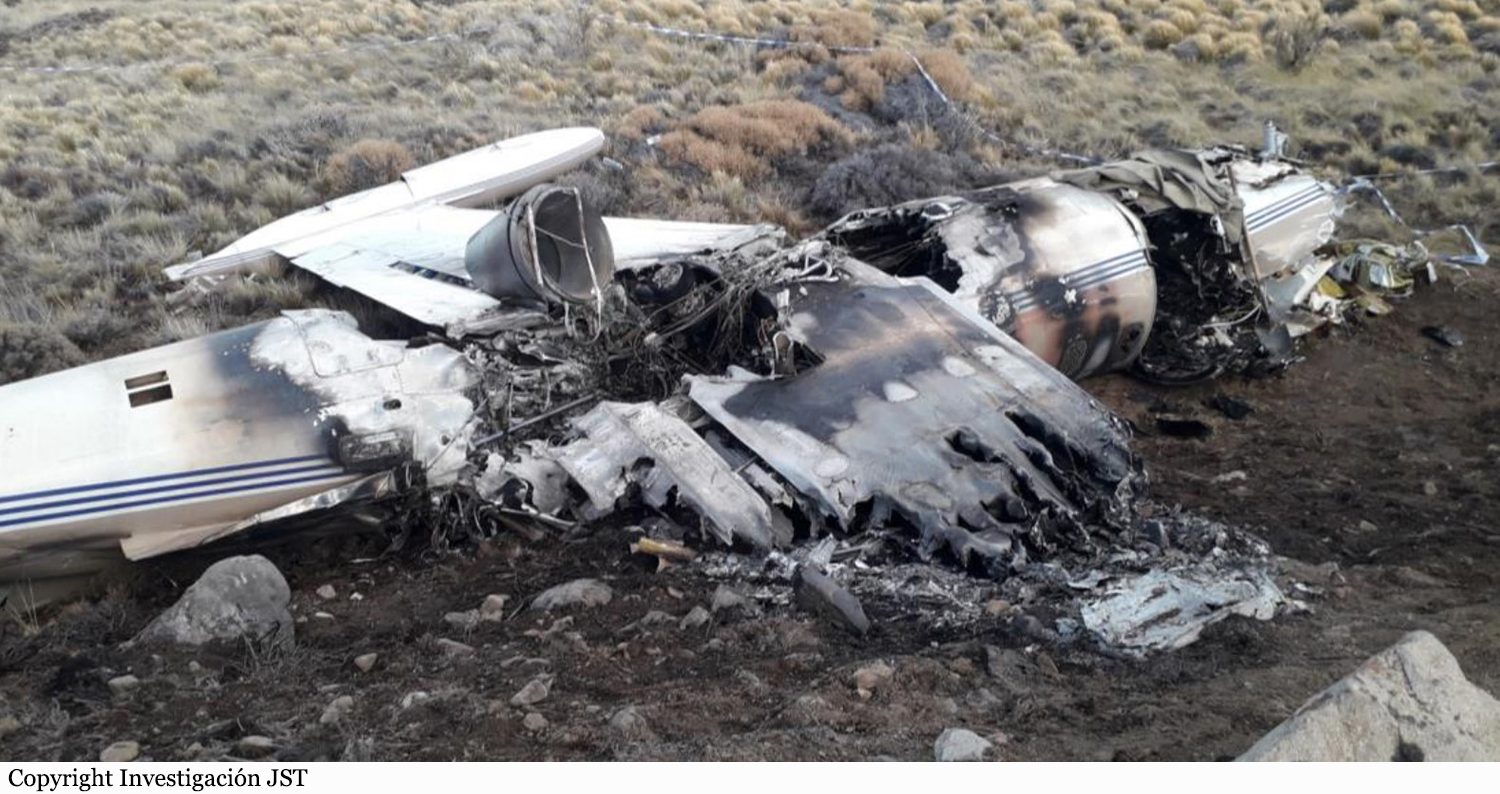
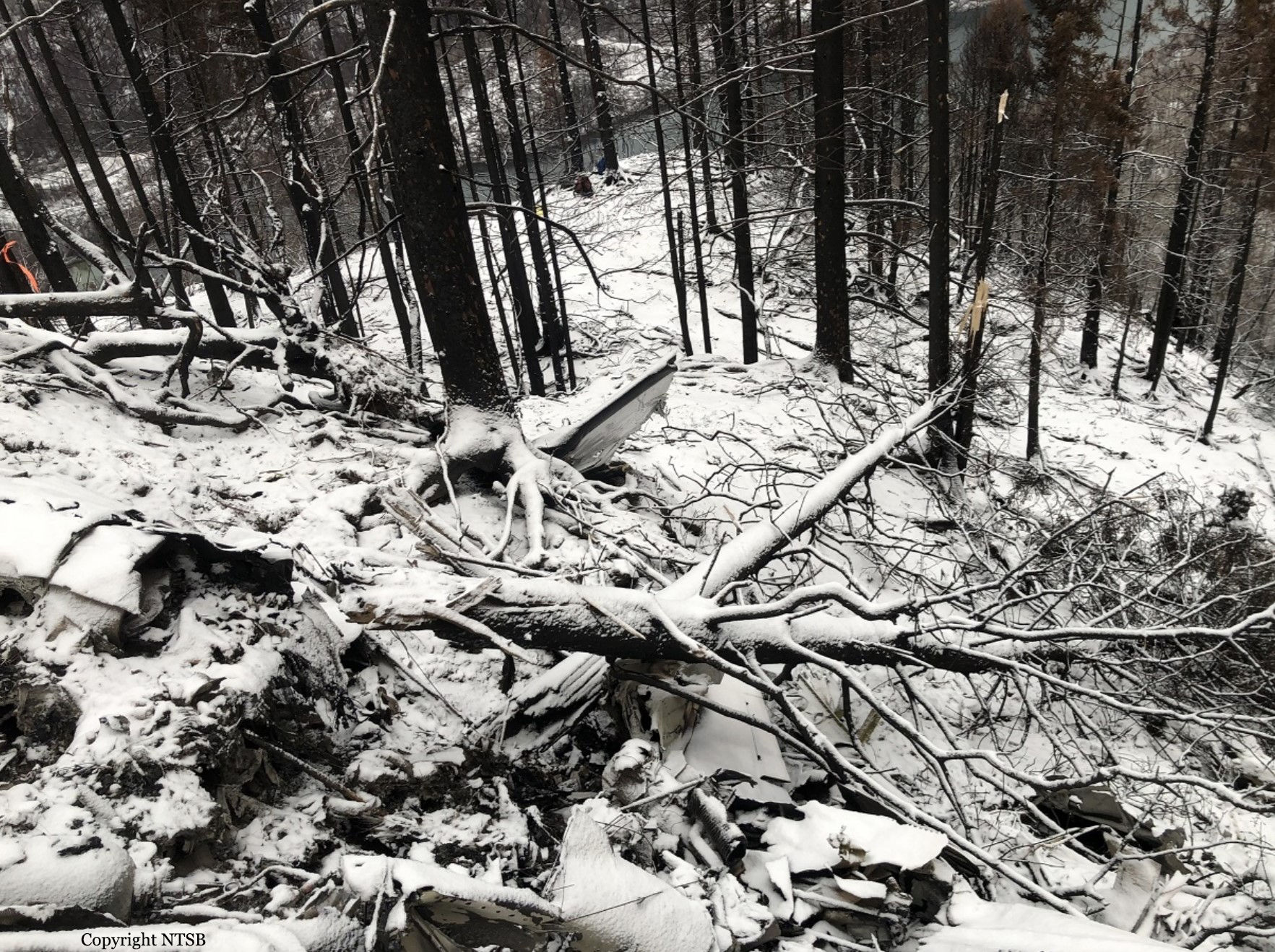
On November 29, 2019, about 1911 Alaska standard time, a Piper PA-31-350 airplane, N4087G, was destroyed by impact and postcrash fire when it collided with mountainous terrain about 15 miles west of Cooper Landing, Alaska. The three occupants; the airline transport pilot, a flight nurse, and the flight paramedic were fatally injured. The airplane was operated by Fly 4 You Inc., doing business as Security Aviation, as a Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 135 visual flight rules air ambulance flight. Dark night visual meteorological conditions existed at the departure and destination locations and company flight following procedures were in effect. The flight departed Ted Stevens International Airport (PANC), Anchorage, Alaska, about 1848, destined for Seward Airport (PAWD), Seward, Alaska. Dispatch records indicated that, on November 29, Providence Seward Medical Center emergency clinic personnel contacted multiple air ambulance companies with a "weather check" for possible air ambulance transportation of a patient from Seward to Anchorage. The first company contacted was Guardian Flight, who declined the flight at 1624 due to limited daylight hours. The second company, LifeMed Alaska, declined the flight at 1637 due to weather. The third and final company contacted for the flight was Medevac Alaska. Their dispatch officer was not notified of the previous declined flight requests and forwarded the request to Security Aviation, who is their sole air charter provider. At 1731 Security Aviation accepted the flight, and Medevac Alaska flight SVX36 was staffed with a nurse and paramedic. A preliminary review of archived Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) radar and automatic dependent surveillance (ADS-B) data revealed that the accident airplane departed PANC and