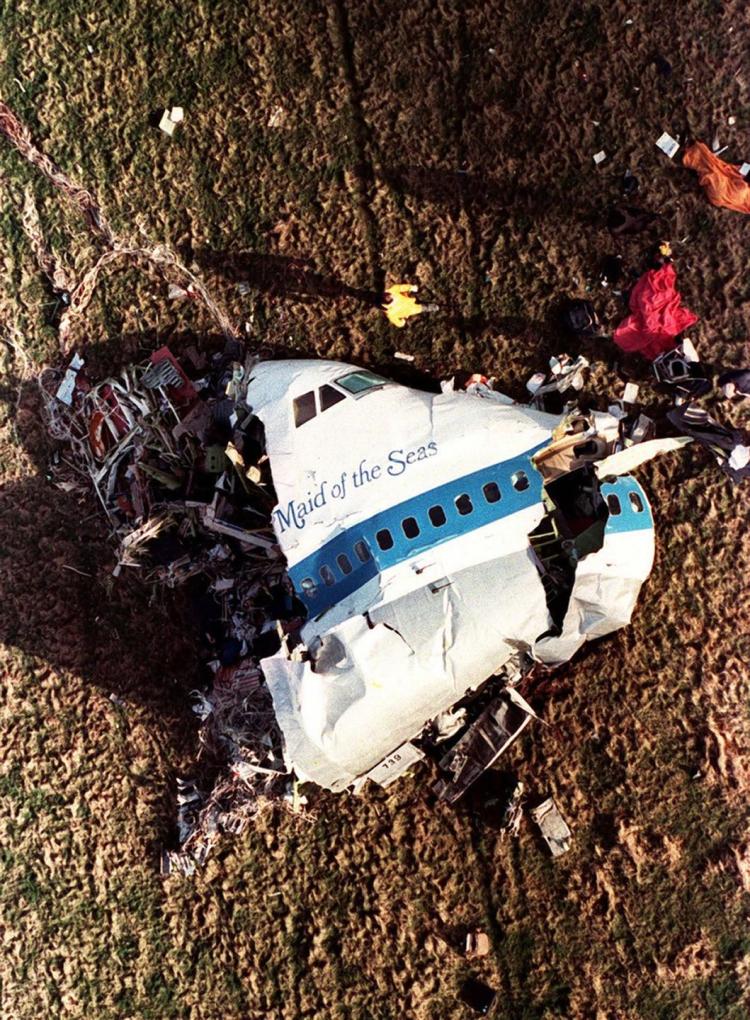
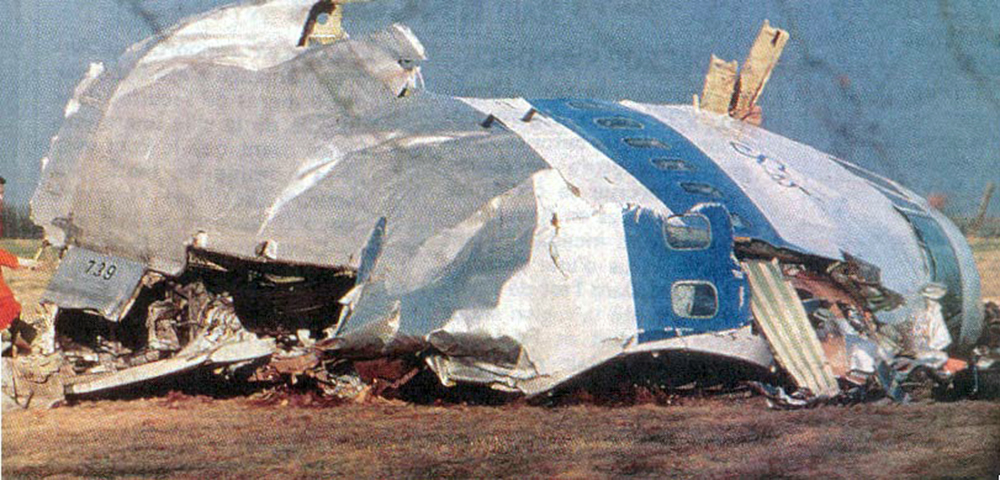
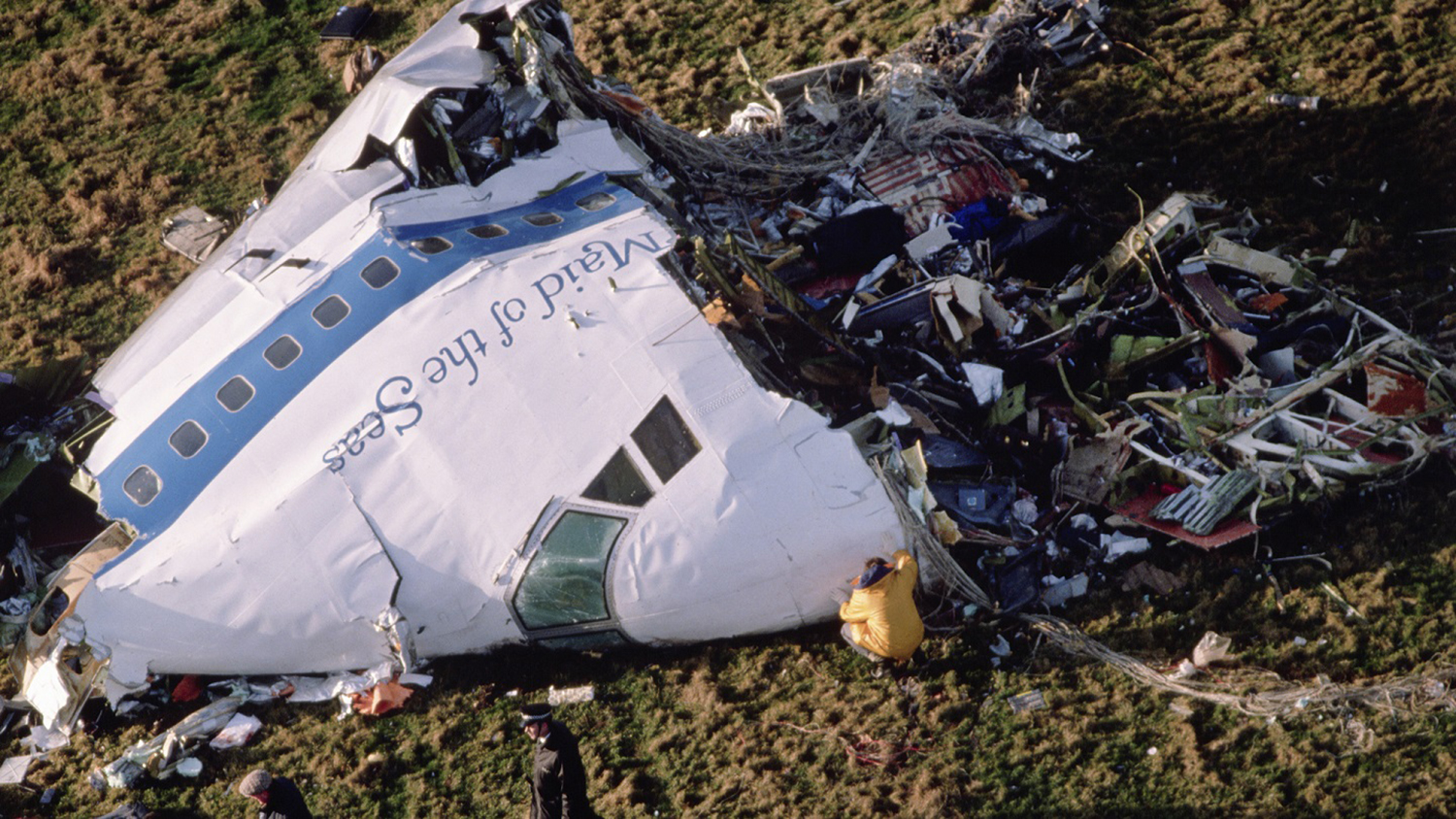
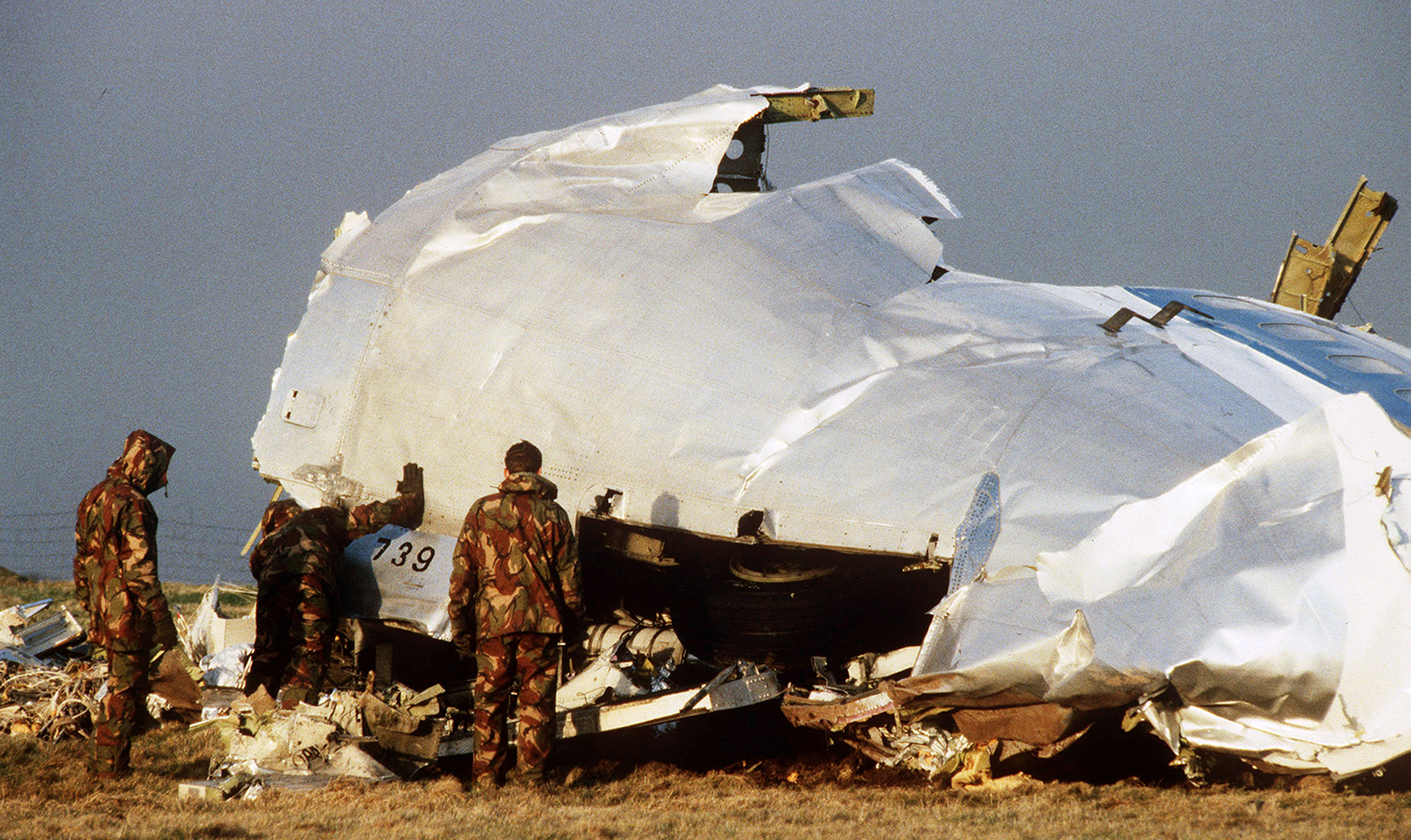
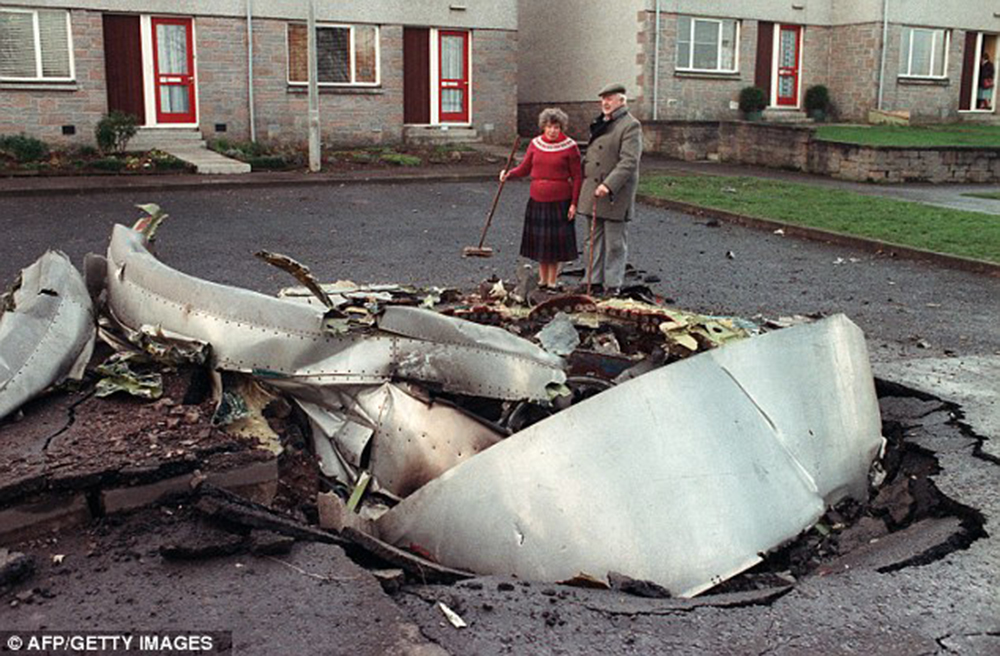
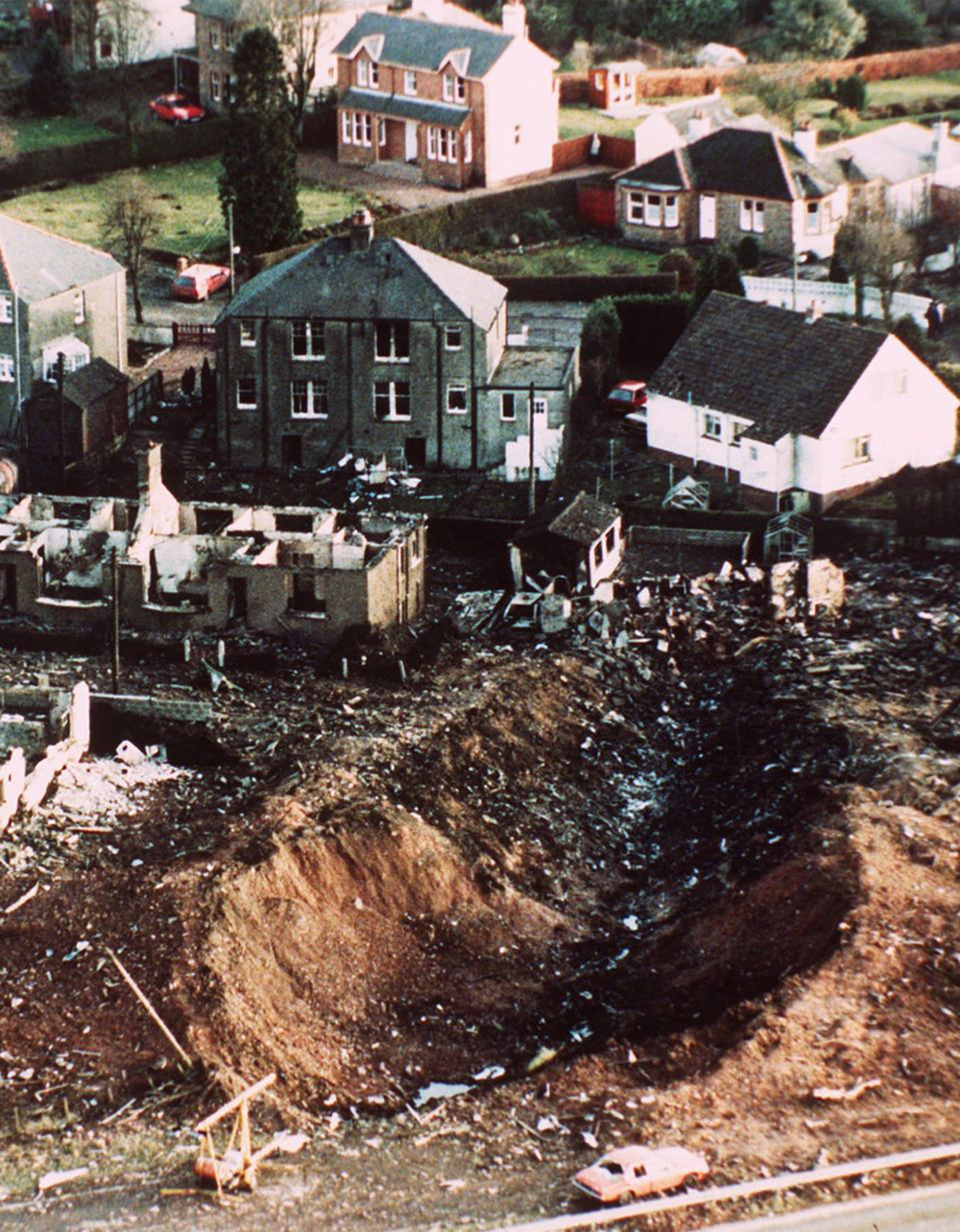
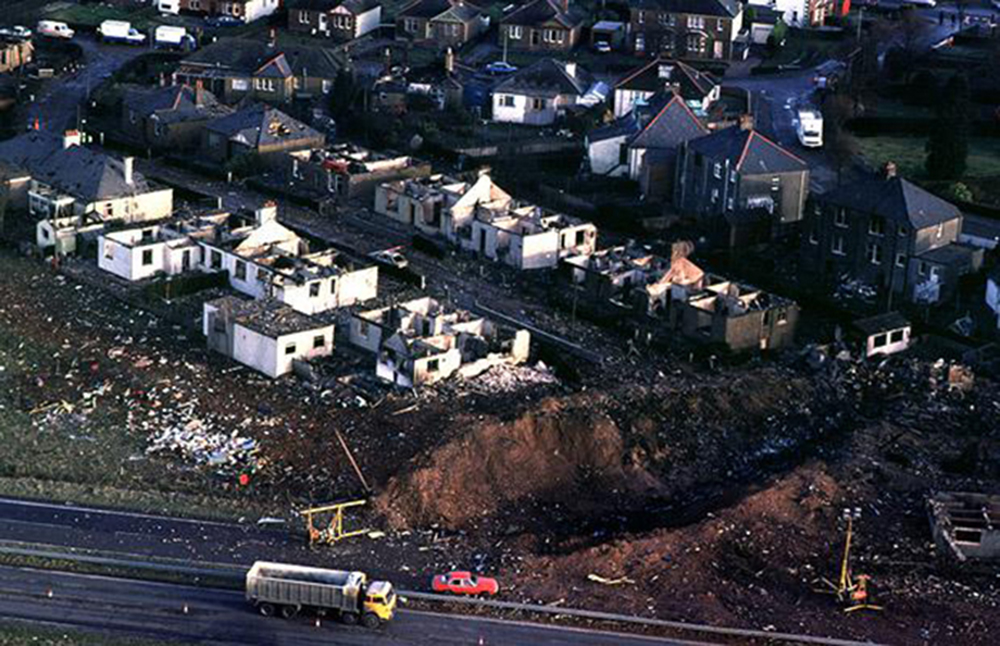
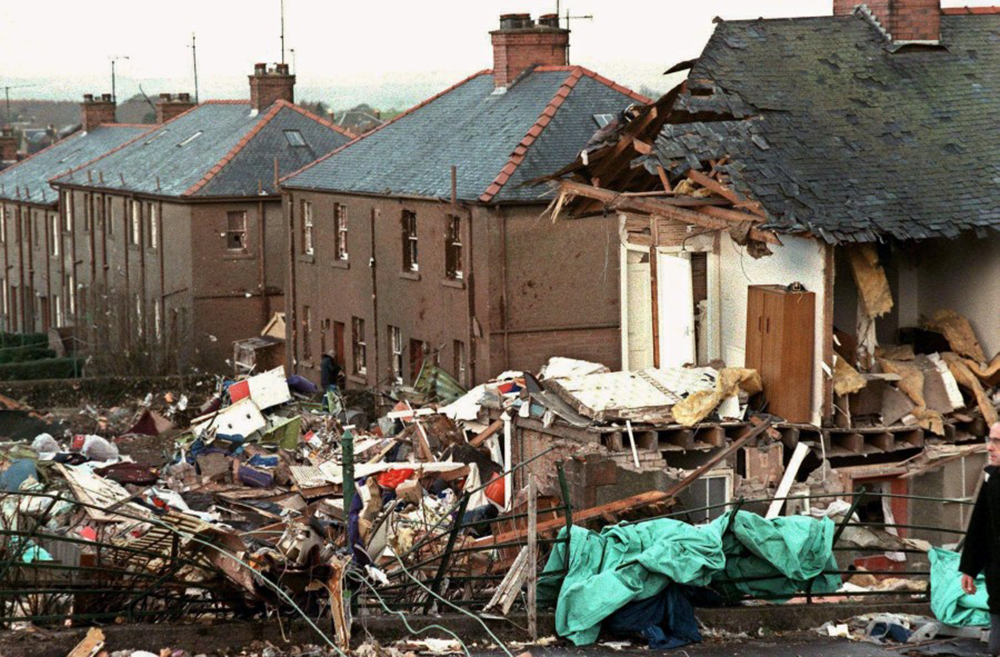
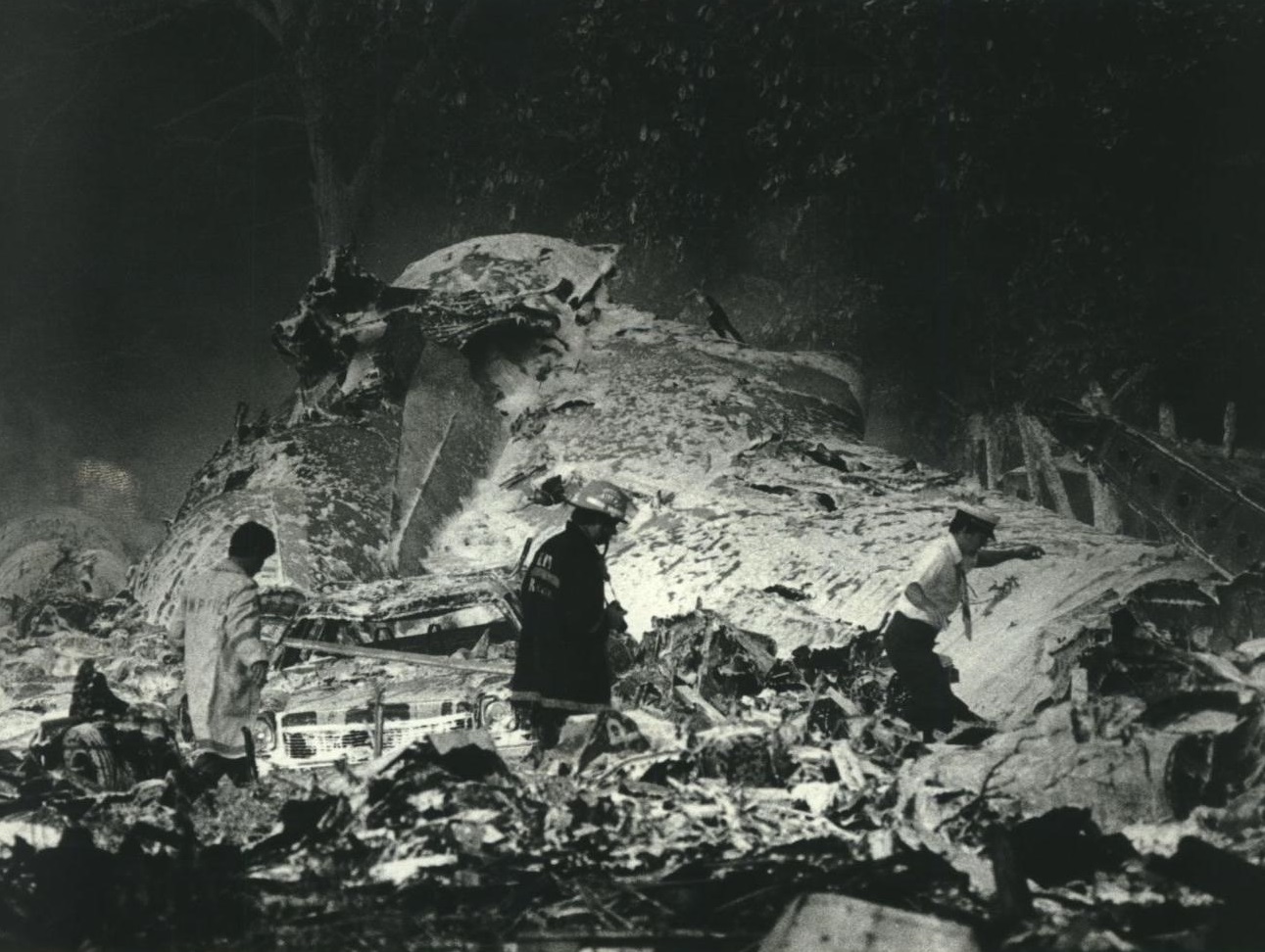
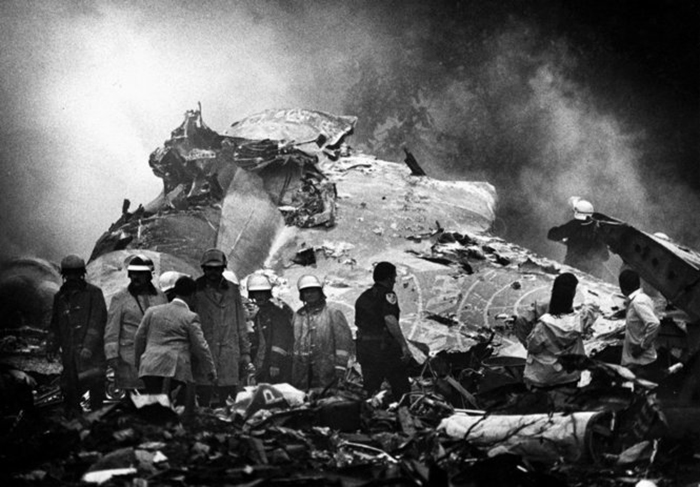
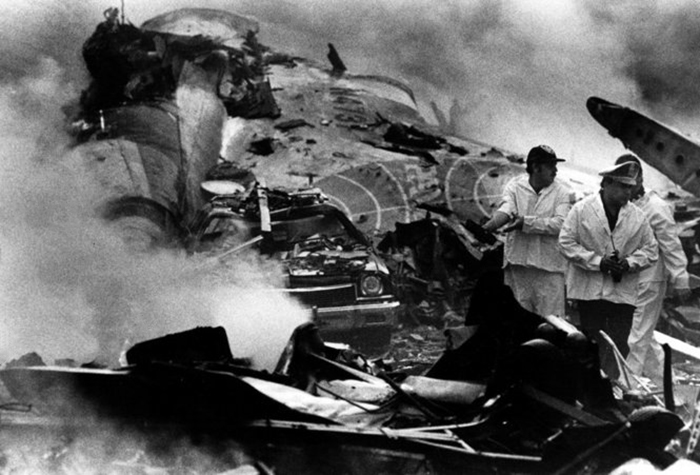
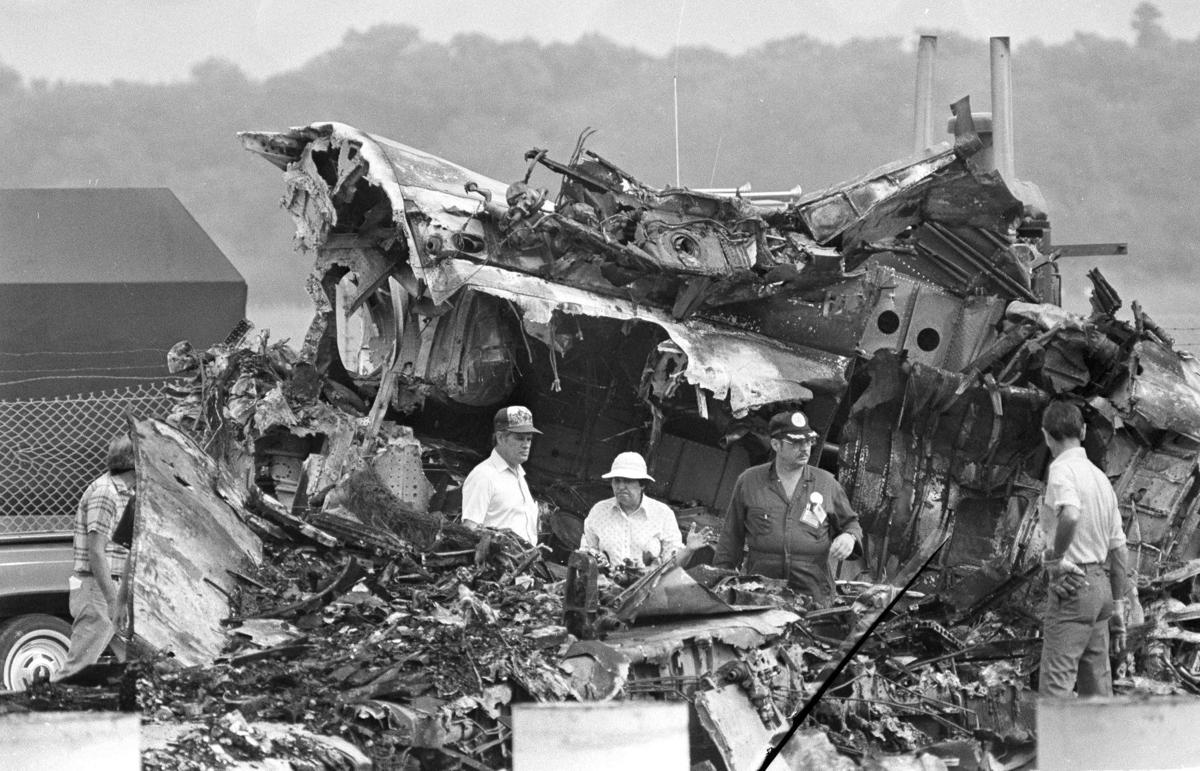
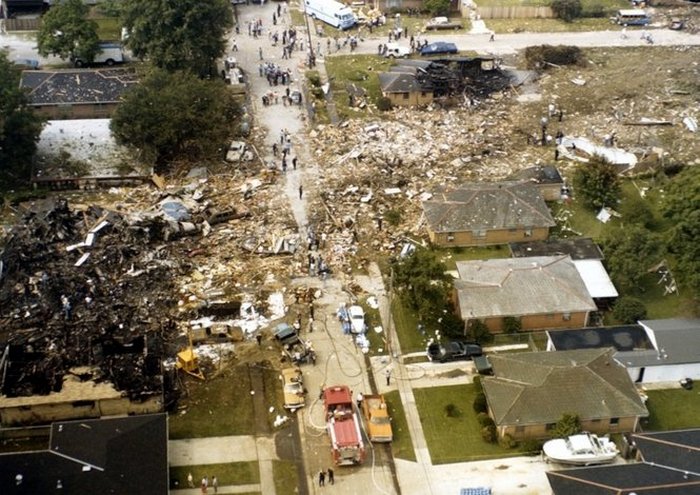
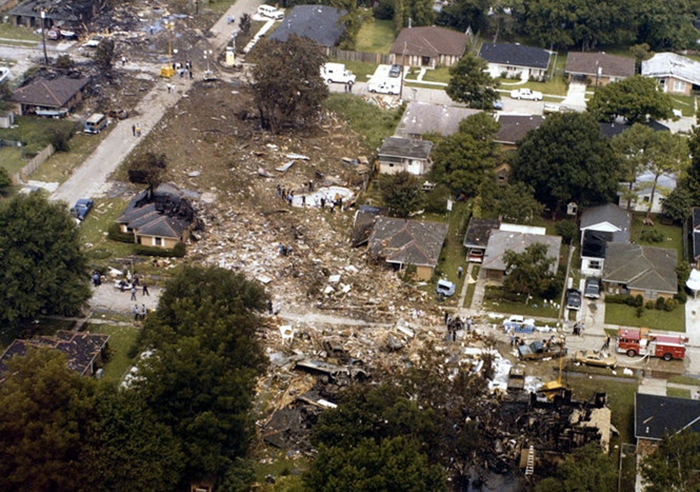
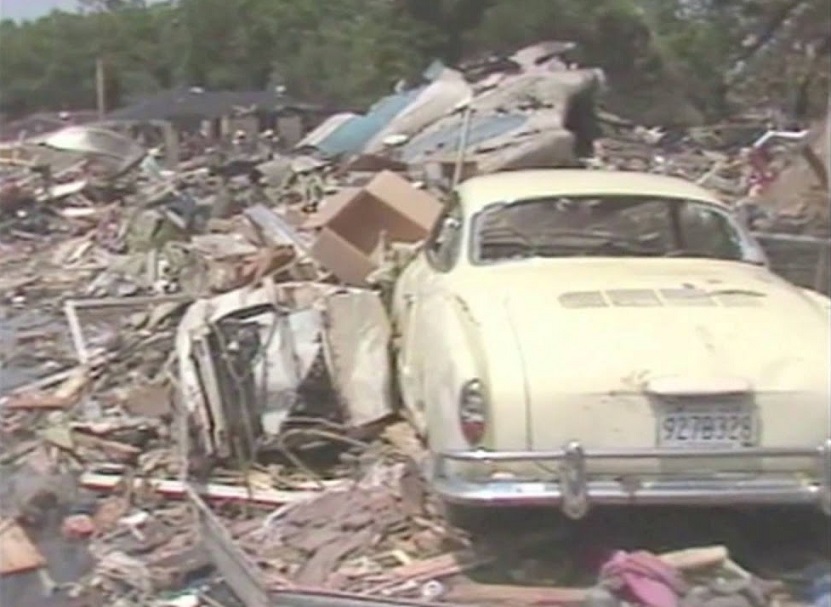
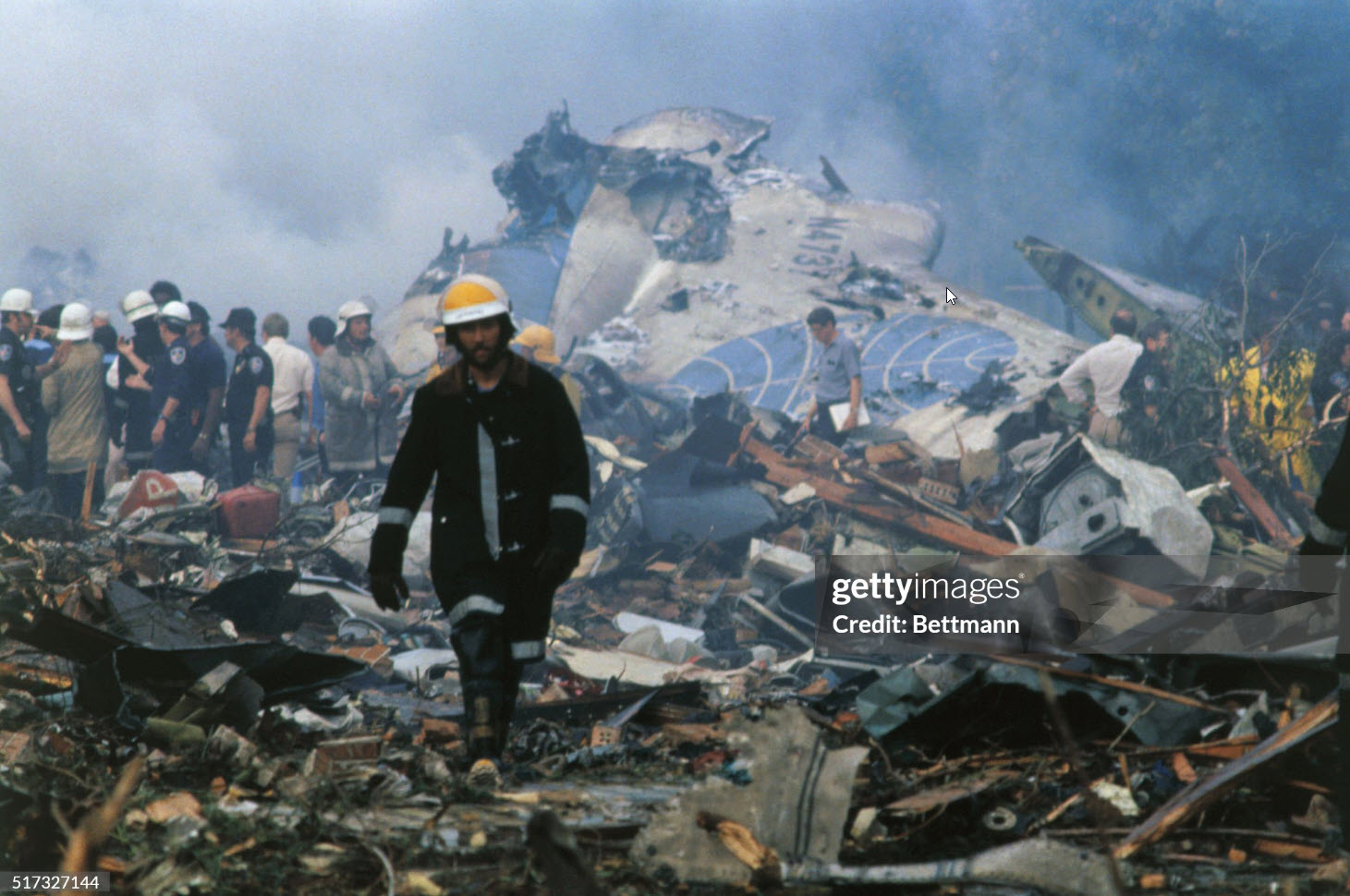
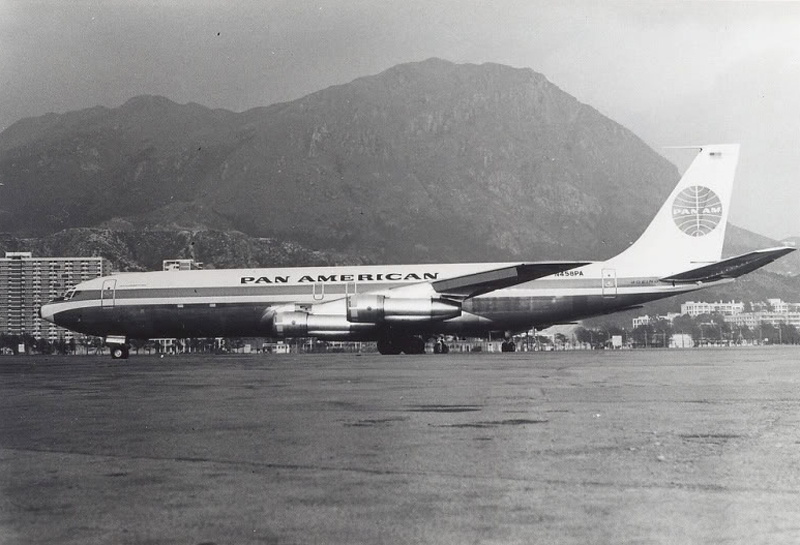
Circumstances:
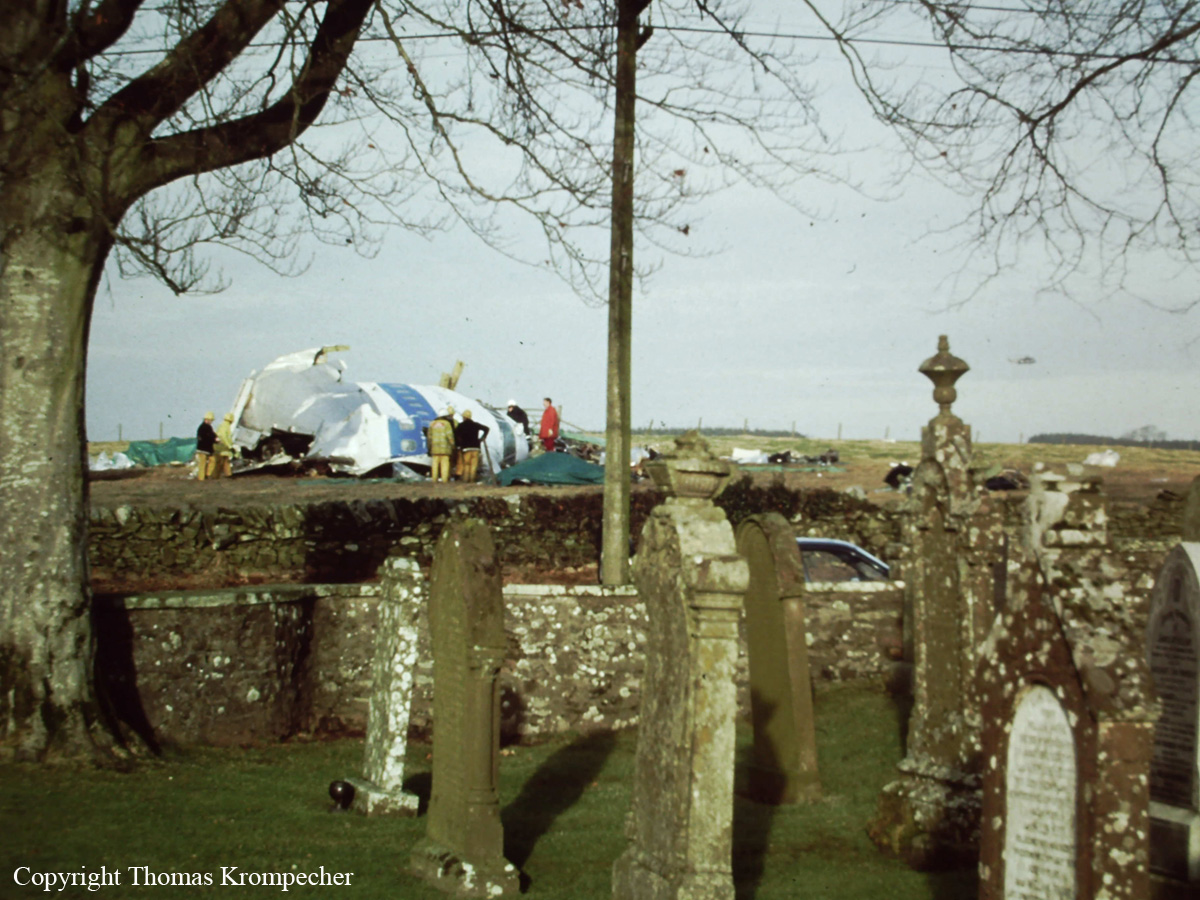
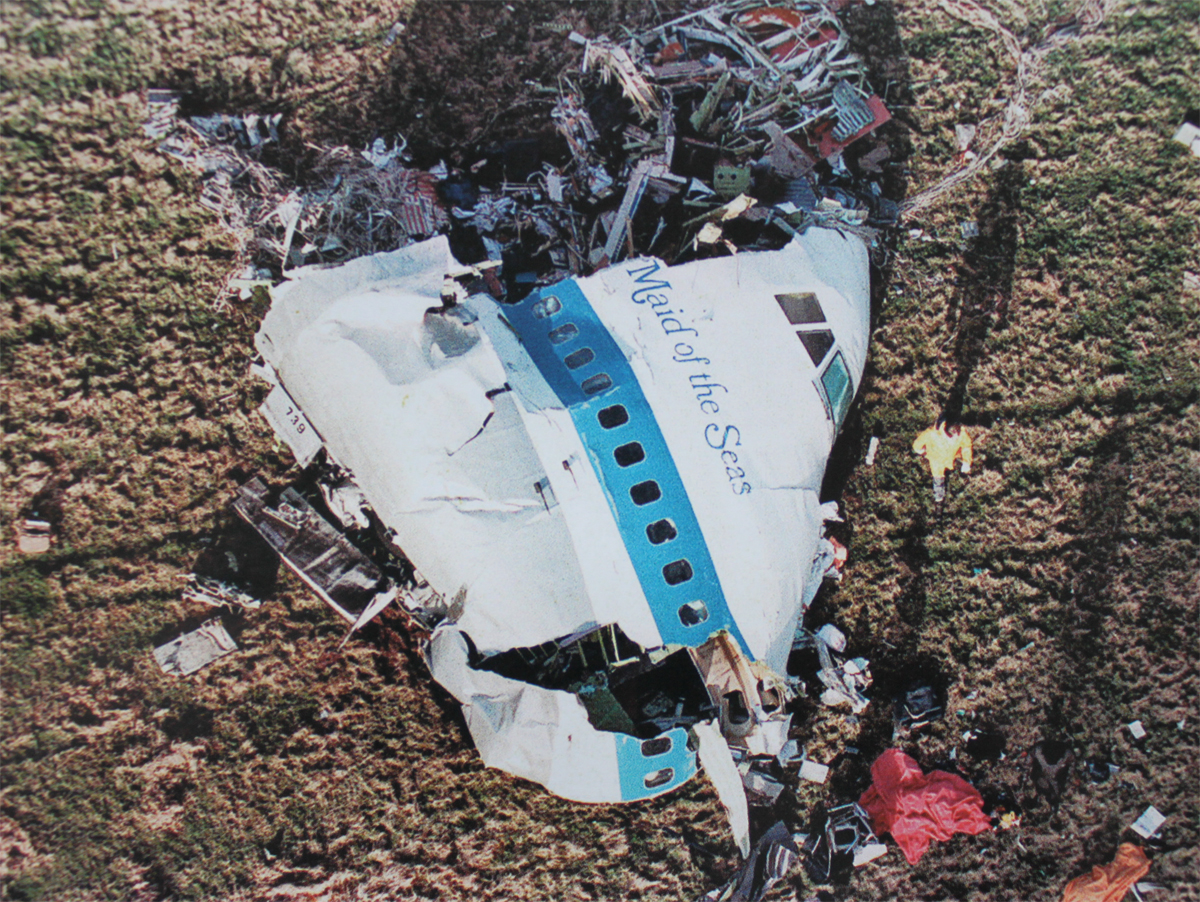
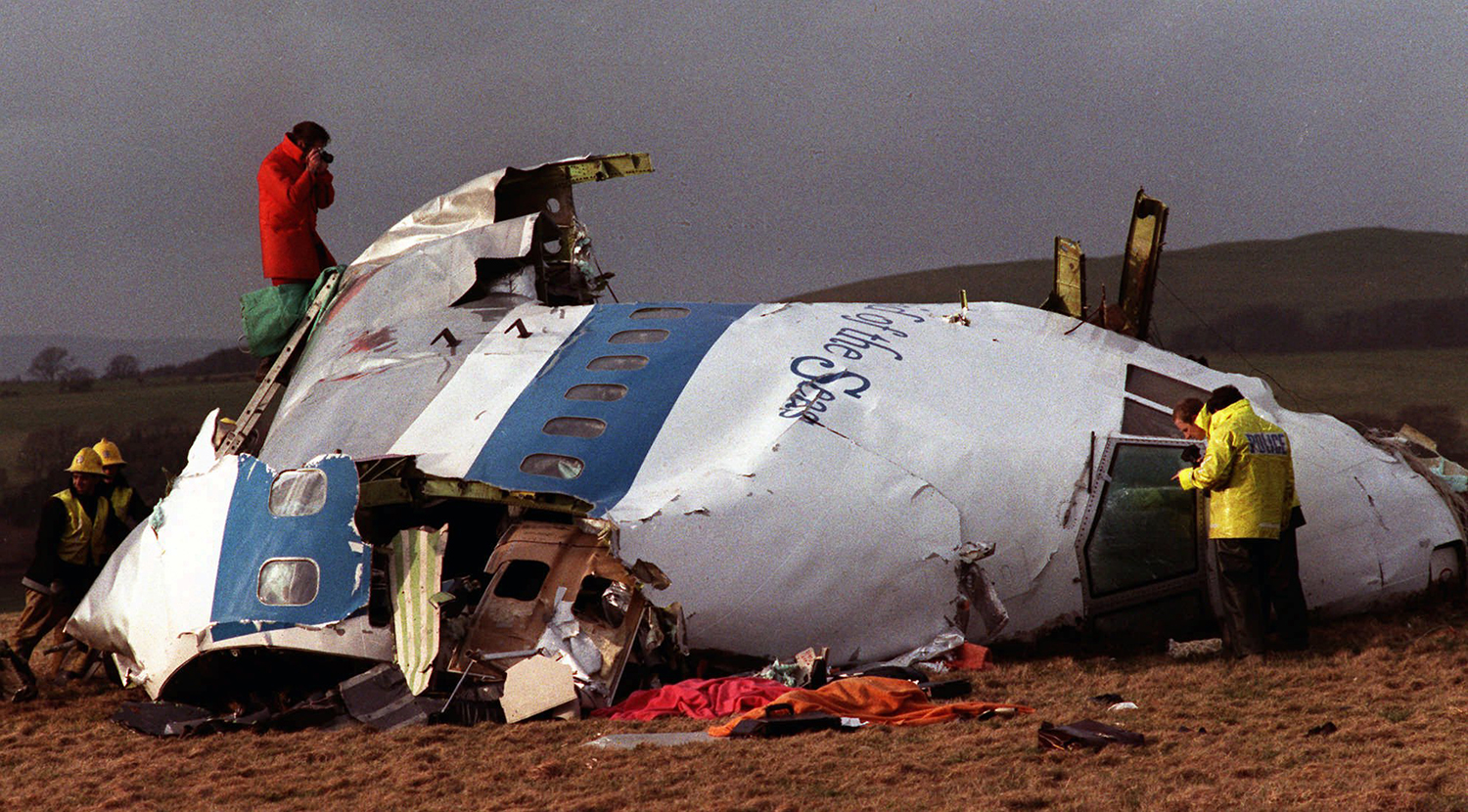
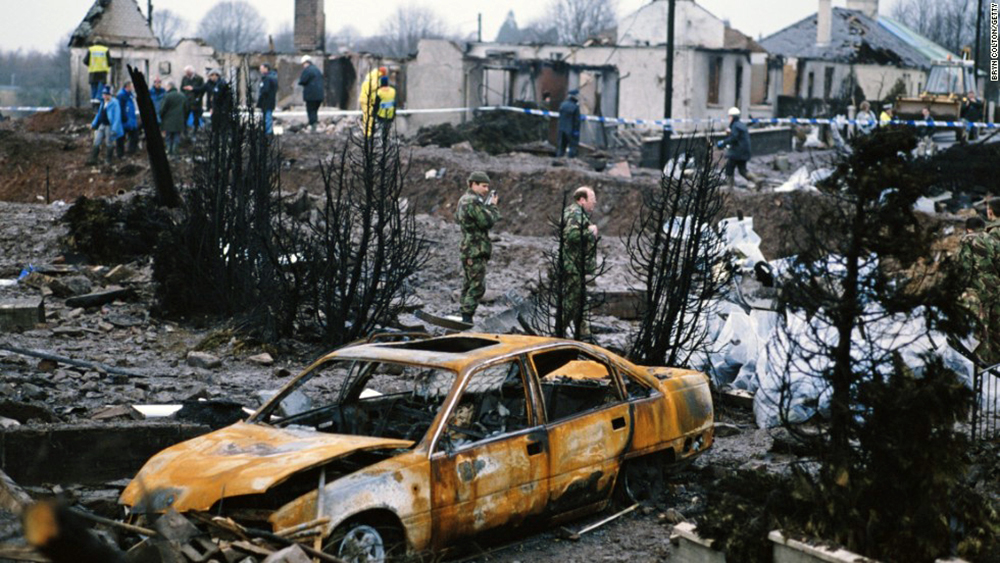
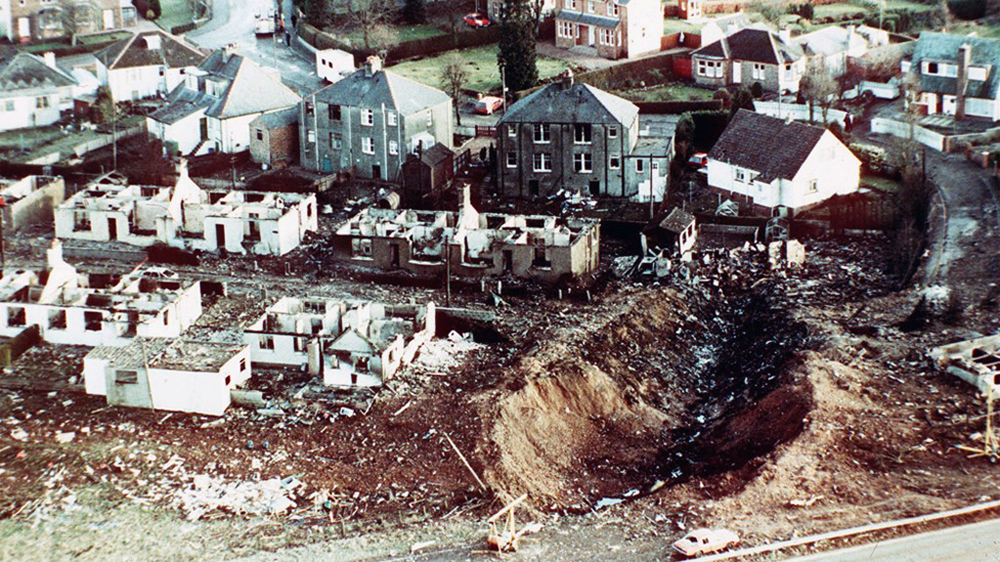
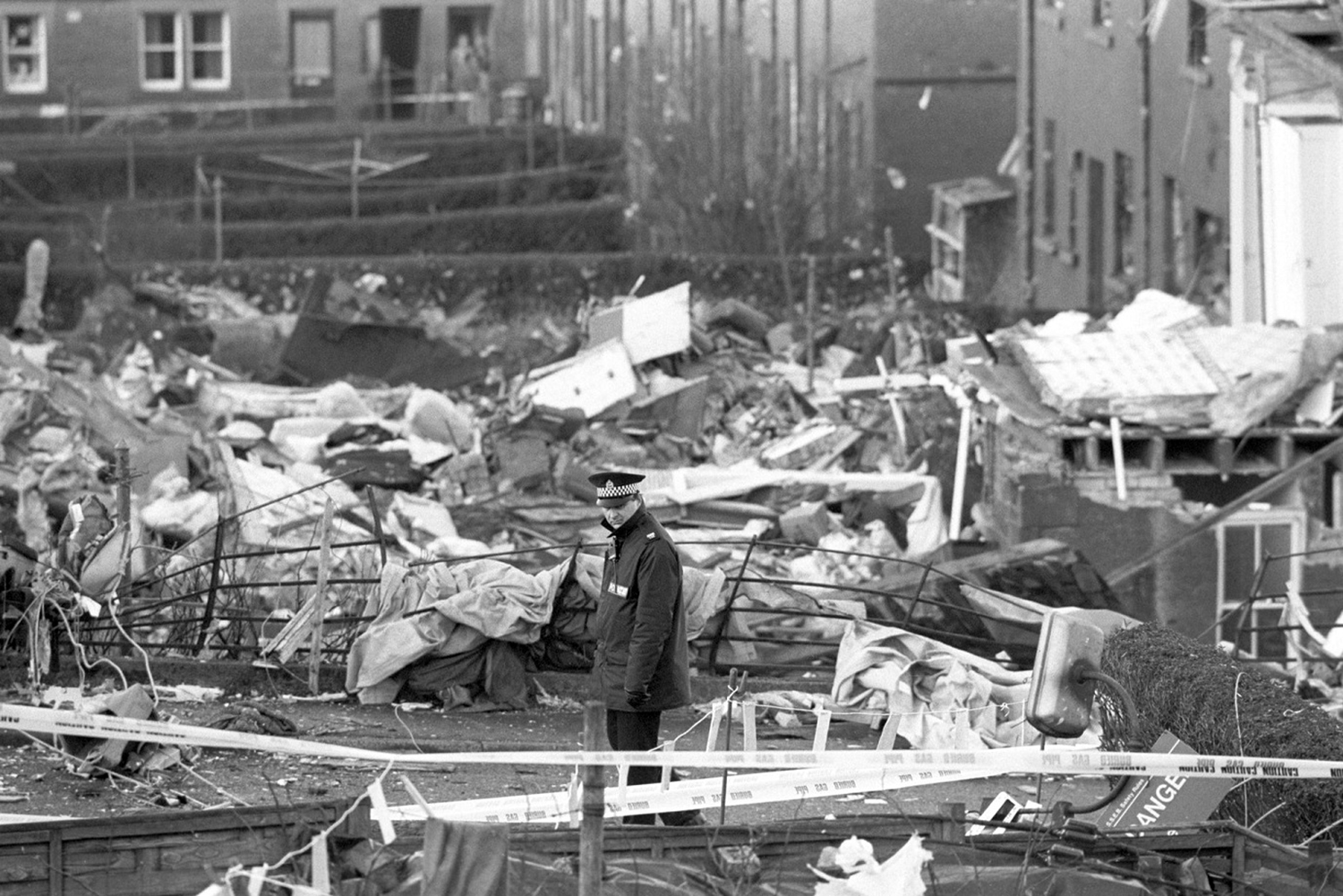
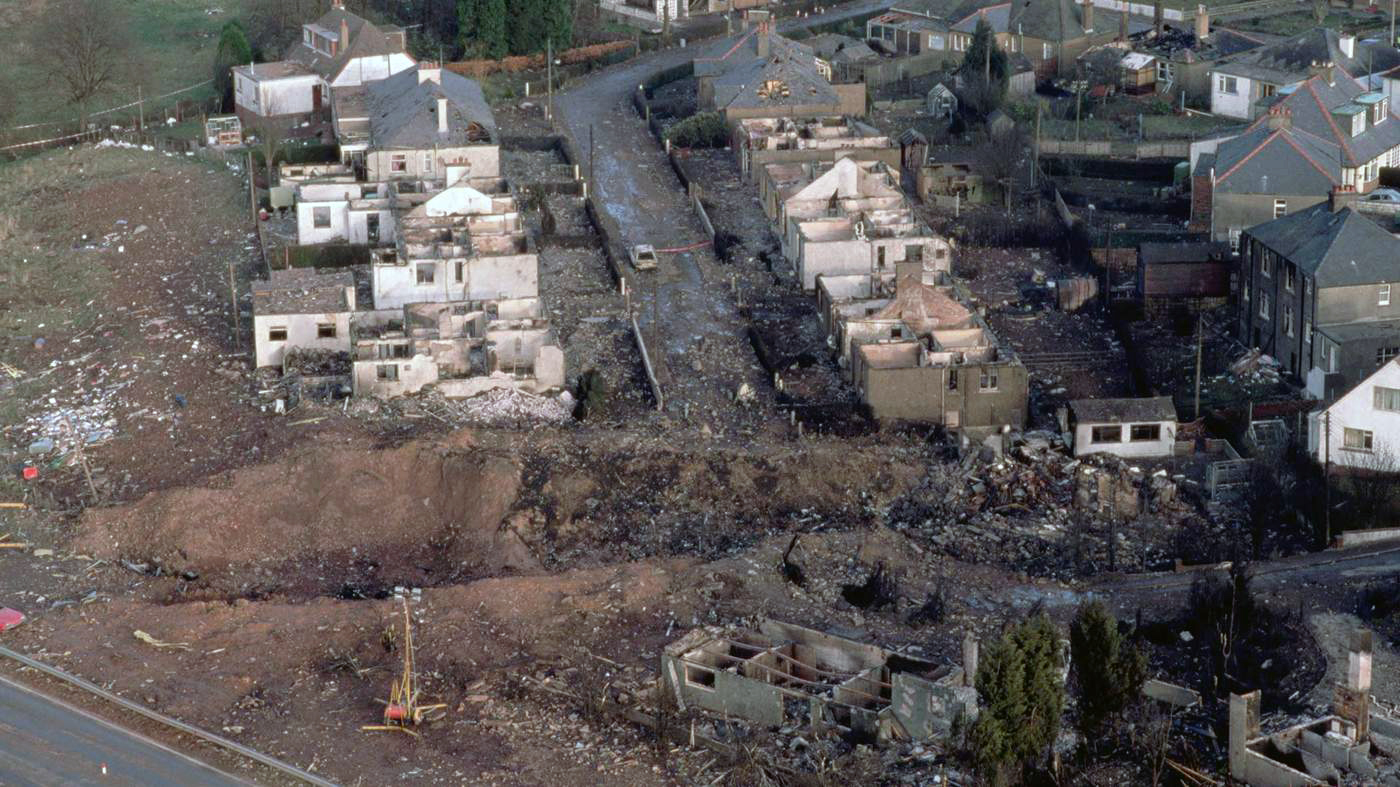
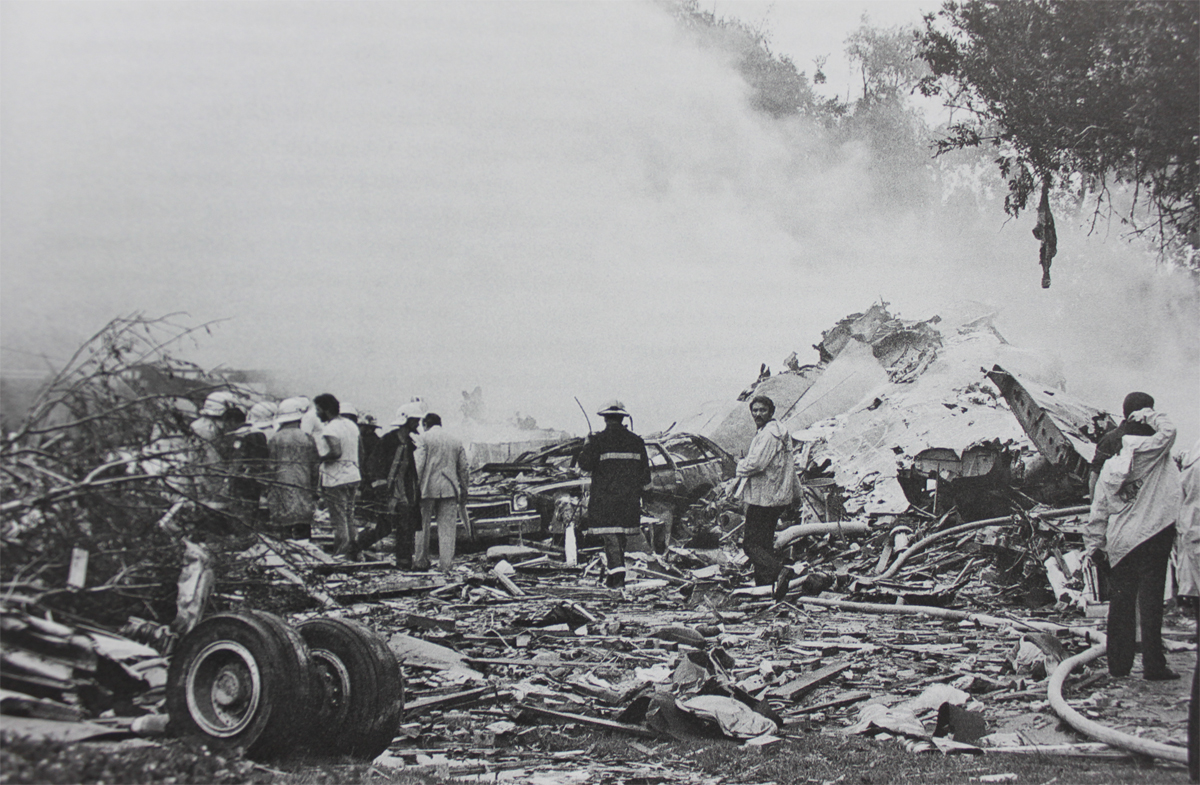
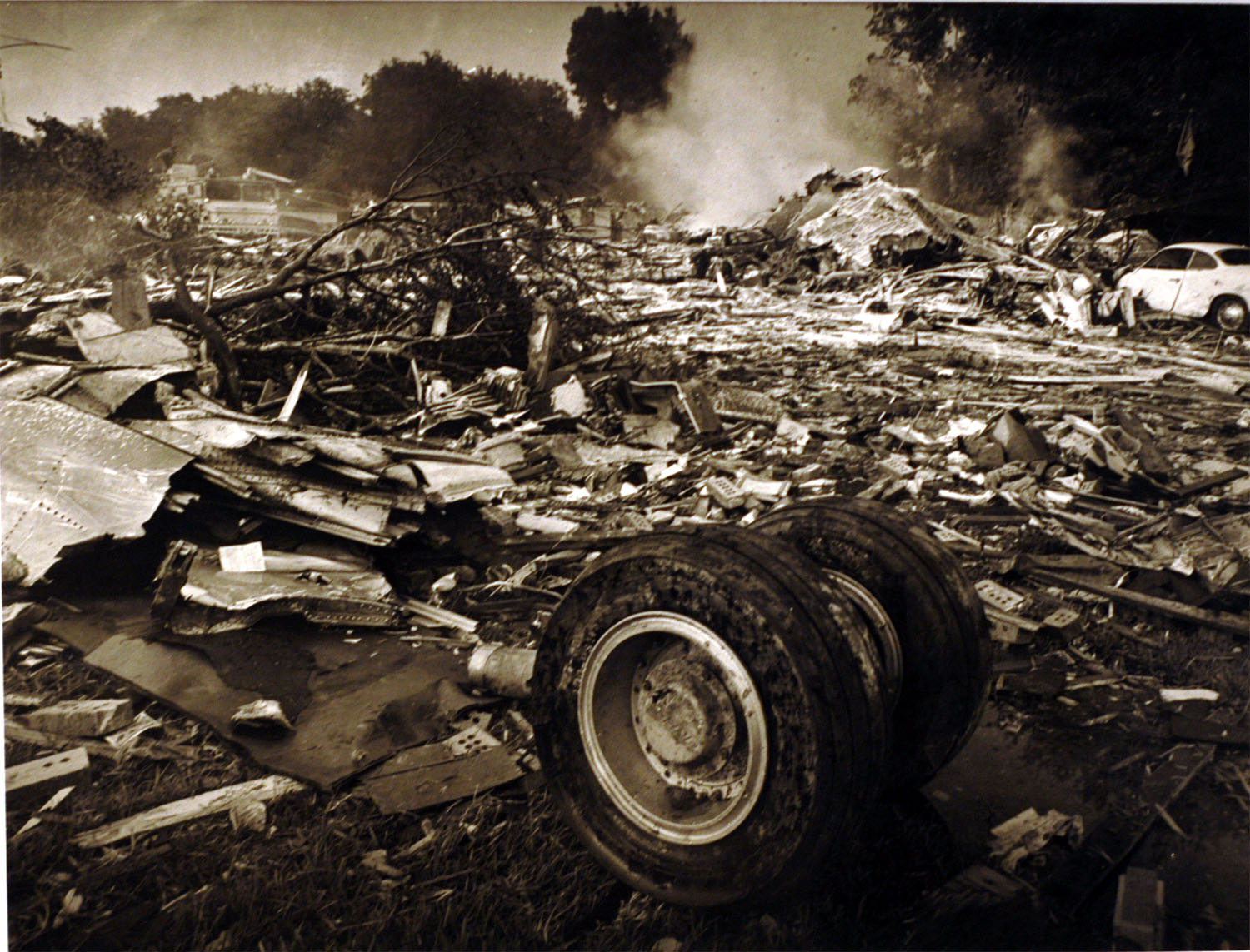
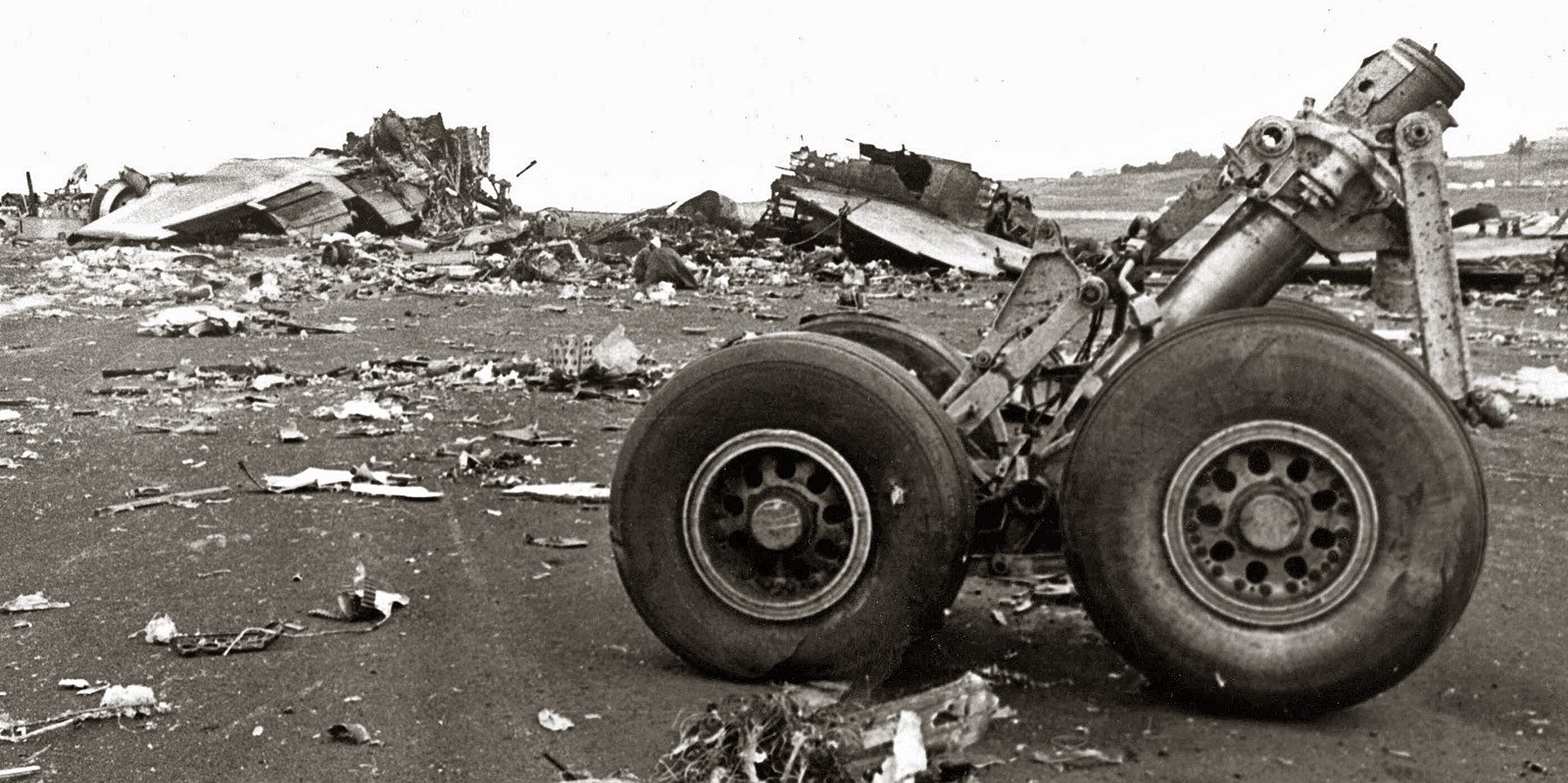