flew south about 3,000 ft mean sea level (msl) toward the Sterling Highway. The airplane was then observed descending to 2,200 ft msl while flying a right racetrack pattern before flying into the valley toward Cooper Landing. The last data point indicated that at 1911:14 the airplane was over the west end of Jean Lake at 2,100 ft msl, on a 127° course, and 122 kts groundspeed. Ground witnesses who were in vehicles on the Sterling Highway near milepost 63, reported that they saw the lights of the airplane flying over the highway that night. One witness stated that he saw the airplane west of the mountains turn in a circle as it descended and then entered the valley. He observed the wings rocking back and forth and while he was looking elsewhere, he heard an explosion and observed a large fire on the mountainside. Another witness reported seeing the airplane flying low and explode when it impacted the mountain. Witnesses to the fire called 911 and observed the wreckage high on the mountainside burning for a long time after impact. The airplane was reported overdue by the chief pilot for Security Aviation and the FAA issued an alert notice (ALNOT) at 2031. The Alaska Rescue Coordination Center dispatched an MH-60 helicopter to the last known position and located the burning wreckage that was inaccessible due to high winds in the area. On December 1, 2019, the Alaska State Troopers coordinated a mountain recovery mission with Alaska Mountain Rescue Group. The wreckage was observed on the mountain at an elevation of about 1,425 ft msl in an area of steep, heavily tree-covered terrain near the southeast end of Jean Lake in the Kenai National Wildlife Refuge. The airplane was highly fragmented and burned, however all major airplane components were accounted for. Multiple large trees around the wreckage were fractured and indicated an easterly heading prior to the initial impact.