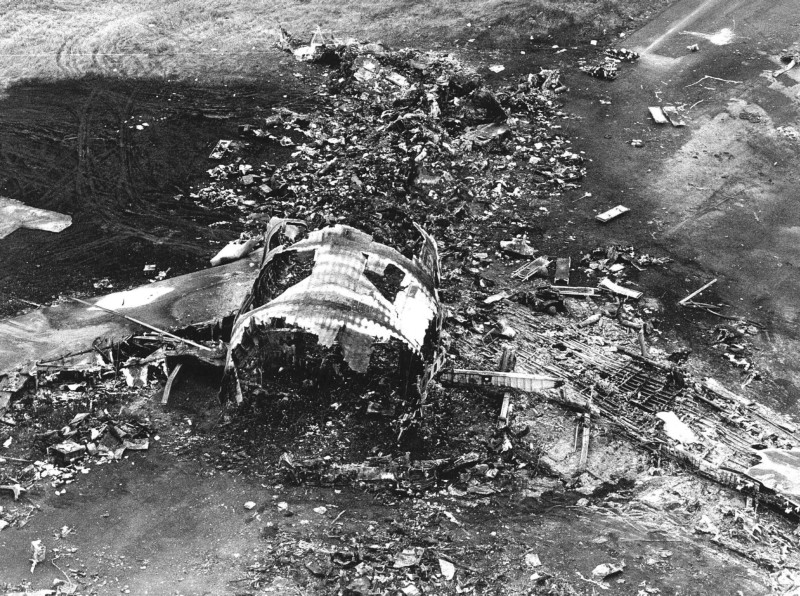
Pan American World Airways Clipper Flight 160 was a scheduled cargo flight from New York-JFK to Frankfurt (FRA), Germany, with a scheduled stop at Prestwick (PIK), Scotland. At 08:25 the flight departed JFK. The aircraft was carrying 52912 lb (24000 kg) of cargo, 15,360 lb (6967 kg) of which were chemicals. After departure, Clipper 160 was vectored on course while climbing to FL330. At 08:44, Clipper 160's clearance was amended, and it was instructed to maintain FL310 as a final cruising altitude. Clipper 160 reported level at FL310 at 08:50. As the flight approached Sherbrooke VORTAC 100 miles east of Montreal, Canada, at about 09:04, it advised Pan American Operations (PANOP) in New York that smoke had accumulated in the "lower 41" electrical compartment, and that the flight was diverting to Boston. At 09:08, Clipper 160 advised Montreal Center that they were level at FL310 and wanted to return to JFK. Montreal Center cleared Clipper 160 for a right turn to a heading of 180 degrees. At 09:10, Clipper 160 advised PANOP that it was returning to New York and that the smoke seemed to be "getting a little thicker in here." At 09:11, the crew advised PANOP that they were now going to Boston and that "this smoke is getting too thick." They also requested that emergency equipment be available when they arrived at Boston. During this conversation, the comment was made that the "cockpit's full back there." During its return to Boston, the flight was given preferential air traffic control treatment, although it had not declared an emergency. After issuing appropriate descent clearances en route so that fuel could be burned off more rapidly at lower altitudes, at 09:26:30 Boston Center advised Boston Arrival Radar that the flight was at 2,000 feet. At 09:29, Clipper 160 asked Boston Center for the flight's distance from Boston, and added, "The DME's don't seem to be working." The Center answered, "You're passing abeam, Pease Air Force Base, right now, sir, and you're about 40 to 45 miles to the northwest of Boston." The first communication between Clipper 160 and the arrival radar controller was at 09:31:21. The flight was cleared "direct Boston, maintain 2,000." The controller asked if the flight was declaring an emergency; the reply was "negative on the emergency, and may we have runway 33 left?" The controller approved the request, and the flight proceeded to Boston as cleared. At approximately the same time, the captain instructed the crew to "shut down everything you don't need." At 09:34:20, the controller asked, "Clipper 160, what do you show for a compass heading right now?" Clipper 160 answered, "Compass heading at this time is 205." The controller then asked, "will you accept a vector for a visual approach to a 5-mile final for runway 33 left, or do you want to be extended out further?" The crew replied, "Negative, we want to get it on the ground as soon as possible." At 09:35:46, the controller stated, "Clipper 160, advise anytime you have the airport in sight." Clipper 160 did not reply. At 09:37:04, the arrival controller made the following transmission: "Clipper 160, this is Boston approach control. If you read, squawk ident on any transponder. I see your transponder just became inoperative. Continue inbound now for runway 33 left, you're No. 1. There is a Lufthansa 747 on a 3-mile final for runway 27, the spacing is good. Remain on this frequency, Clipper 160." There was no reply from the flight. With flaps and spoilers had been extended for speed reduction, the airplane approached runway 33L. The yaw damper was rendered inoperative by the uncoordinated execution of emergency procedures earlier. This made the 707 extremely difficult to control at low speeds. Control was lost and the airplane struck the ground nose down about 262 feet from the right edge of the approach end of runway 33.Pan American World Airways Clipper Flight 160 was a scheduled cargo flight from New York-JFK to Frankfurt (FRA), Germany, with a scheduled stop at Prestwick (PIK), Scotland. At 08:25 the flight departed JFK. The aircraft was carrying 52912 lb (24000 kg) of cargo, 15,360 lb (6967 kg) of which were chemicals. After departure, Clipper 160 was vectored on course while climbing to FL330. At 08:44, Clipper 160's clearance was amended, and it was instructed to maintain FL310 as a final cruising altitude. Clipper 160 reported level at FL310 at 08:50. As the flight approached Sherbrooke VORTAC 100 miles east of Montreal, Canada, at about 09:04, it advised Pan American Operations (PANOP) in New York that smoke had accumulated in the "lower 41" electrical compartment, and that the flight was diverting to Boston. At 09:08, Clipper 160 advised Montreal Center that they were level at FL310 and wanted to return to JFK. Montreal Center cleared Clipper 160 for a right turn to a heading of 180 degrees. At 09:10, Clipper 160 advised PANOP that it was returning to New York and that the smoke seemed to be "getting a little thicker in here." At 09:11, the crew advised PANOP that they were now going to Boston and that "this smoke is getting too thick." They also requested that emergency equipment be available when they arrived at Boston. During this conversation, the comment was made that the "cockpit's full back there." During its return to Boston, the flight was given preferential air traffic control treatment, although it had not declared an emergency. After issuing appropriate descent clearances en route so that fuel could be burned off more rapidly at lower altitudes, at 09:26:30 Boston Center advised Boston Arrival Radar that the flight was at 2,000 feet. At 09:29, Clipper 160 asked Boston Center for the flight's distance from Boston, and added, "The DME's don't seem to be working." The Center answered, "You're passing abeam, Pease Air Force Base, right now, sir, and you're about 40 to 45 miles to the northwest of Boston." The first communication between Clipper 160 and the arrival radar controller was at 09:31:21. The flight was cleared "direct Boston, maintain 2,000." The controller asked if the flight was declaring an emergency; the reply was "negative on the emergency, and may we have runway 33 left?" The controller approved the request, and the flight proceeded to Boston as cleared. At approximately the same time, the captain instructed the crew to "shut down everything you don't need." At 09:34:20, the controller asked, "Clipper 160, what do you show for a compass heading right now?" Clipper 160 answered, "Compass heading at this time is 205." The controller then asked, "will you accept a vector for a visual approach to a 5-mile final for runway 33 left, or do you want to be extended out further?" The crew replied, "Negative, we want to get it on the ground as soon as possible." At 09:35:46, the controller stated, "Clipper 160, advise anytime you have the airport in sight." Clipper 160 did not reply. At 09:37:04, the arrival controller made the following transmission: "Clipper 160, this is Boston approach control. If you read, squawk ident on any transponder. I see your transponder just became inoperative. Continue inbound now for runway 33 left, you're No. 1. There is a Lufthansa 747 on a 3-mile final for runway 27, the spacing is good. Remain on this frequency, Clipper 160." There was no reply from the flight. With flaps and spoilers had been extended for speed reduction, the airplane approached runway 33L. The yaw damper was rendered inoperative by the uncoordinated execution of emergency procedures earlier. This made the 707 extremely difficult to control at low speeds. Control was lost and the airplane struck the ground nose down about 262 feet from the right edge of the approach end of runway 33. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all three crew members were killed.